Identification of NS2B-NS3 Protease Inhibitors for Therapeutic Application in ZIKV Infection: A Pharmacophore-Based High-Throughput Virtual Screening and MD Simulations Approaches
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Molecular Databases Used
2.2. Ligand Preparation
2.3. Protein Preparation
2.4. Molecular Docking
2.5. Energy-Optimised Pharmacophore
2.6. ADME/T Analysis and High-Throughput Virtual Screening
2.7. Binding Free Energy Calculation Using MM-GBSA
2.8. Molecular Dynamics Simulation
3. Results
3.1. E-Pharmacophore Model
3.2. E-Pharmacophore-Based High Throughput Virtual Screening
3.3. Description of the ADME Properties of the Hit Molecules
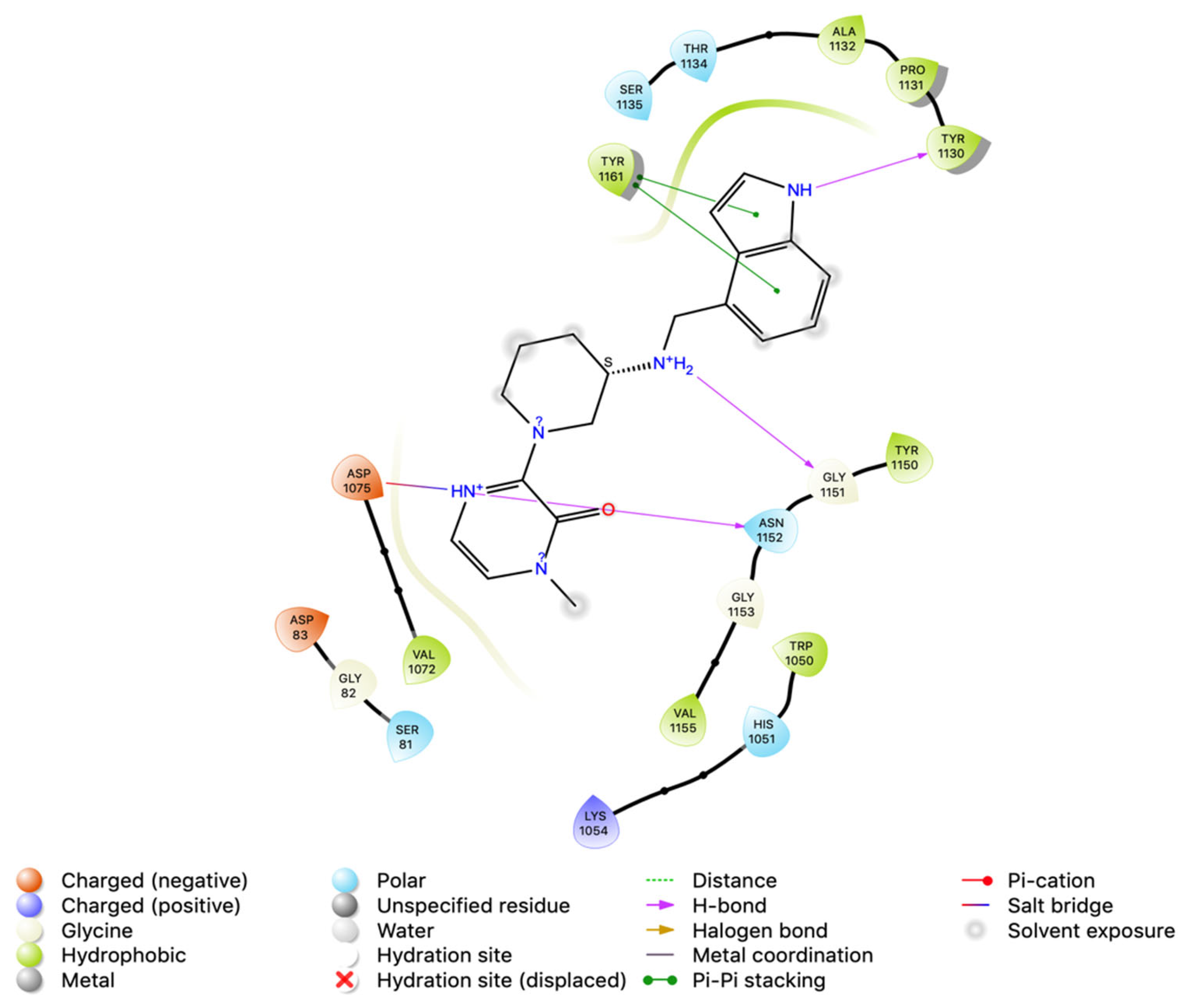
3.4. Intermolecular Interactions of Hit Molecules with NS2B-NS3 Protein
3.5. Binding Free Energy Calculation Using MM-GBSA
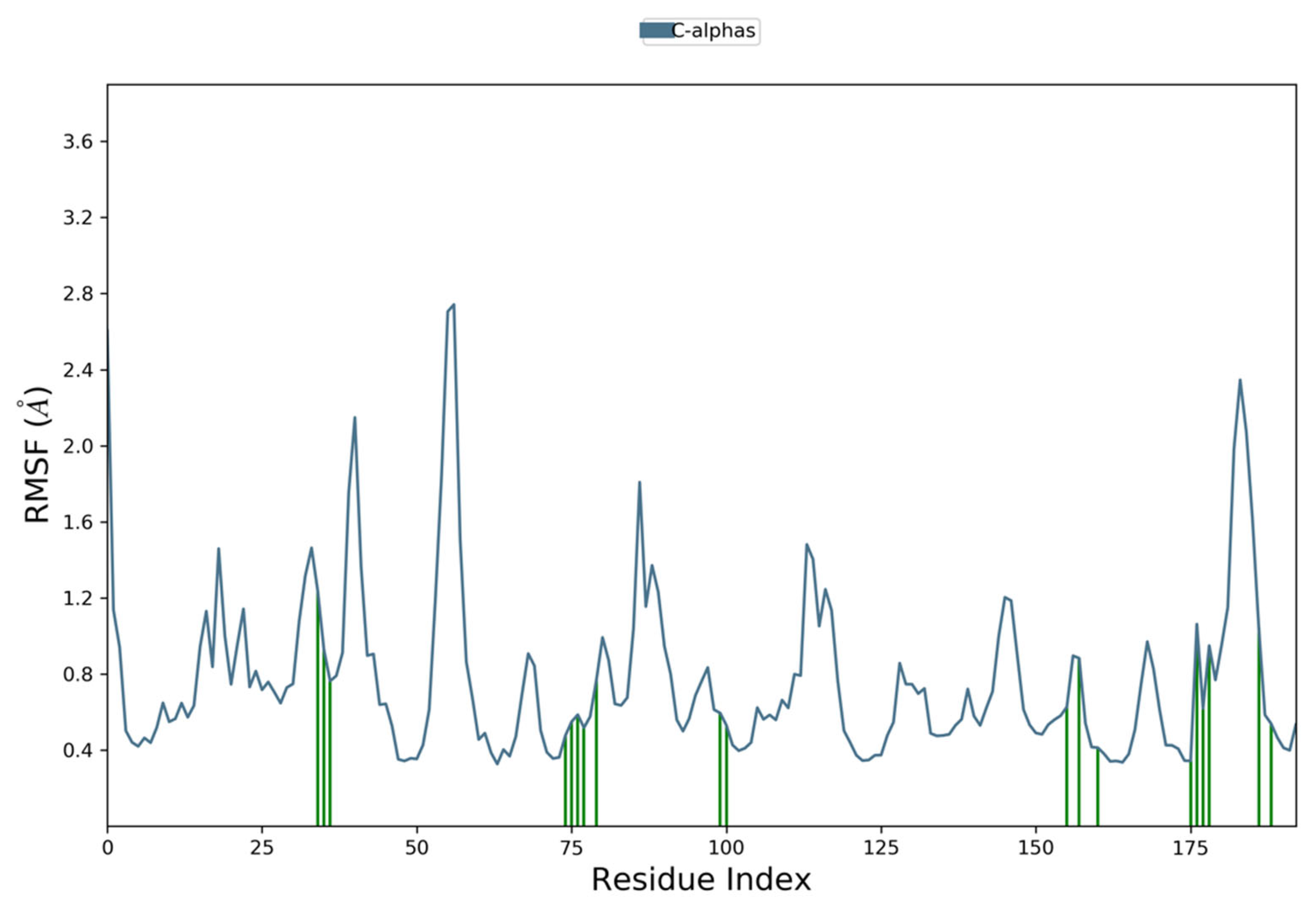
3.6. Molecular Dynamics Simulation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shi, Y.; Li, S.; Wu, Q.; Sun, L.; Zhang, J.; Pan, N.; Wang, Q.; Bi, Y.; An, J.; Lu, X.; et al. Vertical transmission of the Zika virus causes neurological disorders in mouse offspring. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 3541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Musso, D.; Gubler, D.J. Zika virus. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2016, 29, 487–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Duffy, M.R.; Chen, T.H.; Hancock, W.T.; Powers, A.M.; Kool, J.L.; Lanciotti, R.S.; Pretrick, M.; Marfel, M.; Holzbauer, S.; Dubray, C.; et al. Zika virus outbreak on Yap Island, federated states of Micronesia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 360, 2536–2543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao-Lormeau, V.M.; Roche, C.; Teissier, A.; Robin, E.; Berry, A.L.; Mallet, H.P.; Sall, A.A.; Musso, D. Zika virus, French polynesia, South Pacific, 2013. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2014, 20, 1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baud, D.; Gubler, D.J.; Schaub, B.; Lanteri, M.C.; Musso, D. An update on Zika virus infection. Lancet 2017, 390, 2099–2109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bollati, M.; Alvarez, K.; Assenberg, R.; Baronti, C.; Canard, B.; Cook, S.; Coutard, B.; Decroly, E.; de Lamballerie, X.; Gould, E.A.; et al. Structure and functionality in flavivirus NS-proteins: Perspectives for drug design. Antivir. Res. 2010, 87, 125–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuno, G.; Chang, G.J. Full-length sequencing and genomic characterization of Bagaza, Kedougou, and Zika viruses. Arch. Virol. 2007, 152, 687–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faye, O.; Freire, C.C.; Iamarino, A.; Faye, O.; de Oliveira, J.V.C.; Diallo, M.; Zanotto, P.M. Molecular evolution of Zika virus during its emergence in the 20th century. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2014, 8, e2636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Paixão, E.S.; Barreto, F.; da Glória Teixeira, M.; da Conceição, N.; Costa, M.; Rodrigues, L.C. History, epidemiology, and clinical manifestations of Zika: A systematic review. Am. J. Public Health 2016, 106, 606–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguirre, S.; Maestre, A.M.; Pagni, S.; Patel, J.R.; Savage, T.; Gutman, D.; Maringer, K.; Bernal-Rubio, D.; Shabman, R.S.; Simon, V.; et al. DENV inhibits type I IFN production in infected cells by cleaving human STING. PLoS Pathog. 2012, 8, e1002934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preethi, B.; Shanthi, V.; Ramanathan, K. Investigation of nalidixic acid resistance mechanism in Salmonella enterica using molecular simulation techniques. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2015, 177, 528–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rohini, K.; Shanthi, V. Discovery of potent neuraminidase inhibitors using a combination of pharmacophore-based virtual screening and molecular simulation approach. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2018, 184, 1421–1440. [Google Scholar]
- James, N.; Shanthi, V.; Ramanathan, K. Drug design for ALK-positive NSCLC: An integrated pharmacophore-based 3D QSAR and virtual screening strategy. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2018, 185, 289–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirza, S.B.; Lee, R.C.H.; Chu, J.J.H.; Salmas, R.E.; Mavromoustakos, T.; Durdagi, S. Discovery of selective dengue virus inhibitors using combination of molecular fingerprint-based virtual screening protocols, structure-based pharmacophore model development, molecular dynamics simulations and in vitro studies. J. Mol. Graphics. Model. 2018, 79, 88–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Li, J.; Qing, J.; Huang, M.; Wu, M.; Gao, F.; Li, D.; Hong, Z.; Kong, L.; Huang, W.; et al. Discovery of novel hepatitis C virus NS5B polymerase inhibitors by combining random forest, multiple e-pharmacophore modeling and docking. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0148181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirza, M.U.; Alanko, I.; Vanmeert, M.; Muzzarelli, K.M.; Salo-Ahen, O.M.; Abdullah, I.; Froeyen, M. The discovery of Zika virus NS2B-NS3 inhibitors with antiviral activity via an integrated virtual screening approach. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2022, 175, 106220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, J.; Hansen, G.; Nitsche, C.; Klein, C.D.; Zhang, L.; Hilgenfeld, R. Crystal structure of Zika virus NS2B-NS3 protease in complex with a boronate inhibitor. Science 2016, 353, 503–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pérez-Regidor, L.; Zarioh, M.; Ortega, L.; Martín-Santamaría, S. Virtual screening approaches towards the discovery of toll-like receptor modulators. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van Den Driessche, G.; Fourches, D. Adverse drug reactions triggered by the common HLA-B* 57: 01 variant: A molecular docking study. J. Cheminf. 2017, 9, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Banerjee, K.; Gupta, U.; Gupta, S.; Wadhwa, G.; Gabrani, R.; Sharma, S.K.; Jain, C.K. Molecular docking of glucosamine-6-phosphate synthase in Rhizopus oryzae. Bioinformation 2011, 7, 285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ramatenki, V.; Dumpati, R.; Vadija, R.; Vellanki, S.; Potlapally, S.R.; Rondla, R.; Vuruputuri, U. Identification of new lead molecules against UBE2NL enzyme for cancer therapy. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2017, 182, 1497–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jorgensen, W.L.; Tirado-Rives, J. The OPLS [optimized potentials for liquid simulations] potential functions for proteins, energy minimizations for crystals of cyclic peptides and crambin. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1988, 110, 1657–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Falco, F.; Di Giovanni, C.; Cerchia, C.; De Stefano, D.; Capuozzo, A.; Irace, C.; Iuvone, T.; Santamaria, R.; Carnuccio, R.; Lavecchia, A. Novel non-peptide small molecules preventing IKKβ/NEMO association inhibit NF-κB activation in LPS-stimulated J774 macrophages. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2016, 104, 83–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalliokoski, T.; Salo, H.S.; Lahtela-Kakkonen, M.; Poso, A. The effect of ligand-based tautomer and protomer prediction on structure-based virtual screening. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2009, 49, 2742–2748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lanciotti, R.S.; Kosoy, O.L.; Laven, J.J.; Velez, J.O.; Lambert, A.J.; Johnson, A.J.; Stanfield, S.M.; Duffy, M.R. Genetic and serologic properties of Zika virus associated with an epidemic, Yap State, Micronesia, 2007. Emerging Infect. Dis. 2008, 14, 1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friesner, R.A.; Murphy, R.B.; Repasky, M.P.; Frye, L.L.; Greenwood, J.R.; Halgren, T.A.; Sanschagrin, P.C.; Mainz, D.T. Extra precision glide: Docking and scoring incorporating a model of hydrophobic enclosure for protein-ligand complexes. J. Med. Chem. 2006, 49, 6177–6196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yoo, J.; Medina-Franco, J.L. Homology modeling, docking and structure-based pharmacophore of inhibitors of DNA methyltransferase. J. Comput. Aided Mol. Des. 2011, 25, 555–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friesner, R.A.; Banks, J.L.; Murphy, R.B.; Halgren, T.A.; Klicic, J.J.; Mainz, D.T.; Repasky, M.P.; Knoll, E.H.; Shelley, M.; Perry, J.K.; et al. Glide: A new approach for rapid, accurate docking and scoring. 1. Method and assessment of docking accuracy. J. Med. Chem. 2004, 47, 1739–1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salam, N.K.; Nuti, R.; Sherman, W. Novel method for generating structure-based pharmacophores using energetic analysis. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2009, 49, 2356–2368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthusamy, K.; Singh, K.D.; Chinnasamy, S.; Nagamani, S.; Krishnasamy, G.; Thiyagarajan, C.; Premkumar, P.; Anusuyadevi, M. High throughput virtual screening and E-pharmacophore filtering in the discovery of new BACE-1 inhibitors. Interdiscip. Sci. Comput. Life Sci. 2013, 5, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathee, D.; Lather, V.; Dureja, H. Pharmacophore modeling and 3D QSAR studies for prediction of matrix metalloproteinases inhibitory activity of hydroxamate derivatives. Biotechnol. Res. Innov. 2017, 1, 112–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, N.; Ramanathan, K. Discovery of potent ALK inhibitors using pharmacophore-informatics strategy. Cell Biochem. Biophy. 2018, 76, 111–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baell, J.; Congreve, M.; Leeson, P.; Abad-Zapatero, C. Ask the experts: Past, present and future of the rule of five. Future Med. Chem. 2013, 5, 745–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinheiro, A.S.; Duarte, J.B.C.; Alves, C.N.; de Molfetta, F.A. Virtual screening and molecular dynamics simulations from a bank of molecules of the amazon region against functional NS3-4A protease-helicase enzyme of hepatitis C virus. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2015, 176, 1709–1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, K.K.; Sethi, G.; Jayaraman, M. Molecular docking and simulation studies of gustatory receptor of Aedes aegypti: A potent drug target to distract host-seeking behaviour in mosquitoes. J. Vector Borne Dis. 2016, 53, 179. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rohini, K.; Agarwal, P.; Preethi, B.; Shanthi, V.; Ramanathan, K. Exploring the lead compounds for Zika Virus NS2B-NS3 protein: An e-pharmacophore-based approach. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2019, 187, 194–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cappel, D.; Hall, M.L.; Lenselink, E.B.; Beuming, T.; Qi, J.; Bradner, J.; Sherman, W. Relative Binding Free Energy Calculations Applied to Protein Homology Models. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2016, 56, 2388–2400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Onufriev, A.; Bashford, D.; Case, D.A. Exploring protein native states and large-scale conformational changes with a modified generalized born model. Proteins Struct. Funct. Bioinf. 2004, 55, 383–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ash, J.; Fourches, D. Characterizing the chemical space of ERK2 kinase inhibitors using descriptors computed from molecular dynamics trajectories. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2017, 57, 1286–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Meng, F.; Cheng, S.; Ding, H.; Liu, S.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, K.; Chen, S.; Lu, J.; Xie, Y.; Li, L.; et al. Discovery and optimization of novel, selective histone methyltransferase SET7 inhibitors by pharmacophore-and docking-based virtual screening. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 58, 8166–8181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, M.; Chandra, S.; Tiwari, N.; Subbarao, N. 3D QSAR, pharmacophore and molecular docking studies of known inhibitors and designing of novel inhibitors for M18 aspartyl aminopeptidase of Plasmodium falciparum. BMC Struct. Biol. 2016, 16, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kandakatla, N.A.; Ramakrishnan, G.; Karthikeyan, J.; Chekkara, R. Pharmacophore modeling, atom based 3D-QSAR and docking studies of chalcone derivatives as tubulin inhibitors. Orient. J. Chem. 2014, 30, 1083–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pradeep, N.; Munikumar, M.; Swargam, S.; Hema, K.; Sudheer Kumar, K.; Umamaheswari, A. 197 Combination of e-pharmacophore modeling, multiple docking strategies and molecular dynamic simulations to discover of novel antagonists of BACE1. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2015, 33 (Suppl. S1), 129–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pradhan, D.; Priyadarshini, V.; Munikumar, M.; Swargam, S.; Umamaheswari, A.; Bitla, A. Para-(benzoyl)-phenylalanine as a potential inhibitor against LpxC of Leptospira spp.: Homology modeling, docking, and molecular dynamics study. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2014, 32, 171–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chikan, N.A.; Bhavaniprasad, V.; Anbarasu, K.; Shabir, N.; Patel, T.N. From natural products to drugs for epimutation computer-aided drug design. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2013, 170, 164–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laskowski, R.A.; Swindells, M.B. LigPlot+: Multiple ligand-protein interaction diagrams for drug discovery. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2011, 51, 2778–2786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patil, R.; Das, S.; Stanley, A.; Yadav, L.; Sudhakar, A.; Varma, A.K. Optimized hydrophobic interactions and hydrogen bonding at the target-ligand interface leads the pathways of drug-designing. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e12029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, J.F.; Chik, K.K.; Yuan, S.; Yip, C.C.; Zhu, Z.; Tee, K.M.; Tsang, J.O.; Chan, C.C.; Poon, V.K.; Lu, G.; et al. Novel antiviral activity and mechanism of bromocriptine as a Zika virus NS2B-NS3 protease inhibitor. Antivir. Res. 2017, 141, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voss, S.; Nitsche, C. Inhibitors of the Zika virus protease NS2B-NS3. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2020, 30, 126965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, R.; Selvaraj, C.; Aarthy, M.; Kumar, P.; Kumar, A.; Singh, S.K.; Giri, R. Investigating into the molecular interactions of flavonoids targeting NS2B-NS3 protease from ZIKA virus through in-silico approaches. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2021, 39, 272–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saudi, M.; Zmurko, J.; Kaptein, S.; Rozenski, J.; Neyts, J.; Van Aerschot, A. Synthesis and evaluation of imidazole-4, 5-and pyrazine-2, 3-dicarboxamides targeting dengue and yellow fever virus. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 87, 529–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, N.; Chen, H.M.; Koch, V.; Schmitz, H.; Liao, C.L.; Bretner, M.; Bhadti, V.S.; Fattom, A.I.; Naso, R.B.; Hosmane, R.S.; et al. Ring-expanded (“fat”) nucleoside and nucleotide analogues exhibit potent in vitro activity against flaviviridae NTPases/helicases, including those of the West Nile virus, hepatitis C virus, and Japanese encephalitis virus. J. Med. Chem. 2003, 46, 4149–4164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Situation Report: Zika Virus Microcephaly Guillain-Barré Syndrome; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar]









| Compound | XP GScore | MMGBSA | Mol MW | Docking Score | Rule of Five Violation | Prime vdw |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Comp 1 | −7.399 | −64.58 | 317.387 | −7.228 | 0 | −833.91 |
| Comp 2 | −8.040 | −55.15 | 337.424 | −8.040 | 0 | −828.84 |
| Comp 3 | −5.792 | −50.16 | 303.323 | −5.792 | 0 | −829.43 |
| Ranges Sr. No. | QPlogPo/w (−2.0–6.5) | QPlogBB (−3.0–1.2) | Mol MW (130.0–725) | Percent Human-Oral Absorption (>80% Is High <25% Is Poor) | FISA (7.0–330) | PISA (0.0–450) | QPlogHERG (Concern below −5) | QPlogS (−6.5–0.5) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Comp 1 | 2.307 | 0.158 | 342.827 | 90.439 | 115.470 | 242.988 | −3.454 | −2.855 |
| Comp 2 | 0.681 | −2.206 | 343.359 | 58.803 | 257.159 | 304.534 | −5.85 | −3.726 |
| Comp 3 | 0.288 | −1.553 | 303.323 | 69.379 | 181.286 | 166.144 | −4.592 | −2.086 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rehman, H.M.; Sajjad, M.; Ali, M.A.; Gul, R.; Irfan, M.; Naveed, M.; Bhinder, M.A.; Ghani, M.U.; Hussain, N.; Said, A.S.A.; et al. Identification of NS2B-NS3 Protease Inhibitors for Therapeutic Application in ZIKV Infection: A Pharmacophore-Based High-Throughput Virtual Screening and MD Simulations Approaches. Vaccines 2023, 11, 131. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11010131
Rehman HM, Sajjad M, Ali MA, Gul R, Irfan M, Naveed M, Bhinder MA, Ghani MU, Hussain N, Said ASA, et al. Identification of NS2B-NS3 Protease Inhibitors for Therapeutic Application in ZIKV Infection: A Pharmacophore-Based High-Throughput Virtual Screening and MD Simulations Approaches. Vaccines. 2023; 11(1):131. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11010131
Chicago/Turabian StyleRehman, Hafiz Muzzammel, Muhammad Sajjad, Muhammad Akhtar Ali, Roquyya Gul, Muhammad Irfan, Muhammad Naveed, Munir Ahmad Bhinder, Muhammad Usman Ghani, Nadia Hussain, Amira S. A. Said, and et al. 2023. "Identification of NS2B-NS3 Protease Inhibitors for Therapeutic Application in ZIKV Infection: A Pharmacophore-Based High-Throughput Virtual Screening and MD Simulations Approaches" Vaccines 11, no. 1: 131. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11010131
APA StyleRehman, H. M., Sajjad, M., Ali, M. A., Gul, R., Irfan, M., Naveed, M., Bhinder, M. A., Ghani, M. U., Hussain, N., Said, A. S. A., Al Haddad, A. H. I., & Saleem, M. (2023). Identification of NS2B-NS3 Protease Inhibitors for Therapeutic Application in ZIKV Infection: A Pharmacophore-Based High-Throughput Virtual Screening and MD Simulations Approaches. Vaccines, 11(1), 131. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11010131







