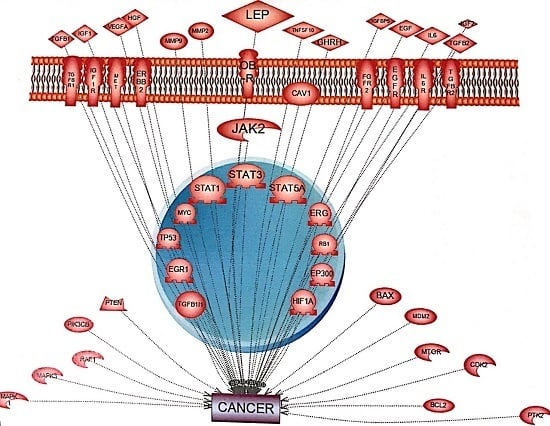
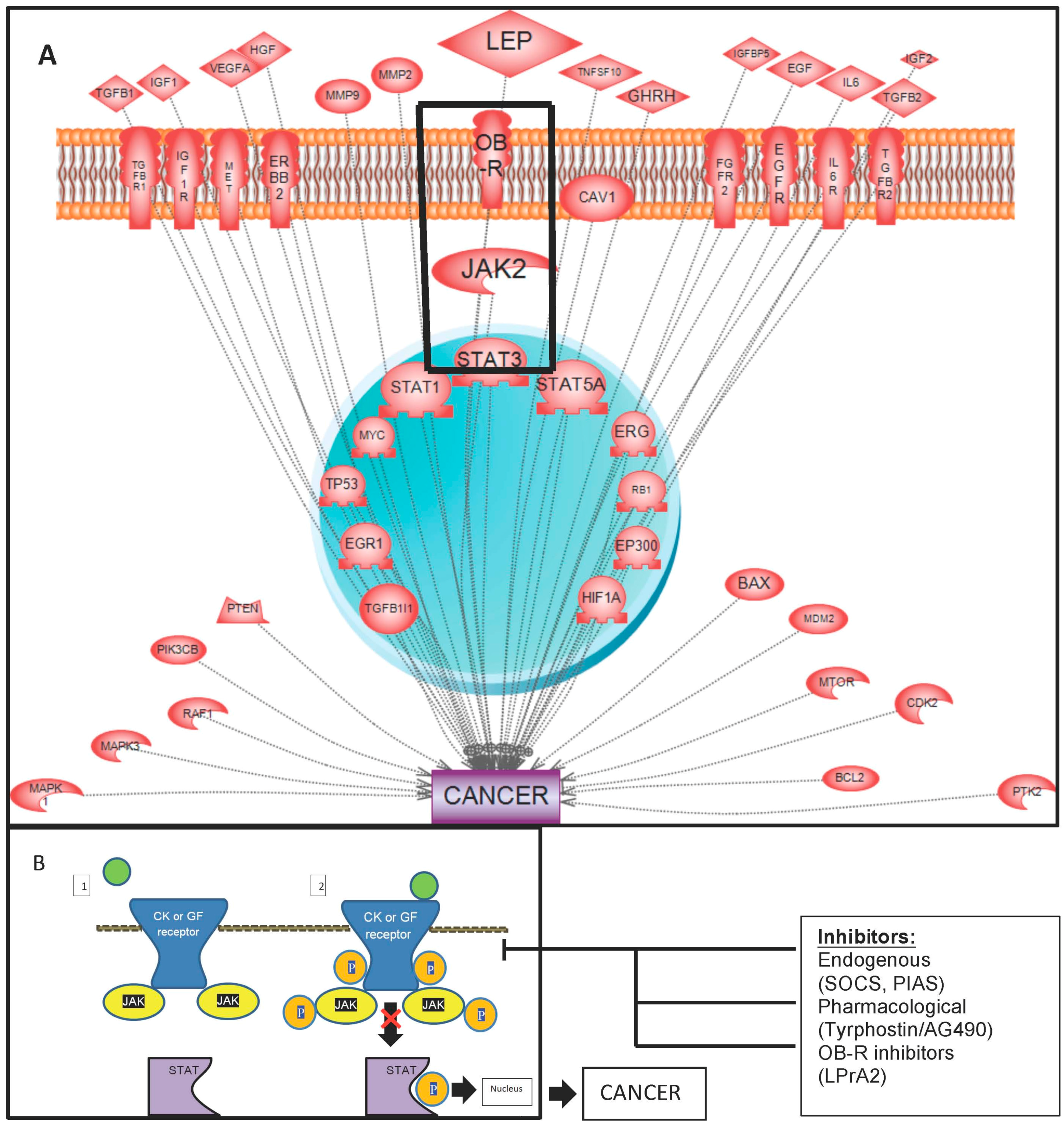
Leptin-Induced JAK/STAT Signaling and Cancer Growth
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. JAK/STAT Pathway
3. Leptin-Induced Activation of the JAK/STAT Pathway and Cancer
4. Leptin and Insulin
5. IGF-1 and Leptin
6. Leptin, C-Src, Grb2 and EGF
7. Leptin, HGF and c-Met
8. Leptin, IFN-γ and IFN-α
9. Leptin and IL-1
10. Leptin, ATM and IL-6
11. Inhibition of the JAK-STAT Pathway and Cancer
12. SOCS
13. TGF-Beta
14. PTPN9
15. Caveolin-1
16. PIAS
17. Highlights
18. Future Directions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AKT | serine threonine protein kinase 1 |
| BCL2 | B-cell lymphoma 2 |
| CDK | cyclin dependent kinase |
| CK | cytokine |
| EGF | epidermal growth factor |
| EGFR | epidermal growth factor receptor |
| EP300 | E1A binding protein P300 |
| EPAS | endothelial PAS domain protein 1 |
| ERBB2 | erb-b2 receptor tyrosine kinase 2 |
| ERG | v-ets avian erythroblastosis virus E-26 oncogene homolog |
| ETS1 | v-ets avian erythroblastosis virus E26 homolog 1 |
| FGF | fibroblast growth factor |
| FGFR | fibroblast growth factor receptor |
| GF | growth factor |
| GHRH | growth hormone releasing hormone |
| GRB2 | growth factor receptor-bound protein 2 |
| HGF | hepatocyte growth factor |
| HIF1A | hypoxia inducing factor 1A |
| IGF | insulin growth factor |
| IGFR | insulin growth factor receptor |
| IL-8 | interleukin 8 |
| LEP | Leptin |
| LPrA2 | leptin peptide receptor antagonist |
| MAPK | mitogen activated protein kinase |
| MET | proto-oncogene, receptor tyrosine kinase |
| MMP | matrix metalloproteinase |
| MTC | v-myc avian myelocytomatosis viral oncogene homolog |
| MTOR | mammalian target of rampamycin |
| NOS | nitric oxide synthase |
| OB-R | leptin receptor |
| PIAS | protein inhibitor of activated stats |
| PIK3CB | phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate-3 kinase, catalytic subunit beta |
| PGF | placental growth factor |
| PTEN | phosphate and tensin homolog |
| RAS | raf1, proto-oncogene, serine/threonine kinase, ras viral oncogene homolog |
| RB | retinoblastoma 1 |
| RHOA | ras homolog family member A |
| SHC1 | (src homology 2 domain containing) transforming protein 1 |
| SOS1 | son of sevenless 1 |
| SRC | proto-oncogene, non-receptor tyrosine kinase |
| TGFA | transforming growth factor A |
| TP53 | tumor protein 53 |
| VEGF | vascular endothelial growth factor |
References
- Fruhbeck, G. Intracellular signalling pathways activated by leptin. Biochem. J. 2006, 393, 7–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhaskaran, K.; Douglass, I.; Forbes, H.; dos-Santos-Silva, I.; Leon, D.A.; Smeeth, L. Body-Mass index and Risk of 22 Specific Cancers: A population-based cohort study of 5.24 UK adults. Lancet 2014, 384, 755–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodwin, P.; Stambolic, V. Impact of the obesity epidemic on cancer. Annu. Rev. Med. 2015, 66, 281–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Baker, J.; Hill, J.; Dietz, W.H. Controversies regarding reported trends: Has the obesity epidemic leveled off in the United States? Adv. Nutr. 2012, 3, 751–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lumeng, C.N.; Bodzin, J.L.; Saltiel, A.R. Obesity induces a phenotypic switch in adipose tissue macrophage polarization. J. Clin. Investig. 2007, 117, 175–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez, R.R.; Cherfils, S.; Escobar, M.; Yoo, J.H.; Carino, C.; Styer, A.K.; Sullivan, B.T.; Sakamoto, H.; Olawaiye, A.; Serikawa, T.; et al. Leptin signaling promotes the growth of mammarytumors and increases the expression of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and its receptor type two (VEGF-R2). J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 26320–26328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez-Perez, R.R.; Xu, Y.; Guo, S.; Watters, A.; Zhou, W.; Leibovich, S.J. Leptin upregulates VEGF in breast cancer via canonic and non-canonical signalling pathways and NFkappaB/HIF-1alpha activation. Cell Signal. 2010, 22, 1350–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lipsey, C.C.; Harbuzariu, A.; Daley-Brown, D.; Gonzalez-Perez, R.R. Oncogenic role of leptin and Notch interleukin-1 leptin crosstalk outcome in cancer. World J. Methodol. 2016, 6, 43–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Shea, J.; Plenge, R. JAK and STAT signaling molecules in immunoregulation and immune-mediated disease. Immunity 2012, 36, 542–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rawlings, J.; Rosler, K.; Harrinson, D. The JAK/STAT signaling pathway. J. Cell Sci. 2004, 117, 1281–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Shea, J.; Schwartz, D.; Villarino, A.; Gadina, M.; McInnes, I.; Laurence, A. The JAK-STAT pathway: Impact on human disease and therapeutic intervention. Annu. Rev. Med. 2015, 66, 311–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furth, P.A.; Nakles, R.E.; Millman, S.; Diaz-Cruz, E.S.; Cabrera, M.C. Signal transducer and activator of transcription 5 as a key signaling pathway in normal mammary gland development biology and breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richard, A.; Stephens, J. The role of JAK-STAT signaling in adipose tissue function. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2014, 1842, 431–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooper, G.M. The Cell: A Molecular Approach, 2nd ed.; Pathways of Intracellular Signal Transduction; Sinauer Associates: Sunderland, MA, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, H.; Zhao, T.; Wang, X.; Gao, C.; Wang, J.; Yu, M.; Hao, J. Leptin upregulates telomerase activity and transcription of human telomerase reverse transcriptase in MCF-7 breast cancer cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2010, 394, 59–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meraz, M.A.; White, J.M.; Sheehan, K.C.; Bach, E.A.; Rodig, S.J.; Dighe, A.S.; Kaplan, D.H.; Riley, J.K.; Greenlund, A.C.; Campbell, D.; et al. Targeted disruption of the Stat1 gene in mice reveals unexpected physiologic specificity in the JAK-STAT signaling pathway. Cell 1996, 84, 431–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aparicio-Siegmund, S.; Sommer, J.; Monhasery, N.; Schwanbeck, R.; Keil, E.; Finkenstädt, D.; Pfeffer, K.; Rose-John, S.; Scheller, J.; Garbers, C. Inhibition of protein kinase II (CK2) prevents induced signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT) 1/3 and constitutive STAT3 activation. Oncotarget 2014, 5, 2131–2148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharrocks, A.D.; Brown, A.L.; Ling, Y.; Yates, P.R. The ETS-domain transcription factor family. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 1997, 29, 1371–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mankan, A.K.; Greten, F.R. Inhibiting signal transducer and activator of transcription 3: Rationality and rationale design of inhibitors. Exp. Opin. Investig. Drugs 2011, 20, 1263–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tartaglia, L.A. The leptin receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 6093–6096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frankenberry, K.; Skinner, H.; Somasundar, P.; McFadden, D.; Vona-Davis, L. Leptin receptor expression and cell signaling in breast cancer. Int. J. Oncol. 2006, 28, 985–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murakami, M.; Hibi, M.; Nakagawa, N.; Nakawaga, T.; Yasukawa, K.; Yamanishi, K.; Taga, T.; Kishimoto, T. IL-6-induced homodimerization of GPL30 and associated activation of a tyrosine kinase. Science 1993, 260, 1808–1810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zabeau, L.; Defeau, D.; Van der Heyden, J.; Iserentant, H.; Vandekerckhove, J.; Tavernier, J. functional analysis of leptin receptor activation using a janus kinase/signal transducer and activator of transcription complementation assay. Mol. Endocrinol. 2004, 18, 150–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, C.; Yang, X.; Wub, Y.; Yang, L.; Mi, S.; Liub, Z.; Jia, K.; Huang, Y.; Weng, S.; Yuc, X.; et al. Involvement of caveolin-1 in the Jak–Stat signaling pathway and infectious spleen and kidney necrosis virus infection in mandarin fish (Siniperca chuatsi). Mol. Immunol. 2011, 48, 992–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, S.; Liu, M.; Gonzalez-Perez, R.R. Role of Notch and its oncogenic signaling crosstalk in breast cancer. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2011, 1815, 197–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, S.; Liu, M.; Wang, G.; Torroella-Kouri, M.; Gonzalez-Perez, R.R. Oncogenic role and therapeutic target of leptin signaling in breast cancer and cancer stem cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2012, 1825, 207–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carpenter, L.R.; Farruggella, T.J.; Symes, A.; Karow, M.L.; Yancopoulos, G.D.; Stahl, N. Enhancing leptin response by preventing SH2-containing phosphatase 2 interaction with Ob receptor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 6061–6066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banks, A.S.; Davis, S.M.; Bates, S.H.; Myers, M.G., Jr. Activation of downstream signals by the long form of the leptin receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 14563–14572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bates, S.H.; Kulkarni, R.N.; Seifert, M.; Myers, M.G., Jr. Roles for leptin receptor/STAT3-dependent and -independent signals in the regulation of glucose homeostasis. Cell Metab. 2005, 1, 169–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bjorbaek, C.; Uotani, S.; da Silva, B.; Flier, J.S. Divergent signaling capacities of the long and short isoforms of the leptin receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 32686–32695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aleffi, S.; Petrai, I.; Bertolani, C.; Parola, M.; Colombatto, S.; Novo, E.; Vizzutti, F.; Anania, F.A.; Milani, S.; Rombouts, K.; et al. Upregulation of proinflammatory and proangiogenic cytokines by leptin in human hepatic stellate cells. Hepatology 2005, 42, 1339–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hegyi, K.; Fulop, K.; Kovacs, K.; Toth, S.; Falus, A. Leptin-induced signal transduction pathways. Cell Boil. Int. 2004, 28, 159–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catalano, S.; Giordano, C.; Rizza, P.; Gu, G.; Barone, I.; Bonofiglio, D.; Giordano, F.; Malivindi, R.; Gaccione, D.; Lanzino, M.; et al. Evidence that leptin through STAT and CREB signaling enhances cyclin D1 expression and promotes human endometrial cancer proliferation. J. Cell Physiol. 2009, 218, 490–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saxena, N.K.; Taliaferro-Smith, L.; Knight, B.B.; Merlin, D.; Anania, F.A.; O’Regan, R.M.; Sharma, D. Bidirectional crosstalk between leptin and insulin-like growth factor-I signaling promotes invasion and migration of breast cancer cells via transactivation of epidermal growth factor receptor. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 9712–9722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ratke, J.; Entschladen, F.; Niggemann, B.; Zanker, K.; Lang, K. Leptin stimulates the migration of colon carcinoma cell by multiple signaling pathways. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2010, 17, 179–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, Y.; Satoh, M.; Tabuchi, T.; Nakamura, M. Prospective, randomized, single-blind comparison of effects of 6 months’ treatment with atorvastatin versus pravastatin on leptin and angiogenic factors in patients with coronary artery disease. Heart Vessels 2012, 27, 337–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, J.; Tian, J.; Lv, Y.; Shi, F.; Kong, F.; Shi, H.; Zhao, L. Leptin induces functional activation of cyclooxygenase-2 through JAK2/STAT3, MAPK/ERK, and PI3K/AKT pathways in human endometrial cancer cells. Cancer Sci. 2009, 100, 389–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, H.; Yu, J.; Guo, H.; Song, H.; Chen, S. Upregulation of survivin by leptin/STAT3 signaling in MCF-7 cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2008, 368, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cascio, S.; Ferla, R.; D’Andrea, A.; Gerbino, A.; Bazan, V.; Surmacz, E.; Russo, A. Expression of angiogenic regulators, VEGF, leptin, is regulated by the EGF/PI3K/STAT3 pathway in colorectal cancer cells. J. Cell Physiol. 2009, 221, 189–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, W.; Gonzalez-Perez, R. Leptin pro-angiogenic signature in breast cancer is linked to IL-1 signalling. Br. J. Cancer 2011, 104, 128–137. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Guo, S.; Gonzalez-Perez, R.R. Notch, IL-1 and Leptin Crosstalk Outcome (NILCO) is critical for leptin-induced proliferation, migration and VEGF/VEGFR-2 expression in breast cancer. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e21467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palianopoulou, M.; Papanikolaou, V.; Stefanou, N.; Tsezou, A. The activation of leptin-mediated survivin is limited by the inducible suppressor SOCS-3 in MCF-7 cells. Exp. Biol. Med. 2011, 236, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nath, A.K.; Brown, R.M.; Michaud, M.; Sierra-Honigmann, M.R.; Snyder, M.; Madri, J.A. Leptin affects endocardial cushion formation by modulating EMT and migration via Akt signaling cascades. J. Cell Biol. 2008, 181, 367–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feldman, D.E.; Chen, C.; Punj, V.; Tsukamoto, H.; Machida, K. Pluripotency factor-mediated expression of the leptin receptor (OB-R) links obesity to oncogenesis through tumor-initiating stem cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 829–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Hulver, M.; McMillan, R.P.; Cai, L.; Kershaw, E.E.; Yu, L.; Xue, B.; Shi, H. Regulation of insulin and leptin signaling by muscle suppressor of cytokine signaling 3 (SOCS3). PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e47493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carvalheira, J.; Ribeiro, E.; Folli, F.; Velloso, L.; Laad, M. Interaction between Leptin and Insulin Signaling Pathways Differentially Affects JAK-STAT and PI 3-Kinase-Mediated Signaling in Rat Liver. Biol. Chem. 2005, 384, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, T.; Fukuda, K.; Pan, J.; Kodama, H.; Sano, M.; Makino, S.; Kato, T.; Manabe, T.; Ogawa, S. Characterization of insulin-like growth factor-1–induced activation of the JAK/STAT pathway in Rat cardiomyocytes. Circ. Res. 1999, 85, 884–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Himpe, E.; Kooijman, R. Insulin-like growth factor-I receptor signal transduction and the Janus Kinase/Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription (JAK-STAT) pathway. Biofactors 2009, 35, 76–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebong, S.; Yu, C.R.; Carper, D.A.; Chepelinsky, A.B.; Egwuagu, C.E. Activation of STAT signaling pathways and induction of suppressors of cytokine signaling (SOCS) proteins in mammalian lens by growth factors. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2004, 45, 872–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yadav, A.; Kalita, A.; Dhillon, S.; Banerjee, K. JAK/STAT3 pathway is involved in survival of neurons in response to insulin-like growth factor and negatively regulated by suppressor of cytokine signaling-3. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 31830–31840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zong, C.S.; Chan, J.; Levy, D.E.; Horvath, C.; Sadowski, H.B.; Wang, L.H. Mechanism of STAT3 activation by insulin-like growth factor I receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 15099–15105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soma, D.; Kitayama, J.; Yamashita, H.; Miyato, H.; Ishikawa, M.; Nagawa, H. Leptin augments proliferation of breast cancer cells via transactivation of HER2. J. Surg. Res. 2008, 149, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gay, B.; Suarez, S.; Weber, C.; Rahuel, J.; Fabbro, D.; Furet, P.; Caravatti, G.; Schoepfer, J. Effect of Potent and Selective Inhibitors of the Grb2 SH2 Domain on Cell Motility. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 23311–23315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giubellino, A.; Burke, T.; Bottaro, D. Grb2 Signaling in Cell Motility and Cancer. Expert Opinion Ther. Targets 2008, 12, 1021–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gualillo, O.; Eiras, S.; White, D.W.; Diéguez, C.; Casanueva, F.F. Leptin promotes the tyrosine phosphorylation of SHC proteins and SHC association with GRB2. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2002, 190, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, Z.; Signore, A.P.; Gao, Y.; Wang, S.; Zhang, F.; Hastings, T.; Yin, X.M.; Chen, J. Leptin protects against 6-hydroxydopamine-induced dopaminergic cell death via mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 34479–34491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasi, W.; Ye, L.; Jiang, W.; Sharma, A.; Mokbel, K. In vitro and in vivo effects of suppressor of cytokine signaling 7 knockdown in breast cancer: The influence on cellular response to hepatocyte growth factor. Biomed. Res. Int. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bocaccio, C.; Tmagnone, L.; Bardelli, A.; Michieli, P.; Battistini, C.; Ando, M. Induction of epithelial tubules by growth factor HGF depends on the STAT pathway. Nature 1998, 391, 285–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamaji, D.; Kamikawa, A.; Soliman, M.M.; Ito, T.; Ahmed, M.M.; Makondo, K.; Watanabe, A.; Saito, M.; Kimura, K. Leptin inhibits hepatocyte growth factor-induced ductal morphogenesis of bovine mammary epithelial cells. Jpn. J. Vet. Res. 2007, 54, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Darnell, J.; Kerr, I.; Stark, G. Jak-STAT Pathways and Transcriptional Activation in Response to IFNs and Other Extracellular Signaling Proteins. Science 1994, 264, 1415–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caldenhoven, E.; Buitenhuis, M.; van Dijk, T.B.; Raaijmakers, J.A.; Lammers, J.W.; Koenderman, L.; de Groot, R.P. Lineage-specific activation of STAT3 by interferon-gamma in human neutrophils. J. Leukoc. Biol. 1999, 65, 391–396. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Smit, L.S.; Meyer, D.J.; Billestrup, N.; Norstedt, G.; Schwartz, J.; Carter-Su, C. The role of the growth hormone (GH) receptor and JAK1 and JAK2 kinases in the activation of Stats 1, 3, and 5 by GH. Mol. Endocrinol. 1996, 10, 519–533. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Au-Yeung, N.; Mandhana, R.; Horvath, C.M. Transcriptional Regulation of STAT1 and STAT2 in the interferon JAK-STAT pathway. JAKSTAT 2013, 2, e23931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaser, S.; Kaser, A.; Vogel, W.; Patsch, J.R.; Tilg, H. Interferon-alpha suppresses leptin levels: Studies in interferon-alpha treated patients with hepatitis C virus infection and murine adipocytes. Eur. Cytokine Netw. 2002, 13, 225–229. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Raso, G.M.; Pacilio, M.; Esposito, E.; Coppola, A.; di Carlo, R.; Meli, R. Leptin potentiates IFN-gamma-induced expression of nitric oxide synthase and cyclo-oxygenase-2 in murine macrophage J774A.1. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2002, 137, 799–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martín-Romero, C.; Santos-Alvarez, J.; Goberna, R.; Sánchez-Margalet, V. Human leptin enhances activation and proliferation of human circulating T lymphocytes. Cell. Immunol. 2000, 199, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calle, E.D.; Rodriguez, C.; Walker-Thurmond, K.; Thun, M.J. Overweight, Obesity, and Mortality from Cancer in a Prospectively Studied Cohort of U.S. Adults. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003, 348, 1625–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koivisto, V.A.; Pelkonen, R.; Cantell, K. Effect of interferon on glucose tolerance and insulin sensitivity. Diabetes 1989, 38, 641–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heinrich, P.C.; Behrmann, I.; Haan, S.; Hermanns, H.M.; Muller-Newen, G.; Schaper, F. Principles of interleukin (IL)-6-type cytokine signalling and its regulation. Biochem. J. 2003, 374, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghilardi, N.; Ziegler, S.; Wiestner, A.; Stoffel, R.; Heim, M.H.; Skoda, R.C. Defective STAT signaling by the leptin receptor in diabetic mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 6231–6235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heinrich, P.; Behrmann, I.; Muller-Newen, G.; Schaper, F.; Graeve, L. interleukin-6-type cytokine signalling through the gp130/jak/stat pathway. Biochem. J. 1998, 334, 297–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, C.H.; Lu, D.Y.; Yang, R.S.; Tsai, H.Y.; Kao, M.C.; Fu, W.M.; Chen, Y.F. Leptin-induced IL-6 production is mediated by leptin receptor, insulin receptor substrate-1, phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase, Akt, NF-kappaB, and p300 pathway in microglia. J. Immunol. 2007, 179, 1292–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, W.H.; Liu, S.C.; Tsai, C.H.; Fong, Y.C.; Wang, S.J.; Chang, Y.S.; Tang, C.H. Leptin Induces IL-6 Expression through OBRl Receptor Signaling Pathway in Human Synovial Fibroblasts. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e75551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trujillo, M.E.; Sullivan, S.; Harten, I.; Schneider, S.H.; Greenberg, A.S.; Fried, S.K. Interleukin-6 regulates human adipose tissue lipid metabolism and leptin production in vitro. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2004, 89, 5577–5582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slattery, M.L.; Lundgreen, A.; Hines, L.M.; Torres-Mejia, G.; Wolff, R.K.; Stern, M.C.; John, E.M. Genetic variation in the JAK/STAT/SOCS signaling pathway influences breast cancer-specific mortality through interaction with cigarette smoking and use of aspirin/NSAIDs: Breast cancer health disparities study. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2014, 147, 145–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia, R.; Bowman, T.L.; Niu, G.; Yu, H.; Minton, S.; Muro-Cacho, C.A.; Cox, C.E.; Falcone, R.; Fairclough, R.; Parsons, S.; et al. Constitutive activation of Stat3 by the Src and JAK tyrosine kinases participates in growth regulation in human breast carcinoma cells. Oncogenes 2001, 20, 2499–2513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andorfer, P.; Heuwieser, A.; Heinzel, A.; Lukas, A.; Mayer, B.; Perco, P. Vascular endothelial growth factor A as predictive marker for mTOR inhibition in relapsing high-grade serous ovarian cancer. BMC Syst. Biol. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bak, M.; Jazwa, A.; Kasper, L.; Kachamakova-Trojanowska, N.; Jozkowicz, A.; Sladek, K.; Dulak, J. Involvement of microRNAs in The Inflammatory Pathways of Pulmonary Sarcoidosis. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2015, 66, 635–642. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Das, L.; Torres-Castillo, L.; Gill, T.; Levine, A. TGF-β conditions intestinal T cells to express increased levels of miR-155, associated with down-regulation of IL-2 and ITK mRNA. Mucosal Immunol. 2013, 6, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa-da-Silva, A.; Marinotti, O.; Ribeiro, J.M.; Silva, M.C.; Lopes, A.R.; Barros, M.S.; Sá-Nunes, A.; Kojin, B.B.; Carvalho, E.; Suesdek, L.; et al. Transcriptome Sequencing and Developmental Regulation of Gene Expression in Anopheles aquasalis. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2014, 8, e3005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frank, P.G.; Pavlides, S.; Cheung, M.W.; Daumer, K.; Lisanti, M.P. Role of caveolin-1 in the regulation of lipoprotein metabolism. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2008, 295, 242–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, P.; Peterson, T.E.; Sert-Kuniyoshi, F.H.; Jensen, M.D.; Somers, V.K. Leptin upregulates caveolin-1 expression: Implications for development of atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis 2011, 217, 499–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Razani, B.; Combs, T.; Wang, X.; Frank, P.; Park, D.; Russell, R.; Li, M.; Tang, B.; Jelicks, L.; Scherer, P.; et al. Caveolin-1-deficient mice are lean, resistant to diet-induced obesity, and show hypertriglyceridemia with adipocyte abnormalities. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 8635–8647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greenhalgh, C.J.; Hilton, D.J. Negative regulation of cytokine signaling. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2001, 70, 348–356. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jackson, P.K. A new RING for SUMO: Wrestling transcriptional responses into nuclear bodies with PIAS family E3 SUMO ligases. Genes Dev. 2001, 15, 3053–3058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catalano, S.; Leggio, A.; Barone, I.; De Marco, R.; Gelsomino, L.; Campana, A.; Malivindi, R.; Panza, S.; Giordano, C.; Liguori, A.; et al. A novel leptin antagonist peptide inhibits breast cancer growth in vitro and in vivo. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2015, 19, 1122–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buchert, M.; Burns, C.; Ernst, M. Targeting JAK kinase in solid tumors: Emerging opportunities and challenges. Oncogene 2016, 35, 939–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldstein, J.D.; Burlion, A.; Zaragoza, B.; Sendeyo, K.; Polansky, J.K.; Huehn, J.; Piaggio, E.; Salomon, B.L.; Marodon, G. Inhibition of JAK/STAT pathway in regulatory T-cells reveals a very dynamic regulation of Foxop3 expression. PLoS ONE 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucet, I.S.; Fantino, E.; Styles, M.; Bamert, R.; Patel, O.; Broughton, S.E.; Walter, M.; Burns, C.J.; Treutlein, H.; Wilks, A.F.; et al. The structural basis of Janus kinase 2 inhibition by a potent and specific pan-Janus kinase inhibitor. Blood 2006, 107, 176–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pardanani, A.; Laborde, R.R.; Lasho, T.L.; Finke, C.; Begna, K.; Al-Kali, A.; Hogan, W.J.; Litzow, M.R.; Leontovich, A.; Kowalski, M.; et al. Safety and efficacy of CYT387, a JAK1 and JAK2 inhibitor, in myelofibrosis. Leukemia 2013, 27, 1322–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plimack, E.R.; LoRusso, P.M.; McCoon, P.; Tang, W.; Krebs, A.D.; Curt, G.; Eckhardt, S.G. AZD1480: A phase I study of a novel JAK2 inhibitor in solid tumors. Oncologist 2013, 18, 819–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, M.; Jiang, B.; Gao, F. Small molecule inhibitors of STAT3 for cancer therapy. Curr. Med. Chem. 2011, 18, 4012–4018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dorritie, K.A.; Redner, R.L.; Johnson, D.E. STAT transcription factors in normall and cancer stem cells. Adv. Biol. Regul. 2014, 56, 30–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stark, G.R.; Darnell, J.E., Jr. The JAK-STAT pathway at twenty. Immunity 2012, 36, 503–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Pharmacologic Inhibitor | Targets | Diseases | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tofacitinib (Xeljanz) | Inhibition of JAK1 and JAK3 signaling | Ulcerative colitis, Crohn’s disease Ulcerative colitis | [87] |
| ZM39923 (ZM) | ZM has been described as the most specific JAK3 inhibitor | Rheumatoid arthritis | [88] |
| Tyrphostin/AG490 (AG) | JAK2 and JAK3 signaling | Rheumatoid arthritis | [88] |
| Ruxolitinib (JAKafi) | Potent inhibitor of JAK1 and JAK2 signaling | Solid tumor, metastatic pancreatic cancer Lung adenocarcinoma, metastatic breast cancer metastatic prostate cancer, NSCLC, breast cancer | [11,87] |
| Pyridone 6 | Binds to the ATP pocket of the active conformation of JAK2 | Myelofibrosis | [89] |
| CYT387 | Inhibition of JAK2 signaling | Myelofibrosis | [90] |
| AZD1480 | Inhibition of JAK2 and JAK1 signaling | Gastric cancer, hepatocellular carcinoma, metastatic lung cancer, NSCLC, solid tumor | [11,91] |
| Momelotinib | Inhibition of JAK1 and JAK2 signaling | Lung cancer, colon cancer, pancreatic cancer Metastatic pancreatic cancer, pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma | [11,87] |
| INCB-39110 | Inhibition of JAK1 signaling | Adenocarcinoma, solid tumor, metastatic pancreatic cancer | [11,87] |
| Peficitinib | Inhibition of JAK1 and JAK3 signaling | Ulcerative colitis | [87] |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mullen, M.; Gonzalez-Perez, R.R. Leptin-Induced JAK/STAT Signaling and Cancer Growth. Vaccines 2016, 4, 26. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines4030026
Mullen M, Gonzalez-Perez RR. Leptin-Induced JAK/STAT Signaling and Cancer Growth. Vaccines. 2016; 4(3):26. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines4030026
Chicago/Turabian StyleMullen, McKay, and Ruben Rene Gonzalez-Perez. 2016. "Leptin-Induced JAK/STAT Signaling and Cancer Growth" Vaccines 4, no. 3: 26. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines4030026
APA StyleMullen, M., & Gonzalez-Perez, R. R. (2016). Leptin-Induced JAK/STAT Signaling and Cancer Growth. Vaccines, 4(3), 26. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines4030026