Superior Efficacy of Apathogenic Genotype I (V4) over Lentogenic Genotype II (LaSota) Live Vaccines against Newcastle Disease Virus Genotype VII.1.1 in Pathogen-Associated Molecular Pattern-H9N2 Vaccinated Broiler Chickens
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethical Approval
2.2. Challenge Virus
2.3. Birds’ Management, Experimental Design, and Evaluation Parameters
2.3.1. Clinical Observation and Performance Parameters
2.3.2. Histopathological Assessment
2.3.3. Evaluation of the Virus Shedding
2.3.4. Serological Evaluation
2.3.5. Immune Mediators Analysis
2.3.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
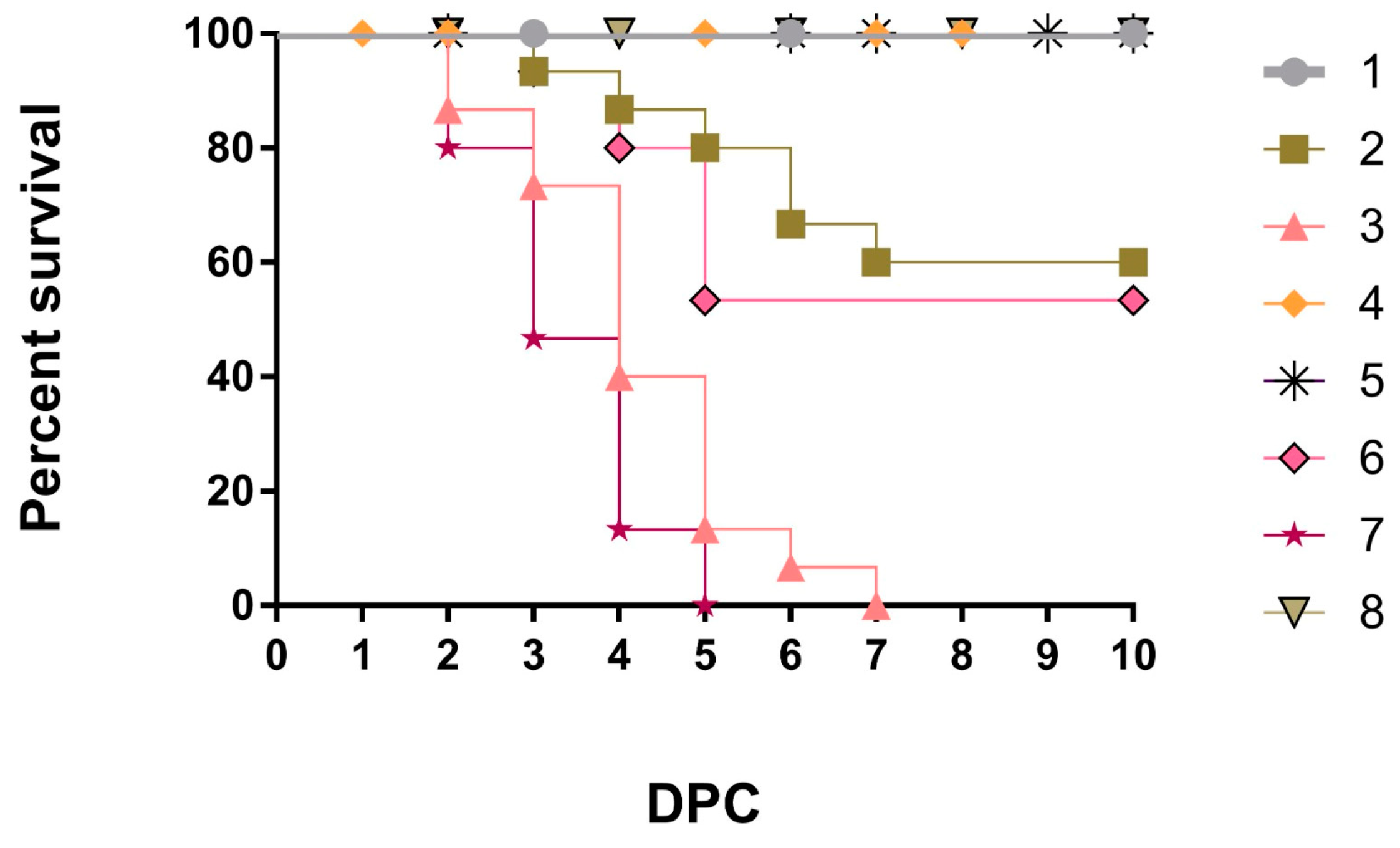
3.1. Clinical Observation and Performance Parameters
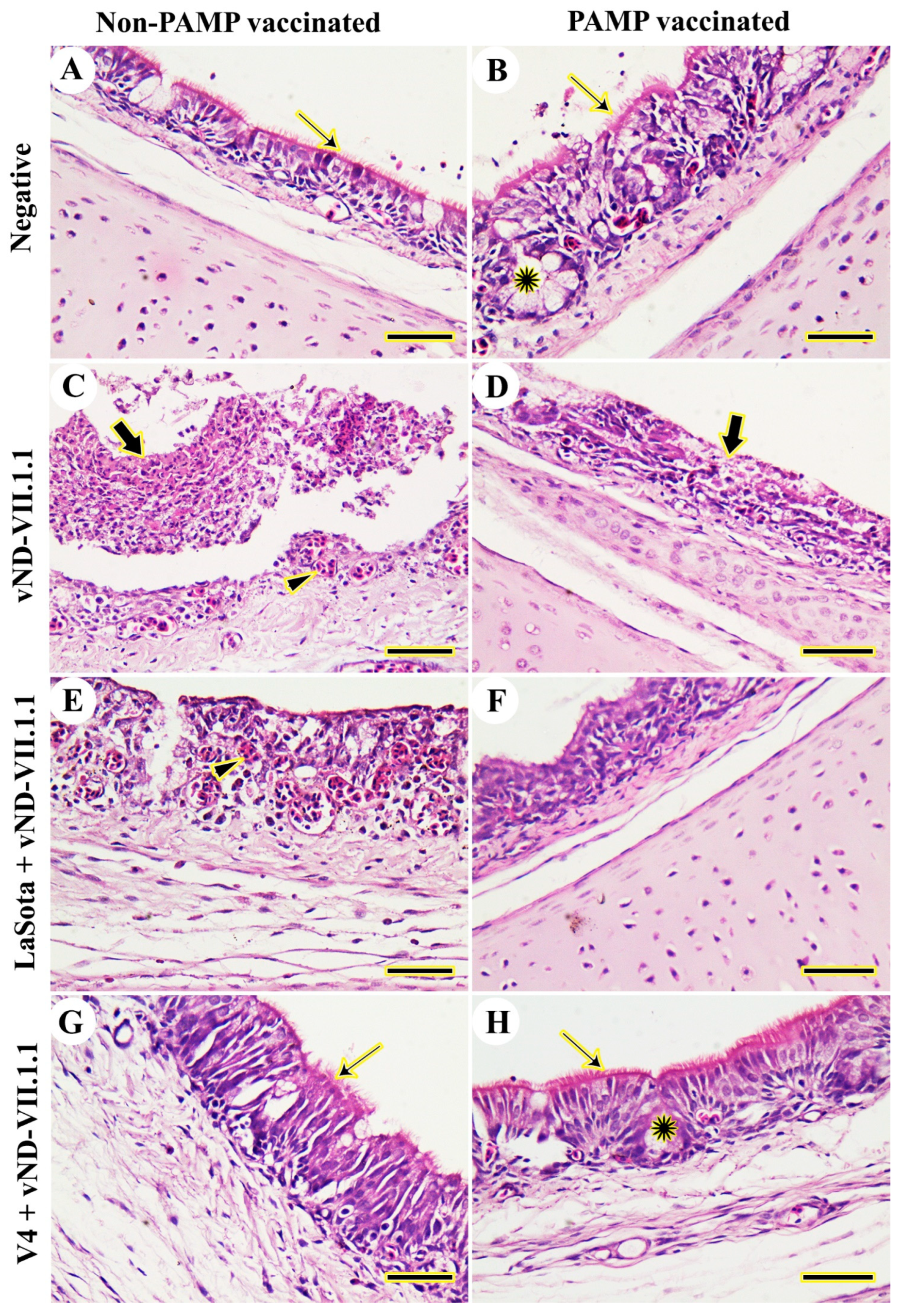
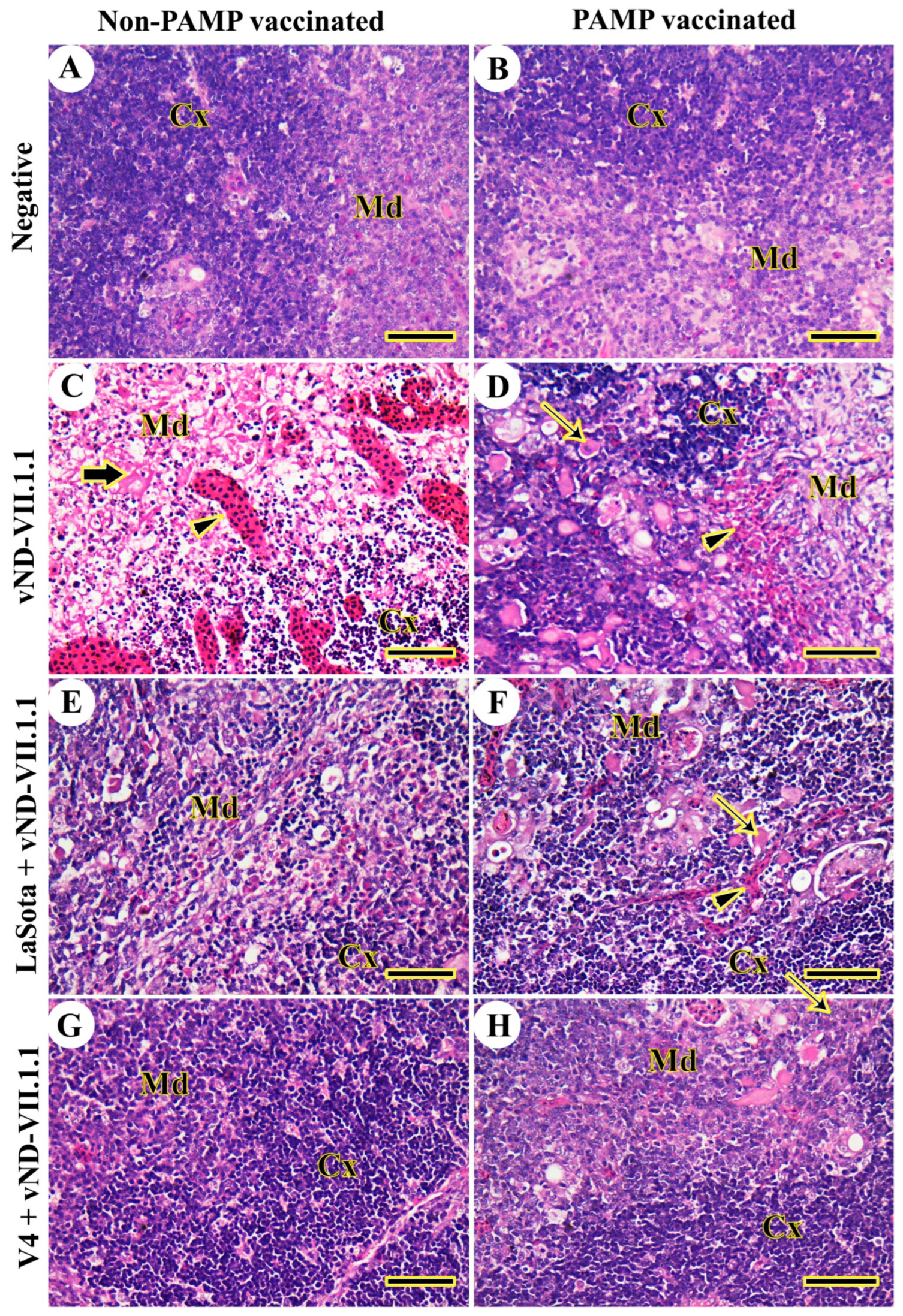
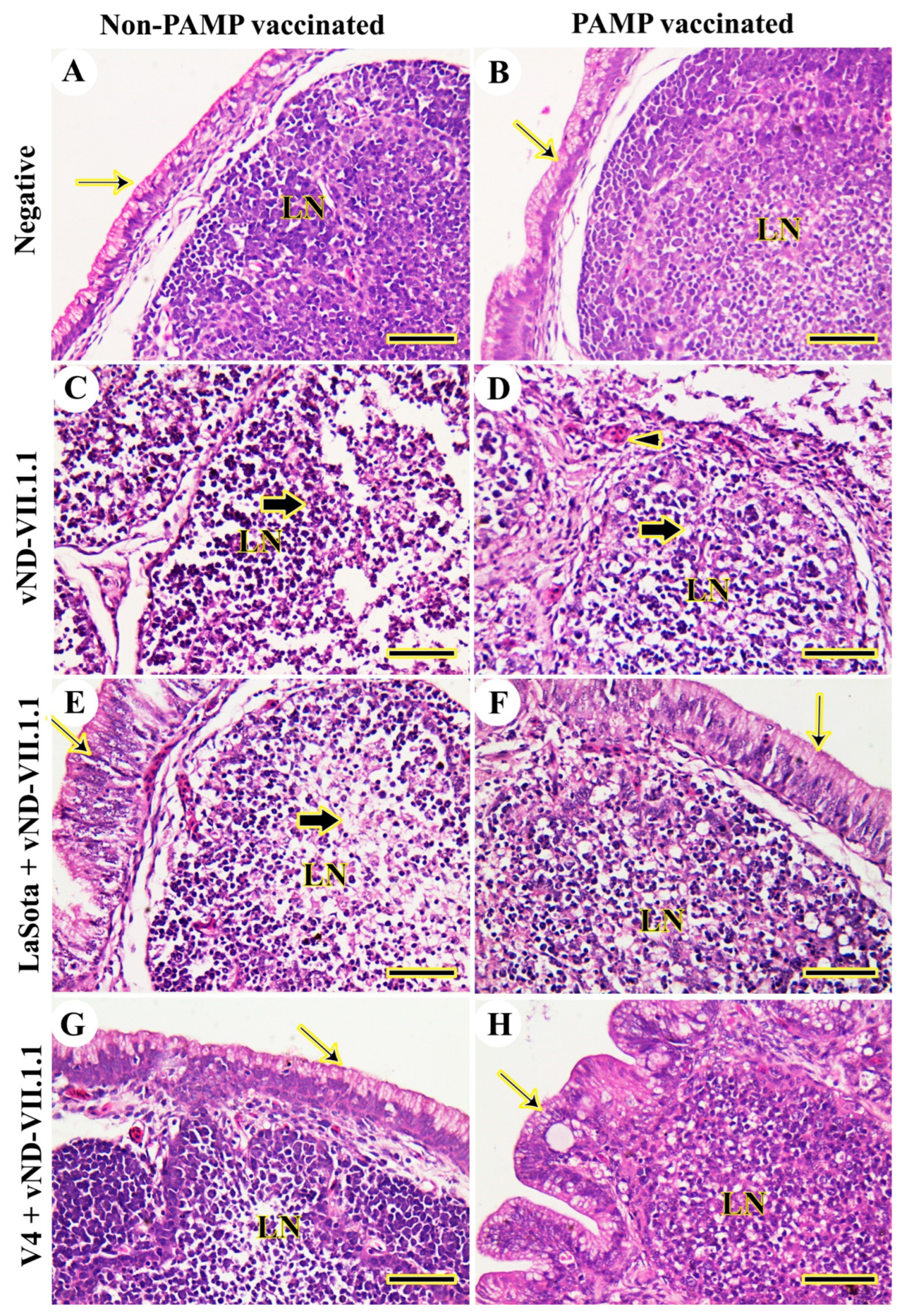
3.2. Histopathology
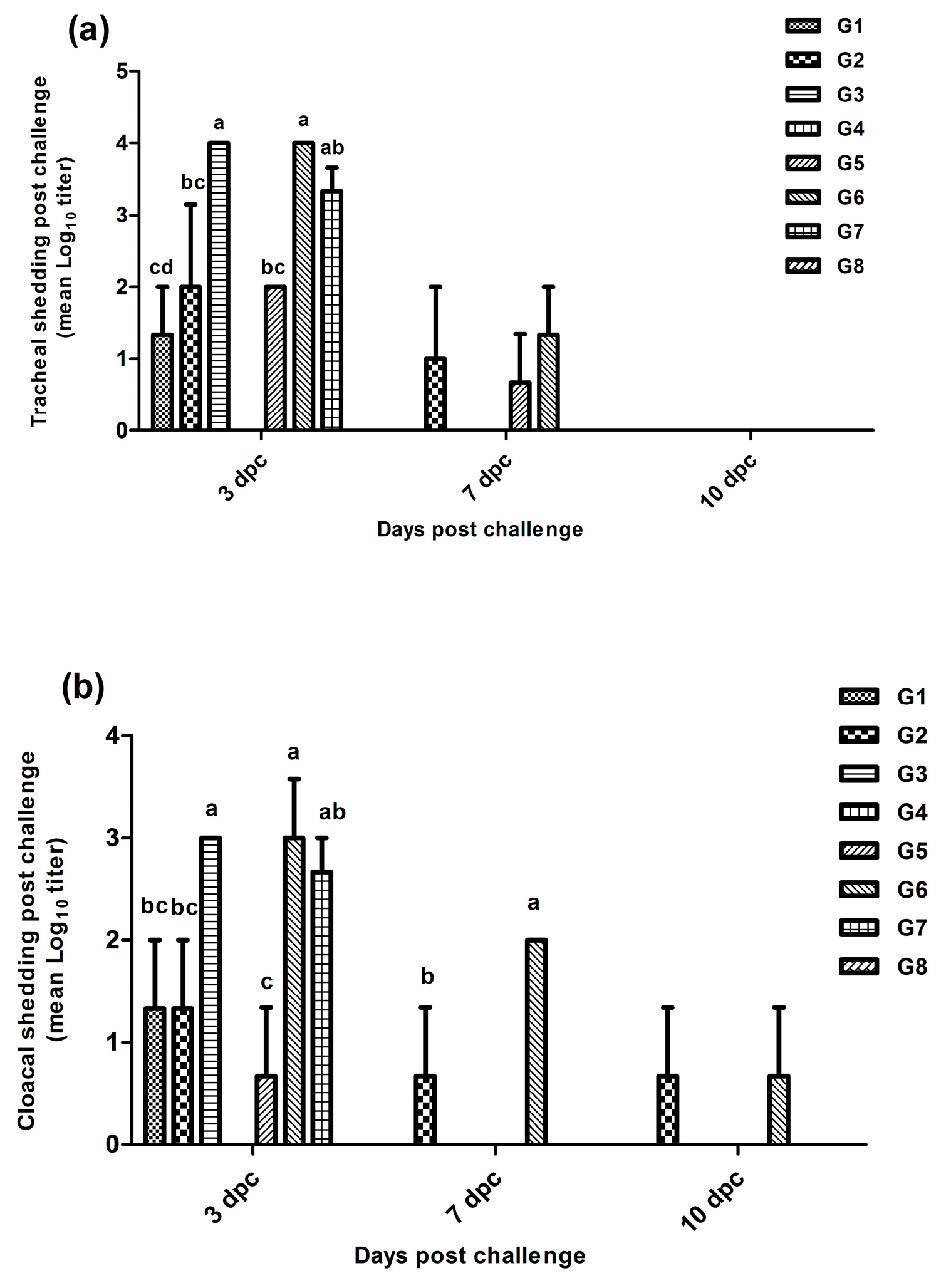
3.3. Virus Shedding
3.4. Serology
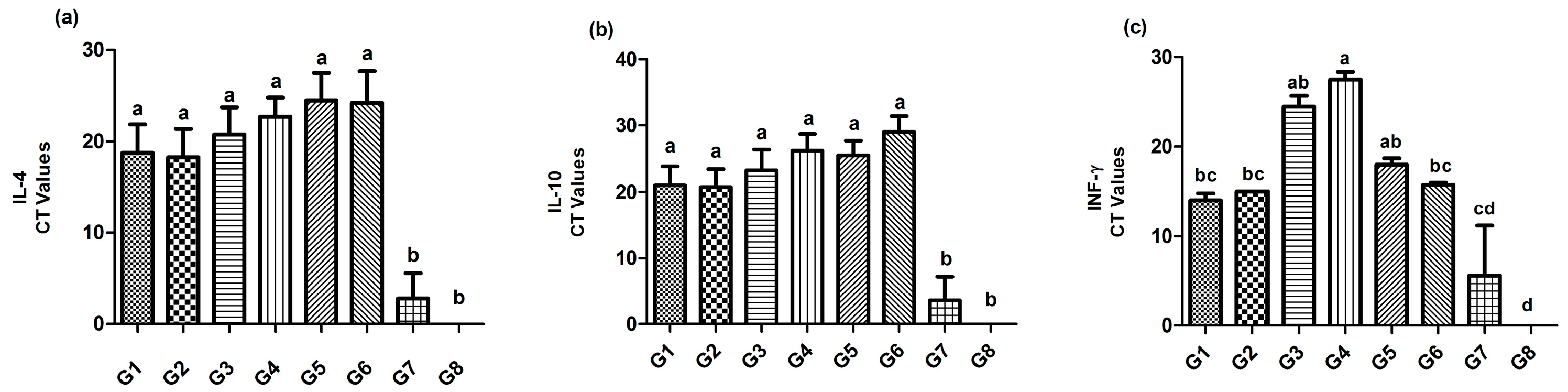
3.5. Immune Mediators
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Miller, P.J.; Koch, G. Newcastle Disease. In Diseases of Poultry, 14th ed.; Swayne, D., Ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Wiley Blackwell: Ames, IA, USA, 2020; pp. 112–129. [Google Scholar]
- Elfatah, K.S.A.; Elabasy, M.A.; El-Khyate, F.; Elmahallawy, E.K.; Mosad, S.M.; El-Gohary, A.F.; Abdo, W.; Al-Brakati, A.; Seadawy, M.G.; Tahoon, A.E.; et al. Molecular characterization of velogenic Newcastle disease virus (Sub-genotype VII.1.1) from wild birds, with assessment of its pathogenicity in susceptible chickens. Animals 2021, 11, 505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ICTV, International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses. Virus Taxonomy, 2019. Available online: https://talk.ictvonline.org/taxonomy/ (accessed on 2 June 2023).
- Dimitrov, H.; Choi, K.S.; Chvala, I.; Diel, D.G.; Durr, P.A.; Ferreira, H.L.; Fusaro, A.; Gil, P.; Goujgoulova, G.V.; Grund, C.; et al. Updated unified phylogenetic classification system and revised nomenclature for Newcastle disease virus. Infec. Gen. Evol. 2019, 74, 103917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afonso, C.L. Virulence during Newcastle disease viruses cross species adaptation. Viruses 2021, 13, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, P.J.; Afonso, C.L.; El Attrache, J.; Dorsey, K.M.; Courtney, S.C.; Guo, Z.; Kapczynski, D.R. Effects of Newcastle disease virus vaccine antibodies on the shedding and transmission of challenge viruses. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2013, 41, 505–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, P.J.; Haddas, R.; Simanov, L.; Lublin, A.; Rehmani, S.F.; Wajid, A.; Bibi, T.; Ahmad, S.; Khan, T.; Yaqub, T.; et al. Identification of new subgenotypes of virulent Newcastle disease virus with potential panzootic features. Infect. Gen. Evol. 2015, 29, 216–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbestawy, A.R.; Ellakany, H.F.; Abd El-Hamid, H.S.; Zedan, R.E.; Gado, A.R.; Sedeik, M.E.; Abd El-Hack, M.E.; Saadeldin, I.M.; Alowaimer, A.N.; Ba-Awadh, H.A.; et al. Muscovy ducks infected with velogenic Newcastle disease virus (genotype VIId) act as carriers to infect in-contact chickens. Poult. Sci. 2019, 98, 4441–4448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellakany, H.F.; Elbestawy, A.R.; Abd El-Hamid, H.S.; Zedan, R.E.; Gado, A.R.; Taha, A.E.; Soliman, M.A.; Abd El-Hack, M.E.; Swelum, A.A.; Saadeldin, I.M.; et al. Role of pigeons in the transmission of Avian Avulavirus (Newcastle disease-genotype VIId) to chickens. Animals 2019, 9, 338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd-Ellatieff, H.A.; Abd El Aziem, A.N.; Elbestawy, A.R.; Goda, A.R.; Belih, S.M.; Ellakany, H.F.; Abd El-Hamid, H.S.; Yanai, T.; AbouRawash, A.A.; El-Habashi, N. Efficacy of vaccination against infection with velogenic Newcastle disease virus genotypes VI and VII 1.1 strains in Japanese quails. J. Comp. Path. 2021, 186, 35–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.J.; Sung, H.W.; Choi, J.G.; Lee, E.K.; Yoon, H.; Kim, J.H.; Song, C.S. Protection of chickens from Newcastle disease with a recombinant baculovirus subunit vaccine expressing the fusion and hemagglutinin-neuraminidase proteins. J. Vet. Sci. 2008, 9, 301–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.H.; Wanasen, N.; Paldurai, A.; Xiao, S.; Collins, P.L.; Samal, S.K. Newcastle disease virus fusion protein is the major contributor to protective immunity of genotype-matched vaccine. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e74022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhu, J.; Xu, H.; Li, J.; Hu, Z.; Hu, S.; Wang, X.; Liu, X. Effects of the HN antigenic difference between the vaccine strain and the challenge strain of Newcastle Disease virus on virus shedding and transmission. Viruses 2017, 9, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitrov, K.M.; Afonso, C.L.; Yu, Q.; Miller, P.J. Newcastle disease vaccines-A solved problem or a continuous challenge? Vet. Microbiol. 2017, 206, 126–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, P.J.; King, D.J.; Afonso, C.L.; Suarez, D.L. Antigenic differences among Newcastle disease virus strains of different genotypes used in vaccine formulation affect viral shedding after a virulent challenge. Vaccine 2007, 25, 7238–7246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dortmans, J.C.F.M.; Peeters, B.P.H.; Koch, G. Newcastle disease virus outbreaks: Vaccine mismatch or inadequate application? Vet. Microbiol. 2012, 160, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, P.J.; Estevez, C.; Yu, Q.; Suarez, D.L.; King, D.J. Comparison of viral shedding following vaccination with inactivated and live Newcastle disease vaccines formulated with wild-type and recombinant viruses. Avian Dis. 2009, 53, 39–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.M.; Zhao, J.; Xue, J.; Yang, Y.L.; Zhang, G.Z. Antigenic variation of LaSota and genotype VII Newcastle disease virus (NDV) and their efficacy against challenge with velogenic NDV. Vaccine 2017, 35, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahar, E.; Haddas, R.; Goldenberg, D.; Lublin, A.; Bloch, I.; Hinenzon, N.B.; Pitcovski, J. Newcastle disease virus: Is an updated attenuated vaccine needed? Avian Pathol. 2018, 47, 467–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdoshah, M.; Hassanzadeh, M.; Masoudi, S.; Ashtari, A.; Yousefi, A.R.; Nasr, M.P. Thermoresistant Newcastle disease vaccine effectively protects SPF, native, and commercial chickens in challenge with virulent virus. Vet. Med. Sci. 2022, 8, 1539–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassanzadeh, M.; Abdoshah, M.; Yousefi, A.R.; Moluki, I.; Haghshenas, F. Evaluation of virulence and phylogenetic study of Newcastle disease virus isolated from 295 broiler poultry farms in Mazandaran province. Iran. Vet. J. 2022, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qureshi, M.A.; Heggen, C.L.; Hussain, I. Avian macrophage: Effector functions in health and disease. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2000, 24, 103–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasare, C.; Medzhitov, R. Toll-like receptors and acquired immunity. Semin. Immunol. 2004, 16, 23–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akira, S.; Uematsu, S.; Takeuchi, O. Pathogen recognition and innate immunity. Cell 2006, 124, 783–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geeraedts, F.; Goutagny, N.; Hornung, V.; Severa, M.; de Haan, A.; Pool, J.; Wilschut, J.; Fitzgerald, K.A.; Huckriede, A. Superior immunogenicity of inactivated whole virus H5N1 influenza vaccine is primarily controlled by Toll-like Receptor Signaling. PLoS Pathog. 2008, 4, e1000138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellakany, H.F.; Abd El-Hamid, H.S.; Nasef, S.A.; Elbestawy, A.R.; Nasr, S.M.; Abd El Aziz, M.N.; Gado, A.R.; Zedan, R.E.; Yonis, A.E. Evaluation of the protection of commercial live and inactivated NDV vaccines against Newcastle virus genotype VIId circulating in the field. Daman. J. Vet. Sci. 2019, 1, 17–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reed, L.J.; Muench, L.H. A simple method of estimating fifty percent end points. Amer. J. Hyg. 1938, 27, 493–497. [Google Scholar]
- World Organization for Animal Health (WOAH). Newcastle Disease (Infection with Newcastle Disease Virus). In Manual of Diagnostic Tests and Vaccines for Terrestrial Animals; Chapter 3.3.14; OIE: Paris, France, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Aviagen, R. Broiler Nutrition Specifications (All Plant-Protein Based Feeds). USA. 2022. Available online: https://aviagen.com/assets/Tech_Center/Ross_Broiler/Ross-PlantProteinBasedBroilerNutritionSpecifications2022-EN.pdf (accessed on 12 November 2022).
- NRC. Nutrient Requirements of Poultry, 10th ed.; National Academy Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Terregino, C.; Capua, I. Conventional Diagnosis of Newcastle Disease Virus Infection. In Avian Influenza and Newcastle Disease: A Field and Laboratory Manual; Chapter 10; Capua, I., Alexander, D.J., Eds.; Springer: Milan, Italy, 2009; pp. 123–126. [Google Scholar]
- Bancroft, J.D.; Layton, C. The hematoxylin and eosin. In Theory and Practice of Histological Techniques, 7th ed.; Suvarna, S.K., Layton, C., Bancroft, J.D., Eds.; Churchill Livingstone: Pennsylvania, PA, USA, 2013; pp. 179–220. [Google Scholar]
- Gibson-Corley, K.N.; Olivier, A.K.; Meyerholz, D.K. Principles for valid histopathologic scoring in research. Vet. Pathol. 2013, 50, 1007–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wise, M.G.; Suarez, D.L.; Seal, B.S.; Pedersen, J.C.; Senne, D.A.; King, D.J.; Kapczynski, D.R.; Spackman, E.E. Development of a real-time reverse-transcription PCR for detection of Newcastle disease virus RNA in clinical samples. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2004, 42, 329–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Organization for Animal Health (WOAH). Avian Influenza (Including Infection with High Pathogenicity Avian Influenza Viruses). In Manual of Diagnostic Tests and Vaccines for Terrestrial Animals; Chapter 3.3.4; OIE: Paris, France, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Kaiser, P.; Rothwell, L.; Goodchild, M.; Bumstead, N. The chicken proinflammatory cytokines interleukin-1beta and interleukin-6: Differences in gene structure and genetic location compared with their mammalian orthologues. Anim. Genet. 2004, 35, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Rui, L.; Shao, Q.; Liu, H.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Z. Changes of CD4+CD25+ cells ratio in immune organs from chickens challenged with infectious bursal disease virus strains with varying virulences. Viruses 2015, 7, 1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Sang, S.; Yuan, Z.; Duan, Q.; Guo, X.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, C. Magnetoelastic immunosensor via antibody immobilization for the specific detection of lysozymes. ACS Sens. 2021, 6, 3933–3939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ariaans, M.P.; Matthijs, M.G.R.; van Haarlem, D.; van de Haar, P.; van Eck, J.H.H.; Hensen, E.J.; Vervelde, L. The role of phagocytic cells in enhanced susceptibility of broilers to colibacillosis after infectious bronchitis virus infection. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2008, 123, 240–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y.H.; Lillehoj, H.S.; Lee, S.H.; Dalloul, R.A.; Lillehoj, E.P. Analysis of chicken cytokine and chemokine gene expression following Eimeria acervulina and Eimeria tenella infections. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2006, 114, 209–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y.H.; Lillehoj, H.S.; Lillehoj, E.P.; Lee, S.H. Changes in immune-related gene expression and intestinal lymphocyte subpopulations following Eimeria maxima infection of chickens. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2006, 114, 259–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, S.C.; Xing, Z.; Li, J.; Cardona, C.J. Immune-related gene expression in response to H11N9 low pathogenic avian influenza virus infection in chicken and Pekin duck peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Mol. Immunol. 2009, 46, 1744–1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SAS. SAS User’s Guide Statistics; SAS Institute, Inc.: Cary, NC, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Westbury, H. Newcastle disease virus: An evolving pathogen? Avian Pathol. 2001, 30, 5–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.Y.; Kye, S.J.; Lee, H.J.; Gaikwad, S.; Lee, H.S.; Jung, S.C.; Choi, K.S. Development of a highly immunogenic Newcastle disease virus chicken vaccine strain of duck origin. Poult. Sci. 2016, 95, 790–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Z.; Hu, S.; Meng, C.; Wang, X.; Zhu, J.; Liu, X. Generation of a genotype VII Newcastle disease virus vaccine candidate with high yield in embryonated chicken eggs. Avian Dis. 2011, 55, 391–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Y.; Sheng, D.; Li, X.; Hong, S.; Guo, L.; Zhao, S.; Yuan, Y.; Xue, J.; Tian, H.; Ren, Y.; et al. Efficacy of a recombinant genotype VII vaccine against challenge with velogenic Newcastle disease virus. J. Vac. Immunol. 2016, 2, 019–022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, N.K.; El-Deeb, A.H.; Emara, M.M.; Abd El-Khaleck, M.A.; Hussein, H.A. Genotypes II and VIId-based inactivated Newcastle disease vaccine reduces virus shedding. Virus Dis. 2019, 30, 453–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palya, V.; Kiss, I.; Tatár-Kis, T.; Mató, T.; Felföldi, B.; Gardin, Y. Advancement in vaccination against Newcastle disease: Recombinant HVT NDV provides high clinical protection and reduces challenge virus shedding with the absence of vaccine reactions. Avian Dis. 2012, 56, 282–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palya, V.; Tatár-Kis, T.; Mato, T.; Felfoldi, B.; Kovacs, E.; Gardin, Y. Onset and long-term duration of immunity provided by a single vaccination with a turkey herpesvirus vector ND vaccine in commercial layers. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2014, 158, 105–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palya, V.; Tatár-Kis, T.; Arafa, A.S.A.; Felföldi, B.; Mató, T.; Setta, A. Efficacy of a turkey herpesvirus vectored Newcastle disease vaccine against genotype VII.1.1 virus: Challenge route affects shedding pattern. Vaccines 2021, 9, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tatar-Kis, T.; Fischer, E.A.J.; Cazaban, C.; Walko-Kovacs, E.; Homonnay, Z.G.; Velkers, F.C.; Palya, V.; Stegeman, J.A. A herpesvirus of turkey-based vector vaccine reduces transmission of Newcastle disease virus in commercial broiler chickens with maternally derived antibodies. Vaccines 2020, 8, 614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sultan, H.A.; Elfeil, W.K.; Nour, A.A.; Tantawy, L.; Kamel, E.G.; Eed, E.M.; El Askary, A.; Talaat, S. Efficacy of the Newcastle disease virus genotype VII.1.1-matched vaccines in commercial broilers. Vaccines 2021, 10, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sultan, H.A.; Talaat, S.; Elfeil, W.K.; Selim, K.; Kutkat, M.A.; Amer, S.A.; Choi, K.S. Protective efficacy of the Newcastle disease virus genotype VII–matched vaccine in commercial layers. Poult. Sci. 2020, 99, 1275–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dewidar, A.A.A.; Kilany, W.H.; El-Sawah, A.A.; Shany, S.A.S.; Dahshan, A.H.M.; Hisham, I.; Elkady, M.F.; Ali, A. Genotype VII.1.1-based Newcastle disease virus vaccines afford better protection against field isolates in commercial broiler chickens. Animals 2022, 12, 1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bello, M.B.; Mahamud, S.N.A.; Yusoff, K.; Ideris, A.; Hair-Bejo, M.; Peeters, B.P.H.; Omar, A.R. Development of an effective and stable genotype-matched live attenuated Newcastle disease virus vaccine based on a novel naturally recombinant Malaysian isolate using reverse genetics. Vaccines 2020, 8, 270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, M.H.; Abdelaziz, A.M.; Kumar, S.; Al-Habib, M.A.; Megahed, M.M. Effect of phylogenetic diversity of velogenic Newcastle disease virus challenge on virus shedding post homologous and heterologous DNA vaccination in chickens. Avian Pathol. 2016, 45, 228–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapczynski, D.R.; Afonso, C.L.; Miller, P.J. Immune responses of poultry to Newcastle disease virus. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2013, 41, 447–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardenas-Garcia, S.; Dunwoody, R.P.; Marcano, V.; Diel, D.G.; Williams, R.J.; Gogal, R.M., Jr.; Brown, C.C.; Miller, P.J.; Afonso, C.L. Effects of chicken interferon gamma on Newcastle disease virus vaccine immunogenicity. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0159153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perozo, F.; Villegas, P.; Dolz, R.; Afonso, C.L.; Purvis, L.B. The VG/GA strain of Newcastle disease virus: Mucosal immunity, protection against lethal challenge and molecular analysis. Avian Pathol. 2008, 37, 237–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, C.; King, D.J.; Seal, B.S. Pathogenesis of Newcastle disease in chickens experimentally infected with viruses of different virulence. Vet. Pathol. 1999, 36, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merz, D.C.; Scheid, A.; Choppin, P. Importance of antibodies to the fusion glycoprotein of paramyxoviruses in the prevention of spread of infection. J. Exp. Med. 1980, 151, 275–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boursnell, M.; Green, P.; Samson, A.; Campbell, J.; Deuter, A.; Peters, R.; Millar, N.; Emmerson, P.; Binns, M. A recombinant fowlpox virus expressing the hemagglutinin-neuraminidase gene of Newcastle disease virus (NDV) protects chickens against challenge NDV. Virology 1990, 178, 297–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reynolds, D.; Maraqa, A. Protective immunity against Newcastle disease: The role of antibodies specific to Newcastle disease virus polypeptides. Avian Dis. 2000, 44, 138–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabatabaeizadeh, S.E. Immunoinformatic analysis and antibody epitope comparison of Newcastle disease virus classical vaccines with a virus involved in the fifth NDV panzootic. Mapp. Intimacies 2021, 1, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chambers, P.; Nesbit, M.; Yusoff, K.; Millar, N.; Samson, A.; Emmerson, P. Location of a neutralizing epitope for the haemagglutinin-neuraminidase glycoprotein of Newcastle disease virus. J. Gen. Virol. 1988, 69, 2115–2122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toyoda, T.; Gotoh, B.; Sakaguchi, T.; Kida, H.; Nagai, Y. Identification of amino acids relevant to three antigenic determinants on the fusion protein of Newcastle disease virus that are involved in fusion inhibition and neutralization. J. Virol. 1988, 62, 4427–4430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neyt, C.; Geliebter, J.; Slaoui, M.; Morales, D.; Meulemans, G.; Burny, A. Mutations located on both F1 and F2 subunits of the Newcastle disease virus fusion protein confer resistance to neutralization with monoclonal antibodies. J. Virol. 1989, 63, 952–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iorio, R.M.; Syddall, R.J.; Sheehan, J.P.; Bratt, M.A.; Glickman, R.L.; Riel, A.M. Neutralization map of the hemagglutinin-neuraminidase glycoprotein of Newcastle disease virus: Domains recognized by monoclonal antibodies that prevent receptor recognition. J. Virol. 1991, 65, 4999–5006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iorio, R.M.; Glickman, R.L.; Sheehan, J.P. Inhibition of fusion by neutralizing monoclonal antibodies to the haemagglutinin-neuraminidase glycoprotein of Newcastle disease virus. J. Gen. Virol. 1992, 73, 1167–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, Y.; Cui, Z. Epitope variation in the Newcastle disease virus HN gene under antibody immune selective pressure in cell culture. Sci. China Life Sci. 2011, 54, 474–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, M.; Liu, W.; Xu, L.; Cao, Y.; Yao, C.; Hu, S.; Liu, X. Positive selection in the hemagglutinin neuraminidase gene of Newcastle disease virus and its effect on vaccine efficacy. Virol. J. 2011, 8, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Shen, X.; Li, J.; Yu, Y.; Fan, J.; Jia, X.; Dai, Y. Efficacy of Newcastle disease LaSota vaccine-induced hemagglutination inhibition antibodies against challenges with heterologous virulent strains of genotypes VII and IX. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2023, 259, 110591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Chicken Groups (Number) | Age (Days) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vaccination | Challenge | ||||
| 4 | 8 | 15 | 28 | ||
| G1 | 25 | H9N2-PAMP | V4 | V4 | vND-VII.1.1 |
| G2 | 25 | H9N2-PAMP | LaSota | LaSota | vND-VII.1.1 |
| G3 | 25 | H9N2-PAMP | - | - | vND-VII.1.1 |
| G4 | 25 | H9N2-PAMP | - | - | - |
| G5 | 25 | - | V4 | V4 | vND-VII.1.1 |
| G6 | 25 | - | LaSota | LaSota | vND-VII.1.1 |
| G7 | 25 | - | - | - | vND-VII.1.1 |
| G8 | 25 | - | - | - | - |
| Groups | Organ Histopathological Lesion Score | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Trachea | Lung | Thymus Glands | Spleen | Bursa of Fabricius | |||
| Hemorrhage | Mucosal Hyperplasia and Metaplasia | Hemorrhage | Congestion | Necrosis and Lymphoid Depletion | Necrosis and Multifocal Lymphoid Depletion | Necrosis and Lymphoid Depletion | |
| 1 | 0.3 ± 0.2 de | 0.5 ± 0.2 d | 0.30 ± 0.2 de | 0.6 ± 0.2 c | 0.3 ± 0.2 de | 0.6 ± 0.2 c | 0.3 ± 0.2 de |
| 2 | 2.1 ± 0.2 c | 2.5 ± 0.3 c | 2.0 ± 0.3 c | 3.1 ± 0.2 ab | 1.8 ± 0.2 c | 2.2 ± 0.2 b | 1.7 ± 0.2 bc |
| 3 | 2.8 ± 0.2 bc | 3.5 ± 0.2 ab | 3.4 ± 0.2 ab | 2.6 ± 0.2 b | 2.5 ± 0.2 bc | 3.2 ± 0.3 a | 3.3 ± 0.2 a |
| 4 | 0.0 ± 0 e | 0.0 ± 0 d | 0.0 ± 0 e | 0.0 ± 0 c | 0.0 ± 0 e | 0.0 ± 0 c | 0.0 ± 0 e |
| 5 | 1.0 ± 0.1 de | 0.6 ± 0.2 d | 0.9 ± 0.2 d | 0.8 ± 0.2 c | 1.0 ± 0.0 d | 0.7 ± 0.3 c | 1.0 ± 0.3 cd |
| 6 | 3.0 ± 0.3 ab | 2.9 ± 0.2 bc | 2.8 ± 0.3 b | 2.9 ± 0.2 ab | 3.2 ± 0.2 ab | 3.0 ± 0.2 ab | 2.4 ± 0.2 b |
| 7 | 3.8 ± 0.1 ab | 3.9 ± 0.1 a | 3.7 ± 0.2 a | 3.5 ± 0.2 a | 3.7 ± 0.2 a | 3.5 ± 0.2 a | 3.8 ± 0.2 a |
| 8 | 0.0 ± 0 e | 0.0 ± 0 d | 0.0 ± 0 e | 0.0 ± 0 c | 0.0 ± 0 e | 0.0 ± 0 c | 0.0 ± 0 e |
| Groups | HI Titers for ND | HI Titers for LPAIV-H9N2 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (Days) | Age (Days) | |||||||||
| 7 | 14 | 21 | 28 | 35 | 7 | 14 | 21 | 28 | 35 | |
| 1 | 7.38 ± 1 a | 3.13 ± 0.4 bcd | 4.63 ± 0.4 a | 4.75 ± 0.4 a | 8.00 ± 0.3 c | 7.00 ± 0 b | 4.00 ± 0.3 ab | 2.13 ± 0.3 ab | 3.25 ± 0.9 ab | 7.25 ± 0.6 a |
| 2 | 6.88 ± 0.9 ab | 3.00 ± 0 cd | 2.13 ± 0.2 bc | 4.13 ± 0.5 a | 10.63 ± 0.3 ab | 11.13 ± 0.5 a | 4.00 ± 0.2 ab | 1.63 ± 0.3 abc | 1.63 ± 0.5 bcd | 6.00 ± 0.5 a |
| 3 | 6.50 ± 0.8 ab | 3.75 ± 0.3 abc | 1.75 ± 0.2 c | 1.00 ± 0.0 b | 0.00 ± 0 d (NA) | 6.75 ± 0.4 b | 4.13 ± 0.1 a | 1.75 ± 0.2 bc | 5.00 ± 0.5 a | 0.00 ± 0 b (NA) |
| 4 | 4.50 ± 0.2 b | 3.13 ± 0.1 bcd | 2.63 ± 0.7 bc | 1.38 ± 0.2 b | 0.13 ± 0.2 d | 7.63 ± 0.6 b | 3.75 ± 0.2 ab | 1.00 ± 0 c | 2.88 ± 0.4 bc | 6.88 ± 0.8 a |
| 5 | 4.63 ± 0.4 ab | 3.00 ± 0.0 cd | 4.25 ± 0.2 a | 5.25 ± 0.3 a | 9.38 ± 0.6 b | 7.75 ± 0.4 b | 3.25 ± 0.2 b | 1.75 ± 0.3 abc | 1.25 ± 0.2 cd | 1.25 ± 0.5 b |
| 6 | 5.00 ± 0.4 ab | 4.25 ± 0.2 a | 4.63 ± 0.5 a | 2.13 ± 0.1 b | 11.00 ± 0.4 a | 7.00 ± 0 b | 4.00 ± 0.2 ab | 1.38 ± 0.2 bc | 1.00 ± 0 cd | 0.25 ± 0.3 b |
| 7 | 5.13 ± 0.3 ab | 2.63 ± 0.3 d | 2.63 ± 0.3 bc | 1.50 ± 0.2 b | 0.00 ± 0 d (NA) | 7.00 ± 0 b | 3.88 ± 0.1 ab | 2.13 ± 0.2 ab | 0.88 ± 0.1 d | 0.13 ± 0.1 b (NA) |
| 8 | 5.25 ± 0.4 ab | 4.13 ± 0.3 ab | 3.63 ± 0.2 ab | 1.00 ± 0 b | 0.38 ± 0.2 d | 8.13 ± 0.4 b | 3.88 ± 0.2 ab | 2.63 ± 0.3 a | 1.13 ± 0.1 b | 0.13 ± 0.1 b |
| Age (Days) | Groups | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | ||
| IL1β (pg/mL) | 17 | 280.2 ± 7.8 a | 220 ± 4.9 d | 274.2 ± 2 ab | 237.8 ± 14 cd | 256.6 ± 1 abc | 243.2 ± 0.7 bcd | 260.8 ± 11.8 abc | 263.4 ± 0.2 abc |
| 21 | 312.2 ± 15.4 bc | 376.8 ± 1.7 ab | 349.2 ± 22.8 abc | 410.8 ± 0.5 a | 256.2 ± 46.5 c | 377 ± 3.7 ab | 406.2 ± 7.8 ab | 374.4 ± 22.3 ab | |
| 28 | 364.8 ± 14 ab | 264.6 ± 5.1 c | 323.2 ± 0.7 a | 306 ± 2.4 ab | 256.4 ± 1.5 c | 268.6 ± 9.6 bc | 258.2 ± 14.2 c | 290.6 ± 9.6 abc | |
| 31 | 284.4 ± 8.3 | 319.6 ± 18.1 | 318.4 ± 20.576 | 263.8 ± 37.2 | 299.2 ± 7.8 | 255.2 ± 4.2 | 281.4 ± 1 | 303.8 ± 6.2 | |
| CD4 (ng/mL) | 17 | 4.4 ± 0.2 b | 5.0 ± 0 ab | 5.0 ± 0 ab | 4.6 ± 0.2 b | 4.4 ± 0.2 b | 5.0 ± 0 ab | 5.0 ± 0 ab | 5.6 ± 0.2 a |
| 21 | 5.0 ± 0 bc | 6.0 ± 0 a | 5.6 ± 0.2 ab | 6.0 ± 0 a | 4.6 ± 0.2 c | 4.6 ± 0.2 c | 5.0 ± 0 bc | 5.0 ± 0 bc | |
| 28 | 5.0 ± 0 c | 5.0 ± 0 c | 5.0 ± 0 c | 5.6 ± 0.2 bc | 5.2 ± 0.2 c | 6.0 ± 0 ab | 5.6 ± 0.2 bc | 6.4 ± 0.2 a | |
| 31 | 5.6 ± 0.2 b | 5.6 ± 0.2 b | 5.0 ± 0 b | 5.4 ± 0.2 b | 6.0 ± 0 ab | 5.0 ± 0 b | 6.0 ± 0 ab | 7.2 ± 0.7 a | |
| LYZ (ng/mL) | 17 | 112.2 ± 1.7 b | 113.8 ± 0.7 ab | 116.6 ± 01 ab | 115 ± 1.2 ab | 115 ± 2.4 ab | 111.4 ± 1 b | 115.6 ± 0.2 ab | 119.2 ± 0.5 a |
| 21 | 112.2 ± 0.7 cd | 115 ± 0 bc | 109.6 ± 1.5 d | 113.4 ± 0.2 c | 111.6 ± 1 cd | 120.6 ± 0.2 a | 112.2 ± 0.73 d | 118.2 ± 0.5 ab | |
| 28 | 107.2 ± 1.7 c | 109 ± 0 bc | 111.4 ± 2.7 bc | 113.8 ± 0.5 ab | 106.4 ± 0.2 c | 109.2 ± 0.5 bc | 111.8 ± 0.8 bc | 119.8 ± 1.7 a | |
| 31 | 104.4 ± 1 c | 116.4 ± 0.2 bc | 113.4 ± 2.7 bc | 117.4 ± 0.5 bc | 113.2 ± 0.490 bc | 119.8 ± 7.8 ab | 132.6 ± 3.4 a | 123 ± 0 ab | |
| NO (μmol/L) | 17 | 62.2 ± 1.7 b | 63.8 ± 0.7 ab | 66.6 ± 1 ab | 65 ± 1.2 ab | 65 ± 2.4 ab | 61.4 ± 1 b | 65.6 ± 0.2 ab | 69.2 ± 0.5 a |
| 21 | 62.2 ± 0.7 cd | 65 ± 0 bc | 59.6 ± 1.5 d | 63.4 ± 0.2 c | 61.6 ± 1 cd | 70.6 ± 0.2 a | 62.2 ± 0.7 cd | 68.2 ± 0.5 ab | |
| 28 | 57.2 ± 1.7 c | 59 ± 0 bc | 61.4 ± 2.7 bc | 63.8 ± 0.5 ab | 56.8 ± 0.4 c | 59.2 ± 0.5 bc | 61.8 ± 0.8 bc | 69.8 ± 1.7 a | |
| 31 | 54.4 ± 1 c | 66.4 ± 0.2 bc | 63.4 ± 2.7 bc | 67.4 ± 1 bc | 63.2 ± 0.5 bc | 69.8 ± 7.8 ab | 82.6 ± 3.4 a | 73 ± 0 ab | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Elbestawy, A.; Ellakany, H.; Sedeik, M.; Gado, A.; Abdel-Latif, M.; Noreldin, A.; Orabi, A.; Radwan, I.; El-Ghany, W.A. Superior Efficacy of Apathogenic Genotype I (V4) over Lentogenic Genotype II (LaSota) Live Vaccines against Newcastle Disease Virus Genotype VII.1.1 in Pathogen-Associated Molecular Pattern-H9N2 Vaccinated Broiler Chickens. Vaccines 2023, 11, 1638. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11111638
Elbestawy A, Ellakany H, Sedeik M, Gado A, Abdel-Latif M, Noreldin A, Orabi A, Radwan I, El-Ghany WA. Superior Efficacy of Apathogenic Genotype I (V4) over Lentogenic Genotype II (LaSota) Live Vaccines against Newcastle Disease Virus Genotype VII.1.1 in Pathogen-Associated Molecular Pattern-H9N2 Vaccinated Broiler Chickens. Vaccines. 2023; 11(11):1638. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11111638
Chicago/Turabian StyleElbestawy, Ahmed, Hany Ellakany, Mahmoud Sedeik, Ahmed Gado, Mervat Abdel-Latif, Ahmed Noreldin, Ahmed Orabi, Ismail Radwan, and Wafaa Abd El-Ghany. 2023. "Superior Efficacy of Apathogenic Genotype I (V4) over Lentogenic Genotype II (LaSota) Live Vaccines against Newcastle Disease Virus Genotype VII.1.1 in Pathogen-Associated Molecular Pattern-H9N2 Vaccinated Broiler Chickens" Vaccines 11, no. 11: 1638. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11111638
APA StyleElbestawy, A., Ellakany, H., Sedeik, M., Gado, A., Abdel-Latif, M., Noreldin, A., Orabi, A., Radwan, I., & El-Ghany, W. A. (2023). Superior Efficacy of Apathogenic Genotype I (V4) over Lentogenic Genotype II (LaSota) Live Vaccines against Newcastle Disease Virus Genotype VII.1.1 in Pathogen-Associated Molecular Pattern-H9N2 Vaccinated Broiler Chickens. Vaccines, 11(11), 1638. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11111638








