In Vitro Efficacy of Antivirals and Monoclonal Antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 Omicron Lineages XBB.1.9.1, XBB.1.9.3, XBB.1.5, XBB.1.16, XBB.2.4, BQ.1.1.45, CH.1.1, and CL.1
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection and RT-PCR Testing
2.2. Cell Culture and Virus Isolation
2.3. Sequencing and NGS Data Analysis
2.4. Choice of SARS-CoV-2 Variants
2.5. Evaluation of the Neutralization Efficacy of Monoclonal Antibody
2.6. Evaluation of the Antiviral Efficacy of Drugs
3. Results
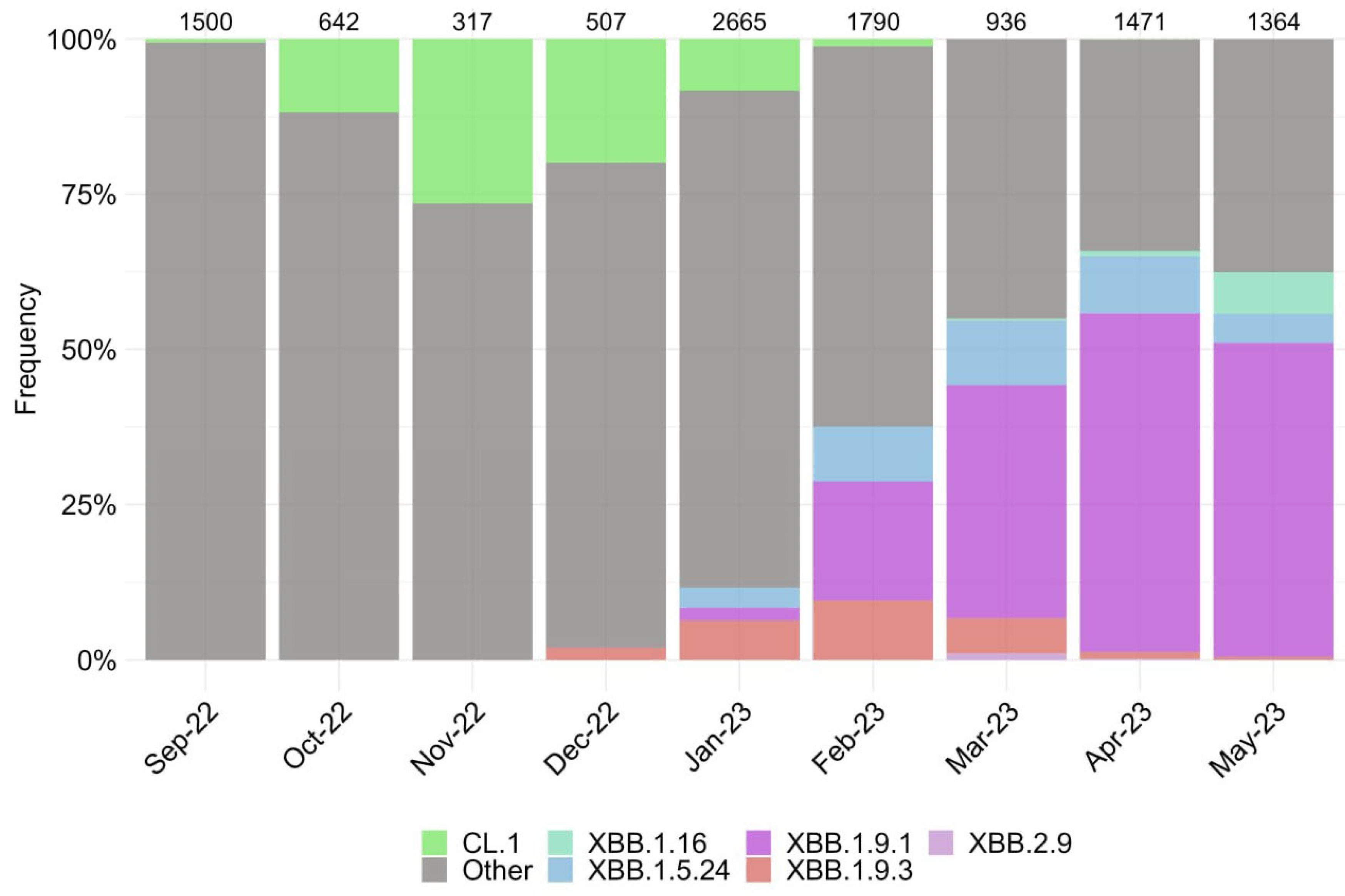
3.1. Characterization of SARS-CoV-2 Genetic Variants in Moscow
3.2. Evaluation of Monoclonal Antibody Efficacy In Vitro
3.3. Evaluation of the Antiviral Efficacy of Drugs In Vitro
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- WHO Coronavirus (COVID-19). 2023. Available online: https://covid19.who.int/ (accessed on 1 August 2023).
- Polack, F.P.; Thomas, S.J.; Kitchin, N.; Absalon, J.; Gurtman, A.; Lockhart, S.; Perez, J.L.; Marc, G.P.; Moreira, E.D.; Zerbini, C.; et al. Safety and Efficacy of the BNT162b2 mRNA Covid-19 Vaccine. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 2603–2615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baden, L.R.; El Sahly, H.M.; Essink, B.; Kotloff, K.; Frey, S.; Novak, R.; Diemert, D.; Spector, S.A.; Rouphael, N.; Creech, C.B.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of the mRNA-1273 SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 403–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Logunov, D.Y.; Dolzhikova, I.V.; Shcheblyakov, D.V.; Tukhvatulin, A.I.; Zubkova, O.V.; Dzharullaeva, A.S.; Kovyrshina, A.V.; Lubenets, N.L.; Grousova, D.M.; Erokhova, A.S.; et al. Safety and Efficacy of an rAd26 and rAd5 Vector-Based Heterologous Prime-Boost COVID-19 Vaccine: An Interim Analysis of a Randomised Controlled Phase 3 Trial in Russia. Lancet 2021, 397, 671–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voysey, M.; Clemens, S.A.C.; Madhi, S.A.; Weckx, L.Y.; Folegatti, P.M.; Aley, P.K.; Angus, B.; Baillie, V.L.; Barnabas, S.L.; Bhorat, Q.E.; et al. Safety and Efficacy of the ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 Vaccine (AZD1222) against SARS-CoV-2: An Interim Analysis of Four Randomised Controlled Trials in Brazil, South Africa, and the UK. Lancet 2021, 397, 99–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Medicines Agency. COVID-19 Medicines. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/human-regulatory/overview/public-health-threats/coronavirus-disease-covid-19/covid-19-medicines (accessed on 1 August 2023).
- Emergency Use Authorization (EUA) for the Treatment of COVID-19. Available online: https://www.covid19.lilly.com/bebtelovimab (accessed on 1 August 2023).
- Dubey, A.; Choudhary, S.; Kumar, P.; Tomar, S. Emerging SARS-CoV-2 Variants: Genetic Variability and Clinical Implications. Curr. Microbiol. 2022, 79, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, J.J.; Cheng, S.M.S.; Leung, K.; Lee, C.K.; Hachim, A.; Tsang, L.C.H.; Yam, K.W.H.; Chaothai, S.; Kwan, K.K.H.; Chai, Z.Y.H.; et al. Real-World COVID-19 Vaccine Effectiveness against the Omicron BA.2 Variant in a SARS-CoV-2 Infection-Naive Population. Nat. Med. 2023, 29, 348–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godkov, M.A.; Ogarkova, D.A.; Gushchin, V.A.; Kleymenov, D.A.; Mazunina, E.P.; Bykonia, E.N.; Pochtovyi, A.A.; Shustov, V.V.; Shcheblyakov, D.V.; Komarov, A.G.; et al. Revaccination in Age-Risk Groups with Sputnik V Is Immunologically Effective and Depends on the Initial Neutralizing SARS-CoV-2 IgG Antibodies Level. Vaccines 2022, 11, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miteva, D.; Kitanova, M.; Batselova, H.; Lazova, S.; Chervenkov, L.; Peshevska-Sekulovska, M.; Sekulovski, M.; Gulinac, M.; Vasilev, G.V.; Tomov, L.; et al. The End or a New Era of Development of SARS-CoV-2 Virus: Genetic Variants Responsible for Severe COVID-19 and Clinical Efficacy of the Most Commonly Used Vaccines in Clinical Practice. Vaccines 2023, 11, 1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurhade, C.; Zou, J.; Xia, H.; Liu, M.; Chang, H.C.; Ren, P.; Xie, X.; Shi, P.Y. Low Neutralization of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron BA.2.75.2, BQ.1.1 and XBB.1 by Parental mRNA Vaccine or a BA.5 Bivalent Booster. Nat. Med. 2023, 29, 344–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Addetia, A.; Piccoli, L.; Case, J.B.; Park, Y.-J.; Beltramello, M.; Guarino, B.; Dang, H.; de Melo, G.D.; Pinto, D.; Sprouse, K.; et al. Neutralization, Effector Function and Immune Imprinting of Omicron Variants. Nature 2023, 621, 592–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazawa, S.; Yamazaki, E.; Saga, Y.; Itamochi, M.; Inasaki, N.; Shimada, T.; Oishi, K.; Tani, H. Evaluation of SARS-CoV-2 Isolation in Cell Culture from Nasal/nasopharyngeal Swabs or Saliva Specimens of Patients with COVID-19. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 8893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reed, L.J.; Muench, H. A Simple Method of estimating fifty per cent endpoints. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1938, 27, 493–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gushchin, V.A.; Pochtovyi, A.A.; Kustova, D.D.; Ogarkova, D.A.; Tarnovetskii, I.Y.; Belyaeva, E.D.; Divisenko, E.V.; Vasilchenko, L.A.; Shidlovskaya, E.V.; Kuznetsova, N.A.; et al. Dynamics of SARS-CoV-2 Major Genetic Lineages in Moscow in the Context of Vaccine Prophylaxis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 14670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klink, G.V.; Safina, K.R.; Nabieva, E.; Shvyrev, N.; Garushyants, S.; Alekseeva, E.; Komissarov, A.B.; Danilenko, D.M.; Pochtovyi, A.A.; Divisenko, E.V.; et al. The Rise and Spread of the SARS-CoV-2 AY.122 Lineage in Russia. Virus Evol. 2022, 8, veac017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, M. Cutadapt Removes Adapter Sequences from High- Throughput Sequencing Reads. EMBnet. J. 2011, 17, 10–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rognes, T.; Flouri, T.; Nichols, B.; Quince, C.; Mahé, F. VSEARCH: A Versatile Open Source Tool for Metagenomics. PeerJ 2016, 2016, e2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Durbin, R. Fast and Accurate Short Read Alignment with Burrows-Wheeler Transform. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1754–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrison, E.; Marth, G. Haplotype-Based Variant Detection from Short-Read Sequencing. arXiv 2012, arXiv:1207.3907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Handsaker, B.; Wysoker, A.; Fennell, T.; Ruan, J.; Homer, N.; Marth, G.; Abecasis, G.; Durbin, R. The Sequence Alignment/Map Format and SAMtools. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 2078–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinlan, A.R.; Hall, I.M. BEDTools: A Flexible Suite of Utilities for Comparing Genomic Features. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 841–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ARTIC: A Bioinformatics Pipeline for Working with Virus Sequencing Data Sequenced with Nanopore. Available online: https://artic.network/ (accessed on 1 August 2023).
- Official Website U.S. Food & Drug. Coronavirus (COVID-19). Drugs. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/drugs/emergency-preparedness-drugs/coronavirus-covid-19-drugs (accessed on 1 August 2023).
- Temporary Guidelines «Prevention, Diagnosis and Treatment of New Coronavirus Infection (COVID-19)», Version 17. 2022. Available online: https://static-0.minzdrav.gov.ru/system/attachments/attaches/000/061/252/original/%D0%92%D0%9C%D0%A0_COVID-19_V17.pdf (accessed on 1 August 2023).
- Siniavin, A.E.; Streltsova, M.A.; Nikiforova, M.A.; Kudryavtsev, D.S.; Grinkina, S.D.; Gushchin, V.A.; Mozhaeva, V.A.; Starkov, V.G.; Osipov, A.V.; Lummis, S.C.R.; et al. Snake Venom Phospholipase A2s Exhibit Strong Virucidal Activity against SARS-CoV-2 and Inhibit the Viral Spike Glycoprotein Interaction with ACE2. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2021, 78, 7777–7794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imai, M.; Ito, M.; Kiso, M.; Yamayoshi, S.; Uraki, R.; Fukushi, S.; Watanabe, S.; Suzuki, T.; Maeda, K.; Sakai-Tagawa, Y.; et al. Efficacy of Antiviral Agents against Omicron Subvariants BQ.1.1 and XBB. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 388, 89–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arora, P.; Kempf, A.; Nehlmeier, I.; Schulz, S.R.; Jäck, H.-M.; Pöhlmann, S.; Hoffmann, M. Omicron Sublineage BQ.1.1 Resistance to Monoclonal Antibodies. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2023, 23, 22–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, A.; Malla, M.A.; Dubey, A. With Corona Outbreak: Nature Started Hitting the Reset Button Globally. Front. Public Health 2020, 8, 569353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodell, J.W. COVID-19 and Finance: Agendas for Future Research. Financ. Res. Lett. 2020, 35, 101512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akimkin, V.G.; Popova, A.Y.; Khafizov, K.F.; Dubodelov, D.V.; Ugleva, S.V.; Semenenko, T.A.; Ploskireva, A.A.; Gorelov, A.V.; Pshenichnaya, N.Y.; Yezhlova, E.B.; et al. COVID-19: Evolution of the Pandemic in Russia. Report II: Dynamics of the Circulation of SARS-CoV-2 Genetic Variants. J. Mikrobiol. Epidemiol. Immunobiol. 2022, 99, 381–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, R.; Edwards, K.M.; Adam, D.C.; Leung, K.S.M.; Tsang, T.K.; Gurung, S.; Xiong, W.; Wei, X.; Ng, D.Y.M.; Liu, G.Y.Z.; et al. Resurgence of Omicron BA.2 in SARS-CoV-2 Infection-Naive Hong Kong. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 2422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamasoba, D.; Uriu, K.; Plianchaisuk, A.; Kosugi, Y.; Pan, L.; Zahradnik, J.; Ito, J.; Sato, K. Virological Characteristics of the SARS-CoV-2 Omicron XBB.1.16 Variant. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2023, 23, 655–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Planas, D.; Bruel, T.; Staropoli, I.; Guivel-Benhassine, F.; Porrot, F.; Maes, P.; Grzelak, L.; Prot, M.; Mougari, S.; Planchais, C.; et al. Resistance of Omicron Subvariants BA.2.75.2, BA.4.6, and BQ.1.1 to Neutralizing Antibodies. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Focosi, D.; Spezia, P.G.; Capria, A.-L.; Gueli, F.; McConnell, S.; Novazzi, F.; Pistello, M. Rise of the BQ.1.1.37 SARS-CoV-2 Sublineage, Italy. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Guo, Y.; Iketani, S.; Nair, M.S.; Li, Z.; Mohri, H.; Wang, M.; Yu, J.; Bowen, A.D.; Chang, J.Y.; et al. Antibody Evasion by SARS-CoV-2 Omicron Subvariants BA.2.12.1, BA.4 and BA.5. Nature 2022, 608, 603–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, M.; Woo, H.G. Omicron: A Heavily Mutated SARS-CoV-2 Variant Exhibits Stronger Binding to ACE2 and Potently Escapes Approved COVID-19 Therapeutic Antibodies. Front. Immunol. 2022, 12, 830527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lan, J.; Ge, J.; Yu, J.; Shan, S.; Zhou, H.; Fan, S.; Zhang, Q.; Shi, X.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, L.; et al. Structure of the SARS-CoV-2 Spike Receptor-Binding Domain Bound to the ACE2 Receptor. Nature 2020, 581, 215–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, D.; Park, Y.-J.; Beltramello, M.; Walls, A.C.; Tortorici, M.A.; Bianchi, S.; Jaconi, S.; Culap, K.; Zatta, F.; De Marco, A.; et al. Cross-Neutralization of SARS-CoV-2 by a Human Monoclonal SARS-CoV Antibody. Nature 2020, 583, 290–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iketani, S.; Mohri, H.; Culbertson, B.; Hong, S.J.; Duan, Y.; Luck, M.I.; Annavajhala, M.K.; Guo, Y.; Sheng, Z.; Uhlemann, A.-C.; et al. Multiple Pathways for SARS-CoV-2 Resistance to Nirmatrelvir. Nature 2023, 613, 558–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jochmans, D.; Liu, C.; Donckers, K.; Stoycheva, A.; Boland, S.; Stevens, S.K.; De Vita, C.; Vanmechelen, B.; Maes, P.; Trüeb, B.; et al. The Substitutions L50F, E166A, and L167F in SARS-CoV-2 3CLpro Are Selected by a Protease Inhibitor In Vitro and Confer Resistance to Nirmatrelvir. mBio 2023, 14, e0281522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greasley, S.E.; Noell, S.; Plotnikova, O.; Ferre, R.; Liu, W.; Bolanos, B.; Fennell, K.; Nicki, J.; Craig, T.; Zhu, Y.; et al. Structural Basis for the in Vitro Efficacy of Nirmatrelvir against SARS-CoV-2 Variants. J. Biol. Chem. 2022, 298, 101972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Official Website Chemical & Engineering News. Pfizer Unveils Its Oral SARS-CoV-2 Inhibitor. Available online: https://cen.acs.org/acs-news/acs-meeting-news/Pfizer-unveils-oral-SARS-CoV/99/i13 (accessed on 1 August 2023).
- Moeller, N.H.; Passow, K.T.; Harki, D.A.; Aihara, H. SARS-CoV-2 nsp14 Exoribonuclease Removes the Natural Antiviral 3′-Deoxy-3′,4′-Didehydro-Cytidine Nucleotide from RNA. Viruses 2022, 14, 1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Focosi, D.; Maggi, F.; McConnell, S.; Casadevall, A. Very Low Levels of Remdesivir Resistance in SARS-COV-2 Genomes after 18 Months of Massive Usage during the COVID19 Pandemic: A GISAID Exploratory Analysis. Antivir. Res. 2022, 198, 105247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fong, W.; Rockett, R.J.; Agius, J.E.; Chandra, S.; Johnson-Mckinnon, J.; Sim, E.; Lam, C.; Arnott, A.; Gall, M.; Draper, J.; et al. SABRes: In Silico Detection of Drug Resistance Conferring Mutations in Subpopulations of SARS-CoV-2 Genomes. BMC Infect. Dis. 2023, 23, 303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, L.J.; Pruijssers, A.J.; Lee, H.W.; Gordon, C.J.; Tchesnokov, E.P.; Gribble, J.; George, A.S.; Hughes, T.M.; Lu, X.; Li, J.; et al. Mutations in the SARS-CoV-2 RNA-Dependent RNA Polymerase Confer Resistance to Remdesivir by Distinct Mechanisms. Sci. Transl. Med. 2022, 14, eabo0718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uraki, R.; Ito, M.; Kiso, M.; Yamayoshi, S.; Iwatsuki-Horimoto, K.; Furusawa, Y.; Sakai-Tagawa, Y.; Imai, M.; Koga, M.; Yamamoto, S.; et al. Antiviral and Bivalent Vaccine Efficacy against an Omicron XBB.1.5 Isolate. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2023, 23, 402–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| mAb | XBB.1.9.1 | XBB.1.9.3 | XBB.1.5.24 | XBB.1.16 | XBB.2.9 | BQ.1.1.45 | CL.1 | CH.1.1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cilgavimab | >1.8 M | >1.8 M | >1.8 M | >1.8 M | >1.8 M | >1.8 M | >50 K | >50 K |
| Tixagevimab | >11.9 M | >11.9 M | >11.9 M | >11.9 M | >11.9 M | >11.9 M | >50 K | >50 K |
| Sotrovimab | >30 K | 8 | 256 | N/D | 304 | >55 K | 362 | >30 K |
| Imdevimab | >2.1 M | >2.1 M | >2.1 M | >2.1 M | >2.1 M | >2.1 M | >50 K | >50 K |
| Etesevimab | >260 K | >260 K | >260 K | >260 K | >260 K | >260 K | >50 K | >50 K |
| Casirivimab | >4.2 M | >4.2 M | >4.2 M | >4.2 M | >4.2 M | >4.2 M | >50 K | >50 K |
| Bamlanivimab | >110 K | >110 K | >110 K | >110 K | >110 K | >110 K | N/D | N/D |
| Regdanvimab | >8.4 M | >8.4 M | >8.4 M | >8.4 M | >8.4 M | >8.4 M | N/D | N/D |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pochtovyi, A.A.; Kustova, D.D.; Siniavin, A.E.; Dolzhikova, I.V.; Shidlovskaya, E.V.; Shpakova, O.G.; Vasilchenko, L.A.; Glavatskaya, A.A.; Kuznetsova, N.A.; Iliukhina, A.A.; et al. In Vitro Efficacy of Antivirals and Monoclonal Antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 Omicron Lineages XBB.1.9.1, XBB.1.9.3, XBB.1.5, XBB.1.16, XBB.2.4, BQ.1.1.45, CH.1.1, and CL.1. Vaccines 2023, 11, 1533. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11101533
Pochtovyi AA, Kustova DD, Siniavin AE, Dolzhikova IV, Shidlovskaya EV, Shpakova OG, Vasilchenko LA, Glavatskaya AA, Kuznetsova NA, Iliukhina AA, et al. In Vitro Efficacy of Antivirals and Monoclonal Antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 Omicron Lineages XBB.1.9.1, XBB.1.9.3, XBB.1.5, XBB.1.16, XBB.2.4, BQ.1.1.45, CH.1.1, and CL.1. Vaccines. 2023; 11(10):1533. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11101533
Chicago/Turabian StylePochtovyi, Andrei A., Daria D. Kustova, Andrei E. Siniavin, Inna V. Dolzhikova, Elena V. Shidlovskaya, Olga G. Shpakova, Lyudmila A. Vasilchenko, Arina A. Glavatskaya, Nadezhda A. Kuznetsova, Anna A. Iliukhina, and et al. 2023. "In Vitro Efficacy of Antivirals and Monoclonal Antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 Omicron Lineages XBB.1.9.1, XBB.1.9.3, XBB.1.5, XBB.1.16, XBB.2.4, BQ.1.1.45, CH.1.1, and CL.1" Vaccines 11, no. 10: 1533. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11101533
APA StylePochtovyi, A. A., Kustova, D. D., Siniavin, A. E., Dolzhikova, I. V., Shidlovskaya, E. V., Shpakova, O. G., Vasilchenko, L. A., Glavatskaya, A. A., Kuznetsova, N. A., Iliukhina, A. A., Shelkov, A. Y., Grinkevich, O. M., Komarov, A. G., Logunov, D. Y., Gushchin, V. A., & Gintsburg, A. L. (2023). In Vitro Efficacy of Antivirals and Monoclonal Antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 Omicron Lineages XBB.1.9.1, XBB.1.9.3, XBB.1.5, XBB.1.16, XBB.2.4, BQ.1.1.45, CH.1.1, and CL.1. Vaccines, 11(10), 1533. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11101533






