Third BNT162b2 mRNA SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine Dose Significantly Enhances Immunogenicity in Recipients of Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Patients and Methods
2.1. Serology Testing for Anti-S SARS-CoV-2 Antibodies
2.2. Cellular Response
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patients
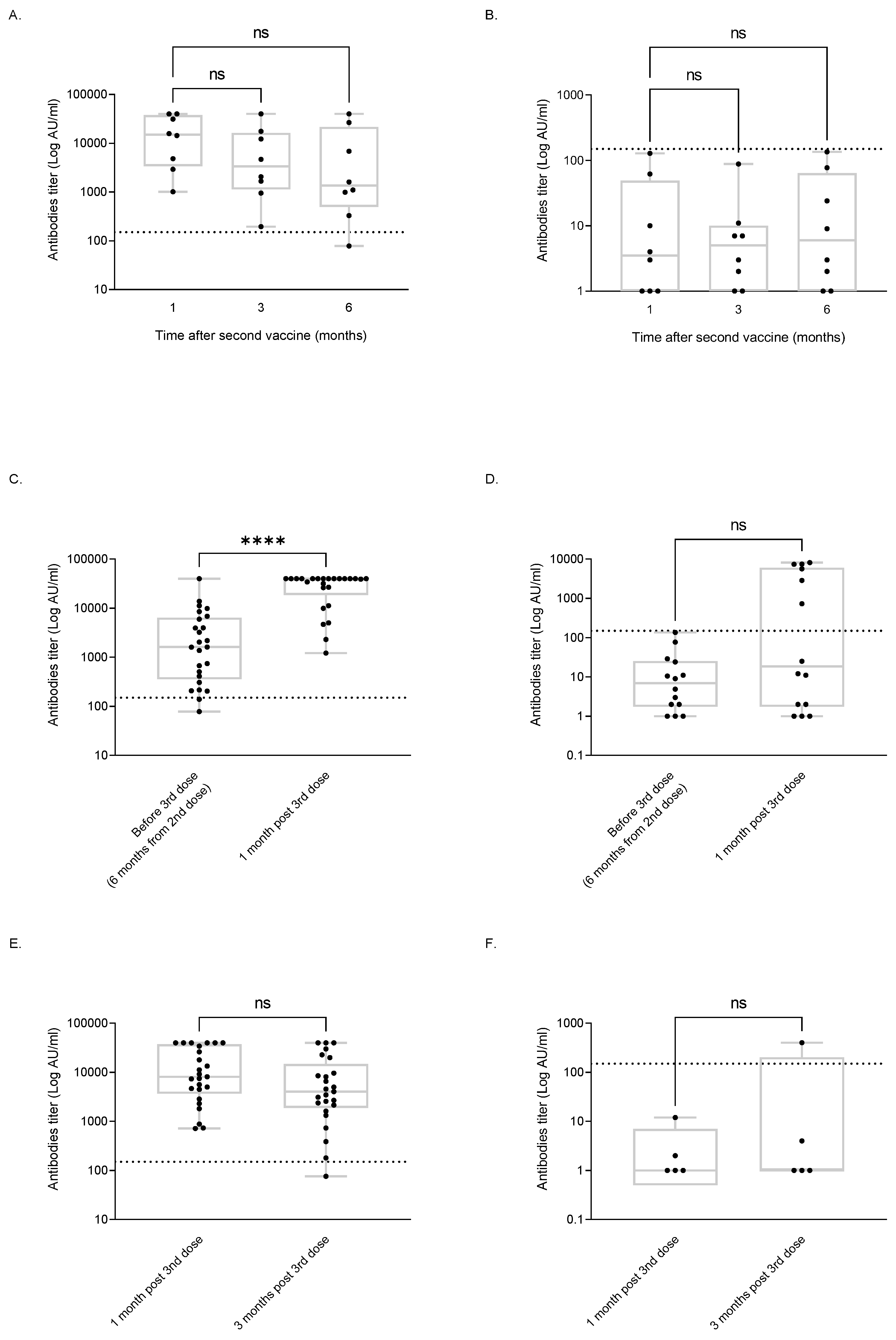
3.2. Serological Response to Vaccine
3.3. Serological Response Dynamics
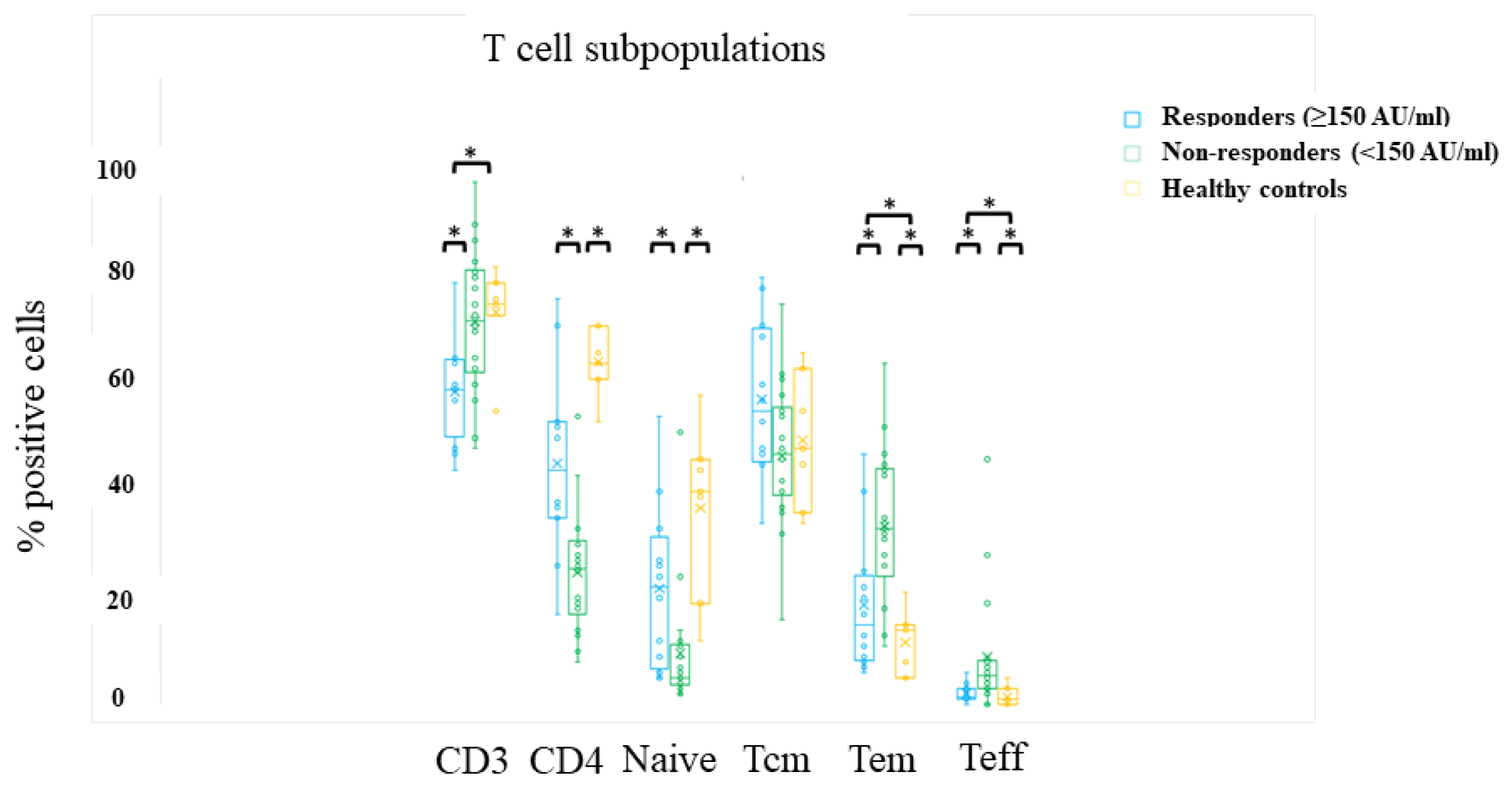
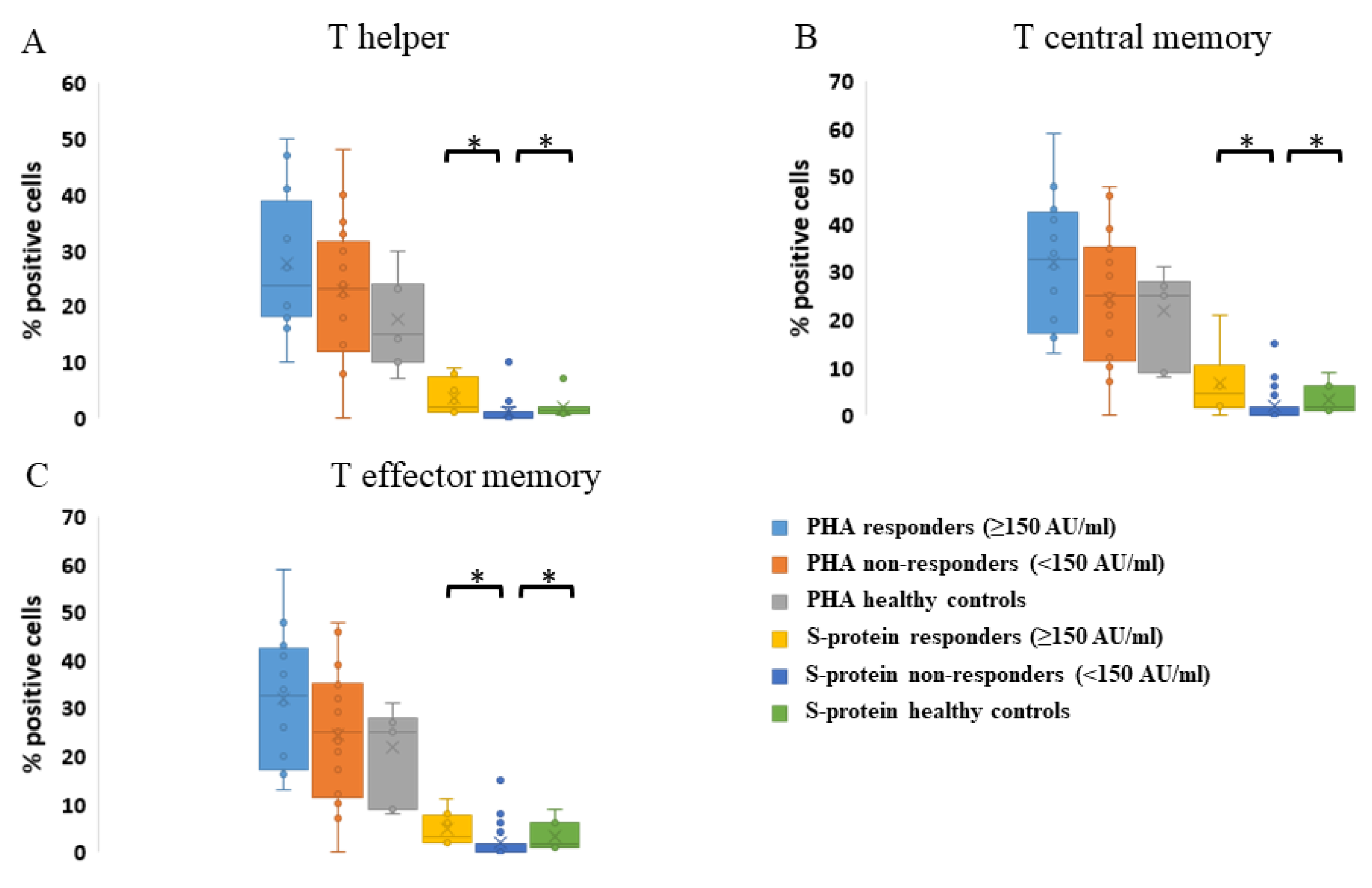
3.4. Cellular Response
3.5. Clinical Effects of SARS-CoV-2 on HSCT Recipients
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dai, M.; Liu, D.; Liu, M.; Zhou, F.; Li, G.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, Z.; You, H.; Wu, M.; Zheng, Q.; et al. Patients with cancer appear more vulnerable to SARS-COV-2: A multicenter study during the COVID-19 outbreak. Cancer Discov. 2020, 10, 783–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robilotti, E.V.; Babady, N.E.; Mead, P.A.; Rolling, T.; Perez-Johnston, R.; Bernardes, M.; Bogler, Y.; Caldararo, M.; Figueroa, C.J.; Glickman, M.S.; et al. Determinants of COVID-19 disease severity in patients with cancer. Nat. Med. 2020, 26, 1218–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vijenthira, A.; Gong, I.Y.; Fox, T.A.; Booth, S.; Cook, G.; Fattizzo, B.; Martín-Moro, F.; Razanamahery, J.; Riches, J.C.; Zwicker, J.; et al. Outcomes of patients with hematologic malignancies and COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis of 3377 patients. Blood 2020, 136, 2881–2892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ljungman, P.; de la Camara, R.; Mikulska, M.; Tridello, G.; Aguado, B.; Al Zahrani, M.; Apperley, J.; Berceanu, A.; Bofarull, R.M.; Calbacho, M.; et al. COVID-19 and stem cell transplantation; results from an EBMT and GETH multicenter prospective survey. Leukemia 2021, 35, 2885–2894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, A.; Bhatt, N.S.; Martin, A.S.; Abid, M.B.; Bloomquist, J.; Chemaly, R.F.; Dandoy, C.; Gauthier, J.; Gowda, L.; Perales, M.-A.; et al. Clinical characteristics and outcomes of COVID-19 in haematopoietic stem-cell transplantation recipients: An observational cohort study. Lancet Haematol. 2021, 8, e185–e193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrett, J. Why is a 3-year NRM following allogeneic transplantation still stuck at approximately 20%? Best Pract. Res. Clin. Haematol. 2018, 31, 414–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berro, M.; Chhabra, S.; Piñana, J.L.; Arbelbide, J.; Rivas, M.M.; Basquiera, A.L.; Vitriu, A.; Requejo, A.; Milovic, V.; Yantorno, S.; et al. Predicting Mortality after Autologous Transplant: Development of a Novel Risk Score. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2020, 26, 1828–1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baden, L.R.; El Sahly, H.M.; Essink, B.; Kotloff, K.; Frey, S.; Novak, R.; Diemert, D.; Spector, S.A.; Rouphael, N.; Creech, C.B.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of the mRNA-1273 SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 403–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polack, F.P.; Thomas, S.J.; Kitchin, N.; Absalon, J.; Gurtman, A.; Lockhart, S.; Perez, J.L.; Pérez Marc, G.; Moreira, E.D.; Zerbini, C.; et al. Safety and efficacy of the BNT162b2 mRNA COVID-19 vaccine. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 2603–2615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avetisyan, G.; Aschan, J.; Hassan, M.; Ljungman, P. Evaluation of Immune Responses to Seasonal Influenza Vaccination in Healthy Volunteers and in Patients After Stem Cell Transplantation. Transplantation 2008, 86, 257–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Issa, N.C.; Marty, F.M.; Gagne, L.S.; Koo, S.; Verrill, K.A.; Alyea, E.P.; Cutler, C.S.; Koreth, J.; Armand, P.; Ho, V.T.; et al. Seroprotective Titers against 2009 H1N1 Influenza A Virus after Vaccination in Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation Recipients. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2011, 17, 434–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canti, L.; Humblet-Baron, S.; Desombere, I.; Neumann, J.; Pannus, P.; Heyndrickx, L.; Henry, A.; Servais, S.; Willems, E.; Ehx, G.; et al. Predictors of neutralizing antibody response to BNT162b2 vaccination in allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplant recipients. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2021, 14, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiarucci, M.; Paolasini, S.; Isidori, A.; Guiducci, B.; Loscocco, F.; Capalbo, M.; Visani, G. Immunological Response Against SARS-COV-2 After BNT162b2 Vaccine Administration Is Impaired in Allogeneic but Not in Autologous Stem Cell Transplant Recipients. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 737300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Redjoul, R.; Le Bouter, A.; Parinet, V.; Fourati, S.; Maury, S. Antibody response after third BNT162b2 dose in recipients of allogeneic HSCT. Lancet Haematol. 2021, 8, e681–e683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhakal, B.; Abedin, S.M.; Fenske, T.S.; Chhabra, S.; Ledeboer, N.; Hari, P.; Hamadani, M. Response to SARS-CoV-2 vaccination in patients after hematopoietic cell transplantation and CAR T-cell therapy. Blood 2021, 138, 1278–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Easdale, S.; Shea, R.; Ellis, L.; Bazin, J.; Davis, K.; Dallas, F.; Thistlethwayte, E.; Ethell, M.; Potter, M.; Arias, C.; et al. Serologic Responses following a Single Dose of SARS-Cov-2 Vaccination in Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplantation Recipients. Transplant. Cell. Ther. 2021, 27, 880.e1–880.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, H.; Ngo, D.; Aribi, A.; Arslan, S.; Dadwal, S.; Marcucci, G.; Nakamura, R.; Forman, S.J.; Chen, J.; Al Malki, M.M. Safety and Tolerability of SARS-CoV2 Emergency-Use Authorized Vaccines for Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplant Recipients. Transplant. Cell. Ther. 2021, 27, 938.e1–938.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ram, R.; Hagin, D.; Kikozashvilli, N.; Freund, T.; Amit, O.; Bar-On, Y.; Beyar-Katz, O.; Shefer, G.; Moshiashvili, M.M.; Karni, C.; et al. Safety and Immunogenicity of the BNT162b2 mRNA COVID-19 Vaccine in Patients after Allogeneic HCT or CD19-based CART therapy—A Single-Center Prospective Cohort Study. Transplant. Cell Ther. 2021, 27, 788–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matkowska-Kocjan, A.; Owoc-Lempach, J.; Chruszcz, J.; Kuźnik, E.; Szenborn, F.; Jurczenko, L.; Wójcik, M.; Banyś, D.; Szenborn, L.; Ussowicz, M. The COVID-19 mRNA BNT163b2 Vaccine Was Well Tolerated and Highly Immunogenic in Young Adults in Long Follow-Up after Haematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation. Vaccines 2021, 9, 1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shem-Tov, N.; Yerushalmi, R.; Danylesko, I.; Litachevsky, V.; Levy, I.; Olmer, L.; Lusitg, Y.; Avigdor, A.; Nagler, A.; Shimoni, A.; et al. Immunogenicity and safety of the BNT162b2 mRNA COVID-19 vaccine in haematopoietic stem cell transplantation recipients. Br. J. Haematol. 2021, 196, 884–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeshurun, M.; Pasvolsky, O.; Shargian, L.; Yahav, D.; Ben-Zvi, H.; Rubinstein, M.; Sela-Navon, M.; Wolach, O.; Raanani, P.; Rozovski, U. Humoral serological response to the BNT162b2 vaccine after allogeneic haematopoietic cell transplantation. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2022, 28, 303.e1–303.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levin, E.G.; Lustig, Y.; Cohen, C.; Fluss, R.; Indenbaum, V.; Amit, S.; Doolman, R.; Asraf, K.; Mendelson, E.; Ziv, A.; et al. Waning Immune Humoral Response to BNT162b2 Covid-19 Vaccine over 6 Months. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, e84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barda, N.; Dagan, N.; Cohen, C.; Hernán, M.A.; Lipsitch, M.; Kohane, I.S.; Reis, B.Y.; Balicer, R.D. Effectiveness of a third dose of the BNT162b2 mRNA COVID-19 vaccine for preventing severe outcomes in Israel: An observational study. Lancet 2021, 398, 2093–2100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ljungman, P.; Cesaro, S.; Cordonnier, C.; Mikulska, M.; Styczynski, J.; de la Camara, R. COVID-19 Vaccines. Version 2.0. 21 December 2020. Available online: https://www.ebmt.org/sites/default/files/2020-12/COVID%20vaccines%20version%202.03%20with%20table.pdf (accessed on 3 December 2021).
- Marín, N.D.; Rojas, M.; París, S.C.; Garcia, L.F. Phenotypic and Functional Heterogeneity of Circulating CD4+ and CD8+ T Cell Subsets and Their Age Related Changes. Available online: https://www.frontiersin.org/10.3389/conf.fimmu.2013.02.00753/event_abstract (accessed on 21 March 2023).
- Zaunders, J.J.; Munier, M.L.; Seddiki, N.; Pett, S.; Ip, S.; Bailey, M.; Xu, Y.; Brown, K.; Dyer, W.B.; Kim, K. High levels of human antigen-specific CD4+ T cells in peripheral blood revealed by stimulated coexpression of CD25 and CD134 (OX40). J. Immunol. 2009, 183, 2827–2836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shachor-Meyouhas, Y.; Hussein, K.; Dabaja-Younis, H.; Szwarcwort-Cohen, M.; Almog, R.; Weissman, A.; Mekel, M.; Hyams, G.; Horowitz, N.A.; Gepstein, V.; et al. Immunogenicity trends 1 and 3 months after second BNT162B2 vaccination among healthcare workers in Israel. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2021, 28, 450.e1–450.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrari, D.; Clementi, N.; Criscuolo, E.; Ambrosi, A.; Corea, F.; Di Resta, C.; Tomaiuolo, R.; Mancini, N.; Locatelli, M.; Plebani, M.; et al. Antibody Titer Kinetics and SARS-CoV-2 Infections Six Months after Administration with the BNT162b2 Vaccine. Vaccines 2021, 9, 1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldberg, Y.; Mandel, M.; Bar-On, Y.M.; Bodenheimer, O.; Freedman, L.; Haas, E.J.; Milo, R.; Alroy-Preis, S.; Ash, N.; Huppert, A. Waning Immunity after the BNT162b2 Vaccine in Israel. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, e85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chemaitelly, H.; Tang, P.; Hasan, M.R.; AlMukdad, S.; Yassine, H.M.; Benslimane, F.M.; Al Khatib, H.A.; Coyle, P.; Ayoub, H.H.; Al Kanaani, Z.; et al. Waning of BNT162b2 Vaccine Protection against SARS-CoV-2 Infection in Qatar. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, e83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilboa, M.; Mandelboim, M.; Indenbaum, V.; Lustig, Y.; Cohen, C.; Rahav, G.; Asraf, K.; Amit, S.; Jaber, H.; Nemet, I.; et al. Early Immunogenicity and Safety of the Third Dose of BNT162b2 Messenger RNA Coronavirus Disease 2019 Vaccine Among Adults Older Than 60 Years: Real-World Experience. J. Infect. Dis. 2022, 225, 785–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, Q.J.; Bivona, C.R.; Ben Liu, B.; Nelson, M.; Martin, G.A.; Mushtaq, M.U.; Sharma, P.; Streeter, N.R.; Hoffmann, M.; Doolittle, G.C.; et al. Prospective longitudinal study of kinetics of humoral response to one, two, or three doses of SARS-CoV-2 vaccine in hematopoietic cell transplant recipients. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2022, 57, 1013–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Bourgeois, A.; Coste-Burel, M.; Guillaume, T.; Peterlin, P.; Garnier, A.; Imbert, B.; Drumel, T.; Mahé, B.; Dubruille, V.; Blin, N.; et al. Interest of a third dose of BNT162b2 anti-SARS-CoV-2 messenger RNA vaccine after allotransplant. Br. J. Haematol. 2022, 196, e38–e40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, M.; Ferreira, V.H.; Kothari, S.; Pasic, I.; Mattsson, J.I.; Kulasingam, V.; Humar, A.; Mah, A.; Delisle, J.-S.; Ierullo, M.; et al. Safety and Immunogenicity After a Three-Dose SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine Schedule in Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplant Recipients. Transplant. Cell. Ther. 2022, 28, 706.e1–706.e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maillard, A.; Redjoul, R.; Klemencie, M.; Wallet, H.L.; Le Bourgeois, A.; D’Aveni, M.; Huynh, A.; Berceanu, A.; Marchand, T.; Chantepie, S.P.; et al. Antibody response after 2 and 3 doses of SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccine in allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplant recipients. Blood 2022, 139, 134–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mittelman, M.; Magen, O.; Barda, N.; Dagan, N.; Oster, H.S.; Leader, A.; Balicer, R. Effectiveness of the BNT162b2mRNA COVID-19 vaccine in patients with hematological neoplasms in a nationwide mass vaccination setting. Blood 2022, 139, 1439–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canti, L.; Ariën, K.K.; Desombere, I.; Humblet-Baron, S.; Pannus, P.; Heyndrickx, L.; Henry, A.; Servais, S.; Willems, E.; Ehx, G.; et al. Antibody response against SARS-CoV-2 Delta and Omicron variants after third-dose BNT162b2 vaccination in allo-HCT recipients. Cancer Cell. 2022, 40, 335–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, N.; Stowe, J.; Kirsebom, F.; Toffa, S.; Rickeard, T.; Gallagher, E.; Gower, C.; Kall, M.; Groves, N.; O’Connell, A.-M.; et al. Covid-19 Vaccine Effectiveness against the Omicron (B.1.1.529) Variant. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 386, 1532–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Storek, J.; Geddes, M.; Khan, F.; Huard, B.; Helg, C.; Chalandon, Y.; Passweg, J.R.; Roosnek, E. Reconstitution of the immune system after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in humans. Semin. Immunopathol. 2008, 30, 425–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Painter, M.M.; Mathew, D.; Goel, R.R.; Apostolidis, S.A.; Pattekar, A.; Kuthuru, O.; Baxter, A.E.; Herati, R.S.; Oldridge, D.A.; Gouma, S.; et al. Rapid induction of antigen-specific CD4+ T cells is associated with coordinated humoral and cellular immunity to SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccination. Immunity 2021, 54, 2133–2142.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Evaluated Parameters | All Patients (%) | Responders (Ab Titer ≥ 150 AU/mL); n = 51 (%) | Non-Responders (Ab Titer < 150 AU/mL); n = 26 (%) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age, years; mean ± SD | 55 ± 15.4 | 48.7 ± 16.1 | 57.1 ± 12.2 | 0.022 |
| Female gender | 41 (53) | 33 (65) | 8 (31) | 0.007 |
| Diagnosis | 0.097 | |||
| AML | 43 (56) | 31 (61) | 12 (46) | |
| ALL | 11 (14) | 8 (16) | 3 (12) | |
| MDS | 12 (15.5) | 6 (12) | 6 (23) | |
| MPN | 5 (6.5) | 1 (2) | 4 (15) | |
| LY | 6 (8) | 5 (10) | 1 (4) | |
| HSCT-CI; median [IQR] | 1.5 [0–3] | 2.5 [0.25–3.75] | 1 [0–2] | 0.18 |
| Number of pre-transplant lines of therapy | 0.15 | |||
| 1 | 45 (83.3) | 22 (76) | 23 (92) | |
| ≥2 | 9 (16) | 7 (24) | 2 (8) | |
| Donor | 0.003 | |||
| MRD | 31 (40.8) | 27 (53) | 4 (16) | |
| MUD | 38 (50) | 22 (43) | 16 (64) | |
| Haploidentical | 7 (9.2) | 2 (4) | 5 (20) | |
| Conditioning intensity | 0.73 | |||
| MAC | 43 (55.8) | 29 (57) | 14 (54) | |
| RTC | 19 (24.6) | 11 (22) | 8 (31) | |
| RIC | 14 (18.2) | 10 (20) | 4 (15) | |
| NMA | 1 (1.4) | 1 (2) | 0 | |
| * Disease status at transplant | 0.028 | |||
| CR | 57 (74) | 42 (82) | 15 (58) | |
| Other | 20 (26) | 9 (18) | 11 (42) | |
| ATG | 43 (56) | 26 (51) | 17 (65) | 0.33 |
| TBI | 12 (15.6) | 8 (16) | 4 (15) | >0.99 |
| GVHD prophylaxis | 0.56 | |||
| CSA MTX | 48 (62.3) | 30 (59) | 18 (69) | |
| CSA MMF | 28 (36.4) | 20 (39) | 8 (31) | |
| CSA only | 1 (1.3) | 1 (2) | 0 | |
| PTCy | 5 (6.5) | 1 (2) | 5 (19) | 0.084 |
| Anti-CD20 therapy within previous 12 months | 4 (5.2) | 1 (2) | 3 (11.5) | 0.038 |
| Time from transplant to vaccine administration | <0.0001 | |||
| Early, <6 months | 13 (16.9) | 4 (8) | 9 (35) | |
| Intermediate, 6–12 months | 21 (27.3) | 11 (22) | 10 (38) | |
| Late, >12 months | 43 (55.8) | 36 (70) | 7 (27) | |
| Chronic GVHD at time of vaccination | 34 (44.1) | 21 (41) | 13 (50) | 0.48 |
| Steroid treatment at time of vaccination | 23 (29.9) | 11 (22) | 12 (46) | 0.036 |
| Stem cell donor age, years, mean ± SD (n = 47) | 33.5 ± 14.9 | 37.4 ± 16.3 | 30.04 ± 13.4 | 0.095 |
| Female donor (n = 47) | 11 (23.4) | 5 (22) | 6 (25) | 0.99< |
| % donor chimerism at 1 month post-HSCT, mean ± SD (n = 47) | 99.3 ± 1.6 | 99.04 ± 1.85; n = 23 | 99.5 ± 1.56; n = 24 | 0.32 |
| GVHD exacerbation or onset at 1 month post-vaccination (n = 41) | 7 (17) | 4 (22) | 3 (13) | 0.68 |
| Disease relapse | 5 (6.5) | 1 (2) | 5 (19) | 0.015 |
| Alive 7 months after second vaccine dose (n = 41) | 37 (90) | 17 (94); n = 18 | 20 (87); n = 23 | 0.62 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Henig, I.; Isenberg, J.; Yehudai-Ofir, D.; Leiba, R.; Ringelstein-Harlev, S.; Ram, R.; Avni, B.; Amit, O.; Grisariu, S.; Azoulay, T.; et al. Third BNT162b2 mRNA SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine Dose Significantly Enhances Immunogenicity in Recipients of Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation. Vaccines 2023, 11, 775. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11040775
Henig I, Isenberg J, Yehudai-Ofir D, Leiba R, Ringelstein-Harlev S, Ram R, Avni B, Amit O, Grisariu S, Azoulay T, et al. Third BNT162b2 mRNA SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine Dose Significantly Enhances Immunogenicity in Recipients of Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation. Vaccines. 2023; 11(4):775. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11040775
Chicago/Turabian StyleHenig, Israel, Jonathan Isenberg, Dana Yehudai-Ofir, Ronit Leiba, Shimrit Ringelstein-Harlev, Ron Ram, Batia Avni, Odelia Amit, Sigal Grisariu, Tehila Azoulay, and et al. 2023. "Third BNT162b2 mRNA SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine Dose Significantly Enhances Immunogenicity in Recipients of Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation" Vaccines 11, no. 4: 775. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11040775
APA StyleHenig, I., Isenberg, J., Yehudai-Ofir, D., Leiba, R., Ringelstein-Harlev, S., Ram, R., Avni, B., Amit, O., Grisariu, S., Azoulay, T., Slouzkey, I., & Zuckerman, T. (2023). Third BNT162b2 mRNA SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine Dose Significantly Enhances Immunogenicity in Recipients of Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation. Vaccines, 11(4), 775. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11040775





