Enhanced Immunogenicity and Protective Effects against SARS-CoV-2 Following Immunization with a Recombinant RBD-IgG Chimeric Protein
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
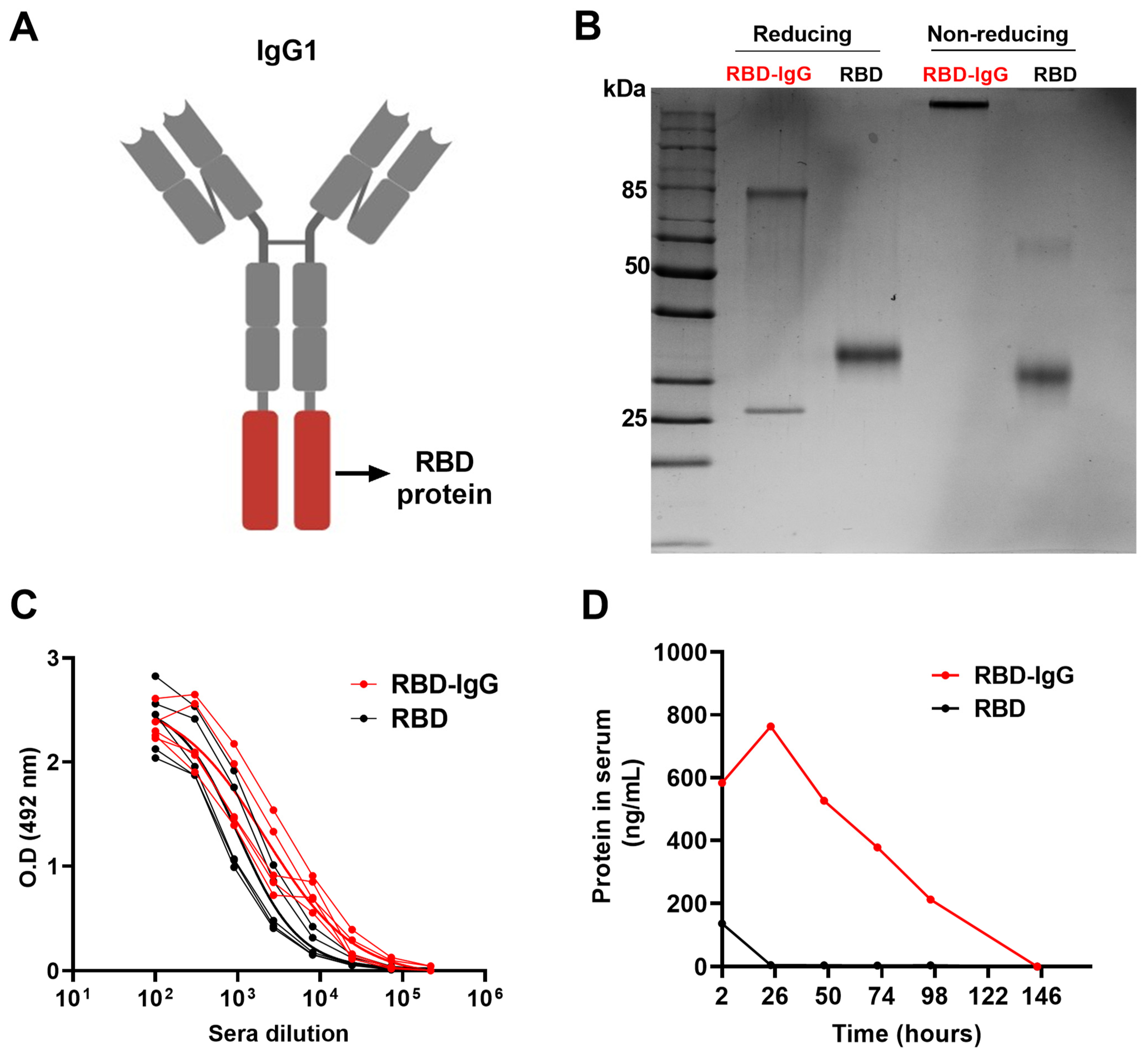
2.1. Construction and Preparation of Recombinant Proteins
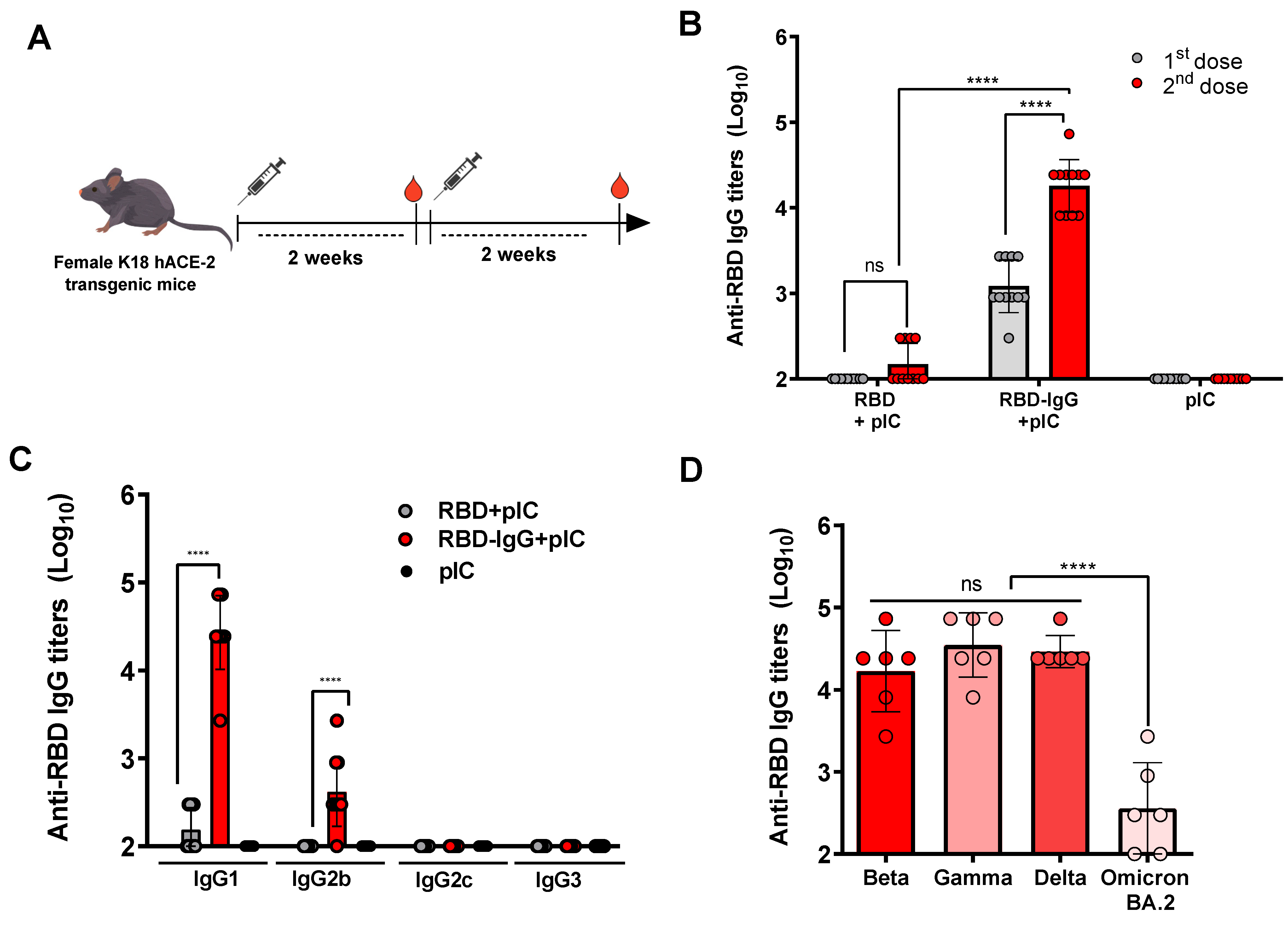
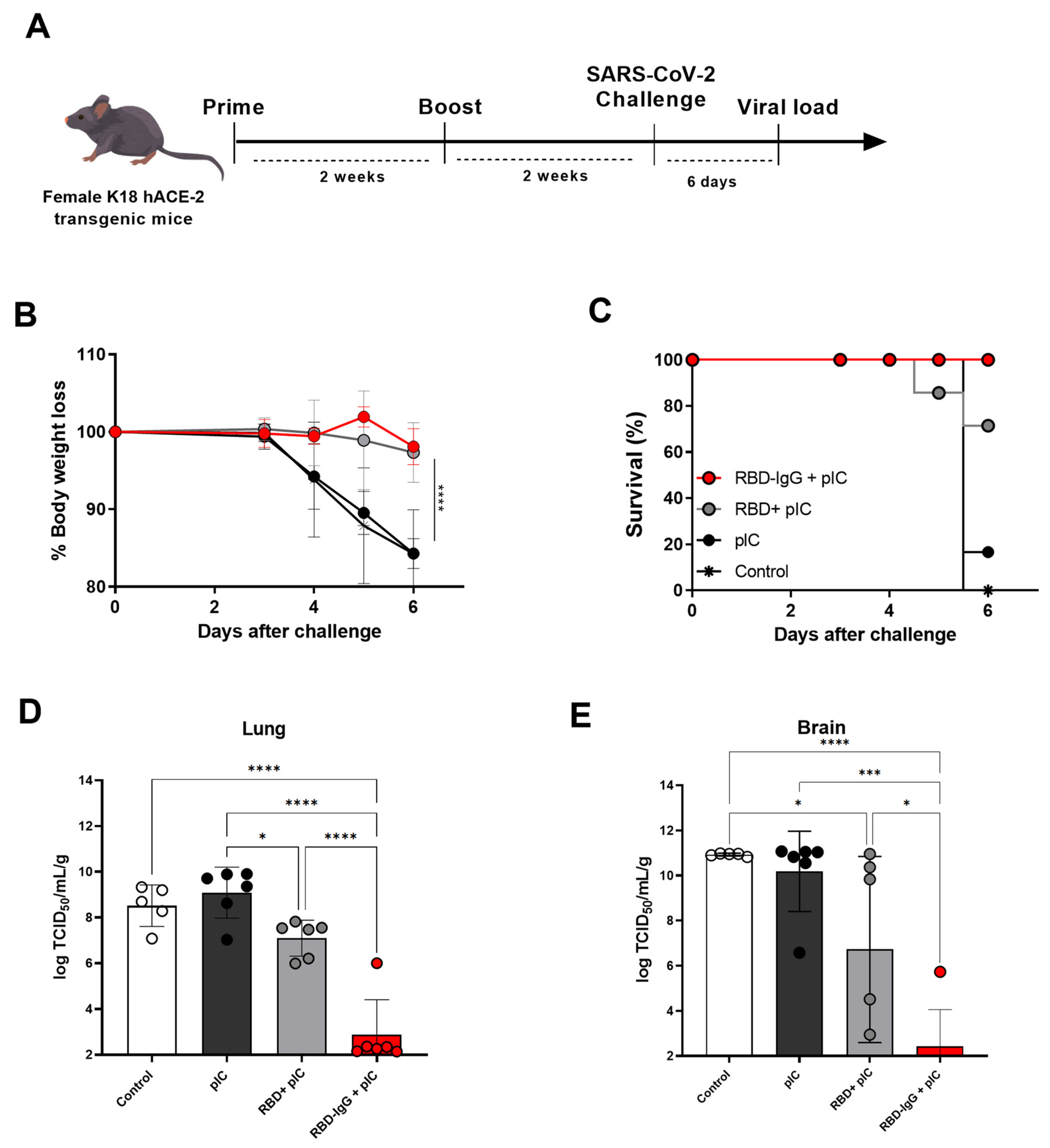
2.2. Immunization and Protection Experiments
2.3. Plasma Persistence of the Recombinant Protein
2.4. Pseudovirus Production and Neutralization Assays
2.5. Live Virus-Neutralizing Antibody Assay
2.6. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assays (ELISA)
2.7. Quantification of Viral Load by RT-qPCR
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Generation of the Recombinant RBD-IgG Antigen, Antigenicity and Persistence in the Blood
3.2. RBD Fused to IgG Induces Strong Anti-Viral Antibody Responses
3.3. Immunization with the Chimeric RBD-IgG Enhances the Induction of SARS-CoV-2-Neutralizing Antibodies
3.4. Immunization with the Chimeric RBD-IgG Confers Protective Immunity to Lethal Challenge with SARS-CoV-2
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhu, N.; Zhang, D.; Wang, W.; Li, X.; Yang, B.; Song, J.; Zhao, X.; Huang, B.; Shi, W.; Lu, R.; et al. A Novel Coronavirus from Patients with Pneumonia in China, 2019. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 727–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. WHO COVID-19 Dashboard. Available online: https://covid19.who.int/ (accessed on 29 September 2023).
- Jackson, L.A.; Anderson, E.J.; Rouphael, N.G.; Roberts, P.C.; Makhene, M.; Coler, R.N.; McCullough, M.P.; Chappell, J.D.; Denison, M.R.; Stevens, L.J.; et al. An MRNA Vaccine against SARS-CoV-2—Preliminary Report. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 1920–1931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heath, P.T.; Galiza, E.P.; Baxter, D.N.; Boffito, M.; Browne, D.; Burns, F.; Chadwick, D.R.; Clark, R.; Cosgrove, C.; Galloway, J.; et al. Safety and Efficacy of NVX-CoV2373 Covid-19 Vaccine. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 1172–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, E.E.; Frenck, R.W.; Falsey, A.R.; Kitchin, N.; Absalon, J.; Gurtman, A.; Lockhart, S.; Neuzil, K.; Mulligan, M.J.; Bailey, R.; et al. Safety and Immunogenicity of Two RNA-Based Covid-19 Vaccine Candidates. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 2439–2450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Q.; Bao, L.; Mao, H.; Wang, L.; Xu, K.; Yang, M.; Li, Y.; Zhu, L.; Wang, N.; Lv, Z.; et al. Development of an Inactivated Vaccine Candidate for SARS-CoV-2. Science 2020, 369, 77–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krause, P.R.; Fleming, T.R.; Longini, I.M.; Peto, R.; Briand, S.; Heymann, D.L.; Beral, V.; Snape, M.D.; Rees, H.; Ropero, A.-M.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Variants and Vaccines. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; Zhao, S.; Yu, B.; Chen, Y.-M.; Wang, W.; Song, Z.-G.; Hu, Y.; Tao, Z.-W.; Tian, J.-H.; Pei, Y.-Y.; et al. A New Coronavirus Associated with Human Respiratory Disease in China. Nature 2020, 579, 265–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, P.; Yang, X.-L.; Wang, X.-G.; Hu, B.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, W.; Si, H.-R.; Zhu, Y.; Li, B.; Huang, C.-L.; et al. A Pneumonia Outbreak Associated with a New Coronavirus of Probable Bat Origin. Nature 2020, 579, 270–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letko, M.; Marzi, A.; Munster, V. Functional Assessment of Cell Entry and Receptor Usage for SARS-CoV-2 and Other Lineage B Betacoronaviruses. Nat. Microbiol. 2020, 5, 562–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, R.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Xia, L.; Guo, Y.; Zhou, Q. Structural Basis for the Recognition of SARS-CoV-2 by Full-Length Human ACE2. Science 2020, 367, 1444–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, P.-H.; Tsai, H.-H.; Liao, B.-H.; Lin, Y.-L.; Jan, J.-T.; Tao, M.-H.; Chou, Y.-C.; Hu, C.-M.J.; Chen, H.-W. Neutralizing Antibody Response Elicited by SARS-CoV-2 Receptor-Binding Domain. Hum. Vaccin. Immunother. 2021, 17, 654–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, L.; Gao, G.F. Viral Targets for Vaccines against COVID-19. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2021, 21, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, L.; Gao, L.; Tao, L.; Hadinegoro, S.R.; Erkin, M.; Ying, Z.; He, P.; Girsang, R.T.; Vergara, H.; Akram, J.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of the RBD-Dimer–Based Covid-19 Vaccine ZF2001 in Adults. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 386, 2097–2111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, K.; Gao, P.; Liu, S.; Lu, S.; Lei, W.; Zheng, T.; Liu, X.; Xie, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Guo, S.; et al. Protective Prototype-Beta and Delta-Omicron Chimeric RBD-Dimer Vaccines against SARS-CoV-2. Cell 2022, 185, 2265–2278.e14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Yuan, R.Y.; Wang, M.Y.; He, P.; Su, J.G.; Han, Z.B.; Jin, Y.Q.; Hou, J.W.; Zhang, H.; et al. Design of a Mutation-Integrated Trimeric RBD with Broad Protection against SARS-CoV-2. Cell Discov. 2022, 8, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malladi, S.K.; Patel, U.R.; Rajmani, R.S.; Singh, R.; Pandey, S.; Kumar, S.; Khaleeq, S.; van Vuren, P.J.; Riddell, S.; Goldie, S.; et al. Immunogenicity and Protective Efficacy of a Highly Thermotolerant, Trimeric SARS-CoV-2 Receptor Binding Domain Derivative. ACS Infect. Dis. 2021, 7, 2546–2564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Routhu, N.K.; Cheedarla, N.; Bollimpelli, V.S.; Gangadhara, S.; Edara, V.V.; Lai, L.; Sahoo, A.; Shiferaw, A.; Styles, T.M.; Floyd, K.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 RBD Trimer Protein Adjuvanted with Alum-3M-052 Protects from SARS-CoV-2 Infection and Immune Pathology in the Lung. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 3587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues-Jesus, M.J.; Teixeira de Pinho Favaro, M.; Venceslau-Carvalho, A.A.; de Castro-Amarante, M.F.; da Silva Almeida, B.; de Oliveira Silva, M.; Andreata-Santos, R.; Gomes Barbosa, C.; Brito, S.C.M.; Freitas-Junior, L.H.; et al. Nano-Multilamellar Lipid Vesicles Promote the Induction of SARS-CoV-2 Immune Responses by a Protein-Based Vaccine Formulation. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2022, 45, 102595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walls, A.C.; Fiala, B.; Schäfer, A.; Wrenn, S.; Pham, M.N.; Murphy, M.; Tse, L.V.; Shehata, L.; O’Connor, M.A.; Chen, C.; et al. Elicitation of Potent Neutralizing Antibody Responses by Designed Protein Nanoparticle Vaccines for SARS-CoV-2. Cell 2020, 183, 1367–1382.e17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.Y.; Copland, A.; Nayak, K.; Chandele, A.; Ahmed, M.S.; Zhang, Q.; Diogo, G.R.; Paul, M.J.; Hofmann, S.; Yang, M.; et al. Plant-expressed Fc-fusion Protein Tetravalent Dengue Vaccine with Inherent Adjuvant Properties. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2018, 16, 1283–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loureiro, S.; Ren, J.; Phapugrangkul, P.; Colaco, C.A.; Bailey, C.R.; Shelton, H.; Molesti, E.; Temperton, N.J.; Barclay, W.S.; Jones, I.M. Adjuvant-Free Immunization with Hemagglutinin-Fc Fusion Proteins as an Approach to Influenza Vaccines. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 3010–3014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Diamos, A.G.; Pardhe, M.D.; Sun, H.; Hunter, J.G.L.; Kilbourne, J.; Chen, Q.; Mason, H.S. A Highly Expressing, Soluble, and Stable Plant-Made IgG Fusion Vaccine Strategy Enhances Antigen Immunogenicity in Mice without Adjuvant. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 576012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amanat, F.; Stadlbauer, D.; Strohmeier, S.; Nguyen, T.H.O.; Chromikova, V.; McMahon, M.; Jiang, K.; Arunkumar, G.A.; Jurczyszak, D.; Polanco, J.; et al. A Serological Assay to Detect SARS-CoV-2 Seroconversion in Humans. Nat. Med. 2020, 26, 1033–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hawiger, D.; Inaba, K.; Dorsett, Y.; Guo, M.; Mahnke, K.; Rivera, M.; Ravetch, J.V.; Steinman, R.M.; Nussenzweig, M.C. Dendritic Cells Induce Peripheral T Cell Unresponsiveness under Steady State Conditions in Vivo. J. Exp. Med. 2001, 194, 769–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clynes, R.A.; Towers, T.L.; Presta, L.G.; Ravetch, J.V. Inhibitory Fc Receptors Modulate In Vivo Cytoxicity against Tumor Targets. Nat. Med. 2000, 6, 443–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sulczewski, F.B.; Martino, L.A.; da Silva Almeida, B.; Zaneti, A.B.; Ferreira, N.S.; da Silva Amorim, K.N.; Yamamoto, M.M.; de Souza Apostolico, J.; Rosa, D.S.; Boscardin, S.B. Conventional Type 1 Dendritic Cells Induce T H 1, T H 1-like Follicular Helper T Cells and Regulatory T Cells after Antigen Boost via DEC205 Receptor. Eur. J. Immunol. 2020, 50, 1895–1911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ViralZone. Sars-CoV-2 Circulating Variants. Available online: https://viralzone.expasy.org/9556 (accessed on 25 December 2023).
- Stadlbauer, D.; Amanat, F.; Chromikova, V.; Jiang, K.; Strohmeier, S.; Arunkumar, G.A.; Tan, J.; Bhavsar, D.; Capuano, C.; Kirkpatrick, E.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Seroconversion in Humans: A Detailed Protocol for a Serological Assay, Antigen Production, and Test Setup. Curr. Protoc. Microbiol. 2020, 57, e100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCray, P.B.; Pewe, L.; Wohlford-Lenane, C.; Hickey, M.; Manzel, L.; Shi, L.; Netland, J.; Jia, H.P.; Halabi, C.; Sigmund, C.D.; et al. Lethal Infection of K18- HACE2 Mice Infected with Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 813–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, F.; Weisblum, Y.; Muecksch, F.; Hoffmann, H.-H.; Michailidis, E.; Lorenzi, J.C.C.; Mendoza, P.; Rutkowska, M.; Bednarski, E.; Gaebler, C.; et al. Measuring SARS-CoV-2 Neutralizing Antibody Activity Using Pseudotyped and Chimeric Viruses. J. Exp. Med. 2020, 217, e20201181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendrone-Junior, A.; Dinardo, C.L.; Ferreira, S.C.; Nishya, A.; Salles, N.A.; de Almeida Neto, C.; Hamasaki, D.T.; Facincani, T.; de Oliveira Alves, L.B.; Machado, R.R.G.; et al. Correlation between SARS-COV-2 Antibody Screening by Immunoassay and Neutralizing Antibody Testing. Transfusion 2021, 61, 1181–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corman, V.M.; Landt, O.; Kaiser, M.; Molenkamp, R.; Meijer, A.; Chu, D.K.; Bleicker, T.; Brünink, S.; Schneider, J.; Schmidt, M.L.; et al. Detection of 2019 Novel Coronavirus (2019-NCoV) by Real-Time RT-PCR. Eurosurveillance 2020, 25, 2000045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Zhang, H.; Li, M.; Wu, B.; Zhang, Z.; Gong, R. An Intranasal Vaccine Targeting the Receptor Binding Domain of SARS-CoV-2 Elicits a Protective Immune Response. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 1005321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, F.-C.; Guan, X.-H.; Li, Y.-H.; Huang, J.-Y.; Jiang, T.; Hou, L.-H.; Li, J.-X.; Yang, B.-F.; Wang, L.; Wang, W.-J.; et al. Immunogenicity and Safety of a Recombinant Adenovirus Type-5-Vectored COVID-19 Vaccine in Healthy Adults Aged 18 Years or Older: A Randomised, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Phase 2 Trial. Lancet 2020, 396, 479–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Fattah Yahaya, A.A.; Khalid, K.; Lim, H.X.; Poh, C.L. Development of Next Generation Vaccines against SARS-CoV-2 and Variants of Concern. Viruses 2023, 15, 624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syed, Y.Y. Recombinant Zoster Vaccine (Shingrix®): A Review in Herpes Zoster. Drugs Aging 2018, 35, 1031–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Shang, J.; Jiang, S.; Du, L. Subunit Vaccines Against Emerging Pathogenic Human Coronaviruses. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reed, S.G.; Orr, M.T.; Fox, C.B. Key Roles of Adjuvants in Modern Vaccines. Nat. Med. 2013, 19, 1597–1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, L.; Zheng, T.; Xu, K.; Han, Y.; Xu, L.; Huang, E.; An, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Li, S.; Liu, M.; et al. A Universal Design of Betacoronavirus Vaccines against COVID-19, MERS, and SARS. Cell 2020, 182, 722–733.e11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.-F.; Sun, C.; Zhuang, Z.; Yuan, R.-Y.; Zheng, Q.; Li, J.-P.; Zhou, P.-P.; Chen, X.-C.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, X.; et al. Rapid Development of SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein Receptor-Binding Domain Self-Assembled Nanoparticle Vaccine Candidates. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 2738–2752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Cai, Y.; Song, T.-Z.; Pu, Y.; Cheng, L.; Xu, H.; Sun, J.; Meng, C.; Lin, Y.; Huang, H.; et al. Interferon-Armed RBD Dimer Enhances the Immunogenicity of RBD for Sterilizing Immunity against SARS-CoV-2. Cell Res. 2021, 31, 1011–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alleva, D.G.; Delpero, A.R.; Scully, M.M.; Murikipudi, S.; Ragupathy, R.; Greaves, E.K.; Sathiyaseelan, T.; Haworth, J.R.; Shah, N.J.; Rao, V.; et al. Development of an IgG-Fc Fusion COVID-19 Subunit Vaccine, AKS-452. Vaccine 2021, 39, 6601–6613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laotee, S.; Duangkaew, M.; Jivapetthai, A.; Tharakhet, K.; Kaewpang, P.; Prompetchara, E.; Phumiamorn, S.; Sapsutthipas, S.; Trisiriwanich, S.; Somsaard, T.; et al. CHO-Produced RBD-Fc Subunit Vaccines with Alternative Adjuvants Generate Immune Responses against SARS-CoV-2. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0288486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kontermann, R.E. Strategies for Extended Serum Half-Life of Protein Therapeutics. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2011, 22, 868–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konduru, K.; Bradfute, S.B.; Jacques, J.; Manangeeswaran, M.; Nakamura, S.; Morshed, S.; Wood, S.C.; Bavari, S.; Kaplan, G.G. Ebola Virus Glycoprotein Fc Fusion Protein Confers Protection against Lethal Challenge in Vaccinated Mice. Vaccine 2011, 29, 2968–2977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahoud, M.H.; Ahmet, F.; Kitsoulis, S.; Wan, S.S.; Vremec, D.; Lee, C.-N.; Phipson, B.; Shi, W.; Smyth, G.K.; Lew, A.M.; et al. Targeting Antigen to Mouse Dendritic Cells via Clec9A Induces Potent CD4 T Cell Responses Biased toward a Follicular Helper Phenotype. J. Immunol. 2011, 187, 842–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Addetia, A.; Crawford, K.H.D.; Dingens, A.; Zhu, H.; Roychoudhury, P.; Huang, M.-L.; Jerome, K.R.; Bloom, J.D.; Greninger, A.L. Neutralizing Antibodies Correlate with Protection from SARS-CoV-2 in Humans during a Fishery Vessel Outbreak with a High Attack Rate. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2020, 58, e02107-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oladunni, F.S.; Park, J.-G.; Pino, P.A.; Gonzalez, O.; Akhter, A.; Allué-Guardia, A.; Olmo-Fontánez, A.; Gautam, S.; Garcia-Vilanova, A.; Ye, C.; et al. Lethality of SARS-CoV-2 Infection in K18 Human Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme 2 Transgenic Mice. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 6122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unverdorben, F.; Richter, F.; Hutt, M.; Seifert, O.; Malinge, P.; Fischer, N.; Kontermann, R.E. Pharmacokinetic Properties of IgG and Various Fc Fusion Proteins in Mice. MAbs 2016, 8, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Kankala, R.K.; Yang, Z.; Li, W.; Xie, S.; Li, H.; Chen, A.-Z.; Zou, L. Antibody-Based Drug Delivery Systems for Cancer Therapy: Mechanisms, Challenges, and Prospects. Theranostics 2022, 12, 3719–3746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Souza-Silva, G.A.; Sulczewski, F.B.; Boscardin, S.B. Recombinant Antigen Delivery to Dendritic Cells as a Way to Improve Vaccine Design. Exp. Biol. Med. 2023, 248, 1616–1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; He, L.; Zhao, Z.; Gu, H.; Fang, X.; Wang, T.; Yang, X.; Chen, S.; Deng, Y.; Li, J.; et al. Recombinant Vaccine Containing an RBD-Fc Fusion Induced Protection against SARS-CoV-2 in Nonhuman Primates and Mice. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2021, 18, 1070–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Silva, M.d.O.; Castro-Amarante, M.F.; Venceslau-Carvalho, A.A.; Almeida, B.d.S.; Daher, I.P.; Souza-Silva, G.A.d.; Yamamoto, M.M.; Koike, G.; de Souza, E.E.; Wrenger, C.; et al. Enhanced Immunogenicity and Protective Effects against SARS-CoV-2 Following Immunization with a Recombinant RBD-IgG Chimeric Protein. Vaccines 2024, 12, 356. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines12040356
Silva MdO, Castro-Amarante MF, Venceslau-Carvalho AA, Almeida BdS, Daher IP, Souza-Silva GAd, Yamamoto MM, Koike G, de Souza EE, Wrenger C, et al. Enhanced Immunogenicity and Protective Effects against SARS-CoV-2 Following Immunization with a Recombinant RBD-IgG Chimeric Protein. Vaccines. 2024; 12(4):356. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines12040356
Chicago/Turabian StyleSilva, Mariângela de Oliveira, Maria Fernanda Castro-Amarante, Alexia Adrianne Venceslau-Carvalho, Bianca da Silva Almeida, Isabela Pazotti Daher, Guilherme Antonio de Souza-Silva, Marcio Massao Yamamoto, Gabriela Koike, Edmarcia Elisa de Souza, Carsten Wrenger, and et al. 2024. "Enhanced Immunogenicity and Protective Effects against SARS-CoV-2 Following Immunization with a Recombinant RBD-IgG Chimeric Protein" Vaccines 12, no. 4: 356. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines12040356
APA StyleSilva, M. d. O., Castro-Amarante, M. F., Venceslau-Carvalho, A. A., Almeida, B. d. S., Daher, I. P., Souza-Silva, G. A. d., Yamamoto, M. M., Koike, G., de Souza, E. E., Wrenger, C., Ferreira, L. C. d. S., & Boscardin, S. B. (2024). Enhanced Immunogenicity and Protective Effects against SARS-CoV-2 Following Immunization with a Recombinant RBD-IgG Chimeric Protein. Vaccines, 12(4), 356. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines12040356






