Studying T Cell Responses to Hepatotropic Viruses in the Liver Microenvironment
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Animal Models of the Hepatic T Cell Response to Hepatitis A–E Infection
2.1. Immune-Competent Non-Infection Mouse Models
2.2. Immune-Compromised Infection Mouse Models
2.3. Surrogate Models
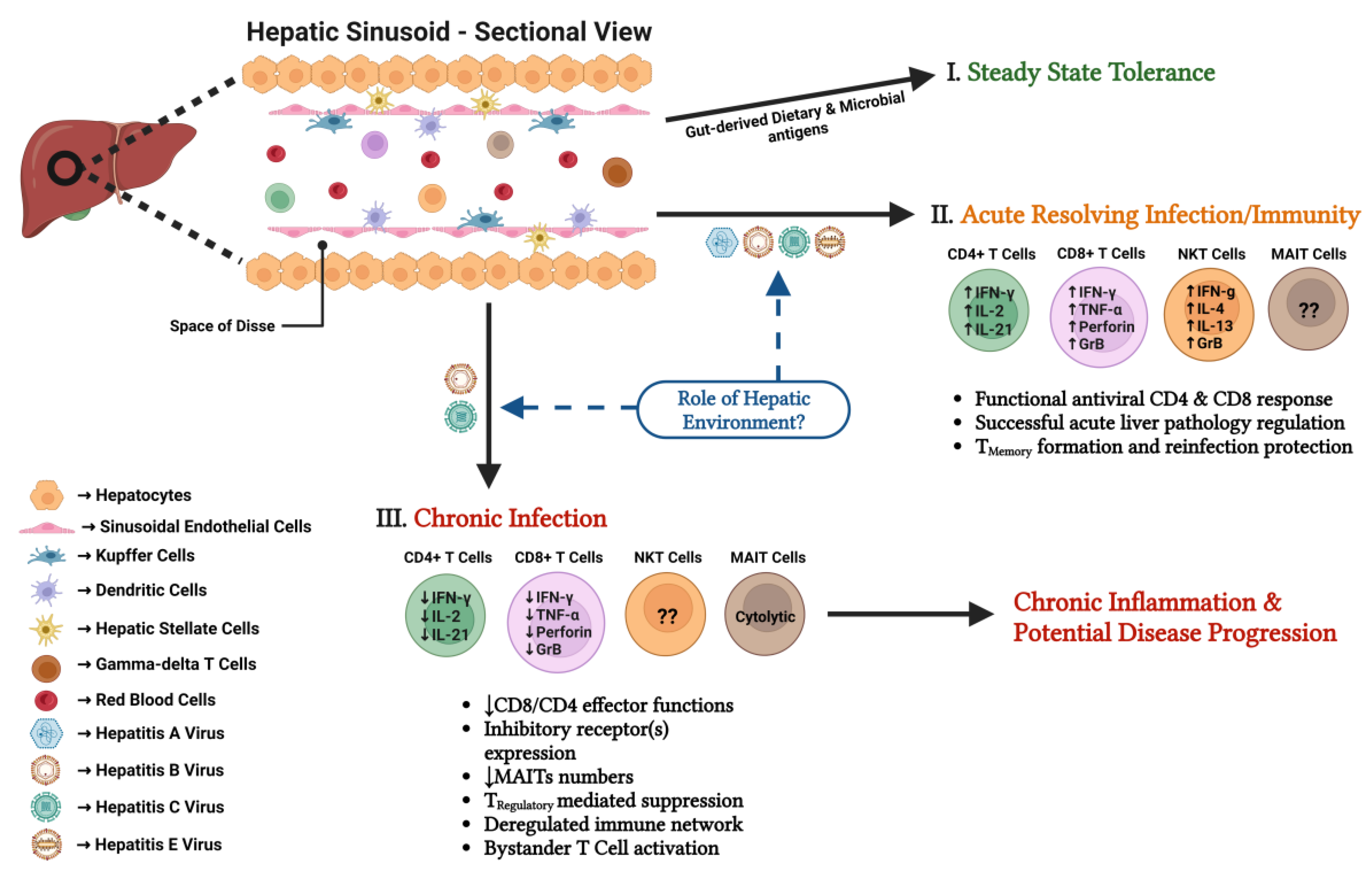
3. The Hepatic Immune Environment
3.1. Liver Structure and Hepatic Cells
3.2. Hepatic Immune Cell Subsets
3.3. Liver Immune Tolerance in the Steady State
4. Hepatic T Cell Subsets during Acute-Resolving Viral Hepatitis
4.1. CD8+ T Cells
4.2. CD4+ T Cells
4.3. Regulatory T Cells
4.4. Unconventional T Cell Subsets
5. Hepatic T Cell Subsets during Chronic Viral Hepatitis
5.1. CD8+ T Cells
5.2. CD4+ T Cells
5.3. Regulatory T Cells
5.4. Unconventional T Cell Subsets
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lemon, S.M.; Walker, C.M. Hepatitis A Virus and Hepatitis E Virus: Emerging and Re-Emerging Enterically Transmitted Hepatitis Viruses. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2019, 9, a031823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO. Fact Sheet Hepatitis E; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/hepatitis-e (accessed on 24 June 2022).
- WHO. Fact Sheet Hepatitis A; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/hepatitis-a (accessed on 24 June 2022).
- Manns, M.P.; Maasoumy, B. Breakthroughs in hepatitis C research: From discovery to cure. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 19, 533–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuen, M.F.; Chen, D.S.; Dusheiko, G.M.; Janssen, H.L.A.; Lau, D.T.Y.; Locarnini, S.A.; Peters, M.G.; Lai, C.L. Hepatitis B virus infection. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2018, 4, 18035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO. Fact Sheet Hepatitis C; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/hepatitis-c (accessed on 24 June 2022).
- WHO. Fact Sheet Hepatitis B; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/hepatitis-b (accessed on 24 June 2022).
- Urban, S.; Neumann-Haefelin, C.; Lampertico, P. Hepatitis D virus in 2021: Virology, immunology and new treatment approaches for a difficult-to-treat disease. Gut 2021, 70, 1782–1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Fact Sheet Hepatitis D; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/hepatitis-d (accessed on 24 June 2022).
- Shlomai, A.; de Jong, Y.P.; Rice, C.M. Virus associated malignancies: The role of viral hepatitis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2014, 26, 78–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Manne, V.; Ryan, J.; Wong, J.; Vengayil, G.; Basit, S.A.; Gish, R.G. Hepatitis C Vaccination: Where We Are and Where We Need to Be. Pathogens 2021, 10, 1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, E.C.; Sung, P.S.; Park, S.H. Immune responses and immunopathology in acute and chronic viral hepatitis. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2016, 16, 509–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, C.M. Adaptive Immune Responses in Hepatitis A Virus and Hepatitis E Virus Infections. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2019, 9, a033472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thimme, R. T cell immunity to hepatitis C virus: Lessons for a prophylactic HCV vaccine. J. Hepatol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gehring, A.J.; Protzer, U. Targeting Innate and Adaptive Immune Responses to Cure Chronic HBV Infection. Gastroenterology 2019, 156, 325–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kubes, P.; Jenne, C. Immune Responses in the Liver. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2018, 36, 247–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Maya, S.; Ploss, A. Animal Models of Hepatitis B Virus Infection-Success, Challenges, and Future Directions. Viruses 2021, 13, 777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berggren, K.A.; Suzuki, S.; Ploss, A. Animal Models Used in Hepatitis C Virus Research. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirai-Yuki, A.; Whitmire, J.K.; Joyce, M.; Tyrrell, D.L.; Lemon, S.M. Murine Models of Hepatitis A Virus Infection. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2019, 9, a031674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corneillie, L.; Banda, D.H.; Meuleman, P. Animal Models for Hepatitis E virus. Viruses 2019, 11, 564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Giersch, K.; Dandri, M. In Vivo Models of HDV Infection: Is Humanizing NTCP Enough? Viruses 2021, 13, 588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanford, R.E.; Walker, C.M.; Lemon, S.M. The Chimpanzee Model of Viral Hepatitis: Advances in Understanding the Immune Response and Treatment of Viral Hepatitis. ILAR J. 2017, 58, 172–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Engle, R.E.; De Battista, D.; Danoff, E.J.; Nguyen, H.; Chen, Z.; Lusso, P.; Purcell, R.H.; Farci, P. Distinct Cytokine Profiles Correlate with Disease Severity and Outcome in Longitudinal Studies of Acute Hepatitis B Virus and Hepatitis D Virus Infection in Chimpanzees. mBio 2020, 11, e02580-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwoerer, M.P.; Ploss, A. Barriers to hepatitis C virus infection in mice. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2022, 56, 101273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Urban, S. Entry of hepatitis B and hepatitis D virus into hepatocytes: Basic insights and clinical implications. J. Hepatol. 2016, 64, S32–S40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chisari, F.V.; Filippi, P.; Buras, J.; McLachlan, A.; Popper, H.; Pinkert, C.A.; Palmiter, R.D.; Brinster, R.L. Structural and pathological effects of synthesis of hepatitis B virus large envelope polypeptide in transgenic mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1987, 84, 6909–6913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chisari, F.V.; Pinkert, C.A.; Milich, D.R.; Filippi, P.; McLachlan, A.; Palmiter, R.D.; Brinster, R.L. A transgenic mouse model of the chronic hepatitis B surface antigen carrier state. Science 1985, 230, 1157–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guidotti, L.G.; Matzke, B.; Schaller, H.; Chisari, F.V. High-level hepatitis B virus replication in transgenic mice. J. Virol. 1995, 69, 6158–6169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Benechet, A.P.; De Simone, G.; Di Lucia, P.; Cilenti, F.; Barbiera, G.; Le Bert, N.; Fumagalli, V.; Lusito, E.; Moalli, F.; Bianchessi, V.; et al. Dynamics and genomic landscape of CD8(+) T cells undergoing hepatic priming. Nature 2019, 574, 200–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iannacone, M.; Guidotti, L.G. Immunobiology and pathogenesis of hepatitis B virus infection. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2022, 22, 19–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.L.; Wang, H.Y.; Chen, P.J. Hydrodynamic HBV Transfection Mouse Model. Methods Mol. Biol. 2017, 1540, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, L.; Yu, H.; Li, C.; Hirsch, M.L.; Zhang, L.; Samulski, R.J.; Li, W.; Liu, Z. Adeno-Associated Virus Vector Mediated Delivery of the HBV Genome Induces Chronic Hepatitis B Virus Infection and Liver Fibrosis in Mice. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0130052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sprinzl, M.F.; Oberwinkler, H.; Schaller, H.; Protzer, U. Transfer of hepatitis B virus genome by adenovirus vectors into cultured cells and mice: Crossing the species barrier. J. Virol. 2001, 75, 5108–5118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, L.R.; Wu, H.L.; Chen, P.J.; Chen, D.S. An immunocompetent mouse model for the tolerance of human chronic hepatitis B virus infection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 17862–17867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Z.; Zhu, K.; Bai, W.; Jia, B.; Hu, H.; Zhou, D.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, X.; Xie, Y.; Bourgine, M.M.; et al. Adenoviral delivery of recombinant hepatitis B virus expressing foreign antigenic epitopes for immunotherapy of persistent viral infection. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 3004–3015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dion, S.; Bourgine, M.; Godon, O.; Levillayer, F.; Michel, M.L. Adeno-associated virus-mediated gene transfer leads to persistent hepatitis B virus replication in mice expressing HLA-A2 and HLA-DR1 molecules. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 5554–5563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, D.; Liu, L.; Zhu, D.; Peng, H.; Su, L.; Fu, Y.X.; Zhang, L. A mouse model for HBV immunotolerance and immunotherapy. Cell Mol. Immunol. 2014, 11, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Suarez-Amaran, L.; Usai, C.; Di Scala, M.; Godoy, C.; Ni, Y.; Hommel, M.; Palomo, L.; Segura, V.; Olague, C.; Vales, A.; et al. A new HDV mouse model identifies mitochondrial antiviral signaling protein (MAVS) as a key player in IFN-beta induction. J. Hepatol. 2017, 67, 669–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirai-Yuki, A.; Hensley, L.; McGivern, D.R.; Gonzalez-Lopez, O.; Das, A.; Feng, H.; Sun, L.; Wilson, J.E.; Hu, F.; Feng, Z.; et al. MAVS-dependent host species range and pathogenicity of human hepatitis A virus. Science 2016, 353, 1541–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Misumi, I.; Mitchell, J.E.; Lund, M.M.; Cullen, J.M.; Lemon, S.M.; Whitmire, J.K. T cells protect against hepatitis A virus infection and limit infection-induced liver injury. J. Hepatol. 2021, 75, 1323–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartlage, A.S.; Cullen, J.M.; Kapoor, A. The Strange, Expanding World of Animal Hepaciviruses. Annu. Rev. Virol. 2016, 3, 53–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Scheel, T.K.; Kapoor, A.; Nishiuchi, E.; Brock, K.V.; Yu, Y.; Andrus, L.; Gu, M.; Renshaw, R.W.; Dubovi, E.J.; McDonough, S.P.; et al. Characterization of nonprimate hepacivirus and construction of a functional molecular clone. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 2192–2197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Firth, C.; Bhat, M.; Firth, M.A.; Williams, S.H.; Frye, M.J.; Simmonds, P.; Conte, J.M.; Ng, J.; Garcia, J.; Bhuva, N.P.; et al. Detection of zoonotic pathogens and characterization of novel viruses carried by commensal Rattus norvegicus in New York City. mBio 2014, 5, e01933-14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kapoor, A.; Simmonds, P.; Scheel, T.K.; Hjelle, B.; Cullen, J.M.; Burbelo, P.D.; Chauhan, L.V.; Duraisamy, R.; Sanchez Leon, M.; Jain, K.; et al. Identification of rodent homologs of hepatitis C virus and pegiviruses. mBio 2013, 4, e00216-13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Billerbeck, E.; Wolfisberg, R.; Fahnoe, U.; Xiao, J.W.; Quirk, C.; Luna, J.M.; Cullen, J.M.; Hartlage, A.S.; Chiriboga, L.; Ghoshal, K.; et al. Mouse models of acute and chronic hepacivirus infection. Science 2017, 357, 204–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Trivedi, S.; Murthy, S.; Sharma, H.; Hartlage, A.S.; Kumar, A.; Gadi, S.V.; Simmonds, P.; Chauhan, L.V.; Scheel, T.K.H.; Billerbeck, E.; et al. Viral persistence, liver disease, and host response in a hepatitis C-like virus rat model. Hepatology 2018, 68, 435–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hartlage, A.S.; Murthy, S.; Kumar, A.; Trivedi, S.; Dravid, P.; Sharma, H.; Walker, C.M.; Kapoor, A. Vaccination to prevent T cell subversion can protect against persistent hepacivirus infection. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Meng, X.J.; Purcell, R.H.; Halbur, P.G.; Lehman, J.R.; Webb, D.M.; Tsareva, T.S.; Haynes, J.S.; Thacker, B.J.; Emerson, S.U. A novel virus in swine is closely related to the human hepatitis E virus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 9860–9865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cheng, X.; Wang, S.; Dai, X.; Shi, C.; Wen, Y.; Zhu, M.; Zhan, S.; Meng, J. Rabbit as a novel animal model for hepatitis E virus infection and vaccine evaluation. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e51616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purcell, R.H.; Engle, R.E.; Rood, M.P.; Kabrane-Lazizi, Y.; Nguyen, H.T.; Govindarajan, S.; St Claire, M.; Emerson, S.U. Hepatitis E virus in rats, Los Angeles, California, USA. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2011, 17, 2216–2222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mulrooney-Cousins, P.M.; Michalak, T.I. Asymptomatic Hepadnaviral Persistence and Its Consequences in the Woodchuck Model of Occult Hepatitis B Virus Infection. J. Clin. Transl. Hepatol. 2015, 3, 211–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Summers, J.; Smolec, J.M.; Snyder, R. A virus similar to human hepatitis B virus associated with hepatitis and hepatoma in woodchucks. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1978, 75, 4533–4537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Roggendorf, M.; Kosinska, A.D.; Liu, J.; Lu, M. The Woodchuck, a Nonprimate Model for Immunopathogenesis and Therapeutic Immunomodulation in Chronic Hepatitis B Virus Infection. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2015, 5, a021451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, S.P.; Zhou, G.P.; Sun, J.; Cui, B.; Zhang, H.M.; Wei, L.; Sun, L.Y.; Zhu, Z.J. Multiplex Immunofluorescence for Detection of Spatial Distributions of Infiltrating T Cells Within Different Regions of Hepatic Lobules During Liver Transplantation Rejection. Inflammation 2022, 45, 651–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zong, Y.; Stanger, B.Z. Molecular mechanisms of liver and bile duct development. Wiley Interdiscip Rev. Dev.Biol. 2012, 1, 643–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macchiarelli, G.; Motta, P.M. The three-dimensional microstructure of the liver. A review by scanning electron microscopy. Scan. Electron. Microsc. 1986, III Pt 3, 1019–1038. [Google Scholar]
- Braet, F.; Wisse, E. AFM imaging of fenestrated liver sinusoidal endothelial cells. Micron 2012, 43, 1252–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senoo, H.; Yoshikawa, K.; Morii, M.; Miura, M.; Imai, K.; Mezaki, Y. Hepatic stellate cell (vitamin A-storing cell) and its relative--past, present and future. Cell Biol. Int. 2010, 34, 1247–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorente, S.; Hautefeuille, M.; Sanchez-Cedillo, A. The liver, a functionalized vascular structure. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 16194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crispe, I.N. Immune tolerance in liver disease. Hepatology 2014, 60, 2109–2117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thomson, A.W.; Knolle, P.A. Antigen-presenting cell function in the tolerogenic liver environment. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2010, 10, 753–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ficht, X.; Iannacone, M. Immune surveillance of the liver by T cells. Sci. Immunol. 2020, 5, aba2351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Yamane, H.; Paul, W.E. Differentiation of effector CD4 T cell populations (*). Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2010, 28, 445–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Plitas, G.; Rudensky, A.Y. Regulatory T Cells: Differentiation and Function. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2016, 4, 721–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Constantinides, M.G.; Belkaid, Y. Early-life imprinting of unconventional T cells and tissue homeostasis. Science 2021, 374, eabf0095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hackstein, C.P.; Klenerman, P. Emerging features of MAIT cells and other unconventional T cell populations in human viral disease and vaccination. Semin. Immunol. 2022, 61–64, 101661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ataide, M.A.; Knopper, K.; Cruz de Casas, P.; Ugur, M.; Eickhoff, S.; Zou, M.; Shaikh, H.; Trivedi, A.; Grafen, A.; Yang, T.; et al. Lymphatic migration of unconventional T cells promotes site-specific immunity in distinct lymph nodes. Immunity 2022, 55, 1813–1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, W.; Wu, X. Diverse Functions of gammadelta T Cells in the Progression of Hepatitis B Virus and Hepatitis C Virus Infection. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 619872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pellicci, D.G.; Koay, H.F.; Berzins, S.P. Thymic development of unconventional T cells: How NKT cells, MAIT cells and gammadelta T cells emerge. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2020, 20, 756–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Suryadevara, N.; Hill, T.M.; Bezbradica, J.S.; Van Kaer, L.; Joyce, S. Natural Killer T Cells: An Ecological Evolutionary Developmental Biology Perspective. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thimme, R.; Wieland, S.; Steiger, C.; Ghrayeb, J.; Reimann, K.A.; Purcell, R.H.; Chisari, F.V. CD8(+) T cells mediate viral clearance and disease pathogenesis during acute hepatitis B virus infection. J. Virol. 2003, 77, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shoukry, N.H.; Grakoui, A.; Houghton, M.; Chien, D.Y.; Ghrayeb, J.; Reimann, K.A.; Walker, C.M. Memory CD8+ T cells are required for protection from persistent hepatitis C virus infection. J. Exp. Med. 2003, 197, 1645–1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Callendret, B.; Xu, D.; Brasky, K.M.; Feng, Z.; Hensley, L.L.; Guedj, J.; Perelson, A.S.; Lemon, S.M.; Lanford, R.E.; et al. Dominance of the CD4(+) T helper cell response during acute resolving hepatitis A virus infection. J. Exp. Med. 2012, 209, 1481–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bremer, W.; Blasczyk, H.; Yin, X.; Salinas, E.; Grakoui, A.; Feng, Z.; Walker, C. Resolution of hepatitis E virus infection in CD8+ T cell-depleted rhesus macaques. J. Hepatol. 2021, 75, 557–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoukry, N.H. Towards a Systems Immunology Approach to Understanding Correlates of Protective Immunity against HCV. Viruses 2021, 13, 1871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoukry, N.H.; Walker, C.M. T cell responses during HBV and HCV infections: Similar but not quite the same? Curr. Opin. Virol. 2021, 51, 80–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoogeveen, R.C.; Robidoux, M.P.; Schwarz, T.; Heydmann, L.; Cheney, J.A.; Kvistad, D.; Aneja, J.; Melgaco, J.G.; Fernandes, C.A.; Chung, R.T.; et al. Phenotype and function of HBV-specific T cells is determined by the targeted epitope in addition to the stage of infection. Gut 2019, 68, 893–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guidotti, L.G.; Ishikawa, T.; Hobbs, M.V.; Matzke, B.; Schreiber, R.; Chisari, F.V. Intracellular inactivation of the hepatitis B virus by cytotoxic T lymphocytes. Immunity 1996, 4, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Guidotti, L.G.; Rochford, R.; Chung, J.; Shapiro, M.; Purcell, R.; Chisari, F.V. Viral clearance without destruction of infected cells during acute HBV infection. Science 1999, 284, 825–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Chang, D.Y.; Lee, H.W.; Lee, H.; Kim, J.H.; Sung, P.S.; Kim, K.H.; Hong, S.H.; Kang, W.; Lee, J.; et al. Innate-like Cytotoxic Function of Bystander-Activated CD8(+) T Cells Is Associated with Liver Injury in Acute Hepatitis A. Immunity 2018, 48, 161–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kemming, J.; Gundlach, S.; Panning, M.; Huzly, D.; Huang, J.; Lutgehetmann, M.; Pischke, S.; Schulze Zur Wiesch, J.; Emmerich, F.; Llewellyn-Lacey, S.; et al. Mechanisms of CD8+ T-cell failure in chronic hepatitis E virus infection. J. Hepatol. 2022, 77, 978–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Boon, D.; McDonald, S.L.; Myers, T.G.; Tomioka, K.; Nguyen, H.; Engle, R.E.; Govindarajan, S.; Emerson, S.U.; Purcell, R.H. Pathogenesis of hepatitis E virus and hepatitis C virus in chimpanzees: Similarities and differences. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 11264–11278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lanford, R.E.; Feng, Z.; Chavez, D.; Guerra, B.; Brasky, K.M.; Zhou, Y.; Yamane, D.; Perelson, A.S.; Walker, C.M.; Lemon, S.M. Acute hepatitis A virus infection is associated with a limited type I interferon response and persistence of intrahepatic viral RNA. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 11223–11228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wieland, S.; Thimme, R.; Purcell, R.H.; Chisari, F.V. Genomic analysis of the host response to hepatitis B virus infection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 6669–6674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Suslov, A.; Heim, M.H.; Wieland, S. Studying Hepatitis Virus-Host Interactions in Patient Liver Biopsies. Viruses 2022, 14, 2490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bigger, C.B.; Brasky, K.M.; Lanford, R.E. DNA microarray analysis of chimpanzee liver during acute resolving hepatitis C virus infection. J. Virol. 2001, 75, 7059–7066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Su, A.I.; Pezacki, J.P.; Wodicka, L.; Brideau, A.D.; Supekova, L.; Thimme, R.; Wieland, S.; Bukh, J.; Purcell, R.H.; Schultz, P.G.; et al. Genomic analysis of the host response to hepatitis C virus infection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 15669–15674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wieland, S.; Makowska, Z.; Campana, B.; Calabrese, D.; Dill, M.T.; Chung, J.; Chisari, F.V.; Heim, M.H. Simultaneous detection of hepatitis C virus and interferon stimulated gene expression in infected human liver. Hepatology 2014, 59, 2121–2130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thomas, D.L.; Thio, C.L.; Martin, M.P.; Qi, Y.; Ge, D.; O’Huigin, C.; Kidd, J.; Kidd, K.; Khakoo, S.I.; Alexander, G.; et al. Genetic variation in IL28B and spontaneous clearance of hepatitis C virus. Nature 2009, 461, 798–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Prokunina-Olsson, L.; Muchmore, B.; Tang, W.; Pfeiffer, R.M.; Park, H.; Dickensheets, H.; Hergott, D.; Porter-Gill, P.; Mumy, A.; Kohaar, I.; et al. A variant upstream of IFNL3 (IL28B) creating a new interferon gene IFNL4 is associated with impaired clearance of hepatitis C virus. Nat. Genet. 2013, 45, 164–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Coto-Llerena, M.; Suslov, A.; Teixeira, R.D.; Fofana, I.; Nuciforo, S.; Hofmann, M.; Thimme, R.; Hensel, N.; Lohmann, V.; et al. Interferon lambda 4 impairs hepatitis C viral antigen presentation and attenuates T cell responses. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 4882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murata, Y.; Kawashima, K.; Sheikh, K.; Tanaka, Y.; Isogawa, M. Intrahepatic Cross-Presentation and Hepatocellular Antigen Presentation Play Distinct Roles in the Induction of Hepatitis B Virus-Specific CD8(+) T Cell Responses. J. Virol. 2018, 92, e00920-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Simone, G.; Andreata, F.; Bleriot, C.; Fumagalli, V.; Laura, C.; Garcia-Manteiga, J.M.; Di Lucia, P.; Gilotto, S.; Ficht, X.; De Ponti, F.F.; et al. Identification of a Kupffer cell subset capable of reverting the T cell dysfunction induced by hepatocellular priming. Immunity 2021, 54, 2089–2100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.R.; Wohlleber, D.; Reisinger, F.; Jenne, C.N.; Cheng, R.L.; Abdullah, Z.; Schildberg, F.A.; Odenthal, M.; Dienes, H.P.; van Rooijen, N.; et al. Intrahepatic myeloid-cell aggregates enable local proliferation of CD8(+) T cells and successful immunotherapy against chronic viral liver infection. Nat. Immunol. 2013, 14, 574–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, S.; Seo, D.J.; Yeo, D.; Wang, Z.; Min, A.; Zhao, Z.; Song, M.; Choi, I.S.; Myoung, J.; Choi, C. Experimental infection of hepatitis E virus induces pancreatic necroptosis in miniature pigs. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 12022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nimgaonkar, I.; Ding, Q.; Schwartz, R.E.; PLoSs, A. Hepatitis E virus: Advances and challenges. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 15, 96–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grakoui, A.; Shoukry, N.H.; Woollard, D.J.; Han, J.H.; Hanson, H.L.; Ghrayeb, J.; Murthy, K.K.; Rice, C.M.; Walker, C.M. HCV persistence and immune evasion in the absence of memory T cell help. Science 2003, 302, 659–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Asabe, S.; Wieland, S.F.; Chattopadhyay, P.K.; Roederer, M.; Engle, R.E.; Purcell, R.H.; Chisari, F.V. The size of the viral inoculum contributes to the outcome of hepatitis B virus infection. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 9652–9662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, X.; Dong, Q.; Li, Q.; Li, Y.; Zhao, D.; Sun, J.; Fu, J.; Meng, F.; Lin, H.; Luan, J.; et al. Dysregulated Response of Follicular Helper T Cells to Hepatitis B Surface Antigen Promotes HBV Persistence in Mice and Associates With Outcomes of Patients. Gastroenterology 2018, 154, 2222–2236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.; Brunner, L.; Oz, E.A.; Sacherl, J.; Frank, G.; Kerth, H.A.; Thiele, F.; Wiegand, M.; Mogler, C.; Aguilar, J.C.; et al. Activation of CD4 T cells during prime immunization determines the success of a therapeutic hepatitis B vaccine in HBV-carrier mouse models. J. Hepatol. 2022, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolski, D.; Lauer, G.M. Hepatitis C Virus as a Unique Human Model Disease to Define Differences in the Transcriptional Landscape of T Cells in Acute versus Chronic Infection. Viruses 2019, 11, 683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Song, X.F.; Hu, T.T.; Lei, Y.; Li, H.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, M.; Liu, B.; Chen, M.; Hu, H.D.; Ren, H.; et al. Activation of intrahepatic CD4+CXCR5+ T and CD19+ B cells is associated with viral clearance in a mouse model of acute hepatitis B virus infection. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 50952–50962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wu, J.; Guo, Y.; Lu, X.; Huang, F.; Lv, F.; Wei, D.; Shang, A.; Yang, J.; Pan, Q.; Jiang, B.; et al. Th1/Th2 Cells and Associated Cytokines in Acute Hepatitis E and Related Acute Liver Failure. J. Immunol. Res. 2020, 2020, 6027361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.S.; Lee, J.; Lee, H.W.; Chang, D.Y.; Sung, P.S.; Jung, M.K.; Park, J.Y.; Kim, J.K.; Lee, J.I.; Park, H.; et al. Liver injury in acute hepatitis A is associated with decreased frequency of regulatory T cells caused by Fas-mediated apoptosis. Gut 2015, 64, 1303–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.S.; Jung, M.K.; Lee, J.; Choi, S.J.; Choi, S.H.; Lee, H.W.; Lee, J.J.; Kim, H.J.; Ahn, S.H.; Lee, D.H.; et al. Tumor Necrosis Factor-producing T-regulatory Cells Are Associated With Severe Liver Injury in Patients With Acute Hepatitis A. Gastroenterology 2018, 154, 1047–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathod, S.B.; Das, R.; Thanapati, S.; Arankalle, V.A.; Tripathy, A.S. Suppressive activity and altered conventional phenotype markers/mediators of regulatory T cells in patients with self-limiting hepatitis E. J. Viral. Hepat. 2014, 21, 141–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, M.K.; Shin, E.C. Regulatory T Cells in Hepatitis B and C Virus Infections. Immune Netw. 2016, 16, 330–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kared, H.; Fabre, T.; Bedard, N.; Bruneau, J.; Shoukry, N.H. Galectin-9 and IL-21 mediate cross-regulation between Th17 and Treg cells during acute hepatitis C. PLoS Pathog. 2013, 9, e1003422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xue-Song, L.; Cheng-Zhong, L.; Ying, Z.; Mo-Bin, W. Changes of Treg and Th17 cells balance in the development of acute and chronic hepatitis B virus infection. BMC Gastroenterol. 2012, 12, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dolina, J.S.; Braciale, T.J.; Hahn, Y.S. Liver-primed CD8+ T cells suppress antiviral adaptive immunity through galectin-9-independent T-cell immunoglobulin and mucin 3 engagement of high-mobility group box 1 in mice. Hepatology 2014, 59, 1351–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fioravanti, J.; Di Lucia, P.; Magini, D.; Moalli, F.; Boni, C.; Benechet, A.P.; Fumagalli, V.; Inverso, D.; Vecchi, A.; Fiocchi, A.; et al. Effector CD8(+) T cell-derived interleukin-10 enhances acute liver immunopathology. J. Hepatol. 2017, 67, 543–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeissig, S.; Murata, K.; Sweet, L.; Publicover, J.; Hu, Z.; Kaser, A.; Bosse, E.; Iqbal, J.; Hussain, M.M.; Balschun, K.; et al. Hepatitis B virus-induced lipid alterations contribute to natural killer T cell-dependent protective immunity. Nat. Med. 2012, 18, 1060–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hou, X.; Hao, X.; Zheng, M.; Xu, C.; Wang, J.; Zhou, R.; Tian, Z. CD205-TLR9-IL-12 axis contributes to CpG-induced oversensitive liver injury in HBsAg transgenic mice by promoting the interaction of NKT cells with Kupffer cells. Cell Mol. Immunol. 2017, 14, 675–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Du, X.; Liu, Y.; Song, X.; Wang, T.; Tan, S.; Liang, X.; Gao, L.; Ma, C. Tim-3 blockade promotes iNKT cell function to inhibit HBV replication. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2018, 22, 3192–3201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Das, R.; Tripathy, A. Increased expressions of NKp44, NKp46 on NK/NKT-like cells are associated with impaired cytolytic function in self-limiting hepatitis E infection. Med. Microbiol. Immunol. 2014, 203, 303–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senff, T.; Menne, C.; Cosmovici, C.; Lewis-Ximenez, L.L.; Aneja, J.; Broering, R.; Kim, A.Y.; Westendorf, A.M.; Dittmer, U.; Scherbaum, N.; et al. Peripheral blood iNKT cell activation correlates with liver damage during acute hepatitis C. JCI Insight 2022, 7, e155432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raus, S.; Lopez-Scarim, J.; Luthy, J.; Billerbeck, E. Hepatic iNKT cells produce type 2 cytokines and restrain antiviral T cells during acute hepacivirus infection. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 953151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, L.; Wang, L.; Ling, N.; Peng, H.; Chen, M. Increase in liver gammadelta T cells with concurrent augmentation of IFN-beta production during the early stages of a mouse model of acute experimental hepatitis B virus infection. Exp. Ther. Med. 2020, 19, 67–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Guan, Y.; Hu, Y.; Li, Y.; Lu, N.; Zhang, C. Murine CXCR3(+)CXCR6(+)gammadeltaT Cells Reside in the Liver and Provide Protection Against HBV Infection. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 757379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Khera, T.; Strunz, B.; Deterding, K.; Todt, D.; Woller, N.; Engelskircher, S.A.; Hardtke, S.; Port, K.; Ponzetta, A.; et al. Imprint of unconventional T-cell response in acute hepatitis C persists despite successful early antiviral treatment. Eur. J. Immunol. 2022, 52, 472–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rha, M.S.; Han, J.W.; Kim, J.H.; Koh, J.Y.; Park, H.J.; Kim, S.I.; Kim, M.S.; Lee, J.G.; Lee, H.W.; Lee, D.H.; et al. Human liver CD8(+) MAIT cells exert TCR/MR1-independent innate-like cytotoxicity in response to IL-15. J. Hepatol. 2020, 73, 640–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolski, D.; Foote, P.K.; Chen, D.Y.; Lewis-Ximenez, L.L.; Fauvelle, C.; Aneja, J.; Walker, A.; Tonnerre, P.; Torres-Cornejo, A.; Kvistad, D.; et al. Early Transcriptional Divergence Marks Virus-Specific Primary Human CD8(+) T Cells in Chronic versus Acute Infection. Immunity 2017, 47, 648–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Salimi Alizei, E.; Hofmann, M.; Thimme, R.; Neumann-Haefelin, C. Mutational escape from cellular immunity in viral hepatitis: Variations on a theme. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2021, 50, 110–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartlage, A.S.; Walker, C.M.; Kapoor, A. Priming of Antiviral CD8 T Cells without Effector Function by a Persistently Replicating Hepatitis C-Like Virus. J. Virol. 2020, 94, e00035-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossi, M.; Vecchi, A.; Tiezzi, C.; Barili, V.; Fisicaro, P.; Penna, A.; Montali, I.; Daffis, S.; Fletcher, S.P.; Gaggar, A.; et al. Phenotypic CD8 T cell profiling in chronic hepatitis B to predict HBV-specific CD8 T cell susceptibility to functional restoration in vitro. Gut 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Zhu, Y.O.; Becht, E.; Aw, P.; Chen, J.; Poidinger, M.; de Sessions, P.F.; Hibberd, M.L.; Bertoletti, A.; Lim, S.G.; et al. Multifactorial heterogeneity of virus-specific T cells and association with the progression of human chronic hepatitis B infection. Sci. Immunol. 2019, 4, eaau6905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heim, K.; Binder, B.; Sagar; Wieland, D.; Hensel, N.; Llewellyn-Lacey, S.; Gostick, E.; Price, D.A.; Emmerich, F.; Vingerhoet, H.; et al. TOX defines the degree of CD8+ T cell dysfunction in distinct phases of chronic HBV infection. Gut 2020, 70, 1550–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osuch, S.; Laskus, T.; Perlejewski, K.; Berak, H.; Bukowska-Osko, I.; Pollak, A.; Zielenkiewicz, M.; Radkowski, M.; Caraballo Cortes, K. CD8(+) T-Cell Exhaustion Phenotype in Chronic Hepatitis C Virus Infection Is Associated With Epitope Sequence Variation. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 832206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuch, A.; Salimi Alizei, E.; Heim, K.; Wieland, D.; Kiraithe, M.M.; Kemming, J.; Llewellyn-Lacey, S.; Sogukpinar, O.; Ni, Y.; Urban, S.; et al. Phenotypic and functional differences of HBV core-specific versus HBV polymerase-specific CD8+ T cells in chronically HBV-infected patients with low viral load. Gut 2019, 68, 905–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Khakpoor, A.; Ni, Y.; Chen, A.; Ho, Z.Z.; Oei, V.; Yang, N.; Giri, R.; Chow, J.X.; Tan, A.T.; Kennedy, P.T.; et al. Spatiotemporal Differences in Presentation of CD8 T Cell Epitopes during Hepatitis B Virus Infection. J. Virol. 2019, 93, e01457-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rehermann, B.; Thimme, R. Insights From Antiviral Therapy Into Immune Responses to Hepatitis B and C Virus Infection. Gastroenterology 2019, 156, 369–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holz, L.E.; Benseler, V.; Bowen, D.G.; Bouillet, P.; Strasser, A.; O’Reilly, L.; d’Avigdor, W.M.; Bishop, A.G.; McCaughan, G.W.; Bertolino, P. Intrahepatic murine CD8 T-cell activation associates with a distinct phenotype leading to Bim-dependent death. Gastroenterology 2008, 135, 989–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, W.; Sun, H.; Sun, R.; Lian, Z.; Wei, H.; Tian, Z.; Chen, Y. HBV immune tolerance of HBs-transgenic mice observed through parabiosis with WT mice. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 993246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lercher, A.; Bhattacharya, A.; Popa, A.M.; Caldera, M.; Schlapansky, M.F.; Baazim, H.; Agerer, B.; Gurtl, B.; Kosack, L.; Majek, P.; et al. Type I Interferon Signaling Disrupts the Hepatic Urea Cycle and Alters Systemic Metabolism to Suppress T Cell Function. Immunity 2019, 51, 1074–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liou, J.W.; Mani, H.; Yen, J.H. Viral Hepatitis, Cholesterol Metabolism, and Cholesterol-Lowering Natural Compounds. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 3897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, R.J.; Singh, P.K.; Mehla, K. The cholesterol pathway: Impact on immunity and cancer. Trends Immunol. 2022, 43, 78–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, N.M.; Wing, P.A.C.; Diniz, M.O.; Pallett, L.J.; Swadling, L.; Harris, J.M.; Burton, A.R.; Jeffery-Smith, A.; Zakeri, N.; Amin, O.E.; et al. Targeting human Acyl-CoA:cholesterol acyltransferase as a dual viral and T cell metabolic checkpoint. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 2814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H.; Yu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, L.; Yang, A.; Hu, Y.; Pan, Z.; Wang, Z.; Yang, J.; Han, Q.; et al. Cholesterol accumulation on dendritic cells reverses chronic hepatitis B virus infection-induced dysfunction. Cell Mol. Immunol. 2022, 19, 1347–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamataki, Z.; Swadling, L. The liver as an immunological barrier redefined by single-cell analysis. Immunology 2020, 160, 157–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gill, U.S.; Pallett, L.J.; Kennedy, P.T.F.; Maini, M.K. Liver sampling: A vital window into HBV pathogenesis on the path to functional cure. Gut 2018, 67, 767–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khanam, A.; Chua, J.V.; Kottilil, S. Immunopathology of Chronic Hepatitis B Infection: Role of Innate and Adaptive Immune Response in Disease Progression. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 5497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Li, J.; Cheng, Y.; Meng, F.; Song, J.W.; Fan, X.; Fan, H.; Li, J.; Fu, Y.L.; Zhou, M.J.; et al. Single-cell RNA sequencing reveals intrahepatic and peripheral immune characteristics related to disease phases in HBV-infected patients. Gut 2023, 72, 153–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montanari, N.R.; Ramirez, R.; Aggarwal, A.; van Buuren, N.; Doukas, M.; Moon, C.; Turner, S.; Diehl, L.; Li, L.; Debes, J.D.; et al. Multi-parametric analysis of human livers reveals variation in intrahepatic inflammation across phases of chronic hepatitis B infection. J. Hepatol. 2022, 77, 332–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Buuren, N.; Ramirez, R.; Turner, S.; Chen, D.; Suri, V.; Aggarwal, A.; Moon, C.; Kim, S.; Kornyeyev, D.; Bui, N.; et al. Characterization of the liver immune microenvironment in liver biopsies from patients with chronic HBV infection. JHEP Rep. 2022, 4, 100388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abel, M.; Sene, D.; Pol, S.; Bourliere, M.; Poynard, T.; Charlotte, F.; Cacoub, P.; Caillat-Zucman, S. Intrahepatic virus-specific IL-10-producing CD8 T cells prevent liver damage during chronic hepatitis C virus infection. Hepatology 2006, 44, 1607–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wu, B.; Li, L.; Hu, L.; Lin, J.; Jiang, C.; Cai, G.; Shen, Q. Hepatic expansion of virus-specific CD8(+)BTLA(+) T cells with regulatory properties in chronic hepatitis B virus infection. Cell Immunol. 2017, 311, 36–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Liu, Y.; Yang, X.; Sun, H.; Shu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Cao, H.; Wu, M.; Liu, N.; Zou, Y.; et al. HBV promotes the recruitment of IL-17 secreting T cells via chemokines CCL22 and CCL17. Liver Int. 2020, 40, 1327–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grafmueller, S.; Billerbeck, E.; Blum, H.E.; Neumann-Haefelin, C.; Thimme, R. Differential antigen specificity of hepatitis C virus-specific interleukin 17- and interferon gamma-producing CD8(+) T cells during chronic infection. J. Infect. Dis. 2012, 205, 1142–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pallett, L.J.; Davies, J.; Colbeck, E.J.; Robertson, F.; Hansi, N.; Easom, N.J.W.; Burton, A.R.; Stegmann, K.A.; Schurich, A.; Swadling, L.; et al. IL-2(high) tissue-resident T cells in the human liver: Sentinels for hepatotropic infection. J. Exp. Med. 2017, 214, 1567–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.H.; Han, J.W.; Choi, Y.J.; Rha, M.S.; Koh, J.Y.; Kim, K.H.; Kim, C.G.; Lee, Y.J.; Kim, A.R.; Park, J.; et al. Functions of human liver CD69(+)CD103(-)CD8(+) T cells depend on HIF-2alpha activity in healthy and pathologic livers. J. Hepatol. 2020, 72, 1170–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stelma, F.; de Niet, A.; Sinnige, M.J.; van Dort, K.A.; van Gisbergen, K.; Verheij, J.; van Leeuwen, E.M.M.; Kootstra, N.A.; Reesink, H.W. Human intrahepatic CD69 + CD8+ T cells have a tissue resident memory T cell phenotype with reduced cytolytic capacity. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 6172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nkongolo, S.; Mahamed, D.; Kuipery, A.; Sanchez Vasquez, J.D.; Kim, S.C.; Mehrotra, A.; Patel, A.; Hu, C.; McGilvray, I.; Feld, J.J.; et al. Longitudinal liver sampling in patients with chronic hepatitis B starting antiviral therapy reveals hepatotoxic CD8+ T cells. J. Clin. Investig. 2023, 133, e158903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kefalakes, H.; Horgan, X.J.; Jung, M.K.; Amanakis, G.; Kapuria, D.; Bolte, F.J.; Kleiner, D.E.; Koh, C.; Heller, T.; Rehermann, B. Liver-Resident Bystander CD8(+) T Cells Contribute to Liver Disease Pathogenesis in Chronic Hepatitis D Virus Infection. Gastroenterology 2021, 161, 1567–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.H.; Fan, J.H.; Jeng, W.J.; Chang, S.T.; Yang, C.K.; Teng, W.; Wu, T.H.; Hsieh, Y.C.; Chen, W.T.; Chen, Y.C.; et al. Innate-like bystander-activated CD38(+) HLA-DR(+) CD8(+) T cells play a pathogenic role in patients with chronic hepatitis C. Hepatology 2022, 76, 803–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, U.S. The immune landscape in hepatitis delta virus infection-Still an open field! J. Viral. Hepat. 2022. early view. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulze Zur Wiesch, J.; Ciuffreda, D.; Lewis-Ximenez, L.; Kasprowicz, V.; Nolan, B.E.; Streeck, H.; Aneja, J.; Reyor, L.L.; Allen, T.M.; Lohse, A.W.; et al. Broadly directed virus-specific CD4+ T cell responses are primed during acute hepatitis C infection, but rapidly disappear from human blood with viral persistence. J. Exp. Med. 2012, 209, 61–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, D.Y.; Wolski, D.; Aneja, J.; Matsubara, L.; Robilotti, B.; Hauck, G.; de Sousa, P.S.F.; Subudhi, S.; Fernandes, C.A.; Hoogeveen, R.C.; et al. Hepatitis C virus-specific CD4+ T cell phenotype and function in different infection outcomes. J. Clin. Investig. 2020, 130, 768–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, S.; Honegger, J.R.; Walker, C. T-Cell Immunity against the Hepatitis C Virus: A Persistent Research Priority in an Era of Highly Effective Therapy. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2021, 11, a036954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buschow, S.I.; Jansen, D. CD4(+) T Cells in Chronic Hepatitis B and T Cell-Directed Immunotherapy. Cells 2021, 10, 1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanam, A.; Ayithan, N.; Tang, L.; Poonia, B.; Kottilil, S. IL-21-Deficient T Follicular Helper Cells Support B Cell Responses Through IL-27 in Patients With Chronic Hepatitis B. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 599648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spaan, M.; Kreefft, K.; de Graav, G.N.; Brouwer, W.P.; de Knegt, R.J.; ten Kate, F.J.; Baan, C.C.; Vanwolleghem, T.; Janssen, H.L.; Boonstra, A. CD4+ CXCR5+ T cells in chronic HCV infection produce less IL-21, yet are efficient at supporting B cell responses. J. Hepatol. 2015, 62, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.W.; Shi, X.; Li, C.; Ayana, D.A.; Niu, J.Q.; Feng, J.Y.; Wang, J.; Jiang, Y.F. IL-33 Enhances Humoral Immunity Against Chronic HBV Infection Through Activating CD4(+)CXCR5(+) TFH Cells. J. Interferon Cytokine Res. 2015, 35, 454–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ji, Y.; Dang, X.; Nguyen, L.N.T.; Nguyen, L.N.; Zhao, J.; Cao, D.; Khanal, S.; Schank, M.; Wu, X.Y.; Morrison, Z.D.; et al. Topological DNA damage, telomere attrition and T cell senescence during chronic viral infections. Immun. Ageing 2019, 16, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, L.N.T.; Nguyen, L.N.; Zhao, J.; Schank, M.; Dang, X.; Cao, D.; Khanal, S.; Wu, X.Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, J.; et al. TRF2 inhibition rather than telomerase disruption drives CD4T cell dysfunction during chronic viral infection. J. Cell Sci. 2022, 135, jcs259481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smits, M.; Zoldan, K.; Ishaque, N.; Gu, Z.; Jechow, K.; Wieland, D.; Conrad, C.; Eils, R.; Fauvelle, C.; Baumert, T.F.; et al. Follicular T helper cells shape the HCV-specific CD4+ T cell repertoire after virus elimination. J. Clin. Investig. 2020, 130, 998–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khanam, A.; Kottilil, S.; Wilson, E. Reconstitution of T follicular helper-humoral immune axis with elimination of hepatitis C virus. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 19924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiggins, B.G.; Pallett, L.J.; Li, X.; Davies, S.P.; Amin, O.E.; Gill, U.S.; Kucykowicz, S.; Patel, A.M.; Aliazis, K.; Liu, Y.S.; et al. The human liver microenvironment shapes the homing and function of CD4(+) T-cell populations. Gut 2022, 71, 1399–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Luo, H.; Wan, X.; Fu, X.; Mao, Q.; Xiang, X.; Zhou, Y.; He, W.; Zhang, J.; Guo, Y.; et al. TNF-alpha/IFN-gamma profile of HBV-specific CD4 T cells is associated with liver damage and viral clearance in chronic HBV infection. J. Hepatol. 2020, 72, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paquissi, F.C. Immunity and Fibrogenesis: The Role of Th17/IL-17 Axis in HBV and HCV-induced Chronic Hepatitis and Progression to Cirrhosis. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Losikoff, P.T.; Mishra, S.; Terry, F.; Gutierrez, A.; Ardito, M.T.; Fast, L.; Nevola, M.; Martin, W.D.; Bailey-Kellogg, C.; De Groot, A.S.; et al. HCV epitope, homologous to multiple human protein sequences, induces a regulatory T cell response in infected patients. J. Hepatol. 2015, 62, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ji, X.J.; Ma, C.J.; Wang, J.M.; Wu, X.Y.; Niki, T.; Hirashima, M.; Moorman, J.P.; Yao, Z.Q. HCV-infected hepatocytes drive CD4+ CD25+ Foxp3+ regulatory T-cell development through the Tim-3/Gal-9 pathway. Eur. J. Immunol. 2013, 43, 458–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tang, R.; Lei, Z.; Wang, X.; Qi, Q.; He, J.; Liu, D.; Wang, X.; Chen, X.; Zhu, J.; Li, Y.; et al. Hepatitis B envelope antigen increases Tregs by converting CD4+CD25(-) T cells into CD4(+)CD25(+)Foxp3(+) Tregs. Exp. Ther. Med. 2020, 20, 3679–3686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Rudra, D. Emerging Functions of Regulatory T Cells in Tissue Homeostasis. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gu, X.; Chu, Q.; Ma, X.; Wang, J.; Chen, C.; Guan, J.; Ren, Y.; Wu, S.; Zhu, H. New insights into iNKT cells and their roles in liver diseases. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 1035950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolte, F.J.; O’Keefe, A.C.; Webb, L.M.; Serti, E.; Rivera, E.; Liang, T.J.; Ghany, M.; Rehermann, B. Intra-Hepatic Depletion of Mucosal-Associated Invariant T Cells in Hepatitis C Virus-Induced Liver Inflammation. Gastroenterology 2017, 153, 1392–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Beudeker, B.J.B.; van Oord, G.W.; Arends, J.E.; Schulze Zur Wiesch, J.; van der Heide, M.S.; de Knegt, R.J.; Verbon, A.; Boonstra, A.; Claassen, M.A.A. Mucosal-associated invariant T-cell frequency and function in blood and liver of HCV mono- and HCV/HIV co-infected patients with advanced fibrosis. Liver Int. 2018, 38, 458–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hengst, J.; Strunz, B.; Deterding, K.; Ljunggren, H.G.; Leeansyah, E.; Manns, M.P.; Cornberg, M.; Sandberg, J.K.; Wedemeyer, H.; Bjorkstrom, N.K. Nonreversible MAIT cell-dysfunction in chronic hepatitis C virus infection despite successful interferon-free therapy. Eur. J. Immunol. 2016, 46, 2204–2210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- van Wilgenburg, B.; Scherwitzl, I.; Hutchinson, E.C.; Leng, T.; Kurioka, A.; Kulicke, C.; de Lara, C.; Cole, S.; Vasanawathana, S.; Limpitikul, W.; et al. MAIT cells are activated during human viral infections. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 11653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yong, Y.K.; Saeidi, A.; Tan, H.Y.; Rosmawati, M.; Enstrom, P.F.; Batran, R.A.; Vasuki, V.; Chattopadhyay, I.; Murugesan, A.; Vignesh, R.; et al. Hyper-Expression of PD-1 Is Associated with the Levels of Exhausted and Dysfunctional Phenotypes of Circulating CD161(++)TCR iValpha7.2(+) Mucosal-Associated Invariant T Cells in Chronic Hepatitis B Virus Infection. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huang, W.; He, W.; Shi, X.; Ye, Q.; He, X.; Dou, L.; Gao, Y. Mucosal-associated invariant T-cells are severely reduced and exhausted in humans with chronic HBV infection. J. Viral. Hepat. 2020, 27, 1096–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhu, P.; Wang, W.; Tan, X.; Liu, C.; Chen, Y.; Pei, R.; Cheng, X.; Wu, M.; Guo, Q.; et al. Mucosal-Associated Invariant T Cell Dysregulation Correlates With Conjugated Bilirubin Level in Chronic HBV Infection. Hepatology 2021, 73, 1671–1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, J.; Hengst, J.; Parrot, T.; Leeansyah, E.; Lunemann, S.; Malone, D.F.G.; Hardtke, S.; Strauss, O.; Zimmer, C.L.; Berglin, L.; et al. Chronic hepatitis delta virus infection leads to functional impairment and severe loss of MAIT cells. J. Hepatol. 2019, 71, 301–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boeijen, L.L.; Montanari, N.R.; de Groen, R.A.; van Oord, G.W.; van der Heide-Mulder, M.; de Knegt, R.J.; Boonstra, A. Mucosal-Associated Invariant T Cells Are More Activated in Chronic Hepatitis B, but Not Depleted in Blood: Reversal by Antiviral Therapy. J. Infect. Dis. 2017, 216, 969–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lopez-Scarim, J.; Nambiar, S.M.; Billerbeck, E. Studying T Cell Responses to Hepatotropic Viruses in the Liver Microenvironment. Vaccines 2023, 11, 681. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11030681
Lopez-Scarim J, Nambiar SM, Billerbeck E. Studying T Cell Responses to Hepatotropic Viruses in the Liver Microenvironment. Vaccines. 2023; 11(3):681. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11030681
Chicago/Turabian StyleLopez-Scarim, Jarrett, Shashank Manohar Nambiar, and Eva Billerbeck. 2023. "Studying T Cell Responses to Hepatotropic Viruses in the Liver Microenvironment" Vaccines 11, no. 3: 681. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11030681
APA StyleLopez-Scarim, J., Nambiar, S. M., & Billerbeck, E. (2023). Studying T Cell Responses to Hepatotropic Viruses in the Liver Microenvironment. Vaccines, 11(3), 681. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11030681




