Exploring T-Cell Immunity to Hepatitis C Virus: Insights from Different Vaccine and Antigen Presentation Strategies
Abstract
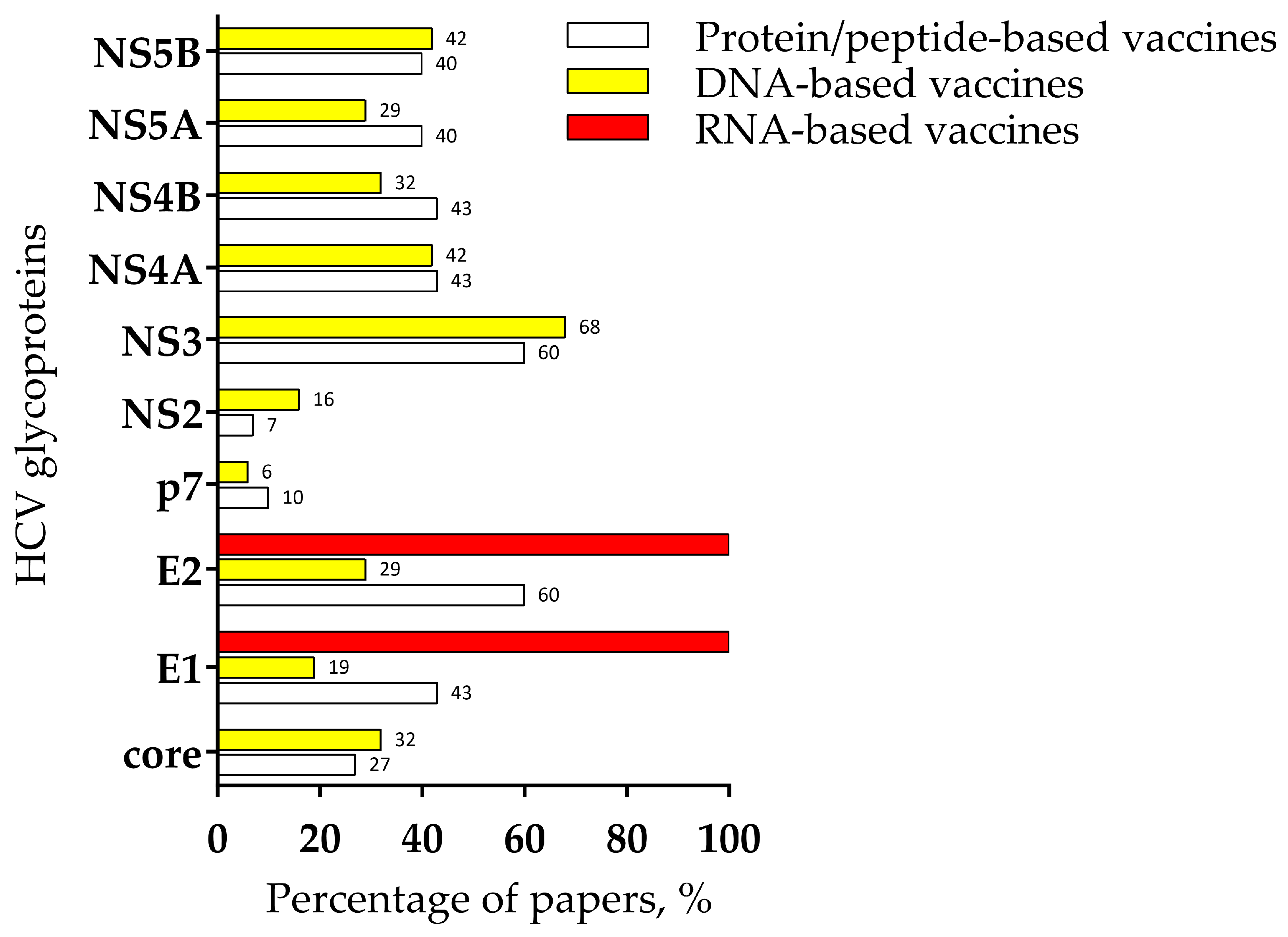
:1. Introduction
The HCV Infection and Cell-Mediated Immune Response
2. Materials and Methods
3. Peptide/Protein-Based Vaccines
3.1. Structural Proteins
3.2. Core Protein
3.3. Envelope Glycoprotein 1 and 2
3.3.1. Soluble E2 Expression Using Different Systems and Their Formulation with Various Adjuvants
3.3.2. Antigen Presentation by Viral Vectors
3.3.3. Antigen Expression by Virus-like Particles
3.4. Non-Structural Proteins
3.4.1. P7
3.4.2. NS3 and NS5B
3.4.3. NS3, NS4A, and NS4B
3.4.4. NS2, NS3, NS4A, NS4B, NS5A, and NS5B
3.5. Combination of the Structural and Non-Structural Proteins
3.5.1. E1, E2, NS3, and NS4A
3.5.2. E1, E2, NS3, NS4A, NS4B, NS5A, and NS5B
3.5.3. Full-Length HCV Genome
3.6. Other Approaches
3.6.1. Core, E1, E2, and NS3
3.6.2. E1, E2, NS4B, NS5A, and NS5B
4. DNA-Based Vaccines
4.1. Structural Proteins
4.1.1. Core
4.1.2. Envelope Glycoprotein 1 and 2
4.2. Non-Structural Proteins
4.2.1. NS2
4.2.2. NS3
4.2.3. NS3 and NS4A
4.2.4. NS5A
4.2.5. NS3, NS4A, NS4B, NS5A, and NS5B
4.3. Viral Vectors in DNA-Based Vaccines
NS3, NS4A, NS4B, and NS5B
4.4. Vaccination of Non-Human Primates
NS3, NS4A, NS4B, NS5A, and NS5B
4.5. Combination of the Structural and Non-Structural Proteins
4.5.1. Core, E2, NS3, and NS5B
4.5.2. Core, E1, E2, p7, NS2, and NS3
4.5.3. Core, E1, E2, NS2, NS3, NS4, and NS5
4.6. HCV DNA Delivered by Viral Vectors
Core, E1, E2, and NS3
4.7. Full-Length HCV Genome
5. RNA-Based Vaccines
Envelope Glycoprotein 1 and 2
6. Human Clinical Trials
6.1. Clinical Trials Involving Viral Vectors
NS3 and NS5B
6.2. NS3, NS4A, NS4B, NS5A, and NS5B
6.3. Intramuscular Electroporation for HCV Vaccine Delivery in Human Clinical Trials
6.3.1. NS3 and NS4A
6.3.2. NS3, NS4A, NS4B, and NS5A
7. Discussion and Future Directions
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization. Global Health Sector Strategies on, Respectively, HIV, Viral Hepatitis and Sexually Transmitted Infections for the Period 2022–2030. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240053779 (accessed on 7 July 2023).
- Messina, J.P.; Humphreys, I.; Flaxman, A.; Brown, A.; Cooke, G.S.; Pybus, O.G.; Barnes, E. Global Distribution and Prevalence of Hepatitis C Virus Genotypes. Hepatology 2015, 61, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borgia, S.M.; Hedskog, C.; Parhy, B.; Hyland, R.H.; Stamm, L.M.; Brainard, D.M.; Subramanian, M.G.; McHutchison, J.G.; Mo, H.; Svarovskaia, E.; et al. Identification of a Novel Hepatitis C Virus Genotype from Punjab, India: Expanding Classification of Hepatitis C Virus into 8 Genotypes. J. Infect. Dis. 2018, 218, 1722–1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, D.B.; Bukh, J.; Kuiken, C.; Muerhoff, A.S.; Rice, C.M.; Stapleton, J.T.; Simmonds, P. Expanded Classification of Hepatitis C Virus into 7 Genotypes and 67 Subtypes: Updated Criteria and Genotype Assignment Web Resource. Hepatology 2014, 59, 318–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moradpour, D.; Penin, F.; Rice, C.M. Replication of Hepatitis C Virus. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2007, 5, 453–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fried, M.W.; Shiffman, M.L.; Reddy, K.R.; Smith, C.; Marinos, G.; Gonçales, F.L.; Häussinger, D.; Diago, M.; Carosi, G.; Dhumeaux, D.; et al. Peginterferon Alfa-2a plus Ribavirin for Chronic Hepatitis C Virus Infection. N. Engl. J. Med. 2002, 347, 975–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pawlotsky, J.M. New Hepatitis C Therapies: The Toolbox, Strategies, and Challenges. Gastroenterology 2014, 146, 1176–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leoni, M.C.; Ustianowski, A.; Farooq, H.; Arends, J.E. HIV, HCV and HBV: A Review of Parallels and Differences. Infect. Dis. Ther. 2018, 7, 407–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morris, M.D.; Mirzazadeh, A.; Evans, J.L.; Briceno, A.; Coffin, P.; Hahn, J.A.; Page, K.A. Treatment Cascade for Hepatitis C Virus in Young Adult People Who Inject Drugs in San Francisco: Low Number Treated. Drug Alcohol. Depend. 2019, 198, 133–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Global Health Sector Strategy on Viral Hepatitis 2016–2021. Available online: https://iris.who.int/bitstream/handle/10665/246177/WHO-HIV-2016.06-eng.pdf?sequence=1 (accessed on 22 March 2024).
- Bowen, D.G.; Walker, C.M. Adaptive Immune Responses in Acute and Chronic Hepatitis C Virus Infection. Nature 2005, 436, 946–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seeff, L.B. Natural History of Chronic Hepatitis C. Hepatology 2002, 36, s35–s46. [Google Scholar]
- Bailey, J.R.; Barnes, E.; Cox, A.L. Approaches, Progress, and Challenges to Hepatitis C Vaccine Development. Gastroenterology 2019, 156, 418–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luxenburger, H.; Neumann-Haefelin, C.; Thimme, R.; Boettler, T. HCV-Specific T Cell Responses During and After Chronic HCV Infection. Viruses 2018, 10, 645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grakoui, A.; Shoukry, N.H.; Woollard, D.J.; Han, J.-H.; Hanson, H.L.; Ghrayeb, J.; Murthy, K.K.; Rice, C.M.; Walker, C.M. HCV Persistence and Immune Evasion in the Absence of Memory T Cell Help. Science 2003, 302, 659–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shoukry, N.H.; Grakoui, A.; Houghton, M.; Chien, D.Y.; Ghrayeb, J.; Reimann, K.A.; Walker, C.M. Memory CD8+ T Cells Are Required for Protection from Persistent Hepatitis C Virus Infection. J. Exp. Med. 2003, 197, 1645–1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lechner, F.; Wong, D.K.H.; Dunbar, P.R.; Chapman, R.; Chung, R.T.; Dohrenwend, P.; Robbins, G.; Phillips, R.; Klenerman, P.; Walker, B.D. Analysis of Successful Immune Responses in Persons Infected with Hepatitis C Virus. J. Exp. Med. 2000, 191, 1499–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fitzmaurice, K.; Hurst, J.; Dring, M.; Rauch, A.; McLaren, P.J.; Günthard, H.F.; Gardiner, C.; Klenerman, P.; Irish HCV Research Consortium; Swiss HIV Cohort Study. Additive Effects of HLA Alleles and Innate Immune Genes Determine Viral Outcome in HCV Infection. Gut 2015, 64, 813–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neumann-Haefelin, C.; Thimme, R. Adaptive Immune Responses in Hepatitis C Virus Infection BT-Hepatitis C Virus: From Molecular Virology to Antiviral Therapy; Bartenschlager, R., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; pp. 243–262. ISBN 978-3-642-27340-7. [Google Scholar]
- Alfei, F.; Kanev, K.; Hofmann, M.; Wu, M.; Ghoneim, H.E.; Roelli, P.; Utzschneider, D.T.; von Hoesslin, M.; Cullen, J.G.; Fan, Y.; et al. TOX Reinforces the Phenotype and Longevity of Exhausted T Cells in Chronic Viral Infection. Nature 2019, 571, 265–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.Y.; Wolski, D.; Aneja, J.; Matsubara, L.; Robilotti, B.; Hauck, G.; de Sousa, P.S.F.; Subudhi, S.; Fernandes, C.A.; Hoogeveen, R.C.; et al. Hepatitis C Virus–Specific CD4+ T Cell Phenotype and Function in Different Infection Outcomes. J. Clin. Investig. 2020, 130, 768–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.K.; Shukla, P. Microbial Platform Technology for Recombinant Antibody Fragment Production: A Review. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2017, 43, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, G.; Walsh, E. Biopharmaceutical Benchmarks 2022. Nat. Biotechnol. 2022, 40, 1722–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Travieso, T.; Li, J.; Mahesh, S.; Mello, J.D.F.R.E.; Blasi, M. The Use of Viral Vectors in Vaccine Development. NPJ Vaccines 2022, 7, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Banskota, S.; Raguram, A.; Suh, S.; Du, S.W.; Davis, J.R.; Choi, E.H.; Wang, X.; Nielsen, S.C.; Newby, G.A.; Randolph, P.B.; et al. Engineered Virus-like Particles for Efficient in Vivo Delivery of Therapeutic Proteins. Cell 2022, 185, 250–265.e16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yazdanian, M.; Memarnejadian, A.; Mahdavi, M.; Sadat, S.M.; Motevali, F.; Vahabpour, R.; Khanahmad, H.; Siadat, S.D.; Aghasadeghi, M.R.; Roohvand, F. Immunization of Mice by BCG Formulated HCV Core Protein Elicited Higher Th1-Oriented Responses Compared to Pluronic-F127 Copolymer. Hepat. Mon. 2013, 13, e14178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; von Schaewen, M.; Wang, X.; Tao, W.; Zhang, Y.; Li, L.; Heller, B.; Hrebikova, G.; Deng, Q.; Ploss, A.; et al. Altered Glycosylation Patterns Increase Immunogenicity of a Subunit Hepatitis C Virus Vaccine, Inducing Neutralizing Antibodies Which Confer Protection in Mice. J. Virol. 2016, 90, 10486–10498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Wang, X.; Von Schaewen, M.; Tao, W.; Zhang, Y.; Heller, B.; Hrebikova, G.; Deng, Q.; Sun, Q.; Ploss, A.; et al. Immunization with a Subunit Hepatitis C Virus Vaccine Elicits Pan-Genotypic Neutralizing Antibodies and Intrahepatic T-Cell Responses in Nonhuman Primates. J. Infect. Dis. 2017, 215, 1824–1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czarnota, A.; Tyborowska, J.; Peszyńska-Sularz, G.; Gromadzka, B.; Bieńkowska-Szewczyk, K.; Grzyb, K. Immunogenicity of Leishmania-Derived Hepatitis B Small Surface Antigen Particles Exposing Highly Conserved E2 Epitope of Hepatitis C Virus. Microb. Cell Fact. 2016, 15, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kord, E.; Roohvand, F.; Dubuisson, J.; Vausselin, T.; Nasr Azadani, H.; Keshavarz, A.; Nejati, A.; Samimi-Rad, K. BacMam Virus-Based Surface Display for HCV E2 Glycoprotein Induces Strong Cross-Neutralizing Antibodies and Cellular Immune Responses in Vaccinated Mice. Infect. Agent. Cancer 2021, 16, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donnison, T.; McGregor, J.; Chinnakannan, S.; Hutchings, C.; Center, R.J.; Poumbourios, P.; Klenerman, P.; Drummer, H.E.; Barnes, E. A Pan-Genotype Hepatitis C Virus Viral Vector Vaccine Generates T Cells and Neutralizing Antibodies in Mice. Hepatology 2022, 76, 1190–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Fu, J.; Lu, J.; Deng, Y.; Wang, H.; Wei, Y.; Deng, L.; Tan, W.; Liang, G. Induction of Humoral and Cellular Immune Responses against Hepatitis C Virus by Vaccination with Replicon Particles Derived from Sindbis-like Virus XJ-160. Arch. Virol. 2013, 158, 1013–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Earnest-Silveira, L.; Chua, B.; Chin, R.; Christiansen, D.; Johnson, D.; Herrmann, S.; Ralph, S.A.; Vercauteren, K.; Mesalam, A.; Meuleman, P.; et al. Characterization of a Hepatitis C Virus-like Particle Vaccine Produced in a Human Hepatocyte-Derived Cell Line. J. General. Virol. 2016, 97, 1865–1876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christiansen, D.; Earnest-Silveira, L.; Chua, B.; Meuleman, P.; Boo, I.; Grubor-Bauk, B.; Jackson, D.C.; Keck, Z.Y.; Foung, S.K.H.; Drummer, H.E.; et al. Immunological Responses Following Administration of a Genotype 1a/1b/2/3a Quadrivalent HCV VLP Vaccine. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 6483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christiansen, D.; Earnest-Silveira, L.; Grubor-Bauk, B.; Wijesundara, D.K.; Boo, I.; Ramsland, P.A.; Vincan, E.; Drummer, H.E.; Gowans, E.J.; Torresi, J. Pre-Clinical Evaluation of a Quadrivalent HCV VLP Vaccine in Pigs Following Microneedle Delivery. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 9251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filskov, J.; Andersen, P.; Agger, E.M.; Bukh, J. HCV P7 as a Novel Vaccine-Target Inducing Multifunctional CD4+ and CD8+ T-Cells Targeting Liver Cells Expressing the Viral Antigen. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 14085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capone, S.; Naddeo, M.; D’Alise, A.M.; Abbate, A.; Grazioli, F.; Del Gaudio, A.; Del Sorbo, M.; Esposito, M.L.; Ammendola, V.; Perretta, G.; et al. Fusion of HCV Nonstructural Antigen to MHC Class II-Associated Invariant Chain Enhances T-Cell Responses Induced by Vectored Vaccines in Nonhuman Primates. Mol. Ther. 2014, 22, 1039–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grujic, M.; Holst, P.J.; Christensen, J.P.; Thomsen, A.R. Fusion of a Viral Antigen to Invariant Chain Leads to Augmented T-Cell Immunity and Improved Protection in Gene-Gun DNA-Vaccinated Mice. J. General. Virol. 2009, 90, 414–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holst, P.J.; Sorensen, M.R.; Mandrup Jensen, C.M.; Orskov, C.; Thomsen, A.R.; Christensen, J.P. MHC Class II-Associated Invariant Chain Linkage of Antigen Dramatically Improves Cell-Mediated Immunity Induced by Adenovirus Vaccines. J. Immunol. 2008, 180, 3339–3346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, F.; Chen, T.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, H.; Cao, H.; Lu, J.; Zhao, L.; Li, G. A Novel Adeno-Associated Virus-Based Genetic Vaccine Encoding the Hepatitis c Virus NS3/4 Protein Exhibits Immunogenic Properties in Mice Superior to Those of an NS3-Protein-Based Vaccine. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0142349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agrawal, B.; Gupta, N.; Vedi, S.; Singh, S.; Li, W.; Garg, S.; Li, J.; Kumar, R. Heterologous Immunity between Adenoviruses and Hepatitis C Virus (HCV): Recombinant Adenovirus Vaccine Vectors Containing Antigens from Unrelated Pathogens Induce Cross-Reactive Immunity against HCV Antigens. Cells 2019, 8, 507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ip, P.P.; Boerma, A.; Regts, J.; Meijerhof, T.; Wilschut, J.; Nijman, H.W.; Daemen, T. Alphavirus-Based Vaccines Encoding Nonstructural Proteins of Hepatitis c Virus Induce Robust and Protective T-Cell Responses. Mol. Ther. 2014, 22, 881–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koutsoumpli, G.; Ip, P.P.; Schepel, I.; Hoogeboom, B.N.; Boerma, A.; Daemen, T. Alphavirus-Based Hepatitis C Virus Therapeutic Vaccines: Can Universal Helper Epitopes Enhance HCV-Specific Cytotoxic T Lymphocyte Responses? Ther. Adv. Vaccines Immunother. 2019, 7, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, B.; Deng, Y.; Chen, H.; Guan, J.; Chuai, X.; Ruan, L.; Kong, W.; Tan, W. The Novel Replication-Defective Vaccinia Virus (Tiantan Strain)-Based Hepatitis C Virus Vaccine Induces Robust Immunity in Macaques. Mol. Ther. 2013, 21, 1787–1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusim, K.; Dilan, R.; Borducchi, E.; Stanley, K.; Giorgi, E.; Fischer, W.; Theiler, J.; Marcotrigiano, J.; Korber, B.; Barouch, D.H. Hepatitis C Genotype 1 Mosaic Vaccines Are Immunogenic in Mice and Induce Stronger T-Cell Responses than Natural Strains. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2013, 20, 302–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, S.; Zhang, P.; Wang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Ma, X.; Deng, Q.; Zou, P.; Wang, C.; Zhang, L.; Li, Y.; et al. Adenoviruses Vectored Hepatitis C Virus Vaccine Cocktails Induce Broadly Specific Immune Responses against Multi-Genotypic HCV in Mice. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2024, 170, 115901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, S.; Zhao, W.; Ma, X.; Zhang, P.; Liu, B.; Zhang, L.; Wang, W.; Wang, Y.; Fu, Y.; Allain, J.P.; et al. A High Infectious Simian Adenovirus Type 23 Vector Based Vaccine Efficiently Protects Common Marmosets against Zika Virus Infection. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2020, 14, e0008027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, S.; Zhang, P.; Liu, B.; Yang, C.; Liang, C.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, L.; Tang, X.; Li, J.; Hou, S.; et al. Prime-Boost Vaccination of Mice and Rhesus Macaques with Two Novel Adenovirus Vectored COVID-19 Vaccine Candidates. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2021, 10, 1002–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marín, M.Q.; Pérez, P.; Gómez, C.E.; Sorzano, C.Ó.S.; Esteban, M.; García-Arriaza, J. Removal of the C6 Vaccinia Virus Interferon-β Inhibitor in the Hepatitis C Vaccine Candidate MVA-HCV Elicited in Mice High Immunogenicity in Spite of Reduced Host Gene Expression. Viruses 2018, 10, 414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- von Delft, A.; Donnison, T.A.; Lourenço, J.; Hutchings, C.; Mullarkey, C.E.; Brown, A.; Pybus, O.G.; Klenerman, P.; Chinnakannan, S.; Barnes, E. The Generation of a Simian Adenoviral Vectored HCV Vaccine Encoding Genetically Conserved Gene Segments to Target Multiple HCV Genotypes. Vaccine 2018, 36, 313–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez-Donato, G.; Amador-Cañizares, Y.; Alvarez-Lajonchere, L.; Guerra, I.; Pérez, A.; Dubuisson, J.; Wychowsk, C.; Musacchio, A.; Aguilar, D.; Dueñas-Carrera, S. Neutralizing Antibodies and Broad, Functional T Cell Immune Response Following Immunization with Hepatitis C Virus Proteins-Based Vaccine Formulation. Vaccine 2014, 32, 1720–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez-Donato, G.; Piniella, B.; Aguilar, D.; Olivera, S.; Pérez, A.; Castañedo, Y.; Alvarez-Lajonchere, L.; Dueñas-Carrera, S.; Lee, J.W.; Burr, N.; et al. Protective T Cell and Antibody Immune Responses against Hepatitis C Virus Achieved Using a Biopolyester-Bead-Based Vaccine Delivery System. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2016, 23, 370–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Feng, X.; Chen, Z.; Yang, X.; Shen, Z.; Guo, M.; Deng, F.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Chen, C. The Adjuvant Effect of C 60 (OH) 22 Nanoparticles Promoting Both Humoral and Cellular Immune Responses to HCV Recombinant Proteins. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 97, 753–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawood, R.M.; Moustafa, R.I.; Abdelhafez, T.H.; El-Shenawy, R.; El-Abd, Y.; Bader El Din, N.G.; Dubuisson, J.; El Awady, M.K. A Multiepitope Peptide Vaccine against HCV Stimulates Neutralizing Humoral and Persistent Cellular Responses in Mice. BMC Infect. Dis. 2019, 19, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fynan, E.F.; Webster, R.G.; Fuller, D.H.; Haynes, J.R.; Santoro, J.C.; Robinson, H.L. DNA Vaccines: Protective Immunizations by Parenteral, Mucosal, and Gene-Gun Inoculations. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1993, 90, 11478–11482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polack, F.P.; Thomas, S.J.; Kitchin, N.; Absalon, J.; Gurtman, A.; Lockhart, S.; Perez, J.L.; Pérez Marc, G.; Moreira, E.D.; Zerbini, C.; et al. Safety and Efficacy of the BNT162b2 MRNA Covid-19 Vaccine. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 2603–2615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardi, N.; Hogan, M.J.; Porter, F.W.; Weissman, D. MRNA Vaccines-a New Era in Vaccinology. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2018, 17, 261–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogel, A.B.; Kanevsky, I.; Che, Y.; Swanson, K.A.; Muik, A.; Vormehr, M.; Kranz, L.M.; Walzer, K.C.; Hein, S.; Güler, A.; et al. BNT162b Vaccines Protect Rhesus Macaques from SARS-CoV-2. Nature 2021, 592, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartoonian, C.; Sepehrizadeh, Z.; Tabatabai Yazdi, M.; Jang, Y.S.; Langroudi, L.; Amir Kalvanagh, P.; Negahdari, B.; Karami, A.; Ebtekar, M.; Azadmanesh, K. Enhancement of Immune Responses by Co-Delivery of CCL19/MIP-3beta Chemokine Plasmid with HCV Core DNA/Protein Immunization. Hepat. Mon. 2014, 14, e14611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazdanian, M.; Memarnejadian, A.; Mahdavi, M.; Motevalli, F.; Sadat, S.; Vahabpour, R.; Khanahmad, H.; Soleimanjahi, H.; Budkowska, A.; Roohvand, F. Evaluation of Cellular Responses for a Chimeric HBsAg-HCV Core DNA Vaccine in BALB/c Mice. Adv. Biomed. Res. 2015, 4, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeedi, A.; Ghaemi, A.; Tabarraei, A.; Moradi, A.; Gorji, A.; Semnani, S.; Soleimanjahi, H.; Adli, A.H.; Hosseini, S.Y.; Vakili, M.A. Enhanced Cell Immune Responses to Hepatitis c Virus Core by Novel Heterologous DNA Prime/Lambda Nanoparticles Boost in Mice. Virus Genes. 2014, 49, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masavuli, M.G.; Wijesundara, D.K.; Underwood, A.; Christiansen, D.; Earnest-Silveira, L.; Bull, R.; Torresi, J.; Gowans, E.J.; Grubor-Bauk, B. A Hepatitis C Virus DNA Vaccine Encoding a Secreted, Oligomerized Form of Envelope Proteins Is Highly Immunogenic and Elicits Neutralizing Antibodies in Vaccinated Mice. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadeem, R.; Maghraby, A.S.; Abd-Elshafy, D.N.; Barakat, A.B.; Bahgat, M.M. Individual Expression and Processing of Hepatitis C Virus E1/E2 Epitopes-Based DNA Vaccine Candidate in Healthy Humans’ Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells. Clin. Exp. Vaccine Res. 2023, 12, 47–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorzin, Z.; Gorzin, A.A.; Tabarraei, A.; Behnampour, N.; Irani, S.; Ghaemi, A. Immunogenicity Evaluation of a DNA Vaccine Expressing the Hepatitis C Virus Non-Structural Protein 2 Gene in C57BL/6 Mice. Iran. Biomed. J. 2014, 18, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratnoglik, S.L.; Jiang, D.P.; Aoki, C.; Sudarmono, P.; Shoji, I.; Deng, L.; Hotta, H. Induction of Cell-Mediated Immune Responses in Mice by DNA Vaccines That Express Hepatitis C Virus NS3 Mutants Lacking Serine Protease and NTPase/RNA Helicase Activities. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e98877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pouriayevali, M.H.; Bamdad, T.; Aghasadeghi, M.R.; Sadat, S.M.; Sabahi, F. Construction and Immunogenicity Analysis of Hepatitis C Virus (HCV) Truncated Non-Structural Protein 3 (NS3) Plasmid Vaccine. Jundishapur J. Microbiol. 2016, 9, e33909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, L.D.; Ren, X.H.; Ma, R.L.; Wang, Y.; Yuan, H.W.; Lv, H.J. Efficacy of Artemisia Annua Polysaccharides as an Adjuvant to Hepatitis C Vaccination. Genet. Mol. Res. 2015, 14, 4957–4965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, Y.; Zhang, S.; Ji, S. Delivery of a Hepatitis C Virus Vaccine Encoding NS3 Linked to the MHC Class II Chaperone Protein Invariant Chain Using Bacterial Ghosts. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huter, V.; Szostak, M.P.; Gampfer, J.; Prethaler, S.; Wanner, G.; Gabor, F.; Lubitz, W. Bacterial Ghosts as Drug Carrier and Targeting Vehicles. J. Control. Release 1999, 61, 51–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levander, S.; Sällberg, M.; Ahlén, G.; Frelin, L. A Non-Human Hepadnaviral Adjuvant for Hepatitis C Virus-Based Genetic Vaccines. Vaccine 2016, 34, 2821–2833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmström, F.; Pasetto, A.; Nähr, V.; Brass, A.; Kriegs, M.; Hildt, E.; Broderick, K.E.; Chen, M.; Ahlén, G.; Frelin, L. A Synthetic Codon-Optimized Hepatitis C Virus Nonstructural 5A DNA Vaccine Primes Polyfunctional CD8+ T Cell Responses in Wild-Type and NS5A-Transgenic Mice. J. Immunol. 2013, 190, 1113–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijesundara, D.K.; Gummow, J.; Li, Y.; Yu, W.; Quah, B.J.; Ranasinghe, C.; Torresi, J.; Gowans, E.J.; Grubor-Bauk, B. Induction of Genotype Cross-Reactive, Hepatitis C Virus-Specific, Cell-Mediated Immunity in DNA-Vaccinated Mice. J. Virol. 2018, 92, 10–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gummow, J.; Li, Y.; Yu, W.; Garrod, T.; Wijesundara, D.; Brennan, A.J.; Mullick, R.; Voskoboinik, I.; Grubor-Bauk, B.; Gowans, E.J. A Multiantigenic DNA Vaccine That Induces Broad Hepatitis C Virus-Specific T-Cell Responses in Mice. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 7991–8002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Jeong, M.; Oh, J.; Cho, Y.; Shen, X.; Stone, J.; Yan, J.; Rothkopf, Z.; Khan, A.S.; Cho, B.M.; et al. Preclinical Evaluation of Multi Antigenic HCV DNA Vaccine for the Prevention of Hepatitis C Virus Infection. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, srep43531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masalova, O.V.; Lesnova, E.I.; Klimova, R.R.; Ivanov, A.V.; Kushch, A.A. Mesenchymal Stem Cells Can both Enhance and Inhibit the Cellular Response to Dna Immunization by Genes of Nonstructural Proteins of the Hepatitis c Virus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 8121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, W.G.; Zubkova, I.; Kachko, A.; Wells, F.; Adler, H.; Sutter, G.; Major, M.E. Qualitative Differences in Cellular Immunogenicity Elicited by Hepatitis C Virus T-Cell Vaccines Employing Prime-Boost Regimens. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0181578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fournillier, A.; Frelin, L.; Jacquier, E.; Ahlén, G.; Brass, A.; Gerossier, E.; Holmström, F.; Broderick, K.E.; Sardesai, N.Y.; Bonnefoy, J.Y.; et al. A Heterologous Prime/Boost Vaccination Strategy Enhances the Immunogenicity of Therapeutic Vaccines for Hepatitis C Virus. J. Infect. Dis. 2013, 208, 1008–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mekonnen, Z.A.; Grubor-Bauk, B.; English, K.; Leung, P.; Masavuli, M.G.; Shrestha, A.C.; Bertolino, P.; Bowen, D.G.; Lloyd, A.R.; Gowans, E.J.; et al. Single-Dose Vaccination with a Hepatotropic Adeno-Associated Virus Efficiently Localizes T Cell Immunity in the Liver with the Potential to Confer Rapid Protection against Hepatitis C Virus. J. Virol. 2019, 93, 10–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latimer, B.; Toporovski, R.; Yan, J.; Pankhong, P.; Morrow, M.P.; Khan, A.S.; Sardesai, N.Y.; Welles, S.L.; Jacobson, J.M.; Weiner, D.B.; et al. Strong HCV NS3/4a, NS4b, NS5a, NS5b-Specific Cellular Immune Responses Induced in Rhesus Macaques by a Novel HCV Genotype 1a/1b Consensus DNA Vaccine. Hum. Vaccin. Immunother. 2014, 10, 2357–2365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callendret, B.; Eccleston, H.B.; Satterfield, W.; Capone, S.; Folgori, A.; Cortese, R.; Nicosia, A.; Walker, C.M. Persistent Hepatitis C Viral Replication despite Priming of Functional CD8+ T Cells by Combined Therapy with a Vaccine and a Direct-Acting Antiviral. Hepatology 2016, 63, 1442–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pishraft-Sabet, L.; Taheri, T.; Memarnejadian, A.; Azad, T.M.; Asgari, F.; Rahimnia, R.; Alavian, S.M.; Rafati, S.; Rad, K.S. Immunogenicity of Multi-Epitope DNA and Peptide Vaccine Candidates Based on Core, E2, NS3 and NS5B HCV Epitopes in BALB/c Mice. Hepat. Mon. 2014, 14, e22215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pishraft-Sabet, L.; Kosinska, A.D.; Rafati, S.; Bolhassani, A.; Taheri, T.; Memarnejadian, A.; Alavian, S.M.; Roggendorf, M.; Samimi-Rad, K. Enhancement of HCV Polytope DNA Vaccine Efficacy by Fusion to an N-Terminal Fragment of Heat Shock Protein Gp96. Arch. Virol. 2015, 160, 141–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, N.; Rafati, S.; Taheri, T.; Roohvand, F.; Farahmand, M.; Hajikhezri, Z.; Keshavarz, A.; Samimi-Rad, K. A Non-Pathogenic Leishmania Tarentolae Vector Based- HCV Polytope DNA Vaccine Elicits Potent and Long Lasting Th1 and CTL Responses in BALB/c Mice Model. Mol. Immunol. 2019, 111, 152–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marín, M.Q.; Pérez, P.; Ljungberg, K.; Sorzano, C.Ó.S.; Gómez, C.E.; Liljeström, P.; Esteban, M.; García-Arriaza, J. Potent Anti-Hepatitis C Virus (HCV) T Cell Immune Responses Induced in Mice Vaccinated with DNA-Launched RNA Replicons and Modified Vaccinia Virus Ankara-HCV. J. Virol. 2019, 93, 10–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wada, T.; Kohara, M.; Yasutomi, Y. DNA Vaccine Expressing the Non-Structural Proteins of Hepatitis C Virus Diminishes the Expression of HCV Proteins in a Mouse Model. Vaccine 2013, 31, 5968–5974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rollier, C.S.; Verschoor, E.J.; Verstrepen, B.E.; Drexhage, J.A.R.; Paranhos-Baccala, G.; Liljeström, P.; Sutter, G.; Arribillaga, L.; Lasarte, J.J.; Bartosch, B.; et al. T-and B-Cell Responses to Multivalent Prime-Boost DNA and Viral Vectored Vaccine Combinations against Hepatitis C Virus in Non-Human Primates. Gene Ther. 2016, 23, 753–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gómez, C.E.; Perdiguero, B.; Cepeda, M.V.; Mingorance, L.; García-Arriaza, J.; Vandermeeren, A.; Sorzano, C.Ó.S.; Esteban, M. High, Broad, Polyfunctional, and Durable T Cell Immune Responses Induced in Mice by a Novel Hepatitis C Virus (HCV) Vaccine Candidate (MVA-HCV) Based on Modified Vaccinia Virus Ankara Expressing the Nearly Full-Length HCV Genome. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 7282–7300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patra, T.; Meyer, K.; Haga, Y.; Reagan, E.K.; Weissman, D.; Ray, R. Hepatitis C Virus E1 and Modified E2 Delivered from an MRNA Vaccine Induces Protective Immunity. NPJ Vaccines 2023, 8, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swadling, L.; Capone, S.; Antrobus, R.D.; Brown, A.; Richardson, R.; Newell, E.W.; Halliday, J.; Kelly, C.; Bowen, D.; Fergusson, J.; et al. A Human Vaccine Strategy Based on Chimpanzee Adenoviral and MVA Vectors That Primes, Boosts, and Sustains Functional HCV-Specific T Cell Memory. Sci. Transl. Med. 2014, 6, 261ra153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swadling, L.; Halliday, J.; Kelly, C.; Brown, A.; Capone, S.; Ansari, M.A.; Bonsall, D.; Richardson, R.; Hartnell, F.; Collier, J.; et al. Highly-Immunogenic Virally-Vectored T-Cell Vaccines Cannot Overcome Subversion of the T-Cell Response by HCV during Chronic Infection. Vaccines 2016, 4, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelly, C.; Swadling, L.; Brown, A.; Capone, S.; Folgori, A.; Salio, M.; Klenerman, P.; Barnes, E. Cross-Reactivity of Hepatitis C Virus Specific Vaccine-Induced T Cells at Immunodominant Epitopes. Eur. J. Immunol. 2015, 45, 309–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelly, C.; Swadling, L.; Capone, S.; Brown, A.; Richardson, R.; Halliday, J.; von Delft, A.; Oo, Y.; Mutimer, D.; Kurioka, A.; et al. Chronic Hepatitis C Viral Infection Subverts Vaccine-Induced T-Cell Immunity in Humans. Hepatology 2016, 63, 1455–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, K.; Melia, M.T.; Veenhuis, R.T.; Winter, M.; Rousseau, K.E.; Massaccesi, G.; Osburn, W.O.; Forman, M.; Thomas, E.; Thornton, K.; et al. Randomized Trial of a Vaccine Regimen to Prevent Chronic HCV Infection. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 541–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wherry, E.J.; Blattman, J.N.; Ahmed, R. Low CD8 T-Cell Proliferative Potential and High Viral Load Limit the Effectiveness of Therapeutic Vaccination. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 8960–8968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnes, E.; Gelderblom, H.C.; Humphreys, I.; Semmo, N.; Reesink, H.W.; Beld, M.G.H.M.; Van Lier, R.A.W.; Klenerman, P. Cellular Immune Responses during High-Dose Interferon-α Induction Therapy for Hepatitis C Virus Infection. J. Infect. Dis. 2009, 199, 819–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baral, S.; Sherman, S.G.; Millson, P.; Beyrer, C. Vaccine Immunogenicity in Injecting Drug Users: A Systematic Review. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2007, 7, 667–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiland, O.; Ahlén, G.; Diepolder, H.; Jung, M.C.; Levander, S.; Fons, M.; Mathiesen, I.; Sardesai, N.Y.; Vahlne, A.; Frelin, L.; et al. Therapeutic DNA Vaccination Using in Vivo Electroporation Followed by Standard of Care Therapy in Patients with Genotype 1 Chronic Hepatitis C. Mol. Ther. 2013, 21, 1796–1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.W.; Sung, P.S.; Hong, S.H.; Lee, H.; Koh, J.Y.; Lee, H.; White, S.; Maslow, J.N.; Weiner, D.B.; Park, S.H.; et al. IFNL3-Adjuvanted HCV DNA Vaccine Reduces Regulatory T Cell Frequency and Increases Virus-Specific T Cell Responses. J. Hepatol. 2020, 73, 72–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobson, J.M.; Zahrieh, D.; Strand, C.A.; Cruz-Correa, M.; Pungpapong, S.; Roberts, L.R.; Mandrekar, S.J.; Rodriguez, L.M.; Boyer, J.; Marrero, I.; et al. Phase I Trial of a Therapeutic DNA Vaccine for Preventing Hepatocellular Carcinoma from Chronic Hepatitis C Virus (HCV) Infection. Cancer Prev. Res. 2023, 16, 163–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, K.W.; Fiore-Gartland, A.; Walsh, S.R.; Yusim, K.; Frahm, N.; Elizaga, M.L.; Maenza, J.; Scott, H.; Mayer, K.H.; Goepfert, P.A.; et al. Trivalent Mosaic or Consensus HIV Immunogens Prime Humoral and Broader Cellular Immune Responses in Adults. J. Clin. Investig. 2023, 133, e163338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhao, T.; Wang, L.; Yang, Z.; Luo, C.; Li, M.; Luo, H.; Sun, C.; Yan, H.; Shu, Y. A Mosaic Influenza Virus-like Particles Vaccine Provides Broad Humoral and Cellular Immune Responses against Influenza A Viruses. NPJ Vaccines 2023, 8, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wu, S.; Liu, J.; Chen, R.; Zhang, Y.; Lin, Y.; Xi, Z.; Deng, J.; Pu, Z.; Liang, C.; et al. A Mosaic Nanoparticle Vaccine Elicits Potent Mucosal Immune Response with Significant Cross-Protection Activity against Multiple SARS-CoV-2 Sublineages. Adv. Sci. 2023, 10, e2301034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alspach, E.; Lussier, D.M.; Schreiber, R.D. Interferon γ and Its Important Roles in Promoting and Inhibiting Spontaneous and Therapeutic Cancer Immunity. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2019, 11, a028480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cramp, M.E.; Rossol, S.; Chokshi, S.; Carucci, P.; Williams, R.; Naoumov, N.V. Hepatitis C Virus-Specific T-Cell Reactivity during Interferon and Ribavirin Treatment in Chronic Hepatitis C. Gastroenterology 2000, 118, 346–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, M.T.; Chen, S.S.L. Emerging Roles of Interferon-Stimulated Genes in the Innate Immune Response to Hepatitis C Virus Infection. Cell Mol. Immunol. 2016, 13, 11–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Zhong, J.Y.; Li, J.W. Hepatitis C Virus Infection and Vaccine Development. J. Clin. Exp. Hepatol. 2018, 8, 195–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bachmann, M.F.; Oxenius, A. Interleukin 2: From Immunostimulation to Immunoregulation and Back Again. EMBO Rep. 2007, 8, 1142–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, T.J. Current Progress in Development of Hepatitis C Virus Vaccines. Nat. Med. 2013, 19, 869–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morshed, S.A.; Fukuma, H.; Kimura, Y.; Watanabe, S.; Nishioka, M. Interferon-γ, Interleukin (IL)-2 and IL-2 Receptor Expressions in Hepatitis C Virus-Infected Liver. Gastroenterol. Jpn. 1993, 28, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Idriss, H.T.; Naismith, J.H. TNFα and the TNF Receptor Superfamily: Structure-Function Relationship(s). Microsc. Res. Tech. 2000, 50, 184–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Tian, Y.; Chan, S.T.; Kim, J.Y.; Cho, C.; Ou, J. hsiung J. TNF-α Induced by Hepatitis C Virus via TLR7 and TLR8 in Hepatocytes Supports Interferon Signaling via an Autocrine Mechanism. PLoS Pathog. 2015, 11, e1004937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, D.R.; Lim, H.L.; Marousis, C.G.; Fang, J.W.S.; Davis, G.L.; Shen, L.; Urdea, M.S.; Kolberg, J.A.; Lau, J.Y.N. Activation of Tumor Necrosis Factor-α System in Chronic Hepatitis C Virus Infection. Dig. Dis. Sci. 1997, 42, 2487–2494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pompili, M.; Biolato, M.; Miele, L.; Grieco, A. Tumor Necrosis Factor-α Inhibitors and Chronic Hepatitis C: A Comprehensive Literature Review. World J. Gastroenterol. 2013, 19, 7867–7873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heeb, L.E.M.; Egholm, C.; Boyman, O. Evolution and Function of Interleukin-4 Receptor Signaling in Adaptive Immunity and Neutrophils. Genes. Immun. 2020, 21, 143–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reiser, M.; Marousis, C.G.; Nelson, D.R.; Lauer, G.; González-Peralta, R.P.; Davis, G.L.; Lau, J.Y.N. Serum Interleukin 4 and Interleukin 10 Levels in Patients with Chronic Hepatitis C Virus Infection. J. Hepatol. 1997, 26, 471–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fallahi, P.; Ferri, C.; Ferrari, S.M.; Corrado, A.; Sansonno, D.; Antonelli, A. Cytokines and HCV-Related Disorders. Clin. Dev. Immunol. 2012, 2012, 468107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertoletti, A.; D’Elios, M.M.; Boni, C.; De Carli, M.; Zignego, A.L.; Durazzo, M.; Missale, G.; Penna, A.; Fiaccadori, F.; Del Prete, G.; et al. Different Cytokine Profiles of Intrahepatic T Cells in Chronic Hepatitis B and Hepatitis C Virus Infections. Gastroenterology 1997, 112, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, K.W.; De Waal Malefyt, R.; Coffman, R.L.; O’Garra, A. Interleukin-10 and the Interleukin-10 Receptor. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2001, 19, 683–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pang, X.; Wang, Z.; Zhai, N.; Zhang, Q.; Song, H.; Zhang, Y.; Li, T.; Li, H.; Su, L.; Niu, J.; et al. IL-10 Plays a Central Regulatory Role in the Cytokines Induced by Hepatitis C Virus Core Protein and Polyinosinic Acid:Polycytodylic Acid. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2016, 38, 284–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruno, C.M.; Valenti, M.; Bertino, G.; Ardiri, A.; Amoroso, A.; Consolo, M.; Mazzarino, C.M.; Neri, S. Relationship between Circulating Interleukin-10 and Histological Features in Patients with Chronic C Hepatitis. Ann. Saudi Med. 2011, 31, 360–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Chen, H.Y.; Luo, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, D.; Song, N.; Wang, F.B.; Li, Q.; Zhang, X.L.; Pan, Q. Neutralization of IL-10 Produced by B Cells Promotes Protective Immunity during Persistent HCV Infection in Humanized Mice. Eur. J. Immunol. 2020, 50, 1350–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ihim, S.A.; Abubakar, S.D.; Zian, Z.; Sasaki, T.; Saffarioun, M.; Maleknia, S.; Azizi, G. Interleukin-18 Cytokine in Immunity, Inflammation, and Autoimmunity: Biological Role in Induction, Regulation, and Treatment. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 919973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asadipour, M.; Fazeli, P.; Zohouri, M.; Bemani, P.; Mohebbiniya, M.; Khansalar, S.; Fattahi, M.R.; Kalantar, K. IL-18 in Blood Serum of Hepatitis C Patients Might Be of Predictive Value for Individual Outcomes. Infect. Disord. Drug Targets 2020, 21, 389–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dearborn, A.D.; Marcotrigiano, J. Hepatitis C Virus Structure: Defined by What It Is Not. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2019, 10, a036822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzarum, N.; Wilson, I.A.; Law, M. The Neutralizing Face of Hepatitis C Virus E2 Envelope Glycoprotein. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Law, M. Antibody Responses in Hepatitis C Infection. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2021, 11, a036962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frelin, L.; Ahlén, G.; Alheim, M.; Weiland, O.; Barnfield, C.; Liljeström, P.; Sällberg, M. Codon Optimization and MRNA Amplification Effectively Enhances the Immunogenecity of the Hepatitis C Virus Nonstructural 3/4A Gene. Gene Ther. 2004, 11, 522–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenberg, B.R.; Depla, M.; Freije, C.A.; Gaucher, D.; Mazouz, S.; Boisvert, M.; Bédard, N.; Bruneau, J.; Rice, C.M.; Shoukry, N.H. Longitudinal Transcriptomic Characterization of the Immune Response to Acute Hepatitis C Virus Infection in Patients with Spontaneous Viral Clearance. PLoS Pathog. 2018, 14, e1007290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henning, A.N.; Budeebazar, M.; Boldbaatar, D.; Yagaanbuyant, D.; Duger, D.; Batsukh, K.; Zhou, H.; Baumann, R.; Allison, R.D.; Alter, H.J.; et al. Peripheral B Cells from Patients with Hepatitis C Virus-Associated Lymphoma Exhibit Clonal Expansion and an Anergic-like Transcriptional Profile. iScience 2023, 26, 105801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boldanova, T.; Suslov, A.; Heim, M.H.; Necsulea, A. Transcriptional Response to Hepatitis C Virus Infection and Interferon-Alpha Treatment in the Human Liver. EMBO Mol. Med. 2017, 9, 816–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliviero, B.; Mantovani, S.; Ludovisi, S.; Varchetta, S.; Mele, D.; Paolucci, S.; Baldanti, F.; Mondelli, M.U. Skewed B Cells in Chronic Hepatitis C Virus Infection Maintain Their Ability to Respond to Virus-Induced Activation. J. Viral Hepat. 2015, 22, 391–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, J.; Brouwer, W.P.; Kreefft, K.; Gama, L.; Price, S.L.; Janssen, H.L.A.; French, P.J.; Vanwolleghem, T.; Boonstra, A. Unique Intrahepatic Transcriptomics Profiles Discriminate the Clinical Phases of a Chronic HBV Infection. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0179920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montanari, N.R.; Ramírez, R.; Aggarwal, A.; van Buuren, N.; Doukas, M.; Moon, C.; Turner, S.; Diehl, L.; Li, L.; Debes, J.D.; et al. Multi-Parametric Analysis of Human Livers Reveals Variation in Intrahepatic Inflammation across Phases of Chronic Hepatitis B Infection. J. Hepatol. 2022, 77, 332–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pestka, J.M.; Zeisel, M.B.; Bläser, E.; Schürmann, P.; Bartosch, B.; Cosset, F.-L.; Patel, A.H.; Meisel, H.; Baumert, J.; Viazov, S.; et al. Rapid Induction of Virus-Neutralizing Antibodies and Viral Clearance in a Single-Source Outbreak of Hepatitis C. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 6025–6030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bailey, J.R.; Flyak, A.I.; Cohen, V.J.; Li, H.; Wasilewski, L.N.; Snider, A.E.; Wang, S.; Learn, G.H.; Kose, N.; Loerinc, L.; et al. Broadly Neutralizing Antibodies with Few Somatic Mutations and Hepatitis C Virus Clearance. JCI Insight 2017, 2, e92872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mancini, N.; Diotti, R.A.; Perotti, M.; Sautto, G.; Clementi, N.; Nitti, G.; Patel, A.H.; Ball, J.K.; Clementi, M.; Burioni, R. Hepatitis C Virus (HCV) Infection May Elicit Neutralizing Antibodies Targeting Epitopes Conserved in All Viral Genotypes. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e8254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yokokawa, H.; Shinohara, M.; Teraoka, Y.; Imamura, M.; Nakamura, N.; Watanabe, N.; Date, T.; Aizaki, H.; Iwamura, T.; Narumi, H.; et al. Patient-Derived Monoclonal Antibody Neutralizes HCV Infection in Vitro and Vivo without Generating Escape Mutants. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0274283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mailly, L.; Wrensch, F.; Heydmann, L.; Fauvelle, C.; Brignon, N.; Zeisel, M.B.; Pessaux, P.; Keck, Z.Y.; Schuster, C.; Fuerst, T.R.; et al. In Vivo Combination of Human Anti-Envelope Glycoprotein E2 and -Claudin-1 Monoclonal Antibodies for Prevention of Hepatitis C Virus Infection. Antivir. Res. 2019, 162, 136–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desombere, I.; Mesalam, A.A.; Urbanowicz, R.A.; Van Houtte, F.; Verhoye, L.; Keck, Z.Y.; Farhoudi, A.; Vercauteren, K.; Weening, K.E.; Baumert, T.F.; et al. A Novel Neutralizing Human Monoclonal Antibody Broadly Abrogates Hepatitis C Virus Infection in Vitro and in Vivo. Antivir. Res. 2017, 148, 53–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pilewski, K.A.; Wall, S.; Richardson, S.I.; Manamela, N.P.; Clark, K.; Hermanus, T.; Binshtein, E.; Venkat, R.; Sautto, G.A.; Kramer, K.J.; et al. Functional HIV-1/HCV Cross-Reactive Antibodies Isolated from a Chronically Co-Infected Donor. Cell Rep. 2023, 42, 112044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raghuraman, S.; Park, H.; Osburn, W.O.; Winkelstein, E.; Edlin, B.R.; Rehermann, B. Spontaneous Clearance of Chronic Hepatitis C Virus Infection Is Associated with Appearance of Neutralizing Antibodies and Reversal of T-Cell Exhaustion. J. Infect. Dis. 2012, 205, 763–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eliyahu, S.; Sharabi, O.; Elmedvi, S.; Timor, R.; Davidovich, A.; Vigneault, F.; Clouser, C.; Hope, R.; Nimer, A.; Braun, M.; et al. Antibody Repertoire Analysis of Hepatitis C Virus Infections Identifies Immune Signatures Associated with Spontaneous Clearance. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 3004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colbert, M.D.; Flyak, A.I.; Ogega, C.O.; Kinchen, V.J.; Massaccesi, G.; Hernandez, M.; Davidson, E.; Doranz, B.J.; Cox, A.L.; Crowe, J.E.; et al. Broadly Neutralizing Antibodies Targeting New Sites of Vulnerability in Hepatitis C Virus E1E2. J. Virol. 2019, 93, 10–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merat, S.J.; Bru, C.; van de Berg, D.; Molenkamp, R.; Tarr, A.W.; Koekkoek, S.; Kootstra, N.A.; Prins, M.; Ball, J.K.; Bakker, A.Q.; et al. Cross-Genotype AR3-Specific Neutralizing Antibodies Confer Long-Term Protection in Injecting Drug Users after HCV Clearance. J. Hepatol. 2019, 71, 14–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilman, A.J.; Le, A.K.; Zhao, C.; Hoang, J.; Yasukawa, L.A.; Weber, S.C.; Vierling, J.M.; Nguyen, M.H. Autoantibodies in Chronic Hepatitis C Virus Infection: Impact on Clinical Outcomes and Extrahepatic Manifestations. BMJ Open Gastroenterol. 2018, 5, e000203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Priora, M.; Borrelli, R.; Parisi, S.; Ditto, M.C.; Realmuto, C.; Laganà, A.; Di Vittorio, C.C.; Degiovanni, R.; Peroni, C.L.; Fusaro, E. Autoantibodies and Rheumatologic Manifestations in Hepatitis c Virus Infection. Biology 2021, 10, 1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sautto, G.; Mancini, N.; Clementi, M.; Burioni, R. Molecular Signatures of Hepatitis C Virus (HCV)-Induced Type II Mixed Cryoglobulinemia (MCII). Viruses 2012, 4, 2924–2944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sautto, G.; Mancini, N.; Solforosi, L.; Diotti, R.A.; Clementi, M.; Burioni, R. HCV Proteins and Immunoglobulin Variable Gene (IgV) Subfamilies in HCV-Induced Type II Mixed Cryoglobulinemia: A Concurrent Pathogenetic Role. Clin. Dev. Immunol. 2012, 2012, 705013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dvir, R.; Sautto, G.A.; Mancini, N.; Racca, S.; Diotti, R.A.; Clementi, M.; Memoli, M. Autoimmune Hepatitis and Occult HCV Infection: A Prospective Single-Centre Clinical Study. Autoimmun. Rev. 2017, 16, 323–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Priora, M.; Realmuto, C.; Parisi, S.; Ditto, M.C.; Borrelli, R.; Peroni, C.L.; Laganà, A.; Fusaro, E. Rheumatologic Manifestations of Hepatitis C in the Era of Direct-Acting Antiviral Agents. Minerva Gastroenterol. Dietol. 2020, 66, 280–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roccatello, D.; Sciascia, S.; Rossi, D.; Solfietti, L.; Fenoglio, R.; Menegatti, E.; Baldovino, S. The Challenge of Treating Hepatitis C Virus-Associated Cryoglobulinemic Vasculitis in the Era of Anti-CD20 Monoclonal Antibodies and Direct Antiviral Agents. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 41764–41777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muramatsu, M.; Kinoshita, K.; Fagarasan, S.; Yamada, S.; Shinkai, Y.; Honjo, T. Class Switch Recombination and Hypermutation Require Activation-Induced Cytidine Deaminase (AID), a Potential RNA Editing Enzyme. Cell 2000, 102, 553–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferri, S.; Muratori, L.; Lenzi, M.; Granito, A.; Bianchi, F.; Vergani, D. HCV and Autoimmunity. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2008, 14, 1678–1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muratori, P.; Muratori, L.; Guidi, M.; Granito, A.; Susca, M.; Lenzi, M.; Bianchi, F.B. Clinical Impact of Non-Organ-Specific Autoantibodies on the Response to Combined Antiviral Treatment in Patients with Hepatitis C. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2005, 40, 501–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cacoub, P.; Commarmond, C.; Sadoun, D.; Desbois, A.C. Hepatitis C Virus Infection and Rheumatic Diseases: The Impact of Direct-Acting Antiviral Agents. Rheum. Dis. Clin. N. Am. 2017, 43, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geoghegan, S.; O’Callaghan, K.P.; Offit, P.A. Vaccine Safety: Myths and Misinformation. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esposito, I.; Cicconi, P.; D’Alise, A.M.; Brown, A.; Esposito, M.; Swadling, L.; Holst, P.J.; Bassi, M.R.; Stornaiuolo, M.; Mori, F.; et al. MHC Class II Invariant Chain-Adjuvanted Viral Vectored Vaccines Enhances T Cell Responses in Humans. Sci. Transl. Med. 2020, 12, eaaz7715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, M.R.; Leung, P.; Eltahla, A.A.; Underwood, A.; Abayasingam, A.; Brasher, N.A.; Li, H.; Wu, B.R.; Maher, L.; Luciani, F.; et al. Clearance of Hepatitis C Virus Is Associated with Early and Potent but Narrowly-Directed, Envelope-Specific Antibodies. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 13300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Underwood, A.P.; Walker, M.R.; Brasher, N.A.; Eltahla, A.A.; Maher, L.; Luciani, F.; Lloyd, A.R.; Bull, R.A. Understanding the Determinants of BnAb Induction in Acute HCV Infection. Viruses 2018, 10, 659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarr, A.W.; Urbanowicz, R.A.; Hamed, M.R.; Albecka, A.; McClure, C.P.; Brown, R.J.P.; Irving, W.L.; Dubuisson, J.; Ball, J.K. Hepatitis C Patient-Derived Glycoproteins Exhibit Marked Differences in Susceptibility to Serum Neutralizing Antibodies: Genetic Subtype Defines Antigenic but Not Neutralization Serotype. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 4246–4257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blach, S.; Zeuzem, S.; Manns, M.; Altraif, I.; Duberg, A.S.; Muljono, D.H.; Waked, I.; Alavian, S.M.; Lee, M.H.; Negro, F.; et al. Global Prevalence and Genotype Distribution of Hepatitis C Virus Infection in 2015: A Modelling Study. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 2, 161–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapa, D.; Garbuglia, A.R.; Capobianchi, M.R.; Porto, P. Del Hepatitis C Virus Genetic Variability, Human Immune Response, and Genome Polymorphisms: Which Is the Interplay? Cells 2019, 8, 305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, K.S.M.; Her, Z.; Chen, Q. Humanized Mouse Models for the Study of Hepatitis C and Host Interactions. Cells 2019, 8, 604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

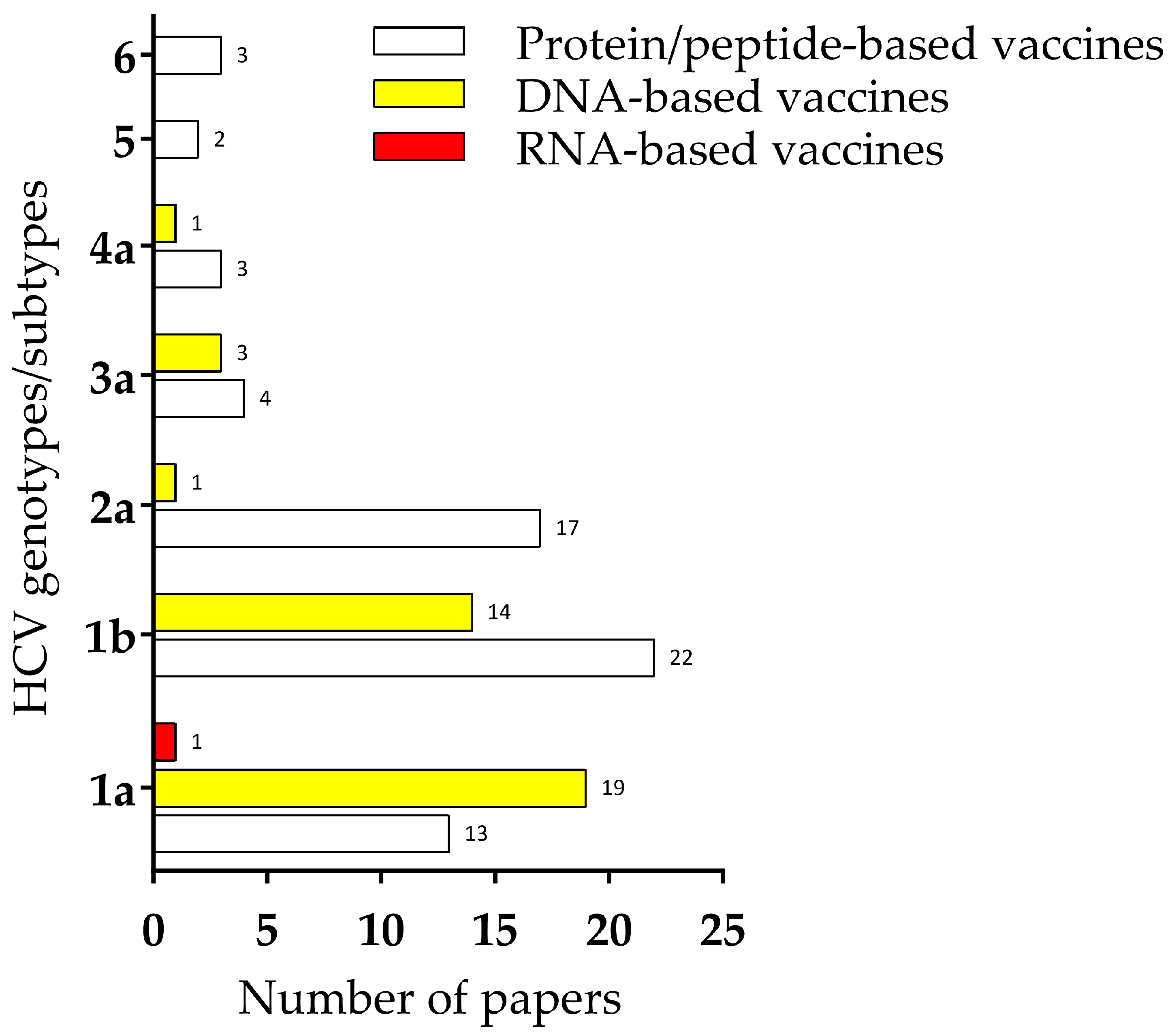
| Reference | Cytokines | Cellular Response | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Protein-Based Vaccines | ||||||||||
| [26] | IFN-γ | IL-4 | ||||||||
| [27] | IFN-γ | IL-4 | ||||||||
| [28] | IFN-γ | IL-4 | ||||||||
| [30] | IFN-γ | IL-4 | ||||||||
| [40] | IFN-γ | IL-2 | IL-4 | |||||||
| [44] | IFN-γ | TNF-α | IL-2 | IL-12 | IL-6 | |||||
| [92] | IFN-γ | TNF-α | IL-2 | IL-17 | granzyme A, granzyme B | |||||
| [84] | IFN-γ | TNF-α | IL-2 | |||||||
| [42] | IFN-γ | TNF-α | IL-2 | |||||||
| [91] | IFN-γ | TNF-α | IL-2 | |||||||
| [90] | IFN-γ | TNF-α | IL-2 | |||||||
| [49] | IFN-γ | TNF-α | IL-2 | |||||||
| [36] | IFN-γ | TNF-α | IL-2 | |||||||
| [50] | IFN-γ | TNF-α | ||||||||
| [31] | IFN-γ | TNF-α | ||||||||
| [46] | IFN-γ | TNF-α | ||||||||
| [32] | IFN-γ | IL-6 | IL-10 | |||||||
| [41] | IFN-γ | IL-10 | ||||||||
| [35] | IFN-γ | IL-12 | IL-18 | granzyme B | ||||||
| [34] | IFN-γ | granzyme B | ||||||||
| [51] | IFN-γ | |||||||||
| [37] | IFN-γ | |||||||||
| [33] | IFN-γ | |||||||||
| [29] | IFN-γ | |||||||||
| [52] | IFN-γ | |||||||||
| [53] | IFN-γ | |||||||||
| [54] | IFN-γ | |||||||||
| [43] | IFN-γ | |||||||||
| [93] | IFN-γ | |||||||||
| DNA-Based Vaccines | ||||||||||
| [98] | IFN-γ | TNF-α | IL-2 | IL-17 | ||||||
| [79] | IFN-γ | TNF-α | IL-2 | granzyme B | ||||||
| [87] | IFN-γ | TNF-α | IL-2 | |||||||
| [71] | IFN-γ | TNF-α | IL-2 | |||||||
| [73] | IFN-γ | TNF-α | IL-2 | |||||||
| [82] | IFN-γ | TNF-α | IL-2 | |||||||
| [80] | IFN-γ | TNF-α | IL-2 | |||||||
| [76] | IFN-γ | TNF-α | IL-2 | |||||||
| [84] | IFN-γ | TNF-α | IL-2 | |||||||
| [83] | IFN-γ | TNF-α | IL-4 | IL-17 | ||||||
| [77] | IFN-γ | IL-2 | ||||||||
| [70] | IFN-γ | IL-2 | ||||||||
| [86] | IFN-γ | IL-2 | IL-4 | |||||||
| [59] | IFN-γ | IL-4 | granzyme B | |||||||
| [64] | IFN-γ | IL-4 | ||||||||
| [81] | IFN-γ | IL-4 | ||||||||
| [61] | IFN-γ | IL-4 | ||||||||
| [60] | IFN-γ | IL-4 | ||||||||
| [67] | IFN-γ | IL-4 | ||||||||
| [66] | IFN-γ | IL-4 | ||||||||
| [85] | IFN-γ | |||||||||
| [97] | IFN-γ | |||||||||
| [65] | IFN-γ | |||||||||
| [74] | IFN-γ | |||||||||
| [72] | IFN-γ | |||||||||
| [62] | IFN-γ | |||||||||
| [75] | IFN-γ | |||||||||
| [99] | IFN-γ | |||||||||
| RNA-Based Vaccines | ||||||||||
| [88] | IFN-γ | IL-2 | IL-4 | IL-10 | granzyme B | |||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Costa, G.L.; Sautto, G.A. Exploring T-Cell Immunity to Hepatitis C Virus: Insights from Different Vaccine and Antigen Presentation Strategies. Vaccines 2024, 12, 890. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines12080890
Costa GL, Sautto GA. Exploring T-Cell Immunity to Hepatitis C Virus: Insights from Different Vaccine and Antigen Presentation Strategies. Vaccines. 2024; 12(8):890. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines12080890
Chicago/Turabian StyleCosta, Gabriel L., and Giuseppe A. Sautto. 2024. "Exploring T-Cell Immunity to Hepatitis C Virus: Insights from Different Vaccine and Antigen Presentation Strategies" Vaccines 12, no. 8: 890. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines12080890
APA StyleCosta, G. L., & Sautto, G. A. (2024). Exploring T-Cell Immunity to Hepatitis C Virus: Insights from Different Vaccine and Antigen Presentation Strategies. Vaccines, 12(8), 890. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines12080890







