S2 Peptide-Conjugated SARS-CoV-2 Virus-like Particles Provide Broad Protection against SARS-CoV-2 Variants of Concern
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Design and Synthesis of Antigenic Peptides for the SARS-CoV-2 S2 Region
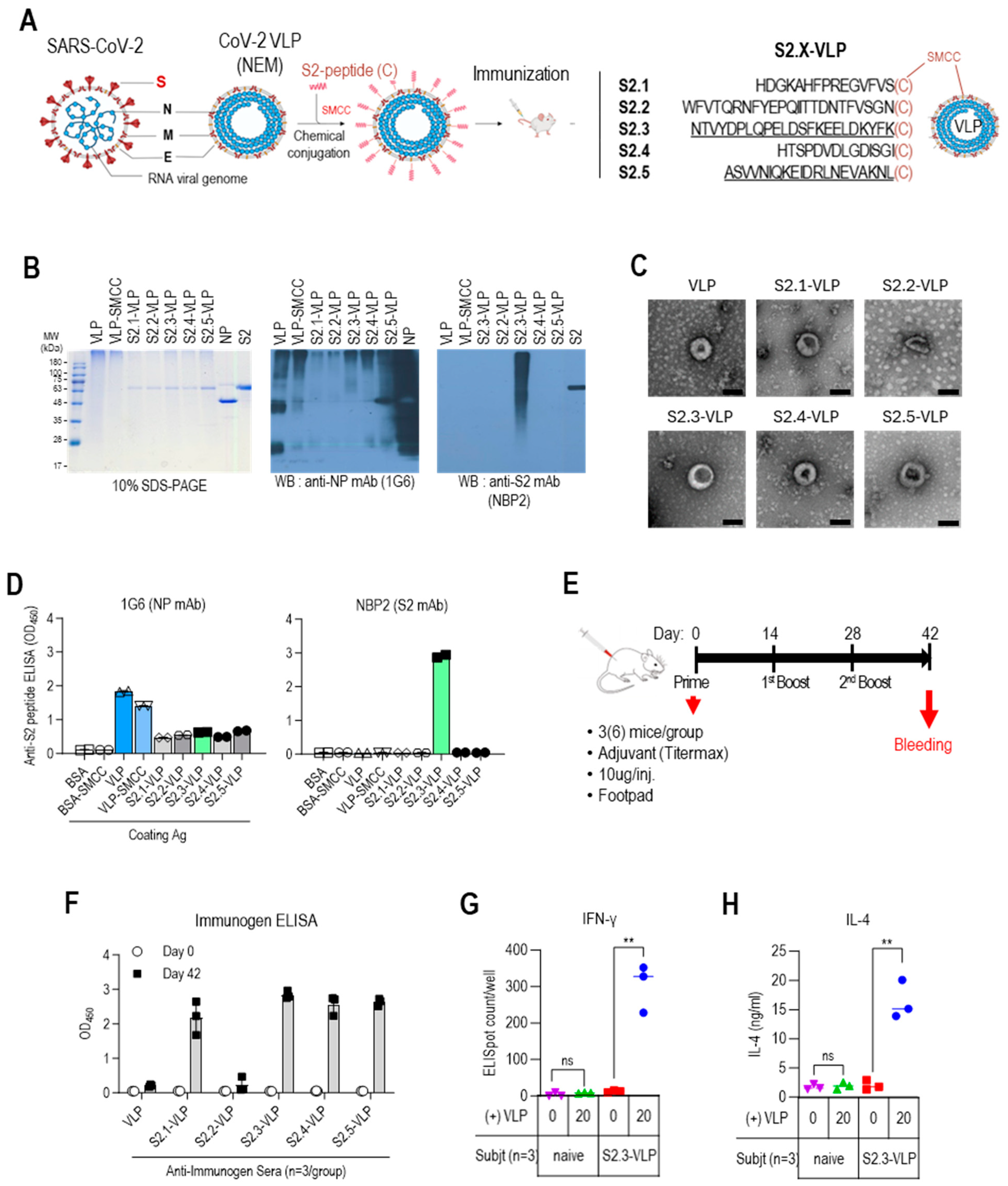
2.2. Production of SARS-CoV-2-NEM VLPs
2.3. Conjugation of S2 Peptides to CoV-2-NEM VLPs
2.4. Characterization of S2 Peptide-Displaying VLPs (or BSA)
2.5. Mouse Immunization
2.6. Western Blot Analysis
2.7. ELISA
2.8. Splenocyte T-Cell Activation Assay
2.9. SARS-CoV-2 Pseudovirus-Based Neutralization Assay
2.10. Competitive ELISA
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Selection of Antigenic Peptide Sequence for a Universal Vaccine against SARS-CoV-2
3.2. Vaccination with S2 Peptide-Conjugated CoV-2-VLPs Elicits Antigen-Specific Humoral and Cellular Immune Responses in BALB/c Mice
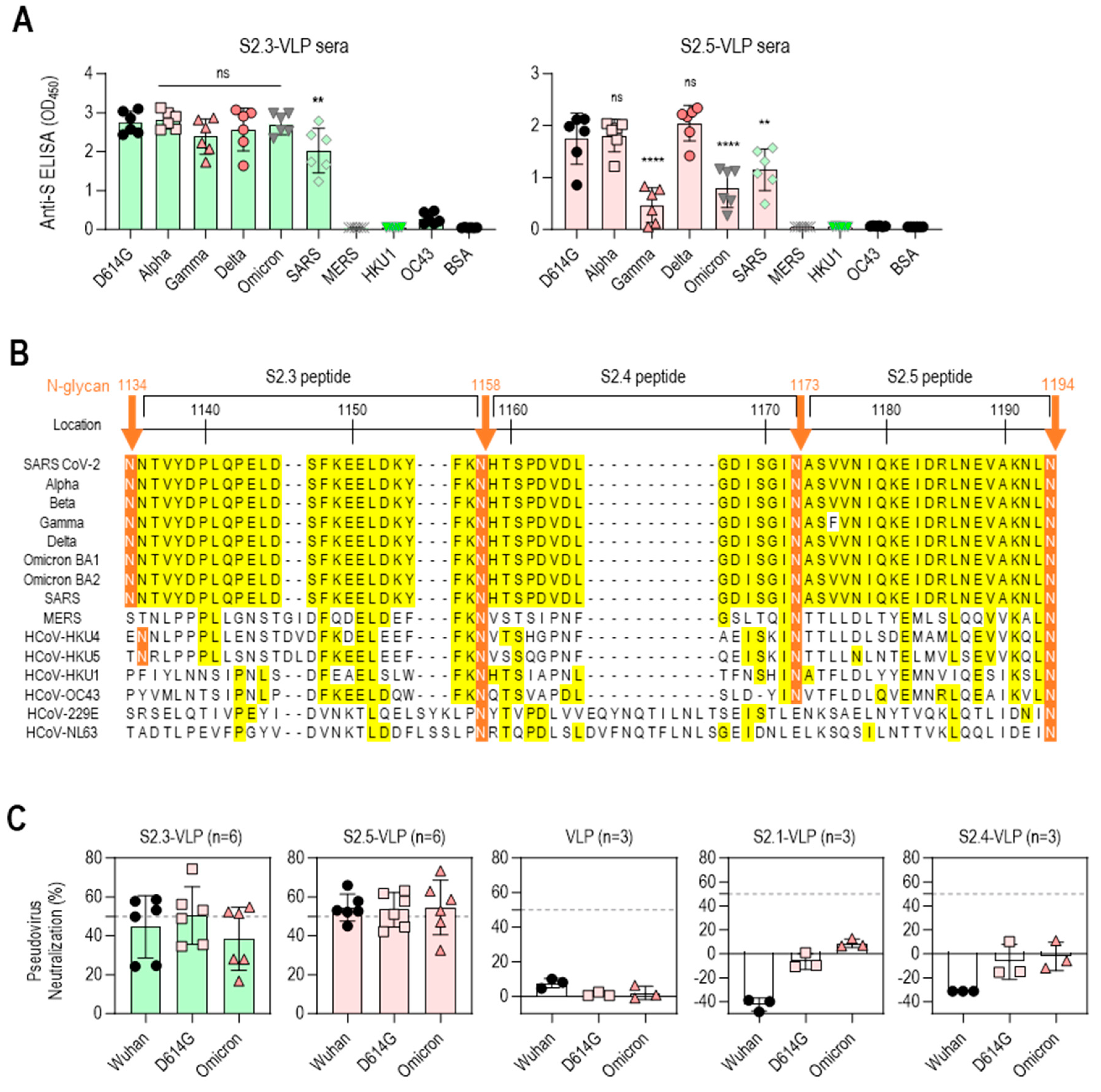
3.3. S2 Peptide-Conjugated VLPs Elicit Broadly Reactive Antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 Variants
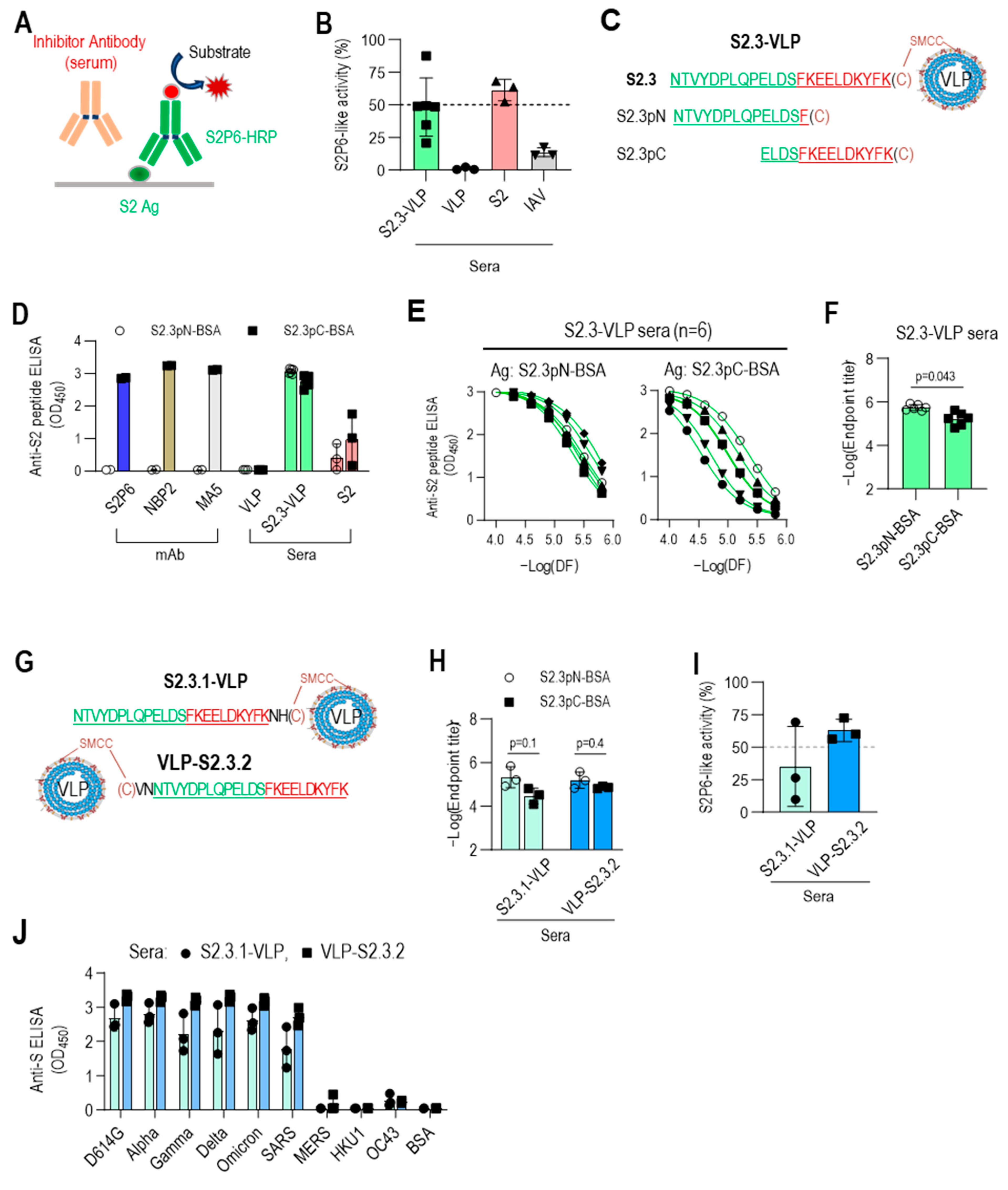
3.4. C-Terminal Exposure of S2.3 Peptide Confers an Epitope That Induces S2P6-like Broadly Neutralizing Antibodies against SARS-CoV-2
3.5. Immune Sera Elicited with Peptide Lacking N-Terminal Sequence Containing V1176 of S2.5 Peptide Showed Enhanced Reactivity toward S Antigen Variants
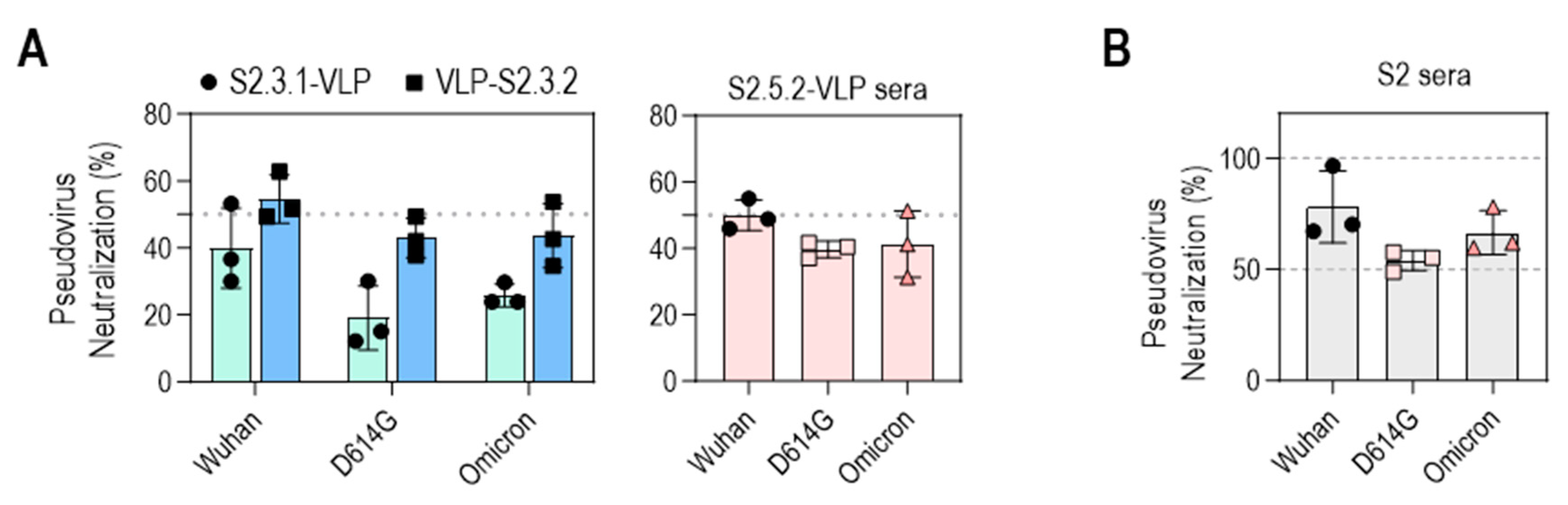
3.6. Neutralizing Capacities of the S2 Peptide–VLP Antisera Were Induced to the Level of the Neutralizing Activity of the S2 Antigen Antisera
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chow, E.J.; Uyeki, T.M.; Chu, H.Y. The effects of the COVID-19 pandemic on community respiratory virus activity. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2023, 21, 195–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kyriakidis, N.C.; López-Cortés, A.; González, E.V.; Grimaldos, A.B.; Prado, E.O. SARS-CoV-2 vaccines strategies: A comprehensive review of phase 3 candidates. NPJ Vaccines 2021, 6, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voysey, M.; Clemens, S.A.C.; Madhi, S.A.; Weckx, L.Y.; Folegatti, P.M.; Aley, P.K.; Angus, B.; Baillie, V.L.; Barnabas, S.L.; Bhorat, Q.E.; et al. Safety and efficacy of the ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 vaccine (AZD1222) against SARS-CoV-2: An interim analysis of four randomised controlled trials in Brazil, South Africa, and the UK. Lancet 2021, 397, 99–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polack, F.P.; Thomas, S.J.; Kitchin, N.; Absalon, J.; Gurtman, A.; Lockhart, S.; Perez, J.L.; Pérez Marc, G.; Moreira, E.D.; Zerbini, C.; et al. Safety and Efficacy of the BNT162b2 mRNA Covid-19 Vaccine. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 2603–2615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadoff, J.; Gray, G.; Vandebosch, A.; Cárdenas, V.; Shukarev, G.; Grinsztejn, B.; Goepfert, P.A.; Truyers, C.; Fennema, H.; Spiessens, B.; et al. Safety and Efficacy of Single-Dose Ad26.COV2.S Vaccine against COVID-19. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 2187–2201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baden, L.R.; El Sahly, H.M.; Essink, B.; Kotloff, K.; Frey, S.; Novak, R.; Diemert, D.; Spector, S.A.; Rouphael, N.; Creech, C.B.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of the mRNA-1273 SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 403–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunkle, L.M.; Kotloff, K.L.; Gay, C.L.; Áñez, G.; Adelglass, J.M.; Barrat Hernández, A.Q.; Harper, W.L.; Duncanson, D.M.; McArthur, M.A.; Florescu, D.F.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of NVX-CoV2373 in Adults in the United States and Mexico. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 386, 531–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thuluva, S.; Paradkar, V.; Gunneri, S.; Yerroju, V.; Mogulla, R.; Suneetha, P.V.; Turaga, K.; Kyasani, M.; Manoharan, S.K.; Adabala, S.; et al. Immunogenicity and safety of Biological E’s CORBEVAX™ vaccine compared to COVISHIELD™ (ChAdOx1 nCoV-19) vaccine studied in a phase-3, single blind, multicentre, randomized clinical trial. Hum. Vaccin. Immunother. 2023, 19, 2203632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Beltran, W.F.; Lam, E.C.; St Denis, K.; Nitido, A.D.; Garcia, Z.H.; Hauser, B.M.; Feldman, J.; Pavlovic, M.N.; Gregory, D.J.; Poznansky, M.C.; et al. Multiple SARS-CoV-2 variants escape neutralization by vaccine-induced humoral immunity. Cell 2021, 184, 2372–2383.e9. [Google Scholar]
- Madhi, S.A.; Baillie, V.; Cutland, C.L.; Voysey, M.; Koen, A.L.; Fairlie, L.; Padayachee, S.D.; Dheda, K.; Barnabas, S.L.; Bhorat, Q.E.; et al. Efficacy of the ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 Covid-19 Vaccine against the B.1.351 Variant. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 1885–1898. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, P.; Nair, M.S.; Liu, L.; Iketani, S.; Luo, Y.; Guo, Y.; Wang, M.; Yu, J.; Zhang, B.; Kwong, P.D.; et al. Antibody resistance of SARS-CoV-2 variants B.1.351 and B.1.1.7. Nature 2021, 593, 130–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffmann, M.; Krüger, N.; Schulz, S.; Cossmann, A.; Rocha, C.; Kempf, A.; Nehlmeier, I.; Graichen, L.; Moldenhauer, A.S.; Winkler, M.S.; et al. The Omicron variant is highly resistant against antibody-mediated neutralization: Implications for control of the COVID-19 pandemic. Cell 2022, 185, 447–456.e11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menachery, V.D.; Yount, B.L., Jr.; Debbink, K.; Agnihothram, S.; Gralinski, L.E.; Plante, J.A.; Graham, R.L.; Scobey, T.; Ge, X.Y.; Donaldson, E.F.; et al. A SARS-like cluster of circulating bat coronaviruses shows potential for human emergence. Nat. Med. 2015, 21, 1508–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menachery, V.D.; Yount, B.L., Jr.; Sims, A.C.; Debbink, K.; Agnihothram, S.S.; Gralinski, L.E.; Graham, R.L.; Scobey, T.; Plante, J.A.; Royal, S.R.; et al. SARS-like WIV1-CoV poised for human emergence. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 3048–3053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morens, D.M.; Taubenberger, J.K.; Fauci, A.S. Universal Coronavirus Vaccines—An Urgent Need. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 386, 297–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, A.A.; van Doremalen, N.; Greaney, A.J.; Andersen, H.; Sharma, A.; Starr, T.N.; Keeffe, J.R.; Fan, C.; Schulz, J.E.; Gnanapragasam, P.N.P.; et al. Mosaic RBD nanoparticles protect against challenge by diverse sarbecoviruses in animal models. Science 2022, 377, eabq0839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, C.; Cohen, A.A.; Park, M.; Hung, A.F.; Keeffe, J.R.; Gnanapragasam, P.N.P.; Lee, Y.E.; Gao, H.; Kakutani, L.M.; Wu, Z.; et al. Neutralizing monoclonal antibodies elicited by mosaic RBD nanoparticles bind conserved sarbecovirus epitopes. Immunity 2022, 55, 2419–2435.e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Ni, W.; Liang, S.; Dong, L.; Xiang, M.; Cai, Z.; Niu, D.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, D.; Zheng, Y.; et al. Vaccination with Span, an antigen guided by SARS-CoV-2 S protein evolution, protects against challenge with viral variants in mice. Sci. Transl. Med. 2023, 15, eabo3332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, F.; Zai, X.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, J.; Chen, W. Challenges and developments in universal vaccine design against SARS-CoV-2 variants. NPJ Vaccines 2022, 7, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Lin, S.; Chen, Z.; Cao, Y.; He, B.; Lu, G. Targetable elements in SARS-CoV-2 S2 subunit for the design of pan-coronavirus fusion inhibitors and vaccines. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Yang, C.; Xu, X.F.; Xu, W.; Liu, S.W. Structural and functional properties of SARS-CoV-2 spike protein: Potential antivirus drug development for COVID-19. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2020, 41, 1141–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiliveri, S.C.; Louis, J.M.; Ghirlando, R.; Bax, A. Transient lipid-bound states of spike protein heptad repeats provide insights into SARS-CoV-2 membrane fusion. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, eabk2226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kapoor, K.; Chen, T.; Tajkhorshid, E. Posttranslational modifications optimize the ability of SARS-CoV-2 spike for effective interaction with host cell receptors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2119761119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, Y.; Zhang, J.; Xiao, T.; Peng, H.; Sterling, S.M.; Walsh, R.M., Jr.; Rawson, S.; Rits-Volloch, S.; Chen, B. Distinct conformational states of SARS-CoV-2 spike protein. Science 2020, 369, 1586–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, C.B.; Farzan, M.; Chen, B.; Choe, H. Mechanisms of SARS-CoV-2 entry into cells. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2022, 23, 3–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olukitibi, T.A.; Ao, Z.; Warner, B.; Unat, R.; Kobasa, D.; Yao, X. Significance of Conserved Regions in Coronavirus Spike Protein for Developing a Novel Vaccine against SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Vaccines 2023, 11, 545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, K.W.; Faulkner, N.; Finsterbusch, K.; Wu, M.; Harvey, R.; Hussain, S.; Greco, M.; Liu, Y.; Kjaer, S.; Swanton, C.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 S2-targeted vaccination elicits broadly neutralizing antibodies. Sci. Transl. Med. 2022, 14, eabn3715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halfmann, P.J.; Frey, S.J.; Loeffler, K.; Kuroda, M.; Maemura, T.; Armbrust, T.; Yang, J.E.; Hou, Y.J.; Baric, R.; Wright, E.R.; et al. Multivalent S2-based vaccines provide broad protection against SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern and pangolin coronaviruses. EBioMedicine 2022, 86, 104341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.Y.; Liao, H.Y.; Chen, X.; Wang, S.W.; Cheng, C.W.; Shahed-Al-Mahmud, M.; Liu, Y.M.; Mohapatra, A.; Chen, T.H.; Lo, J.M.; et al. Vaccination with SARS-CoV-2 spike protein lacking glycan shields elicits enhanced protective responses in animal models. Sci. Transl. Med. 2022, 14, eabm0899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.Y.; Cheng, C.W.; Kung, C.C.; Liao, K.S.; Jan, J.T.; Ma, C.; Wong, C.H. Glycosite-deleted mRNA of SARS-CoV-2 spike protein as a broad-spectrum vaccine. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2119995119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, W.; Lu, Y.; Zhao, Y.B.; Shen, F.; Fan, C.F.; Wang, Q.; He, W.Q.; He, X.Y.; Li, Z.K.; Chen, T.T.; et al. A variant-proof SARS-CoV-2 vaccine targeting HR1 domain in S2 subunit of spike protein. Cell Res. 2022, 32, 1068–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, P.; Yuan, M.; Song, G.; Beutler, N.; Shaabani, N.; Huang, D.; He, W.T.; Zhu, X.; Callaghan, S.; Yong, P.; et al. A human antibody reveals a conserved site on beta-coronavirus spike proteins and confers protection against SARS-CoV-2 infection. Sci. Transl. Med. 2022, 14, eabi9215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sauer, M.M.; Tortorici, M.A.; Park, Y.J.; Walls, A.C.; Homad, L.; Acton, O.J.; Bowen, J.E.; Wang, C.; Xiong, X.; de van der Schueren, W.; et al. Structural basis for broad coronavirus neutralization. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2021, 28, 478–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinto, D.; Sauer, M.M.; Czudnochowski, N.; Low, J.S.; Tortorici, M.A.; Housley, M.P.; Noack, J.; Walls, A.C.; Bowen, J.E.; Guarino, B.; et al. Broad betacoronavirus neutralization by a stem helix-specific human antibody. Science 2021, 373, 1109–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hurlburt, N.K.; Homad, L.J.; Sinha, I.; Jennewein, M.F.; MacCamy, A.J.; Wan, Y.H.; Boonyaratanakornkit, J.; Sholukh, A.M.; Jackson, A.M.; Zhou, P.; et al. Structural definition of a pan-sarbecovirus neutralizing epitope on the spike S2 subunit. Commun. Biol. 2022, 5, 342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, W.L.; Chiang, C.Y.; Lai, S.C.; Yu, C.Y.; Huang, Y.L.; Liao, H.C.; Liao, C.L.; Chen, H.W.; Liu, S.J. Monoclonal antibody targeting the conserved region of the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein to overcome viral variants. JCI Insight 2022, 7, e157597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heo, C.K.; Lim, W.H.; Yang, J.; Son, S.; Kim, S.J.; Kim, D.J.; Poo, H.; Cho, E.W. Novel S2 subunit-specific antibody with broad neutralizing activity against SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1307693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watanabe, Y.; Allen, J.D.; Wrapp, D.; McLellan, J.S.; Crispin, M. Site-specific glycan analysis of the SARS-CoV-2 spike. Science 2020, 369, 330–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, W.; Cai, Y.; Zhu, H.; Peng, H.; Voyer, J.; Rits-Volloch, S.; Cao, H.; Mayer, M.L.; Song, K.; Xu, C.; et al. Cryo-EM structure of SARS-CoV-2 postfusion spike in membrane. Nature 2023, 619, 403–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, K.B.; Jeon, J.H.; Choi, H.; Park, J.S.; Park, S.J.; Lee, H.J.; Park, J.M.; Cho, H.S.; Moon, J.S.; Oh, H.; et al. Construction of SARS-CoV-2 virus-like particles in plant. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Phan, V.M.; Heo, C.K.; Nguyen, H.V.; Lim, W.H.; Cho, E.W.; Poo, H.; Seo, T.S. Development of nucleocapsid-specific monoclonal antibodies for SARS-CoV-2 and their ELISA diagnostics on an automatic microfluidic device. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2023, 380, 133331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, S.; Ahn, S.B.; Kim, G.; Jang, Y.; Ko, C.; Kim, M.; Kim, S.J. Identification of broad-spectrum neutralizing antibodies against influenza A virus and evaluation of their prophylactic efficacy in mice. Antivir. Res. 2023, 213, 105591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- SARS-CoV-2 Circulating Variants. Available online: https://viralzone.expasy.org/9556 (accessed on 7 August 2023).
- Malonis, R.J.; Lai, J.R.; Vergnolle, O. Peptide-Based Vaccines: Current Progress and Future Challenges. Chem. Rev. 2020, 120, 3210–3229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Yuan, Y.; Liu, B.; Epstein, N.D.; Yang, Y. Protein-based nano-vaccines against SARS-CoV-2: Current design strategies and advances of candidate vaccines. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 236, 123979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mogus, A.T.; Liu, L.; Jia, M.; Ajayi, D.T.; Xu, K.; Kong, R.; Huang, J.; Yu, J.; Kwong, P.D.; Mascola, J.R.; et al. Virus-Like Particle Based Vaccines Elicit Neutralizing Antibodies against the HIV-1 Fusion Peptide. Vaccines 2020, 8, 765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hopp, T.P. and K. R. Woods A computer program for predicting protein antigenic determinants. Mol. Immunol. 1983, 20, 483–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaobotse, G.; Venkataraman, S.; Mmereke, K.M.; Moustafa, K.; Hefferon, K.; Makhzoum, A. Recent Progress on Vaccines Produced in Transgenic Plants. Vaccines 2022, 10, 1861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
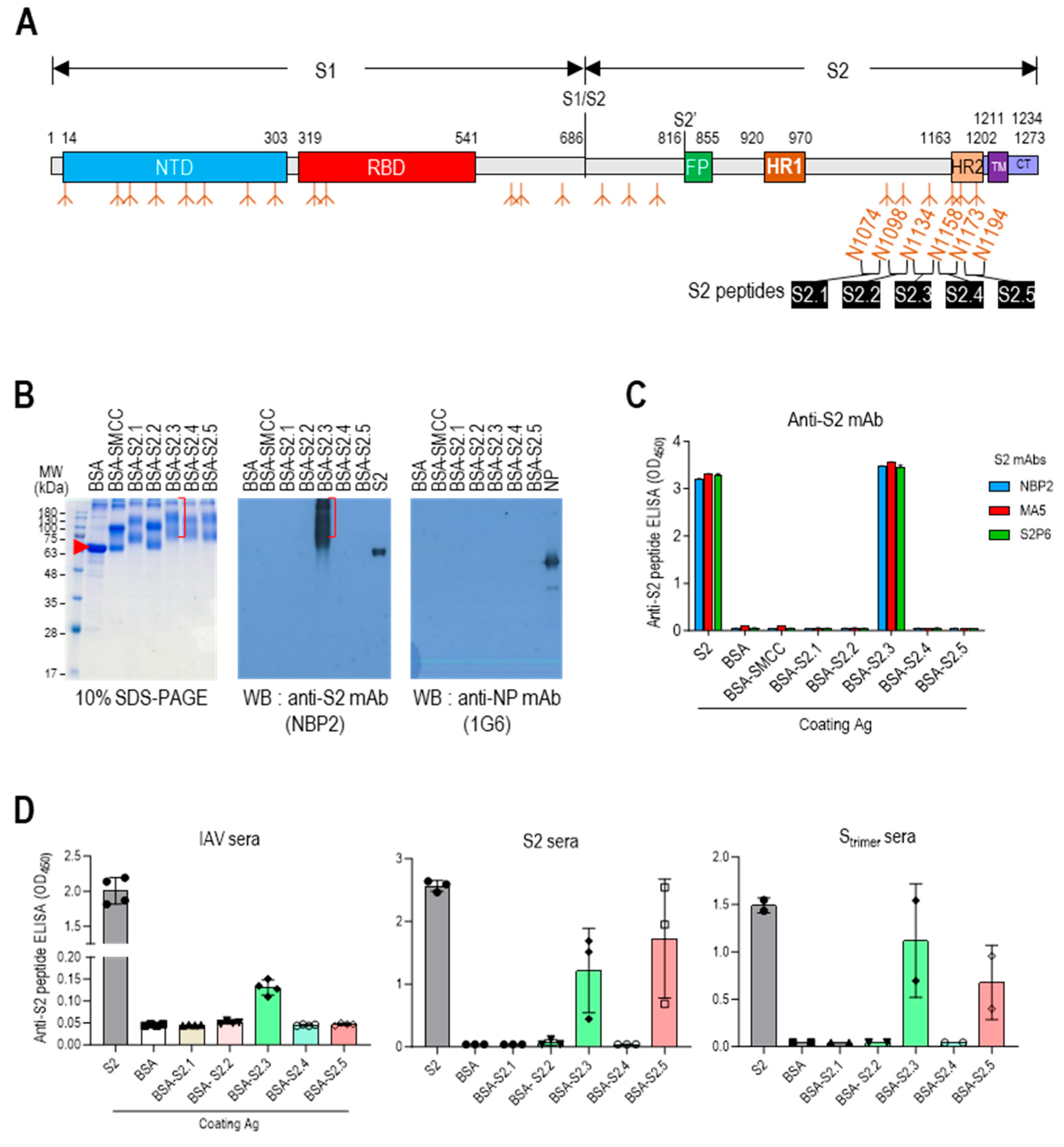


| Synthetic Peptide | Location * | Sequence | Number of Residues | Molecular Weight (g/mol) | pI † | Avg. Hydrophilicity ‡ | Hydrophilic Residues (%) § |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S2.1 | S (1083-1097) | HDGKAHFPREGVFVS (C) ** | 15 | 1682.86 | 7.98 | 0.19 | 33 |
| S2.2 | S (1102-1125) | WFVTQRNFYEPQIITTDNTFVSGN (C) | 24 | 2878.15 | 4.09 | −0.46 | 38 |
| S2.3 | S (1135-1157) | NTVYDPLQPELDSFKEELDKYFK (C) | 23 | 2819.12 | 4.08 | 0.47 | 52 |
| S2.4 | S (1159-1172) | HTSPDVDLGDISGI (C) | 14 | 1425.52 | 3.53 | 0.13 | 36 |
| S2.5 | S (1174-1193) | ASVVNIQKEIDRLNEVAKNL (C) | 20 | 2253.58 | 7.06 | 0.32 | 55 |
| S2.3pN | S (1135-1148) | NTVYDPLQPELDSF (C) | 14 | 1637.76 | 2.85 | −0.04 | 43 |
| S2.3pC | S (1144-1157) | ELDSFKEELDKYFK (C) | 14 | 1790.99 | 4.36 | 0.96 | 64 |
| S2.3.1 | S (1135-1159) | NTVYDPLQPELDSFKEELDKYFKNH (C) | 25 | 3070.36 | 4.45 | 0.42 | 52 |
| S2.3.2 | S (1133-1157) | (C) VNNTVYDPLQPELDSFKEELDKYFK # | 25 | 3032.35 | 4.08 | 0.38 | 52 |
| S2.5.1 | S (1174-1198) | ASVVNIQKEIDRLNEVAKNLNESLI (C) | 25 | 2810.20 | 4.74 | 0.25 | 56 |
| S2.5.2 | S (1177-1201) | VNIQKEIDRLNEVAKNLNESLIDLQ (C) | 25 | 2909.29 | 4.36 | 0.38 | 60 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Heo, C.-K.; Lim, W.-H.; Moon, K.-B.; Yang, J.; Kim, S.J.; Kim, H.-S.; Kim, D.-J.; Cho, E.-W. S2 Peptide-Conjugated SARS-CoV-2 Virus-like Particles Provide Broad Protection against SARS-CoV-2 Variants of Concern. Vaccines 2024, 12, 676. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines12060676
Heo C-K, Lim W-H, Moon K-B, Yang J, Kim SJ, Kim H-S, Kim D-J, Cho E-W. S2 Peptide-Conjugated SARS-CoV-2 Virus-like Particles Provide Broad Protection against SARS-CoV-2 Variants of Concern. Vaccines. 2024; 12(6):676. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines12060676
Chicago/Turabian StyleHeo, Chang-Kyu, Won-Hee Lim, Ki-Beom Moon, Jihyun Yang, Sang Jick Kim, Hyun-Soon Kim, Doo-Jin Kim, and Eun-Wie Cho. 2024. "S2 Peptide-Conjugated SARS-CoV-2 Virus-like Particles Provide Broad Protection against SARS-CoV-2 Variants of Concern" Vaccines 12, no. 6: 676. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines12060676
APA StyleHeo, C.-K., Lim, W.-H., Moon, K.-B., Yang, J., Kim, S. J., Kim, H.-S., Kim, D.-J., & Cho, E.-W. (2024). S2 Peptide-Conjugated SARS-CoV-2 Virus-like Particles Provide Broad Protection against SARS-CoV-2 Variants of Concern. Vaccines, 12(6), 676. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines12060676





