Comparison of BNT162b2-, mRNA-1273- and Ad26.COV2.S-Elicited IgG and Neutralizing Titers against SARS-CoV-2 and Its Variants
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Sample Collection
2.2. Anti-Spike S1 IgG Quantification
2.3. Recombinant VSV-Pseudovirus Synthesis
2.4. Neutralization Assay
2.5. Statistics
3. Results
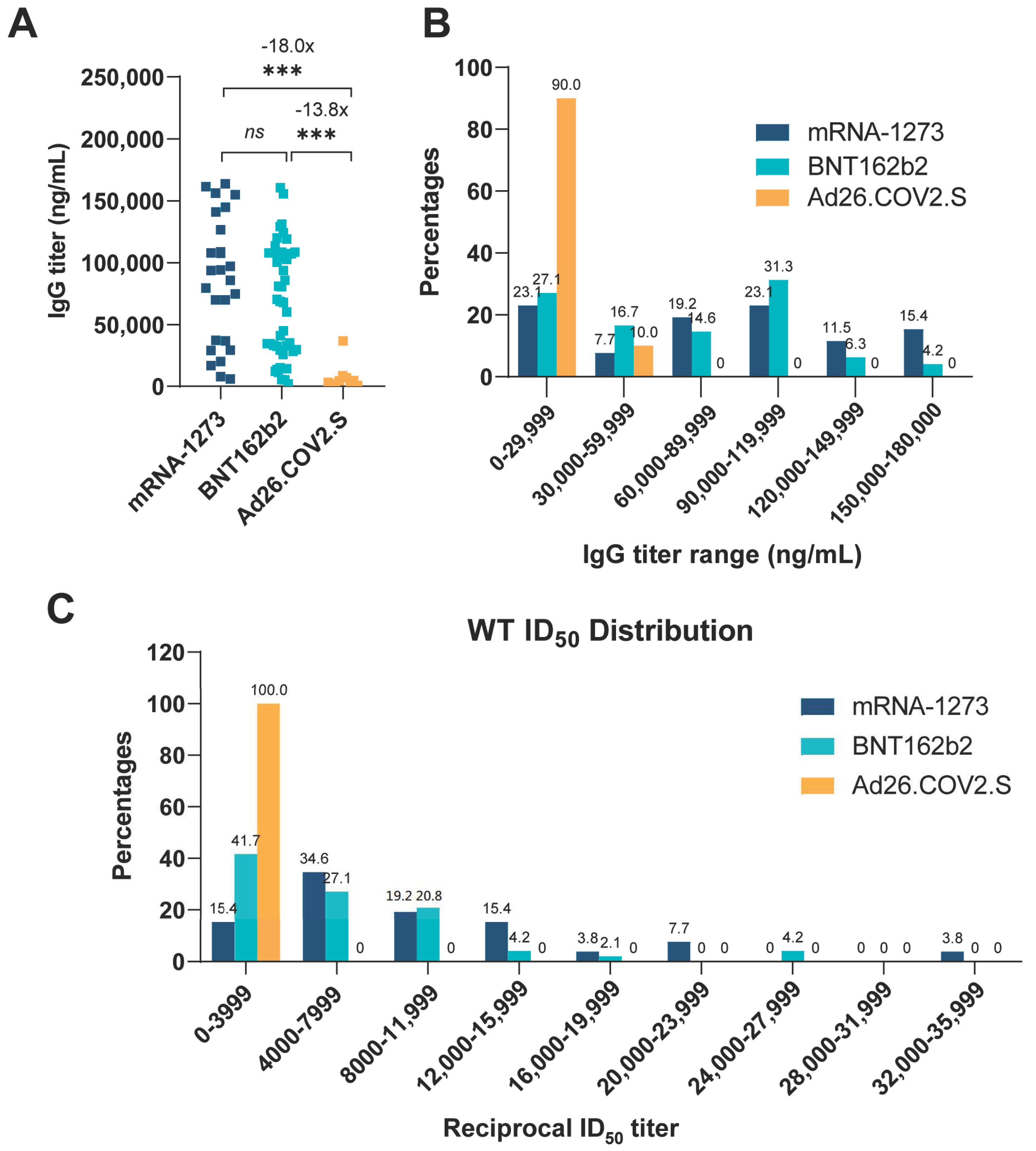
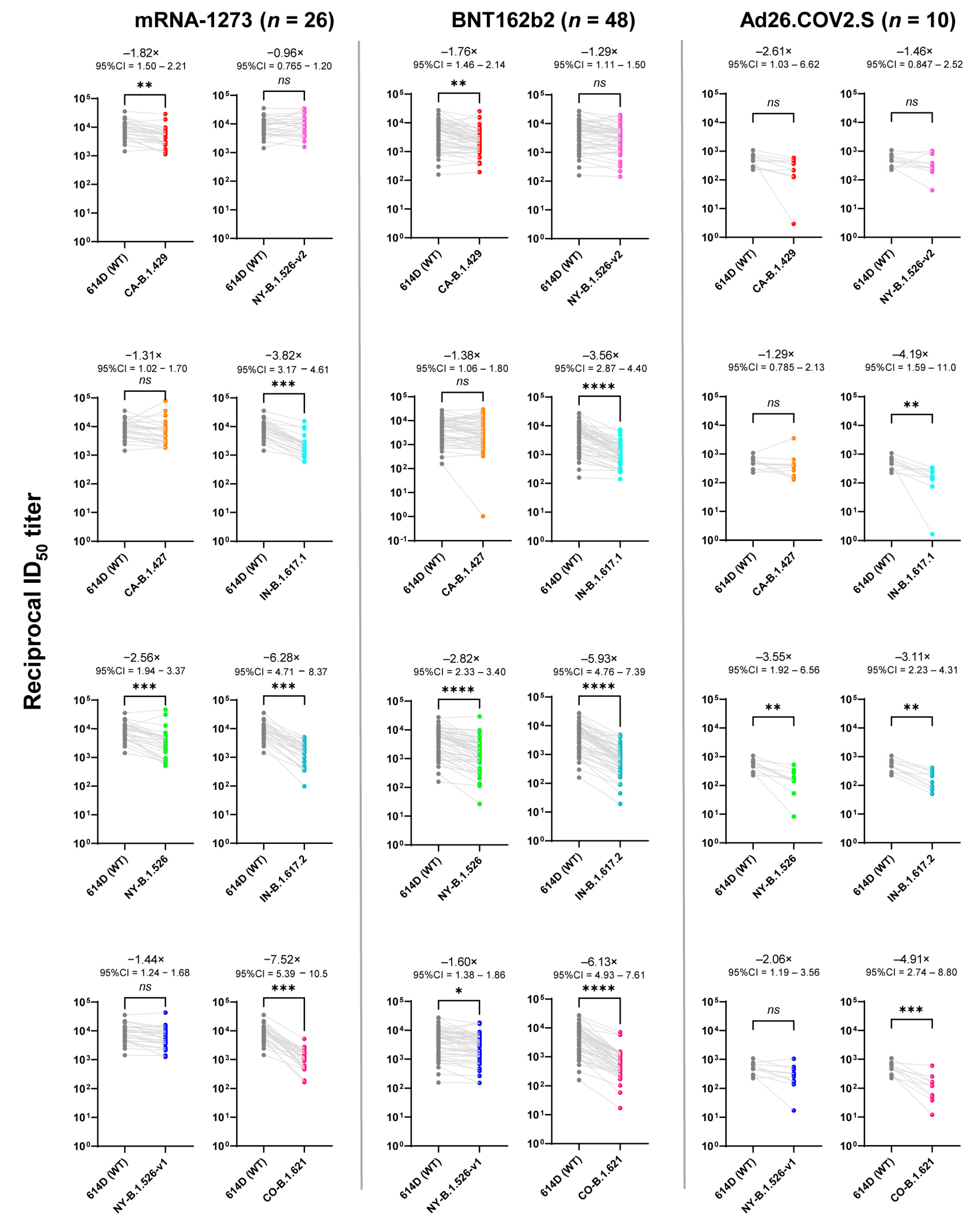
3.1. Comparison of Vaccine-Elicited IgG and Neutralization Titers
3.2. Linear Regression Analysis
3.3. Supplementary Analyses
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
6. Limitations of the Study
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- COVID-19 Vaccinations in the United States; Centers for Disease Control and Prevention: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2021.
- Baden, L.R.; El Sahly, H.M.; Essink, B.; Kotloff, K.; Frey, S.; Novak, R.; Diemert, D.; Spector, S.A.; Rouphael, N.; Creech, C.B.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of the mRNA-1273 SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 403–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polack, F.P.; Thomas, S.J.; Kitchin, N.; Absalon, J.; Gurtman, A.; Lockhart, S.; Perez, J.L.; Pérez Marc, G.; Moreira, E.D.; Zerbini, C.; et al. Safety and Efficacy of the BNT162b2 mRNA COVID-19 Vaccine. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 2603–2615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadoff, J.; Gray, G.; Vandebosch, A.; Cárdenas, V.; Shukarev, G.; Grinsztejn, B.; Goepfert, P.A.; Truyers, C.; Fennema, H.; Spiessens, B.; et al. Safety and Efficacy of Single-Dose Ad26.COV2.S Vaccine against COVID-19. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 2187–2201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.; Hwang, H.Y.; Ji, E.S.; Kim, J.Y.; Yoo, J.S.; Kwon, H.J. Activation of mitochondrial TUFM ameliorates metabolic dysregulation through coordinating autophagy induction. Commun. Biol. 2021, 4, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Röltgen, K.; Powell, A.E.; Wirz, O.F.; Stevens, B.A.; Hogan, C.A.; Najeeb, J.; Hunter, M.; Wang, H.; Sahoo, M.K.; Huang, C.; et al. Defining the features and duration of antibody responses to SARS-CoV-2 infection associated with disease severity and outcome. Sci. Immunol. 2020, 5, eabe0240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wajnberg, A.; Amanat, F.; Firpo, A.; Altman, D.R.; Bailey, M.J.; Mansour, M.; McMahon, M.; Meade, P.; Mendu, D.R.; Muellers, K.; et al. Robust neutralizing antibodies to SARS-CoV-2 infection persist for months. Science 2020, 370, 1227–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoury, D.S.; Cromer, D.; Reynaldi, A.; Schlub, T.E.; Wheatley, A.K.; Juno, J.A.; Subbarao, K.; Kent, S.J.; Triccas, J.A.; Davenport, M.P. Neutralizing antibody levels are highly predictive of immune protection from symptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infection. Nat. Med. 2021, 27, 1205–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Overbaugh, J. Understanding protection from SARS-CoV-2 by studying reinfection. Nat. Med. 2020, 26, 1680–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, V.J.; Foulkes, S.; Charlett, A.; Atti, A.; Monk, E.J.M.; Simmons, R.; Wellington, E.; Cole, M.J.; Saei, A.; Oguti, B.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 infection rates of antibody-positive compared with antibody-negative health-care workers in England: A large, multicentre, prospective cohort study (SIREN). Lancet 2021, 397, 1459–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lumley, S.F.; O’Donnell, D.; Stoesser, N.E.; Matthews, P.C.; Howarth, A.; Hatch, S.B.; Marsden, B.D.; Cox, S.; James, T.; Warren, F.; et al. Antibody Status and Incidence of SARS-CoV-2 Infection in Health Care Workers. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 533–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimeglio, C.; Herin, F.; Martin-Blondel, G.; Miedougé, M.; Izopet, J. Antibody titers and protection against a SARS-CoV-2 infection. J. Infect. 2021, 84, 248–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Bodnar, B.H.; Padhiar, N.H.; Khan, A.I.; Meng, F.; Saribas, S.; Wang, P.; Wang, X.; McCluskey, E.; Shah, S.; et al. Correlation of vaccine-elicited antibody levels and neutralizing activities against SARS-CoV-2 and its variants. Clin. Transl. Med. 2021, 11, e644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bates, T.A.; Leier, H.C.; Lyski, Z.L.; McBride, S.K.; Coulter, F.J.; Weinstein, J.B.; Goodman, J.R.; Lu, Z.; Siegel, S.A.R.; Sullivan, P.; et al. Neutralization of SARS-CoV-2 variants by convalescent and BNT162b2 vaccinated serum. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 5135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, A.; Koch, M.; Wu, K.; Dixon, G.; Oestreicher, J.; Legault, H.; Stewart-Jones, G.B.E.; Colpitts, T.; Pajon, R.; Bennett, H.; et al. Serum Neutralizing Activity of mRNA-1273 Against SARS-CoV-2 Variants. J. Virol. 2021, 95, JVI0131321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Dcosta, B.M.; Samanovic, M.I.; Mulligan, M.J.; Landau, N.R.; Tada, T.B. 1.526 SARS-CoV-2 Variants Identified in New York City are Neutralized by Vaccine-Elicited and Therapeutic Monoclonal Antibodies. mBio 2021, 12, e0138621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doria-Rose, N.; Suthar, M.S.; Makowski, M.; O’Connell, S.; McDermott, A.B.; Flach, B.; Ledgerwood, J.E.; Mascola, J.R.; Graham, B.S.; Lin, B.C.; et al. Antibody Persistence through 6 Months after the Second Dose of mRNA-1273 Vaccine for COVID-19. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 2259–2261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naaber, P.; Tserel, L.; Kangro, K.; Sepp, E.; Jürjenson, V.; Adamson, A.; Haljasmägi, L.; Rumm, A.P.; Maruste, R.; Kärner, J.; et al. Dynamics of antibody response to BNT162b2 vaccine after six months: A longitudinal prospective study. Lancet Reg. Health Eur. 2021, 10, 100208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terpos, E.; Karalis, V.; Ntanasis-Stathopoulos, I.; Gavriatopoulou, M.; Gumeni, S.; Malandrakis, P.; Papanagnou, E.D.; Kastritis, E.; Trougakos, I.P.; Dimopoulos, M.A. Robust Neutralizing Antibody Responses 6 Months Post Vaccination with BNT162b2: A Prospective Study in 308 Healthy Individuals. Life 2021, 11, 1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narowski, T.M.; Raphel, K.; Adams, L.E.; Huang, J.; Vielot, N.A.; Jadi, R.; de Silva, A.M.; Baric, R.S.; Lafleur, J.E.; Premkumar, L. SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccine induces robust specific and cross-reactive IgG and unequal neutralizing antibodies in naive and previously infected people. Cell Rep. 2022, 38, 110336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Bodnar, B.H.; Meng, F.; Khan, A.I.; Wang, X.; Saribas, S.; Wang, T.; Lohani, S.C.; Wang, P.; Wei, Z.; et al. Epigallocatechin gallate from green tea effectively blocks infection of SARS-CoV-2 and new variants by inhibiting spike binding to ACE2 receptor. Cell Biosci. 2021, 11, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tracking SARS-CoV-2 Variants. World Health Organization. 2021. Available online: https://www.who.int/en/activities/tracking-SARS-CoV-2-variants/ (accessed on 26 April 2022).
- Hodcroft, E.B. CoVariants: SARS-CoV-2 Mutations and Variants of Interest. 2021. Available online: https://covariants.org/ (accessed on 26 April 2022).
- Anand, S.; Montez-Rath, M.E.; Han, J.; Garcia, P.; Cadden, L.; Hunsader, P.; Kerschmann, R.; Beyer, P.; Dittrich, M.; Block, G.A.; et al. Antibody Response to COVID-19 Vaccination in Patients Receiving Dialysis. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2021, 32, 2435–2438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyarsky, B.J.; Chiang, T.P.; Ou, M.T.; Werbel, W.A.; Massie, A.B.; Segev, D.L.; Garonzik-Wang, J.M. Antibody Response to the Janssen COVID-19 Vaccine in Solid Organ Transplant Recipients. Transplantation 2021, 105, e82–e83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiang, T.P.; Connolly, C.M.; Ruddy, J.A.; Boyarsky, B.J.; Alejo, J.L.; Werbel, W.A.; Massie, A.; Christopher-Stine, L.; Garonzik-Wang, J.; Segev, D.L.; et al. Antibody response to the Janssen/Johnson & Johnson SARS-CoV-2 vaccine in patients with rheumatic and musculoskeletal diseases. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2021, 80, 1365–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puranik, A.; Lenehan, P.J.; Silvert, E.; Niesen, M.J.M.; Corchado-Garcia, J.; O’Horo, J.C.; Virk, A.; Swift, M.D.; Halamka, J.; Badley, A.D.; et al. Comparison of two highly-effective mRNA vaccines for COVID-19 during periods of Alpha and Delta variant prevalence. medRxiv 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jangra, S.; Ye, C.; Rathnasinghe, R.; Stadlbauer, D.; Krammer, F.; Simon, V.; Martinez-Sobrido, L.; Garcia-Sastre, A.; Schotsaert, M. The E484K mutation in the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein reduces but does not abolish neutralizing activity of human convalescent and post-vaccination sera. medRxiv 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, A.; Irie, T.; Suzuki, R.; Maemura, T.; Nasser, H.; Uriu, K.; Kosugi, Y.; Shirakawa, K.; Sadamasu, K.; Kimura, I.; et al. Enhanced fusogenicity and pathogenicity of SARS-CoV-2 Delta P681R mutation. Nature 2022, 602, 300–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, L.; Triche, T.J.; Bard, J.D.; Biegel, J.A.; Judkins, A.R.; Gai, X. Spike Protein NTD mutation G142D in SARS-CoV-2 Delta VOC lineages is associated with frequent back mutations, increased viral loads, and immune evasion. medRxiv 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, H.Y.; Cai, A. SARS-CoV2 spike protein gene variants with N501T and G142D mutation-dominated infections in mink in the United States. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2021, 33, 939–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.Y.; Juthani, P.V.; Borges, K.A.; Shallow, M.K.; Gupta, A.; Price, C.; Won, C.H.; Chun, H.J. Severe breakthrough COVID-19 cases in the SARS-CoV-2 delta (B.1.617.2) variant era. Lancet Microbe 2022, 3, e4–e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torjesen, I. COVID-19: Delta variant is now UK’s most dominant strain and spreading through schools. BMJ 2021, 373, n1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadfield, J.; Megill, C.; Bell, S.M.; Huddleston, J.; Potter, B.; Callender, C.; Sagulenko, P.; Bedford, T.; Neher, R.A. Nextstrain: Real-time tracking of pathogen evolution. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, 4121–4123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bates, T.A.; Leier, H.C.; Lyski, Z.L.; Goodman, J.R.; Curlin, M.E.; Messer, W.B.; Tafesse, F.G. Age-Dependent Neutralization of SARS-CoV-2 and P.1 Variant by Vaccine Immune Serum Samples. JAMA 2021, 326, 868–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steensels, D.; Pierlet, N.; Penders, J.; Mesotten, D.; Heylen, L. Comparison of SARS-CoV-2 Antibody Response Following Vaccination With BNT162b2 and mRNA-1273. JAMA 2021, 326, 1533–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collier, D.A.; Ferreira, I.A.T.M.; Kotagiri, P.; Datir, R.P.; Lim, E.Y.; Touizer, E.; Meng, B.; Abdullahi, A.; Baker, S.; Dougan, G.; et al. Age-related immune response heterogeneity to SARS-CoV-2 vaccine BNT162b2. Nature 2021, 596, 417–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| WT | CA- | CA- | NY- | NY- | NY- | IN- | IN- | CO- | IgG | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B.1.429 | B.1.427 | B.1.526 | B.1.526-v1 | B.1.526-v2 | B.1.617.1 | B.1.617.2 | B.1.621 | Titers | |||
| BNT162b2 Group (n = 48) | Minimum | 158 | 193 | 1 | 27 | 153 | 143 | 140 | 19 | 17 | 1960 |
| Maximum | 27,400 | 25,300 | 29,500 | 29,500 | 18,400 | 20,000 | 7,390 | 4,860 | 7,160 | 160,000 | |
| Geometric mean | 3830 | 2170 | 2770 | 1360 | 2390 | 2970 | 1080 | 646 | 626 | 48,600 | |
| Geometric SD factor | 3 | 3 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 | |
| Lower 95% CI | 2730 | 1630 | 1720 | 939 | 1730 | 2130 | 838 | 462 | 456 | 36,200 | |
| Upper 95% CI | 5380 | 2900 | 4470 | 1970 | 3310 | 4150 | 1390 | 905 | 859 | 65,300 | |
| mRNA-1273 Group (n = 26) | Minimum | 1440 | 1140 | 1830 | 514 | 1260 | 1580 | 594 | 98 | 165 | 6020 |
| Maximum | 35,600 | 28,800 | 79,000 | 46,300 | 43,200 | 34,700 | 15,400 | 5100 | 5230 | 164,000 | |
| Geometric mean | 8040 | 4420 | 6120 | 3140 | 5570 | 8390 | 2100 | 1300 | 1010 | 63,700 | |
| Geometric SD factor | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 3 | |
| Lower 95% CI | 5960 | 3220 | 4200 | 2010 | 4000 | 6020 | 1530 | 883 | 729 | 43,800 | |
| Upper 95% CI | 10,800 | 6050 | 8940 | 4910 | 7740 | 11,700 | 2900 | 1900 | 1410 | 92,700 | |
| Ad26.COV2.S Group (n = 10) | Minimum | 224 | 3 | 129 | 8 | 17 | 44 | 2 | 50 | 12 | 746 |
| Maximum | 1090 | 589 | 3520 | 530 | 1060 | 1030 | 340 | 413 | 601 | 36,900 | |
| Geometric mean | 482 | 185 | 372 | 136 | 234 | 330 | 115 | 155 | 98 | 3530 | |
| Geometric SD factor | 2 | 5 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 5 | 2 | 3 | 3 | |
| Lower 95% CI | 339 | 61 | 190 | 59 | 107 | 169 | 38 | 91 | 45 | 1520 | |
| Upper 95% CI | 685 | 560 | 730 | 311 | 514 | 645 | 350 | 265 | 215 | 8190 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Padhiar, N.H.; Liu, J.-B.; Wang, X.; Wang, X.-L.; Bodnar, B.H.; Khan, S.; Wang, P.; Khan, A.I.; Luo, J.-J.; Hu, W.-H.; et al. Comparison of BNT162b2-, mRNA-1273- and Ad26.COV2.S-Elicited IgG and Neutralizing Titers against SARS-CoV-2 and Its Variants. Vaccines 2022, 10, 858. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines10060858
Padhiar NH, Liu J-B, Wang X, Wang X-L, Bodnar BH, Khan S, Wang P, Khan AI, Luo J-J, Hu W-H, et al. Comparison of BNT162b2-, mRNA-1273- and Ad26.COV2.S-Elicited IgG and Neutralizing Titers against SARS-CoV-2 and Its Variants. Vaccines. 2022; 10(6):858. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines10060858
Chicago/Turabian StylePadhiar, Nigam H., Jin-Biao Liu, Xu Wang, Xiao-Long Wang, Brittany H. Bodnar, Shazheb Khan, Peng Wang, Adil I. Khan, Jin-Jun Luo, Wen-Hui Hu, and et al. 2022. "Comparison of BNT162b2-, mRNA-1273- and Ad26.COV2.S-Elicited IgG and Neutralizing Titers against SARS-CoV-2 and Its Variants" Vaccines 10, no. 6: 858. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines10060858
APA StylePadhiar, N. H., Liu, J.-B., Wang, X., Wang, X.-L., Bodnar, B. H., Khan, S., Wang, P., Khan, A. I., Luo, J.-J., Hu, W.-H., & Ho, W.-Z. (2022). Comparison of BNT162b2-, mRNA-1273- and Ad26.COV2.S-Elicited IgG and Neutralizing Titers against SARS-CoV-2 and Its Variants. Vaccines, 10(6), 858. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines10060858







