Respiratory Efficacy of a Multivalent Marker Vaccine Against Bovine Viral Diarrhoea Virus Types 1 and 2, Infectious Bovine Rhinotracheitis Virus, Bovine Respiratory Syncytial Virus, and Bovine Parainfluenza-3 Virus in Young Calves
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
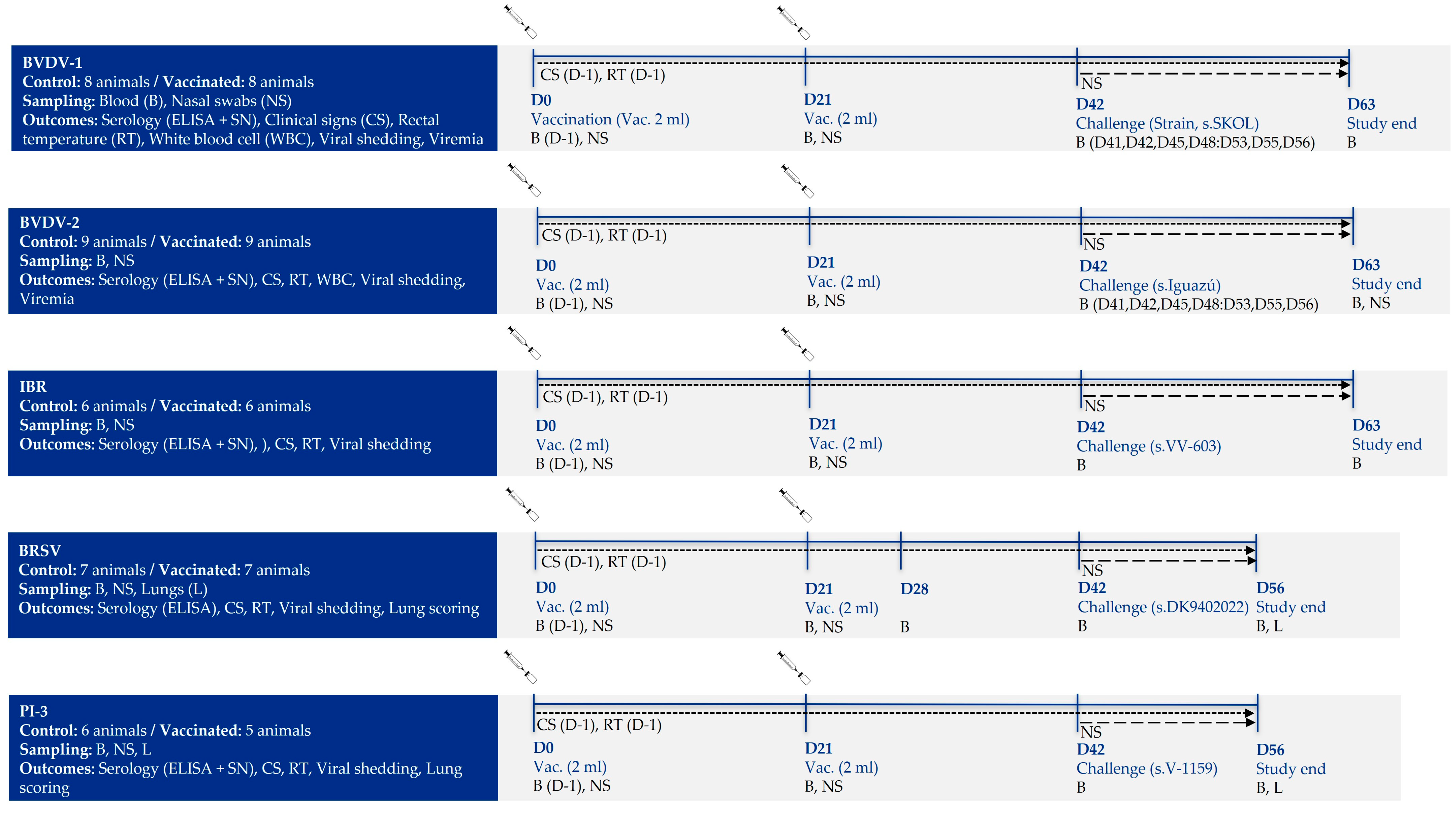
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Animals and Housing
2.3. Vaccination
2.4. Challenge Viruses
2.5. Clinical Assessment
2.6. Sample Collection
2.7. Sample Testing
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
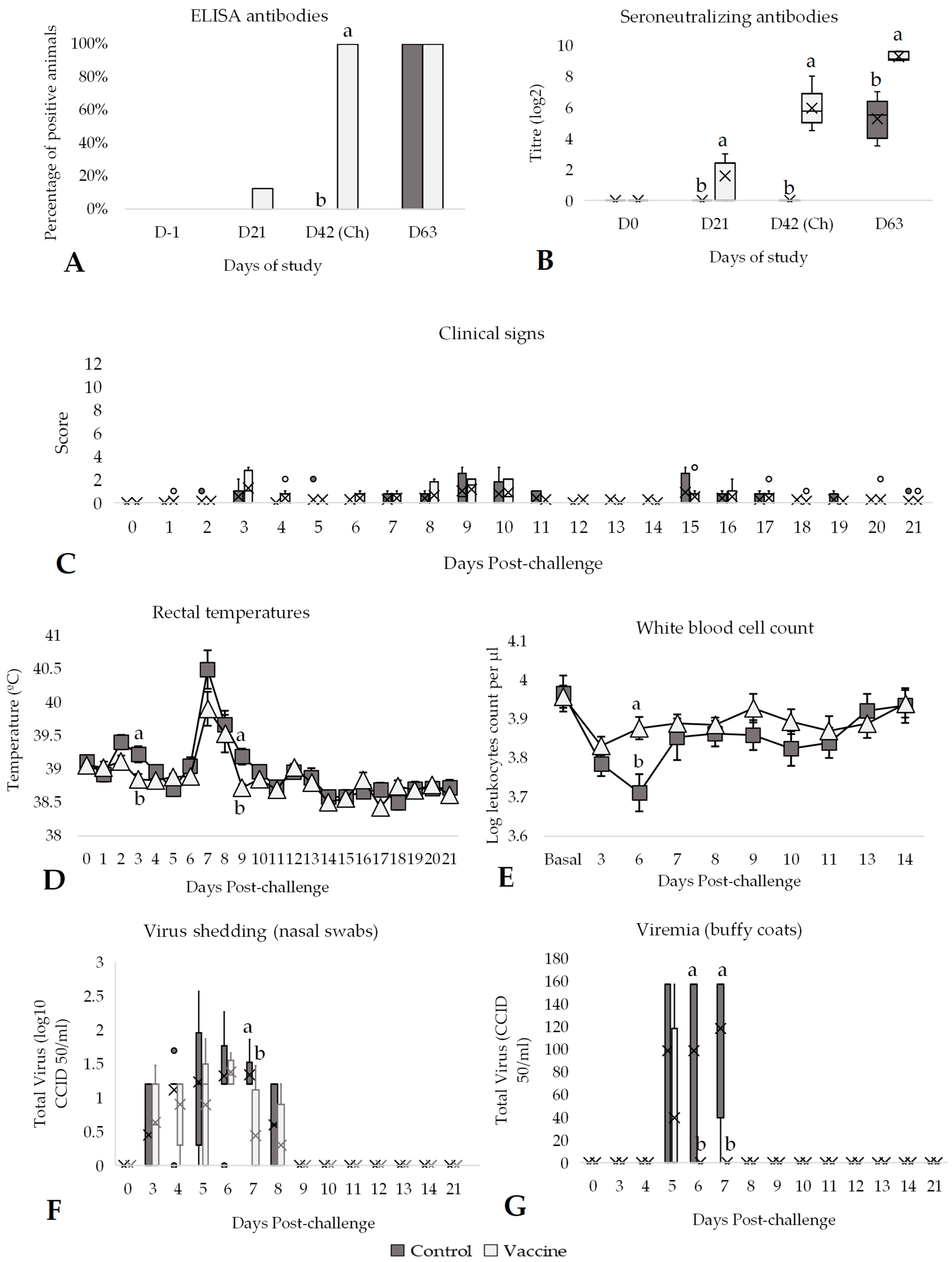
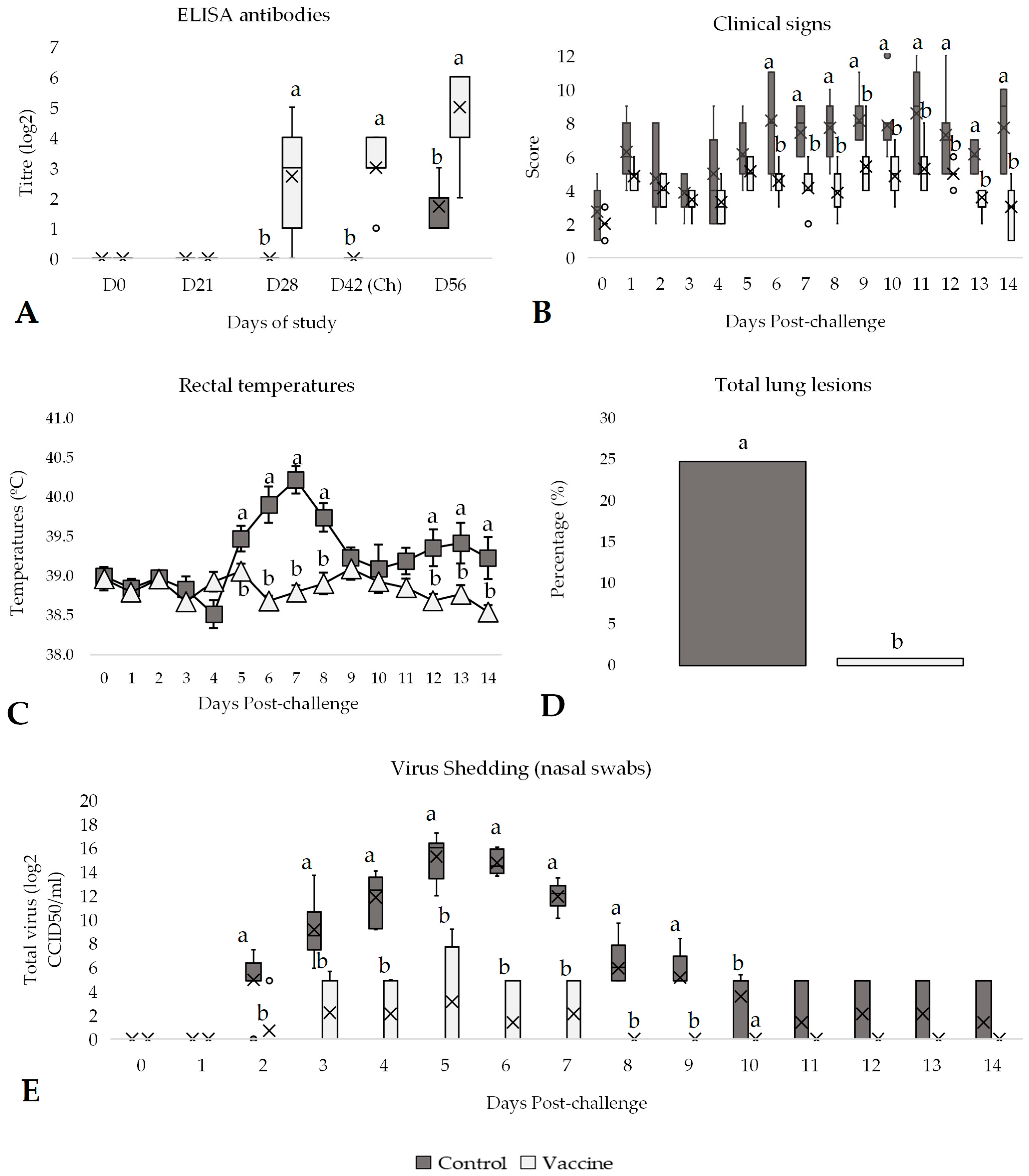
3.1. Efficacy Against BVDV-1 Challenge
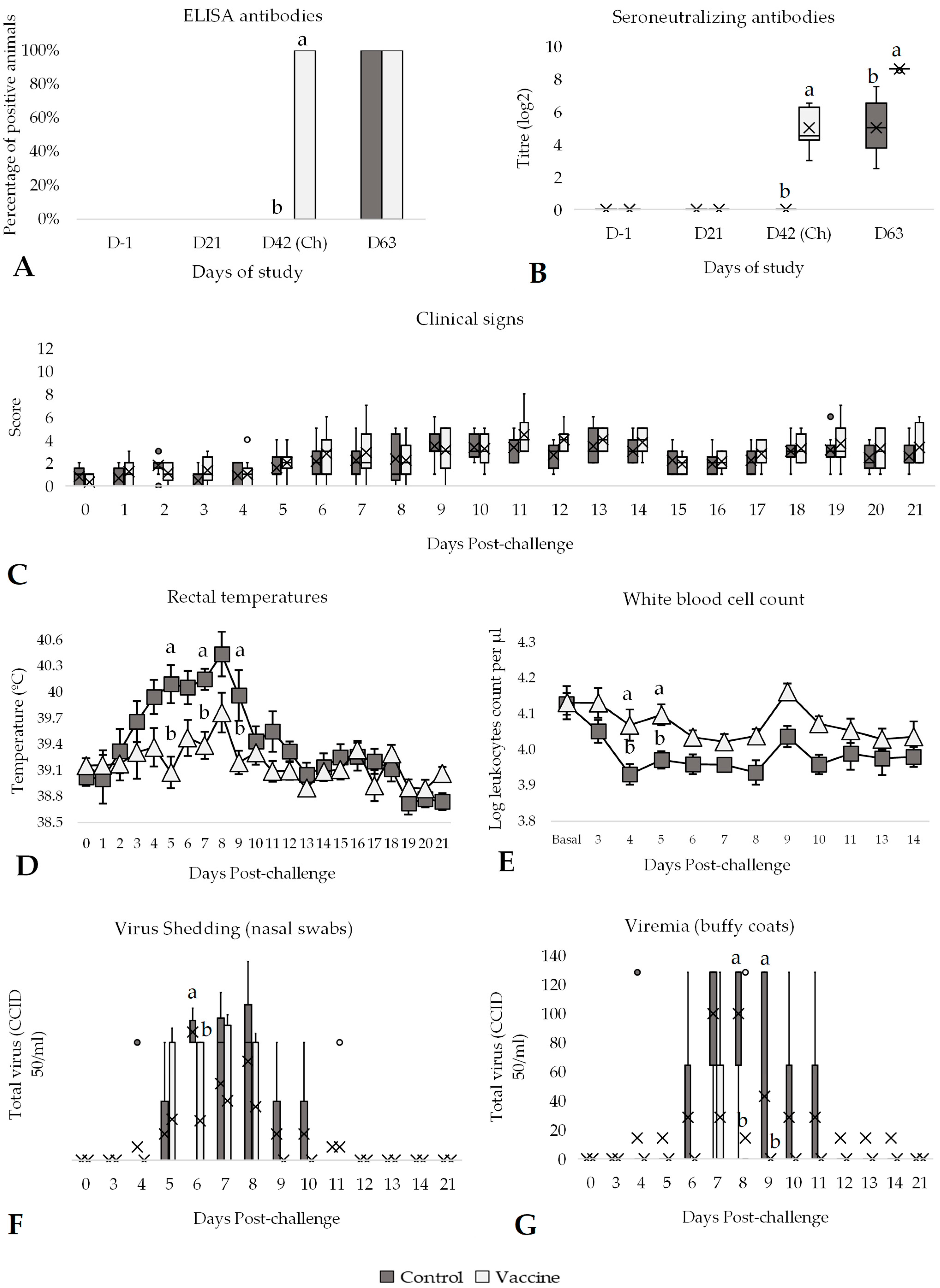
3.2. Efficacy Against BVDV-2 Challenge
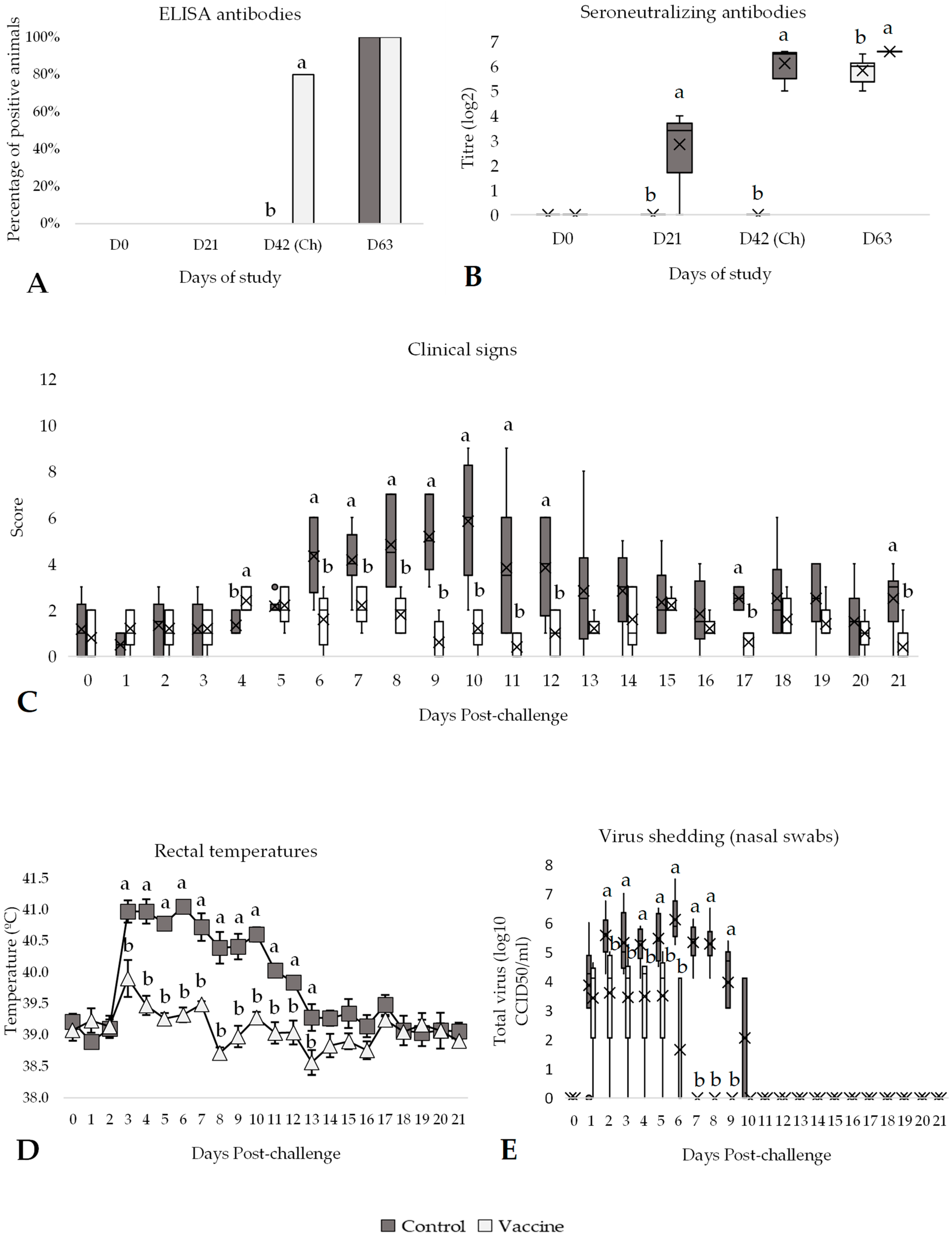
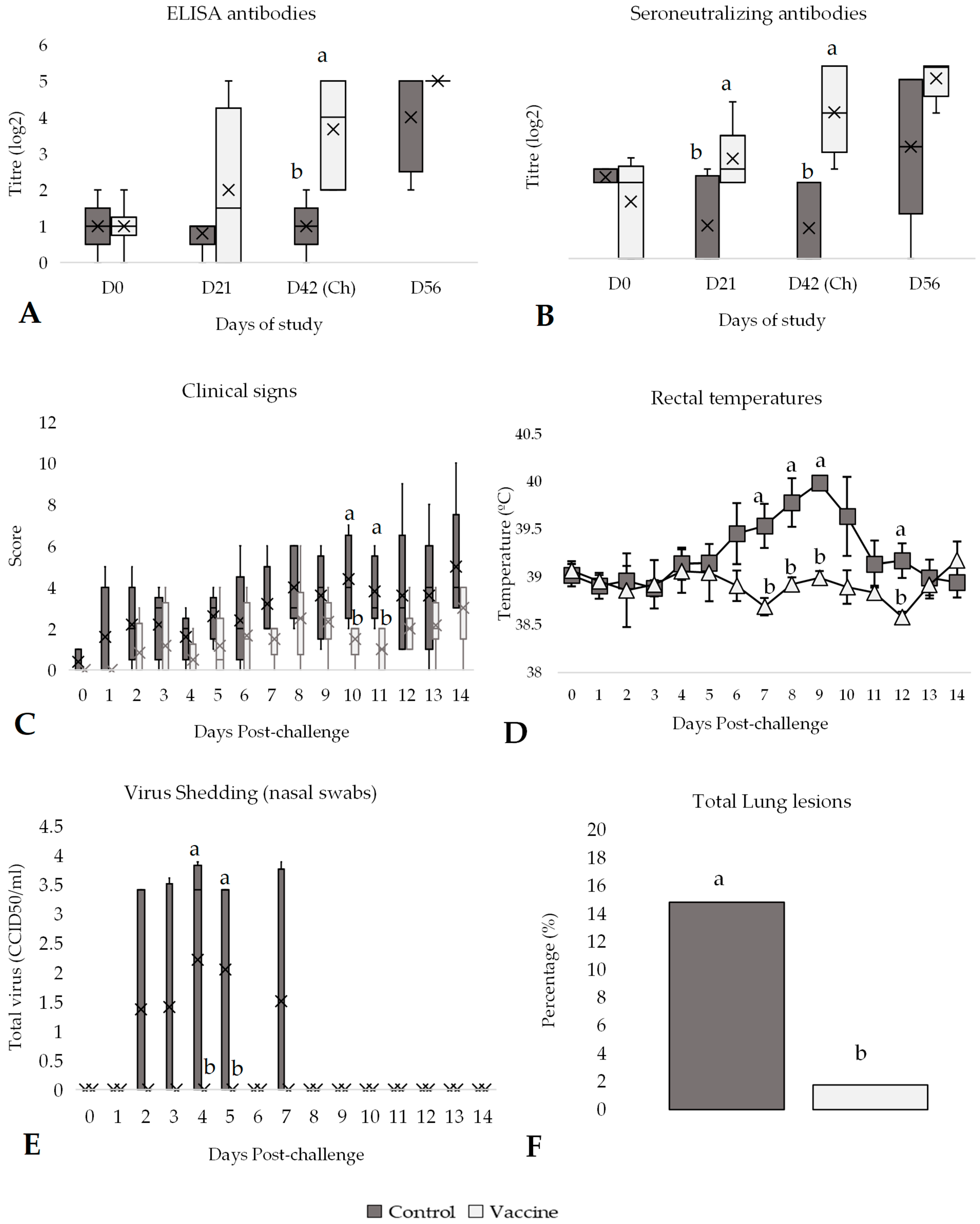
3.3. Efficacy Against IBR Challenge
3.4. Efficacy Against BRSV Challenge
3.5. Efficacy Against PI-3 Challenge
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
6. Patents
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BoHV-1 | Bovine herpesvirus type 1 |
| BRD | Bovine respiratory disease |
| BRSV | Bovine respiratory syncytial virus |
| BVDV | Bovine viral diarrhoea virus |
| DIVA | Differentiating infected from vaccinated animals |
| ELISA | Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay |
| gE | Glycoprotein E |
| IBR | Infectious bovine rhinotracheitis |
| IgA | Immunoglobulin A |
| MLV | Modified-live vaccine |
| PBS | Phosphate-buffered saline |
| PI-3 | Bovine parainfluenza-3 virus |
| RT-qPCR | Reverse-transcription quantitative PCR |
| SN | Serum-neutralisation (antibody) test |
| WBC | White blood cell |
References
- Kirchhoff, J.; Uhlenbruck, S.; Goris, K.; Keil, G.M.; Herrler, G. Three viruses of the bovine respiratory disease complex apply different strategies to initiate infection. Vet. Res. 2014, 45, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cummings, D.B.; Meyer, N.F.; Step, D.L. Bovine Respiratory Disease Considerations in Young Dairy Calves. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Food Anim. Pract. 2022, 38, 93–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferraro, S.; Fecteau, G.; Dubuc, J.; Francoz, D.; Rousseau, M.; Roy, J.P.; Buczinski, S. Scoping review on clinical definition of bovine respiratory disease complex and related clinical signs in dairy cows. J. Dairy Sci. 2021, 104, 7095–7108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holman, D.B.; McAllister, T.A.; Topp, E.; Wright, A.D.G.; Alexander, T.W. The nasopharyngeal microbiota of feedlot cattle that develop bovine respiratory disease. Vet. Microbiol. 2015, 180, 90–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fulton, R.W. Bovine Respiratory Disease Research (1983–2009). Anim. Health Res. Rev. 2009, 10, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Timsit, E.; Hallewell, J.; Booker, C.; Tison, N.; Amat, S.; Alexander, T.W. Prevalence and antimicrobial susceptibility of Mannheimia haemolytica, Pasteurella multocida, and Histophilus somni isolated from the lower respiratory tract of healthy feedlot cattle and those diagnosed with bovine respiratory disease. Vet. Microbiol. 2017, 208, 118–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santo Tomás, H.; Barreto, M.; Vazquez, B.; Villoria, P.; Teixeira, R.; Solé, M. Bovine Respiratory Disease Complex: Prevalence of the Main Respiratory Viruses Involved in Pneumonia in Spain. J. Anim. Sci. Res. 2023, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santo Tomás, H.; Teixeira, R.; Chacón, G.; Lázaro, S.; Sánchez-Matamorors, A.; Villoria, P. Bovine Respiratory Disease Complex: Prevalence of the Different Bacteria Involved in Pneumonia in the Iberian Peninsula. J. Anim. Sci. Res. 2023, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simjee, S.; Ippolito, G. European regulations on prevention use of antimicrobials from January 2022. Braz. J. Vet. Med. 2022, 44, e000822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, T.A. Control Methods for Bovine Respiratory Disease for Feedlot Cattle. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Food Anim. Pract. 2010, 26, 273–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Donkersgoed, J.; van den Hurk, J.V.; McCartney, D.; Harland, R.J. Comparative serological response in calves to eight commercial vaccines against infectious bovine rhinotracheitis, parainfluenza-3, bovine respiratory syncytial, and bovine viral diarrhea viruses. Can. Vet. J. 1991, 32, 727–733. [Google Scholar]
- Fulton, R.W.; Confer, A.W.; Burge, L.J.; Perino, L.J.; d’Offay, J.M.; Payton, M.E.; Mock, R.E. Antibody responses by cattle after vaccination with commercial viral vaccines containing bovine herpesvirus-1, bovine viral diarrhea virus, parainfluenza-3 virus, and bovine respiratory syncytial virus immunogens and subsequent revaccination at day 140. Vaccine 1995, 13, 725–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marzo, E.; Montbrau, C.; Moreno, M.C.; Roca, M.; Sitjà, M.; March, R.; Gow, S.; Lacoste, S.; Ellis, J. NASYM, a live intranasal vaccine, protects young calves from bovine respiratory syncytial virus in the presence of maternal antibodies. Vet. Rec. 2021, 188, e83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, D.A.; Newcomer, B.; Passler, T.; Chamorro, M.F. Efficacy of Bovine Respiratory Syncytial Virus Vaccines to Reduce Morbidity and Mortality in Calves Within Experimental Infection Models: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 906636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mars, M.H.; de Jong, M.C.; Franken, P.; van Oirschot, J.T. Efficacy of a live glycoprotein E-negative bovine herpesvirus 1 vaccine in cattle in the field. Vaccine 2001, 19, 1924–1930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Commission Delegated Regulation (EU) 2020/689. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/eli/reg_del/2020/689/oj/eng#ntr1-L_2020174EN.01027101-E0001 (accessed on 28 May 2025).
- Tapiolas, M.; Gibert, M.; Montbrau, C.; Taberner, E.; Solé, M.; Santo Tomás, H.; Puig, A.; March, R. Efficacy of a New Multivalent Vaccine for the Control of Bovine Respiratory Disease (BRD) in a Randomized Clinical Trial in Commercial Fattening Units. Vaccines 2024, 12, 1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taberner, E.; Gibert, M.; Montbrau, C.; Muñoz Ruiz, I.; Mallorquí, J.; Santo Tomás, H.; Prenafeta, A.; March, R. Efficacy of Vaccination with the DIVENCE® Vaccine Against Bovine Viral Diarrhea Virus Types 1 and 2 in Terms of Fetal Protection. Vet. Med. Res. Rep. 2024, 15, 221–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montbrau, C.; Gibert, M.; Taberner, E.; Tapiolas, M.; Teixeira, R.; Prenafeta, A. Immunological responses against bovine viral diarrhoea virus types 1 and 2 after administration of a commercial subunit vaccine measured by ELISA and serum neutralisation on serum and milk samples. Vet. Rec. 2025, 12, e70006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, B.J.; Anderson, D.E.; Renter, D.G.; Larson, R.L.; Mosier, D.A.; Kelly, L.L.; Theurer, M.E.; Robért, B.D.; Walz, M.L. Clinical, behavioral, and pulmonary changes in calves following inoculation with Mycoplasma bovis. Am. J. Vet. Res. 2012, 73, 490–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patterson, C. Veterinary Medicine: A Textbook of the Diseases of Cattle, Horses, Sheep, Pigs, and Goats, 11th edition, Volumes 1 and 2. Can. Vet. J. 2017, 58, 1116. [Google Scholar]
- Theurer, M.E.; Larson, R.L.; White, B.J. Systematic review and meta-analysis of the effectiveness of commercially available vaccines against bovine herpesvirus, bovine viral diarrhea virus, bovine respiratory syncytial virus, and parainfluenza type 3 virus for mitigation of bovine respiratory disease complex in cattle. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2015, 246, 126–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newcomer, B.W.; Chamorro, M.F.; Walz, P.H. Vaccination of cattle against bovine viral diarrhea virus. Vet. Microbiol. 2017, 206, 78–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chamorro, M.F.; Palomares, R.A. Bovine Respiratory Disease Vaccination Against Viral Pathogens: Modified-Live Versus Inactivated Antigen Vaccines, Intranasal Versus Parenteral, What Is the Evidence? Vet. Clin. Food Anim. Pract. 2020, 36, 461–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howard, C.J. Immunological responses to bovine virus diarrhoea virus infections. Rev. Sci. Tech. Off. Int. Epiz. 1990, 9, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolin, S.R.; Ridpath, J.F. Differences in virulence between two noncytopathic bovine viral diarrhea viruses in calves. Am. J. Vet. Res. 1992, 53, 2157–2163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina, V.; Risalde, M.A.; Sánchez-Cordón, P.J.; Pedrera, M.; Romero-Palomo, F.; Luzzago, C.; Gómez-Villamandos, J.C. Effect of infection with BHV-1 on peripheral blood leukocytes and lymphocyte subpopulations in calves with subclinical BVD. Res. Vet. Sci. 2013, 95, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walz, P.H.; Bell, T.G.; Wells, J.L.; Grooms, D.L.; Kaiser, L.; Maes, R.K.; Baker, J.C. Relationship between degree of viremia and disease manifestation in calves with experimentally induced bovine viral diarrhea virus infection. Am. J. Vet. Res. 2001, 62, 1095–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beer, M.; Hehnen, H.R.; Wolfmeyer, A.; Poll, G.; Kaaden, O.R.; Wolf, G. A new inactivated BVDV genotype I and II vaccine. An immunisation and challenge study with BVDV genotype I. Vet. Microbiol. 2000, 77, 195–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loy, J.D.; Gander, J.; Mogler, M.; Vander Veen, R.; Ridpath, J.; Harris, D.H.; Kamrud, K. Development and evaluation of a replicon particle vaccine expressing the E2 glycoprotein of bovine viral diarrhea virus (BVDV) in cattle. Virol. J. 2013, 10, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, W.; Ellis, J.; Mattick, D.; Smith, L.; Brady, R.; Trigo, E. Immunogenicity of a modified-live virus vaccine against bovine viral diarrhea virus types 1 and 2, infectious bovine rhinotracheitis virus, bovine parainfluenza-3 virus, and bovine respiratory syncytial virus when administered intranasally in young calves. Vaccine 2010, 28, 3784–3792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaashoek, M.J.; van Oirschot, J.T. Early immunity induced by a live gE-negative bovine herpesvirus 1 marker vaccine. Vet. Microbiol. 1996, 53, 191–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spilki, F.R.; Silva, A.D.; Ruthner Batista, H.B.C.; Oliveira, A.P.; Winkelmann, E.; Franco, A.C.; Porciúncula, J.A.; Roehe, P.M. Field evaluation of safety during gestation and horizontal spread of a recombinant differential bovine herpesvirus 1 (BoHV-1) vaccine. Pesq. Vet. Bras. 2005, 25, 54–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ollivett, T.L.; Leslie, K.E.; Duffield, T.F.; Nydam, D.V.; Hewson, J.; Caswell, J.; Dunn, P.; Kelton, D.F. Field trial to evaluate the effect of an intranasal respiratory vaccine protocol on calf health, ultrasonographic lung consolidation, and growth in Holstein dairy calves. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 8159–8168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perkins-Oines, S.; Senevirathne, N.D.; Krafsur, G.M.; Abdelsalam, K.; Renter, D.; Meyer, B.; Chase, C.C.L. The Detection of Vaccine Virus and Protection of a Modified Live, Intranasal, Trivalent Vaccine in Neonatal, Colostrum-Fed Calves with an Experimental Bovine Respiratory Syncytial Virus Challenge. Pathogens 2024, 13, 517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellis, J.; Gow, S.; West, K.; Waldner, C.; Rhodes, C.; Mutwiri, G.; Rosenberg, H. Response of calves to challenge exposure with virulent bovine respiratory syncytial virus following intranasal administration of vaccines formulated for parenteral administration. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2007, 230, 233–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guzman, E.; Taylor, G. Immunology of bovine respiratory syncytial virus in calves. Mol. Immunol. 2015, 66, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jourquin, S.; Lowie, T.; Debruyne, F.; Chantillon, L.; Clinquart, J.; Pas, M.L.; Boone, R.; Hoflack, G.; Vertenten, G.; Sustronck, B.; et al. Effect of on-arrival bovine respiratory disease vaccination on ultrasound-confirmed pneumonia and production parameters in male dairy calves: A randomized clinical trial. J. Dairy Sci. 2023, 106, 9260–9275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Montbrau, C.; Gibert, M.; Solé, M.; Barril, I.; Roca, M.; Acal, L.; Vázquez, B.; Mallorqui, J.; March, R. Respiratory Efficacy of a Multivalent Marker Vaccine Against Bovine Viral Diarrhoea Virus Types 1 and 2, Infectious Bovine Rhinotracheitis Virus, Bovine Respiratory Syncytial Virus, and Bovine Parainfluenza-3 Virus in Young Calves. Vaccines 2025, 13, 999. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines13100999
Montbrau C, Gibert M, Solé M, Barril I, Roca M, Acal L, Vázquez B, Mallorqui J, March R. Respiratory Efficacy of a Multivalent Marker Vaccine Against Bovine Viral Diarrhoea Virus Types 1 and 2, Infectious Bovine Rhinotracheitis Virus, Bovine Respiratory Syncytial Virus, and Bovine Parainfluenza-3 Virus in Young Calves. Vaccines. 2025; 13(10):999. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines13100999
Chicago/Turabian StyleMontbrau, Carlos, Marta Gibert, Marina Solé, Isabel Barril, Mercè Roca, Lucia Acal, Berta Vázquez, Joaquim Mallorqui, and Ricard March. 2025. "Respiratory Efficacy of a Multivalent Marker Vaccine Against Bovine Viral Diarrhoea Virus Types 1 and 2, Infectious Bovine Rhinotracheitis Virus, Bovine Respiratory Syncytial Virus, and Bovine Parainfluenza-3 Virus in Young Calves" Vaccines 13, no. 10: 999. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines13100999
APA StyleMontbrau, C., Gibert, M., Solé, M., Barril, I., Roca, M., Acal, L., Vázquez, B., Mallorqui, J., & March, R. (2025). Respiratory Efficacy of a Multivalent Marker Vaccine Against Bovine Viral Diarrhoea Virus Types 1 and 2, Infectious Bovine Rhinotracheitis Virus, Bovine Respiratory Syncytial Virus, and Bovine Parainfluenza-3 Virus in Young Calves. Vaccines, 13(10), 999. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines13100999





