A Hidden Guardian: The Stability and Spectrum of Antibody-Dependent Cell-Mediated Cytotoxicity in COVID-19 Response in Chinese Adults
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. The Study Cohort
2.2. The Cell Lines
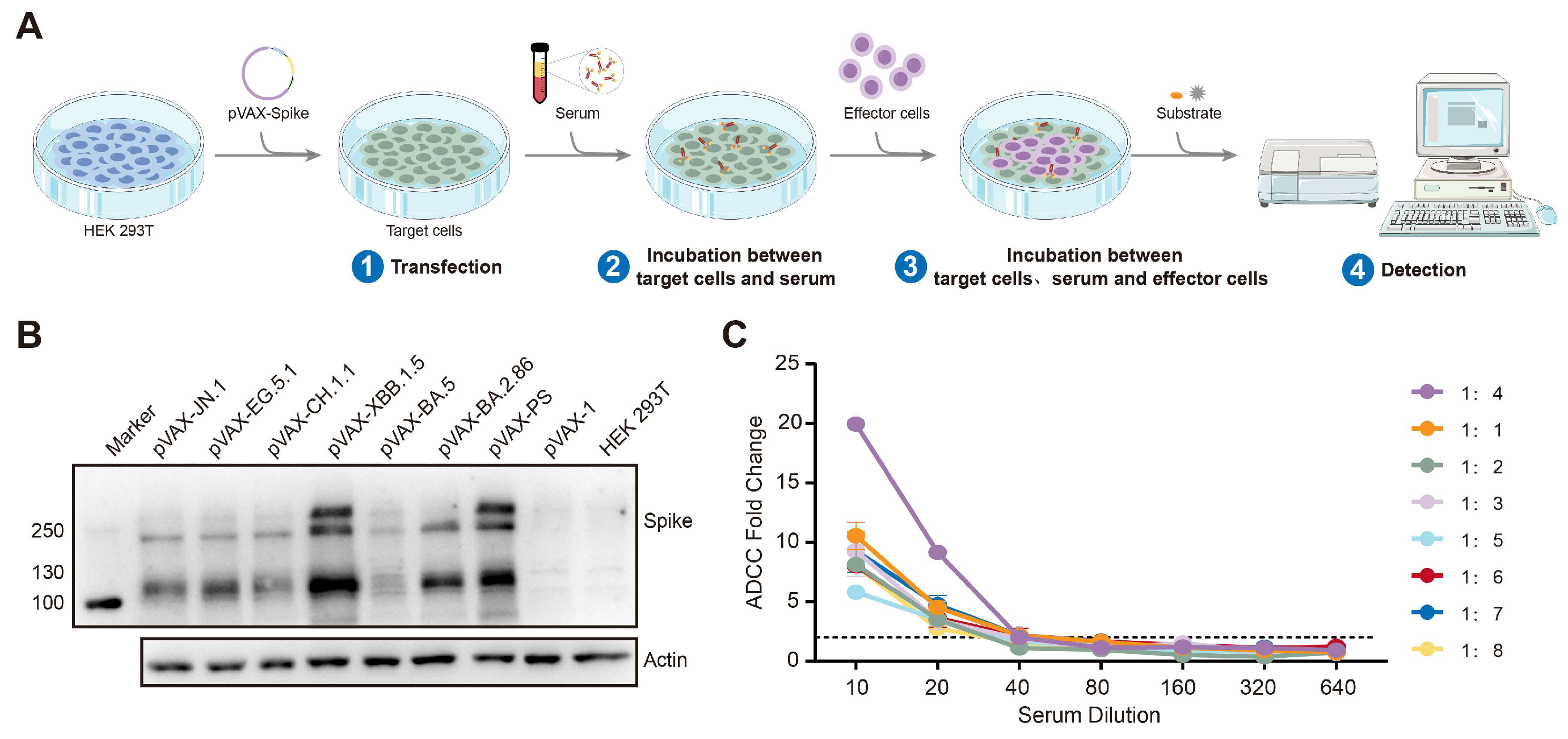
2.3. The ADCC Assay
2.4. Pseudovirus Neutralization Assays
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
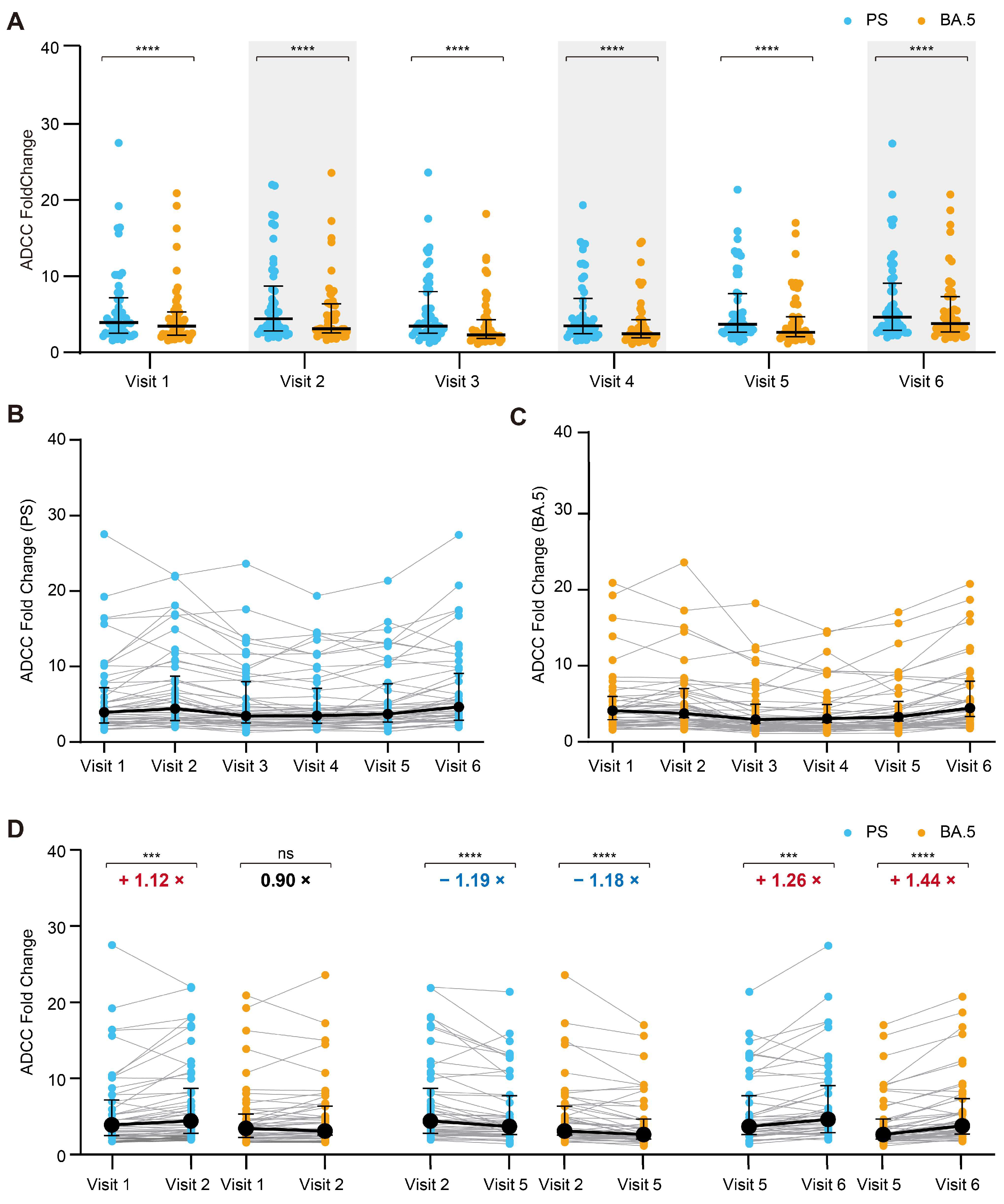
3.1. The Dynamics of the nAb Responses to the SARS-CoV-2 PS and Omicron BA.5
3.2. The Establishment of the ADCC Detection Technology Platform
3.3. Dynamics of the ADCC Responses to the SARS-CoV-2 PS and Omicron BA.5
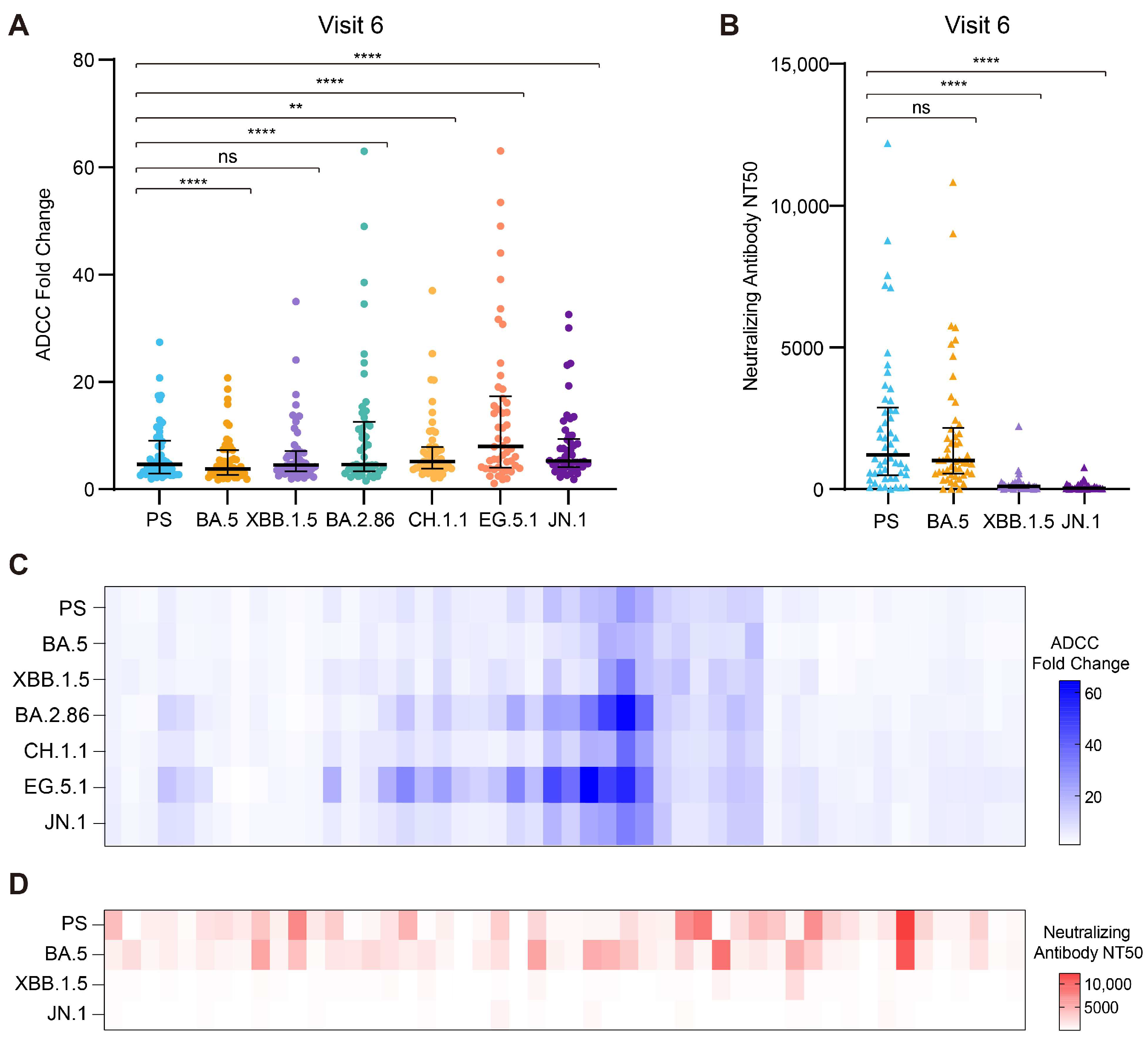
3.4. The ADCC Effect Against the Prospective Omicron Variant XBB.1.5
3.5. The Broad-Spectrum Activity of ADCC Against the Prospective Circulating Omicron Variants
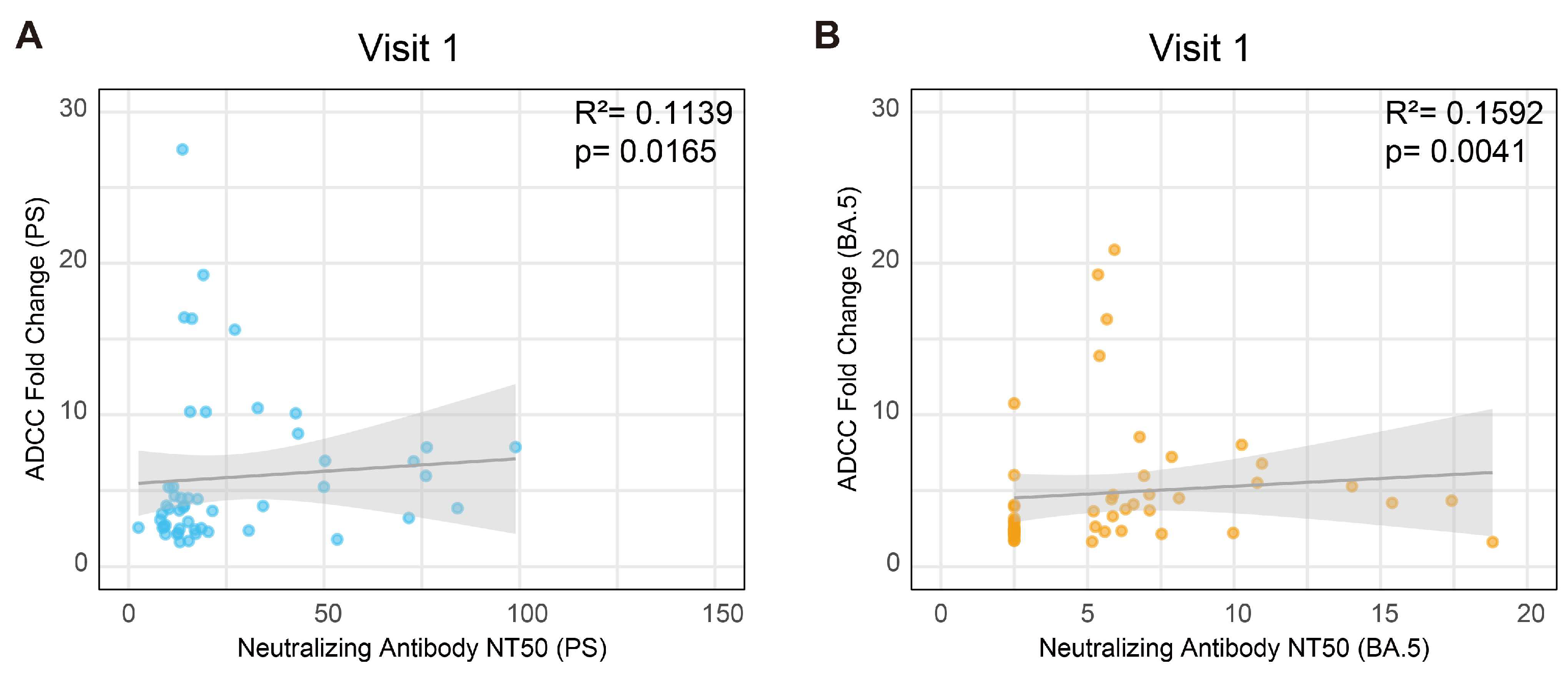
3.6. The Correlation Between the ADCC Effect and Neutralizing Activity
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization (WHO). Available online: https://www.who.int/ (accessed on 23 January 2025).
- Garcia-Beltran, W.F.; Lam, E.C.; St Denis, K.; Nitido, A.D.; Garcia, Z.H.; Hauser, B.M.; Feldman, J.; Pavlovic, M.N.; Gregory, D.J.; Poznansky, M.C.; et al. Multiple SARS-CoV-2 variants escape neutralization by vaccine-induced humoral immunity. Cell 2021, 184, 2372–2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Planas, D.; Saunders, N.; Maes, P.; Guivel-Benhassine, F.; Planchais, C.; Buchrieser, J.; Bolland, W.; Porrot, F.; Staropoli, I.; Lemoine, F.; et al. Considerable escape of SARS-CoV-2 omicron to antibody neutralization. Nature 2022, 602, 671–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Iketani, S.; Li, Z.; Liu, L.; Guo, Y.; Huang, Y.; Bowen, A.D.; Liu, M.; Wang, M.; Yu, J.; et al. Alarming antibody evasion properties of rising SARS-CoV-2 BQ and XBB subvariants. Cell 2023, 186, 279–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Y.; Yisimayi, A.; Jian, F.; Song, W.; Xiao, T.; Wang, L.; Du, S.; Wang, J.; Li, Q.; Chen, X.; et al. BA.2.12.1, BA.4 and BA.5 escape antibodies elicited by omicron infection. Nature 2022, 608, 593–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Y.; Jian, F.; Wang, J.; Yu, Y.; Song, W.; Yisimayi, A.; Wang, J.; An, R.; Chen, X.; Zhang, N.; et al. Imprinted SARS-CoV-2 humoral immunity induces convergent omicron RBD evolution. Nature 2023, 614, 521–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Liang, Z.; Nie, J.; Gao, W.B.; Li, X.; Zhang, L.; Yu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Huang, W. Sera from breakthrough infections with SARS-CoV-2 BA.5 or BF.7 showed lower neutralization activity against XBB.1.5 and CH.1.1. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2023, 12, 2225638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Xue, Q.; Zhang, H.; Yuan, G.; Wang, X.; Sheng, K.; Li, C.; Cai, J.; Sun, Y.; Zhao, J.; et al. Neutralization against omicron subvariants after BA.5/BF.7 breakthrough infection weakened as virus evolution and aging despite repeated prototype-based vaccination1. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2023, 12, 2249121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Wang, J.; Jian, F.; Xiao, T.; Song, W.; Yisimayi, A.; Huang, W.; Li, Q.; Wang, P.; An, R.; et al. Omicron escapes the majority of existing SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibodies. Nature 2022, 602, 657–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Wu, L.; Xu, Z.; Wang, X.; Xie, Y.; Chai, Y.; Zheng, A.; Zhou, J.; Qiao, S.; Huang, M.; et al. An updated atlas of antibody evasion by SARS-CoV-2 omicron sub-variants including BQ.1.1 and XBB. Cell reports. Medicine 2023, 4, 100991. [Google Scholar]
- Walls, A.C.; Park, Y.; Tortorici, M.A.; Wall, A.; Mcguire, A.T.; Veesler, D. Structure, function, and antigenicity of the SARS-CoV-2 spike glycoprotein. Cell 2020, 181, 281–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, L.B.; Foster, C.; Rawlinson, W.; Tedla, N.; Bull, R.A. Evolution of the SARS-CoV-2 omicron variants BA.1 to BA.5: Implications for immune escape and transmission. Rev. Med. Virol. 2022, 32, e2381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuekprakhon, A.; Nutalai, R.; Dijokaite-Guraliuc, A.; Zhou, D.; Ginn, H.M.; Selvaraj, M.; Liu, C.; Mentzer, A.J.; Supasa, P.; Duyvesteyn, H.M.E.; et al. Antibody escape of SARS-CoV-2 omicron BA.4 and BA.5 from vaccine and BA.1 serum. Cell 2022, 185, 2422–2433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, P.; Evans, J.P.; Faraone, J.N.; Zheng, Y.; Carlin, C.; Anghelina, M.; Stevens, P.; Fernandez, S.; Jones, D.; Lozanski, G.; et al. Enhanced neutralization resistance of SARS-CoV-2 omicron subvariants BQ.1, BQ.1.1, BA.4.6, BF.7, and BA.2.75.2. Cell Host Microbe 2023, 31, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarke, A.; Sidney, J.; Methot, N.; Yu, E.D.; Zhang, Y.; Dan, J.M.; Goodwin, B.; Rubiro, P.; Sutherland, A.; Wang, E.; et al. Impact of SARS-CoV-2 variants on the total CD4+ and CD8+ t cell reactivity in infected or vaccinated individuals. Cell Rep. Med. 2021, 2, 100355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emmelot, M.E.; Vos, M.; Boer, M.C.; Rots, N.Y.; de Wit, J.; van Els, C.A.C.M.; Kaaijk, P. Omicron BA.1 mutations in SARS-CoV-2 spike lead to reduced t-cell response in vaccinated and convalescent individuals. Viruses 2022, 14, 1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Xu, S.; Liu, J.; Wu, L.; Qiu, J.; Wang, N.; Ren, J.; Li, Z.; Guo, X.; Tao, F.; et al. Effectiveness of inactivated and ad5-nCoV COVID-19 vaccines against SARS-CoV-2 omicron BA. 2 variant infection, severe illness, and death. BMC Med. 2022, 20, 400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, D.; Gu, Y.; Xu, Y.; Wheeler, B.; Young, H.; Sunny, S.K.; Moore, Z.; Zeng, D. Association of primary and booster vaccination and prior infection with SARS-CoV-2 infection and severe COVID-19 outcomes. JAMA 2022, 328, 1415–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Vries, R.D.; Nieuwkoop, N.J.; Pronk, M.; de Bruin, E.; Leroux-Roels, G.; Huijskens, E.G.W.; van Binnendijk, R.S.; Krammer, F.; Koopmans, M.P.G.; Rimmelzwaan, G.F. Influenza virus-specific antibody dependent cellular cytoxicity induced by vaccination or natural infection. Vaccine 2017, 35, 238–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanderven, H.A.; Jegaskanda, S.; Wheatley, A.K.; Kent, S.J. Antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity and influenza virus. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2017, 22, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanderven, H.A.; Kent, S.J. The protective potential of fc-mediated antibody functions against influenza virus and other viral pathogens. Immunol. Cell Biol. 2020, 98, 253–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Balligand, T.; Carpenet, C.; Ploegh, H.L. An armed anti-immunoglobulin light chain nanobody protects mice against influenza a and b infections. Sci. Immunol. 2023, 8, eadg9459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Fan, C.; Li, Q.; Zhou, S.; Huang, W.; Wang, L.; Sun, C.; Wang, M.; Wu, X.; Ma, J.; et al. Antibody-dependent-cellular-cytotoxicity-inducing antibodies significantly affect the post-exposure treatment of ebola virus infection. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 45552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gunn, B.M.; Lu, R.; Slein, M.D.; Ilinykh, P.A.; Huang, K.; Atyeo, C.; Schendel, S.L.; Kim, J.; Cain, C.; Roy, V.; et al. A fc engineering approach to define functional humoral correlates of immunity against ebola virus. Immunity 2021, 54, 815–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagstaffe, H.R.; Clutterbuck, E.A.; Bockstal, V.; Stoop, J.N.; Luhn, K.; Douoguih, M.; Shukarev, G.; Snape, M.D.; Pollard, A.J.; Riley, E.M.; et al. Antibody-dependent natural killer cell activation after ebola vaccination. J. Infect. Dis. 2021, 223, 1171–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milligan, C.; Richardson, B.A.; John-Stewart, G.; Nduati, R.; Overbaugh, J. Passively acquired antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC) activity in HIV-infected infants is associated with reduced mortality. Cell Host Microbe 2015, 17, 500–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, G.K.; Pazgier, M.; Evans, D.T.; Ferrari, G.; Bournazos, S.; Parsons, M.S.; Bernard, N.F.; Finzi, A. Beyond viral neutralization. AIDS Res. Hum. Retroviruses 2017, 33, 760–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, W.S.; Kent, S.J. Anti-HIV-1 antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity: Is there more to antibodies than neutralization? Curr. Opin. HIV AIDS 2018, 13, 160–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abuharfeil, N.M.; Yaseen, M.M.; Alsheyab, F.M. Harnessing antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity to control HIV-1 infection. ACS Infect. Dis. 2019, 5, 158–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suryawanshi, P.; Bagul, R.; Shete, A.; Thakar, M. Anti-HIV-1 ADCC and HIV-1 env can be partners in reducing latent HIV reservoir. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 663919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.S.; Selva, K.J.; Davis, S.K.; Wines, B.D.; Reynaldi, A.; Esterbauer, R.; Kelly, H.G.; Haycroft, E.R.; Tan, H.; Juno, J.A.; et al. Decay of fc-dependent antibody functions after mild to moderate COVID-19. Cell Rep. Med. 2021, 2, 100296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tso, F.Y.; Lidenge, S.J.; Poppe, L.K.; Peña, P.B.; Privatt, S.R.; Bennett, S.J.; Ngowi, J.R.; Mwaiselage, J.; Belshan, M.; Siedlik, J.A.; et al. Presence of antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC) against SARS-CoV-2 in COVID-19 plasma. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0247640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y.; Wang, M.; Zhang, X.; Li, S.; Lu, Q.; Zeng, H.; Hou, H.; Li, H.; Zhang, M.; Jiang, F.; et al. Antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity response to SARS-CoV-2 in COVID-19 patients. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2021, 6, 346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Deng, C.; Liu, M.; Liu, Y.; Li, L.; Huang, Z.; Shang, L.; Jiang, J.; Li, Y.; Mo, R.; et al. A fourth dose of the inactivated SARS-CoV-2 vaccine redistributes humoral immunity to the n-terminal domain. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 6866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Yu, J.; Issa, R.; Wang, L.; Ning, M.; Yin, S.; Li, J.; Wu, C.; Chen, Y. CoronaVac-induced antibodies that facilitate fc-mediated neutrophil phagocytosis track with COVID-19 disease resolution. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2024, 14, 2434567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Zhang, Q.; Zhong, J.; Chen, L.; Jiang, W.; Huang, T.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, L.; Wang, X.; et al. Omicron BA.1 breakthrough infections in inactivated COVID-19 vaccine recipients induced distinct pattern of antibody and t cell responses to different omicron sublineages. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2023, 12, 2202263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, L.; Wu, Z.; Li, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Mcgoogan, J.M.; Li, Q.; Dong, X.; Ren, R.; Feng, L.; Qi, X.; et al. One hundred days of coronavirus disease 2019 prevention and control in china. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2021, 72, 332–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Liu, M.; Liang, W. The dynamic COVID-zero strategy in china. China CDC Wkly. 2022, 4, 74–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Liu, M.; Liang, W. Persevere in the dynamic COVID-zero strategy in china to gain a precious time window for the future. China CDC Wkly. 2022, 4, 393–394. [Google Scholar]
- Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention. Available online: https://www.chinacdc.cn/ (accessed on 7 January 2025).
- Gan, M.; Cao, J.; Zhang, Y.; Fu, H.; Lin, X.; Ouyang, Q.; Xu, X.; Yuan, Y.; Fan, X. Landscape of t cell epitopes displays hot mutations of SARS-CoV-2 variant spikes evading cellular immunity. J. Med. Virol. 2024, 96, e29452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Gan, M.; Wu, B.; Zeng, R.; Wang, Z.; Xu, J.; Li, J.; Zhang, Y.; Cao, J.; Chen, L.; et al. Humoral and cellular immunity of two-dose inactivated COVID-19 vaccination in chinese children: A prospective cohort study. J. Med. Virol. 2023, 95, e28380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, K.; Karim, F.; Ganga, Y.; Bernstein, M.; Jule, Z.; Reedoy, K.; Cele, S.; Lustig, G.; Amoako, D.; Wolter, N.; et al. Omicron BA.4/BA.5 escape neutralizing immunity elicited by BA.1 infection. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 4686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rössler, A.; Netzl, A.; Knabl, L.; Schäfer, H.; Wilks, S.H.; Bante, D.; Falkensammer, B.; Borena, W.; von Laer, D.; Smith, D.J.; et al. BA.2 and BA.5 omicron differ immunologically from both BA.1 omicron and pre-omicron variants. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 7701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ao, D.; He, X.; Hong, W.; Wei, X. The rapid rise of SARS-CoV-2 omicron subvariants with immune evasion properties: XBB.1.5 and BQ.1.1 subvariants. MedComm 2023, 4, e239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ju, B.; Fan, Q.; Liu, C.; Shen, S.; Wang, M.; Guo, H.; Zhou, B.; Ge, X.; Zhang, Z. Omicron BQ.1.1 and XBB.1 unprecedentedly escape broadly neutralizing antibodies elicited by prototype vaccination. Cell Rep. 2023, 42, 112532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, J.; Hachmann, N.P.; Collier, A.Y.; Lasrado, N.; Mazurek, C.R.; Patio, R.C.; Powers, O.; Surve, N.; Theiler, J.; Korber, B.; et al. Substantial neutralization escape by SARS-CoV-2 omicron variants BQ.1.1 and XBB.1. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 388, 662–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faraone, J.N.; Qu, P.; Goodarzi, N.; Zheng, Y.; Carlin, C.; Saif, L.J.; Oltz, E.M.; Xu, K.; Jones, D.; Gumina, R.J.; et al. Immune evasion and membrane fusion of SARS-CoV-2 XBB subvariants EG.5.1 and XBB.2.3. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2023, 12, 2270069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Q.; An, Y.; Zhou, X.; Xie, H.; Tao, L.; Li, D.; Zheng, A.; Li, L.; Xu, Z.; Yu, S.; et al. Neutralization of EG.5, EG.5.1, BA.2.86, and JN.1 by antisera from dimeric receptor-binding domain subunit vaccines and 41 human monoclonal antibodies. Med 2024, 5, 401–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Zhao, X.; Shi, J.; Wang, Y.; Liu, H.; Hu, Y.; Hu, B.; Shuai, H.; Yuen, T.T.; Chai, Y.; et al. Lineage-specific pathogenicity, immune evasion, and virological features of SARS-CoV-2 BA.2.86/JN.1 and EG.5.1/HK.3. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 8728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, K.; Lustig, G.; Römer, C.; Reedoy, K.; Jule, Z.; Karim, F.; Ganga, Y.; Bernstein, M.; Baig, Z.; Jackson, L.; et al. Evolution and neutralization escape of the SARS-CoV-2 BA.2.86 subvariant. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 8078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeworowski, L.M.; Mühlemann, B.; Walper, F.; Schmidt, M.L.; Jansen, J.; Krumbholz, A.; Simon-Lorière, E.; Jones, T.C.; Corman, V.M.; Drosten, C. Humoral immune escape by current SARS-CoV-2 variants BA.2.86 and JN.1, december 2023. Euro Surveill. Bull. Eur. Mal. Transm. Eur. Commun. Dis. Bull. 2024, 29, 2300740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Liu, Y.; Faraone, J.N.; Hsu, C.C.; Chamblee, M.; Zheng, Y.; Carlin, C.; Bednash, J.S.; Horowitz, J.C.; Mallampalli, R.K.; et al. Distinct patterns of SARS-CoV-2 BA.2.87.1 and JN.1 variants in immune evasion, antigenicity, and cell-cell fusion. mBio 2024, 15, e0075124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvey, W.T.; Carabelli, A.M.; Jackson, B.; Gupta, R.K.; Thomson, E.C.; Harrison, E.M.; Ludden, C.; Reeve, R.; Rambaut, A.; Peacock, S.J.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 variants, spike mutations and immune escape. Nature reviews. Microbiology 2021, 19, 409–424. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Baum, L.L.; Cassutt, K.J.; Knigge, K.; Khattri, R.; Margolick, J.; Rinaldo, C.; Kleeberger, C.A.; Nishanian, P.; Henrard, D.R.; Phair, J. HIV-1 gp120-specific antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity correlates with rate of disease progression. J. Immunol. 1996, 157, 2168–2173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Excler, J.; Michael, N.L. Lessons from the RV144 Thai phase III HIV-1 vaccine trial and the search for correlates of protection. Annu. Rev. Med. 2015, 66, 423–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischinger, S.; Dolatshahi, S.; Jennewein, M.F.; Rerks-Ngarm, S.; Pitisuttithum, P.; Nitayaphan, S.; Michael, N.; Vasan, S.; Ackerman, M.E.; Streeck, H.; et al. IgG3 collaborates with IgG1 and IgA to recruit effector function in RV144 vaccinees. JCI Insight 2020, 5, e140925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mdluli, T.; Jian, N.; Slike, B.; Paquin-Proulx, D.; Donofrio, G.; Alrubayyi, A.; Gift, S.; Grande, R.; Bryson, M.; Lee, A.; et al. RV144 HIV-1 vaccination impacts post-infection antibody responses. PLoS Pathog. 2020, 16, e1009101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ko, Y.; Yu, Y.; Wu, Y.; Tseng, Y.; Chen, C.; Goh, K.; Liao, H.; Chen, T.; Cheng, T.R.; Yang, A.; et al. A non-neutralizing antibody broadly protects against influenza virus infection by engaging effector cells. PLoS Pathog. 2021, 17, e1009724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, R.; Wang, Z.; Uprety, T.; Sreenivasan, C.C.; Sheng, Z.; Hause, B.M.; Brunick, C.; Wu, H.; Luke, T.; Bausch, C.L.; et al. A fully human monoclonal antibody possesses antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC) activity against the h1 subtype of influenza a virus by targeting a conserved epitope at the HA1 protomer interface. J. Med. Virol. 2023, 95, e28901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edgar, J.E.; Trezise, S.; Anthony, R.M.; Krammer, F.; Palese, P.; Ravetch, J.V.; Bournazos, S. Antibodies elicited in humans upon chimeric hemagglutinin-based influenza virus vaccination confer FcγR-dependent protection in vivo. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2023, 120, e1980062176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richardson, S.I.; Madzorera, V.S.; Spencer, H.; Manamela, N.P.; van der Mescht, M.A.; Lambson, B.E.; Oosthuysen, B.; Ayres, F.; Makhado, Z.; Moyo-Gwete, T.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 omicron triggers cross-reactive neutralization and fc effector functions in previously vaccinated, but not unvaccinated, individuals. Cell Host Microbe 2022, 30, 880–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balinsky, C.A.; Jiang, L.; Jani, V.; Cheng, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Belinskaya, T.; Qiu, Q.; Long, T.K.; Schilling, M.A.; Jenkins, S.A.; et al. Antibodies to s2 domain of SARS-CoV-2 spike protein in moderna mRNA vaccinated subjects sustain antibody-dependent NK cell-mediated cell cytotoxicity against omicron BA.1. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1266829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaudoin-Bussières, G.; Tauzin, A.; Dionne, K.; Gendron-Lepage, G.; Medjahed, H.; Perreault, J.; Levade, I.; Alfadhli, L.; Bo, Y.; Bazin, R.; et al. A recent SARS-CoV-2 infection enhances antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity against several omicron subvariants following a fourth mRNA vaccine dose. Viruses 2023, 15, 1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richardson, S.I.; Kgagudi, P.; Manamela, N.P.; Kaldine, H.; Venter, E.M.; Pillay, T.; Lambson, B.E.; van der Mescht, M.A.; Hermanus, T.; Balla, S.R.; et al. Antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity against SARS-CoV-2 omicron sub-lineages is reduced in convalescent sera regardless of infecting variant. Cell Rep. Med. 2023, 4, 100910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abba Moussa, D.; Vazquez, M.; Chable-Bessia, C.; Roux-Portalez, V.; Tamagnini, E.; Pedotti, M.; Simonelli, L.; Ngo, G.; Souchard, M.; Lyonnais, S.; et al. Discovery of a pan anti-SARS-CoV-2 monoclonal antibody with highly efficient infected cell killing capacity for novel immunotherapeutic approaches. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2025, 14, 2432345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsugawa, Y.; Furukawa, K.; Ise, T.; Takayama, M.; Ota, T.; Kuroda, T.; Shano, S.; Hashimoto, T.; Konishi, H.; Ishihara, T.; et al. Discovery of anti-SARS-CoV-2 s2 protein antibody CV804 with broad-spectrum reactivity with various beta coronaviruses and analysis of its pharmacological properties in vitro and in vivo. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0300297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, S.; Lin, Y.L.; Reed, C.; Ng, C.; Cheng, Z.J.; Malavasi, F.; Yang, J.; Quarmby, V.; Song, A. Characterization of in vitro antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity activity of therapeutic antibodies—Impact of effector cells. J. Immunol. Methods 2014, 407, 63–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, Y.; Aggarwal, P.; Cirelli, D.; Gu, L.; Surowy, T.; Mozier, N.M. Characterization of FcγRIIIA effector cells used in in vitro ADCC bioassay: Comparison of primary NK cells with engineered NK-92 and jurkat t cells. J. Immunol. Methods 2017, 441, 56–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Rostad, C.A.; Anderson, L.J.; Sun, H.; Lapp, S.A.; Stephens, K.; Hussaini, L.; Gibson, T.; Rouphael, N.; Anderson, E.J. The development and kinetics of functional antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC) to SARS-CoV-2 spike protein. Virology 2021, 559, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Natarajan, H.; Crowley, A.R.; Butler, S.E.; Xu, S.; Weiner, J.A.; Bloch, E.M.; Littlefield, K.; Wieland-Alter, W.; Connor, R.I.; Wright, P.F.; et al. Markers of polyfunctional SARS-CoV-2 antibodies in convalescent plasma. mBio 2021, 12, e00765-21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, A.; Stacey, H.D.; D’Agostino, M.R.; Tugg, Y.; Marzok, A.; Miller, M.S. Beyond neutralization: Fc-dependent antibody effector functions in SARS-CoV-2 infection. Nature reviews. Immunology 2023, 23, 381–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cao, J.; Gan, M.; Zhang, Z.; Lin, X.; Ouyang, Q.; Fu, H.; Xu, X.; Wang, Z.; Li, X.; Wang, Y.; et al. A Hidden Guardian: The Stability and Spectrum of Antibody-Dependent Cell-Mediated Cytotoxicity in COVID-19 Response in Chinese Adults. Vaccines 2025, 13, 262. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines13030262
Cao J, Gan M, Zhang Z, Lin X, Ouyang Q, Fu H, Xu X, Wang Z, Li X, Wang Y, et al. A Hidden Guardian: The Stability and Spectrum of Antibody-Dependent Cell-Mediated Cytotoxicity in COVID-19 Response in Chinese Adults. Vaccines. 2025; 13(3):262. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines13030262
Chicago/Turabian StyleCao, Jinge, Mengze Gan, Zhihao Zhang, Xiaosong Lin, Qi Ouyang, Hui Fu, Xinyue Xu, Zhen Wang, Xinlian Li, Yaxin Wang, and et al. 2025. "A Hidden Guardian: The Stability and Spectrum of Antibody-Dependent Cell-Mediated Cytotoxicity in COVID-19 Response in Chinese Adults" Vaccines 13, no. 3: 262. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines13030262
APA StyleCao, J., Gan, M., Zhang, Z., Lin, X., Ouyang, Q., Fu, H., Xu, X., Wang, Z., Li, X., Wang, Y., Cai, H., Lei, Q., Liu, L., Wang, H., & Fan, X. (2025). A Hidden Guardian: The Stability and Spectrum of Antibody-Dependent Cell-Mediated Cytotoxicity in COVID-19 Response in Chinese Adults. Vaccines, 13(3), 262. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines13030262





