Calcinosis Cutis and Calciphylaxis in Autoimmune Connective Tissue Diseases
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Calcinosis Cutis and Systemic Sclerosis
3. Calcinosis Cutis and Poly-Dermatomyositis
4. Calcinosis Cutis and Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
5. Calcinosis Cutis and Other Autoimmune Conditions
6. Calciphylaxis and Autoimmune Diseases
7. Therapeutic Approaches for Calcinosis Cutis and Calciphylaxis in Autoimmune Conditions
8. The Potential Role of Immunosuppressive Therapies
9. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Baron, M.; Pope, J.; Robinson, D.; Jones, N.; Khalidi, N.; Docherty, P.; Kaminska, E.; Masetto, A.; Sutton, E.; Mathieu, J.P.; et al. Calcinosis is associated with digital ischaemia in systemic sclerosis—A longitudinal study. Rheumatology 2016, 55, 2148–2155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boulman, N.; Slobodin, G.; Rozenbaum, M.; Rosner, I. Calcinosis in rheumatic diseases. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2005, 34, 805–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, A.B.; Hoeltzel, M.F.; Wahezi, D.M.; Becker, M.L.; Kessler, E.A.; Schmeling, H.; Carrasco, R.; Huber, A.M.; Feldman, B.M.; Reed, A.M.; et al. Clinical characteristics of children with juvenile dermatomyositis: The Childhood Arthritis and Rheumatology Research Alliance Registry. Arthritis Care Res. 2014, 66, 404–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elahmar, H.; Feldman, B.M.; Johnson, S.R. Management of Calcinosis Cutis in Rheumatic Diseases. J. Rheumatol. 2022, 49, 980–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, S.; Larson, A.; Datta, Y. Calciphylaxis in catastrophic antiphospholipid antibody syndrome. Blood Coagul. Fibrinolysis 2015, 26, 467–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, J.J.; Laumann, A.; Martinez, M. Calciphylaxis and antiphospholipid antibody syndrome. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2000, 42, 849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coates, T.; Kirkland, G.S.; Dymock, R.B.; Murphy, B.F.; Brealey, J.K.; Mathew, T.H.; Disney, A.P. Cutaneous necrosis from calcific uremic arteriolopathy. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 1998, 32, 384–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weenig, R.H.; Sewell, L.D.; Davis, M.D.; McCarthy, J.T.; Pittelkow, M.R. Calciphylaxis: Natural history, risk factor analysis, and outcome. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2007, 56, 569–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auriemma, M.; Carbone, A.; Di Liberato, L.; Cupaiolo, A.; Caponio, C.; De Simone, C.; Tulli, A.; Bonomini, M.; Amerio, P. Treatment of cutaneous calciphylaxis with sodium thiosulfate: Two case reports and a review of the literature. Am. J. Clin. Dermatol. 2011, 12, 339–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selye, H.; Gentile, G.; Prioreschi, P. Cutaneous molt induced by calciphylaxis in the rat. Science 1961, 134, 1876–1877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.J. Calciphylaxis: Diagnosis, Pathogenesis, and Treatment. Adv. Ski. Wound Care 2019, 32, 205–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seethapathy, H.; Noureddine, L. Calciphylaxis: Approach to Diagnosis and Management. Adv. Chronic Kidney Dis. 2019, 26, 484–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nigwekar, S.U.; Thadhani, R.; Brandenburg, V.M. Calciphylaxis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 1704–1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balin, S.J.; Wetter, D.A.; Andersen, L.K.; Davis, M.D. Calcinosis cutis occurring in association with autoimmune connective tissue disease: The Mayo Clinic experience with 78 patients, 1996–2009. Arch. Dermatol. 2012, 148, 455–462. [Google Scholar]
- Gutierrez, A., Jr.; Wetter, D.A. Calcinosis cutis in autoimmune connective tissue diseases. Dermatol. Ther. 2012, 25, 195–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hida, T.; Minami, M.; Kubo, Y. Bilateral leg ulcers secondary to dystrophic calcinosis in a patient with rheumatoid arthritis. J. Med. Investig. 2017, 64, 308–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, J.S.; Fairley, J.A. Calcifying disorders of the skin. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 1995, 33, 693–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearson, D.R.; Werth, V.P.; Pappas-Taffer, L. Systemic sclerosis: Current concepts of skin and systemic manifestations. Clin. Dermatol. 2018, 36, 459–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mormile, I.; Mormile, M.; Rea, G.; Petraroli, A.; Barbieri, V.; de Paulis, A.; Rossi, F.W. Spontaneous Pneumo-Mediastinum in a Post-COVID-19 Patient with Systemic Sclerosis. Healthcare 2022, 10, 529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, V.; Herrick, A.L.; Ingegnoli, F.; Damjanov, N.; De Angelis, R.; Denton, C.P.; Distler, O.; Espejo, K.; Foeldvari, I.; Frech, T.; et al. Standardisation of nailfold capillaroscopy for the assessment of patients with Raynaud’s phenomenon and systemic sclerosis. Autoimmun. Rev. 2020, 19, 102458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Napolitano, F.P.L.; Mormile, I.; Barrella, V.; de Paulis, A.; Montuori, N.; Rossi, F.W. Water from Nitrodi’s Spring Induces Dermal Fibroblast and Keratinocyte Activation, Thus Promoting Wound Repair in the Skin: An In Vitro Study. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 5357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cutolo, M.; Soldano, S.; Smith, V. Pathophysiology of systemic sclerosis: Current understanding and new insights. Expert Rev. Clin. Immunol. 2019, 15, 753–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belloli, L.; Ughi, N.; Massarotti, M.; Marasini, B.; Biondi, M.L.; Brambilla, G. Role of fetuin-A in systemic sclerosis-associated calcinosis. J. Rheumatol. 2010, 37, 2638–2639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz-Dominguez, M.P.; Garcia-Collinot, G.; Saavedra, M.A.; Medina, G.; Carranza-Muleiro, R.A.; Vera-Lastra, O.L.; Jara, L.J. Clinical, biochemical, and radiological characterization of the calcinosis in a cohort of Mexican patients with systemic sclerosis. Clin. Rheumatol. 2017, 36, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morgan, N.D.; Shah, A.A.; Mayes, M.D.; Domsic, R.T.; Medsger, T.A., Jr.; Steen, V.D.; Varga, J.; Carns, M.; Ramos, P.S.; Silver, R.M.; et al. Clinical and serological features of systemic sclerosis in a multicenter African American cohort: Analysis of the genome research in African American scleroderma patients clinical database. Medicine 2017, 96, e8980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, C.; Plaas, A.; Varga, J. Calcinosis in Systemic Sclerosis: Updates in Pathophysiology, Evaluation, and Treatment. Curr. Rheumatol. Rep. 2020, 22, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vayssairat, M.; Hidouche, D.; Abdoucheli-Baudot, N.; Gaitz, J.P. Clinical significance of subcutaneous calcinosis in patients with systemic sclerosis. Does diltiazem induce its regression? Ann. Rheum. Dis. 1998, 57, 252–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valenzuela, A.; Song, P.; Chung, L. Calcinosis in scleroderma. Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 2018, 30, 554–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polio, J.L.; Stern, P.J. Digital nerve calcification in CREST syndrome. J. Hand Surg. Am. 1989, 14, 201–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avouac, J.; Mogavero, G.; Guerini, H.; Drape, J.L.; Mathieu, A.; Kahan, A.; Allanore, Y. Predictive factors of hand radiographic lesions in systemic sclerosis: A prospective study. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2011, 70, 630–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koutaissoff, S.; Vanthuyne, M.; Smith, V.; De Langhe, E.; Depresseux, G.; Westhovens, R.; De Keyser, F.; Malghem, J.; Houssiau, F.A. Hand radiological damage in systemic sclerosis: Comparison with a control group and clinical and functional correlations. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2011, 40, 455–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morardet, L.; Avouac, J.; Sammour, M.; Baron, M.; Kahan, A.; Feydy, A.; Allanore, Y. Late Nailfold Videocapillaroscopy Pattern Associated With Hand Calcinosis and Acro-Osteolysis in Systemic Sclerosis. Arthritis Care Res. 2016, 68, 366–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cesoni Marcelli, A.; Loffredo, S.; Petraroli, A.; Carucci, L.; Mormile, I.; Ferrara, A.L.; Spadaro, G.; Genovese, A.; Bova, M. Nailfold Videocapillaroscopy Findings in Bradykinin-Mediated Angioedema. J. Investig. Allergol. Clin. Immunol. 2021, 31, 404–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manning, J.B.; Marjanovic, E.; Moore, T.L.; Dinsdale, G.; Wilkinson, S.; Dickinson, M.R.; Herrick, A.L.; Murray, A.K. A pilot study of cutaneous oxygenation and perfusion in systemic sclerosis-related digital calcinosis. Rheumatology 2020, 59, 3109–3111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fairchild, R.; Chung, M.; Sharpless, L.; Li, S.; Chung, L. Ultrasound Detection of Calcinosis and Association With Ulnar Artery Occlusion in Patients With Systemic Sclerosis. Arthritis Care Res. 2021, 73, 1332–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valenzuela, A.; Baron, M.; Rodriguez-Reyna, T.S.; Proudman, S.; Khanna, D.; Young, A.; Hinchcliff, M.; Steen, V.; Gordon, J.; Hsu, V.; et al. Calcinosis is associated with ischemic manifestations and increased disability in patients with systemic sclerosis. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2020, 50, 891–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muktabhant, C.; Thammaroj, P.; Chowchuen, P.; Foocharoen, C. Prevalence and clinical association with calcinosis cutis in early systemic sclerosis. Mod. Rheumatol. 2021, 31, 1113–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dovio, A.; Data, V.; Carignola, R.; Calzolari, G.; Vitetta, R.; Ventura, M.; Saba, L.; Severino, A.; Angeli, A. Circulating osteoprotegerin and soluble RANK ligand in systemic sclerosis. J. Rheumatol. 2008, 35, 2206–2213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantero-Nieto, L.; Alvarez-Cienfuegos, A.; Garcia-Gomez, J.A.; Martin, J.; Gonzalez-Gay, M.A.; Ortego-Centeno, N. Role of fibroblast growth factor-23 in calcinosis in women with systemic sclerosis. Acta Reumatol. Port. 2020, 45, 259–264. [Google Scholar]
- Bartoli, F.; Fiori, G.; Braschi, F.; Amanzi, L.; Bruni, C.; Blagojevic, J.; Bellando-Randone, S.; Cometi, L.; de Souza Mueller, C.; Guiducci, S.; et al. Calcinosis in systemic sclerosis: Subsets, distribution and complications. Rheumatology 2016, 55, 1610–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, R.G.; Featherstone, G.L.; Raasch, R.H.; McCartney, W.H.; Hadler, N.M. Treatment of calcinosis universalis with low-dose warfarin. Am. J. Med. 1987, 83, 72–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krusche, M.; Schneider, U.; Diekhoff, T. Calcinosis Universalis in Systemic Sclerosis. Dtsch. Arztebl. Int. 2021, 118, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alhassan, E. Calcinosis universalis in systemic sclerosis. ACR Open Rheumatol. 2023, 5, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Modak, R.; Viswanath, V. Calcinosis cutis universalis in systemic sclerosis. Indian J. Dermatol. Venereol. Leprol. 2018, 84, 353–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gushi, A.; Kanekura, T.; Mochitomi, Y.; Kawabata, H.; Kanzaki, T. Pseudoxanthoma elasticum (PXE)-like calcification in adult dermatomyositis. J. Dermatol. 2002, 29, 423–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, A.; Morita, A.; Shintani, Y.; Sakakibara, S.; Tsuji, T. Localized linear scleroderma with cutaneous calcinosis. J. Dermatol. 2002, 29, 112–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zanatta, E.; Desportes, M.; Do, H.H.; Avouac, J.; Doria, A.; Feydy, A.; Allanore, Y. Pseudotumoral calcinosis in systemic sclerosis: Data from systematic literature review and case series from two referral centres. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2020, 50, 1339–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Host, L.V.; Campochiaro, C.; Afonso, A.; Nihtyanova, S.I.; Denton, C.P.; Ong, V.H. High proton pump inhibitor exposure increases risk of calcinosis in systemic sclerosis. Rheumatology 2021, 60, 849–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costarelli, L.; Giacconi, R.; Malavolta, M.; Basso, A.; Piacenza, F.; Provinciali, M.; Maggio, M.G.; Corsonello, A.; Lattanzio, F. Different transcriptional profiling between senescent and non-senescent human coronary artery endothelial cells (HCAECs) by Omeprazole and Lansoprazole treatment. Biogerontology 2017, 18, 217–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamoto, T.; Hatakeyama, S.; Hosogoe, S.; Tanaka, Y.; Imanishi, K.; Takashima, T.; Saitoh, F.; Suzuki, T.; Ohyama, C. Proton pump inhibitor as an independent factor of progression of abdominal aortic calcification in patients on maintenance hemodialysis. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0199160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yepuri, G.; Sukhovershin, R.; Nazari-Shafti, T.Z.; Petrascheck, M.; Ghebre, Y.T.; Cooke, J.P. Proton Pump Inhibitors Accelerate Endothelial Senescence. Circ. Res. 2016, 118, e36–e42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shreiner, A.B.; Murray, C.; Denton, C.; Khanna, D. Gastrointestinal Manifestations of Systemic Sclerosis. J. Scleroderma Relat. Disord. 2016, 1, 247–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mormile, M.; Mormile, I.; Palladino, F.; Molino, A.; Ruggiero, S.; Telesca, D.A.; Cappello, C.; Sivero, L. Gastro-esophageal reflux disease influence on asthma symptoms: Assessment of non-responder to the standard treatment. Minerva. Pneumol. 2015, 54, 157–159. [Google Scholar]
- Hughes, M.; Herrick, A.L. Diagnosis and management of systemic sclerosis-related calcinosis. Expert Rev. Clin. Immunol. 2023, 19, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalakas, M.C.; Hohlfeld, R. Polymyositis and dermatomyositis. Lancet 2003, 362, 971–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Findlay, A.R.; Goyal, N.A.; Mozaffar, T. An overview of polymyositis and dermatomyositis. Muscle Nerve 2015, 51, 638–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahr, Z.A.; Baer, A.N. Malignancy in myositis. Curr. Rheumatol. Rep. 2011, 13, 208–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strowd, L.C.; Jorizzo, J.L. Review of dermatomyositis: Establishing the diagnosis and treatment algorithm. J. Dermatol. Treat. 2013, 24, 418–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Targoff, I.N. Laboratory testing in the diagnosis and management of idiopathic inflammatory myopathies. Rheum. Dis. Clin. N. Am. 2002, 28, 859–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrouk, M.; Nousari, Y.; Waibel, J.S. Novel treatment of calcifications from dermatomyositis with picosecond and carbon dioxide laser. JAAD Case Rep. 2020, 6, 852–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fredi, M.; Bartoli, F.; Cavazzana, I.; Ceribelli, A.; Carabellese, N.; Tincani, A.; Satoh, M.; Franceschini, F. Calcinosis in poly-dermatomyositis: Clinical and laboratory predictors and treatment options. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2017, 35, 303–308. [Google Scholar]
- Clemente, G.; Piotto, D.G.; Barbosa, C.; Peracchi, O.A.; Len, C.A.; Hilario, M.O.; Terreri, M.T. High frequency of calcinosis in juvenile dermatomyositis: A risk factor study. Rev. Bras. Reumatol. 2012, 52, 549–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCann, L.J.; Juggins, A.D.; Maillard, S.M.; Wedderburn, L.R.; Davidson, J.E.; Murray, K.J.; Pilkington, C.A.; Juvenile Dermatomyositis Research Group. The Juvenile Dermatomyositis National Registry and Repository (UK and Ireland)--clinical characteristics of children recruited within the first 5 yr. Rheumatology 2006, 45, 1255–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sallum, A.M.; Pivato, F.C.; Doria-Filho, U.; Aikawa, N.E.; Liphaus, B.L.; Marie, S.K.; Silva, C.A. Risk factors associated with calcinosis of juvenile dermatomyositis. J. Pediatr. 2008, 84, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jawad, A.S.M. Calcinosis cutis universalis in dermatopathic dermatomyositis. Rheumatology 2021, 60, 470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Codina, A.; Camprodon-Gomez, M.; Pope, J.E. Giant Calcinosis in Dermatomyositis and Scleroderma Overlap. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020, 72, 1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowry, C.A.; Pilkington, C.A. Juvenile dermatomyositis: Extramuscular manifestations and their management. Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 2009, 21, 575–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valenzuela, A.; Chung, L.; Casciola-Rosen, L.; Fiorentino, D. Identification of clinical features and autoantibodies associated with calcinosis in dermatomyositis. JAMA Dermatol. 2014, 150, 724–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Yang, H.; Li, S.; Tian, X.; Wang, G. Clinical features, treatments and outcomes of calcinosis in adult patients with dermatomyositis: A single cohort study. Rheumatology 2021, 60, 2958–2962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, M.; Ueno, K.; Ishikawa, S.; Kasahara, Y.; Yachie, A. Role of activated macrophage and inflammatory cytokines in the development of calcinosis in juvenile dermatomyositis. Rheumatology 2014, 53, 766–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamyrova, G.; O’Hanlon, T.P.; Sillers, L.; Malley, K.; James-Newton, L.; Parks, C.G.; Cooper, G.S.; Pandey, J.P.; Miller, F.W.; Rider, L.G.; et al. Cytokine gene polymorphisms as risk and severity factors for juvenile dermatomyositis. Arthritis Rheum. 2008, 58, 3941–3950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avouac, J.; Guerini, H.; Wipff, J.; Assous, N.; Chevrot, A.; Kahan, A.; Allanore, Y. Radiological hand involvement in systemic sclerosis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2006, 65, 1088–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farzaneh-Far, A.; Proudfoot, D.; Weissberg, P.L.; Shanahan, C.M. Matrix gla protein is regulated by a mechanism functionally related to the calcium-sensing receptor. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2000, 277, 736–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weinel, S.; Callen, J.P. Calcinosis cutis complicating adult-onset dermatomyositis. Arch. Dermatol. 2004, 140, 365–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, F.; Williams, P.; Batchelor, R.; Downs, A.; Haigh, R. Successful treatment of dermatomyositis and associated calcinosis with adalimumab. Clin. Exp. Dermatol. 2020, 45, 945–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahn, J.S.; Deverapalli, S.C.; Rosmarin, D.M. JAK-STAT signaling pathway inhibition: A role for treatment of discoid lupus erythematosus and dermatomyositis. Int. J. Dermatol. 2018, 57, 1007–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Illa, I.; Gallardo, E.; Gimeno, R.; Serrano, C.; Ferrer, I.; Juarez, C. Signal transducer and activator of transcription 1 in human muscle: Implications in inflammatory myopathies. Am. J. Pathol. 1997, 151, 81–88. [Google Scholar]
- Wendel, S.; Venhoff, N.; Frye, B.C.; May, A.M.; Agarwal, P.; Rizzi, M.; Voll, R.E.; Thiel, J. Successful treatment of extensive calcifications and acute pulmonary involvement in dermatomyositis with the Janus-Kinase inhibitor tofacitinib—A report of two cases. J. Autoimmun. 2019, 100, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchbinder, R.; Forbes, A.; Hall, S.; Dennett, X.; Giles, G. Incidence of malignant disease in biopsy-proven inflammatory myopathy. A population-based cohort study. Ann. Intern. Med. 2001, 134, 1087–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, R.S.; Agrawal, J.R.; Agrawal, B.L.; Nath, A.R.; Agrawal, A.R.; Gaddipat, J.C.; Garnett, R.F., Jr. Some unusual paraneoplastic syndromes. Case 3. Metastatic pulmonary calcification causing hypoxemia in male breast cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2003, 21, 2622–2624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckardt, J.J.; Ivins, J.C.; Perry, H.O.; Unni, K.K. Osteosarcoma arising in heterotopic ossification of dermatomyositis: Case report and review of the literature. Cancer 1981, 48, 1256–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morris, P.; Herrera-Guerra, A.; Parham, D. Lymphoma arising from a calcinotic lesion in a patient with juvenile dermatomyositis. Pediatr. Dermatol. 2009, 26, 159–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pelosof, L.C.; Gerber, D.E. Paraneoplastic syndromes: An approach to diagnosis and treatment. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2010, 85, 838–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcondes, F.; Scheinberg, M. Belimumab in the treatment of systemic lupus erythematous: An evidence based review of its place in therapy. Autoimmun. Rev. 2018, 17, 103–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mormile, I.; Della Casa, F.; Petraroli, A.; Furno, A.; Granata, F.; Portella, G.; Rossi, F.W.; de Paulis, A. Immunogenicity and Safety of mRNA Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Vaccines in Patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Vaccines 2022, 10, 1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okada, J.; Nomura, M.; Shirataka, M.; Kondo, H. Prevalence of soft tissue calcifications in patients with SLE and effects of alfacarcidol. Lupus 1999, 8, 456–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugimoto, H.; Hyodoh, K.; Kikuno, M.; Furuse, M. Periarticular calcification in systemic lupus erythematosus. J. Rheumatol. 1999, 26, 574–579. [Google Scholar]
- Ammouri, W.; Harmouche, H.; Ahrikat, O.; Maamar, M.; Tazi, M.Z.; Adanaoui, M. Extensive calcinosis cutis in a patient with systemic lupus erythematosus: An exceptional complication. Presse Med. 2018, 47, 410–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.S.; Choi, K.C.; Kim, H.S.; Song, I.G.; Shin, B.S. Calcinosis cutis in systemic lupus erythematosus: A case report and review of the published work. J. Dermatol. 2010, 37, 815–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khudadah, M.; Jawad, A.; Pyne, D. Calcinosis cutis universalis in a patient with systemic lupus erythematosus: A case report. Lupus 2020, 29, 1630–1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Achebe, I.; Mbachi, C.; Asotibe, J.C.; Paintsil, I. Dystrophic Calcinosis Cutis in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Cureus 2020, 12, e8727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dima, A.; Balanescu, P.; Baicus, C. Pharmacological treatment in calcinosis cutis associated with connective-tissue diseases. Rom. J. Intern. Med. 2014, 52, 55–67. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.L.; Wu, W.T.; Ou, T.T. Extensive calcinosis cutis universalis in a patient with systemic lupus erythematosus: 10-year treatment experience. Kaohsiung J. Med. Sci. 2014, 30, 639–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez, A.T.; Grossman, M.E. Facial calcinosis cutis in a patient with systemic lupus erythematosus: A case report of tissue injury owing to photosensitivity as the cause of dystrophic calcification. JAAD Case Rep. 2017, 3, 460–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, H.; Liao, M.; Qiu, S.; Lu, R.; Lu, C. Linear cutaneous lupus erythematosus with calcinosis cutis and milia. Pediatr. Dermatol. 2015, 32, e33–e35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhatia, S.; Silverberg, N.B.; Don, P.C.; Weinberg, J.M. Extensive calcinosis cutis in association with systemic lupus erythematosus. Acta Derm. Venereol. 2001, 81, 446–447. [Google Scholar]
- Rothe, M.J.; Grant-Kels, J.M.; Rothfield, N.F. Extensive calcinosis cutis with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arch. Dermatol. 1990, 126, 1060–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cousins, M.A.; Jones, D.B.; Whyte, M.P.; Monafo, W.W. Surgical management of calcinosis cutis universalis in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1997, 40, 570–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiao, J.; Gaffney, R.; Fedeles, F. A Retrospective Study of Calcinosis Cutis in Patients With Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. J. Drugs Dermatol. 2022, 21, 1137. [Google Scholar]
- Both, T.; Dalm, V.A.; van Hagen, P.M.; van Daele, P.L. Reviewing primary Sjogren’s syndrome: Beyond the dryness—From pathophysiology to diagnosis and treatment. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2017, 14, 191–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carsons, S.E.; Vivino, F.B.; Parke, A.; Carteron, N.; Sankar, V.; Brasington, R.; Brennan, M.T.; Ehlers, W.; Fox, R.; Scofield, H.; et al. Treatment Guidelines for Rheumatologic Manifestations of Sjogren’s Syndrome: Use of Biologic Agents, Management of Fatigue, and Inflammatory Musculoskeletal Pain. Arthritis Care Res. 2017, 69, 517–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mormile, I.; Mormile, M.; Rossi, F.W.; Williams, M.; Valente, T.; Candia, C.; Granata, F.; Rega, R.; Orlandi, M.; Matucci-Cerinic, M.; et al. Radiological patterns and pulmonary function values of lung involvement in primary Sjogren’s syndrome: A pilot analysis. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 998028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aiyegbusi, O.; McGregor, L.; McGeoch, L.; Kipgen, D.; Geddes, C.C.; Stevens, K.I. Renal Disease in Primary Sjogren’s Syndrome. Rheumatol. Ther. 2021, 8, 63–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chatzis, L.G.; Stergiou, I.E.; Goules, A.V.; Pezoulas, V.; Tsourouflis, G.; Fotiadis, D.; Tzioufas, A.G.; Voulgarelis, M. Clinical picture, outcome and predictive factors of lymphoma in primary Sjogren’s syndrome: Results from a harmonized dataset (1981–2021). Rheumatology 2022, 61, 3576–3585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, G.; Dai, F.; Chen, S.; Sun, Y.; Qian, H.; Yang, G.; Liu, Y.; Shi, G. Neurological Involvement in Patients With Primary Sjogren’s Syndrome. J. Clin. Rheumatol. 2021, 27, 50–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llamas-Velasco, M.; Eguren, C.; Santiago, D.; Garcia-Garcia, C.; Fraga, J.; Garcia-Diez, A. Calcinosis cutis and Sjogren’s syndrome. Lupus 2010, 19, 762–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fueki, H.; Hino, R.; Yoshioka, M.; Nakamura, M.; Tokura, Y. Calcinosis cutis associated with primary Sjogren’s syndrome: Strong expression of osteonectin and matrix Gla protein. Rheumatology 2011, 50, 2318–2320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasserman, P.L.; Wiesler, C.; Kurra, C.; Omman, R.; Taylor, K.; Puri, R. MR imaging findings of calcinosis cutis in primary Sjogren syndrome, a rare manifestation. Radiol. Case Rep. 2020, 15, 1029–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuchida, Y.; Sumitomo, S.; Fujio, K.; Yamamoto, K. Massive calcinosis cutis associated with primary Sjogren’s syndrome. BMJ Case Rep. 2016, 2016, bcr2015214006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.H.; Chang, C.W.; Kuo, Y.R.; Huang, S.H. Widespread dystrophic calcinosis cutis in both thighs associated with Sjogren’s syndrome: A case of 20-year follow-up. Kaohsiung J. Med. Sci. 2019, 35, 648–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smolen, J.S.; Landewe, R.B.M.; Bergstra, S.A.; Kerschbaumer, A.; Sepriano, A.; Aletaha, D.; Caporali, R.; Edwards, C.J.; Hyrich, K.L.; Pope, J.E.; et al. EULAR recommendations for the management of rheumatoid arthritis with synthetic and biological disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs: 2022 update. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2023, 82, 3–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrelli, F.; Mariani, F.M.; Alunno, A.; Puxeddu, I. Pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis: One year in review 2022. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2022, 40, 475–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mormile, I.; Rossi, F.W.; Prevete, N.; Granata, F.; Pucino, V.; de Paulis, A. The N-Formyl Peptide Receptors and Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Dangerous Liaison or Confusing Relationship? Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 685214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Spigna, G.; Rossi, F.W.; Mormile, I.; Ladogana, P.; Buonavolonta, L.; Covelli, B.; Salzano, S.; Napolitano, F.; Giannini, A.; Postiglione, L. Serum Metalloprotease 3 (MMP-3) biomarker of therapeutic efficacy during treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. J. Biol. Regul. Homeost. Agents 2021, 35, 1041–1045. [Google Scholar]
- Mormile, I.; Russo, R.; Andolfo, I.; de Paulis, A.; Rossi, F.W.; Rendina, D. Rheumatoid arthritis and osteogenesis imperfecta: Is there a genetic causal association? Osteoporos. Int. 2022, 33, 2233–2235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harigane, K.; Mochida, Y.; Ishii, K.; Ono, S.; Mitsugi, N.; Saito, T. Dystrophic calcinosis in a patient with rheumatoid arthritis. Mod. Rheumatol. 2011, 21, 85–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lembo, C.; Raimondo, A.; de Paulis, A.; Mormile, I.; Rossi, F.W.; Lembo, S.; Balato, A. Clinical predictors of psoriatic arthritis and osteoclast differentiation. Exp. Dermatol. 2021, 30, 1834–1837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, T.; Bettencourt, N.; Mendonca, D.; Vasconcelos, C.; Gama, V.; Silva, B.M.; Selores, M. Epicardial adipose tissue and coronary artery calcification in psoriasis patients. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2015, 29, 270–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honma, M.; Shibuya, T.; Iwasaki, T.; Iinuma, S.; Takahashi, N.; Kishibe, M.; Minami-Hori, M.; Ishida-Yamamoto, A. Prevalence of coronary artery calcification in Japanese patients with psoriasis: A close correlation with bilateral diagonal earlobe creases. J. Dermatol. 2017, 44, 1122–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cutrone, P.; Marson, G. A case of calcinosis combined with psoriasis. Minerva Dermatol. 1954, 29, 211–216. [Google Scholar]
- Azami, A.; Mohebbipour Loron, A.; Anari, H.; Matin, S. Case report: A report of a rare case tumoral calcinosis syndrome in a patient afflicted with psoriatic arthritis. Arch. Osteoporos. 2020, 15, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pozzato, C.; Gattoni, F.; Baldini, U.; Marmini, A.; Cattaneo, M.; Uslenghi, C. Periarticular calcifications. A little-known sign of psoriatic arthritis. Radiol. Med. 1985, 71, 841–842. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Georgin-Lavialle, S.; Fayand, A.; Rodrigues, F.; Bachmeyer, C.; Savey, L.; Grateau, G. Autoinflammatory diseases: State of the art. Presse Med. 2019, 48, e25–e48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Della Casa, F.; Petraroli, A.; Mormile, I.; Lagnese, G.; Di Salvatore, A.; Rossi, F.W.; de Paulis, A. Adult-onset macrophage activation syndrome treated by interleukin-1 inhibition. Rheumatol. Adv. Pract. 2023, 7, rkad014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sota, J.; Vitale, A.; Wiesik-Szewczyk, E.; Frassi, M.; Lopalco, G.; Emmi, G.; Govoni, M.; de Paulis, A.; Marino, A.; Gidaro, A.; et al. Development and implementation of the AIDA international registry for patients with Schnitzler’s syndrome. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 931189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinohara, T.; Hidaka, T.; Matsuki, Y.; Suzuki, K.; Ohsuzu, F. Calcinosis cutis and intestinal pseudoobstruction in a patient with adult onset Still’s disease associated with recurrent relapses of disordered coagulopathy. Intern. Med. 1999, 38, 516–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geissler, B.; Agaimy, A.; Jungert, J.; Hartmann, A.; Carbon, R.; Knorr, C. Tumoral calcinosis of the gluteal region in a 14-year-old girl with juvenile polyarthritis. Eur. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2010, 20, 421–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, M.P.; Richardson, C.; Kirakossian, D.; Orandi, A.B.; Saketkoo, L.A.; Rider, L.G.; Schiffenbauer, A.; von Muhlen, C.A.; Chung, L.; International Myositis, A.; et al. Calcinosis Biomarkers in Adult and Juvenile Dermatomyositis. Autoimmun. Rev. 2020, 19, 102533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunawardena, H.; Wedderburn, L.R.; Chinoy, H.; Betteridge, Z.E.; North, J.; Ollier, W.E.; Cooper, R.G.; Oddis, C.V.; Ramanan, A.V.; Davidson, J.E.; et al. Autoantibodies to a 140-kd protein in juvenile dermatomyositis are associated with calcinosis. Arthritis Rheum. 2009, 60, 1807–1814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nozawa, T.; Bell-Peter, A.; Marcuz, J.A.; Whitney, K.; Vinik, O.; Shupak, R.; Dover, S.; Feldman, B.M. Early Abnormal Nailfold Capillary Changes Are Predictive of Calcinosis Development in Juvenile Dermatomyositis. J. Rheumatol. 2022, 49, 1250–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.E.; Ernste, F.C.; Davis, M.D.P.; Wetter, D.A. Topical sodium thiosulfate for calcinosis cutis associated with autoimmune connective tissue diseases: The Mayo Clinic experience, 2012–2017. Clin. Exp. Dermatol. 2019, 44, e189–e192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mormile, I.; Granata, F.; Punziano, A.; de Paulis, A.; Rossi, F.W. Immunosuppressive Treatment in Antiphospholipid Syndrome: Is It Worth It? Biomedicines 2021, 9, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asherson, R.A.; Frances, C.; Iaccarino, L.; Khamashta, M.A.; Malacarne, F.; Piette, J.C.; Tincani, A.; Doria, A. The antiphospholipid antibody syndrome: Diagnosis, skin manifestations and current therapy. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2006, 24, S46–S51. [Google Scholar]
- Turrent-Carriles, A.; Herrera-Felix, J.P.; Amigo, M.C. Renal Involvement in Antiphospholipid Syndrome. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuchiya, K.; Endo, C.; Kondo, A.; Fukuya, Y.; Honda, S.; Hirahara, S.; Majima, M.; Hanaoka, M.; Harigai, M.; Ishiguro, N. A case of non-uremic calciphylaxis associated with systemic lupus erythematosus and antiphospholipid syndrome. J. Dermatol. 2021, 48, e157–e158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nigwekar, S.U.; Bloch, D.B.; Nazarian, R.M.; Vermeer, C.; Booth, S.L.; Xu, D.; Thadhani, R.I.; Malhotra, R. Vitamin K-Dependent Carboxylation of Matrix Gla Protein Influences the Risk of Calciphylaxis. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2017, 28, 1717–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dominguez, A.R.; Goldman, S.E. Nonuremic calciphylaxis in a patient with rheumatoid arthritis and osteoporosis treated with teriparatide. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2014, 70, e41–e42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korkmaz, C.; Dundar, E.; Zubaroglu, I. Calciphylaxis in a patient with rheumatoid arthritis without renal failure and hyperparathyroidism: The possible role of long-term steroid use and protein S deficiency. Clin. Rheumatol. 2002, 21, 66–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zechlinski, J.J.; Angel, J.R. Calciphylaxis in the absence of renal disease: Secondary hyperparathyroidism and systemic lupus erythematosus. J. Rheumatol. 2009, 36, 2370–2371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliaga, L.G.; Barreira, J.C. Calciphylaxis in a patient with systemic lupus erythematosus without renal insufficiency or hyperparathyroidism. Lupus 2012, 21, 329–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pek, E.A.; Joseph, P.L.; Al Habeeb, A.S.; Albert, L.J. A Fatal Case of Calciphylaxis in a Patient with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus and Normal Renal Function. J. Rheumatol. 2016, 43, 456–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kusari, A.; Cotter, D.; Hinds, B.; Paravar, T. Non-uremic calciphylaxis in a patient with multiple rheumatologic diseases. Dermatol. Online J. 2019, 25, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traineau, H.; Aggarwal, R.; Monfort, J.B.; Senet, P.; Oddis, C.V.; Chizzolini, C.; Barbaud, A.; Frances, C.; Arnaud, L.; Chasset, F. Treatment of calcinosis cutis in systemic sclerosis and dermatomyositis: A review of the literature. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2020, 82, 317–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tristano, A.G.; Villarroel, J.L.; Rodriguez, M.A.; Millan, A. Calcinosis cutis universalis in a patient with systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin. Rheumatol. 2006, 25, 70–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reiter, N.; El-Shabrawi, L.; Leinweber, B.; Berghold, A.; Aberer, E. Calcinosis cutis: Part II. Treatment options. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2011, 65, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdallah-Lotf, M.; Grasland, A.; Vinceneux, P.; Sigal-Grinberg, M. Regression of cutis calcinosis with diltiazem in adult dermatomyositis. Eur. J. Dermatol. 2005, 15, 102–104. [Google Scholar]
- Mukamel, M.; Horev, G.; Mimouni, M. New insight into calcinosis of juvenile dermatomyositis: A study of composition and treatment. J. Pediatr. 2001, 138, 763–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marco Puche, A.; Calvo Penades, I.; Lopez Montesinos, B. Effectiveness of the treatment with intravenous pamidronate in calcinosis in juvenile dermatomyositis. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2010, 28, 135–140. [Google Scholar]
- Tayfur, A.C.; Topaloglu, R.; Gulhan, B.; Bilginer, Y. Bisphosphonates in juvenile dermatomyositis with dystrophic calcinosis. Mod. Rheumatol. 2015, 25, 615–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorge, A.; Szulawski, R.; Abhishek, F. Metastatic calcinosis cutis due to refractory hypercalcaemia responsive to denosumab in a patient with multiple sclerosis. BMJ Case Rep. 2019, 12, e223992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Sundh, A.E.; Quintana-Sancho, A.; Duran-Vian, C.; Reguero-DelCura, L.; Corrales-Martinez, A.F.; Gomez-Fernandez, C.; Gonzalez-Lopez, M.A. Clinical and ultrasound response to intralesional sodium thiosulfate for the treatment of calcinosis cutis in the setting of systemic sclerosis. A case-based review. Clin. Rheumatol. 2021, 40, 2985–2989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russo, D.; Capuano, A.; Cozzolino, M.; Napolitano, P.; Mosella, F.; Russo, L.; Saviano, C.; Zoccali, C. Multimodal treatment of calcific uraemic arteriolopathy (calciphylaxis): A case series. Clin. Kidney J. 2016, 9, 108–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baldwin, C.; Farah, M.; Leung, M.; Taylor, P.; Werb, R.; Kiaii, M.; Levin, A. Multi-intervention management of calciphylaxis: A report of 7 cases. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2011, 58, 988–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zitt, E.; Konig, M.; Vychytil, A.; Auinger, M.; Wallner, M.; Lingenhel, G.; Schilcher, G.; Rudnicki, M.; Salmhofer, H.; Lhotta, K. Use of sodium thiosulphate in a multi-interventional setting for the treatment of calciphylaxis in dialysis patients. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2013, 28, 1232–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badawi, A.H.; Patel, V.; Warner, A.E.; Hall, J.C. Dystrophic calcinosis cutis: Treatment with intravenous sodium thiosulfate. Cutis 2020, 106, E15–E17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mageau, A.; Guigonis, V.; Ratzimbasafy, V.; Bardin, T.; Richette, P.; Urena, P.; Ea, H.K. Intravenous sodium thiosulfate for treating tumoral calcinosis associated with systemic disorders: Report of four cases. Jt. Bone Spine 2017, 84, 341–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nigwekar, S.U.; Brunelli, S.M.; Meade, D.; Wang, W.; Hymes, J.; Lacson, E., Jr. Sodium thiosulfate therapy for calcific uremic arteriolopathy. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2013, 8, 1162–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campanilho-Marques, R.; Deakin, C.T.; Simou, S.; Papadopoulou, C.; Wedderburn, L.R.; Pilkington, C.A.; Juvenile Dermatomyositis Research, G. Retrospective analysis of infliximab and adalimumab treatment in a large cohort of juvenile dermatomyositis patients. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2020, 22, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riley, P.; McCann, L.J.; Maillard, S.M.; Woo, P.; Murray, K.J.; Pilkington, C.A. Effectiveness of infliximab in the treatment of refractory juvenile dermatomyositis with calcinosis. Rheumatology 2008, 47, 877–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daoussis, D.; Antonopoulos, I.; Liossis, S.N.; Yiannopoulos, G.; Andonopoulos, A.P. Treatment of systemic sclerosis-associated calcinosis: A case report of rituximab-induced regression of CREST-related calcinosis and review of the literature. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2012, 41, 822–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Paula, D.R.; Klem, F.B.; Lorencetti, P.G.; Muller, C.; Azevedo, V.F. Rituximab-induced regression of CREST-related calcinosis. Clin. Rheumatol. 2013, 32, 281–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aggarwal, R.; Loganathan, P.; Koontz, D.; Qi, Z.; Reed, A.M.; Oddis, C.V. Cutaneous improvement in refractory adult and juvenile dermatomyositis after treatment with rituximab. Rheumatology 2017, 56, 247–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bader-Meunier, B.; Decaluwe, H.; Barnerias, C.; Gherardi, R.; Quartier, P.; Faye, A.; Guigonis, V.; Pagnier, A.; Brochard, K.; Sibilia, J.; et al. Safety and efficacy of rituximab in severe juvenile dermatomyositis: Results from 9 patients from the French Autoimmunity and Rituximab registry. J. Rheumatol. 2011, 38, 1436–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moazedi-Fuerst, F.C.; Kielhauser, S.M.; Bodo, K.; Graninger, W.B. Dosage of rituximab in systemic sclerosis: 2-year results of five cases. Clin. Exp. Dermatol. 2015, 40, 211–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giuggioli, D.; Lumetti, F.; Colaci, M.; Fallahi, P.; Antonelli, A.; Ferri, C. Rituximab in the treatment of patients with systemic sclerosis. Our experience and review of the literature. Autoimmun. Rev. 2015, 14, 1072–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiblawi, S.H.; Fivenson, D.P. Apremilast as an adjuvant therapy for calcinosis cutis. JAAD Case Rep. 2019, 5, 874–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shneyderman, M.; Ahlawat, S.; Christopher-Stine, L.; Paik, J.J. Calcinosis in refractory dermatomyositis improves with tofacitinib monotherapy: A case series. Rheumatology 2021, 60, e387–e388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabbagh, S.; Almeida de Jesus, A.; Hwang, S.; Kuehn, H.S.; Kim, H.; Jung, L.; Carrasco, R.; Rosenzweig, S.; Goldbach-Mansky, R.; Rider, L.G. Treatment of anti-MDA5 autoantibody-positive juvenile dermatomyositis using tofacitinib. Brain 2019, 142, e59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galimberti, F.; Li, Y.; Fernandez, A.P. Intravenous immunoglobulin for treatment of dermatomyositis-associated dystrophic calcinosis. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2015, 73, 174–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schanz, S.; Ulmer, A.; Fierlbeck, G. Response of dystrophic calcification to intravenous immunoglobulin. Arch. Dermatol. 2008, 144, 585–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poormoghim, H.; Andalib, E.; Almasi, A.R.; Hadibigi, E. Systemic sclerosis and calcinosis cutis: Response to rituximab. J. Clin. Pharm. Ther. 2016, 41, 94–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoeltzel, M.F.; Oberle, E.J.; Robinson, A.B.; Agarwal, A.; Rider, L.G. The presentation, assessment, pathogenesis, and treatment of calcinosis in juvenile dermatomyositis. Curr. Rheumatol. Rep. 2014, 16, 467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
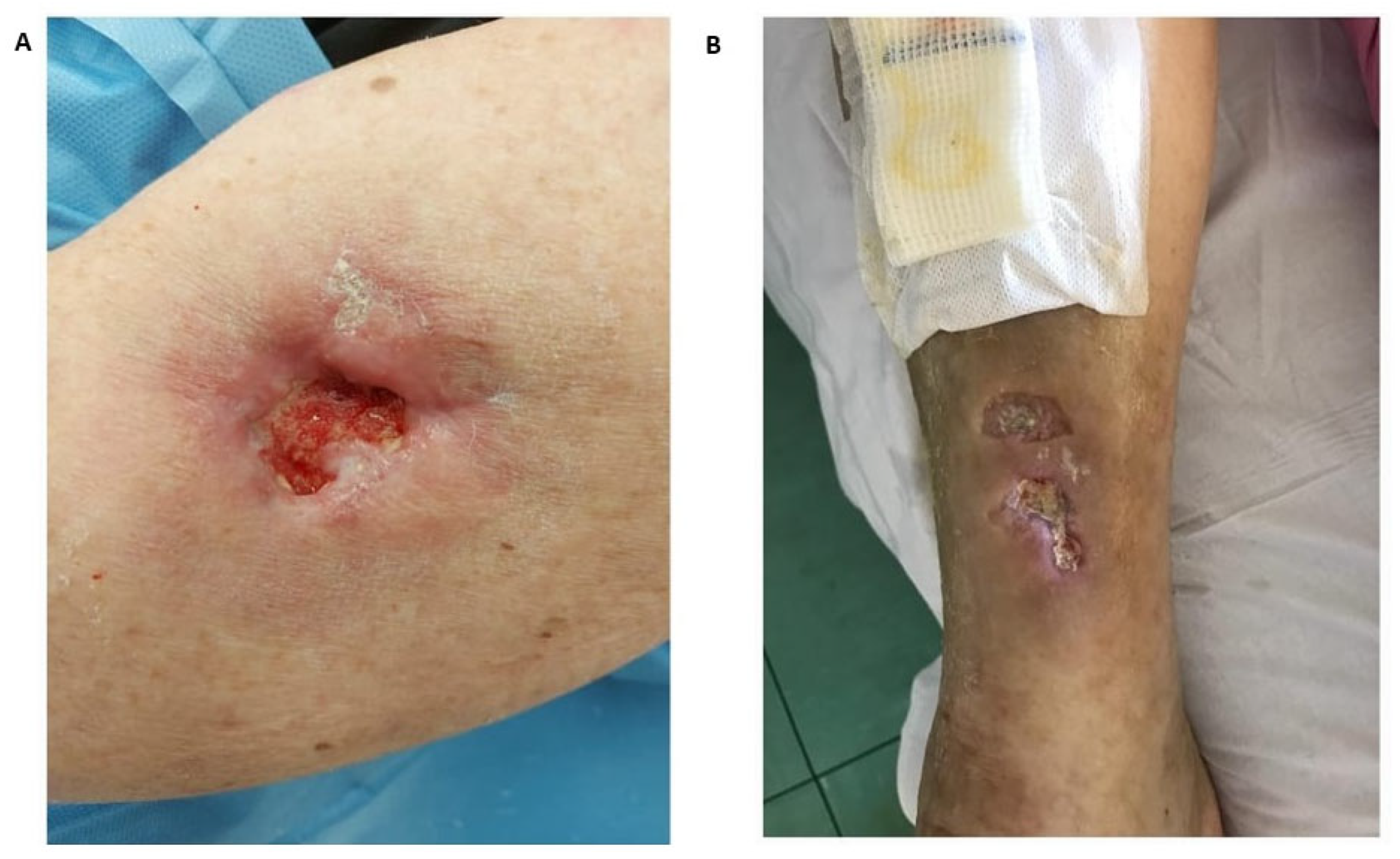
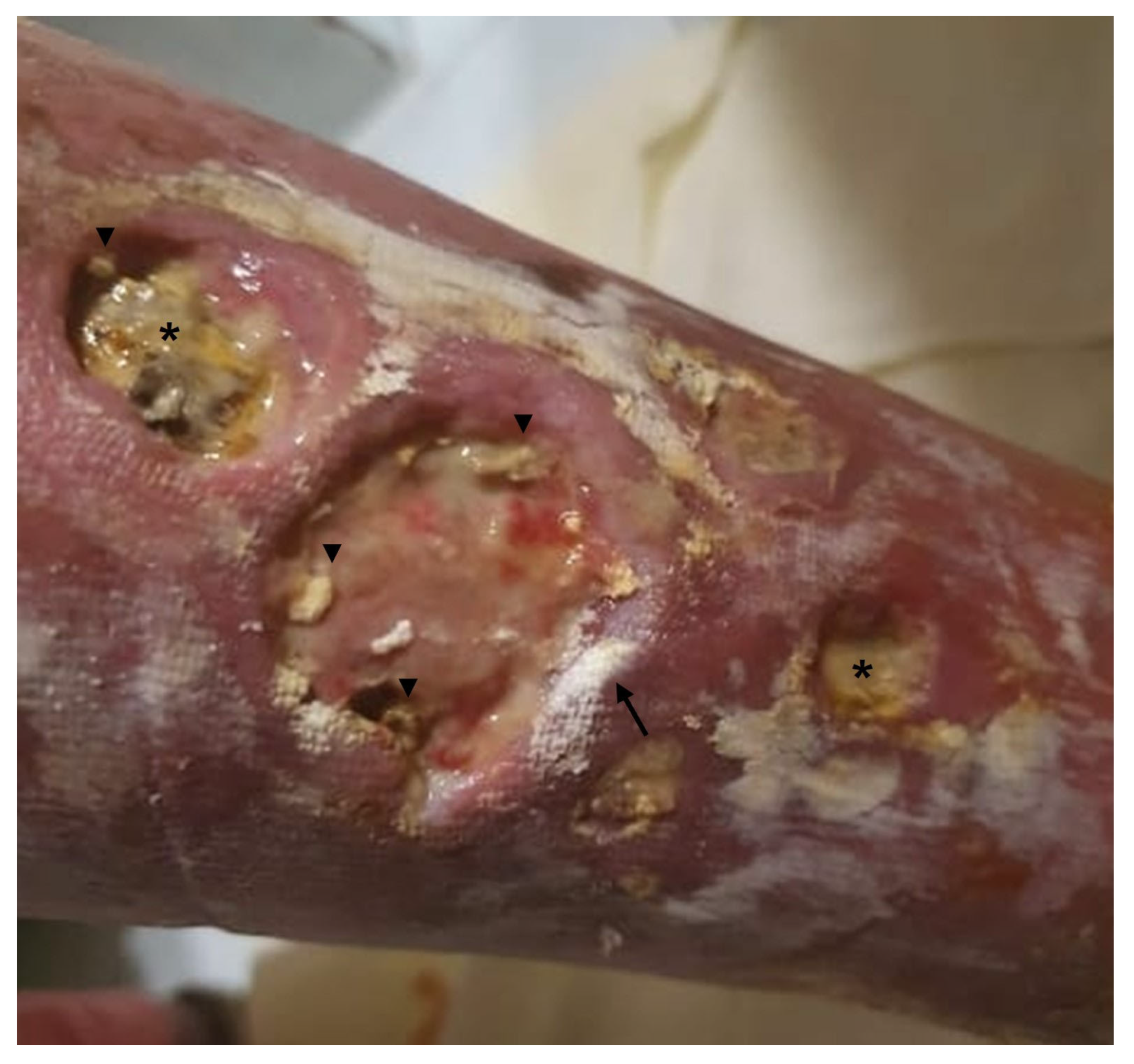
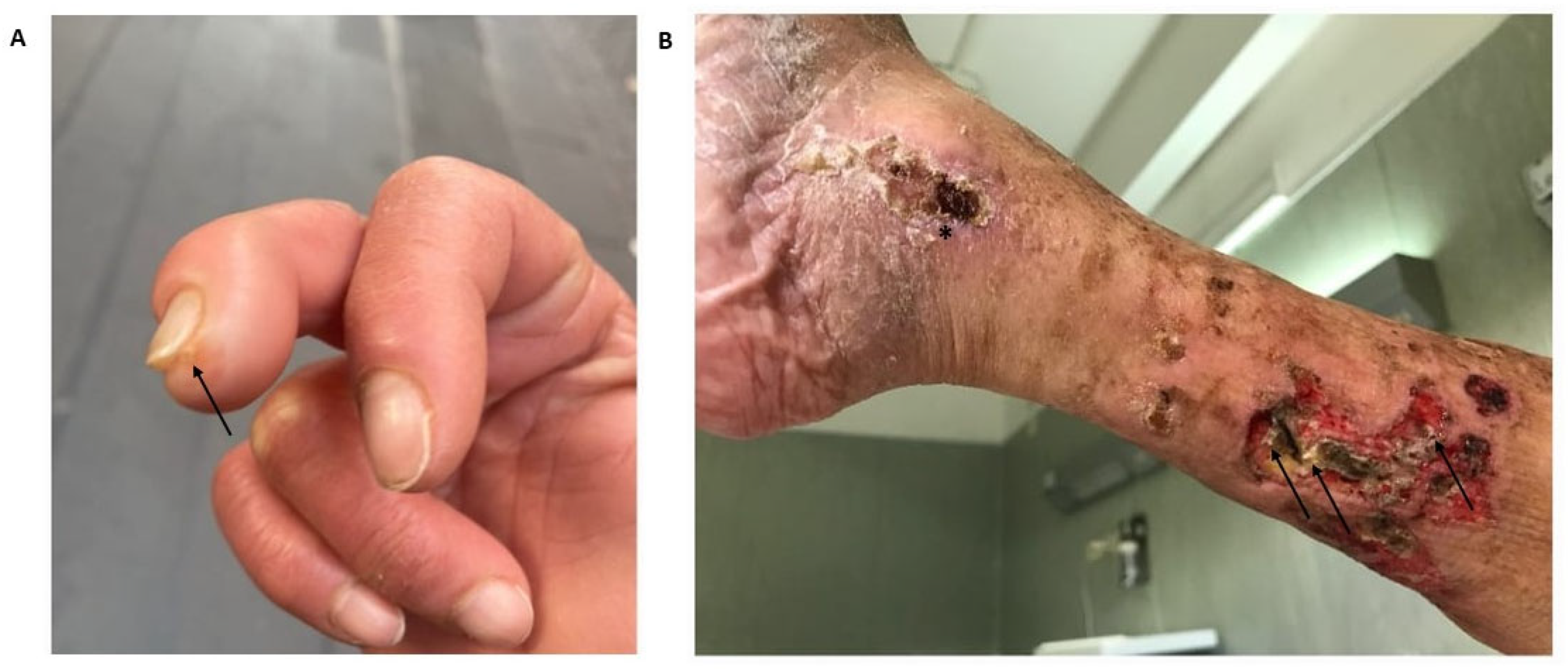
| Underlying Autoimmune Disease | Prevalence (%) | Preferential Locations | Predictive Factors for the Development of Calcinosis Cutis | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Systemic sclerosis | 18–49 |
|
| [1,14,23,24,25,26,28] |
| Dermatomyositis | 30–37 |
|
| [14,61] |
| Polymyositis | 1–3 |
|
| [14,61] |
| Juvenile dermatomyositis | 20–70 |
|
| [62,63,128,129,130] |
| Systemic lupus erythematosus | 3–40 |
|
| [2,14,86,87,88] |
| Undifferentiated connective tissue disease | 8–14 |
| Not available | [14,131] |
| Rheumatoid arthritis | rare |
| Not available | [14,16,116] |
| Primary Sjögren’s syndrome | rare |
| Not available | [106,107,108,109,110] |
| Adult-onset Still’s disease | rare |
| Not available | [126] |
| Juvenile polyarthritis | rare |
| Not available | [127] |
| Drug | Associated Autoimmune Disease | Number of Treated Patients (N) | Dose | Outcome [Number of Patients (%)] | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Adalimumab | DM | 1 | 40 mg/week | CR [1 (100%)] | [75] |
| JDM | 28 a | 24 mg/m2 every other week a | CR [8 (29%)] PR [15 (54%)] | [158] | |
| Infliximab | DM | 2 | 5 mg/kg/4 weeks | NR [2 (100%)] | [61] |
| JDM | 28 a | 6 mg/kg/4 weeks | CR [8 (29%)] PR [15 (54%)] | [158] | |
| JDM | 5 | 3 mg/kg at weeks 0/2/6 and every 8 weeks | PR [5 (100%)] | [159] | |
| Rituximab | CREST syndrome b | 1 | 375 mg/m2, 4 weekly infusions | CR [1 (100%)] | [160] |
| CREST syndrome | 1 | 375 mg/m2, 4 weekly infusions | CR [1 (100%)] | [161] | |
| DM | 7 | 0.575–1 g/m2 at weeks 0/1 | CR [1 (14%)] PR (NA) | [162] | |
| DM | 2 | NA | CR [0 (0%)] PR [1 (50%)] | [61] | |
| JDM | 22 | 0.575–1 g/m2 at weeks 0/1 | CR [1 (4%)] PR (NA) | [162] | |
| JDM | 6 | 2 × 500 mg/m2 (n = 3) 4 × 375 mg/m2 (n = 3) | NR [6 (100%)] | [163] | |
| SSc | 3 | 500 mg/m2 at weeks 0/2 then every 3 months | CR [3 (100%)] | [164] | |
| SSc | 6 | 375 mg/m2 at weeks 0/1/2/3 | CR [0 (0%)] PR [3 (50%)] | [165] | |
| Apremilast | CREST syndrome Morphea | 2 | 30 mg/day | PR [2 (100%)] | [166] |
| Tofacitinib | DM | 3 | NA | CR [3 (100%)] | [167] |
| JDM | 2 | 5–10 mgx2/day | CR [2 (100%)] | [168] | |
| IVIG | ACTD | 6 | 2 g/kg | NA [6 (100%)] | [14] |
| DM | 7 | 2 g/kg | CR [1 (14%)] | [61] | |
| DM | 8 | NA | PR [5 (63%)] | [169] | |
| CREST syndrome | 1 | 2 g/kg | CR [1 (100%)] | [170] | |
| Methotrexate | ACTD c | 1 | 20 mg/week | CR [1 (100%)] | [14] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mormile, I.; Mosella, F.; Turco, P.; Napolitano, F.; de Paulis, A.; Rossi, F.W. Calcinosis Cutis and Calciphylaxis in Autoimmune Connective Tissue Diseases. Vaccines 2023, 11, 898. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11050898
Mormile I, Mosella F, Turco P, Napolitano F, de Paulis A, Rossi FW. Calcinosis Cutis and Calciphylaxis in Autoimmune Connective Tissue Diseases. Vaccines. 2023; 11(5):898. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11050898
Chicago/Turabian StyleMormile, Ilaria, Francesca Mosella, Piergiorgio Turco, Filomena Napolitano, Amato de Paulis, and Francesca Wanda Rossi. 2023. "Calcinosis Cutis and Calciphylaxis in Autoimmune Connective Tissue Diseases" Vaccines 11, no. 5: 898. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11050898
APA StyleMormile, I., Mosella, F., Turco, P., Napolitano, F., de Paulis, A., & Rossi, F. W. (2023). Calcinosis Cutis and Calciphylaxis in Autoimmune Connective Tissue Diseases. Vaccines, 11(5), 898. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11050898








