Immunological Study of Combined Administration of SARS-CoV-2 DNA Vaccine and Inactivated Vaccine
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Lines and DNA Transfection
2.2. Construction and Preparation of Recombinant Plasmid DNA
2.3. In Vitro Expression Analysis of the DNA Vaccine Candidates
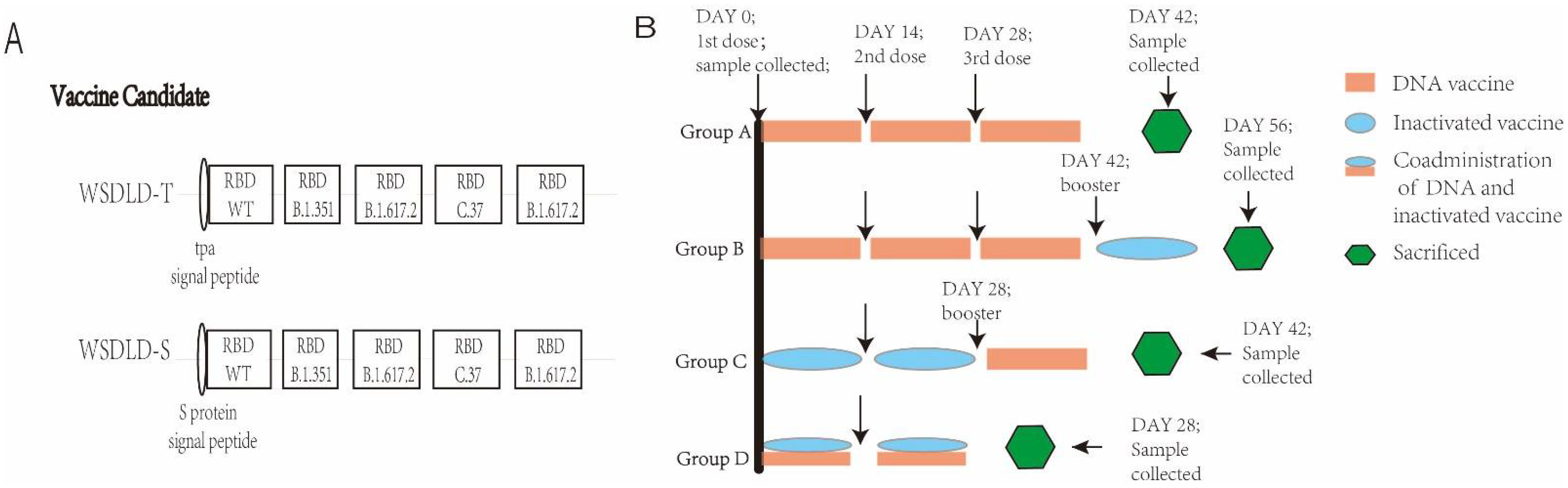
2.4. Animals and Vaccination Programs
2.5. ELISA
2.6. ELISPOT Assay
2.7. Neutralization Antibody Assays
2.8. Flow Cytometry
2.9. Proinflammatory Response
2.10. Statistics
3. Results
3.1. Expression of SARS-CoV-2 DNA Vaccine Candidates
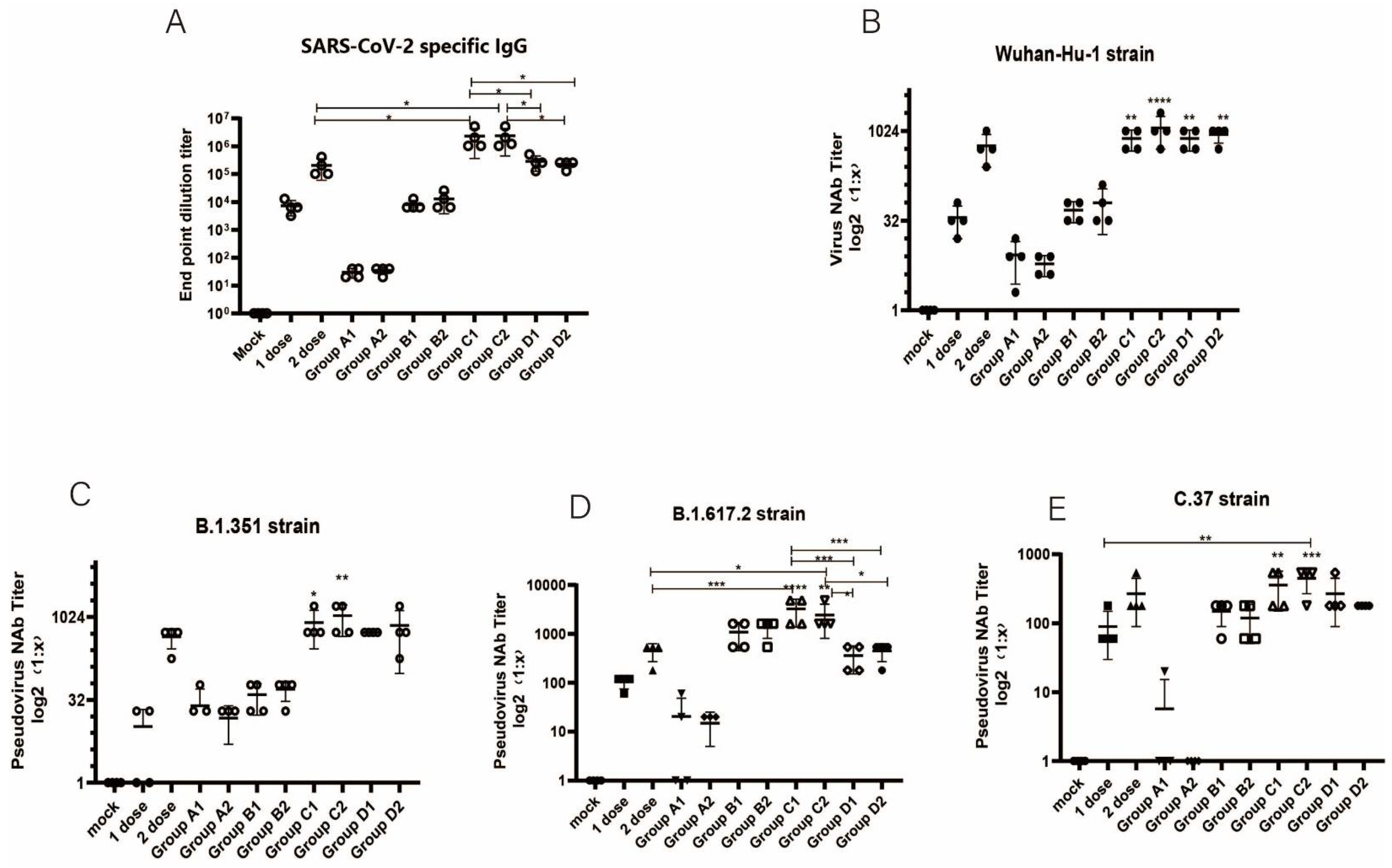
3.2. Humoral Immune Responses
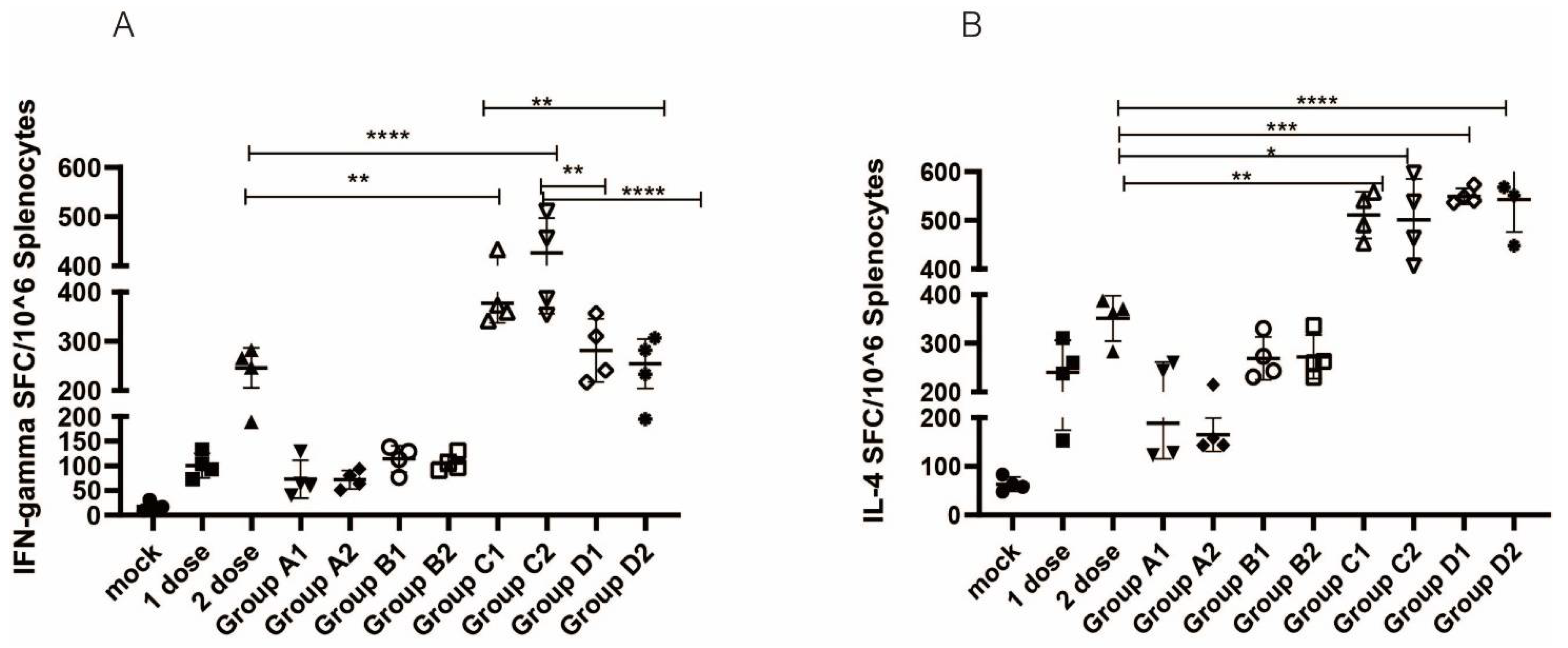
3.3. Cellular Immune Responses
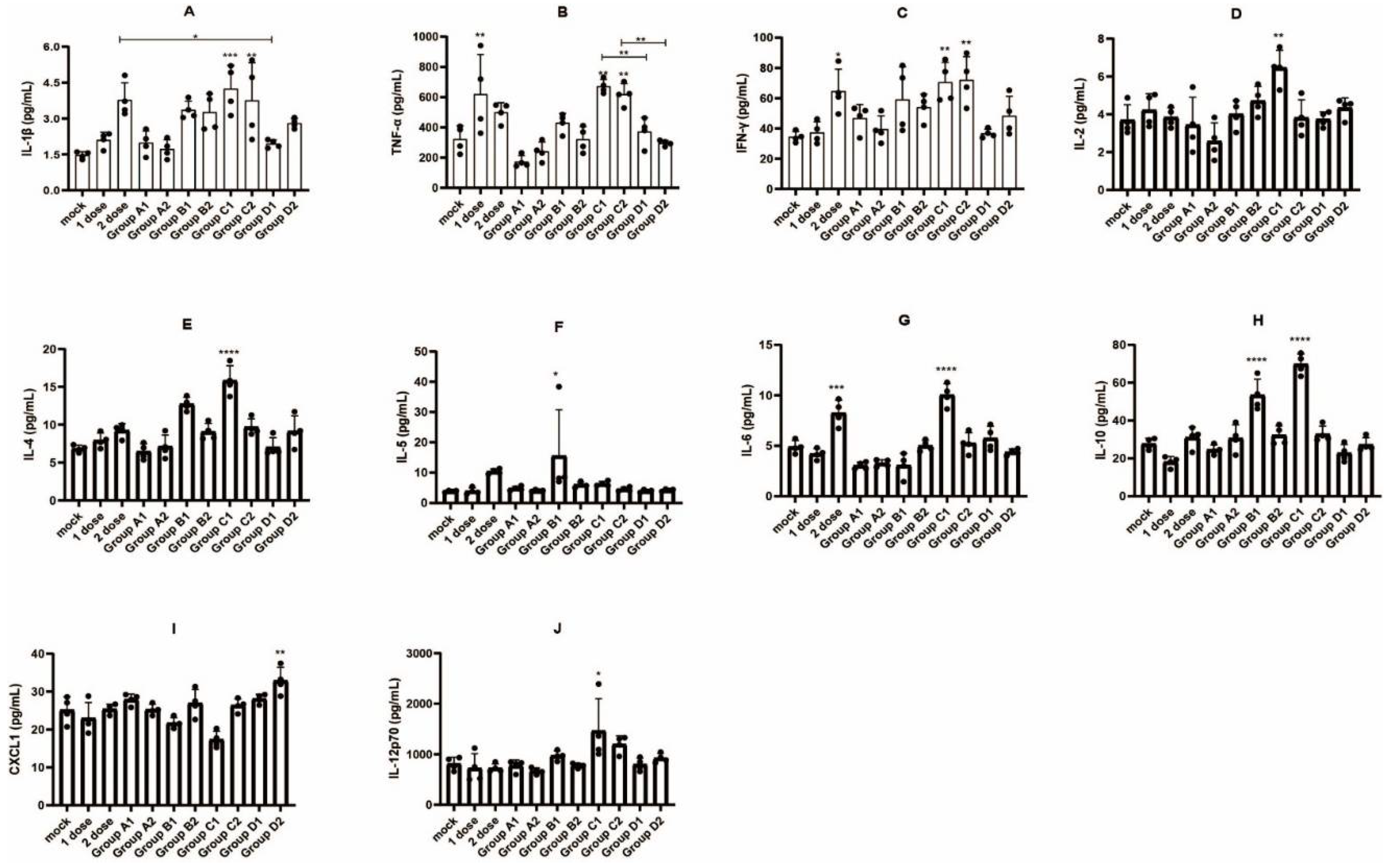
3.4. Detection of Immune Cell Populations and Cytokine Expression
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mackenzie, J.S.; Smith, D.W. COVID-19: A novel zoonotic disease caused by a coronavirus from China: What we know and what we don’t. Microbiol. Aust. 2020, 41, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Virtual Press Conference on COVID-19. 2020. Available online: https://www.who.int/docs/default-source/coronaviruse/transcripts/who-audio-emergencies-coronavirus-press-conference-full-and-final-11mar2020.pdf?sfvrsn=cb432bb3_2 (accessed on 21 April 2022).
- World Health Organization. Home/Diseases/Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19). Available online: https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019 (accessed on 21 April 2022).
- Lu, R.; Zhao, X.; Li, J.; Niu, P.; Yang, B.; Wu, H.; Wang, W.; Song, H.; Huang, B.; Zhu, N.; et al. Genomic characterisation and epidemiology of 2019 novel coronavirus: Implications for virus origins and receptor binding. Lancet 2020, 395, 565–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Lee, J.Y.; Yang, J.S.; Kim, J.W.; Kim, V.N.; Chang, H. The Architecture of SARS-CoV-2 Transcriptome. Cell 2020, 181, 914–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Wang, W.; Zhao, X.; Zai, J.; Zhao, Q.; Li, Y.; Chaillon, A. Transmission dynamics and evolutionary history of 2019-nCoV. J. Med. Virol. 2020, 92, 501–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mistry, P.; Barmania, F.; Mellet, J.; Peta, K.; Strydom, A.; Viljoen, I.M.; James, W.; Gordon, S.; Pepper, M.S. SARS-CoV-2 Variants, Vaccines, and Host Immunity. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 809244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, E.E.; Frenck, R.W., Jr.; Falsey, A.R.; Kitchin, N.; Absalon, J.; Gurtman, A.; Lockhart, S.; Neuzil, K.; Mulligan, M.J.; Bailey, R.; et al. Safety and Immunogenicity of Two RNA-Based COVID-19 Vaccine Candidates. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 2439–2450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folegatti, P.M.; Ewer, K.J.; Aley, P.K.; Angus, B.; Becker, S.; Belij-Rammerstorfer, S.; Bellamy, D.; Bibi, S.; Bittaye, M.; Clutterbuck, E.A.; et al. Safety and immunogenicity of the ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 vaccine against SARS-CoV-2: A preliminary report of a phase 1/2, single-blind, randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2020, 396, 467–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baden, L.R.; El Sahly, H.M.; Essink, B.; Kotloff, K.; Frey, S.; Novak, R.; Diemert, D.; Spector, S.A.; Rouphael, N.; Creech, C.B.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of the mRNA-1273 SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 403–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Li, Y.; Dai, L.; Wang, J.; He, P.; Li, C.; Fang, X.; Wang, C.; Zhao, X.; Huang, E.; et al. Safety and immunogenicity of a recombinant tandem-repeat dimeric RBD-based protein subunit vaccine (ZF2001) against COVID-19 in adults: Two randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 1 and 2 trials. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2021, 21, 1107–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tai, W.; Zhang, X.; Drelich, A.; Shi, J.; Hsu, J.C.; Luchsinger, L.; Hillyer, C.D.; Tseng, C.K.; Jiang, S.; Du, L. A novel receptor-binding domain (RBD)-based mRNA vaccine against SARS-CoV-2. Cell Res. 2020, 30, 932–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silveira, M.M.; Oliveira, T.L.; Schuch, R.A.; McBride, A.J.A.; Dellagostin, O.A.; Hartwig, D.D. DNA vaccines against leptospirosis: A literature review. Vaccine 2017, 35, 5559–5567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, L.Y.Y.; Izzard, L.; Hurt, A.C. A Review of DNA Vaccines Against Influenza. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, T.R.F.; Patel, A.; Ramos, S.; Elwood, D.; Zhu, X.; Yan, J.; Gary, E.N.; Walker, S.N.; Schultheis, K.; Purwar, M.; et al. Immunogenicity of a DNA vaccine candidate for COVID-19. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 2601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dey, A.; Rajanathan, T.M.C.; Chandra, H.; Pericherla, H.P.R.; Kumar, S.; Choonia, H.S.; Bajpai, M.; Singh, A.K.; Sinha, A.; Saini, G.; et al. Immunogenic potential of DNA vaccine candidate, ZyCoV-D against SARS-CoV-2 in animal models. Vaccine 2021, 39, 4108–4116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francis, M.J. Recent Advances in Vaccine Technologies. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Small Anim. Pract. 2018, 48, 231–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Yin, S.; Tong, X.; Tao, Y.; Ni, J.; Pan, J.; Li, M.; Wan, Y.; Mao, M.; Xiong, Y.; et al. Dynamic SARS-CoV-2-specific B-cell and T-cell responses following immunization with an inactivated COVID-19 vaccine. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2022, 28, 410–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Z.; Zhu, H.; Wang, X.; Jing, B.; Li, Z.; Xia, X.; Sun, H.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Shi, L.; et al. Adjuvants for Coronavirus Vaccines. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 589833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- COVID-19 vaccines. In Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed); National Library of Medicine (US): Bethesda, MD, USA, 2006.
- Duerr, G.D.; Heine, A.; Hamiko, M.; Zimmer, S.; Luetkens, J.A.; Nattermann, J.; Rieke, G.; Isaak, A.; Jehle, J.; Held, S.A.E.; et al. Parameters predicting COVID-19-induced myocardial injury and mortality. Life Sci. 2020, 260, 118400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harder, T.; Külper-Schiek, W.; Reda, S.; Treskova-Schwarzbach, M.; Koch, J.; Vygen-Bonnet, S.; Wichmann, O. Effectiveness of COVID-19 vaccines against SARS-CoV-2 infection with the Delta (B.1.617.2) variant: Second interim results of a living systematic review and meta-analysis, 1 January to 25 August 2021. Eurosurveillance 2021, 26, 2100920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, D.; Ferreira, V.H.; Hall, V.G.; Hu, Q.; Samson, R.; Ku, T.; Ierullo, M.; Majchrzak-Kita, B.; Tomlinson, G.; Gingras, A.C.; et al. Neutralization of SARS-CoV-2 Variants in Transplant Recipients After Two and Three Doses of mRNA-1273 Vaccine: Secondary Analysis of a Randomized Trial. Ann. Intern. Med. 2022, 175, 226–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiolet, T.; Kherabi, Y.; MacDonald, C.J.; Ghosn, J.; Peiffer-Smadja, N. Comparing COVID-19 vaccines for their characteristics, efficacy and effectiveness against SARS-CoV-2 and variants of concern: A narrative review. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2022, 28, 202–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melo-González, F.; Soto, J.A.; González, L.A.; Fernández, J.; Duarte, L.F.; Schultz, B.M.; Gálvez, N.M.S.; Pacheco, G.A.; Ríos, M.; Vázquez, Y.; et al. Recognition of Variants of Concern by Antibodies and T Cells Induced by a SARS-CoV-2 Inactivated Vaccine. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 747830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Jiang, Q.; Xu, X.; Wang, Y.; Liu, L.; Lian, Y.; Li, H.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, G.; et al. Immune mechanisms induced by an HSV-1 mutant strain: Discrepancy analysis of the immune system gene profile in comparison with a wild-type strain. Vaccine 2018, 36, 2394–2402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Xie, Z.; Long, R.; Fan, S.; Li, H.; He, Z.; Xu, K.; Liao, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Immunological evaluation of an inactivated SARS-CoV-2 vaccine in rhesus macaques. Mol. Ther. Methods Clin. Dev. 2021, 23, 108–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Y.; Wang, G.; Cai, X.P.; Deng, J.W.; Zheng, L.; Zhu, H.H.; Zheng, M.; Yang, B.; Chen, Z. An overview of COVID-19. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 2020, 21, 343–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luxi, N.; Giovanazzi, A.; Capuano, A.; Crisafulli, S.; Cutroneo, P.M.; Fantini, M.P.; Ferrajolo, C.; Moretti, U.; Poluzzi, E.; Raschi, E.; et al. COVID-19 Vaccination in Pregnancy, Paediatrics, Immunocompromised Patients, and Persons with History of Allergy or Prior SARS-CoV-2 Infection: Overview of Current Recommendations and Pre- and Post-Marketing Evidence for Vaccine Efficacy and Safety. Drug Saf. 2021, 44, 1247–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aleem, A.; Samad, A.B.A.; Slenker, A.K. Emerging Variants of SARS-CoV-2 And Novel Therapeutics Against Coronavirus (COVID-19). In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing Copyright © 2022, StatPearls Publishing LLC.: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, S.; Duan, K.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, D.; Zhang, H.; Xie, Z.; Li, X.; Peng, C.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, W.; et al. Effect of an Inactivated Vaccine Against SARS-CoV-2 on Safety and Immunogenicity Outcomes: Interim Analysis of 2 Randomized Clinical Trials. JAMA 2020, 324, 951–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, S.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, H.; Yang, Y.; Gao, G.F.; Tan, W.; Wu, G.; Xu, M.; Lou, Z.; et al. Safety and immunogenicity of an inactivated SARS-CoV-2 vaccine, BBIBP-CorV: A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 1/2 trial. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2021, 21, 39–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Hu, Y.; Xu, M.; Chen, Z.; Yang, W.; Jiang, Z.; Li, M.; Jin, H.; Cui, G.; Chen, P.; et al. Safety, tolerability, and immunogenicity of an inactivated SARS-CoV-2 vaccine (CoronaVac) in healthy adults aged 60 years and older: A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 1/2 clinical trial. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2021, 21, 803–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polack, F.P.; Thomas, S.J.; Kitchin, N.; Absalon, J.; Gurtman, A.; Lockhart, S.; Perez, J.L.; Pérez Marc, G.; Moreira, E.D.; Zerbini, C.; et al. Safety and Efficacy of the BNT162b2 mRNA COVID-19 Vaccine. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 2603–2615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kremsner, P.G.; Mann, P.; Kroidl, A.; Leroux-Roels, I.; Schindler, C.; Gabor, J.J.; Schunk, M.; Leroux-Roels, G.; Bosch, J.J.; Fendel, R.; et al. Safety and immunogenicity of an mRNA-lipid nanoparticle vaccine candidate against SARS-CoV-2: A phase 1 randomized clinical trial. Wien. Klin. Wochenschr. 2021, 133, 931–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadoff, J.; Le Gars, M.; Shukarev, G.; Heerwegh, D.; Truyers, C.; de Groot, A.M.; Stoop, J.; Tete, S.; Van Damme, W.; Leroux-Roels, I.; et al. Interim Results of a Phase 1-2a Trial of Ad26.COV2.S COVID-19 Vaccine. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 1824–1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, F.C.; Guan, X.H.; Li, Y.H.; Huang, J.Y.; Jiang, T.; Hou, L.H.; Li, J.X.; Yang, B.F.; Wang, L.; Wang, W.J.; et al. Immunogenicity and safety of a recombinant adenovirus type-5-vectored COVID-19 vaccine in healthy adults aged 18 years or older: A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 2 trial. Lancet 2020, 396, 479–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chappell, K.J.; Mordant, F.L.; Li, Z.; Wijesundara, D.K.; Ellenberg, P.; Lackenby, J.A.; Cheung, S.T.M.; Modhiran, N.; Avumegah, M.S.; Henderson, C.L.; et al. Safety and immunogenicity of an MF59-adjuvanted spike glycoprotein-clamp vaccine for SARS-CoV-2: A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 1 trial. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2021, 21, 1383–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richmond, P.; Hatchuel, L.; Dong, M.; Ma, B.; Hu, B.; Smolenov, I.; Li, P.; Liang, P.; Han, H.H.; Liang, J.; et al. Safety and immunogenicity of S-Trimer (SCB-2019), a protein subunit vaccine candidate for COVID-19 in healthy adults: A phase 1, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet 2021, 397, 682–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tebas, P.; Yang, S.; Boyer, J.D.; Reuschel, E.L.; Patel, A.; Christensen-Quick, A.; Andrade, V.M.; Morrow, M.P.; Kraynyak, K.; Agnes, J.; et al. Safety and immunogenicity of INO-4800 DNA vaccine against SARS-CoV-2: A preliminary report of an open-label, Phase 1 clinical trial. EClinicalMedicine 2021, 31, 100689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Momin, T.; Kansagra, K.; Patel, H.; Sharma, S.; Sharma, B.; Patel, J.; Mittal, R.; Sanmukhani, J.; Maithal, K.; Dey, A.; et al. Safety and Immunogenicity of a DNA SARS-CoV-2 vaccine (ZyCoV-D): Results of an open-label, non-randomized phase I part of phase I/II clinical study by intradermal route in healthy subjects in India. EClinicalMedicine 2021, 38, 101020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korang, S.K.; von Rohden, E.; Veroniki, A.A.; Ong, G.; Ngalamika, O.; Siddiqui, F.; Juul, S.; Nielsen, E.E.; Feinberg, J.B.; Petersen, J.J.; et al. Vaccines to prevent COVID-19: A living systematic review with Trial Sequential Analysis and network meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0260733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrović, V.; Vuković, V.; Patić, A.; Marković, M.; Ristić, M. Immunogenicity of BNT162b2, BBIBP-CorV and Gam-COVID-Vac vaccines and immunity after natural SARS-CoV-2 infection-A comparative study from Novi Sad, Serbia. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0263468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.M.; Masum, M.H.U.; Wajed, S.; Talukder, A. A comprehensive review on COVID-19 vaccines: Development, effectiveness, adverse effects, distribution and challenges. VirusDisease 2022, 33, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zee, J.S.T.; Lai, K.T.W.; Ho, M.K.S.; Leung, A.C.P.; Fung, L.H.; Luk, W.P.; Kwok, L.F.; Kee, K.M.; Chan, Q.W.L.; Tang, S.F.; et al. Serological response to mRNA and inactivated COVID-19 vaccine in healthcare workers in Hong Kong: Decline in antibodies 12 weeks after two doses. Hong Kong Med. J. 2021, 27, 380–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, A.; Koch, M.; Wu, K.; Dixon, G.; Oestreicher, J.; Legault, H.; Stewart-Jones, G.B.E.; Colpitts, T.; Pajon, R.; Bennett, H.; et al. Serum Neutralizing Activity of mRNA-1273 against SARS-CoV-2 Variants. J. Virol. 2021, 95, e0131321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández, J.; Bruneau, N.; Fasce, R.; Martín, H.S.; Balanda, M.; Bustos, P.; Ulloa, S.; Mora, J.; Ramírez, E. Neutralization of alpha, gamma, and D614G SARS-CoV-2 variants by CoronaVac vaccine-induced antibodies. J. Med. Virol. 2022, 94, 399–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khateeb, D.; Gabrieli, T.; Sofer, B.; Hattar, A.; Cordela, S.; Chaouat, A.; Spivak, I.; Lejbkowicz, I.; Almog, R.; Mandelboim, M.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 variants with reduced infectivity and varied sensitivity to the BNT162b2 vaccine are developed during the course of infection. PLoS Pathog. 2022, 18, e1010242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanyaolu, A.; Okorie, C.; Marinkovic, A.; Haider, N.; Abbasi, A.F.; Jaferi, U.; Prakash, S.; Balendra, V. The emerging SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern. Ther. Adv. Infect. Dis. 2021, 8, 20499361211024372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, L.; Liu, Y.; Tang, X.; He, D. The Disease Severity and Clinical Outcomes of the SARS-CoV-2 Variants of Concern. Front. Public Health 2021, 9, 775224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fathizadeh, H.; Afshar, S.; Masoudi, M.R.; Gholizadeh, P.; Asgharzadeh, M.; Ganbarov, K.; Köse, Ş.; Yousefi, M.; Kafil, H.S. SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) vaccines structure, mechanisms and effectiveness: A review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 188, 740–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, J.; Yu, Q.; Yin, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Li, X.; Yin, Q.; Chen, H.; Long, R.; Zhao, Z.; Mou, T.; et al. The safety and immunogenicity of an inactivated SARS-CoV-2 vaccine in Chinese adults aged 18-59 years: A phase I randomized, double-blinded, controlled trial. Vaccine 2021, 39, 2746–2754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shekhar, R.; Garg, I.; Pal, S.; Kottewar, S.; Sheikh, A.B. COVID-19 Vaccine Booster: To Boost or Not to Boost. Infect. Dis. Rep. 2021, 13, 924–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S. Heterologous prime-boost vaccination. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2009, 21, 346–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nascimento, I.P.; Leite, L.C. Recombinant vaccines and the development of new vaccine strategies. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 2012, 45, 1102–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fioretti, D.; Iurescia, S.; Fazio, V.M.; Rinaldi, M. DNA vaccines: Developing new strategies against cancer. J. Biomed. Biotechnol. 2010, 2010, 174378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kardani, K.; Bolhassani, A.; Shahbazi, S. Prime-boost vaccine strategy against viral infections: Mechanisms and benefits. Vaccine 2016, 34, 413–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clemens, S.A.C.; Weckx, L.; Clemens, R.; Mendes, A.V.A.; Souza, A.R.; Silveira, M.B.V.; da Guarda, S.N.F.; de Nobrega, M.M.; de Moraes Pinto, M.I.; Gonzalez, I.G.S.; et al. Heterologous versus homologous COVID-19 booster vaccination in previous recipients of two doses of CoronaVac COVID-19 vaccine in Brazil (RHH-001): A phase 4, non-inferiority, single blind, randomised study. Lancet 2022, 399, 521–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groß, R.; Zanoni, M.; Seidel, A.; Conzelmann, C.; Gilg, A.; Krnavek, D.; Erdemci-Evin, S.; Mayer, B.; Hoffmann, M.; Pöhlmann, S.; et al. Heterologous ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 and BNT162b2 prime-boost vaccination elicits potent neutralizing antibody responses and T cell reactivity against prevalent SARS-CoV-2 variants. EBioMedicine 2022, 75, 103761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reindl-Schwaighofer, R.; Heinzel, A.; Mayrdorfer, M.; Jabbour, R.; Hofbauer, T.M.; Merrelaar, A.; Eder, M.; Regele, F.; Doberer, K.; Spechtl, P.; et al. Comparison of SARS-CoV-2 Antibody Response 4 Weeks After Homologous vs Heterologous Third Vaccine Dose in Kidney Transplant Recipients: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Intern. Med. 2022, 182, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. WHO COVID-19 Vaccine Procurement. Available online: https://app.powerbi.com/view?r=eyJrIjoiMWNjNzZkNjctZTNiNy00YmMzLTkxZjQtNmJiZDM2MTYxNzEwIiwidCI6ImY2MTBjMGI3LWJkMjQtNGIzOS04MTBiLTNkYzI4MGFmYjU5MCIsImMiOjh9 (accessed on 18 April 2022).


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Meng, Z.; Ma, D.; Duan, S.; Zhang, J.; Yue, R.; Li, X.; Gao, Y.; Li, X.; Zeng, F.; Xu, X.; et al. Immunological Study of Combined Administration of SARS-CoV-2 DNA Vaccine and Inactivated Vaccine. Vaccines 2022, 10, 929. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines10060929
Meng Z, Ma D, Duan S, Zhang J, Yue R, Li X, Gao Y, Li X, Zeng F, Xu X, et al. Immunological Study of Combined Administration of SARS-CoV-2 DNA Vaccine and Inactivated Vaccine. Vaccines. 2022; 10(6):929. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines10060929
Chicago/Turabian StyleMeng, Ziyan, Danjing Ma, Suqin Duan, Jingjing Zhang, Rong Yue, Xinghang Li, Yang Gao, Xueqi Li, Fengyuan Zeng, Xiangxiong Xu, and et al. 2022. "Immunological Study of Combined Administration of SARS-CoV-2 DNA Vaccine and Inactivated Vaccine" Vaccines 10, no. 6: 929. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines10060929
APA StyleMeng, Z., Ma, D., Duan, S., Zhang, J., Yue, R., Li, X., Gao, Y., Li, X., Zeng, F., Xu, X., Jiang, G., Liao, Y., Fan, S., Niu, Z., Li, D., Yu, L., Zhao, H., Xu, X., Wang, L., ... Li, Q. (2022). Immunological Study of Combined Administration of SARS-CoV-2 DNA Vaccine and Inactivated Vaccine. Vaccines, 10(6), 929. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines10060929





