Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio and Cytokine Profiling as Predictors of Disease Severity and Survival in Unvaccinated COVID-19 Patients
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population and Sampling
2.2. Cytokine Quantification by Flow Cytometry
2.3. Peripheral Blood Cell Quantification
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Dynamic Changes in Cytokine Levels and Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio throughout COVID-19 Hospitalization
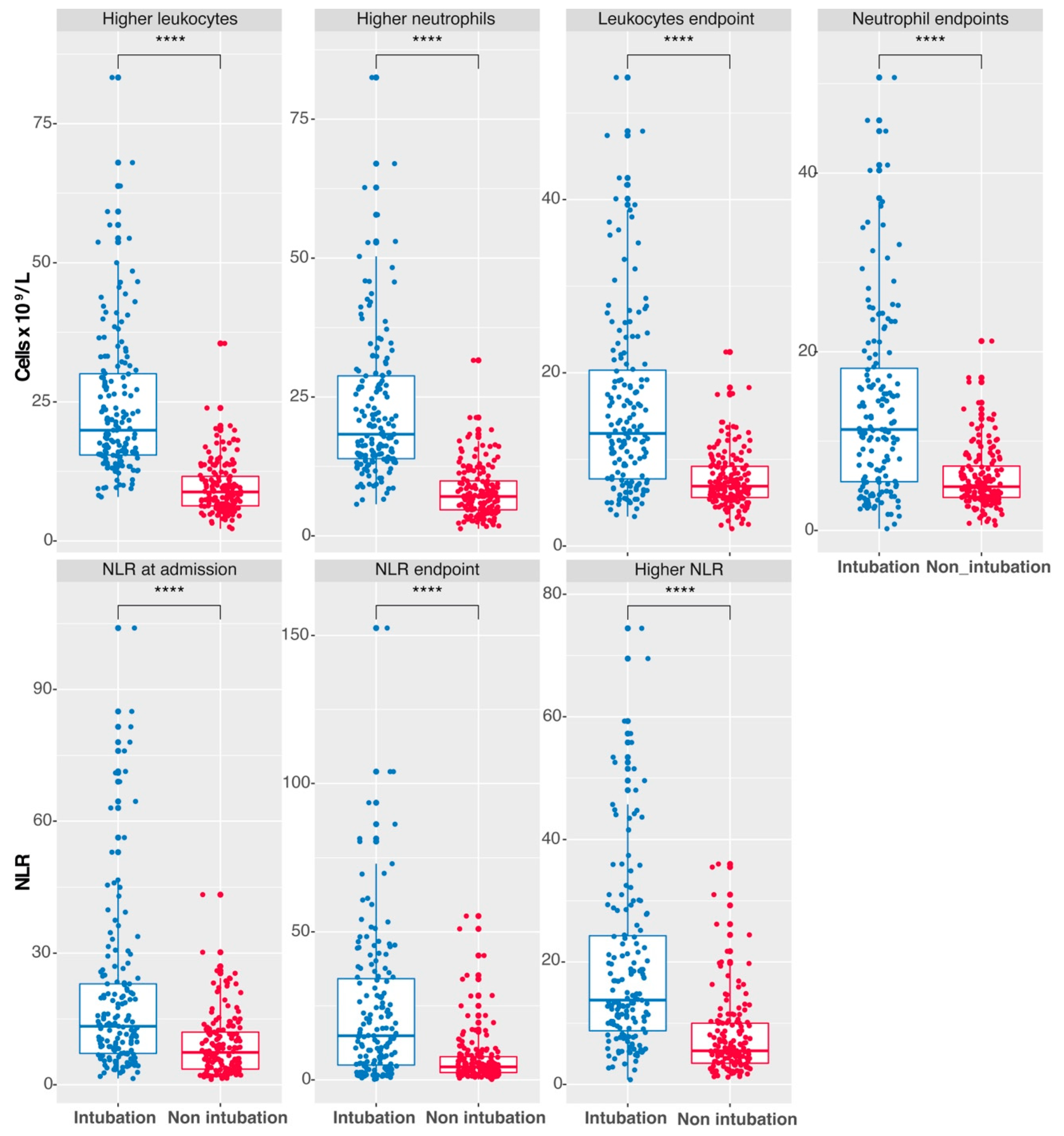
3.2. Elevated Leukocyte, Neutrophil Counts, and NLR as Indicators of Intubation in COVID-19 Patients
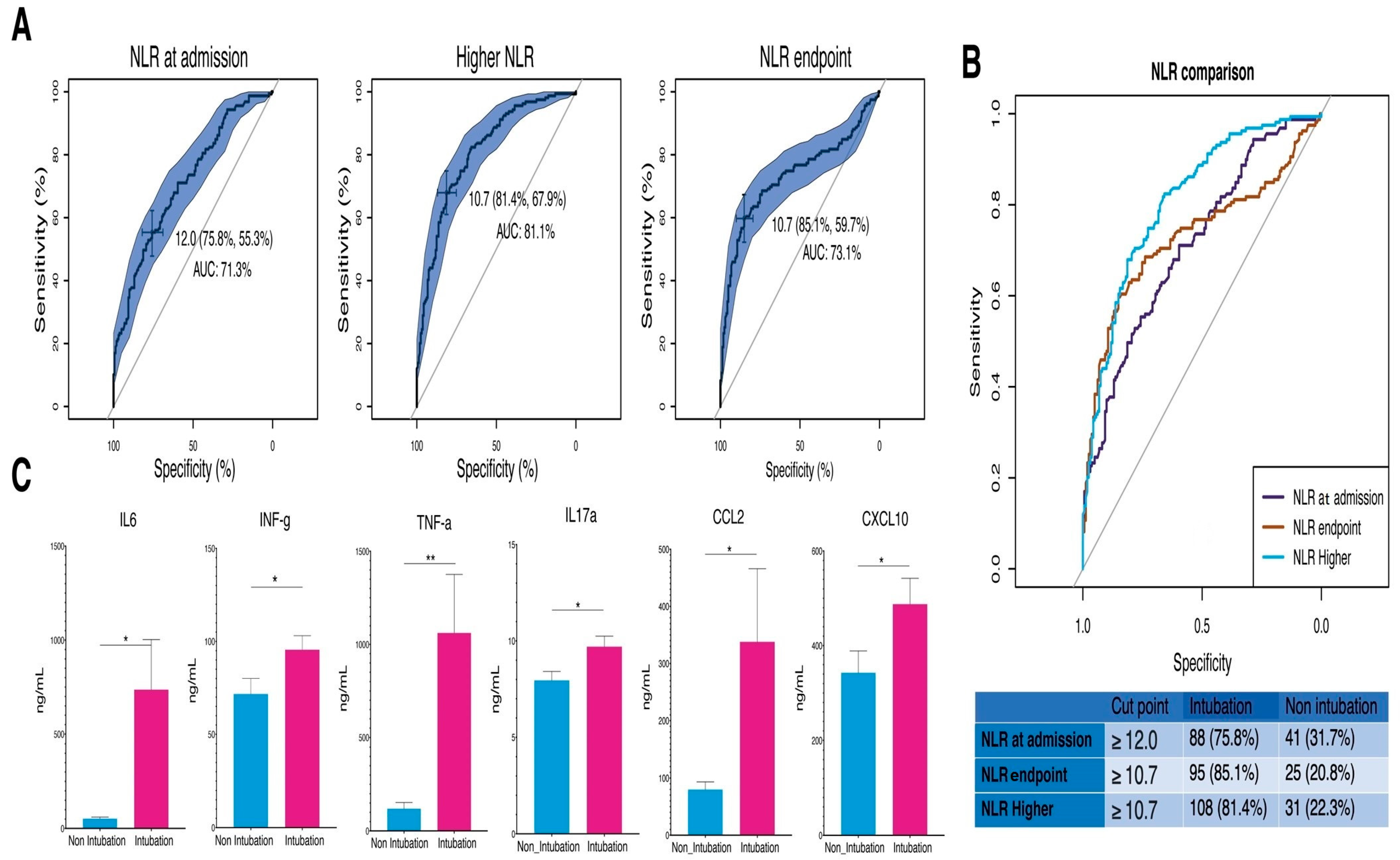
3.3. Assessing NLR Cutoff Points for Predicting Intubation in COVID-19 Patients
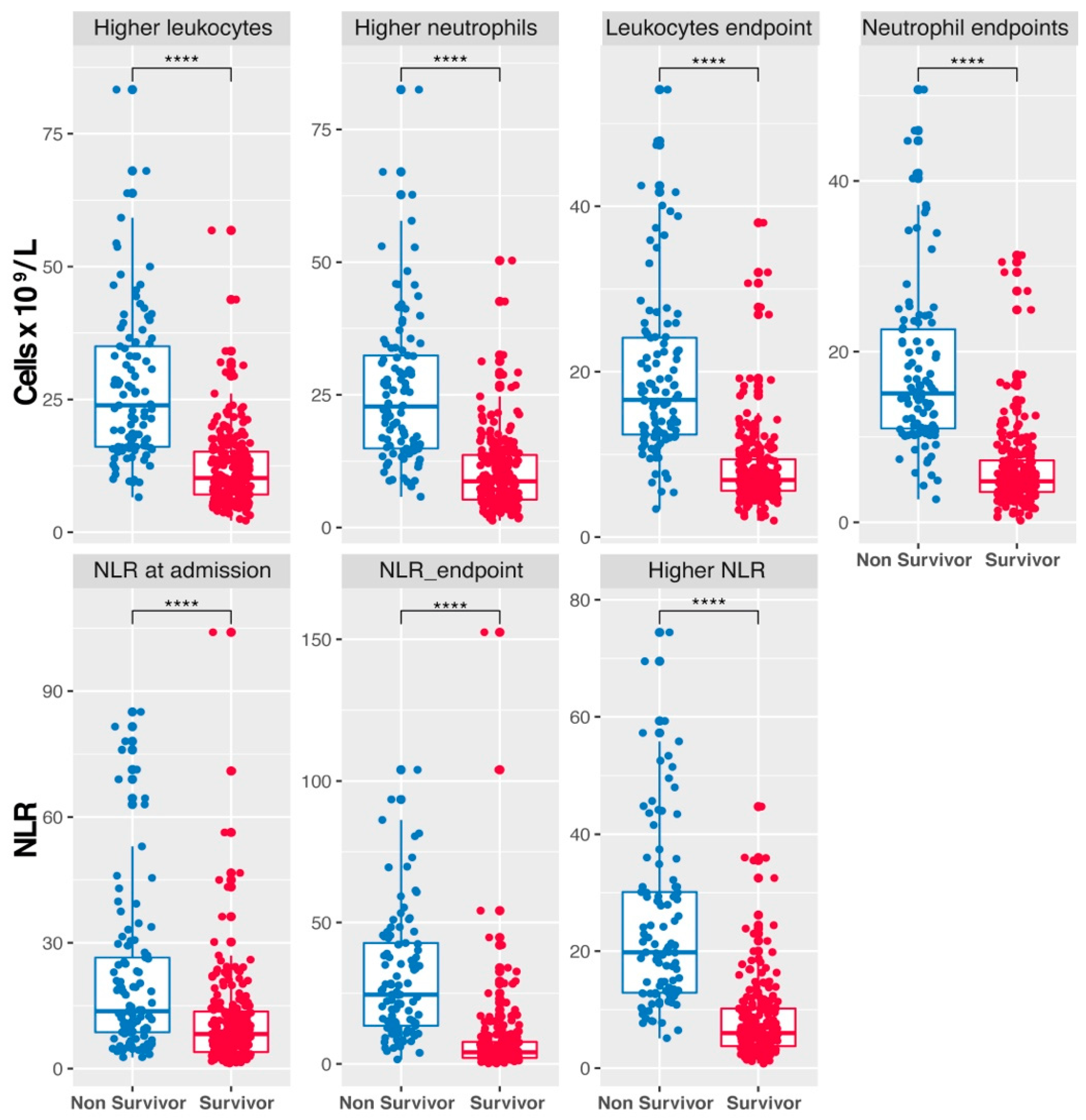
3.4. Differential Leukocyte and Neutrophil Counts and NLR Dynamics in COVID-19 Patient Survival
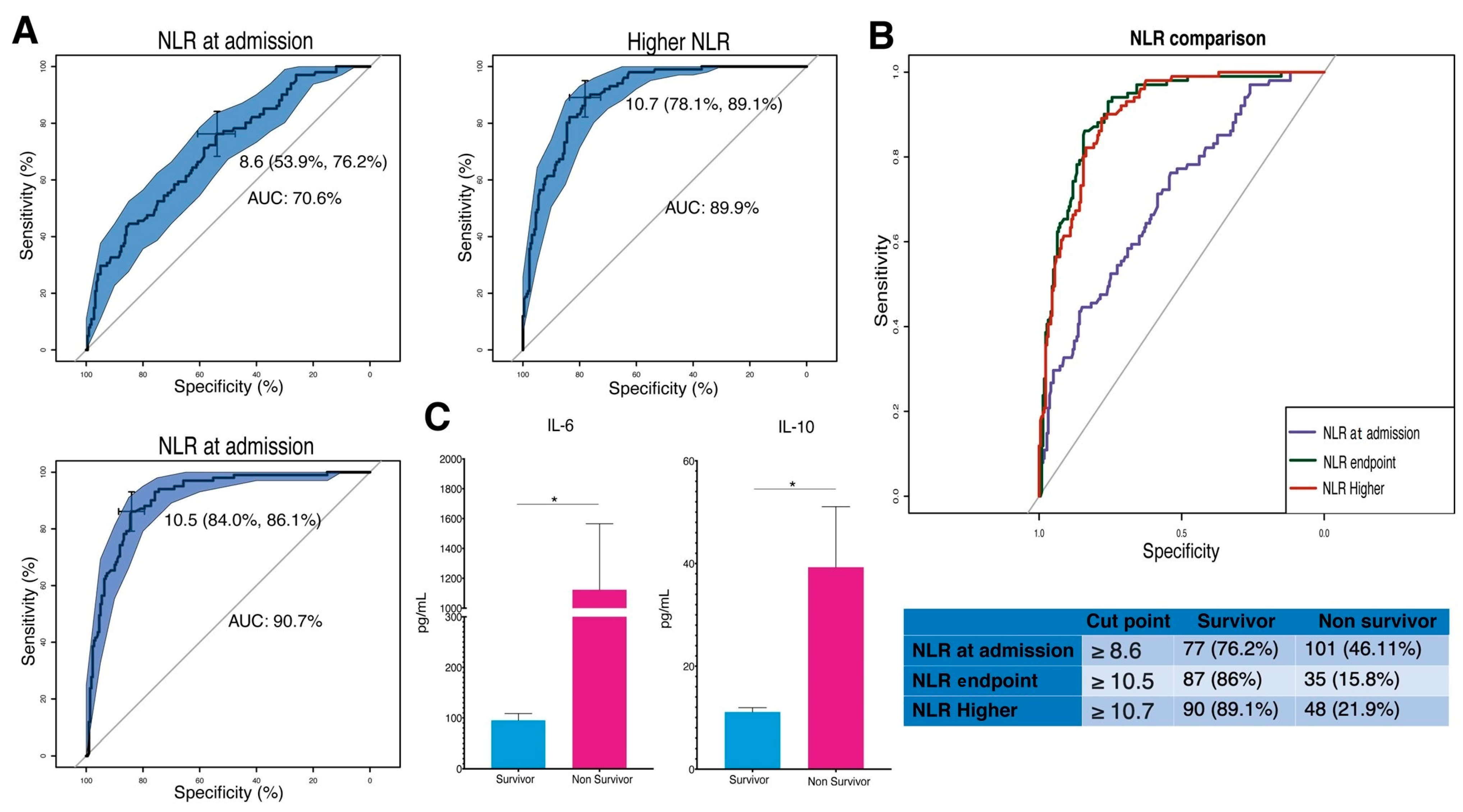
3.5. Predictive Significance of NLR and Cytokine Levels in COVID-19 Survival
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jebril, N. World Health Organization Declared a Pandemic Public Health Menace: A Systematic Review of the Coronavirus Disease 2019 “COVID-19”. SSRN Electron. J. 2020, 24, 2784–2795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Zowalaty, M.E.; Järhult, J.D. From SARS to COVID-19: A Previously Unknown SARS-Related Coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2) of Pandemic Potential Infecting Humans—Call for a One Health Approach. One Health 2020, 9, 100124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Datta, S.D.; Talwar, A.; Lee, J.T. A Proposed Framework and Timeline of the Spectrum of Disease Due to SARS-CoV-2 Infection: Illness beyond Acute Infection and Public Health Implications. JAMA-J. Am. Med. Assoc. 2020, 324, 2251–2252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fisman, D.N.; Amoako, A.; Tuite, A.R. Impact of Population Mixing between Vaccinated and Unvaccinated Subpopulations on Infectious Disease Dynamics: Implications for SARS-CoV-2 Transmission. CMAJ 2022, 194, E573–E580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milman, O.; Yelin, I.; Aharony, N.; Katz, R.; Herzel, E.; Ben-Tov, A.; Kuint, J.; Gazit, S.; Chodick, G.; Patalon, T.; et al. Community-Level Evidence for SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine Protection of Unvaccinated Individuals. Nat. Med. 2021, 27, 1367–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, B.; Huang, S.; Yin, L. The Cytokine Storm and COVID-19. J. Med. Virol. 2021, 93, 250–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.S.; Lee, J.Y.; Yang, J.W.; Lee, K.H.; Effenberger, M.; Szpirt, W.; Kronbichler, A.; Shin, J. Il Immunopathogenesis and Treatment of Cytokine Storm in COVID-19. Theranostics 2020, 11, 316–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soy, M.; Keser, G.; Atagündüz, P. Pathogenesis and Treatment of Cytokine Storm in COVID-19. Turk. J. Biol. 2021, 45, 372–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soy, M.; Keser, G.; Atagündüz, P.; Tabak, F.; Atagündüz, I.; Kayhan, S. Cytokine Storm in COVID-19: Pathogenesis and Overview of Anti-Inflammatory Agents Used in Treatment. Clin. Rheumatol. 2020, 39, 2085–2094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhang, D.; Xu, Z.; Ji, J.; Wen, C. Cytokine Storm in COVID-19: The Current Evidence and Treatment Strategies. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Qin, L.; Li, K.; Wang, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Xu, B.; Liang, L.; Dai, Y.; Feng, Y.; Sun, J.; et al. A Novel Scoring System for Prediction of Disease Severity in COVID-19. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, K.; Liu, X.; Yip, R.; Yankelevitz, D.F.; Henschke, C.I.; Geng, Y.; Fang, Y.; Li, W.; Pan, C.; Chen, X.; et al. Early Prediction of Severity in Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) Using Quantitative CT Imaging. Clin. Imaging 2021, 78, 223–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, T.; Khandakar, A.; Hoque, M.E.; Ibtehaz, N.; Kashem, S.B.; Masud, R.; Shampa, L.; Hasan, M.M.; Islam, M.T.; Al-Maadeed, S.; et al. Development and Validation of an Early Scoring System for Prediction of Disease Severity in COVID-19 Using Complete Blood Count Parameters. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 120422–120441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, C.; Chen, Y.; Ji, Y.; He, X.; Xue, D. Increased Serum Levels of Hepcidin and Ferritin Are Associated with Severity of COVID-19. Med. Sci. Monit. 2020, 26, e926178-1–e926178-6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, C.; Huang, Y.; Shi, F.; Tan, K.; Ma, Q.; Chen, Y.; Jiang, X.; Li, X. C-Reactive Protein Correlates with Computed Tomographic Findings and Predicts Severe COVID-19 Early. J. Med. Virol. 2020, 92, 856–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Yao, M.; Zhu, Z.; Sun, Y.; Han, X. The Application Research of AI Image Recognition and Processing Technology in the Early Diagnosis of the COVID-19. BMC Med. Imaging 2022, 22, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yaşar, Ş.; Çolak, C.; Yoloğlu, S. Artificial Intelligence-Based Prediction of Covid-19 Severity on the Results of Protein Profiling. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2021, 202, 105996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jimeno, S.; Ventura, P.S.; Castellano, J.M.; García-Adasme, S.I.; Miranda, M.; Touza, P.; Lllana, I.; López-Escobar, A. Prognostic Implications of Neutrophil-Lymphocyte Ratio in COVID-19. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2021, 51, e13404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pimentel, G.D.; Dela Vega, M.C.M.; Laviano, A. High Neutrophil to Lymphocyte Ratio as a Prognostic Marker in COVID-19 Patients. Clin. Nutr. ESPEN 2020, 40, 101–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eid, M.M.; Al-Kaisy, M.; Regeia, W.A.L.; Khan, H.J. The Prognostic Accuracy of Neutrophil-Lymphocyte Ratio in COVID-19 Patients. Front. Emerg. Med. 2021, 5, e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkhatip, A.A.A.M.M.; Kamel, M.G.; Hamza, M.K.; Farag, E.M.; Yassin, H.M.; Elayashy, M.; Naguib, A.A.; Wagih, M.; Abd-Elhay, F.A.E.; Algameel, H.Z.; et al. The Diagnostic and Prognostic Role of Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio in COVID-19: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Expert. Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2021, 21, 505–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudjud, R.W.; Zulfariansyah, A.; Ardiana, K. Comparison of Total Lymphocytes, Neutrophils to Lymphocytes Ratio, and C-Reactive Protein in Vaccinated and Non-Vaccinated Severe COVID-19 Patients. Anaesth. Pain. Intensive Care 2022, 26, 656–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayyas, F.; Tashtoush, M.; Tashtoush, Z. Predictors of Intensive Care Unit Length of Stay and Mortality among Unvaccinated COVID-19 Patients in Jordan. Infect. Prev. Pract. 2023, 5, 100278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martynova, E.; Hamza, S.; Markelova, M.; Garanina, E.; Davidyuk, Y.; Shakirova, V.; Kaushal, N.; Baranwal, M.; Stott-Marshall, R.J.; Foster, T.L.; et al. Immunogenic SARS-CoV-2 S and N Protein Peptide and Cytokine Combinations as Biomarkers for Early Prediction of Fatal COVID-19. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 830715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozsurekci, Y.; Aykac, K.; Er, A.G.; Halacli, B.; Arasli, M.; Oygar, P.D.; Gürlevik, S.; Cura Yayla, B.C.; Karakaya, J.; Alp, A.; et al. Predictive Value of Cytokine/Chemokine Responses for the Disease Severity and Management in Children and Adult Cases with COVID-19. J. Med. Virol. 2021, 93, 2828–2837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kagansky, N.; Levy, Y.; Awar, A.; Derazne, E.; Shilovsky, A.; Kagansky, D.; Chepelev, V.; Mazurez, E.; Stambler, I.; Levtzion-Korach, O. Do Neutrophil–Lymphocyte Ratio and Platelet–Lymphocyte Ratio Need to Be Stratified for Age and Comorbidities in COVID-19 Disease? A Subgroup Analysis of Two Distinct Cohorts over Disease Course. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ntalouka, M.P.; Brotis, A.; Mermiri, M.; Pagonis, A.; Chatzis, A.; Bareka, M.; Kotsi, P.; Pantazopoulos, I.; Gourgoulianis, K.; Arnaoutoglou, E.M. Predicting the Outcome of Patients with Severe COVID-19 with Simple Inflammatory Biomarkers: The Utility of Novel Combined Scores—Results from a European Tertiary/Referral Centre. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sayed, A.A. Assessing the Diagnostic Values of the Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio (NLR) and Systematic Immunoinflammatory Index (SII) as Biomarkers in Predicting COVID-19 Severity: A Multicentre Comparative Study. Med. B Aires 2024, 60, 602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grotberg, J.C.; Kraft, B.D. Timing of Intubation in COVID-19: When It Is Too Early and When It Is Too Late. Crit. Care Explor. 2023, 5, e0863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ocaña-Ramm, G.; Gallardo-Pérez, M.M.; Garcés-Eisele, S.J.; Sánchez-Bonilla, D.; Robles-Nasta, M.; Hernández-Flores, E.J.; Hamilton-Avilés, L.E.; Negrete-Rodríguez, P.; Melgar-De-La-Paz, M.; Lira-Lara, O.; et al. Neutrophil to Lymphocyte Ratio and Systemic Immune-Inflammatory Index as Markers of Response to Autologous Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation in Persons with Multiple Sclerosis. Int. J. Lab. Hematol. 2024, 46, 620–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herold, T.; Jurinovic, V.; Arnreich, C.; Lipworth, B.J.; Hellmuth, J.C.; von Bergwelt-Baildon, M.; Klein, M.; Weinberger, T. Elevated Levels of IL-6 and CRP Predict the Need for Mechanical Ventilation in COVID-19. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2020, 146, 128–136.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Singer, M.; Brahier, T.; Ngai, M.; Wright, J.; Weckman, A.M.; Erice, C.; Meuwly, J.Y.; Hugli, O.; Kain, K.C.; Boillat-Blanco, N. COVID-19 Risk Stratification Algorithms Based on STREM-1 and IL-6 in Emergency Department. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2021, 147, 99–106.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gadotti, A.C.; de Castro Deus, M.; Telles, J.P.; Wind, R.; Goes, M.; Garcia Charello Ossoski, R.; de Padua, A.M.; de Noronha, L.; Moreno-Amaral, A.; Baena, C.P.; et al. IFN-γ Is an Independent Risk Factor Associated with Mortality in Patients with Moderate and Severe COVID-19 Infection. Virus Res. 2020, 289, 198171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Resende, G.G.; da Cruz Lage, R.; Lobê, S.Q.; Medeiros, A.F.; Costa e Silva, A.D.; Nogueira Sá, A.T.; de Oliveira, A.J.A.; Sousa, D.; Guimarães, H.C.; Gomes, I.C.; et al. Blockade of Interleukin Seventeen (IL-17A) with Secukinumab in Hospitalized COVID-19 Patients—The BISHOP Study. Infect. Dis. 2022, 54, 591–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ranjbar, M.; Cusack, R.P.; Whetstone, C.E.; Brister, D.L.; Wattie, J.; Wiltshire, L.; Alsaji, N.; Le Roux, J.; Cheng, E.; Srinathan, T.; et al. Immune Response Dynamics and Biomarkers in COVID-19 Patients. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 6427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Fung, E.; Wong, C.-K.; Ling, L.; Lui, G.; Lai, C.K.C.; Ng, R.W.Y.; Sze, R.K.H.; Ho, W.C.S.; Hui, D.S.C.; et al. Early Metabolomic and Immunologic Biomarkers as Prognostic Indicators for COVID-19. Metabolites 2024, 14, 380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moradian, N.; Gouravani, M.; Salehi, M.A.; Heidari, A.; Shafeghat, M.; Hamblin, M.R.; Rezaei, N. Cytokine Release Syndrome: Inhibition of pro-Inflammatory Cytokines as a Solution for Reducing COVID-19 Mortality. Eur. Cytokine Netw. 2020, 31, 81–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halim, C.; Mirza, A.F.; Sari, M.I. The Association between TNF-α, IL-6, and Vitamin D Levels and COVID-19 Severity and Mortality: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Pathogens 2022, 11, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maione, F.; Casillo, G.M.; Raucci, F.; Salvatore, C.; Ambrosini, G.; Costa, L.; Scarpa, R.; Caso, F.; Bucci, M. Interleukin-17A (IL-17A): A Silent Amplifier of COVID-19. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 142, 111980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cîrjaliu, R.-E.; Tofolean, I.-T.; Tofolean, D.-E.; Chisoi, A.; Oancea, C.; Vastag, E.; Marc, M.; Bratosin, F.; Rosca, O.; Fildan, A.-P. Predictive Value and Diagnostic Potential of IL-10, IL-17A, IL1-β, IL-6, CXCL, and MCP for Severe COVID-19 and COVID-19 Mortality. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Yang, G.; Wang, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Ding, K.; Ji, C.; Shi, Z.; Li, H.; Li, Y.; Li, S. C1R, CCL2, and TNFRSF1A Genes in Coronavirus Disease-COVID-19 Pathway Serve as Novel Molecular Biomarkers of GBM Prognosis and Immune Infiltration. Dis. Markers 2022, 2022, 8602068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorè, N.I.; De Lorenzo, R.; Rancoita, P.M.V.; Cugnata, F.; Agresti, A.; Benedetti, F.; Bianchi, M.E.; Bonini, C.; Capobianco, A.; Conte, C.; et al. CXCL10 Levels at Hospital Admission Predict COVID-19 Outcome: Hierarchical Assessment of 53 Putative Inflammatory Biomarkers in an Observational Study. Mol. Med. 2021, 27, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blot, M.; Jacquier, M.; Aho Glele, L.S.; Beltramo, G.; Nguyen, M.; Bonniaud, P.; Prin, S.; Andreu, P.; Bouhemad, B.; Bour, J.B.; et al. CXCL10 Could Drive Longer Duration of Mechanical Ventilation during COVID-19 ARDS. Crit. Care 2020, 24, 632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McElvaney, O.J.; Hobbs, B.D.; Qiao, D.; McElvaney, O.F.; Moll, M.; McEvoy, N.L.; Clarke, J.; O’Connor, E.; Walsh, S.; Cho, M.H.; et al. A Linear Prognostic Score Based on the Ratio of Interleukin-6 to Interleukin-10 Predicts Outcomes in COVID-19. EBioMedicine 2020, 61, 103026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Interleukin-6 Receptor Antagonists in Critically Ill Patients with COVID-19. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 1147–1149. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Udomsinprasert, W.; Jittikoon, J.; Sangroongruangsri, S.; Chaikledkaew, U. Circulating Levels of Interleukin-6 and Interleukin-10, but Not Tumor Necrosis Factor-Alpha, as Potential Biomarkers of Severity and Mortality for COVID-19: Systematic Review with Meta-Analysis. J. Clin. Immunol. 2021, 41, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Méndez Rodríguez, M.L.; Ponciano-Gómez, A.; Campos-Aguilar, M.; Tapia-Sánchez, W.D.; Duarte-Martínez, C.L.; Romero-Herrera, J.S.; Olivas-Quintero, S.; Saucedo-Campos, A.D.; Méndez-Cruz, A.R.; Jimenez-Flores, R.; et al. Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio and Cytokine Profiling as Predictors of Disease Severity and Survival in Unvaccinated COVID-19 Patients. Vaccines 2024, 12, 861. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines12080861
Méndez Rodríguez ML, Ponciano-Gómez A, Campos-Aguilar M, Tapia-Sánchez WD, Duarte-Martínez CL, Romero-Herrera JS, Olivas-Quintero S, Saucedo-Campos AD, Méndez-Cruz AR, Jimenez-Flores R, et al. Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio and Cytokine Profiling as Predictors of Disease Severity and Survival in Unvaccinated COVID-19 Patients. Vaccines. 2024; 12(8):861. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines12080861
Chicago/Turabian StyleMéndez Rodríguez, Miguel Leonardo, Alberto Ponciano-Gómez, Myriam Campos-Aguilar, Wilfrido David Tapia-Sánchez, Carlos Leonardo Duarte-Martínez, Jesús Salvador Romero-Herrera, Sandra Olivas-Quintero, Alberto Daniel Saucedo-Campos, Adolfo Rene Méndez-Cruz, Rafael Jimenez-Flores, and et al. 2024. "Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio and Cytokine Profiling as Predictors of Disease Severity and Survival in Unvaccinated COVID-19 Patients" Vaccines 12, no. 8: 861. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines12080861
APA StyleMéndez Rodríguez, M. L., Ponciano-Gómez, A., Campos-Aguilar, M., Tapia-Sánchez, W. D., Duarte-Martínez, C. L., Romero-Herrera, J. S., Olivas-Quintero, S., Saucedo-Campos, A. D., Méndez-Cruz, A. R., Jimenez-Flores, R., Ortiz-Navarrete, V., Romero-Ramírez, H., Santos-Argumedo, L., & Rosales-García, V. H. (2024). Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio and Cytokine Profiling as Predictors of Disease Severity and Survival in Unvaccinated COVID-19 Patients. Vaccines, 12(8), 861. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines12080861







