Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor-Targeted Neoantigen Peptide Vaccination for the Treatment of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer and Glioblastoma
Abstract
:1. Introduction
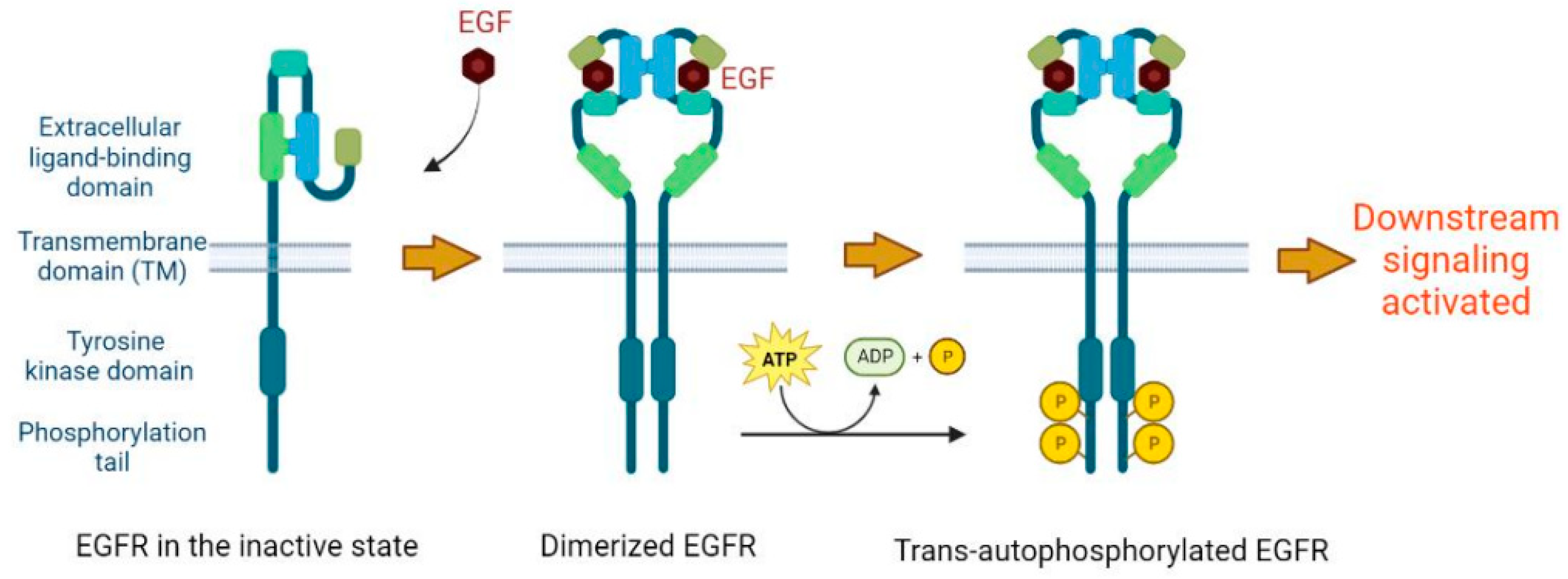
2. Basic Molecular Function of EGFR
3. The Role of EGFR in Cancer Development
4. EGFR Mutations and Implications for Neoantigen Presentation
5. EGFR Targeted Peptide Vaccine Studies in Mouse Models
6. Clinical Studies of EGFR Targeted Peptide Vaccines for the Treatment of Cancer
7. Studies of EGFR-Targeted Peptide Vaccines in Combination with Other Immunotherapies
| NeoAg No. | Epitope | EGFR Mutation | HLA-Restriction | Preclinical Study | Clinical Study | Clinical Trial No. | Trial Status | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | MQLMPFGCLL | T790M | HLA-A*02:01 | NeoAg-specific IFN-γ secretion and cytotoxicity in vitro | N/A | N/A | N/A | [37] |
| 2 | LIMQLMPFGCL | T790M | HLA-A*02:01 | |||||
| 3 | IMQLMPFGC | T790M | HLA-A*02:01 | NeoAg-specific IFN-γ secretion and cytotoxicity in vitro | N/A | N/A | N/A | [38] |
| 4 | MQLMPFGSLL | T790M/C797S | HLA-A*02:01 | NeoAg-specific IFN-γ secretion and cytotoxicity in vitro; peptide vaccine induced NeoAg-specific -specific CTL responses in mice model. | N/A | N/A | N/A | [71] |
| 5 | FGRAKLLGA | L858R | HLA-B*08:01 | In silico predictions and in vitro validation by binding assays | NSCLC patients bearing these mutations and corresponding protective HLAs were associated with better prognosis. | N/A | N/A | [39] |
| 6 | GRAKLLGAEEK | L858R | HLA-B*27:05 | |||||
| 7 | KVKIPVAIKT | E746_A750del | HLA-A*03:01 | |||||
| 8 | KVKIPVAIKTS | E746_A750del | HLA-A*03:01 | |||||
| 9 | KIPVAIKTSPK | E746_A750del | HLA-A*03:01 HLA-A*11:01 | |||||
| 10 | HVKITDFGR | L858R | HLA-A*31:01 | In silico predictions, NeoAg-specific IFN-γ secretion and pMHC tetramer staining | The EGFR L858R-derived NeoAg peptides cocktail vaccine was administered in patients with stage III/IV NSCLC and led to remarkable tumor regression and robust immune response. | ChiCTR-INR-16009867 | Recruiting | [39,60,61] |
| 11 | KITDFGRAK | L858R | HLA-A*11:01 | |||||
| 12 | HVKITDFGRAK | L858R | HLA-A*31:01 | |||||
| 13 | RAKLLGAEEK | L858R | HLA-A*31:01 | |||||
| 14 | LTSTVQLIM | T790M | HLA-C*15:02 | |||||
| 15 | LEEKKGNYVVTDH | EGFRvIII | N/A | Peptide vaccine induced humoral and cell immunity in multiple animal models and significantly inhibited tumor growth in mice with brain or lung cancer. | CDX-110 vaccination led to robust immune responses, greatly improved PFS and OS with low-grade toxicity in GBM patients. However, in a Phase III trial (ACT IV), the vaccine did not show sufficient efficacy. | ACTIVATE: NCT00643097 ACT II: N/A Re-ACT: NCT01498328 ACT III: NCT00458601 ACT IV: NCT01480479 | All completed | [47,48,49,50,51,52,53,54,55,56,57,58,59] |
| 16 | LEEKKGNYV | EGFRvIII | HLA-A*02:01 | NeoAg-specific IFN-γ secretion and cytotoxicity in vitro | N/A | N/A | N/A | [45] |
8. Conclusions and Future Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Levi-Montalcini, R.; Meyer, H.; Hamburger, V. In vitro experiments on the effects of mouse sarcomas 180 and 37 on the spinal and sympathetic ganglia of the chick embryo. Cancer Res. 1954, 14, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cohen, S. The stimulation of epidermal proliferation by a specific protein (EGF). Dev. Biol. 1965, 12, 394–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, S.; Ushiro, H.; Stoscheck, C.; Chinkers, M. A native 170,000 epidermal growth factor receptor-kinase complex from shed plasma membrane vesicles. J. Biol. Chem. 1982, 257, 1523–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uribe, M.L.; Marrocco, I.; Yarden, Y. EGFR in Cancer: Signaling Mechanisms, Drugs, and Acquired Resistance. Cancers 2021, 13, 2748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemmon, M.A.; Schlessinger, J. Cell signaling by receptor tyrosine kinases. Cell 2010, 141, 1117–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talukdar, S.; Emdad, L.; Das, S.K.; Fisher, P.B. EGFR: An essential receptor tyrosine kinase-regulator of cancer stem cells. Adv. Cancer Res. 2020, 147, 161–188. [Google Scholar]
- Lemmon, M.A.; Schlessinger, J.; Ferguson, K.M. The EGFR family: Not. so prototypical receptor tyrosine kinases. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2014, 6, a020768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigismund, S.; Avanzato, D.; Lanzetti, L. Emerging functions of the EGFR in cancer. Mol. Oncol. 2018, 12, 3–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, C.J.; Nussinov, R. Emerging Allosteric Mechanism of EGFR Activation in Physiological and Pathological Contexts. Biophys. J. 2019, 117, 5–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovacs, E.; Zorn, J.A.; Huang, Y.; Barros, T.; Kuriyan, J. A structural perspective on the regulation of the epidermal growth factor receptor. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2015, 84, 739–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levantini, E.; Maroni, G.; Del Re, M.; Tenen, D.G. EGFR signaling pathway as therapeutic target in human cancers. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2022, 85, 253–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergeron, J.J.; Di Guglielmo, G.M.; Dahan, S.; Dominguez, M.; Posner, B.I. Spatial and Temporal Regulation of Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Activation and Intracellular Signal Transduction. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2016, 85, 573–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freed, D.M.; Bessman, N.J.; Kiyatkin, A.; Salazar-Cavazos, E.; Byrne, P.O.; Moore, J.O.; Valley, C.C.; Ferguson, K.M.; Leahy, D.J.; Lidke, D.S.; et al. EGFR Ligands Differentially Stabilize Receptor Dimers to Specify Signaling Kinetics. Cell 2017, 171, 683–695.e18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conte, A.; Sigismund, S. Chapter Six—The Ubiquitin Network in the Control of EGFR Endocytosis and Signaling. Prog. Mol. Biol. Transl. Sci. 2016, 141, 225–276. [Google Scholar]
- Levkowitz, G.; Waterman, H.; Zamir, E.; Kam, Z.; Oved, S.; Langdon, W.Y.; Beguinot, L.; Geiger, B.; Yarden, Y. c-Cbl/Sli-1 regulates endocytic sorting and ubiquitination of the epidermal growth factor receptor. Genes. Dev. 1998, 12, 3663–3674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.J.; Huang, F.T.; Marusyk, A.; Sorkin, A. Grb2 regulates internalization of EGF receptors through clathrin-coated pits. Mol. Biol. Cell 2003, 14, 858–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foroughi, S.; Tie, J.; Gibbs, P.; Burgess, A.W. Epidermal growth factor receptor ligands: Targets for optimizing treatment of metastatic colorectal cancer. Growth Factors 2019, 37, 209–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, K.J.; Mill, C.; Lambert, S.; Buchman, J.; Wilson, T.R.; Hernandez-Gordillo, V.; Gallo, R.M.; Ades, L.M.; Settleman, J.; Riese, D.J. 2nd EGFR ligands exhibit functional differences in models of paracrine and autocrine signaling. Growth Factors 2012, 30, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, X.; Lambert, P.F.; Rapraeger, A.C.; Anderson, R.A. Stress-Induced EGFR Trafficking: Mechanisms, Functions, and Therapeutic Implications. Trends Cell Biol. 2016, 26, 352–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makinoshima, H.; Takita, M.; Matsumoto, S.; Yagishita, A.; Owada, S.; Esumi, H.; Tsuchihara, K. Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) signaling regulates global metabolic pathways in EGFR-mutated lung adenocarcinoma. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 20813–20823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, R.F.; Zhu, M.L.; Liu, M.M.; Xu, Y.T.; Yuan, L.L.; Bian, J.; Xia, Y.Z.; Kong, L.Y. EGFR mutation mediates resistance to EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors in NSCLC: From molecular mechanisms to clinical research. Pharmacol. Res. 2021, 167, 105583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diaz-Serrano, A.; Gella, P.; Jimenez, E.; Zugazagoitia, J.; Paz-Ares Rodriguez, L. Targeting EGFR in Lung Cancer: Current Standards and Developments. Drugs 2018, 78, 893–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Da Cunha Santos, G.; Shepherd, F.A.; Tsao, M.S. EGFR mutations and lung cancer. Annu. Rev. Pathol. 2011, 6, 49–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greenall, S.A.; Johns, T.G. EGFRvIII: The promiscuous mutation. Cell Death Discov. 2016, 2, 16049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, M.H.H.; Furnari, F.B.; Cavenee, W.K.; Bogler, O. Epidermal growth factor receptor signaling intensity determines intracellular protein interactions, ubiquitination, and internalization. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 6505–6510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, I.; Akita, R.; Vandlen, R.; Toomre, D.; Schlessinger, J.; Mellman, I. Spatial control of EGF receptor activation by reversible dimerization on living cells. Nature 2010, 464, 783–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiley, H.S. Anomalous binding of epidermal growth factor to A431 cells is due to the effect of high receptor densities and a saturable endocytic system. J. Cell Biol. 1988, 107, 801–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capuani, F.; Conte, A.; Argenzio, E.; Marchetti, L.; Priami, C.; Polo, S.; Di Fiore, P.P.; Sigismund, S.; Ciliberto, A. Quantitative analysis reveals how EGFR activation and downregulation are coupled in normal but not in cancer cells. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 7999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mellman, I.; Yarden, Y. Endocytosis and cancer. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2013, 5, a016949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roskoski, R., Jr. The ErbB/HER family of protein-tyrosine kinases and cancer. Pharmacol. Res. 2014, 79, 34–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chistiakov, D.A.; Chekhonin, I.V.; Chekhonin, V.P. The EGFR variant III mutant as a target for immunotherapy of glioblastoma multiforme. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2017, 810, 70–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, W.; Zhang, T.; Yu, H.; Foulke, J.G.; Tang, C.K. Hypophosphorylation of residue Y1045 leads to defective downregulation of EGFRvIII. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2006, 5, 1361–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ben-Chetrit, N.; Chetrit, D.; Russell, R.; Korner, C.; Mancini, M.; Abdul-Hai, A.; Itkin, T.; Carvalho, S.; Cohen-Dvashi, H.; Koestler, W.J.; et al. Synaptojanin 2 is a druggable mediator of metastasis and the gene is overexpressed and amplified in breast cancer. Sci. Signal. 2015, 8, ra7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabbah, D.A.; Hajjo, R.; Sweidan, K. Review on Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR) Structure, Signaling Pathways, Interactions, and Recent Updates of EGFR Inhibitors. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2020, 20, 815–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Lu, M.; Qin, Y.; Gao, W.; Tao, L.; Su, W.; Zhong, J. Neoantigen: A New Breakthrough in Tumor Immunotherapy. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 672356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battaglia, S. Neoantigen prediction from genomic and transcriptomic data. Methods Enzymol. 2020, 635, 267–281. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yamada, T.; Azuma, K.; Muta, E.; Kim, J.; Sugawara, S.; Zhang, G.L.; Matsueda, S.; Kasama-Kawaguchi, Y.; Yamashita, Y.; Yamashita, T.; et al. EGFR T790M mutation as a possible target for immunotherapy; identification of HLA-A*0201-restricted T cell epitopes derived from the EGFR T790M mutation. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e78389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ofuji, K.; Tada, Y.; Yoshikawa, T.; Shimomura, M.; Yoshimura, M.; Saito, K.; Nakamoto, Y.; Nakatsura, T. A peptide antigen derived from EGFR T790M is immunogenic in non-small cell lung cancer. Int. J. Oncol. 2015, 46, 497–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimou, A.; Grewe, P.; Sidney, J.; Sette, A.; Norman, P.J.; Doebele, R.C. HLA Class I Binding of Mutant EGFR Peptides in NSCLC Is Associated With Improved Survival. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2021, 16, 104–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Liu, J.; Hao, S.G.; Lan, B.; Zheng, X.B.; Xiong, J.N.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Gao, X.; Chen, C.B.; Chen, L.; et al. An EGFR L858R mutation identified in 1862 Chinese NSCLC patients can be a promising neoantigen vaccine therapeutic strategy. Front Immunol. 2022, 13, 1022598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heimberger, A.B.; Sampson, J.H. The PEPvIII-KLH (CDX-110) vaccine in glioblastoma multiforme patients. Expert. Opin. Biol. Ther. 2009, 9, 1087–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wikstrand, C.J.; Stanley, S.D.; Humphrey, P.A.; Pegram, C.N.; Archer, G.E.; Kurpad, S.; Shibuya, M.; Bigner, D.D. Investigation of a synthetic peptide as immunogen for a variant epidermal growth factor receptor associated with gliomas. J. Neuroimmunol. 1993, 46, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wikstrand, C.J.; McLendon, R.E.; Friedman, A.H.; Bigner, D.D. Cell surface localization and density of the tumor-associated variant of the epidermal growth factor receptor, EGFRvIII. Cancer Res. 1997, 57, 4130–4140. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zebertavage, L.; Bambina, S.; Shugart, J.; Alice, A.; Zens, K.D.; Lauer, P.; Hanson, B.; Gough, M.J.; Crittenden, M.R.; Bahjat, K.S. A microbial-based cancer vaccine for induction of EGFRvIII-specific CD8+ T cells and anti-tumor immunity. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0209153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, A.H.; Xiao, J.; Anker, L.; Hall, W.A.; Gregerson, D.S.; Cavenee, W.K.; Chen, W.; Low, W.C. Identification of EGFRvIII-derived CTL epitopes restricted by HLA A0201 for dendritic cell based immunotherapy of gliomas. J. Neurooncol. 2006, 76, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purev, E.; Cai, D.; Miller, E.; Swoboda, R.; Mayer, T.; Klein-Szanto, A.; Marincola, F.M.; Mick, R.; Otvos, L.; Wunner, W.; et al. Immune responses of breast cancer patients to mutated epidermal growth factor receptor (EGF-RvIII, Delta EGF-R, and de2–7 EGF-R). J. Immunol. 2004, 173, 6472–6480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heimberger, A.B.; Crotty, L.E.; Archer, G.E.; Hess, K.R.; Wikstrand, C.J.; Friedman, A.H.; Friedman, H.S.; Bigner, D.D.; Sampson, J.H. Epidermal growth factor receptor VIII peptide vaccination is efficacious against established intracerebral tumors. Clin. Cancer Res. 2003, 9, 4247–4254. [Google Scholar]
- Sampson, J.H.; Archer, G.E.; Mitchell, D.A.; Heimberger, A.B.; Herndon, J.E., 2nd; Lally-Goss, D.; McGehee-Norman, S.; Paolino, A.; Reardon, D.A.; Friedman, A.H.; et al. An epidermal growth factor receptor variant III-targeted vaccine is safe and immunogenic in patients with glioblastoma multiforme. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2009, 8, 2773–2779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sampson, J.H.; Crotty, L.E.; Lee, S.; Archer, G.E.; Ashley, D.M.; Wikstrand, C.J.; Hale, L.P.; Small, C.; Dranoff, G.; Friedman, A.H.; et al. Unarmed, tumor-specific monoclonal antibody effectively treats brain tumors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 7503–7508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luwor, R.B.; Johns, T.G.; Murone, C.; Huang, H.J.; Cavenee, W.K.; Ritter, G.; Old, L.J.; Burgess, A.W.; Scott, A.M. Monoclonal antibody 806 inhibits the growth of tumor xenografts expressing either the de2-7 or amplified epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) but not wild-type EGFR. Cancer Res. 2001, 61, 5355–5361. [Google Scholar]
- Mishima, K.; Johns, T.G.; Luwor, R.B.; Scott, A.M.; Stockert, E.; Jungbluth, A.A.; Ji, X.D.; Suvarna, P.; Voland, J.R.; Old, L.J.; et al. Growth suppression of intracranial xenografted glioblastomas overexpressing mutant epidermal growth factor receptors by systemic administration of monoclonal antibody (mAb) 806, a novel monoclonal antibody directed to the receptor. Cancer Res. 2001, 61, 5349–5354. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Heimberger, A.B.; Archer, G.E.; Crotty, L.E.; McLendon, R.E.; Friedman, A.H.; Friedman, H.S.; Bigner, D.D.; Sampson, J.H. Dendritic cells pulsed with a tumor-specific peptide induce long-lasting immunity and are effective against murine intracerebral melanoma. Neurosurgery 2002, 50, 158–164; discussion 164–166. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ebben, J.D.; Lubet, R.A.; Gad, E.; Disis, M.L.; You, M. Epidermal growth factor receptor derived peptide vaccination to prevent lung adenocarcinoma formation: An in vivo study in a murine model of EGFR mutant lung cancer. Mol. Carcinog. 2016, 55, 1517–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sampson, J.H.; Heimberger, A.B.; Archer, G.E.; Aldape, K.D.; Friedman, A.H.; Friedman, H.S.; Gilbert, M.R.; Herndon, J.E., 2nd; McLendon, R.E.; Mitchell, D.A.; et al. Immunologic escape after prolonged progression-free survival with epidermal growth factor receptor variant III peptide vaccination in patients with newly diagnosed glioblastoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 28, 4722–4729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudley, M.E.; Wunderlich, J.R.; Robbins, P.F.; Yang, J.C.; Hwu, P.; Schwartzentruber, D.J.; Topalian, S.L.; Sherry, R.; Restifo, N.P.; Hubicki, A.M.; et al. Cancer regression and autoimmunity in patients after clonal repopulation with antitumor lymphocytes. Science 2002, 298, 850–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sampson, J.H.; Aldape, K.D.; Archer, G.E.; Coan, A.; Desjardins, A.; Friedman, A.H.; Friedman, H.S.; Gilbert, M.R.; Herndon, J.E.; McLendon, R.E.; et al. Greater chemotherapy-induced lymphopenia enhances tumor-specific immune responses that eliminate EGFRvIII-expressing tumor cells in patients with glioblastoma. Neuro Oncol. 2011, 13, 324–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reardon, D.A.; Desjardins, A.; Vredenburgh, J.J.; O’Rourke, D.M.; Tran, D.D.; Fink, K.L.; Nabors, L.B.; Li, G.; Bota, D.A.; Lukas, R.V.; et al. Rindopepimut with Bevacizumab for Patients with Relapsed EGFRvIII-Expressing Glioblastoma (ReACT): Results of a Double-Blind Randomized Phase II Trial. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020, 26, 1586–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuster, J.; Lai, R.K.; Recht, L.D.; Reardon, D.A.; Paleologos, N.A.; Groves, M.D.; Mrugala, M.M.; Jensen, R.; Baehring, J.M.; Sloan, A.; et al. A phase II, multicenter trial of rindopepimut (CDX-110) in newly diagnosed glioblastoma: The ACT III study. Neuro Oncol. 2015, 17, 854–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weller, M.; Butowski, N.; Tran, D.D.; Recht, L.D.; Lim, M.; Hirte, H.; Ashby, L.; Mechtler, L.; Goldlust, S.A.; Iwamoto, F.; et al. Rindopepimut with temozolomide for patients with newly diagnosed, EGFRvIII-expressing glioblastoma (ACT IV): A randomised, double-blind, international phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2017, 18, 1373–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Chen, C.; Ju, T.; Gao, J.; Yan, J.; Wang, P.; Xu, Q.; Hwu, P.; Du, X.; Lizee, G. Rapid tumor regression in an Asian lung cancer patient following personalized neo-epitope peptide vaccination. Oncoimmunology 2016, 5, e1238539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Deng, L.; Jackson, K.R.; Talukder, A.H.; Katailiha, A.S.; Bradley, S.D.; Zou, Q.; Chen, C.; Huo, C.; Chiu, Y.; et al. Neoantigen vaccination induces clinical and immunologic responses in non-small cell lung cancer patients harboring EGFR mutations. J. Immunother. Cancer 2021, 9, e002531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ott, P.A.; Hu-Lieskovan, S.; Chmielowski, B.; Govindan, R.; Naing, A.; Bhardwaj, N.; Margolin, K.; Awad, M.M.; Hellmann, M.D.; Lin, J.J.; et al. A Phase Ib Trial of Personalized Neoantigen Therapy Plus Anti-PD-1 in Patients with Advanced Melanoma, Non-small Cell Lung Cancer, or Bladder Cancer. Cell 2020, 183, 347–362.e24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Yuan, Y.; Chen, C.; Lin, J.; Ma, Q.; Liu, G.; Gao, Y.; Huang, Y.; Chen, L.; Chen, L.Z.; et al. Durable complete response to neoantigen-loaded dendritic-cell vaccine following anti-PD-1 therapy in metastatic gastric cancer. NPJ Precis. Oncol. 2022, 6, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Li, Z.; Qiu, L.; Dong, X.; Chen, G.; Shi, Y.; Cai, L.; Liu, W.; Ye, H.; Zhou, Y.; et al. Personalized neoantigen vaccine combined with PD-1 blockade increases CD8+ tissue-resident memory T-cell infiltration in preclinical hepatocellular carcinoma models. J. Immunother. Cancer 2022, 10, e004389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Diao, B.; Huang, Z.; Wang, B.; Yu, J.; Meng, X. The efficacy and possible mechanisms of immune checkpoint inhibitors in treating non-small cell lung cancer patients with epidermal growth factor receptor mutation. Cancer Commun. 2021, 41, 1314–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fruh, M.; Peters, S. EGFR mutation subtype impacts efficacy of immune checkpoint inhibitors in non-small-cell lung cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2019, 30, 1190–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hastings, K.; Yu, H.A.; Wei, W.; Sanchez-Vega, F.; DeVeaux, M.; Choi, J.; Rizvi, H.; Lisberg, A.; Truini, A.; Lydon, C.A.; et al. EGFR mutation subtypes and response to immune checkpoint blockade treatment in non-small-cell lung cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2019, 30, 1311–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.; Wang, Y.; Xue, J.; Zhou, X. Immunotherapy for EGFR-mutant advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: Current status, possible mechanisms and application prospects. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 940288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Han, X. Anti-PD-1/PD-L1 therapy of human cancer: Past, present, and future. J. Clin. Investig. 2015, 125, 3384–3391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, M.; Jiang, T.; Liu, X.; Mao, S.; Zhou, F.; Li, X.; Zhao, C.; Chen, X.; Su, C.; Ren, S.; et al. Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors in EGFR-Mutated NSCLC: Dusk or Dawn? J. Thorac. Oncol. 2021, 16, 1267–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akazawa, Y.; Saito, Y.; Yoshikawa, T.; Saito, K.; Nosaka, K.; Shimomura, M.; Mizuno, S.; Nakamoto, Y.; Nakatsura, T. Efficacy of immunotherapy targeting the neoantigen derived from epidermal growth factor receptor T790M/C797S mutation in non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Sci. 2020, 111, 2736–2746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, F.; Wu, H.; Du, X.; Sun, Y.; Rausseo, B.N.; Talukder, A.; Katailiha, A.; Elzohary, L.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Z.; et al. Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor-Targeted Neoantigen Peptide Vaccination for the Treatment of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer and Glioblastoma. Vaccines 2023, 11, 1460. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11091460
Li F, Wu H, Du X, Sun Y, Rausseo BN, Talukder A, Katailiha A, Elzohary L, Wang Y, Wang Z, et al. Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor-Targeted Neoantigen Peptide Vaccination for the Treatment of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer and Glioblastoma. Vaccines. 2023; 11(9):1460. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11091460
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Fenge, Huancheng Wu, Xueming Du, Yimo Sun, Barbara Nassif Rausseo, Amjad Talukder, Arjun Katailiha, Lama Elzohary, Yupeng Wang, Zhiyu Wang, and et al. 2023. "Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor-Targeted Neoantigen Peptide Vaccination for the Treatment of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer and Glioblastoma" Vaccines 11, no. 9: 1460. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11091460
APA StyleLi, F., Wu, H., Du, X., Sun, Y., Rausseo, B. N., Talukder, A., Katailiha, A., Elzohary, L., Wang, Y., Wang, Z., & Lizée, G. (2023). Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor-Targeted Neoantigen Peptide Vaccination for the Treatment of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer and Glioblastoma. Vaccines, 11(9), 1460. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11091460






