Human Fc-Conjugated Receptor Binding Domain-Based Recombinant Subunit Vaccines with Short Linker Induce Potent Neutralizing Antibodies against Multiple SARS-CoV-2 Variants
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cells, Reagents and Viruses
2.2. Animals
2.3. Protein Expression and Purification
2.4. ELISA Assay
2.5. Flow Cytometry
2.6. ELISpot
2.7. Neutralization Assay
2.8. Cell Surface Marker and Intracellular Cytokine Staining
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
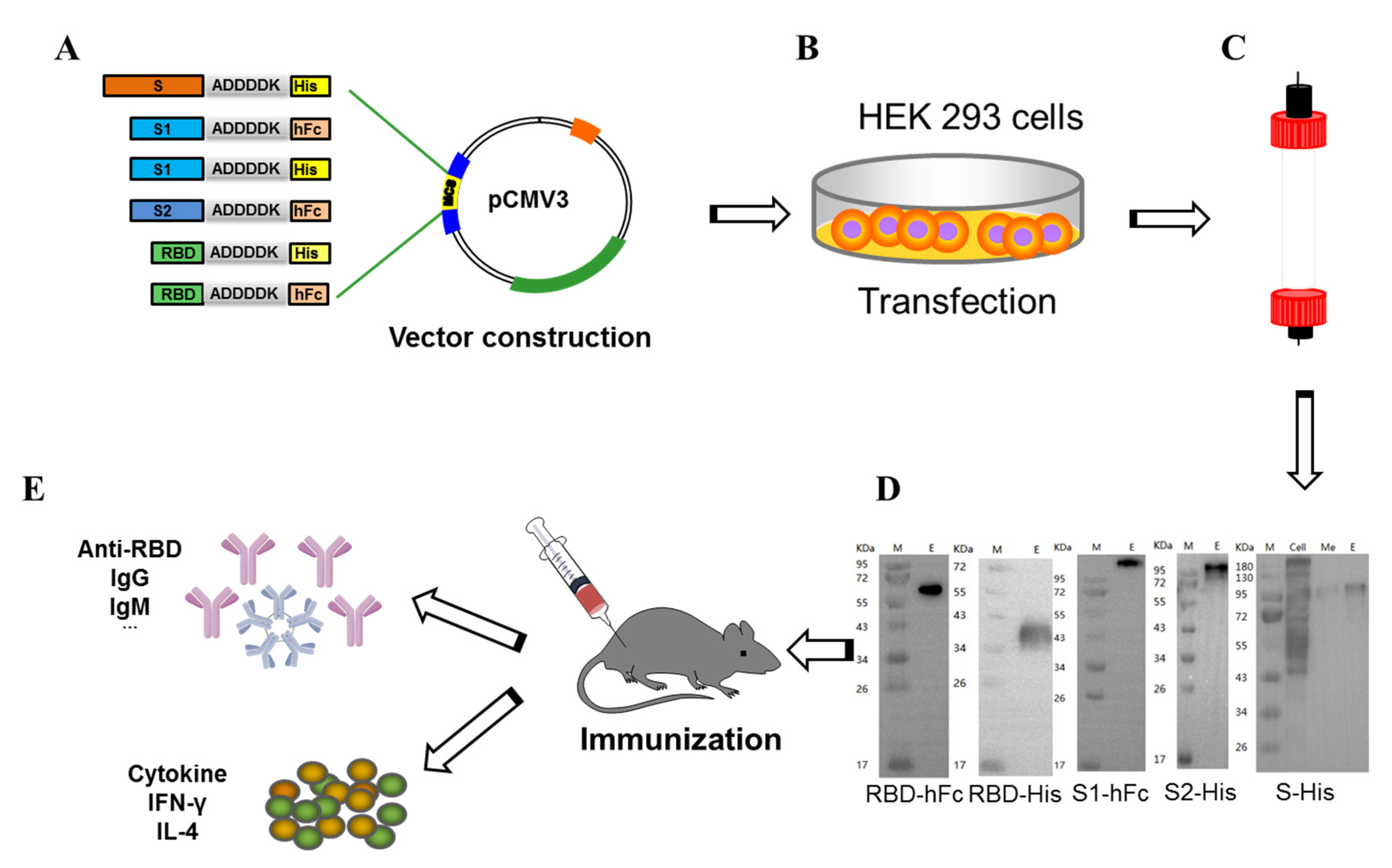
3.1. Construction, Expression, Purification, and Immunoassay of Recombinant Subunit Protein Vaccines
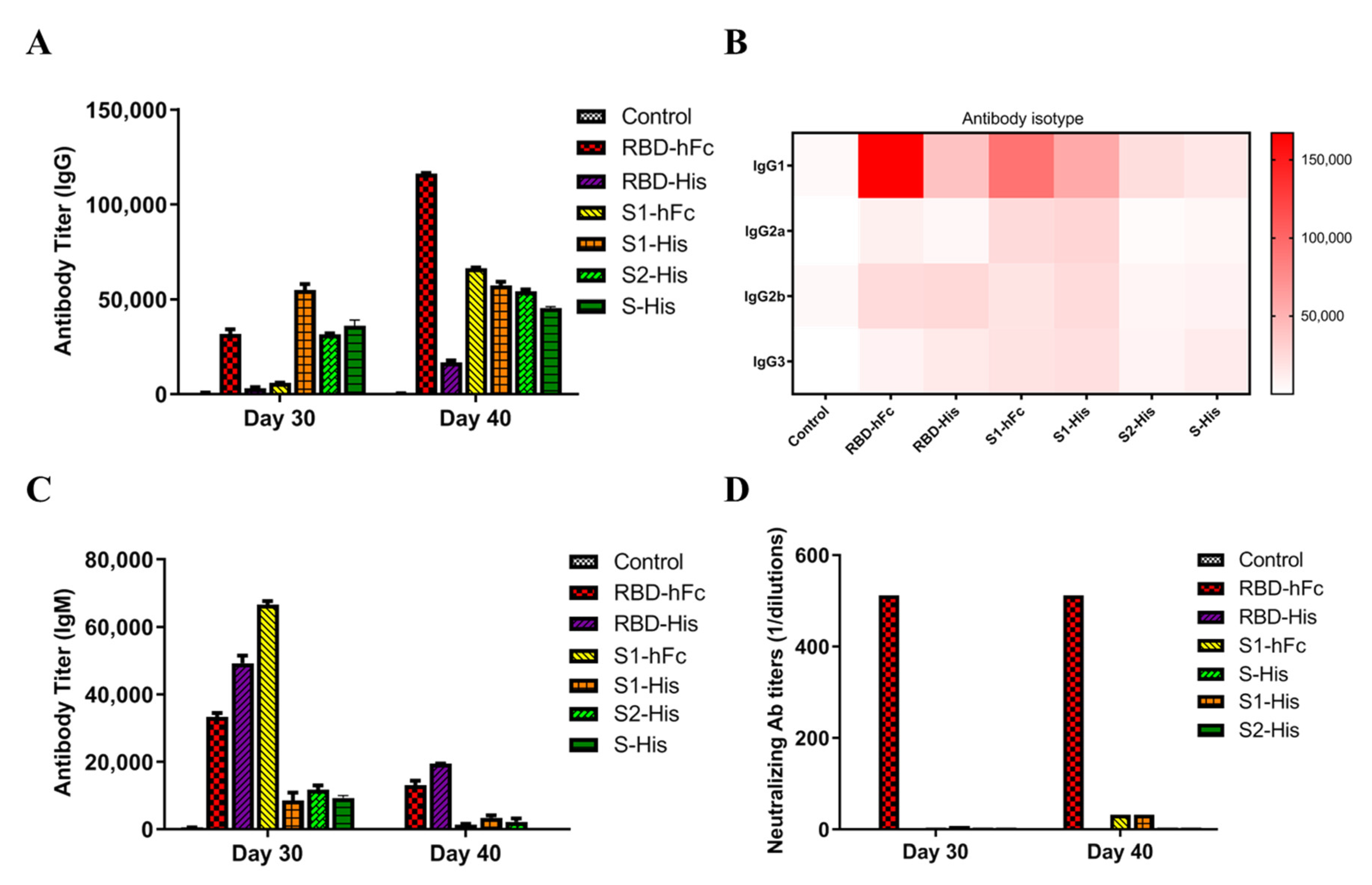
3.2. Recombinant Protein Vaccines with RBD Triggers Specific Powerful Humoral-Mediated Immune Responses in Mice
3.3. RBD-hFc and RBD-His Fusion Vaccines Can Block the Binding of RBD to ACE2
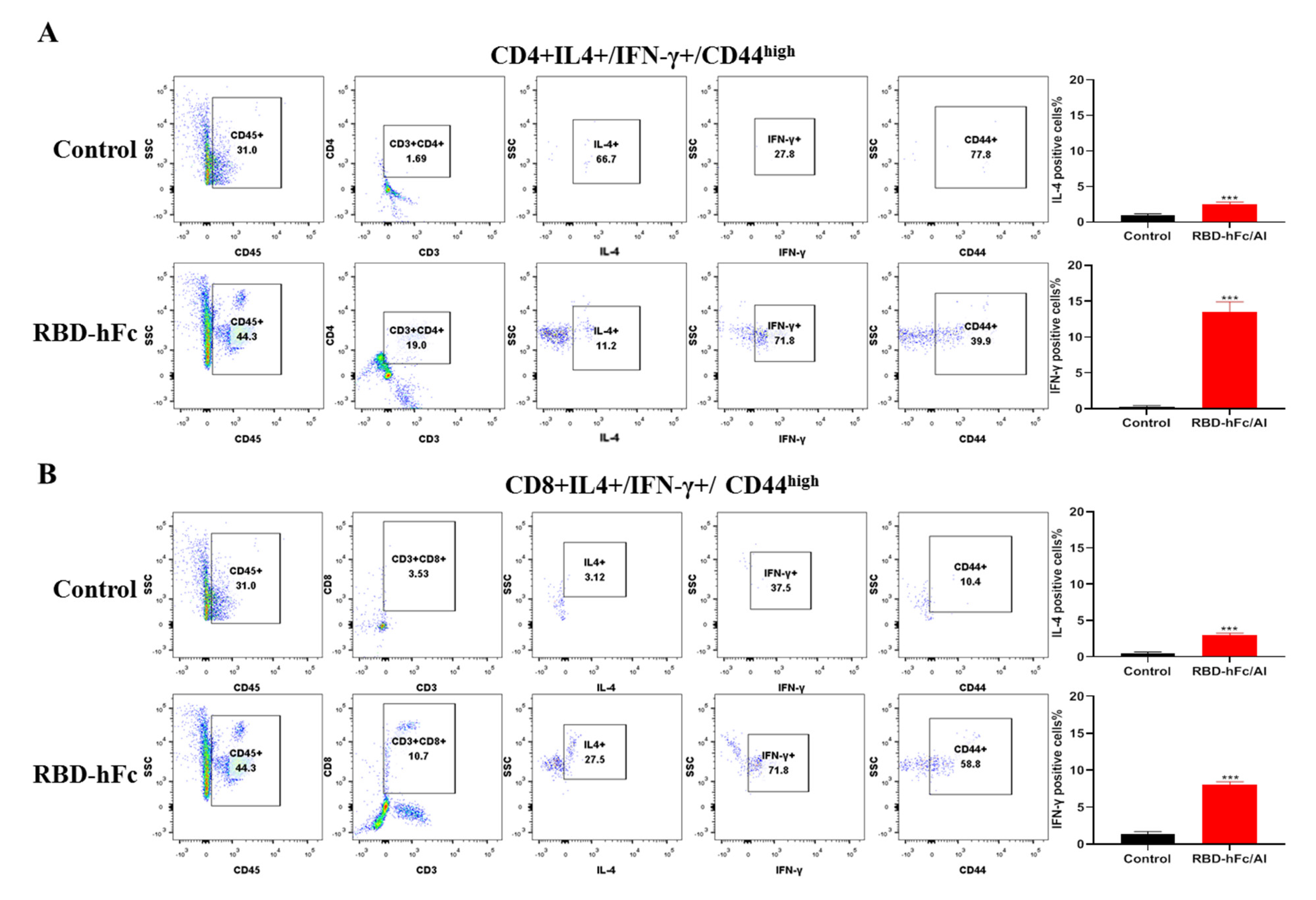
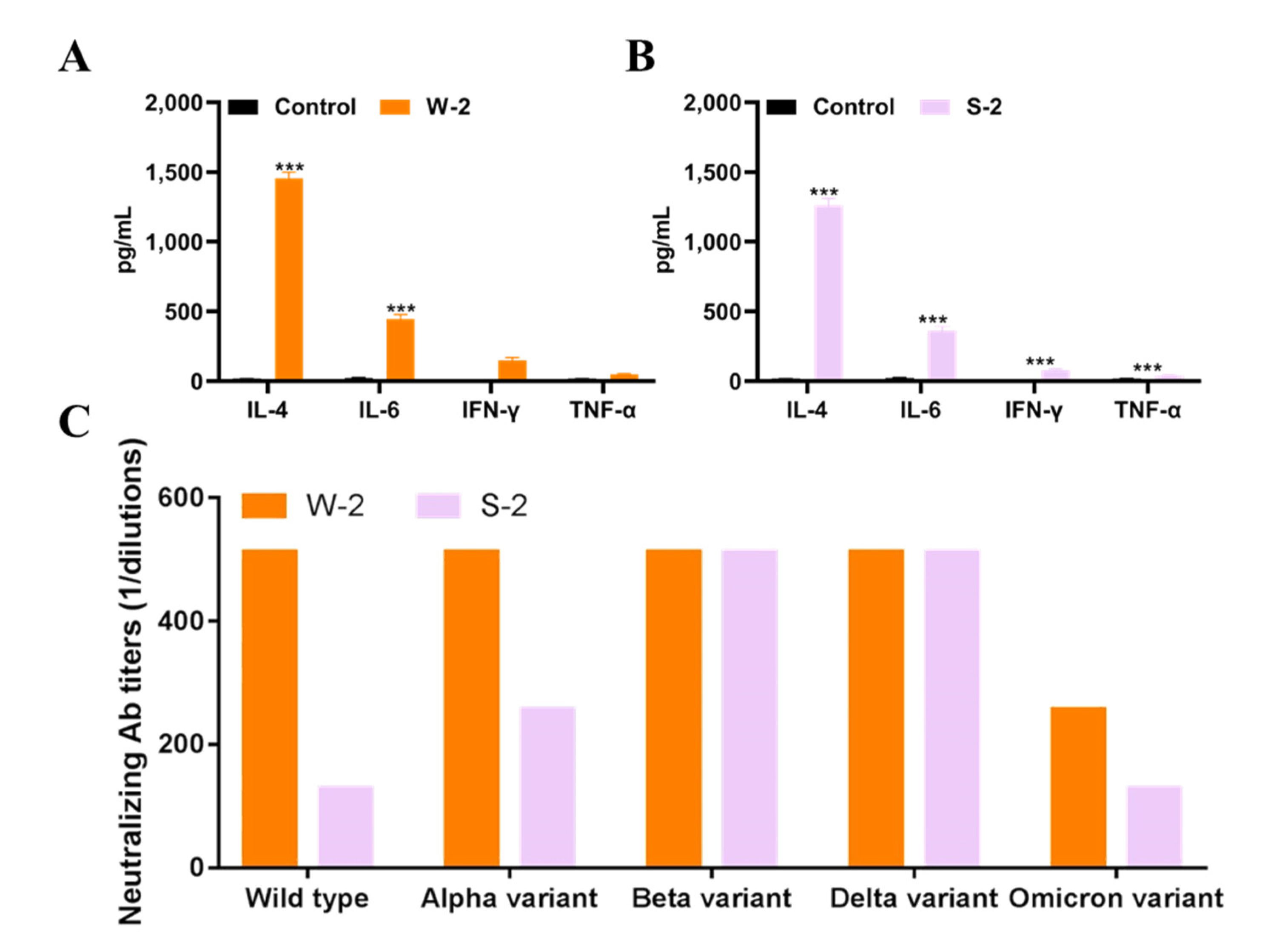
3.4. RBD-hFc Fusion Vaccine Can Induce a Powerful Cell-Mediated Immune Response
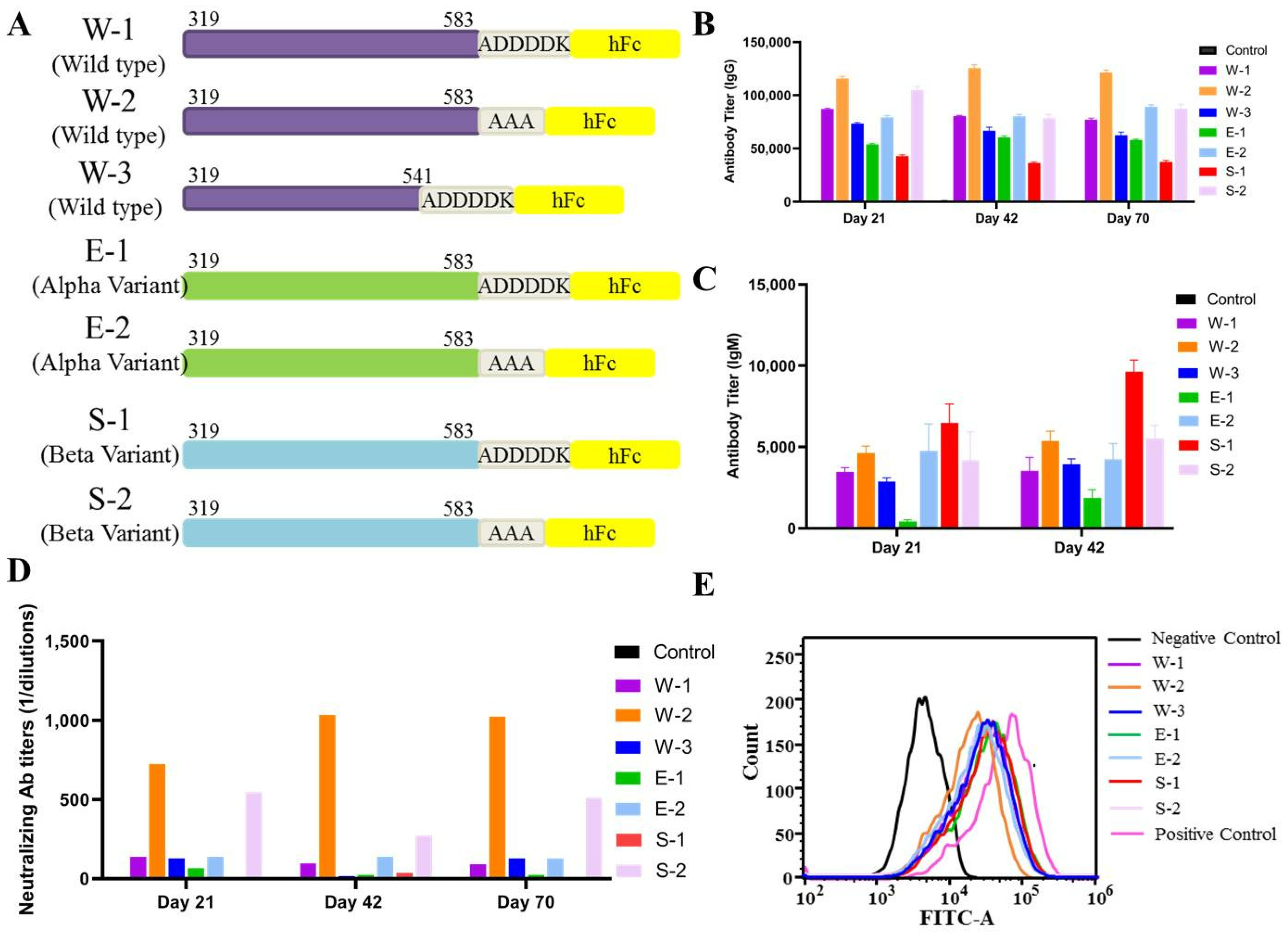
3.5. Wild-Type SARS-CoV-2 RBD-Plus-hFc with a Small Linker Can Elicit a Strong Humoral Immune Response
3.6. SARS-CoV-2 Wild-Type RBD-Plus-hFc with a Small Linker Exhibits a High Titer of Neutralizing Antibodies against Variants Alpha, Beta, Delta and Omicron
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| COVID-19 | Coronavirus Disease 2019 |
| SARS-CoV-2 | Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 |
| ACE2 | Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 |
| S protein | Spike protein |
| RBD | Receptor-binding domain |
| IgG | Immunoglobulin G |
| IgM | Immunoglobulin M |
| IFN-γ | gamma interferon |
| IL-4 | interleukin 4 |
References
- Pollard, C.A.; Morran, M.P.; Nestor-Kalinoski, A.L. The COVID-19 pandemic: A global health crisis. Physiol. Genom. 2020, 52, 549–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheahan, T.P.; Frieman, M.B. The continued epidemic threat of SARS-CoV-2 and implications for the future of global public health. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2020, 40, 37–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakraborty, D.; Agrawal, A.; Maiti, S. Rapid identification and tracking of SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern. Lancet 2021, 397, 1346–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, C.; Zhang, C.; Wang, Y.; Hong, Q.; Xu, S.; Li, Z.; Yang, Y.; Huang, Z.; Cong, Y. Structural basis for SARS-CoV-2 Delta variant recognition of ACE2 receptor and broadly neutralizing antibodies. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.R.; Yin, W.C.; Jiang, Y.; Xu, H.E. Structure genomics of SARS-CoV-2 and its Omicron variant: Drug design templates for COVID-19. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2022, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, K.L.; Wang, C.C.; White, K.I.; Pfuetzner, R.A.; Esquivies, L.; Brunger, A.T. Structural conservation among variants of the SARS-CoV-2 spike postfusion bundle. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2119467119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Planas, D.; Veyer, D.; Baidaliuk, A.; Staropoli, I.; Guivel-Benhassine, F.; Rajah, M.M.; Planchais, C.; Porrot, F.; Robillard, N.; Puech, J.; et al. Reduced sensitivity of SARS-CoV-2 variant Delta to antibody neutralization. Nature 2021, 596, 276–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Zhang, L.; Li, Q.; Wang, B.; Liang, Z.; Sun, Y.; Nie, J.; Wu, J.; Su, X.; Qu, X.; et al. Reduced sensitivity of the SARS-CoV-2 Lambda variant to monoclonal antibodies and neutralizing antibodies induced by infection and vaccination. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2022, 11, 18–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, S.; Cortese, M.; Winter, S.L.; Wachsmuth-Melm, M.; Neufeldt, C.J.; Cerikan, B.; Stanifer, M.L.; Boulant, S.; Bartenschlager, R.; Chlanda, P. SARS-CoV-2 structure and replication characterized by in situ cryo-electron tomography. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 5885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, L.; Zheng, T.; Xu, K.; Han, Y.; Xu, L.; Huang, E.; An, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Li, S.; Liu, M.; et al. A Universal Design of Betacoronavirus Vaccines against COVID-19, MERS, and SARS. Cell 2020, 182, 722–733 e11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zang, J.; Xu, S.; Zhang, X.; Yuan, S.; Wang, H.; Lavillette, D.; Zhang, C.; Huang, Z. Elicitation of Broadly Neutralizing Antibodies against B.1.1.7, B.1.351, and B.1.617.1 SARS-CoV-2 Variants by Three Prototype Strain-Derived Recombinant Protein Vaccines. Viruses 2021, 13, 1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, J.; Ge, J.; Yu, J.; Shan, S.; Zhou, H.; Fan, S.; Zhang, Q.; Shi, X.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, L.; et al. Structure of the SARS-CoV-2 spike receptor-binding domain bound to the ACE2 receptor. Nature 2020, 581, 215–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jawad, B.; Adhikari, P.; Podgornik, R.; Ching, W.Y. Key Interacting Residues between RBD of SARS-CoV-2 and ACE2 Receptor: Combination of Molecular Dynamics Simulation and Density Functional Calculation. J. Chem. Inf. Modeling 2021, 61, 4425–4441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, B.; Zhang, Z.; Li, Y.; Lin, X.; Gu, N. Evaluation of Interactions between SARS-CoV-2 RBD and Full-Length ACE2 with Coarse-Grained Molecular Dynamics Simulations. J. Chem. Inf. Modeling 2022, 62, 936–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, J.; He, X.; Ren, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhou, H.; Fan, S.; Zhu, C.; Liu, D.; Shao, B.; Liu, T.Y.; et al. Structural insights into the SARS-CoV-2 Omicron RBD-ACE2 interaction. Cell Res. 2022, 32, 593–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.G.; Su, D.; Song, T.Z.; Zeng, Y.; Huang, W.; Wu, J.; Xu, R.; Luo, P.; Yang, X.; Zhang, X.; et al. S-Trimer, a COVID-19 subunit vaccine candidate, induces protective immunity in nonhuman primates. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Tian, D.; Han, J.B.; Fan, W.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Sun, W.; Wei, Y.; Tian, X.; Yu, D.D.; et al. A recombinant receptor-binding domain in trimeric form generates protective immunity against SARS-CoV-2 infection in nonhuman primates. Innovation 2021, 2, 100140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Routhu, N.K.; Cheedarla, N.; Bollimpelli, V.S.; Gangadhara, S.; Edara, V.V.; Lai, L.; Sahoo, A.; Shiferaw, A.; Styles, T.M.; Floyd, K.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 RBD trimer protein adjuvanted with Alum-3M-052 protects from SARS-CoV-2 infection and immune pathology in the lung. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 3587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.; Shi, J.; Hu, X.; Wu, Y.; Zeng, L.; Yao, Y.; Shang, W.; Liu, K.; Gao, G.; Guo, W.; et al. RBD-homodimer, a COVID-19 subunit vaccine candidate, elicits immunogenicity and protection in rodents and nonhuman primates. Cell Discov. 2021, 7, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, L.; Gao, L.; Tao, L.; Hadinegoro, S.R.; Erkin, M.; Ying, Z.; He, P.; Girsang, R.T.; Vergara, H.; Akram, J.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of the RBD-Dimer-Based COVID-19 Vaccine ZF2001 in Adults. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 386, 2097–2111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.; Li, Y.; Pei, R.; Fang, X.; Zeng, P.; Fan, R.; Ou, Z.; Deng, J.; Zhou, J.; Guan, W.; et al. Safety and immunogenicity of a recombinant interferon-armed RBD dimer vaccine (V-01) for COVID-19 in healthy adults: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, Phase I trial. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2021, 10, 1589–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, F.Y.; Gao, F.; Jia, S.Y.; Wu, X.H.; Li, J.X.; Guo, X.L.; Zhang, J.L.; Cui, B.P.; Wu, Z.M.; Wei, M.W.; et al. Safety and immunogenicity of a recombinant COVID-19 vaccine (Sf9 cells) in healthy population aged 18 years or older: Two single-center, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 1 and phase 2 trials. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2021, 6, 271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, J.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Lin, K.; Fu, Z.; Song, J.; Zhao, Y.; Fan, M.; Wang, H.; et al. Recombinant protein subunit vaccine booster following two-dose inactivated vaccines dramatically enhanced anti-RBD responses and neutralizing titers against SARS-CoV-2 and Variants of Concern. Cell Res. 2022, 32, 103–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, X.; Ke, B.; Feng, Q.; Yang, D.; Lian, Q.; Li, Z.; Lu, L.; Ke, C.; Liu, Z.; Liao, G. Construction and immunogenic studies of a mFc fusion receptor binding domain (RBD) of spike protein as a subunit vaccine against SARS-CoV-2 infection. Chem. Commun. 2020, 56, 8683–8686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czajkowsky, D.M.; Hu, J.; Shao, Z.F.; Pleass, R.J. Fc-fusion proteins: New developments and future perspectives. Embo. Mol. Med. 2012, 4, 1015–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chun, J.; Cho, Y.; Park, K.H.; Choi, H.; Cho, H.; Lee, H.J.; Jang, H.; Kim, K.H.; Oh, Y.K.; Kim, Y.B. Effect of Fc Fusion on Folding and Immunogenicity of Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus Spike Protein. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. Food Sci. 2019, 29, 813–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, R.; Wang, M.; Liu, Y.; Yin, Y.; Zai, X.; Song, X.; Chen, Y.; Xu, J.; Chen, W. Fc-Based Recombinant Henipavirus Vaccines Elicit Broad Neutralizing Antibody Responses in Mice. Viruses 2020, 12, 480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chichili, V.P.R.; Kumar, V.; Sivaraman, J. Linkers in the structural biology of protein-protein interactions. Protein. Sci. 2013, 22, 153–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.Y.; Zaro, J.L.; Shen, W.C. Fusion protein linkers: Property, design and functionality. Adv. Drug Deliver. Rev. 2013, 65, 1357–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eigenfeld, M.; Kerpes, R.; Becker, T. Recombinant protein linker production as a basis for non-invasive determination of single-cell yeast age in heterogeneous yeast populations. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 31923–31932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Xu, W.; Xia, S.; Gu, C.; Wang, X.; Wang, Q.; Zhou, J.; Wu, Y.; Cai, X.; Qu, D.; et al. RBD-Fc-based COVID-19 vaccine candidate induces highly potent SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibody response. Signal Transduct. Tar. 2020, 5, 282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, Y.H.M.; van Lengerich, B.; Boxer, S.G. Effects of linker sequences on vesicle fusion mediated by lipid-anchored DNA oligonucleotides. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 979–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeGrace, M.M.; Ghedin, E.; Frieman, M.B.; Krammer, F.; Grifoni, A.; Alisoltani, A.; Alter, G.; Amara, R.R.; Baric, R.S.; Barouch, D.H.; et al. Defining the risk of SARS-CoV-2 variants on immune protection. Nature 2022, 605, 640–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koldehoff, M.; Horn, P.A.; Lindemann, M. Cellular Immune Response after Vaccination with an Adjuvanted, Recombinant Zoster Vaccine in Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplant Recipients. Vaccines 2022, 10, 809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paramithiotis, E.; Sugden, S.; Papp, E.; Bonhomme, M.; Chermak, T.; Crawford, S.Y.; Demetriades, S.Z.; Galdos, G.; Lambert, B.L.; Mattison, J.; et al. Cellular Immunity Is Critical for Assessing COVID-19 Vaccine Effectiveness in Immunocompromised Individuals. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 880784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, L.; Qi, X.; Liang, D.; Li, G.; Peng, X.; Li, X.; Ke, B.; Zheng, H.; Liu, Z.; Ke, C.; et al. Human Fc-Conjugated Receptor Binding Domain-Based Recombinant Subunit Vaccines with Short Linker Induce Potent Neutralizing Antibodies against Multiple SARS-CoV-2 Variants. Vaccines 2022, 10, 1502. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines10091502
Chen L, Qi X, Liang D, Li G, Peng X, Li X, Ke B, Zheng H, Liu Z, Ke C, et al. Human Fc-Conjugated Receptor Binding Domain-Based Recombinant Subunit Vaccines with Short Linker Induce Potent Neutralizing Antibodies against Multiple SARS-CoV-2 Variants. Vaccines. 2022; 10(9):1502. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines10091502
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Liqing, Xiaoxiao Qi, Dan Liang, Guiqi Li, Xiaofang Peng, Xiaohui Li, Bixia Ke, Huanying Zheng, Zhongqiu Liu, Changwen Ke, and et al. 2022. "Human Fc-Conjugated Receptor Binding Domain-Based Recombinant Subunit Vaccines with Short Linker Induce Potent Neutralizing Antibodies against Multiple SARS-CoV-2 Variants" Vaccines 10, no. 9: 1502. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines10091502
APA StyleChen, L., Qi, X., Liang, D., Li, G., Peng, X., Li, X., Ke, B., Zheng, H., Liu, Z., Ke, C., Liao, G., Liu, L., & Feng, Q. (2022). Human Fc-Conjugated Receptor Binding Domain-Based Recombinant Subunit Vaccines with Short Linker Induce Potent Neutralizing Antibodies against Multiple SARS-CoV-2 Variants. Vaccines, 10(9), 1502. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines10091502





