Japanese Encephalitis Virus: An Update on the Potential Antivirals and Vaccines
Abstract
:1. Introduction
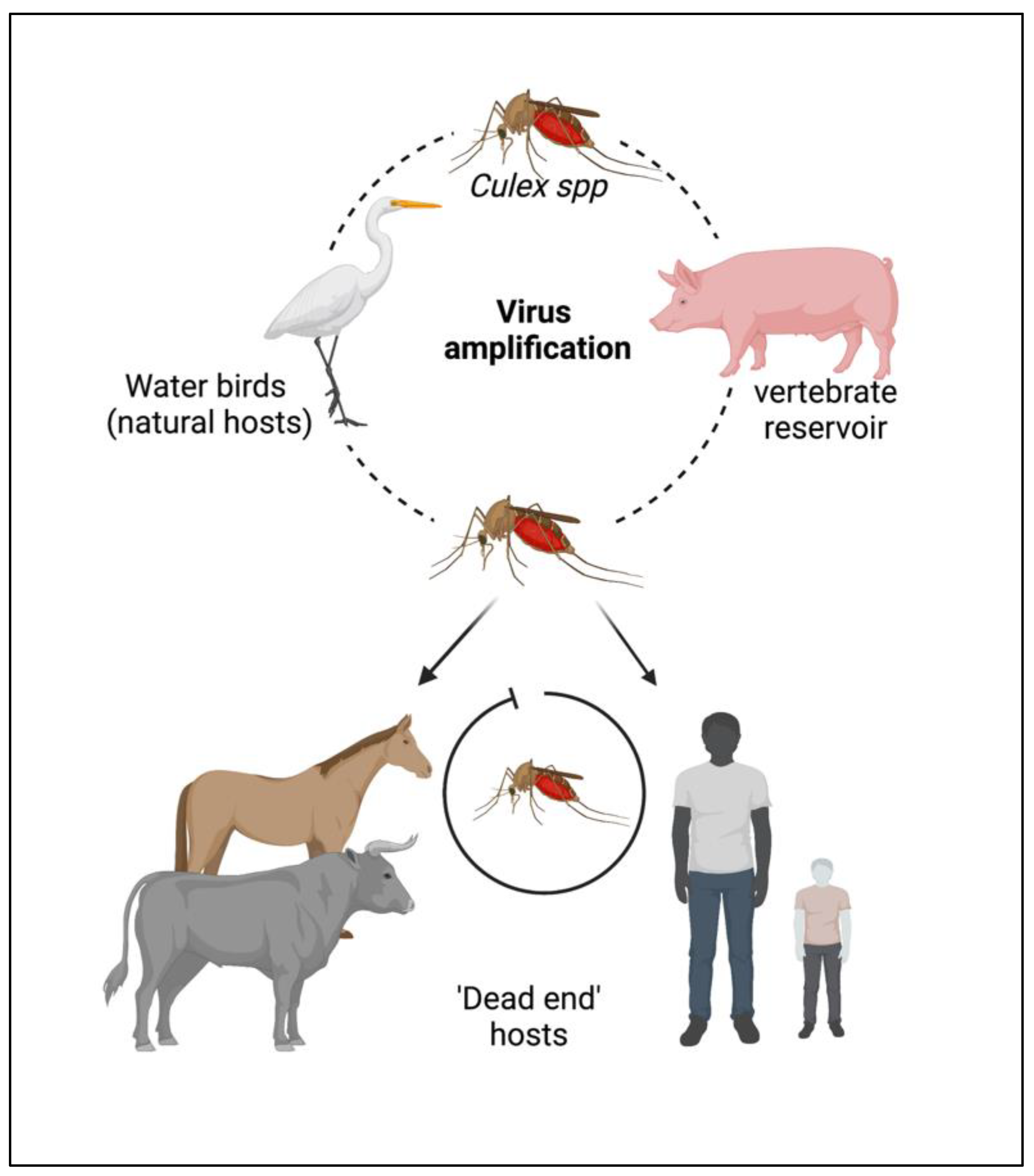
2. Epidemiology
3. JEV Structure and Its Genome
4. JEV Genetic Diversity
5. JEV Pathogenesis
6. Clinical Manifestations
7. Potential Drug Targets
8. Potential Antivirals against JEV
8.1. Broad Spectrum (Non-Specific) Antiviral Molecules Used against JEV
8.2. Nucleic Acid Based Anti-JEV Molecules
8.3. Replication Cycle-Based Anti-JEV Molecules
| Type of Drug/Drug Target | Compound/Drug Name | Mechanism of Action | In Vitro Activity: IC50 or EC50 (Utilised Cell Line) | In Vivo Efficacy: % Survival (Explored Animal Model) | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Broad use | Arctigenin | Anti-oxidative/anti-inflammatory effect | 3.9µM (U937 Cells) | 100% (BALB/c) | [92,93] |
| (anti-inflammatory) | Fenofibrate | ND * | 80% (BALB/c) | [94] | |
| Rosmarinic acid | ND | 80% (BALB/c) | [64] | ||
| Diethyldithiocarbamate (DDTC) | ND | 100% (swiss albino) | [95] | ||
| Astragali radix extracts | ND * | >80% (ICR) | [96] | ||
| Lacidipine | 3.5 µM (Vero cells) | ND | [28] | ||
| Tilapia hepcidin 1–5 | 1 µg/mL (BHK-21 cells) | DM # (C3H/H3N) | [97] | ||
| Curcumin | ND * | DM # (BALB/c) | [30] | ||
| Immune system based | Aloe-emodin | Triggers adaptive immune responses to generate an antiviral state | 0.50 µg/mL–1.51 µg/mL (BHK 21 cells) | ND | [71] |
| Interferons | ND * (LLC-MK2 cells) | ND^ | [98] | ||
| Enanderinanin J | Inhibits autophagosome-lysosome fusion | 16.3 µM (A549 cells) | ND | [97] | |
| Atorvastatin | Reduces secretion of pro-inflammatory cytokines by the neurons and causes neuronal death by evading the miR-21 upregulation, which is induced by the virus in a hn-RNPC-dependent fashion | ND * | ND | [99] | |
| Pimecrolimus | Blocks T-cell activation | 3.1 µM (Vero cells) | ND | [28] | |
| Bafilomycin A1 | Inhibits pH-triggered membrane fusion of the endocytosed JEV and vacuolar type proton pump | ND * | ND | [86] | |
| Artemisinin | Enhances the host type I interferon response | 18.5 µM (A549 cells) | ~50% (C57BL6J) | [100] | |
| Cell signaling based | Aspirin, indomethacin, sodium salicylase | Inhibits cyclooxygenase, modulates the intracellular MAP kinase pathway followed by JEV infection | ND * | ND | [65] |
| Dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA) | Upregulates MAPK pathways; induces ERK activation | ND * | ND | [101] | |
| AR-12 | Inhibits PI3/AKT pathway and GRP78; inhibits mitochondrial enzyme DHODH (dihydroorotate dehydrogenase) | ~509.9 nM (A549 cells) | ND | [102,103] | |
| P12-23 (Derivative of AR-12) | ~53.2 nM (A549 cells) | ND | |||
| P12-34 (Derivative of AR-12) | ~56.1 nM (A549 cells) | ND | |||
| Anisomycin | Restores function of ERK (extracellular signal-regulated kinase); suppresses JEV induced cytotoxicity | ND * | ND | [65,101] | |
| Host factors targeting | Eflorinithine | Inhibits polyamine biosynthesis | ND * | ND | [104] |
| Tubacin | Inhibits histone deacetylases | 1.52 µM (TE671 cells) | ND | [105] | |
| Mitotane | Deregulates cytochrome P450 enzymes | 6.6 µM (Vero cells) | ND | [28] | |
| Digoxin and ouabain | Targets the Na+/K+-ATPase | <0.1031 µM (Vero cells) | ~60% (BALB/c) | [106] | |
| Benidipine hydrochloride | Inhibits the triple calcium channel (L, N, T type calcium channels) | 3.7 µM (Vero cells) | ND | [28] | |
| Berbamine | Blocks TRPMLs to compromise endosomal trafficking of LDLR, decreases its level of plasma membrane, thus blocking JEV entry | 1.62 µM (A549 cells) | ~75% (BALB/c) | [107] | |
| BCX4430(galidesivir) | Inhibits replication | 43.6 µM (Hela cells) | ND | [108] | |
| Apotozole | Inhibits HSP70 | ND * | ND | [76] | |
| Nucleic acid analogues | miRNA | Binds and inhibits genes coding for proteins such as, the E protein Domain II, NS5, capsid (C), membrane (M) protein, envelope(E), prM, NS1, NS2A, NS2B, NS3, NS4A and NS4B | ND * | DM # (BALB/c) | [79,109,110] |
| shRNA | Binds and inhibits genes of E, C and NS4B proteins | ND * | 50–70% (BALB/c) | [79] | |
| PNA (J3U5) | Targets the 5′ untranslated region of JEV genome | ND * | ND | [80] | |
| Morpholino oligomers (PPMO-P10882) | ND * | 60–70% (BALB/c) | [81] | ||
| DNAzymes | 3′ Non-coding sequence of JEV genome | ND * | 100% (BALB/c) | [111] | |
| Viral entry and attachment Inhibitors | Bovine lactoferrin | Binds to heparin sulfate receptors; prevents attachment | 26.1 µg/mL; 518.3 µg/mL (BHK21 cells) $ | ND | [112] |
| Griffithsin | Binds to the E protein; prevents attachment | 265 ng/mL (BHK21 cells) | ND | [89] | |
| Curcumin carbon quantum dots | Binds to the E protein, prevents viral entry into the host cells | 0.9 µg/mL; 100 µg/mL (BHK21 cells) $ | ND | [113] | |
| Carrageenan (sulfated polysaccharide) | Inhibits entry into host cells | 15 µg/mL (WRL68 cells) | ND | [114] | |
| E-protein domain III binding peptide | Inhibits the E-protein and receptor interaction | 1 µM (BHK21 cells) | ND | [115] | |
| Monoclonal antibodies (2F2; 2H4) | Blocks the virus-receptor attachment | ~1.4 ng/mL (Vero cells) | 100% (BALB/c mice) | [116] | |
| Indirubin | Inhibits the viral attachment | 11.79 µg/mL >50 µg/mL (BHK21 cells) $ | >50% (BALB/c mice) | [117] | |
| Indigo | |||||
| Heparin | 10µg/mL (BHK21 cells) | ND | [85] | ||
| Quercetin | Virucidal activity; inhibits adsorption of the virus | ~212.1 µg/mL; ~5.8 µg/mL (Vero cells) $ | ND | [118] | |
| Biacalein | |||||
| PI 88 | Creates steric hindrance to the JEV attachment; immunomodulatory action | 40 µg/mL (BHK21 cells) | ~40% (C57B1/6) | [85] | |
| Methyl-β-cyclodextrin | Inhibits viral replication and entry in the host due to the depletion of cholesterol | ND * | ND | [119] | |
| Filipin III | |||||
| Viral protein inhibitors | Furanonapthoquinone | Inhibits viral RNA and protein synthesis/expression | ND * | ND | [120] |
| Amphoterecin B | Inhibits the viral replication and protein synthesis/expression | 7.8 µg/mL (BHK21 cells) | ND | [121] | |
| Suramin | Blocks production of the viral E and NS3 proteins | 50 µg/mL (BHK21 cells) | ND | [85] | |
| Niclosamide | Inhibitsthe NS2B-NS3 protease; endosomal acidification | 5.80 µM (BHK21 cells) | ND | [122] | |
| SK-12 protein | NS2B-NS3 inhibitors | ~29.81 µM (Vero cells) | ND | [123] | |
| ARDP0006 | |||||
| Temoporfin | 0.011 µM (HDF9 and hNPCs cells) | ND | [59,124] | ||
| NSC 12155 | NS5 inhibitor | 1.4 µM (BHK21 cells) | ND | [125] | |
| N-methylisatin-beta-thiosemicarbazone derivative (SCH 16) | Inhibits early translation | 16 µg/mL (PS cells) | 100% (Swiss albino) | [126] | |
| Scopolamine hydrobromide | Binds to the active site of NS5, thus inhibiting the JEV replication | ND * | ND | [127] | |
| N-nonyl-deoxynojirimycin (NN-DNJ) | Inhibits α-glucosidase enzymes causing misfolding of viral proteins | ND * | ~54% (ICR mice) | [60] | |
| Belladonna | Reduces the NS3 protein caspase 3 and 8 enzymatic activity and its expression | 7.01 µg/mL (CHME3 and SHSY-5Y cells) | ND | [128] | |
| Pentoxyfylline | Interferes with the assembly and release of virions | 50.3 µg/mL (PS cells) | 100% (Swiss albino) | [74,129] | |
| Manidipine | Inhibits NS3 Helicase, targets NS4B and calcium channel | 1.6 µM (Vero cells) | 80% (BALB/c) | [28] | |
| Nitazoxanide | Activates elF2α; targets the JEV replication at the early mid stage | 0.12 µg/mL (BHK21 cells) | ~70–90% (Chinese chumming mice) | [130,131] | |
| Luteolin | Inhibits synthesis of the E protein | 4.56 µg/mL (A549 cells) | ND | [132] | |
| Erythrosine B | Inhibits flaviviral NS2B-NS3 protease | 0.35 µM (A549 cells) | ND | [133] | |
| Ivermectin | Inhibits the NS3 helicase | 0.3 µM (Vero cells) | ND | [134] | |
| Andrographolide | Inhibits the NS3 protease | IC50 = 2 µg/mL (Enzymatic assay) | [135] | ||
| Mycophenlate, P5 | Inhibits the E protein | 3.1 µg/mL (PS cells) | ~75% (Swiss albino) | [136,137] | |
| Monoclonal antibodies (1H7, 2D4, 3C4, 3H7, 3F10) | NS3 and NS5 inhibitors | ND * | ND | [138] | |
| NITD008 | NS5 polymerase inhibitor | 3.09 µM (BHK-21 cells) | ND | [139] | |
| Viral replication inhibitors | Lonafarnib | Inhibits viral replication | 0.982 µM (Huh-7 cells) | ND | [139] |
| Nitroxoline | 2.482 µM (Huh-7 cells) | ND | |||
| Cetylpyridinium chloride | 0.35 µM (A549 cells) | ND | |||
| Cetrimonium bromide | 2.232 µM (Huh-7 cells) | ND | |||
| Hexachlorophene | 0.421 µM (Huh-7 cells) | ND | |||
| Cilindipine | 3.5 µM (Vero cells) | ND | [28] | ||
| FGIN-1-27 | 3.21 µM (BHK21 cells) | ND | [140] | ||
| Ribavirin | Inhibits synthesis of gunanine nucleotides | 3.9 µg/mL (PS cells) | ND | [72] | |
| 2-Deoxy-D-glucose and 3-deazauridine | Interferes in the synthesis of RNA, DNA and glycoprotein of JEV | ND * | ND | [141] | |
| MCPIP1 (Monocyte chemoattractant protein 1-induced protein 1) | Targets various RNA sites and inhibits replication | ND * | ND | [87] | |
| Pokeweed protein (Phytolacca americana) | Depurinates viral RNAs | 300 ng/mL (BHK-21 cells) | ~85% (BALB/c) | [89] | |
| Diadzin | Binds to the frameshift site in RNA; inactivates the virus | 25.9 µM; 40.4 µM (BHK21 cells) $ | ND | [90] | |
| Kaempferol | |||||
| Virus assembly and maturation inhibitors | 10,10′-bis (trifluoromethyl) marinopyrrole A thiophene | Inhibits the proliferation of JEV | 0.05µM (BHK21 and RD cells) | ND | [142] |
| Nelfinavir | Protease inhibitor | 1.6 µM (Vero cells) | ND | [28] | |
| Palmatine | Protease inhibitor | ND * | ND | [143] |
9. JEV Vaccine
9.1. JE-MB
9.2. JE-VC
9.3. JE-CV
9.4. JE-LV
9.5. JENVAC
10. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Burke, D.S.; Leake, C.J. Japanese encephalitis. In The Arboviruses: Epidemiology and Ecology; Monath, T.P., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1988; Volume 3, pp. 63–92. [Google Scholar]
- Simmonds, P.; Becher, P.; Bukh, J.; Gould, E.A.; Meyers, G.; Monath, T.; Muerhoff, S.; Pletnev, A.; Rico-Hesse, R.; Smith, D.B.; et al. ICTV Virus Taxonomy Profile: Flaviviridae. J. Gen. Virol. 2017, 98, 2–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackenzie, J.S.; Williams, D.T.; Hurk, A.F.V.D.; Smith, D.W.; Currie, B.J. Japanese Encephalitis Virus: The Emergence of Genotype IV in Australia and Its Potential Endemicity. Viruses 2022, 14, 2480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Billoir, F.; de Chesse, R.; Tolou, H.; de Micco, P.; Gould, E.A.; de Lamballerie, X. Phylogeny of the genus Flavivirus using complete coding sequences of arthropod-borne viruses and viruses with no known vector. J. Gen. Virol. 2000, 81, 781–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, T.M.; Thao, T.T.N.; Duy, N.M.; Nhat, T.M.; Clapham, H. Estimates of the global burden of Japanese encephalitis and the impact of vaccination from 2000–2015. Elife 2020, 9, e51027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campbell, G.L.; Hills, S.L.; Fischer, M.; Jacobson, J.A.; Hoke, C.H.; Hombach, J.M.; Marfin, A.A.; Solomon, T.; Tsai, T.F.; Tsu, V.D.; et al. Estimated global incidence of Japanese encephalitis: A systematic review. Bull. World Health Organ. 2011, 89, 766–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pearce, J.C.; Learoyd, T.P.; Langendorf, B.J.; Logan, J.G. Japanese encephalitis: The vectors, ecology and potential for expansion. J. Travel Med. 2018, 25, S16–S26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ricklin, M.E.; García-Nicolás, O.; Brechbühl, D.; Python, S.; Zumkehr, B.; Nougairede, A.; Charrel, R.N.; Posthaus, H.; Oevermann, A.; Summerfield, A. Vector-free transmission and persistence of Japanese encephalitis virus in pigs. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 10832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chiou, S.-S.; Chen, J.-M.; Chen, Y.-Y.; Chia, M.-Y.; Fan, Y.-C. The feasibility of field collected pig oronasal secretions as specimens for the virologic surveillance of Japanese encephalitis virus. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2021, 15, e0009977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, S.; Singh, R.K.; Tiwari, R.; Dhole, T.N. Japanese encephalitis: A review of the Indian perspective. Braz. J. Infect. Dis. 2012, 16, 564–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kulkarni, R.; Sapkal, G.N.; Kaushal, H.; Mourya, D.T. Japanese Encephalitis: A Brief Review on Indian Perspectives. Open Virol. J. 2018, 12, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Prakash, P.J.; Kusum, V.; Vijeta, S. Japanese Encephalitis (JE): A curse for people living in Uttar Pradesh, India. J. Vaccines Immunol. 2021, 7, 036–040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomon, T. Control of Japanese encephalitis—Within our grasp? N. Engl. J. Med. 2006, 355, 869–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, M.G.; Pattanaik, A.; Vyas, N.; Saxena, D.; Webb, C.; Sawleshwarkar, S.; Mukhopadhyay, C. High-risk landscapes of Japanese encephalitis virus outbreaks in India converge on wetlands, rain-fed agriculture, wild Ardeidae, and domestic pigs and chickens. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2022, 51, 1408–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, L.S.; Singh, H.L.; Thokchom, N.; Singh, R.M. A Descriptive Study on Prevalence Pattern of Japanese Encephalitis in State of Manipur. Indian J. Med. Microbiol. 2019, 37, 235–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Australian Government Department of Health and Aged Care. Japanese Encephalitis Virus (JEV). Available online: https://www.health.gov.au/health-alerts/japanese-encephalitis-virus-jev/about#current-status (accessed on 25 January 2023).
- Hurk, A.F.V.D.; Pyke, A.T.; Mackenzie, J.S.; Hall-Mendelin, S.; Ritchie, S.A. Japanese Encephalitis Virus in Australia: From Known Known to Known Unknown. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2019, 4, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hurk, A.F.V.D.; Skinner, E.; Ritchie, S.A.; Mackenzie, J.S. The Emergence of Japanese Encephalitis Virus in Australia in 2022: Existing Knowledge of Mosquito Vectors. Viruses 2022, 14, 1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waller, C.; Tiemensma, M.; Currie, B.J.; Williams, D.T.; Baird, R.W.; Krause, V.L. Japanese Encephalitis in Australia—A Sentinel Case. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 387, 661–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poonsiri, T.; Wright, G.S.A.; Solomon, T.; Antonyuk, S.V. Crystal structureof the Japanese Encephalitis virus capsid protein. Viruses 2019, 11, 623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luca, V.C.; AbiMansour, J.; Nelson, C.A.; Fremont, D.H. Crystal Structure of the Japanese Encephalitis Virus Envelope Protein. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 2337–2346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Muller, D.A.; Young, P.R. The flavivirus NS1 protein: Molecular and structural biology, immunology, role in pathogenesis and application as a diagnostic biomarker. Antivir. Res. 2013, 98, 192–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, X.; Cao, S.; Zhou, R.; Xu, G.; Xiao, S.; Yang, Y.; Sun, M.; Li, Y.; Chen, H. Inhibition of Japanese Encephalitis Virus NS1 Protein Expression in Cell by Small Interfering RNAs. Virus Genes 2006, 33, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yen, L.-C.; Liao, J.-T.; Lee, H.-J.; Chou, W.-Y.; Chen, C.-W.; Lin, Y.-L.; Liao, C.-L. The C Terminus of the Core β-Ladder Domain in Japanese Encephalitis Virus Nonstructural Protein 1 Is Flexible for Accommodation of Heterologous Epitope Fusion. J. Virol. 2016, 90, 1178–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, E.; Nam, J.; Park, Y.; Jo, H. Analysis of the NS4 Region of Japanese Encephalitis virus K94P05 Isolated from Korea. J. Bacteriol. Virol. 1997, 27, 197–207. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, G.; Gong, P. Crystal Structure of the Full-Length Japanese Encephalitis Virus NS5 Reveals a Conserved Methyltransferase-Polymerase Interface. PLoS Pathog. 2013, 9, e1003549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Knipe, D.; Howley, P. Fields Virology, 6th ed.; Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Liu, Y.; Guo, J.; Wang, P.; Zhang, L.; Xiao, G.; Wang, W. Screening of FDA-Approved Drugs for Inhibitors of Japanese Encephalitis Virus Infection. J. Virol. 2017, 91, e01055-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vannice, K.S.; Hills, S.L.; Schwartz, L.M.; Barrett, A.D.; Heffelfinger, J.; Hombach, J.; Letson, G.W.; Solomon, T.; Marfin, A.A.; Anderson, K.; et al. The future of Japanese encephalitis vaccination: Expert recommendations for achieving and maintaining optimal JE control. Npj Vaccines 2021, 6, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishikawa, T.; Konishi, E. Potential chemotherapeutic targets for Japanese encephalitis: Current status of antiviral drug development and future challenges. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2015, 19, 1379–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, X.; Liu, H.; Li, M.; Fu, S.; Liang, G. Insights into the evolutionary history of Japanese encephalitis virus (JEV) based on whole-genome sequences comprising the five genotypes. Virol. J. 2015, 12, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Solomon, T.; Ni, H.; Beasley, D.W.C.; Ekkelenkamp, M.; Cardosa, M.J.; Barrett, A.D.T. Origin and Evolution of Japanese Encephalitis Virus in Southeast Asia. J. Virol. 2003, 77, 3091–3098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Romoser, W.S.; Turell, M.J.; Lerdthusnee, K.; Neira, M.; Dohm, D.; Ludwig, G.; Wasieloski, L. Pathogenesis of Rift Valley fever virus in mosquitoes—tracheal conduits & the basal lamina as an extra-cellular barrier. Arch. Virol. Suppl. 2005, 19, 89–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eynde, C.V.D.; Sohier, C.; Matthijs, S.; De Regge, N. Japanese Encephalitis Virus Interaction with Mosquitoes: A Review of Vector Competence, Vector Capacity and Mosquito Immunity. Pathogens 2022, 11, 317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unni, S.K.; Růžek, D.; Chhatbar, C.; Mishra, R.; Johri, M.K.; Singh, S.K. Japanese encephalitis virus: From genome to infectome. Microbes Infect. 2011, 13, 312–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, K.B.; Vrati, S.; Kalia, M. Pathobiology of Japanese encephalitis virus infection. Mol. Asp. Med. 2021, 81, 100994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chauhan, S.; Rathore, D.K.; Sachan, S.; Lacroix-Desmazes, S.; Gupta, N.; Awasthi, A.; Vrati, S.; Kalia, M. Japanese Encephalitis Virus Infected Human Monocyte-Derived Dendritic Cells Activate a Transcriptional Network Leading to an Antiviral Inflammatory Response. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 638694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, K.; Rangarajan, P.N.; Vrati, S.; Basu, A. Japanese encephalitis: Patho-genesis, prophylactics and therapeutics. Curr. Sci. 2010, 98, 326–334. [Google Scholar]
- Banerjee, A.; Tripathi, A. Recent Advancement in understanding Japanese encephalitis. F1000 Res. 2019, 8, 19693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kumar, A.; Sharma, P.; Shukla, K.K.; Misra, S.; Nyati, K.K. Japanese encephalitis virus: Associated immune response and recent progress in vaccine development. Microb. Pathog. 2019, 136, 103678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, R.-J.; Liao, C.-L.; Lin, E.; Lin, Y.-L. Blocking of the Alpha Interferon-Induced Jak-Stat Signaling Pathway by Japanese Encephalitis Virus Infection. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 9285–9294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mukherjee, S.; Sengupta, N.; Chaudhuri, A.; Akbar, I.; Singh, N.; Chakraborty, S.; Suryawanshi, A.R.; Bhattacharyya, A.; Basu, A. PLVAP and GKN3 Are Two Critical Host Cell Receptors Which Facilitate Japanese Encephalitis Virus Entry Into Neurons. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 11784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ghosh, D.; Basu, A. Japanese Encephalitis—A Pathological and Clinical Perspective. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2009, 3, e437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Winter, P.M.; Dung, N.M.; Loan, H.T.; Kneen, R.; Wills, B.; Thu, L.T.; House, D.; White, N.J.; Farrar, J.J.; Hart, C.A.; et al. Proinflammatory cytokines and chemokines in Humans with Japanese Encephalitis. J. Infect. Dis. 2004, 190, 1618–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Singh, S.K. Molecular pathogenesis of Japanese Encephalitis Virus Infection. In Human Emerging and Re-Emerging Infections: Viral and Parasitic Infections, 1st ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2016; Volume I, p. 117. [Google Scholar]
- Nain, M.; Abdin, M.Z.; Kalia, M.; Vrati, S. Japanese encephalitis virus invasion of cell: Allies andalleys. Rev. Med. Virol. 2015, 26, 129–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, R.; Sharma, K.B.; Kumari, A.; Asthana, S.; Kalia, M. Japanese encephalitis virus capside protein interacts with non-lipidated MAP1LC3 on replication membranes and lipid droplets. J. Gen. Virol. 2021, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, M.; Bhattacharyya, S.; Nain, M.; Kaur, M.; Sood, V.; Gupta, V.; Khasa, R.; Abdin, M.Z.; Vrati, S.; Kalia, M. Japanese encephalitis virus replication is negatively regulated by autophagy and occurs on LC3-I- and EDEM1-containing membranes. Autophagy 2014, 10, 1637–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- World Health Organisation. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/japanese-encephalitis (accessed on 26 December 2022).
- Badia, R.; Garcia-Vidal, E.; Ballana, E. Viral-Host Dependency Factors as Therapeutic Targets to Overcome Antiviral Drug-Resistance: A Focus on Innate Immune Modulation. Front. Virol. 2022, 2, 935933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackenzie, J.S.; Barrett, A.D.T.; Deubel, V. Japanese Encephalitis and West Nile Viruses; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Kesson, A.M.; Blanden, R.V.; Mullbacher, A. The Primary in vivo Murine Cytotoxic T Cell Response to the Flavivirus, West Nile. J. Gen. Virol. 1987, 68, 2001–2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiermayr, S.; Kofler, R.M.; Mandl, C.W.; Messner, P.; Heinz, F.X. Isolation of capsid protein dimers from the tick-borne en-cephalitis flavivirusand in vitro assembly of capsid-like particles. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 8078–8084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, S.H.; Syu, W.J.; Huang, K.J.; Lei, H.Y.; Yao, C.W.; King, C.C.; Hu, S.T. Intracellular localization and determination of a nuclear lo-calization signal of the core protein of dengue virus. J. Gen. Virol. 2002, 83, 3093–3102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakaria, M.K.; Carletti, T.; Marcello, A. Cellular Targets for the Treatment of Flavivirus Infections. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2018, 8, 398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sampath, A.; Padmanabhan, R. Molecular targets for flavivirusdrug discovery. Antivir. Res. 2009, 81, 6–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Perera, R.; Khaliq, M.; Kuhn, R.J. Closing the door on flaviviruses: Entry as a target for antiviral drug design. Antivir. Res. 2008, 80, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lescar, J.; Luo, D.; Xu, T.; Sampath, A.; Lim, S.P.; Canard, B.; Vasudevan, S.G. Towards the design of antiviral inhibitors against flaviviruses: The case for the multifunctional NS3 protein from Dengue virus as a target. Antivir. Res. 2008, 80, 94–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, D.; Vasudevan, S.G.; Lescar, J. The flavivirus NS2B–NS3 protease–helicase as a target for antiviral drug development. Antivir. Res. 2015, 118, 148–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.-F.; Lee, C.-J.; Liao, C.-L.; Dwek, R.A.; Zitzmann, N.; Lin, Y.-L. Antiviral effects of animino sugar derivative on flavivirus infections. J. Virol. 2002, 76, 3596–3604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gorbalenya, A.E.; Donchenko, A.P.; Koonin, E.V.; Blinov, V.M. N-terminal domains of putative helicases of flavi- and pestiviruses may be serine proteases. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989, 17, 3889–3897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dong, H.; Zhang, B.; Shi, P.-Y. Flavivirusmethyltransferase: A novel antiviral target. Antivir. Res. 2008, 80, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Murakami, M.; Ota, T.; Nukuzuma, S.; Takegami, T. Inhibitory effect of RNAi on Japanese encephalitis virus replication in vitro and in vivo. Microbiol. Immunol. 2005, 49, 1047–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swarup, V.; Ghosh, J.; Ghosh, S.; Saxena, A.; Basu, A. Antiviral and anti-inflammatory effects of rosmarinic acid in an experimental murine model of Japanese encephalitis. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2007, 51, 3367–3370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, C.-J.; Raung, S.-L.; Kuo, M.-D.; Wang, Y.-M. Suppression of Japanese encephalitis virus infection by non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. J. Gen. Virol. 2002, 83, 1897–1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dutta, K.; Ghosh, D.; Basu, A. Curcumin protects neuronal cells from japanese encephalitis vi-rus-mediated cell death and also inhibits infective viral particle formation by dysregulation of ubiq-uitin-proteasome system. J. Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2009, 4, 328–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michaelis, M.; Kleinschmidt, M.C.; Doerr, H.W.; Cinatl, J. Minocycline inhibits West Nile virus replication and apoptosis in human neuronal cells. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2007, 60, 981–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mishra, M.K.; Ghosh, D.; Duseja, R.; Basu, A. Antioxidant potential of Minocycline in Japanese Encephalitis Virus infection in murine neuroblastoma cells: Correlation with membrane fluidity and cell death. Neurochem. Int. 2009, 54, 464–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, M.K.; Dutta, K.; Saheb, S.K.; Basu, A. Understanding the molecular mechanism of blood–brain barrier damage in anexperimental model of Japanese encephalitis: Correlation with minocycline administra-tion as a therapeutic agent. Neurochem. Int. 2009, 55, 717–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, W.M.; Chevillotte, M.D.; Rice, C.M. Interferon-stimulated genes: A complex web of host de-fenses. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2014, 32, 513–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lin, C.-W.; Wu, C.-F.; Hsiao, N.-W.; Chang, C.-Y.; Li, S.-W.; Wan, L.; Lin, Y.-J.; Lin, W.-Y. Aloe-emodin is an interferon-inducing agent with antiviral ac-tivity against Japanese encephalitis virus and enterovirus 71. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2008, 32, 355–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, R.; Tripathi, P.; Baranwal, M.; Singh, S.; Tripathi, S.N.; Banerjee, G. Randomized, controlledtrial of oral ribavirin for Japanese encephalitis in children in Uttar Pradesh. India Clin. Infect. Dis. 2009, 48, 400–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sebastian, L.; Desai, A.; Yogeeswari, P.; Sriram, D.; Madhusudana, S.; Ravi, V. Combination of N-methylisatin-β-thiosemicarbazone de-rivative (SCH16) with ribavirin and mycophenolic acid potentiates the antiviral activity of SCH16 against Japanese encephalitis virus in vitro. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2012, 55, 234–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sebastian, L.; Desai, A.; Madhusudana, S.N.; Ravi, V. Pentoxifyllineinhibits replication of Japanese enceph-alitis virus: A comparative study with ribavirin. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents. 2009, 33, 168–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takhampunya, R.; Ubol, S.; Houng, H.-S.; Cameron, C.E.; Padmanabhan, R. Inhibition of dengue virus replication by mycophenolic acid and ribavirin. J. Gen. Virol. 2006, 87, 1947–1952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Xu, Y.; Yan, Y.; Li, W.; Zhao, L.; Dai, Q.; Li, Y.; Li, S.; Zhong, J.; Cao, R.; et al. Small molecule inhibitor of ATPase activity of HSP70 as a broad-spectrum inhibitor against flavivirusinfections. ACS Infect Dis. 2020, 6, 832–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anantpadma, M.; Vrati, S. siRNA-mediated suppression of Japanese encephalitis virus replication in cultured cells and mice. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2012, 67, 444–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shen, T.; Liu, K.; Miao, D.; Cao, R.; Zhou, B.; Chen, P. Lentivirus-mediated RNA interference against Japanese encephalitis virus infection in vitro and in vivo. Antivir. Res. 2014, 108, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, T.; Liu, K.; Miao, D.; Cao, R.; Chen, P. Effective inhibition of Japanese encephalitis virus replication byshRNAs targeting various viral genes in vitro and in vivo. Virology 2014, 454–455, 48–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yoo, J.-S.; Kim, C.-M.; Kim, J.-H.; Kim, J.-Y.; Oh, J.-W. Inhibition of Japanese encephalitis virus replication by peptide nucleic acids targetingcis-acting elements on the plus- and minus-strands of viral RNA. Antivir. Res. 2009, 82, 122–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anantpadma, M.; Stein, D.A.; Vrati, S. Inhibition of Japanese encephalitis virus replication in cultured cells and mice by a peptide-conjugated morpholino oligomer. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2010, 65, 953–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lundin, K.E.; Good, L.; Strömberg, R.; Gräslund, A.; Smith, C.I.E. Biological Activity and Biotechnological Aspects of Peptide Nucleic Acid. Adv. Genet. 2006, 56, 1–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Yamada, S.; Hama, Y.; Shetty, A.K.; Kobayashi, T.; Oda, H.; Seiki, K.; Kim, E.; Kimura, T.; Takahashi, N.; et al. Unique heparansulfate from shrimp heads exhibits a strong inhibi-tory effect on infections by dengue virus and Japanese encephalitis virus. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2011, 412, 136–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, E.; Okumura, M.; Sawa, H.; Miyazaki, T.; Fujikura, D.; Yamada, S.; Sugahara, K.; Sasaki, M.; Kimura, T. Paradoxical effects of chondroitin Sulfate-E on Japanese enceph-alitis viral infection. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2011, 409, 717–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, E.; Pavy, M.; Young, N.; Freeman, C.; Lobigs, M. Antiviral effect of the heparin sulfate mimetic, PI-88, against dengue and encephalitic flaviviruses. Antivir. Res. 2006, 69, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, K.; Nazmi, A.; Basu, A. Chemotherapy in Japanese encephalitis: Are we there yet? Infect. Disord. Drug. Targets. 2011, 11, 300–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, R.-J.; Chien, H.-L.; Lin, S.-Y.; Chang, B.-L.; Yu, H.-P.; Tang, W.-C.; Lin, Y.-L. MCPIP1 ribonuclease exhibits broad-spectrum antiviral effects through viral RNA binding and degradation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, 3314–3326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Falgout, B.; Markoff, L. Evidence that flavivirus NS1-NS2A cleavage is mediated by a membrane-bound host protease in the endoplasmic reticulum. J. Virol. 1995, 69, 7232–7243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ishag, H.Z.; Li, C.; Huang, L.; Sun, M.-X.; Ni, B.; Guo, C.-X.; Mao, X. Inhibition of Japanese encephalitis virus infection in vitro and in vivo by pokeweed antiviral protein. Virus Res. 2013, 171, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.; Wu, Z.; Du, J.; Hu, Y.; Liu, L.; Yang, F.; Jin, Q. Anti- Japanese-Encephalitis-Viral Effects of Kaempferol and Daidzin and Their RNA-Binding Characteristics. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e30259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lv, B.-M.; Tong, X.-Y.; Quan, Y.; Liu, M.-Y.; Zhang, Q.-Y.; Song, Y.-F.; Zhang, H.-Y. Drug Repurposing for Japanese Encephalitis Virus Infection by Systems Biology Methods. Molecules 2018, 23, 3346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Swarup, V.; Ghosh, J.; Mishra, M.K.; Basu, A. Novel strategy for treatment of Japanese encephalitis using arctigenin, a plant lignan. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2008, 61, 679–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cho, J.Y.; Kim, A.R.; Yoo, E.S.; Baik, K.U.; Park, M.H. Immunomodulatory effect of arctigenin, a lignan compound, on tu-mour necrosis factor-α and nitric oxide production, and lymphocyte proliferation. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2010, 51, 1267–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sehgal, N.; Kumawat, K.L.; Basu, A.; Ravindranath, V. Fenofibrate reduces mortality and precludes neurological def-icits in survivors in murine model of Japanese encephalitis viral infection. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, 5427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saxena, S.K.; Mathur, A.; Srivastava, R.C. Inhibition of Japanese encephalitis virus infection bydiethyl-dithiocarbamate is independent of its antioxidant potential. Antivir. Chem. Chemother. 2003, 14, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kajimura, K.; Takagi, Y.; Ueba, N.; Yamasaki, K.; Sakagami, Y.; Yokoyama, H.; Yoneda, K. Protective effect of Astragali Radix by intraperitoneal injection against Japanese en-cephalitis virus infection in mice. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 1996, 19, 855–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, H.-N.; Rajanbabu, V.; Pan, C.-Y.; Chan, Y.-L.; Hui, C.-F.; Chen, J.-Y.; Wu, C.-J. Modulation of the immune-related gene responses to protect mice against Japanese encephalitis virus using the antimicrobial peptide, tilapia hepcidin 1–5. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 6804–6814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harinasuta, C.; Wasi, C.; Vithanomsat, S. The effect of interferon on Japanese encephalitis virus in vitro. Southeast Asian J. Trop. Med. Public Health 1984, 15, 564–568. [Google Scholar]
- Wani, M.A.; Mukherjee, S.; Mallick, S.; Akbar, I.; Basu, A. Atorvastatin ameliorates viral burden and neural stem/progenitor cell (NSPC) death in an experimental model of Japanese encephalitis. J. Biosci. 2020, 45, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zheng, B.; Ashraf, U.; Zhang, H.; Cao, C.; Li, Q.; Chen, Z.; Imran, M.; Chen, H.; Cao, S.; et al. Artemisinin inhibits the replication of flaviviruses by promoting the type I interferon production. Antivir. Res. 2020, 179, 104810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.-C.; Ou, Y.-C.; Raung, S.-L.; Chen, C.-J. Antiviral effect of dehydroepiandrosterone on Japanese encephalitis virus infection. J. Gen. Virol. 2005, 86, 2513–2523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, C.F.; Gopula, B.; Liang, J.J.; Li, J.K.; Chen, S.Y.; Lee, Y.L.; Chen, C.S.; Lin, Y.-L. Novel AR-12 derivatives, P12-23 and P12-34, inhibit flavivirus replication by blocking host de novo pyrimidine biosynthesis. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2018, 7, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, H.-H.; Chen, C.-C.; Lin, Y.-S.; Chang, P.-C.; Lu, Z.-Y.; Lin, C.-F.; Chen, C.-L.; Chang, C.-P. AR-12 suppresses dengue virus replication by down-regulation of PI3K/AKT and GRP78. Antivir. Res. 2017, 142, 158–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boldescu, V.; Behnam, M.A.M.; Vasilakis, N.; Klein, C.D. Broad-spectrum agents for flaviviral infections: Dengue, Zika and beyond. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2017, 16, 565–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, C.-Y.; Chang, Y.-C.; Hua, C.-H.; Chuang, C.; Huang, S.-H.; Kung, S.-H.; Hour, M.-J.; Lin, C.-W. Tubacin, an HDAC6 Selective Inhibitor, Reduces the Replication of the Japanese Encephalitis Virus via the Decrease of Viral RNA Synthesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Guo, J.; Jia, X.; Liu, Y.; Wang, S.; Cao, J.; Zhang, B.; Xiao, G.; Wang, W. Screening of Natural Extracts for Inhibitors against Japanese Encephalitis Virus Infection. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2020, 64, e02373-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huang, L.; Li, H.; Ye, Z.; Xu, Q.; Fu, Q.; Sun, W.; Qi, W.; Yue, J. Berbamine inhibits Japanese encephalitis virus (JEV) infection by compromising TPRMLs-mediated endolysosomal trafficking of low-density lipoprotein receptor (LDLR). Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2021, 10, 1257–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warren, T.K.; Wells, J.; Panchal, R.G.; Stuthman, K.S.; Garza, N.L.; Van Tongeren, S.A.; Dong, L.; Retterer, C.J.; Eaton, B.P.; Pegoraro, G.; et al. Protection against filovirus diseases by a novel broad-spectrum nucleoside analogue BCX4430. Nature 2014, 508, 402–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kumar, P.; Lee, S.K.; Shankar, P.; Manjunath, N. A Single siRNA Suppresses Fatal Encephalitis Induced by Two Different Flaviviruses. PLoS Med. 2006, 3, e96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wu, Z.; Xue, Y.; Wang, B.; Du, J.; Jin, Q. Broad-Spectrum Antiviral Activity of RNA Interference against Four Genotypes of Japanese Encephalitis Virus Based on Single MicroRNA Polycistrons. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e26304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Appaiahgari, M.B.; Vrati, S. DNAzyme-mediated Inhibition of Japanese Encephalitis Virus Replication in Mouse Brain. Mol. Ther. 2007, 15, 1593–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chien, Y.-J.; Chen, W.-J.; Hsu, W.-L.; Chiou, S.-S. Bovine lactoferrin inhibits Japanese encephalitis virus by binding to heparansulfate and receptor for low density lipoprotein. Virology 2008, 379, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, H.-H.; Lin, C.-J.; Anand, A.; Lin, H.-J.; Lin, H.-Y.; Mao, J.-Y.; Wang, P.-H.; Tseng, Y.J.; Tzou, W.-S.; Huang, C.-C.; et al. Development of antiviral carbon quantum dots that target the Japanese encephalitis virus envelope protein. J. Bio. Chem. 2022, 298, 101957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talarico, L.B.; Pujol, C.A.; Zibetti, R.G.M.; Faría, P.C.S.; Noseda, M.; Duarte, M.E.R.; Damonte, E.B. The antiviral activity of sulfated polysaccharides against dengue virus is dependent on virus serotype and host cell. Antivir. Res. 2005, 66, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zu, X.; Liu, Y.; Wang, S.; Jin, R.; Zhou, Z.; Liu, H.; Gong, R.; Xiao, G.; Wang, W. Peptide inhibitor of Japanese encephalitis virus infection targeting envelope protein domain III. Antivir. Res. 2014, 104, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, X.; Lei, Y.; Yang, P.; Gao, Q.; Wang, N.; Cao, L.; Yuan, S.; Huang, X.; Deng, Y.; Ma, W.; et al. Structural basis for neutralization of Japanese encephalitis virus by two potent therapeutic antibodies. Nat. Microbiol. 2018, 3, 287–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.-J.; Chang, Y.-C.; Lu, K.-Z.; Tsou, Y.-Y.; Lin, C.-W. Antiviral activity of Isatisindigotica extract and its derived indirubin against Japanese encephalitis virus. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2012, 2012, 925830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Johari, J.; Kianmehr, A.; Mustafa, M.R.; Abubakar, S.; Zandi, K. Antiviral Activity of Baicalein and Quercetin against the Japanese Encephalitis Virus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 16785–16795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.-J.; Lin, H.-R.; Liao, C.-L.; Lin, Y.-L. Cholesterol Effectively Blocks Entry of Flavivirus. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 6470–6480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Takegami, T.; Simamura, E.; Hirai, K.-I.; Koyama, J. Inhibitory effect of furanonaphthoquinone derivatives on the replication of Japanese encephalitis virus. Antivir. Res. 1998, 37, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.-J.; Park, S.-N.; Oh, J.-W. Antiviral effect of amphotericin B on japanese encephalitis virus replication. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2004, 14, 121–127. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, J.; Sun, L.; Peng, G.; Xu, J.; Zhou, R.; Cao, S.; Chen, H.; Song, Y. Identifcation of three antiviral inhibitors against japanese encephalitis virus from library of pharmacologically active compounds 1280. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e78425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pambudi, S.; Kawashita, N.; Phanthanawiboon, S.; Omokoko, M.D.; Masrinoul, P.; Yamashita, A.; Limkittikul, K.; Yasunaga, T.; Takagi, T.; Ikuta, K.; et al. A small compound targeting the interaction between nonstructural proteins 2B and 3 inhibits dengue virus replication. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2013, 440, 393–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Brecher, M.; Deng, Y.-Q.; Zhang, J.; Sakamuru, S.; Liu, B.; Huang, R.; Koetzner, C.A.; Allen, C.; Jones, S.A.; et al. Existing drugs as broad-spectrum and potent inhibitors for Zika virus by targeting NS2B-NS3 interaction. Cell Res. 2017, 27, 1046–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brecher, M.; Chen, H.; Li, Z.; Banavali, N.; Jones, S.; Zhang, J.; Kramer, L.; Li, H. Identifcation and characterization of novel broad-spectrum inhibitors of the flavivirus methyl transferase. ACS Infect. Dis. 2015, 1, 340–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sebastian, L.; Desai, A.; Shampur, M.N.; Perumal, Y.; Sriram, D.; Vasanthapuram, R. N-methylisatin-beta-thiosemicarbazone derivative (SCH 16) is an inhibitor of Japanese encephalitis virus infection in vitro and in vivo. Virol. J. 2008, 5, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bhattacharjee, A.; Chaudhuri, R.; Dash, J.J.; Saha, M.; Choudhury, L.; Roy, S. Pre-treatment with Scopolamine Naturally Suppresses Japanese Encephalitis Viral Load in Embryonated Chick Through Regulation of Multiple Signaling Pathways. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2021, 193, 1654–1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Maurya, V.K.; Kabir, R.; Nayak, D.; Khurana, A.; Manchanda, R.K.; Gadugu, S.; Shanker, K.; Saxena, S.K. Antiviral Activity of Belladonna During Japanese Encephalitis Virus Infection via Inhibition of Microglia Activation and Inflammation Leading to Neuronal Cell Survival. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2020, 11, 3683–3696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saxena, S.K.; Agrawal, P.T.; Nair, M. Current Scenario of Antiviral Drugs for Japanese Encephalitis. J. Med. Microbiol. Diagn. 2014, 3, 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, Z.; Wei, J.; Deng, X.; Li, S.; Qiu, Y.; Shao, D.; Li, B.; Zhang, K.; Xue, F.; Wang, X.; et al. Nitazoxanide inhibits the replication of Japanese encephalitis virus in cultured cells and in a mouse model. Virol. J. 2014, 11, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rossignol, J.-F. Nitazoxanide: A first-in-class broad-spectrum antiviral agent. Antivir. Res. 2014, 110, 94–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fan, W.; Qian, S.; Qian, P.; Li, X. Antiviral activity of luteolin against Japanese encephalitis virus. Virus Res. 2016, 220, 112–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Sakamuru, S.; Huang, R.; Brecher, M.; Koetzner, C.A.; Zhang, J.; Chen, H.; Qin, C.-F.; Zhang, Q.-Y.; Zhou, J.; et al. Erythrosin B is a potent and broad-spectrum orthosteric inhibitor of the flavivirus NS2B-NS3 protease. Antivir. Res. 2017, 150, 217–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mastrangelo, E.; Pezzullo, M.; De Burghgraeve, T.; Kaptein, S.; Pastorino, B.; Dallmeier, K.; de Lamballerie, X.; Neyts, J.; Hanson, A.; Frick, D.N.; et al. Ivermectin is a potent inhibitor of flavivirus replication specifcally targeting NS3 helicase activity: New prospects for an old drug. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2012, 67, 1884–1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bhosale, S.; Kumar, A. Screening of phytoconstituents of Andrographispaniculata against various targets of Japanese encephalitis virus: An in-silico and in-vitro target-based approach. Curr. Res. Pharmacol. Drug. Discov. 2021, 2, 100043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sebastian, L.; Madhusudana, S.N.; Ravi, V.; Desai, A. Mycophenolic Acid Inhibits Replication of Japanese Encephalitis Virus. Chemotherapy 2011, 57, 56–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.K.; Singh, S.; Nischal, A.; Pant, K.K.; Seth, P.K. Molecular docking and simulation studies towards exploring antiviral compounds against envelope protein of Japanese encephalitis virus. Netw. Model. Anal. Health Inform. Bioinform. 2013, 2, 231–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, Z.; Shao, L.; Ye, J.; Li, Y.; Huang, S.; Chen, H.; Cao, S. Monoclonal antibodies against NS3 and NS5 proteins of Japanese encephalitis virus. Hybridoma 2012, 31, 137–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.-R.; Zhang, H.-Q.; Li, X.-D.; Deng, C.-L.; Wang, Z.; Li, J.-Q.; Li, N.; Zhang, Q.-Y.; Zhang, B.; Ye, H.-Q. Generation and characterization of Japanese encephalitis virus expressing GFP reporter gene for high throughput drug screening. Antivir. Res. 2020, 182, 104884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, J.; Li, H.; Kong, D.; Cao, S.; Peng, G.; Zhou, R.; Chen, H.; Song, Y. Structure-based discovery of two antiviral inhibitors targeting the NS3 helicase of Japanese encephalitis virus. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 34550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Woodman, D.R.; Williams, J.C. Effects of 2-Deoxy- d -Glucose and 3-Deazauridine Individually and in Combination on the Replication of Japanese B Encephalitis Virus. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1977, 11, 475–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xiao, Y.; Yang, J.; Zou, L.; Wu, P.; Li, W.; Yan, Y.; Li, Y.; Li, S.; Song, H.; Zhong, W.; et al. Synthesis of 10,10′-bis(trifluoromethyl) marinopyrrole A derivatives and evaluation of their antiviral activities in vitro. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2022, 238, 114436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, Y.-J.; Lu, J.-W.; Huang, Y.-L.; Lai, Z.-Z. Palmatine inhibits Zika virus infection by disrupting virus binding, entry, and stability. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2019, 518, 732–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hills, S.L.; Walter, E.B.; Atmar, R.L.; Fischer, M.; Barnett, E.; Barrett, A.; Bocchini, J.A.; Chen, L.; Deussing, E.; Fink, D.; et al. Japanese Encephalitis Vaccine: Recommendations of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices. MMWR. Recomm. Rep. 2019, 68, 1–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batchelor, P.; Petersen, K. Japanese encephalitis: A review of clinical guidelines and vaccine availability in Asia. Trop. Dis. Travel Med. Vaccines 2015, 1, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Japanese encephalitis: Status of surveillance and immunization in Asia and Western Pacific, 2012. WHO Wkly. Epidemiol. Rec. 2013, 34, 357–364.
- Hegde, N.R.; Gore, M.M.; Hegde, N.R.; Gore, M.M. Japanese encephalitis vaccines: Immunogenicity, protective efficacy, effectiveness, and impact on the burden of disease. Hum. Vaccines Immunother. 2017, 13, 1320–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fischer, M.; Lindsey, N.; Staples, J.E.; Hills, S.; Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Japanese encephalitis vaccines: Recommendations of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP). MMWR Recomm. Rep. 2010, 59, 1–27. [Google Scholar]
- Ginsburg, A.S.; Meghani, A.; Halstead, S.B.; Yaich, M. Use of the live attenuated Japanese Encephalitis vaccine SA 14-14-2 in children: A review of safety and tolerability studies. Hum. Vaccines Immunother. 2017, 13, 2222–2231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oya, A. Japanese encephalitis vaccine. Acta Pediatr. JPN 1988, 30, 175–184S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Update on Japanese encephalitis vaccine for children in United States, May, 2011. MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2011, 60, 664–665. [Google Scholar]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Use of Japanese encephalitis vaccine in children: Recommendations of the advisory committee on immunization practices, 2013. MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2013, 62, 898–900. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, S.; Verma, A.; Yadav, P.; Dubey, S.K.; Azhar, E.I.; Maitra, S.S.; Dwivedi, V.D. Molecular pathogenesis of Japanese encephalitis and possible therapeutic strategies. Arch. Virol. 2022, 167, 1739–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.-L.; Chang, J.-K.; Tang, R.-B. Current recommendations for the Japanese encephalitis vaccine. J. Chin. Med. Assoc. 2015, 78, 271–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jelinek, T. IXIARO® updated: Overview of clinical trials and developments with the inactivated vaccine against Japanese encephalitis. Expert Rev. Vaccines 2013, 12, 859–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taucher, C.; Barnett, E.D.; Cramer, J.P.; Eder-Lingelbach, S.; Jelinek, T.; Kadlecek, V.; Kiermayr, S.; Mills, D.J.; Pandis, D.; Reiner, D.; et al. Neutralizing antibody persistence in pediatric travelers from non-JE-endemic countries following vaccination with IXIARO® Japanese encephalitis vaccine: An uncontrolled, open-label phase 3 follow-up study. Travel Med. Infect. Dis. 2020, 34, 101616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konishi, E.; Yamaoka, M.; Khin Sane, W.; Kurane, I.; Mason, P.W. Induction of protective immunity against Japanese encephalitis in mice by immunization with a plasmid encoding Japanese encephalitis virus pre-membrane and envelope genes. J. Virol. 1998, 72, 4925–4930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Appaiahgari, M.B.; Vrati, S. IMOJEV®: A Yellow fever virus-based novel Japanese encephalitis vaccine. Expert Rev. Vaccines 2010, 9, 1371–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capeding, M.R.; Alberto, E.R.; Bouckenooghe, A.; Laot, T.M.; Chansinghakul, D.; Monfredo, C.; Machabert, T.; Feroldi, E. Five-Year Antibody Persistence Following a Japanese Encephalitis Chimeric Virus Vaccine (JE-CV) Booster in JE-CV–Primed Children in the Philippines. J. Infect. Dis. 2018, 217, 567–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yu, Y. Phenotypic and genotypic characteristics of Japanese encephalitis attenuated live vaccine virus SA14-14-2 and their stabilities. Vaccine 2010, 28, 3635–3641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, H.J.; Lee, S.Y.; Kim, K.H.; Kim, D.S.; Cha, S.H.; Jo, D.S.; Kang, J.H. The Immunogenicity and Safety of the Live-attenuated SA 14-14-2 Japanese Encephalitis Vaccine Given with a Two-dose Primary Schedule in Children. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2015, 30, 612–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Singh, A.; Mitra, M.; Sampath, G.; Venugopal, P.; Rao, J.V.; Krishnamurthy, B.; Gupta, M.K.; Krishna, S.S.; Sudhakar, B.; Rao, N.B.; et al. A Japanese Encephalitis Vaccine From India Induces Durable and Cross-protective Immunity Against Temporally and Spatially Wide-ranging Global Field Strains. J. Infect. Dis. 2015, 212, 715–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vadrevu, K.M.; Potula, V.; Khalatkar, V.; Mahantshetty, N.S.; Shah, A.; Ella, R. Persistence of Immune Responses With an Inactivated Japanese Encephalitis Single-Dose Vaccine, JENVAC and Interchangeability with a Live-Attenuated Vaccine. J. Infect. Dis. 2019, 222, 1478–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ye, C.; Bian, P.; Zhang, J.; Xiao, H.; Zhang, L.; Ye, W.; Dong, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Jia, Z.; Lei, Y. Structure-based discovery of antiviral inhibitors targeting the E dimer interface of Japanese encephalitis virus. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2019, 515, 366–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Wispelaere, M.; Lian, W.; Potisopon, S.; Li, P.-C.; Jang, J.; Ficarro, S.B.; Clark, M.J.; Zhu, X.; Kaplan, J.B.; Pitts, J.D.; et al. Inhibition of Flaviviruses by Targeting a Conserved Pocket on the Viral Envelope Protein. Cell Chem. Biol. 2018, 25, 1006–1016.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navyashree, V.; Kant, K.; Kumar, A. Natural chemical entities from Arisaema genus might be a promising break-through against Japanese encephalitis virus infection: A molecular docking and dynamics approach. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2020, 39, 1404–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Li, H.; Yang, X.; Guo, T.; Wang, L.; Zhao, Z.; Sun, H.; Hou, X.; Ding, X.; Dou, C.; et al. Guillain–Barré Syndrome Associated with JEV Infection. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 1188–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Licensed Vaccines (Types) | Utilized Viral Strain | Trade Name | Licensing Year | Required Doses | Vaccination Age | Route of Administration | Countries Licensed to Use |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| JE-MB ⌂ (Inactivated mouse brain-derived JE vaccine) | Nakayama-NH Beijing-1 | JE-VAX | 1954 1993 | 3 | ≥12 months | Subcutaneous | European Union, India, Japan, Malaysia, North Korea, South Korea, Sri Lanka, Taiwan, Thailand, United States, Vietnam |
| JE-VC (Inactivated Vero cell culture-derived JE vaccine) | SA14-14-2 (with adjuvant) | IXIARO®/ JESPECT®/ JEEV® | 2009 * 2013 * | 2 | ≥17 year ≥2 month | Intramuscular | Australia, Bangladesh, Bhutan, Canada, European Union, Hong Kong, India, Japan, Latin America, Nepal, New Zealand, Pacific Islands, Papua New Guinea, Singapore, South Korea, Switzerland, United States |
| Bejing-I (without adjuvant) | JEBIK-V ENCEVAC TC-JEV | 2009 2011 2013 | 3 | ≥36 month | Subcutaneous | Japan, South Korea | |
| IMOJEV (Recombinant chimeric virus vaccine) | SA14-14-2 | IMOJEV | 2010 | 1 | ≥1 year | Subcutaneous | Australia, South Korea, Thailand |
| JE-LV ⌂ (Live attenuated Japanese encephalitis vaccine) | SA14-14-2 | CD.JEVAX | 1988 | 1 | ≥8 months | Subcutaneous | China, Hong Kong, India, Japan, Nepal, South Korea, Sri Lanka, Thailand |
| JENVAC | 821564XY (Indian Kolar strain) | JENVAC | 2013 | 2 | ≥6 months | Intramuscular | India |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Srivastava, K.S.; Jeswani, V.; Pal, N.; Bohra, B.; Vishwakarma, V.; Bapat, A.A.; Patnaik, Y.P.; Khanna, N.; Shukla, R. Japanese Encephalitis Virus: An Update on the Potential Antivirals and Vaccines. Vaccines 2023, 11, 742. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11040742
Srivastava KS, Jeswani V, Pal N, Bohra B, Vishwakarma V, Bapat AA, Patnaik YP, Khanna N, Shukla R. Japanese Encephalitis Virus: An Update on the Potential Antivirals and Vaccines. Vaccines. 2023; 11(4):742. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11040742
Chicago/Turabian StyleSrivastava, Kumar Saurabh, Vandana Jeswani, Nabanita Pal, Babita Bohra, Vaishali Vishwakarma, Atharva Ashish Bapat, Yamini Prashanti Patnaik, Navin Khanna, and Rahul Shukla. 2023. "Japanese Encephalitis Virus: An Update on the Potential Antivirals and Vaccines" Vaccines 11, no. 4: 742. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11040742
APA StyleSrivastava, K. S., Jeswani, V., Pal, N., Bohra, B., Vishwakarma, V., Bapat, A. A., Patnaik, Y. P., Khanna, N., & Shukla, R. (2023). Japanese Encephalitis Virus: An Update on the Potential Antivirals and Vaccines. Vaccines, 11(4), 742. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11040742







