Toxoplasma gondii eIF-5A Modulates the Immune Response of Murine Macrophages In Vitro
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture
2.2. Recombinant Protein and Polyclonal Antibody of TgeIF-5A
2.3. Immunofluorescence and Confocal Microscopy
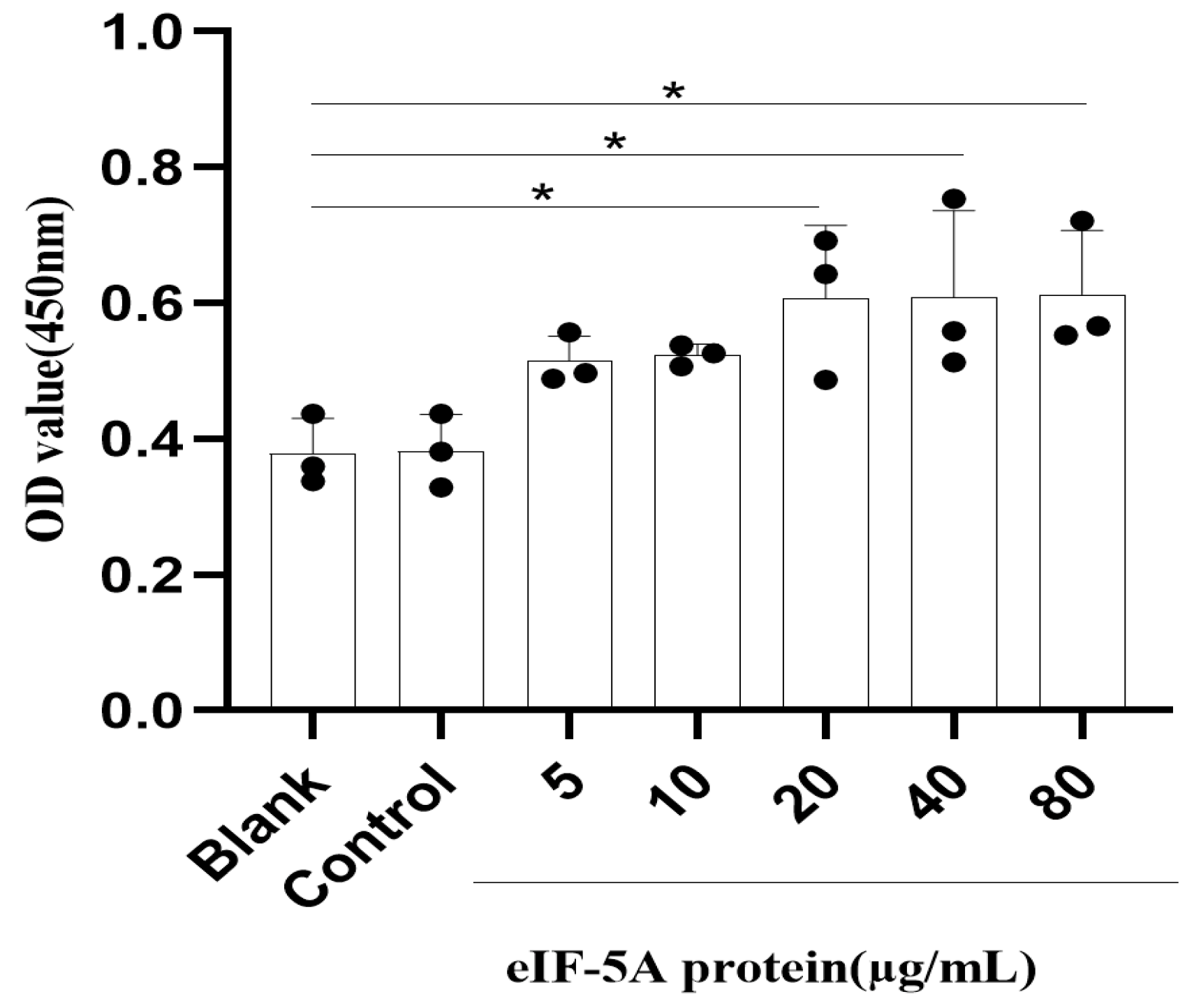
2.4. Cell Viability Assay
2.5. Migration Assays
2.6. Flow Cytometric Assessment of Apoptosis, Phagocytosis and Immunophenotyping
2.7. Secretion Assays
2.8. Statistics
3. Results
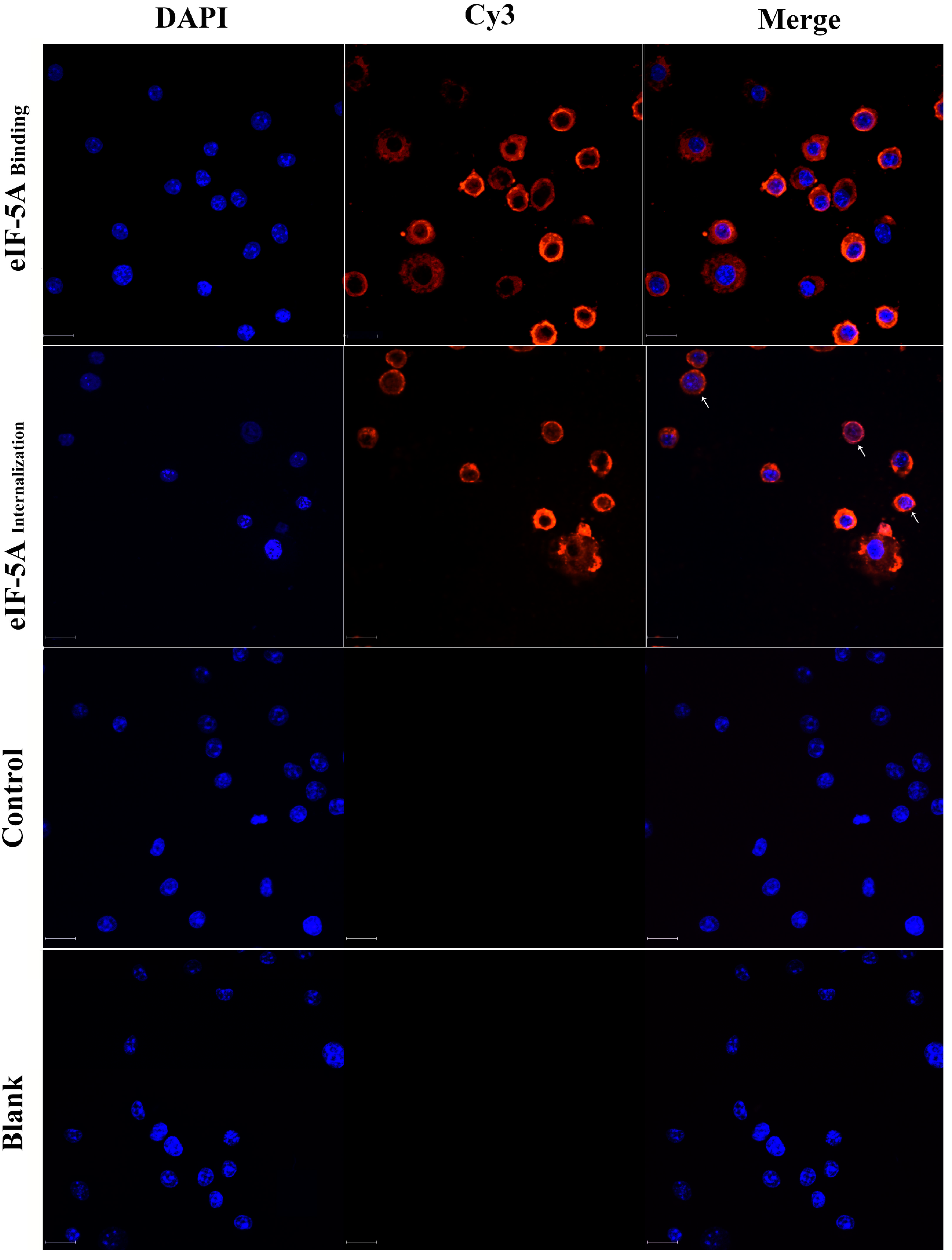
3.1. TgeIF-5A Binds to and Internalizes into Macrophages
3.2. TgeIF-5A Reduces the TLR4 Level of Macrophages
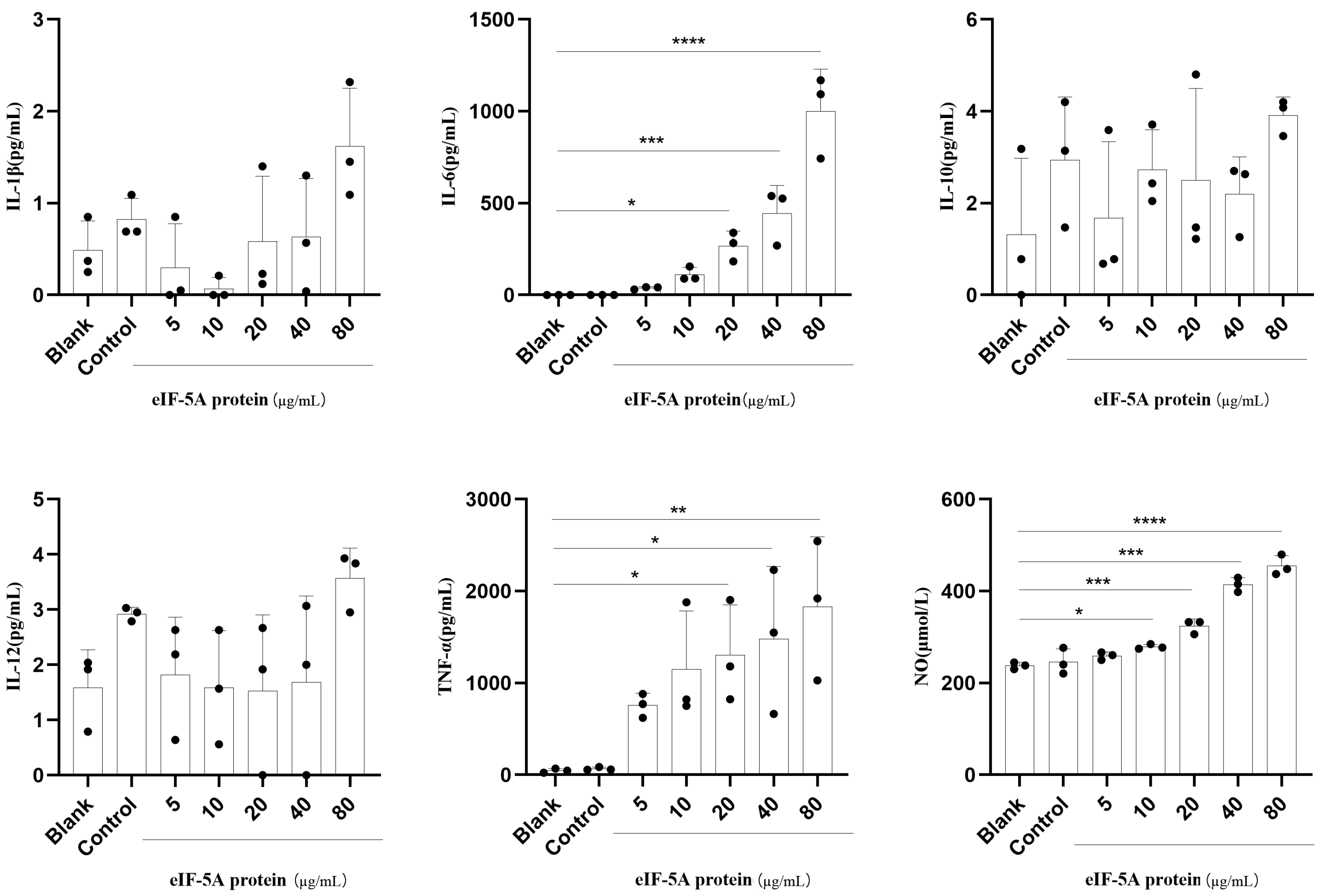
3.3. TgeIF-5A Induces Higher Levels of TNF-α, IL-6 and NO Secretion in Macrophages
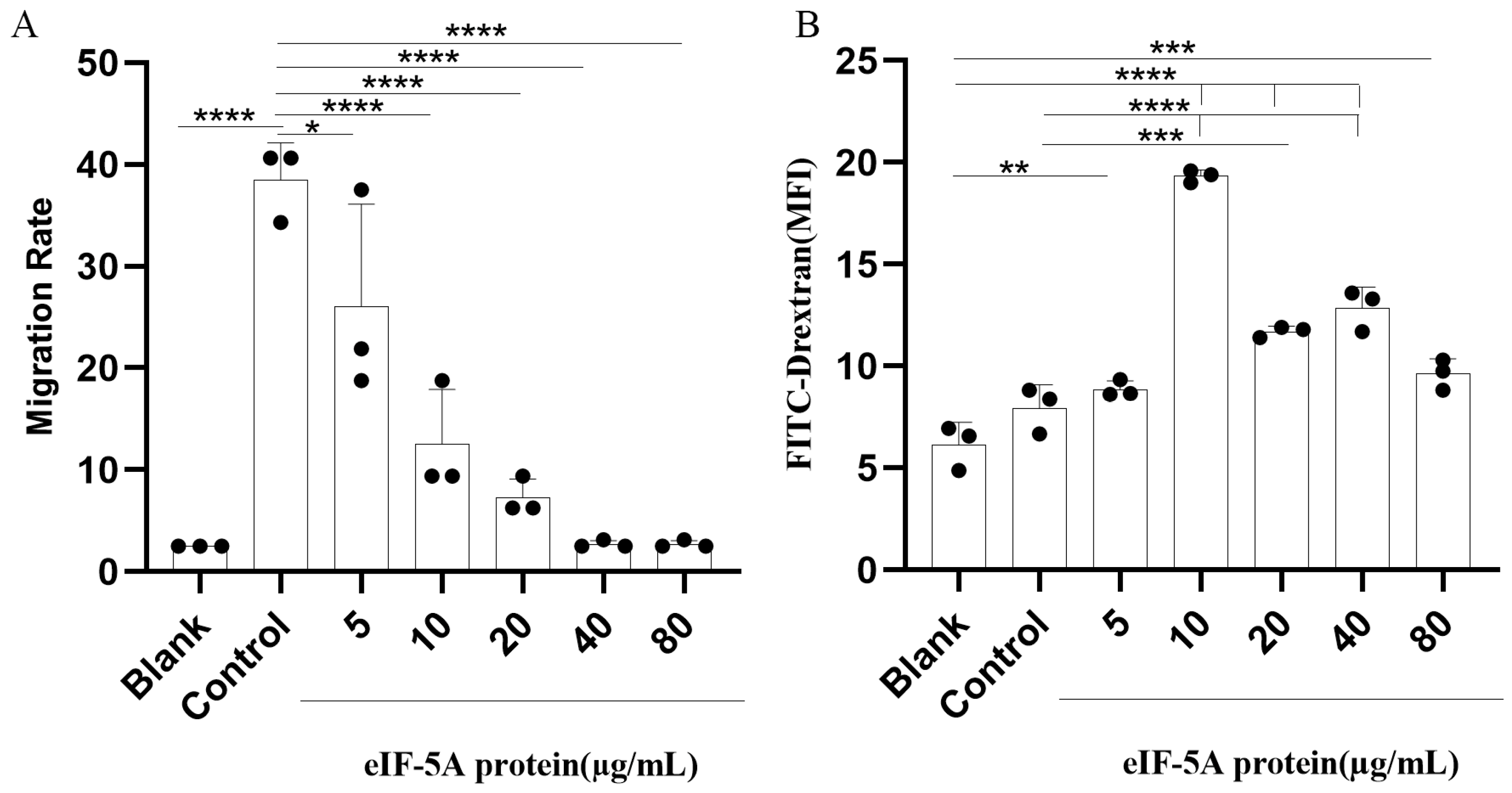
3.4. TgeIF-5A Inhibits the Migration of Macrophages
3.5. TgeIF-5A Induces the Phagocytosis of Macrophages
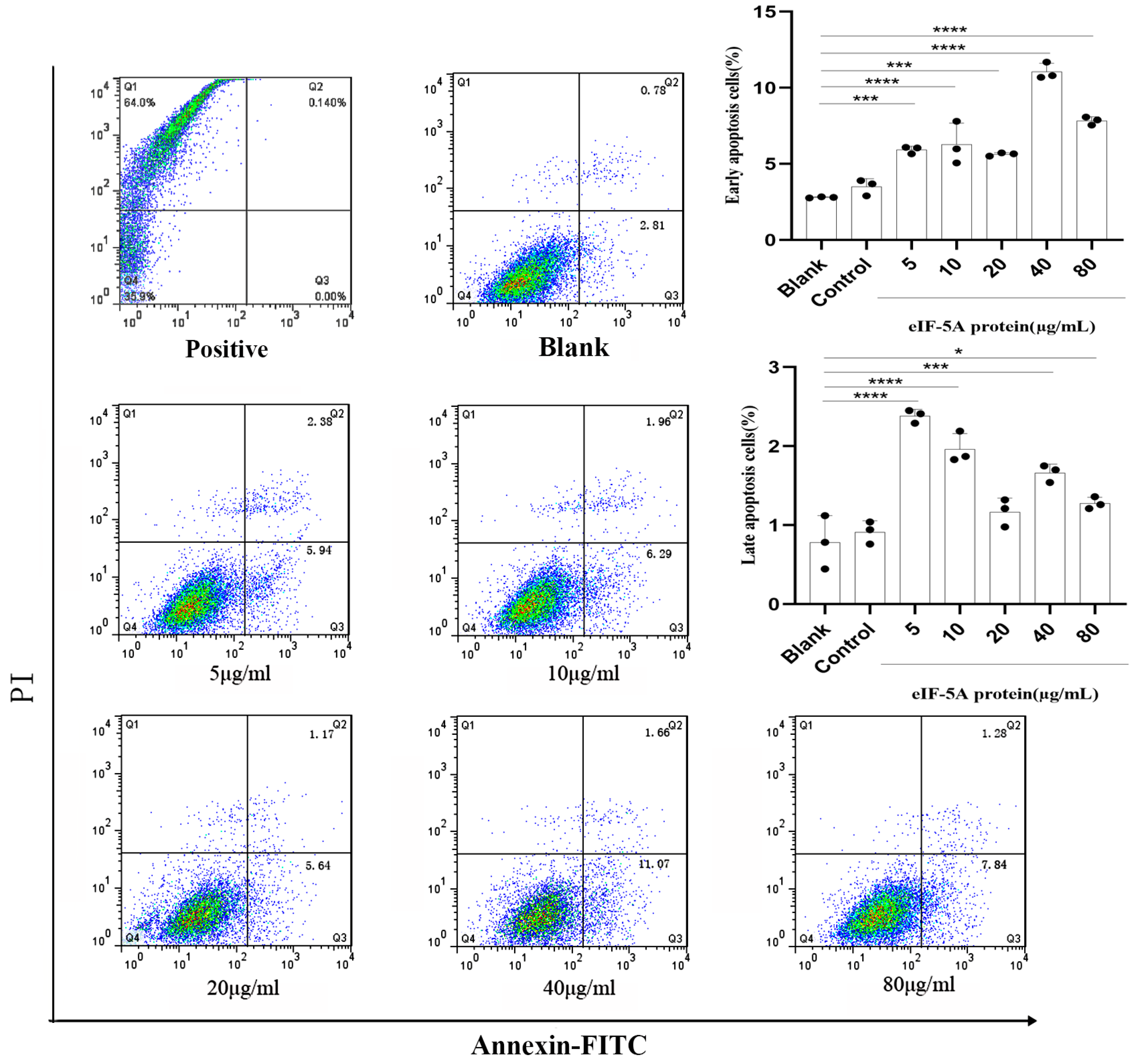
3.6. TgeIF-5A Induces the Apoptosis of Macrophages
3.7. TgeIF-5A Induces the Cell Viability of Macrophages
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Elsheikha, H.M.; Marra, C.M.; Zhu, X.-Q. Epidemiology, Pathophysiology, Diagnosis, and Management of Cerebral Toxoplasmosis. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2020, 34, e00115-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajimohammadi, B.; Ahmadian, S.; Firoozi, Z.; Askari, M.; Mohammadi, M.; Eslami, G.; Askari, V.; Loni, E.; Barzegar-Bafrouei, R.; Boozhmehrani, M.J. A Meta-Analysis of the Prevalence of Toxoplasmosis in Livestock and Poultry Worldwide. Ecohealth 2022, 19, 55–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lourido, S. Toxoplasma gondii. Trends Parasitol. 2019, 35, 944–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kochanowsky, J.A.; Koshy, A.A. Toxoplasma gondii. Curr. Biol. 2018, 28, R770–R771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, Y.J.; Ma, Z.D.; Qiao, X.; Wang, P.T.; Kang, Y.T.; Yang, N.A.; Jia, W.; Zhao, Z.J. Geospatial epidemiology of Toxoplasma gondii infection in livestock, pets, and humans in China, 1984-2020. Parasitol. Res. 2022, 121, 743–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barros, M.; Teixeira, D.; Vilanova, M.; Correia, A.; Borges, M. Vaccines in Congenital Toxoplasmosis: Advances and Perspectives. Front. Immunol. 2021, 11, 621997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gómez-Chávez, F.; Murrieta-Coxca, J.M.; Caballero-Ortega, H.; Morales-Prieto, D.M.; Markert, U.R. Host-pathogen interactions mediated by extracellular vesicles in Toxoplasma gondii infection during pregnancy. J. Reprod. Immunol. 2023, 158, 103957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, T.S.; Lodoen, M.B. Mechanisms of Human Innate Immune Evasion by Toxoplasma gondii. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2019, 9, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.Y.; Ewald, S.E. The molecular biology and immune control of chronic Toxoplasma gondii infection. J. Clin. Investig. 2020, 130, 3370–3380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sana, M.; Rashid, M.; Rashid, I.; Akbar, H.; E Gomez-Marin, J.; Dimier-Poisson, I. Immune response against toxoplasmosis-some recent updates RH: Toxoplasma gondii immune response. Int. J. Immunopathol. Pharmacol. 2022, 36, 03946320221078436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, G.K.; Kim, H.-Y.; Park, J.H. Inhibiting eukaryotic initiation factor 5A (eIF5A) hypusination attenuated activation of the SIK2 (salt-inducible kinase 2)-p4E-BP1 pathway involved in ovarian cancer cell proliferation and migration. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2023, 50, 5807–5816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, J.; Ye, Z.; Shi, S.; Liang, Y.; Meng, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Le, A.D. Targeted inhibition of eIF5A(hpu) suppresses tumor growth and polarization of M2-like tumor-associated macrophages in oral cancer. Cell Death Dis. 2023, 14, 579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez-Férriz, A.; Gandía, C.; Pardo-Sánchez, J.M.; Fathinajafabadi, A.; Ferrando, A.; Farràs, R. Eukaryotic Initiation Factor 5A2 localizes to actively translating ribosomes to promote cancer cell protrusions and invasive capacity. Cell Commun. Signal. 2023, 21, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Li, C.; Li, X.; Ehsan, M.; Li, X.R. Proteomics analysis reveals that the proto-oncogene eIF-5A indirectly influences the growth, invasion and replication of Toxoplasma gondii tachyzoite. Parasites Vectors 2021, 14, 283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawai, T.; Akira, S. The role of pattern-recognition receptors in innate immunity: Update on Toll-like receptors. Nat. Immunol. 2010, 11, 373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lieberman, L.A.; Hunter, C.A. The role of cytokines and their signaling pathways in the regulation of immunity to Toxoplasma gondii. Int. Rev. Immunol. 2002, 21, 373–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Green, S.J.; Scheller, L.F.; Marletta, M.A.; Seguin, M.C.; Klotz, F.W.; Slayter, M.; Nelson, B.J.; Nacy, C.A. Nitric oxide: Cytokine-regulation of nitric oxide in host resistance to intracellular pathogens. Immunol. Lett. 1994, 43, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tosh, K.W.; Mittereder, L.; Bonne-Annee, S.; Hieny, S.; Nutman, T.B.; Singer, S.M.; Sher, A.; Jankovic, D. The IL-12 Response of Primary Human Dendritic Cells and Monocytes to Toxoplasma gondii Is Stimulated by Phagocytosis of Live Parasites Rather Than Host Cell Invasion. J. Immunol. 2015, 2, 345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasai, M.; Yamamoto, M. Innate, adaptive, and cell-autonomous immunity against Toxoplasma gondii infection. Exp. Mol. Med. 2019, 51, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Gadahi, J.A.; Xie, Q.; Xu, L.; Yan, R.; Song, X.; Li, X. Toxoplasma gondii excretory/secretory antigens (TgESAs) suppress pro-inflammatory cytokine secretion by inhibiting TLR-induced NF-κB activation in LPS-stimulated murine macrophages. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 88351–88359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Butcher, B.A.; Fox, B.A.; Rommereim, L.M.; Kim, S.G.; Maurer, K.J.; Yarovinsky, F.; Herbert, D.R.; Bzik, D.J.; Denkers, E.Y. Toxoplasma gondii Rhoptry Kinase ROP16 Activates STAT3 and STAT6 Resulting in Cytokine Inhibition and Arginase-1-Dependent Growth Control. PLoS Pathog. 2011, 11, e1002236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangaré, L.O.; Yang, N.; Konstantinou, E.K.; Lu, D.; Mukhopadhyay, D.; Young, L.H.; Saeij, J.P.J. Toxoplasma GRA15 Activates the NF-κB Pathway through Interactions with TNF Receptor-Associated Factors. mBio 2019, 10, e00808–e00819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, L.J.; Chen, M.; He, C.; Xia, J.; He, C.; Deng, S.Q.; Peng, H.J. Toxoplasma gondii ROP18 Inhibits Human Glioblastoma Cell Apoptosis through Mitochondrial Pathway by Targeting Host Cell P2X1. Parasites Vectors 2018, 12, 284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma’Ayeh, S.Y.; Liu, J.; Peirasmaki, D.; Hrnaeus, K.; Svrd, S.G. Characterization of the Giardia intestinalis secretome during interaction with human intestinal epithelial cells: The impact on host cells. PLoS Neglected Trop. Dis. 2017, 11, e0006120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wu, L.; Liu, X.; Wang, S.; Ehsan, M.; Yan, R.F.; Song, X.K.; Xu, L.X.; Li, X.R. Characterization of a secreted cystatin of the parasitic nematode Haemonchus contortus and its immune-modulatory effect on goat monocytes. Parasites Vectors 2017, 10, 425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sardinha-Silva, A.; Mendonça-Natividade, F.C.; Pinzan, C.F.; Lopes, C.D.; Costa, D.L. The lectin-specific activity of Toxoplasma gondii microneme proteins 1 and 4 binds Toll-like receptor 2 and 4 N-glycans to regulate innate immune priming. PLoS Pathog. 2019, 15, e1007871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishiyama, S.; Pradipta, A.; Ma, J.S.; Sasai, M.; Yamamoto, M. T cell-derived interferon-γ is required for host defense to Toxoplasma gondii. Parasitol. Int. 2020, 75, 102049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldszmid, R.S.; Bafica, A.; Jankovic, D.; Feng, C.G.; Caspar, P.; Winkler-Pickett, R.; Trinchieri, G.; Sher, A. TAP-1 indirectly regulates CD4+ T cell priming in Toxoplasma gondii infection by controlling NK cell IFN-gamma production. J. Exp. Med. 2007, 204, 2591–2602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bessieres, M.H.; Swierczynski, B.; Cassaing, S.; Miedouge, M.; Olle, P.; Seguela, J.P.; Pipy, B. Role of IFN-gamma, TNF-alpha, IL4 and IL10 in the regulation of experimental Toxoplasma gondii infection. J. Eukaryot. Microbiol. 1997, 44, 87s. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delair, E.; Creuzet, C.; Dupouy-Camet, J.; Roisin, M.-P. In vitro effect of TNF-alpha and IFN-gamma in retinal cell infection with Toxoplasma gondii. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2009, 50, 1754–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atmaca, N.; Atmaca, H.T. The correlation of TNF alpha levels with acute phase proteins in acute Toxoplasma gondii infection in mice. Exp. Parasitol. 2022, 239, 108311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabral, G.R.A.; Wang, Z.T.; Sibley, L.D.; DaMatta, R.A. Inhibition of Nitric Oxide Production in Activated Macrophages Caused by Toxoplasma gondii Infection Occurs by Distinct Mechanisms in Different Mouse Macrophage Cell Lines. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fisch, D.; Clough, B.; Frickel, E.-M. Human immunity to Toxoplasma gondii. PLoS Pathog. 2019, 15, e1008097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snyderman, R.; Mergenhagen, S.E. Chemotaxis of Macrophages. In Immunobiology of the Macrophage; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1976. [Google Scholar]
- Campagne, M.v.L.; Wiesmann, C.; Brown, E.J. Macrophage complement receptors and pathogen clearance. Cell. Microbiol. 2007, 9, 2095–2102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, G.T. Programmed cell death: A fundamental protective response to pathogens. Trends Microbiol. 1994, 2, 463–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadpour, E.; Babaie, F.; Kazemi, T.; Mehrani Moghaddam, S.; Moghimi, A.; Hosseinzadeh, R.; Nissapatorn, V.; Pagheh, A.S. Overview of Apoptosis, Autophagy, and Inflammatory Processes in Toxoplasma gondii Infected Cells. Pathogens 2023, 12, 253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, X.; Li, X.; Li, C.; Lu, M.; Xu, L.; Yan, R.; Song, X.; Li, X. Toxoplasma gondii eIF-5A Modulates the Immune Response of Murine Macrophages In Vitro. Vaccines 2024, 12, 101. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines12010101
Liu X, Li X, Li C, Lu M, Xu L, Yan R, Song X, Li X. Toxoplasma gondii eIF-5A Modulates the Immune Response of Murine Macrophages In Vitro. Vaccines. 2024; 12(1):101. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines12010101
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Xinchao, Xiaoyu Li, Chunjing Li, Mingmin Lu, Lixin Xu, Ruofeng Yan, Xiaokai Song, and Xiangrui Li. 2024. "Toxoplasma gondii eIF-5A Modulates the Immune Response of Murine Macrophages In Vitro" Vaccines 12, no. 1: 101. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines12010101
APA StyleLiu, X., Li, X., Li, C., Lu, M., Xu, L., Yan, R., Song, X., & Li, X. (2024). Toxoplasma gondii eIF-5A Modulates the Immune Response of Murine Macrophages In Vitro. Vaccines, 12(1), 101. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines12010101







