Abstract
Viral haemorrhagic septicaemia virus (VHSV) is one of the worst viral threats to fish farming. Non-virion (NV) gene-deleted VHSV (dNV-VHSV) has been postulated as an attenuated virus, because the absence of the NV gene leads to lower induced pathogenicity. However, little is known about the immune responses driven by dNV-VHSV and the wild-type (wt)-VHSV in the context of infection. Here, we obtained the immune transcriptome profiling in trout infected with dNV-VHSV and wt-VHSV and the pathways involved in immune responses. As general results, dNV-VHSV upregulated more trout immune genes than wt-VHSV (65.6% vs 45.7%, respectively), whereas wt-VHSV maintained more non-regulated genes than dNV-VHSV (45.7% vs 14.6%, respectively). The modulated pathways analysis (Gene-Set Enrichment Analysis, GSEA) showed that, when compared to wt-VHSV infected trout, the dNV-VHSV infected trout upregulated signalling pathways (n = 19) such as RIG-I (retinoic acid-inducible gene-I) like receptor signalling, Toll-like receptor signalling, type II interferon signalling, and nuclear factor kappa B (NF-kappa B) signalling, among others. The results from individual genes and GSEA demonstrated that wt-VHSV impaired the activation at short stages of infection of pro-inflammatory, antiviral, proliferation, and apoptosis pathways, delaying innate humoral response and cellular crosstalk, whereas dNV-VHSV promoted the opposite effects. Therefore, these results might support future studies on using dNV-VHSV as a potential live vaccine.
1. Introduction
Viral haemorrhagic septicaemia virus (VHSV) belongs to the Novirhabdovirus genus, together with infectious haematopoietic necrosis virus (IHNV), snakehead rhabdovirus (SHRV), and hirame rhabdovirus (HIRV). They are all enveloped negative-stranded RNA viruses with a single RNA genome of ~11 Kb [1,2,3], which encodes five virion proteins (N, P, M, G, and L proteins) and the non-virion (NV) protein that gives the name to the Novirhabdovirus genus and differentiates it from other fish rhabdoviruses such as spring viremia carp virus (SVCV). VHSV has been isolated from more than 50 fish species from North America, Asia, and Europe, including 15 farmed [4] and free-living marine fish species [5] like trout, salmon, turbot, and eel, among others. Within a farm, the presence of VHSV infection, even if in only one individual fish, has to be notified to the Office International des Epizooties (OIE, Paris, France) and implies the sacrifice of all the farmed fish, thus leading to serious economic losses [6,7]. The NV gene was firstly characterised and named from IHNV genome studies [8]. Some years later, the NV gene from VHSV was further characterised by comparative genome studies [9]. Despite the presence of the NV gene in the four novirhabdovirus species mentioned above, their NV proteins showed very divergent inter-species sequences [10,11]. Initial studies regarding NV role showed that it was required for the highest efficient replication of IHNV in rainbow trout [12,13,14] and that of VHSV in olive flounder [13,15] and in Epithelioma papulosum cyprinid (EPC) cells [13]. However, NV was not essential for in vitro or in vivo SHRV production in warm-water flatfish [16,17]. Further, in vitro studies using the wild-type (wt) and NV knock-out IHNV or VHSV suggested that NV downregulated the host ifn1/mx transcriptional levels during in vitro infection in trout (RTG-2, Rainbow Trout Gonad-2) [18] or EPC cells [15], respectively. The higher levels of IFN-induced mx transcript in NV knock-out VHSV vs. wt-VHSV injected flounder found in these studies suggested that NV also interferes with IFN defences in vivo to favour VHSV replication [15]. The early anti-apoptotic role of NV during the first stages of VHSV infection has been also demonstrated [19]. Using recombinant NV protein (rNV) and a trout immune-targeted microarray, we have previously determined not only an anti-apoptotic role for NV, but also a plethora of novel expression changes (mainly downregulated) in genes associated with immune innate and adaptive response (i.e., interferons, MX, tumour necrosis factors, antigen presentation, interleukins) [6]. However, the effects driven by the injection of the rNV protein alone will probably differ from those induced by the NV in the course of VHSV infection. Recently, a microarray study in olive flounder liver infected with VHSV described differential gene expression and gene ontology classification of these genes [20], resulting in a global transcriptome profiling where only a few genes have been classified as immune-related. Gene expression has been also characterised with microarrays in olive flounder infected with a VHSV strain that produces high mortality in this species [21]. In addition, the protection of olive flounder against VHSV was previously assessed by immunization with the NV gene-knockout recombinant VHSV, which led to good protection against virulent VHSV [22]. However, the underlying mechanisms of olive flounder protection remain unknown. The aim of this work was to characterise the transcriptomic profiling of immune-related genes in trout infected with the wild-type VHSV (expressing NV) and dNV-VHSV (NV gene-deleted) in order to find targeted immune genes and signalling pathways implied in the course of a VHSV infection. This study will contribute to better understand how NV modulates gene expression and how the expression pattern changes in response to dNV-VHSV. The results will help tailoring future vaccines against viral haemorrhagic septicaemia virus and other novirhabdoviruses.
1.1. Viral Haemorrhagic Septicaemia Viruses (VHSV)
Wild type VHSV-23.75 (wt-VHSV) isolated from brown trout [23] (GenBank accession number FN665788) and its derivative NV gene-deleted (dNV-VHSV), obtained as previously described [13], were used to infect rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) by intraperitoneal injection. Both wt- and dNV-VHSV viruses were kindly provided by Dr. Michel Brémont (INRA, France), and further propagated in EPC cells at 14 °C and titrated by the plaque-forming assay (pfu) as previously described [14].
1.2. Virus Dosages and Injection of Fingerling Rainbow Trout
Fingerling rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) of 6–12 g (approximately 10 cm in length), free of IPNV (Infectious Pancreatic Necrosis Virus) and VHSV antibodies, were obtained from a local fish farm (Los Molinos, Madrid). They were maintained at 14 °C in a 200 L aquarium with tap-dechlorinated carbon-filtered water provided with biological filters and fed with a commercial fish diet. After two weeks of acclimation, fish were separated into seven groups of six trout per group. Due to the non-virion (NV) expression by wt-VHSV, a different replication rate of wt-VHSV and dNV-VHSV in the EPC cell line was established [13], and since the maximum NV expression by wt-VHSV is reached at 48 hpi (hours post-infection), we aimed at establishing the equivalent infectious dosage yielding comparable transcriptomic profile for each virus at 48 hpi. For that, we injected trout intraperitoneally with 100 µL of wt-VHSV (104, 105 or 35 × 106 pfu), dNV-VHSV (104, 105 or 35 × 106 pfu) or phosphate-buffered saline (PBS). Each group of injected trout was then released into a 50-L aquarium and maintained at 14 °C. Two days after injection, trout were sacrificed, head kidney and spleen (whole organs) were pooled, and immediately immersed in RNAlater (Ambion, Austin, USA) at 4 °C overnight, before being frozen at −70 °C until further analysis.
1.3. RNA Extraction and cDNA Synthesis
The pooled head kidney and spleen (whole organs) from each individual trout were homogenized using the Tissue Lyser Cell Disruptor (Qiagen Iberia, S.L., Madrid, Spain) for 10 min at 50 Hz with 3 mm glass beads in an RTL buffer (Qiagen Iberia, S.L., Madrid, Spain). RNA was then extracted from the homogenates by using the RNAeasyPlus kit (Qiagen Iberia, S.L., Madrid, Spain) and eluted in RNase-free water. RNA concentrations were estimated by Nanodrop and the presence of 18S and 28S rRNA bands was confirmed by denaturing RNA agarose electrophoresis (Sigma-Aldrich Quimica SA, Madrid, Spain). For qPCR experiments of the nucleoprotein (N) and non-virion (NV) genes, cDNA synthesis was carried out from RNA (1 µg) by using oligo-dT and PrimeScriptTM reverse transcriptase (RR037A TAKARA, Japan) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. For microarray experiments, additional RNA quality controls (RNA integrity number, RIN) were performed by NIMGenetics (Madrid, Spain). For each experimental six-trout group, the four trout with best RNA quality (RIN > 7.0) were chosen for microarray hybridisation. cDNA was synthesized by using SuperScript III reverse transcriptase (Invitrogen) and oligo(dT) primer, labelled with Cy3 (GE Healthcare, Spain), and purified with Microcon YM30 (Merck Millipore, Spain).
1.4. Design of Oligo-Microarrays Enriched in Rainbow Trout Immune-Related Genes (Targeted Microarrays)
Oligo-microarrays were enriched in rainbow trout immune-related genes as previously described (immune-targeted microarrays) [6,24,25]. The final 8 × 15K microarray corresponds to Agilent’s ID032303 (Gene Expression Omnibus GEO platform submission number GPL14155) and contains 1474 annotated immune-related probes (60-mer) per duplicate. In order to simplify the analysis of results, annotated probes were classified according to the following gene groups: VIG, VHSV-induced genes (number of probes, n = 22); IFN, interferons and their receptors (n = 20); MX, interferon-inducible proteins mx (n = 3); CO, complement components (n = 6); IL, interleukins and their receptors (n = 19); APM, antigen-presenting machinery genes (n = 4); TNFSF, tumour necrosis factor superfamily (n = 16); CD, cluster differentiation antigens (n = 15); CK, chemokines and their receptors (n = 32); CASP, caspases (n = 3); and TF, transcription factors (n = 10). The trout microarray used for these experiments was previously validated by real-time quantitative PCR (RTqPCR) [24,25]. The number of biological replicas was four. Four chips of eight samples per chip were used and hybridised simultaneously. This home-made rainbow trout oligo-microarray contains more immune-related genes than any other trout microarray available, since it includes all the immune-related genes from the Agilent’s EST-derived rainbow trout oligo-microarray (ID16271) [6,24,25,26].
1.5. Hybridisation and Gene Expression Changes of Trout Transcripts to the Immune-Targeted Microarrays
The labelling of 2 µg of RNA (approximately 50 µg/mL) and hybridisation to the microarrays were performed by NIMGenetics (Madrid, Spain) complying with the Minimum Information about a Microarray Experiment (MIAME) standards [24].
Normalisations were performed by correcting the individual fluorescence in each microarray with the sum of all the fluorescent values according to the formula: fluorescence of each probe/sum of all the probe fluorescence signals per microarray. Raw and normalised data were deposited in GEO [27,28]. After normalisation, outlier values (defined by those fluorescence values above or below mean ± standard deviation per probe) were identified and eliminated from the calculations programmed in Origin Pro 8.6 (OriginLab Corporation, Northampton, MA, USA). Fold-change (FC) for each probe was calculated by the following formula: values of wt-VHSV or dNV-VHSV injected trout/mean of PBS injected trout (n = 4). Means and standard deviations of individual folds were calculated for each oligonucleotide probe by the following formula: fluorescent value/mean fluorescent value of the control (n = 4). Venn diagrams reflect the percentage of genes which FC value was upregulated, downregulated, and non-regulated for each comparison with these arbitrary criteria previously used [6]: (1) upregulated: FC ≥ 1.5; (2) downregulated: FC ≤ −1.5; and (3) non-regulated (basal) gene expression: −1.5 < FC < 1.5. On the other hand, the heatmap figures reflect the FC for each gene comparison using an arbitrary criteria previously described [6]: (1) non-regulated (basal) gene expression: −1.5 < FC < 1.5 (black); (2) upregulated: 1.5 ≤ FC < 2 (light red box), 2 ≤ FC < 5 (red box), 5 ≤ FC (dark red box); and (3) downregulated: –1.5 ≥ FC > −2 (light green box), −2 ≥ FC > –5 (green box), −5 ≥ FC (dark green box). Differentially expressed gene transcripts were considered significant when FC ≥ 1.5 or FC ≤ −1.5. Negative folds were calculated for those values below 0.66 applying the formula −1/FC. Therefore, FC = 0.66 corresponds to a –1.5 value; FC = 0.5 (more downregulated) corresponds to a −2 value; and FC = 0.2 (even more downregulated) corresponds to a –5 value.
1.6. Quantitative Estimation of Transcripts by Real-Time Quantitative PCR (RTqPCR)
To estimate the wt- or dNV-VHSV replication in rainbow trout head kidney and spleen, both N and NV transcript levels were estimated by RTqPCR amplification after intraperitoneal injection of the corresponding VHSV, as described in Section 1.2. RNA extraction and cDNA synthesis were carried out as described above. RTqPCR was carried out by mixing 100 ng of cDNA, 0.9 μM of forward primer, 0.9 μM of reverse primer, and Power SYBR Green PCR Master Mix (Life Technologies, Madrid, Spain). The thermal profile was 10 min at 95 °C, followed by 40 cycles of 95 °C for 15 s, and 60 °C for 1 min. For each experiment, the expression level of the analysed genes was calculated using the 2-ΔΔCt relative quantitation method. The Ct for each viral gene was normalised to β-actin gene (∆Ctgene = Ctgene − Ctβ-actin), which was used as an internal control due to its low coefficient of variation (CV) among different virus dosages (CV ≤ 3% for 104 pfu/trout and 105 pfu/trout of wt- and dNV-VHSV; trout injected with 35 × 106 pfu of both viruses showed a CV close to 8%). Means and standard deviations were calculated for each experimental infection by intraperitoneal (ip) injection of either the wt- or dNV-VHSV in trout groups (n = 6) with 104, 105, or 35 × 106 pfu/trout. Primer sequences used were: β-actin (accession number AF550583.1) forward 5′CATCACCATCGGCAACGA and reverse 5′GATGTCCACGTCACACTTCAT; nucleoprotein (accession number AJ233396) forward 5′TCTCCGCTCGTCCTCCGTGAG and reverse 5′GTGAGCCCAGAGCCTCTTGTC; and non-virion (NV, accession number AJ233396) forward 5′TCAAGGTGACACAGGCAGTCA and reverse 5′CCAGTTCTCTCATGGGCATCAT. Calculated RTqPCR efficiency was 59% for β-actin, 45% for N, and 43% for NV genes. Efficiency was considered to correct the transcript levels obtained by RTqPCR assays.
1.7. Calculations used for Gene Set Enrichment Analysis (GSEA)
In order to explore the possible biological effects of simultaneous and small changes in several related genes, we screened the transcriptional data with the previously described 51 rainbow trout from the immune-related gene-set (GS) collection [25]. The trout GS collection was manually designed from the KEGG (K) and WIKI (W) trout orthologous human pathways (as accessed in 2013), using the trout genes contained in our home-designed microarray. The trout GS collection was then used for analysis by the Gene-Set Enrichment Analysis (GSEA) program [29,30,31]. Transcriptional data from the dNV-VHSV and wt-VHSV injected trout were analysed by GSEA to assign a normalised enrichment score (NES) for each GS of the collection in each of the three cases [25].
1.8. Ethics Statement
All the animal procedures used in this study were approved by the INIA (National Agricultural and Food Research and Technology Institute) ethical and biosecurity committee (authorization CEEA 2011/022) and performed following the National and European Commission guidelines and regulations on laboratory animals’ care. Periodic examinations were performed several times a day during infections so as to euthanize fish with abnormal behaviour. To minimize animal suffering, fingerling rainbow trout were sacrificed by using a lethal dose of tricaine methanesulfonate (MS-222, 50 mg/mL, Sigma, Madrid, Spain).
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. dNV- and wt-VHSV Dosages used for Microarray Analysis
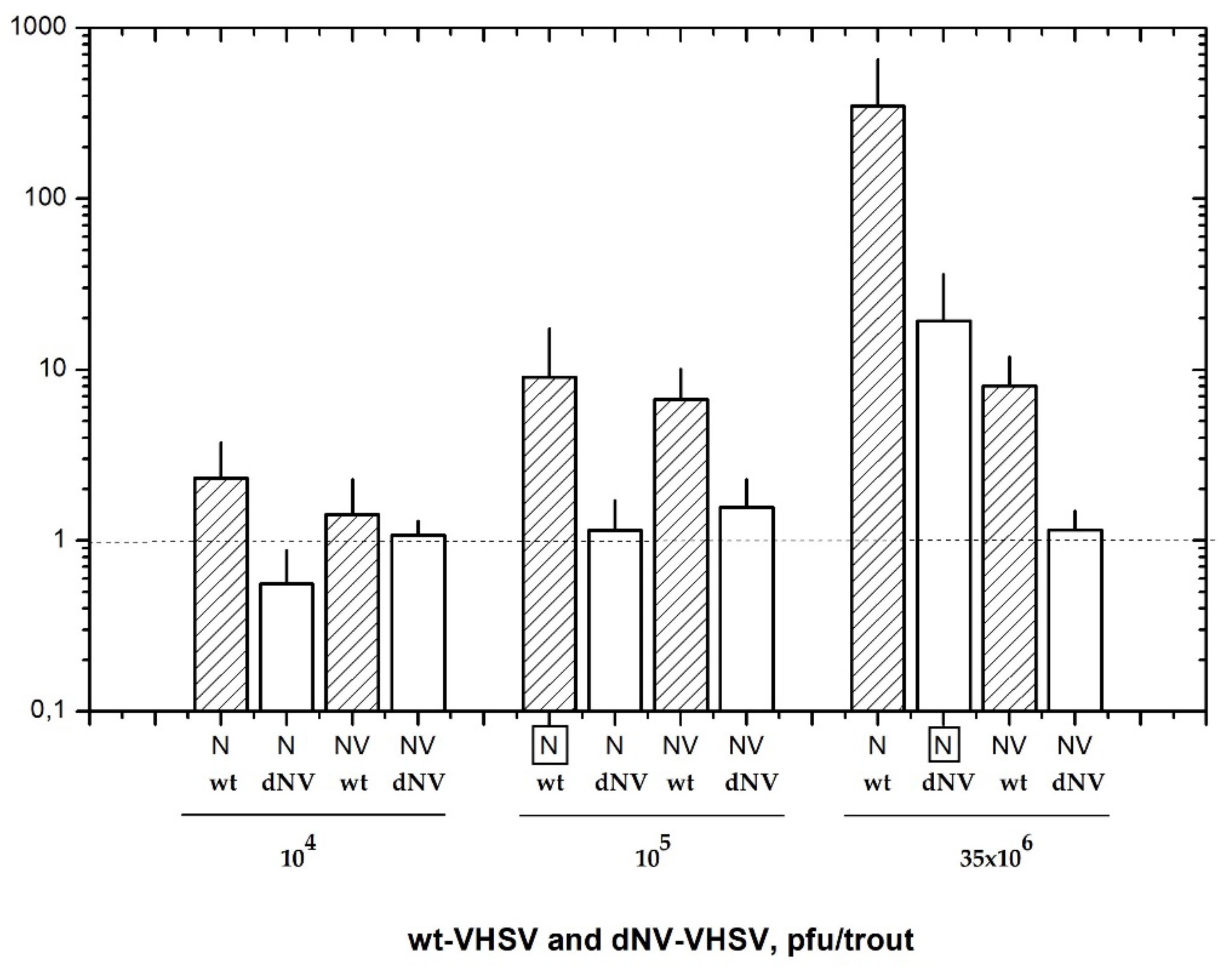
In this work, we have firstly defined the appropriate infectious dosage for wt-VHSV and dNV-VHSV in order to establish the comparative transcriptomic profiling between them. At 48 h post-infection, the RNA transcripts from head kidney and spleen were analysed by RTqPCR to estimate the corresponding viral replication loads based on N transcript levels (Figure 1). The trout injected with 104 pfu, 105 pfu, and 35 × 106 pfu of the wt-VHSV yielded the following N (±SD) values: 2.3 ± 1.1, 9.0 ± 4.1, and 348.8 ± 125, respectively (Figure 1). On the other hand, trout injected with 104 pfu, 105 pfu and 35 × 106 pfu of the dNV-VHSV yielded the following N (±SD) values: 0.6 ± 0.2, 1.1 ± 0.4, and 19.3 ± 7.6, respectively (Figure 1). Wild-type-VHSV/dNV-VHSV ratio for N transcripts yielded an approximately 18-fold higher replication rate for the wt-VHSV when both viruses were applied at a dose of 35 × 106 pfu/trout dose. However, this proportion was close to 1 when with the dose used was 105 pfu for wt-VHSV and 35 × 106 pfu for dNV-VHSV. For this reason, we considered it best to use the latter for the microarray study. Therefore, we compared the transcriptomic profile of trout injected with 105 pfu of wt-VHSV (NV presence) (data deposited on GEO GSE37330) and trout injected with a 350-fold more infectious dose (35 × 106 pfu) of dNV-VHSV (NV absence) (data deposited at GEO GSE43285).
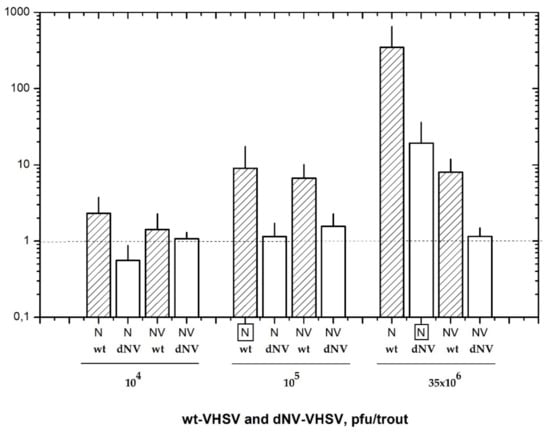
Figure 1.
Nucleoprotein (N) and non-virion (NV) gene expression values (mean ± SD) obtained by RTqPCR of six trout injected with wild-type (wt)-VHSV (hatched bars) and NV gene-deleted (dNV)-VHSV (white bars). Animals were injected with three different dosages (104, 105, and 35 × 106 pfu/trout) of each virus and analysed 48 hpi. The results showed similar nucleoprotein (boxed N) transcript levels of wt-VHSV (105 pfu/trout) and dNV-VHSV (35 × 106 pfu/trout), indicating their similar replication levels. Horizontal dotted line corresponds to negative control. VHSV: viral haemorrhagic septicaemia virus.
2.2. Overview of the Expression Profiles Obtained
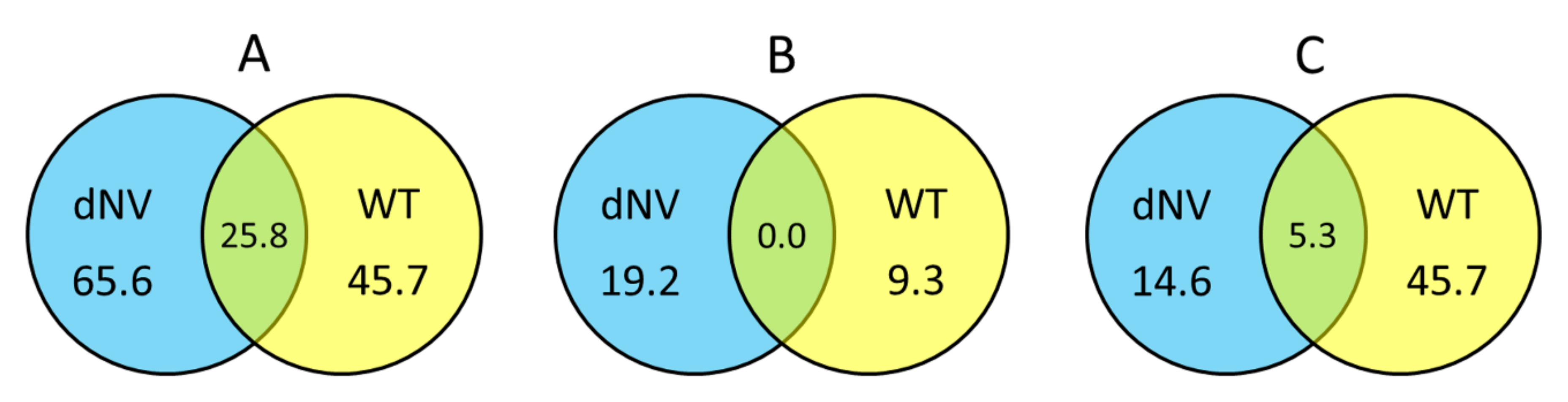
Normalised FC values of microarray datasets from wt-VHSV (105 pfu/trout) and dNV-VHSV (35x106 pfu/trout) were classified based on the groups defined for this study (see Section 1.5) and calculated the percentage of upregulated, downregulated and non-regulated genes. Figure 2A shows the upregulated genes between groups (wt-VHSV and dNV-VHSV) with fold changes (FC) ≥ 1.5 in Venn diagrams. The trout injected with dNV-VHSV showed the highest number of upregulated genes (65.6%), followed by those injected with wt-VHSV (45.7%). Probably, the upregulation increase in the dNV-VHSV injected trout was due to the absence of NV. In addition, dNV-VHSV and wt-VHSV shared 25.8% of the upregulated genes, which should be due to other viral proteins rather than NV.
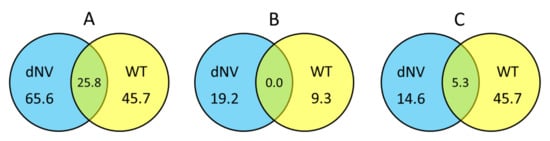
Figure 2.
Venn diagrams showing the general transcriptomic relationships between trout injected with dNV-VHSV and wt-VHSV. Numbers indicate the percentage of upregulated (fold change, FC ≥ 1.5, (A), downregulated (FC ≤ −1.5, (B), and non-regulated (−1.5 < FC < 1.5, (C) genes, 48 h after injection with dNV-VHSV and wt-VHSV.
Figure 2B displays Venn diagrams with downregulated genes (FC ≤ −1.5), which indicate that fish infected with dNV-VHSV downregulated more genes than fish infected with wt-VHSV (19.2% vs 9.3%, respectively). On the other hand, dNV-VHSV and wt-VHSV do not have any downregulated genes in common.
When the non-regulated gene transcript levels with folds −1.5 < FC < 1.5 (Figure 2C) were analysed by Venn diagrams, the trout infected with wt-VHSV had the highest number of non-regulated genes (45.7%), followed by dNV-VHSV (14.6%). The Venn diagram also showed that 5.3% of non-regulated genes were shared by wt-VHSV and dNV-VHSV.
2.3. dNV- and wt-VHSV Infection Effects on Trout Immune-Related Genes
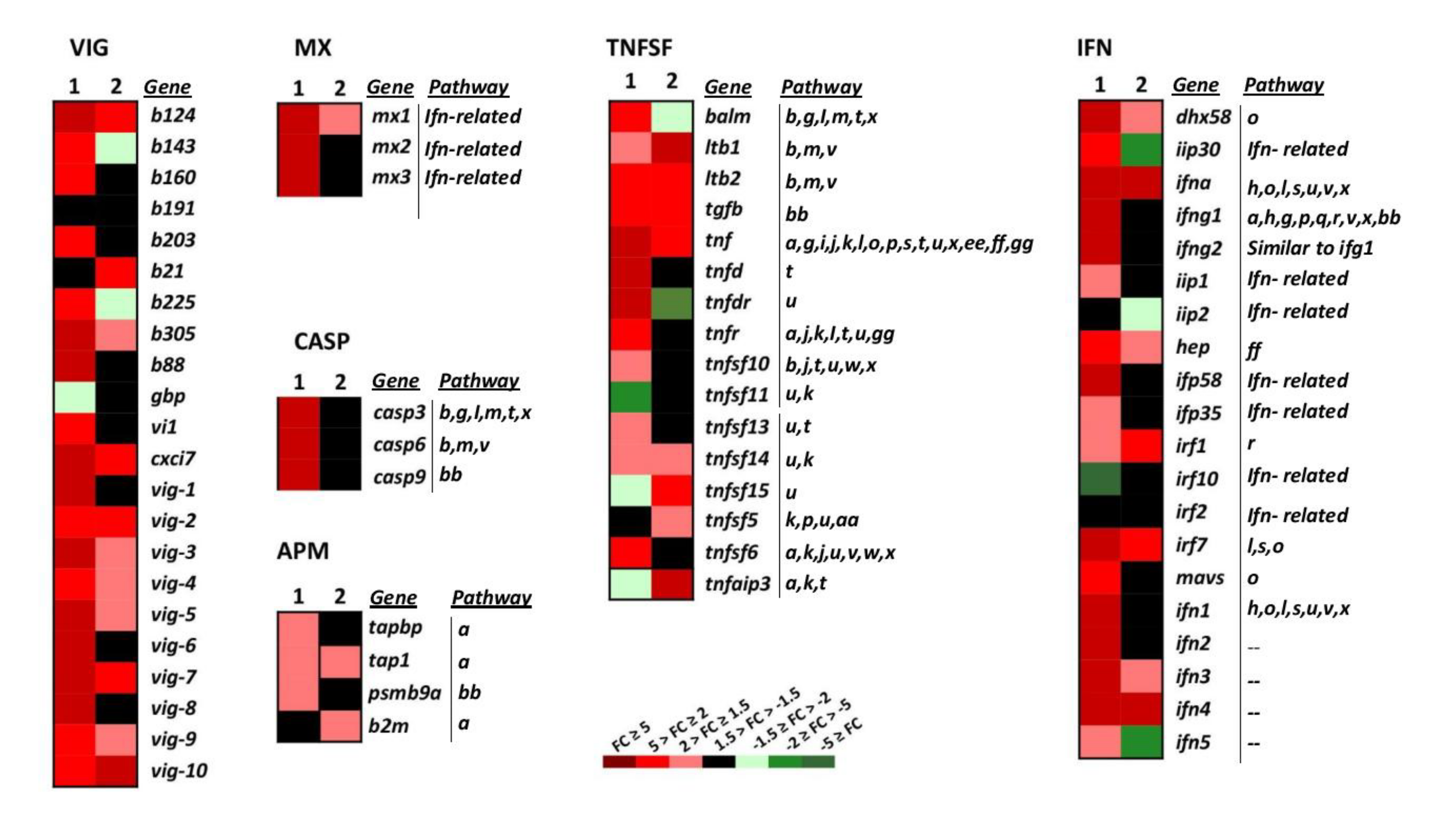
A detailed study of the transcriptomic changes driven by wt-VHSV and dNV-VHSV at 48 hpi was conducted. A heatmap was generated with the FC of the genes grouped in the categories described in methods. In addition, individual genes were also correlated with the pathways (KEGG database) [32] in which they participate (Table 1).

2.3.1. Cytosolic Sensors
Upon infection, viruses are recognised by host receptors and cytosolic sensors that activate mechanisms (signalling molecules) involved in diverse cellular processes such as the antiviral immune response. The cytosolic sensors studied belong to different gene groups and signalling pathways (Figure 3 and Figure 4, and Table 1, RIG-I-like, and NOD-like signalling). Among the genes involved in these pathways, tnf, ifna, irf7, and dhx58 and mavs (Figure 3, IFN and TNFSF) were upregulated by wt-VHSV and slightly more by dNV-VHSV. Mavs, another important cytosolic sensor, was upregulated by dNV-VHSV but non-regulated by wt-VHSV. This fact could be due to the NV expression by wt-VHSV and might indicate that mavs would be more functional for starting an appropriate immune response against dNV-VSHV as vaccine virus. Other important signalling molecules are traf2 and traf3 (Figure 3, TNFSF), and they are also upregulated by dNV-VHSV and non-regulated by wt-VHSV. These findings also support that dNV-VHSV activates better than wt-VHSV at these stages.
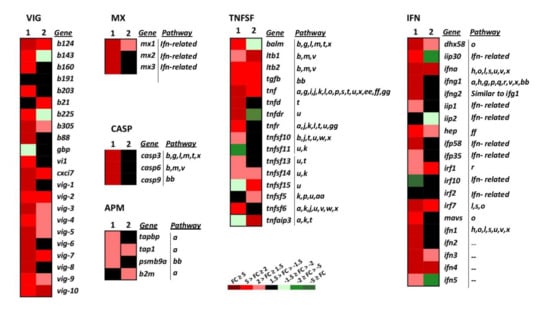
Figure 3.
Heatmap showing the transcriptional expression fold changes (FCs) of the selected gene groups VHSV-induced (VIG), myxovirus resistance proteins (MX), caspases (CASP), tumour necrosis factor superfamily (TNFSF), interferon (IFN), and antigen-presenting machinery (APM) induced by dNV-VHSV and wt-VHSV in infected trout. Gene denotes names, and the Pathway column correlates with Table 1. --, unassigned pathway. Column 1, dNV-VHSV, each box corresponds to the average FC from four trout. Column 2, wt-VHSV, each box corresponds to the average FC from four trout. VIG group: b191 (c-lectin, AF483535), vig-1 (AF076620), vig-2 (AF290477), vig-3 (AF483529), vig-4 (AF483530), vig-5 (clone B17), vig-6 (clone B126), vig-7 (AF483527), vig-8 (clone B68), vig-9 (AF483533), vig-10 (AF483534), b203 (AF483538), b143 (AF483539), b225 (AF483540), b88 (AF483541), b160 (AF483545), b124 (AF483546), b305 (AF483542), cxci7 (VHSV induced protein 7 (vig7)), vi1 (VHSV induced protein 1), gbp (guanylate-binding protein GTPase, b21 (CD9, AF483544)). MX group: mx1 (myxovirus resistance 1), mx2 (myxovirus resistance 2), mx3 (myxovirus resistance 3). CASP group: casp3 (caspase 3), casp6 (caspase 6), casp9 (caspase 9). TNFSF group: balm (BAFF and APRIL-like molecule), ltb1 (lymphotoxin beta 1), ltb2 (lymphotoxin beta 2), tgfb (tumour growth factor beta), tnf (tumour necrosis factor alpha), tnfd (tumour necrosis factor decoy), tnfdr (tumour necrosis factor decoy receptor), tnfr (tumour necrosis factor receptor), tnfsf10 (tumour necrosis factor superfamily 10), tnfsf11 (tumour necrosis factor superfamily 11), tnfsf13 (tumour necrosis factor superfamily 13), tnfsf14 (tumour necrosis factor superfamily 14), tnfsf15 (tumour necrosis factor superfamily 15), tnfsf5 (tumour necrosis factor superfamily 5 (CD40)), tnfsf6 (tumour necrosis factor superfamily 6), tnfaip3 (tumour necrosis factor alpha-induced protein 3). IFN group: dhx58 (RIG-I-like receptor LGP2), iip30 (interferon gamma inducible protein 30), ifna (interferon alpha), ifng1 (interferon gamma 1), ifng2 (interferon gamma 2), iip1 (interferon inducible protein 1), iip2 (interferon inducible protein 2), hep (hepcidin), ifp58 (interferon-induced protein 58), ifp35 (interferon-induced protein 35), irf1 (interferon regulatory factor 1), irf10 (interferon regulatory factor 10), irf2 (interferon regulatory factor 2), irf7 (interferon regulatory factor 7), mavs (mitochondrial antiviral signalling protein), ifn1 (type 1 interferon 1), ifn2 (type 1 interferon 2), ifn3 (type 1 interferon 3), ifn4 (type 1 interferon 4), ifn5 (type 1 interferon 5). APM group: tapbp (tapasin (TAP binding protein)), tap1 (transporter associated with antigen processing 1), psmb9a (proteasome subunit type 9), b2m (beta-2 microglobulin).
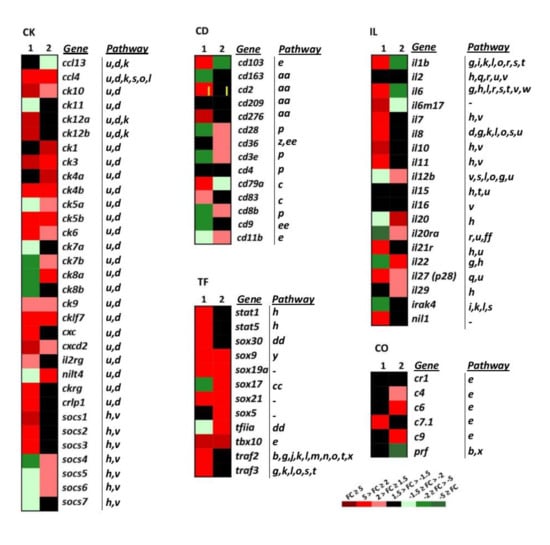
Figure 4.
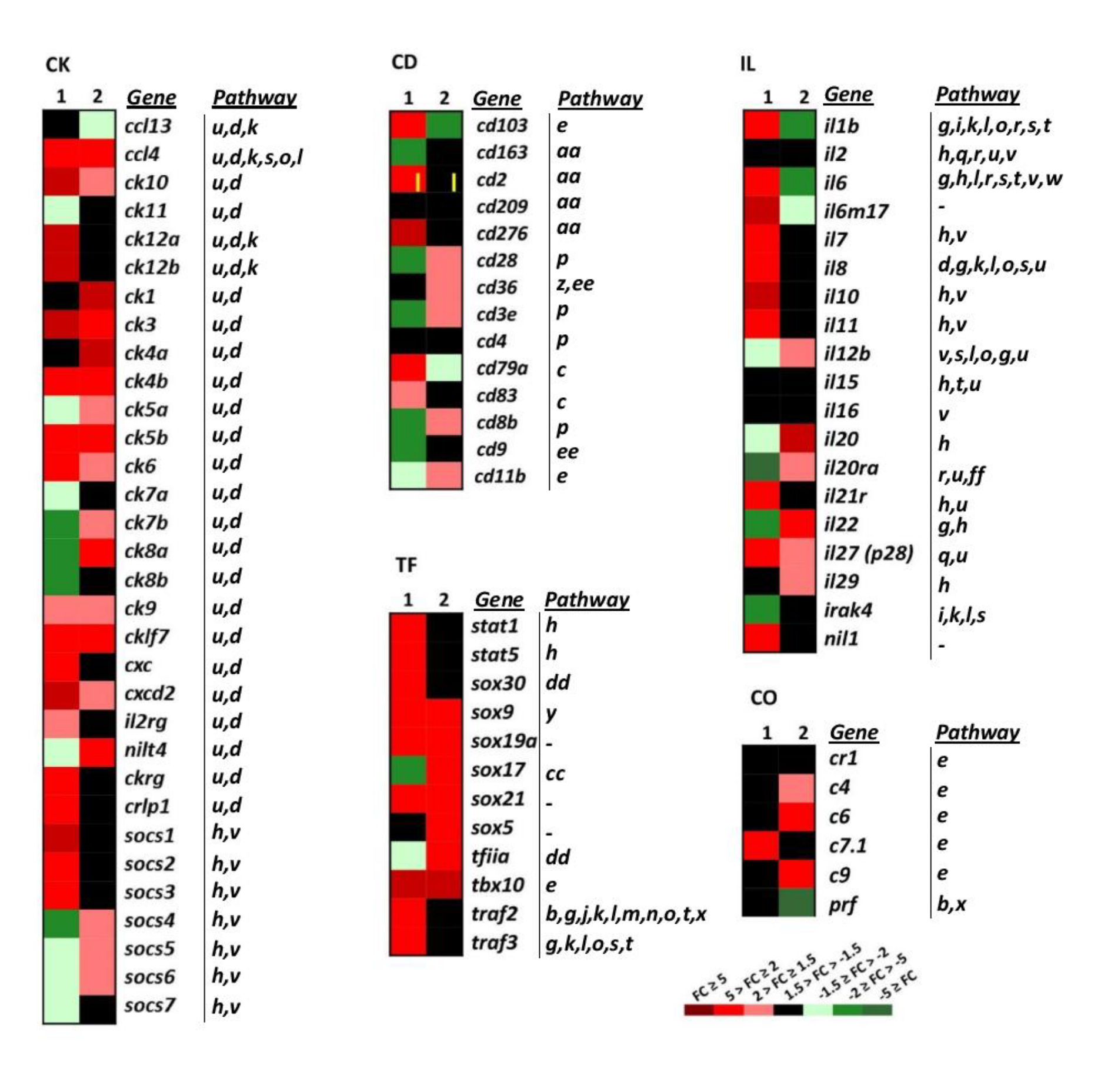
Heatmap showing the transcriptional expression fold changes (FCs) of the selected gene groups cytokines (CK), interleukins (IL), cluster of differentiation antigens (CD), complement (CO) and transcription factor (TF), induced by dNV-VHSV and wt-VHSV. Gene denotes names, and the Pathway column correlates with Table 1. --, unassigned pathway. Column 1, dNV-VHSV, each box corresponds to the average FC from four trout. Column2, wt-VHSV, each box corresponds to the average FC from four trout. CK group: ccl13 (cc-chemokine 13), ccl4 (cc-chemokine 4), ck10 (cc-chemokine 10), ck11 (cc-chemokine 11), ck12a (cc-chemokine 12a), ck12b (cc-chemokine 12b), ck1 (cc-chemokine 1), ck3 (cc-chemokine 3), ck4a (cc-chemokine 4a), ck4b (cc-chemokine 4b), ck5a (cc-chemokine 5a), ck5b (cc-chemokine 5b), ck6 (cc-chemokine 6), ck7a (cc-chemokine 7a), ck7b (cc-chemokine 7b), ck8a (cc-chemokine 8a), ck8b (cc-chemokine 8b), ck9 (cc-chemokine 9), cklf7 (chemokine-like factor superfamily member 7), cxc (α-chemokines), cxcd2 (cxc d2 chemokine), il2rg (il2 receptor gamma), nilt4 (novel immunoglobulin-like transcript 4 (FM200774.1)), ckrg (cytokine receptor gamma), crlp1 (chemokine receptor-like protein 1 (AJ620468.1)), socs1 (suppressor of cytokine signalling 1), socs2 (suppressor of cytokine signalling 2), socs3 (suppressor of cytokine signalling 3), socs4 (suppressor of cytokine signalling 4), socs5 (suppressor of cytokine signalling 5), socs6 (suppressor of cytokine signalling 6), socs7 (suppressor of cytokine signalling 7). IL group (r means receptor): il1b, il2, il6, il6m17, il7, il8, il10, il12b, il15, il16, il20, il20ra, il21r, il22, il27 (p28 subunit), il29, Irak4 (interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase 4), nil1 (novel il-1 cytokine family member). CD group: cd103, cd163, cd2, cd209, cd276, cd28, cd36, cd3e (epsilon), cd4, d79a, cd83, cd8b (beta), cd9. CO group: cr1 (complement receptor type 1), c4 (complement component 4), c6 (complement component 6), c7.1 (complement component 7-1), c9 (complement component 9), prf (perforin). TF group: stat1 (signal transducer and activator of transcription 1), stat5 (signal transducer and activator of transcription 5), sox30 (SRY-related HMG box 30 gene family), sox9 (SRY-related HMG box 9 gene family), sox19a (SRY-related HMG box 19a gene family), sox17 (SRY-related HMG box 17 gene family), sox21 (SRY-related HMG box 21 gene family), sox5 (SRY-related HMG box 5 gene family), tfiia (transcription factor IIA), tbx10 (T-box 10 gene).
2.3.2. IFN System
We studied different genes belonging to the IFN system and IFN-related group of genes that belong to different signalling pathways (Figure 3, IFN pathways, n = 14). Regarding the IFN group of genes (IFN, n = 20), wt-VHSV induced the upregulation of the lowest number of genes (35%) compared to dNV-VHSV (85%) (Figure 3, IFN). This fact might be due to an inhibitory effect driven by NV after its expression from wt-VHSV. Among the downregulated and non-regulated (basal) genes, we found iip30, ifng1, ifng2, iip1, iip2, ifp58, ifp35, mavs, ifn1, ifn2, and ifn5 (Figure 3, IFN). On the other hand, the expressions of dhx58, hep, ifn3, ifna, irf1, irf7, and ifn4 were upregulated by wt-VHSV. Thus, some of them (i.e., dhx58, hep, irf7, ifn3) were even more upregulated by dNV-VHSV, probably due to the lack of the NV protein. The NV protein expressed by wt-VHSV induced the non-regulation of mx2 and mx3, whereas mx1 was slightly upregulated. The results also showed that all mx genes were upregulated by dNV-VHSV (Figure 3, MX). Mx proteins are implicated in the antiviral interferon-mediated response. In summary, in contrast to wt-VHSV, dNV-VHSV improved the antiviral immune response based on interferons (and related molecules), which would support its use as a potential live vaccine.
2.3.3. TNF Superfamily and Caspases
This gene group is comprised of molecules with diverse functionality that participate in several signalling pathways (n = 20, Figure 3 TNFSF, and Table 1). Most of the 16 TNF superfamily genes (tnfsf) studied here were upregulated (75%) by dNV-VHSV, whereas wt-VHSV induced a lower upregulation (50%) of these genes (Figure 3, TNFSF). The tnfsf genes upregulated by dNV-VHSV but downregulated or non-regulated by wt-VHSV were balm, tnfd (decoy), tnfdr (decoy receptor), tnfr, tnfsf10, tnfsf13, tnfsf14, and tnfsf6 (Figure 3, TNFSF), which participate in several multipaths (Figure 3, TNFSF, Table 1). The balm gene is closely related to tnfsf13b (BAFF) and tnfsf13 (APRIL) genes, and seems to be unique to teleost [33]. The balm gene has a constitutive expression in adult trout, mainly in the spleen, lymphocytes, posterior kidney, and anterior kidney and, therefore, balm has been assigned an immunological role [33]. The tnfsf6 (FAS ligand, FASL) and tnfsf13 (APRIL) genes modulate ligand-induced apoptosis [34]. In addition, tnfsf10 (or TRAIL) is an inductor of apoptosis acting through casp3 and casp8. Among the upregulated genes induced by wt- and dNV-VHSV injection were tnfsf14 (stimulator of apoptosis), tnf (most important inducer of systemic inflammation), and ltb1/ltb2 (involved in proliferation, differentiation, survival, and growth). Another member of TNFSF gene group is tnfaip3 (A20 protein), which is upregulated in trout infected with wt-VHSV and downregulated in those infected with dNV-VHSV. Previous studies showed that A20 inhibited NF-kappa B and apoptosis [35,36] and our results support that dNV-VHSV would promote NF-kappa B signalling in order to set up a successful immune response.
TNFs have a role as ‘double-edged swords’ in cellular proliferation, survival, differentiation or apoptosis. Ligands such as APRIL (tnfsf13 gene), LIGHT (tnfsf14 gene), RANKL (tnfsf11 gene), LT-β (ltb1, ltb2 genes), and CD40L (tnfsf5 gene) bind to receptors with a TRAF-interacting motifs (TIM) domain, leading to the recruitment of TRAF molecules, and the activation of multiple signal transduction pathways such as NF-kappa B, Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK), p38, extracellular signal regulated kinase (ERK), and phosphoinositide-3 kinase (PI3K). On the other hand, ligands such as TNF-α (tnf gene), TRAIL (tnfsf10 gene), FASL (tnfsf6 gene), and decoy receptor have a dead domain (DD), which ultimately activates apoptosis through caspases. In summary, most of the tnfsf genes were upregulated by dNV-VHSV, giving rise to both activation signalling (NF-Kappa B, JNK, etc) and apoptosis signalling pathways.
Regarding the caspase group (Figure 3, CASP, and Table 1), the effector (casp3, casp6) and initiator (casp9) caspase genes were highly upregulated in the dNV-VHSV infected group while maintained at normal transcription levels in the wt-VHSV infected group. These results suggest that NV expressed by wt-VHSV impairs the upregulation and, consequently, the activation of apoptosis at 48 h post-infection (Figure 3, CASP). Moreover, the upregulation of the casp genes by dNV-VHSV promotes the activation of different pathways in which they participate, supporting an appropriate immune response developed by dNV-VHSV.
2.3.4. Antigen Presentation
Among the antigen presenting machinery (APM, n = 4) genes studied, TAPASIN (tapbp) and proteasome subunit (psmb9a) were non-regulated genes, whereas tap1 and b2m were upregulated in wt-VHSV (Figure 3, APM). The APM genes belong to innate and adaptive immune responses. They act within the proteasome for peptide generation (psmb9a) and the transport of peptides (tapbp, tap1) into the endoplasmic reticulum. MHC (Major histocompatibility complex) class I molecules (together with b2m) bind these antigenic peptides to present them to CD8+ T-lymphocytes. Other genes belonging to TNFSF and IFN groups are also implicated in the antigen presentation signalling pathway (Figure 3). Overall, the results indicated that dNV-VHSV favoured the antigen processing and presentation in relation to wt-VHSV.
2.3.5. Cluster of Differentiation: B-Cell, T-Cell, and Cell-to-Cell Interactions
Cluster of differentiation genes (CD) conform a functional heterogeneous group of genes that have been involved in cell adhesion, B-cell receptor signalling, T-cell receptor signalling, complement and coagulation cascades, and hematopoietic markers (Figure 4 CD, and Table 1). In this study, 14 CD genes have been analysed. Downregulated and non-regulated CD genes (CD, n = 5 genes, Figure 4 CD) were found in the wt-VHSV dataset. The downregulated genes by wt-VHSV were cd103 (a marker of dendritic cells) [37] and cd79a (associated with membrane-bound immunoglobulin in B-cells). On the other hand, the non-regulated genes in wt-VHSV were cd2 (implicated in the adhesion T cell-APC through the CD58 protein), cd276 (participating in the regulation of the T-cell-mediated immune response), cd83 (involved in the regulation of antigen presentation) [38], and cd163 (exclusively expressed in monocytes and macrophages in humans), which was downregulated by dNV-VHSV. Some of the CD markers were found upregulated by dNV-VHSV (cd103, cd2, cd276, cd279, cd83) and others upregulated by wt-VHSV (cd28, cd36, cd3e, cd83, cd11). This fact might indicate that 48 hpi is a too short time to observe adaptive cellular responses against VHSV.
2.3.6. Cytokines: Chemokines and Interleukins
Among the chemoattractant cytokines or chemokines genes (CK, n = 32), 53% were upregulated by wt-VHSV, whereas dNV-VHSV induced the upregulation by 50%. The chemokines showing downregulated or non-regulated fold changes by wt-VHSV were ccl13, ck11, ck12a, ck12b, ck8b, cxc, ckrg, crlp1, suppressor of cytokine 1 (socs1), socs2, socs3, and socs7 (Figure 4, CK). In addition, dNV-VHSV induced the downregulation or non-regulation of the chemokines ccl13 (basal), ck1, ck4a, ck5a, ck7a, ck7b, ck8a, ck11, nilt4, socs4, and socs5. Chemokines have different roles in the coordination of the immune response and may promote the activation or inhibition of different pathways (Figure 4 IL, Table 1), and for the most of them their function is unknown on the basis of viral infections.
Previous studies in rainbow trout have shown that recombinant CK1 has an attractant effect for blood leukocytes) [39]. In addition, CK6 is a chemoattractant for mature macrophages from the RTS11 rainbow trout monocyte-macrophage cell line and may also induce interleukin 8 (IL-8), inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS), and the CD-18 integrin in these cells, revealing additional immunomodulatory effects [40]. The capacity of trout recombinant CK12 to attract splenocytes has also been reported, establishing that IgM + B cells were one of the target cells recruited [41]. In the present study, CK1, CK6 and CK12 are upregulated by dNV-VHSV in relation to wt-VHSV. Regarding the interleukin genes group (IL, n = 20), the transcriptomic profile obtained after wt-VHSV injection was different from that of dNV-VHSV. Wild-type VHSV downregulated important pleiotropic pro- and anti-inflammatory interleukins such as il1b, il6, and its related il6m17 (Figure 4, IL). On the contrary, interleukins il1, il6, il6m7, il7, il8, il11, il21r, il27 and nil1 were upregulated by dNV-VHSV. These interleukins have a key role in immune pathways (Figure 4 IL, Table 1) and their upregulation are required for an effective immune response followed vaccination, suggesting that dNV-VHSV could be an effective attenuated live vaccine.
2.3.7. General Transcription Factors
This group of genes (TF, n = 10 selected genes, Figure 4) are implicated in important cellular processes and pathways: Jak–Stat signalling (stat1, stat5), general transcription factors and regulatory elements (sox genes), and multipath genes previously mentioned (traf2, traf3). In the dNV-VHSV-injected trout, all the TF selected genes were upregulated except for sox5 (non-regulated) and tfiia (downregulated). In wt-VHSV, all the genes studied were upregulated except for traf2, traf3, sox30, stat5 and stat1, which were non-upregulated. These data reflected that Jak–Stat signalling pathway is upregulated by dNV-VHSV, which in turn promoted interferon responses leading to an improved antiviral stage.
2.3.8. Complement and VIG Genes
Among complement genes studied (CO, n = 6, Figure 4), the trout injected with dNV-VHSV maintained most of the genes non-regulated and only one was upregulated. It is interesting to note that C9 was upregulated by wt-VHSV, whereas perforin (prf) was downregulated by the same virus.
VHSV-induced genes (VIG, n = 22) were firstly identified by subtractive hybridisation performed in a previous work [42]. We found that NV from wt-VHSV inhibited the upregulation of 50% of all vig genes (b143, b160, b191, b203, b225, b88, gbp, vi1, vig-1, vig-6, vig-8) while these genes were upregulated in dNV-VHSV, except for b191 and gbp (Figure 3, VIG). Viperin (vig1) is expressed by mitochondria and is an IFN-inducible protein that inhibits the replication of a variety of viruses [43]. In addition, vig-2 [44], vig-3, vig-4, vig5, and probably vig-6 are also induced by interferon [42]. On the other hand, vig-7, vig-8, vig-9 have chemoattractant function, vig-9 also has an apoptotic function, and vig-10 is related to apoptosis and transcription repression [42].
The present study is the first one describing the trout transcriptomic profile driven by dNV-VHSV. There are scarce studies regarding whole gene effects upon VHSV infection in trout, the most relevant to our study is the characterization of the RNA microarray profile in olive flounder liver after VHSV infection by immersion [20]. Regarding the role of immune-related genes, we found that both wt-VHSV and dNV-VHSV induced an upregulation of hepcidin, (a regulator of the iron metabolism that is implicated in inflammatory processes) in trout similar to the results observed in VHSV infected olive flounder. However, the irf2 gene was found non-regulated in the wt-VHSV injected trout, which differs from the upregulation found in olive flounder .The differences found between trout and olive flounder could be due to the expression profile of immune response genes in spleen/head kidney, which could be slightly different from those in liver.
Another recent study determined the miRNA expression profile after VHSV infection. Among the immunity-associated target genes of 63 differentially expressed miRNA after VHSV infection of olive flounder, the authors described IL (il1b, il8, il10), mx, interferon regulatory factors (irf3, irf5, irf7), TNF (tnfsf), and heat shock proteins (hsp10, hsp60, hsp70, hsp90) [45]. For instance, mx mRNA was regulated by one miRNA (pol-miR-1388-5p) only, for which the highest expression was at 0 hpi and the lowest at 72 hpi. At 48 hpi, the mx expression was not modulated by this miRNA. Our data in trout showed a non-regulation of mx at 48h after wt-VSHV injection, being coincident with those of miRNA in olive flounder. Maybe in the future, a correlation between miRNA and mRNA expression levels could be established in infected VHSV fish, as it has been done for some miRNAs in primary human osteoblasts from healthy individuals [46].
2.4. Modulated Pathways in dNV- and wt-VHSV-Injected Trout using GSEA
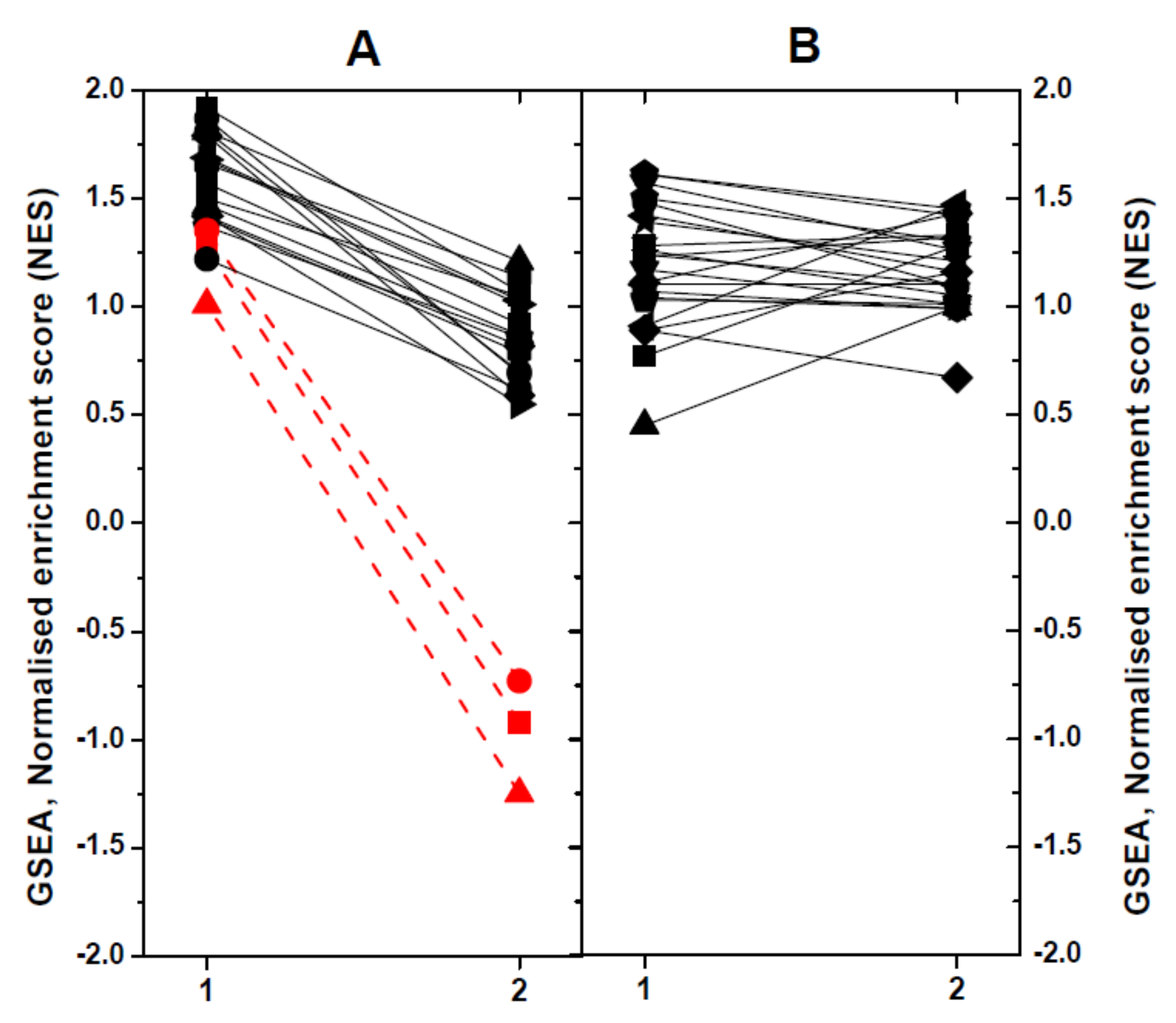
To define the impact of dNV-VHSV or wt-VHSV when targeting different pathways or gene sets (GS) in head kidney/spleen, we used the Gene-Set Enrichment Analysis (GSEA) program. Briefly, 51 trout GS collection previously defined [25] were used to obtain normalised enrichment scores (NES). The GS were then classified according to their NES values, as follows: (1) upregulation in dNV-VHSV in relation to wt-VHSV (n = 19), and (2) no regulation in dNV-VHSV in relation to wt-VHSV (Figure 5). Among the upregulated GS in dNV-VHSV in relation to wt-VHSV (Figure 5A), higher differences were found in those corresponding to “Protein processing in endoplasmic reticulum”, “Regulation of autophagy”, and “Autoimmune thyroid disease” (> 2 to 4-fold) (Figure 5A, red lines and symbols). Other GSs which showed lower improvement of upregulations with dNV-VHSV were those implicated in anti-viral interferon networks (“Toll-like receptor signalling pathway”, “Toll-like receptor wikipathway”, “Type II interferon signalling (IFNG)”), inflammation (“TNFa NF-kappa B signalling”, “Cytokine inflammatory response pathway”), recognition of nucleic acids (“Cytosolic DNA sensing pathway”, “RIG-I-like receptor signalling”), viral- and bacterial-caused diseases (“Hepatitis C”, “Influenza A”, “Measles”, “Herpes simplex infection”, “Epithelial cell Helicobacter pylori”), and others (“NF-kappa B signalling pathway”, “T cell receptor signalling pathway”, “Natural killer cell mediated cytotoxicity-K”, “Interleukin 5”). The remaining GSs showed no differences between dNV-VHSV and wt-VHSV (Figure 5B). The “Type II IFN signalling (IFNG)” pathway was one of the top enriched GS found in VHSV survivor zebrafish [47], indicating that both species share similar mechanisms to fight VHSV. Other improved pathways in dNV-VHSV such as “Toll-like receptor signalling”, “RIG-I-like receptor signalling”, “Natural killer cell-mediated cytotoxicity”, “Hepatitis C”, and “Influenza A and Measles” were among the most targeted pathways in SVCV zebrafish infections [48]. Finally, “NF-kappa B signalling pathway”, “Toll-like receptor wikipathway”, “Natural killer cell mediated cytotoxicity”, “RIG-I-like receptor signalling”, “Autoimmune thyroid disease”, “Influenza A”, and “Herpes simplex infection” were also modulated in trout when injected with thyroid hormone analogues [25]. All the above-mentioned pathways participated in generating resistance to fish viral infections and underlined the importance that their upregulation by dNV-VHSV might have in case this defective virus is used as a potential attenuated live vaccine.
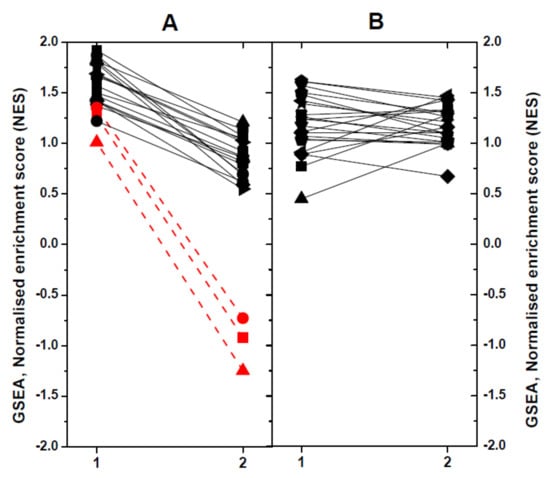
Figure 5.
Comparison of significant normalised enrichment scores (NESs) of rainbow trout gene-sets (GSs) by Gene-Set Enrichment Analysis (GSEA). X axis: 1, dNV-VHSV. 2, wt-VHSV. Trout GSs were obtained from the KEGG (-K) and WIKI (-W) pathway databases as described before [25]. For comparative purposes, the NESs calculated by GSEA were represented in a diagram by linking the results obtained with lines. For better clarity, the results were not individually identified by GS. (A) GS which show upregulation in dNV-VHSV in relation to wt-VHSV: Toll-like receptor wikipathway-W, Hepatitis C-K, Toll-like receptor signalling pathway-W, RIG-I-like receptor signalling-K, Influenza A-K, Type II interferon signalling (IFNG)-W, Measles-K, NF-kappa B signalling pathway-K, TNFa NF-kappa B signalling-W, Herpes simplex infection-K, Epithelial cell Helicobacter pylori-K, T cell receptor signalling pathway-K, Cytosolic DNA sensing pathway-K, Natural killer cell mediated cytotoxicity-K, Interleukin 5-W, Cytokine inflammatory response pathway-W. The most upregulated pathways by dNV-VHSV in relation to wt-VHSV were: Red circle, Autoimmune thyroid disease-K; Red square, Regulation of autophagy-K; and Red triangle, Protein processing in endoplasmic reticulum-K. (B) GS which showed no regulation in relation to wt-VHSV: Interferon type I-W, Interferon alpha beta signalling-W, Apoptosis modulation by HSP70-W, B-cell receptor signalling pathway-W, EGFR1 signalling pathway-W, MAPK signalling pathway-K, Interleukin 6-W, Ubiquitin mediated proteolysis-K, TSH signalling pathway-W, Antigen processing and presentation-K, MAPK signalling pathway-W, Interleukin 2-W, HTLV-K, androgen receptor signalling-W, TP53 network signalling-W, AHR pathway-W, Interleukin 3-W, Hematopoietic cell lineages-K, T-cell receptor pathway-W, JAK–STAT signalling pathway-K, PI3K–AKT signalling pathway-K, FGF signalling pathway-W.
3. Conclusions
The results presented in this study support the hypothesis that dNV-VHSV can be considered an attenuated virus and a potential live vaccine, based on the fact that many critical host gene pathways are activated upon infection. On the contrary, NV expressed at first stages of infection by wt-VHSV modulates the expression levels of interferons, VIG, chemokines, CD, transcription factors, and other immune-related genes, leading to an immune unresponsiveness state that interferes with the early innate immune response. Importantly, this work opens new avenues for the use of NV-deleted novirhabdoviruses as a tool to study the regulation of immune pathways in other teleost fish.
Author Contributions
Experimental design, E.G.C. and J.M.C.; Methodology, B.C., P.E., J.M.C., and E.G.C.; Formal analysis, E.G.C.; Original draft preparation, B.C. and E.G.C; Writing—review and editing, B.C., P.E., and E.G.C.; Funding acquisition, J.M.C. and E.G.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was partially funded by the Ministry of Science, Innovation and Universities of Spain grants AGL2014-51773-C3-3 and AGL2017-85494-C2-2-R, and the APC was funded by Ministry of Science, Innovation and Universities of Spain grant AGL2017-85494-C2-2-R.
Acknowledgments
Authors are in debt to Dr. Rosario Fernández-Godino for her helpful comments.
Conflicts of Interest
Authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
References
- Nishizawa, T.; Iida, H.; Takano, R.; Isshiki, T.; Nakajima, K.; Muroga, K. Genetic relatedness among Japanese, American and European isolates of viral hemorrhagic septicemia virus (VHSV) based on partial G and P genes. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2002, 48, 143–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schutze, H.; Enzmann, P.J.; Kuchling, R.; Mundt, E.; Niemann, H.; Mettenleiter, T.C. Complete genomic sequence of the fish rhabdovirus infectious haematopoietic necrosis virus. J. Gen. Virol. 1995, 76, 2519–2527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schutze, H.; Mundt, E.; Mettenleiter, T.C. Complete genomic sequence of viral hemorrhagic septicemia virus, a fish rhabdovirus. Virus Genes 1999, 19, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skall, H.F.; Olesen, N.J.; Mellergaard, S. Viral haemorrhagic septicaemia virus in marine fish and its implications for fish farming - a review. J. Fish Dis. 2005, 28, 509–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brudeseth, B.E.; Evensen, O. Occurrence of viral haemorrhagic septicaemia virus (VHSV) in wild marine fish species in the coastal regions of Norway. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2002, 52, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Chinchilla, B.; Encinas, P.; Estepa, A.; Coll, J.M.; Gomez-Casado, E. Transcriptome analysis of rainbow trout in response to non-virion (NV) protein of viral haemorrhagic septicaemia virus (VHSV). Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 99, 1827–1843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahli, T.; Bergmann, S.M. Viral haemorrhagic septicaemia (VHS): Detection, distribution and combat. Cab. Rev: Persp. Agric. Vet. Sci. Nutr. Nat. Resour. 2011, 6, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurath, G.; Leong, J.C. Characterization of infectious hematopoietic necrosis virus mRNA species reveals a nonvirion rhabdovirus protein. J. Virol. 1985, 53, 462–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schutze, H.; Enzmann, P.J.; Mundt, E.; Mettenleiter, T.C. Identification of the non-virion (NV) protein of fish rhabdoviruses viral haemorrhagic septicaemia virus and infectious haematopoietic necrosis virus. J. Gen. Virol. 1996, 77, 1259–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Einer-Jensen, K.; Ahrens, P.; Lorenzen, N. Parallel phylogenetic analyses using the N, G or Nv gene from a fixed group of VHSV isolates reveal the same overall genetic typing. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2005, 67, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kurath, G.; Higman, K.H.; Björklund, H.V. Distribution and variation of NV genes in fish rhabdoviruses. J. Gen. Virol. 1997, 78, 113–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biacchesi, S.; Thoulouze, M.I.; Bearzotti, M.; Yu, Y.X.; Bremont, M. Recovery of NV knockout infectious hematopoietic necrosis virus expressing foreign genes. J. Virol. 2000, 74, 11247–11253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biacchesi, S.; Lamoureux, A.; Merour, E.; Bernard, J.; Bremont, M. Limited interference at the early stage of infection between two recombinant novirhabdoviruses: Viral hemorrhagic septicemia virus and infectious hematopoietic necrosis virus. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 10038–10050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thoulouze, M.I.; Bouguyon, E.; Carpentier, C.; Bremont, M. Essential role of the NV protein of Novirhabdovirus for pathogenicity in rainbow trout. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 4098–4107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.S.; Kim, K.H. Effects of NV gene knock-out recombinant viral hemorrhagic septicemia virus (VHSV) on Mx gene expression in Epithelioma papulosum cyprini (EPC) cells and olive flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2012, 32, 459–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso, M.; Kim, C.H.; Johnson, M.C.; Pressley, M.; Leong, J.A. The NV gene of snakehead rhabdovirus (SHRV) is not required for pathogenesis, and a heterologous glycoprotein can be incorporated into the SHRV envelope. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 5875–5882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, M.C.; Simon, B.E.; Kim, C.H.; Leong, J.A. Production of recombinant snakehead rhabdovirus: The NV protein is not required for viral replication. J. Virol. 2000, 74, 2343–2350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, M.K.; Moon, C.H.; Ko, M.S.; Lee, U.H.; Cho, W.J.; Cha, S.J.; Do, J.W.; Heo, G.J.; Jeong, S.G.; Hahm, Y.S.; et al. A nuclear localization of the infectious haematopoietic necrosis virus NV protein is necessary for optimal viral growth. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e22362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ammayappan, A.; Vakharia, V.N. Nonvirion protein of novirhabdovirus suppresses apoptosis at the early stage of virus infection. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 8393–8402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, H.K.; Kim, J.; Moon, J.Y.; Nam, B.H.; Kim, Y.O.; Kim, W.J.; Park, J.Y.; An, C.M.; Cheong, J.; Kong, H.J. Microarray analysis of gene expression in olive flounder liver infected with viral haemorrhagic septicaemia virus (VHSV). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2016, 49, 66–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, J.Y.; Kwon, M.G.; Seo, J.S.; Do, J.W.; Park, M.A.; Jung, S.H.; Ahn, S.J. Differentially expressed genes after viral haemorrhagic septicaemia virus infection in olive flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus). Vet. Microbiol. 2016, 193, 72–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.S.; Kim, K.H. Protection of olive flounder, Paralichthys olivaceus, against viral hemorrhagic septicemia virus (VHSV) by immunization with NV gene-knockout recombinant VHSV. Aquaculture 2011, 314, 39–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Kinkelin, P.; LeBerre, M. Isolament d’un rhabdovirus pathogéne de la truite fario (Salmo trutta L.,1766). C R Acad. Sci. Hebd. Seances Acad. Sci. D 1977, 284, 101–104. (in French). [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ballesteros, N.A.; Saint-Jean, S.S.; Encinas, P.A.; Perez-Prieto, S.I.; Coll, J.M. Oral immunization of rainbow trout to infectious pancreatic necrosis virus (IPNV) induces different immune gene expression profiles in head kidney and pyloric ceca. Fish Shellfish Immunol 2012, 33, 174–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quesada-Garcia, A.; Encinas, P.; Valdehita, A.; Baumann, L.; Segner, H.; Coll, J.M.; Navas, J.M. Thyroid active agents T3 and PTU differentially affect immune gene transcripts in the head kidney of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Aquat. Toxicol. 2016, 174, 159–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salem, M.; Kenney, P.B.; Rexroad, C.E.; Yao, J. Development of a 37 k high-density oligonucleotide microarray: A new tool for functional genome research in rainbow trout. J. Fish Biol. 2008, 72, 2187–2206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gene Expression Omnibus. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/query/acc.cgi?acc=GSE37330 (accessed on 29 January 2020).
- Gene Expression Omnibus. Available online: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/query/acc.cgi?acc=GSE37797 (accessed on 29 January 2020).
- GSEA - Broad Institute. Available online: http://www.broad.mit.edu/GSEA (accessed on 29 January 2020).
- Subramanian, A.; Tamayo, P.; Mootha, V.K.; Mukherjee, S.; Ebert, B.L.; Gillette, M.A.; Paulovich, A.; Pomeroy, S.L.; Golub, T.R.; Lander, E.S.; et al. Gene set enrichment analysis: A knowledge-based approach for interpreting genome-wide expression profiles. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 15545–15550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramanian, A.; Kuehn, H.; Gould, J.; Tamayo, P.; Mesirov, J.P. GSEA-P: A desktop application for Gene Set Enrichment Analysis. Bioinformatics 2007, 23, 3251–3253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- KEGG: Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes. Available online: http://www.kegg.jp (accessed on 29 January 2020).
- Glenney, G.W.; Wiens, G.D. Early diversification of the TNF superfamily in teleosts: Genomic characterization and expression analysis. J. Immunol. 2007, 178, 7955–7973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roth, W.; Wagenknecht, B.; Klumpp, A.; Naumann, U.; Hahne, M.; Tschopp, J.; Weller, M. APRIL, a new member of the tumor necrosis factor family, modulates death ligand-induced apoptosis. Cell Death Differ. 2001, 8, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Valck, D.; Jin, D.Y.; Heyninck, K.; Van de Craen, M.; Contreras, R.; Fiers, W.; Jeang, K.T.; Beyaert, R. The zinc finger protein A20 interacts with a novel anti-apoptotic protein which is cleaved by specific caspases. Oncogene 1999, 18, 4182–4190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelly, C.; Shields, M.D.; Elborn, J.S.; Schock, B.C. A20 regulation of nuclear factor-kappaB: Perspectives for inflammatory lung disease. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2011, 44, 743–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zelante, T.; Wong, A.Y.; Ping, T.J.; Chen, J.; Sumatoh, H.R.; Vigano, E.; Hong Bing, Y.; Lee, B.; Zolezzi, F.; Fric, J.; et al. CD103(+) Dendritic Cells Control Th17 Cell Function in the Lung. Cell Rep. 2015, 12, 1789–1801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chapoval, A.I.; Ni, J.; Lau, J.S.; Wilcox, R.A.; Flies, D.B.; Liu, D.; Dong, H.; Sica, G.L.; Zhu, G.; Tamada, K.; et al. B7-H3: A costimulatory molecule for T cell activation and IFN-gamma production. Nat. Immunol. 2001, 2, 269–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, B.; Shum, B.; Adams, E.J.; Magor, K.E.; Hedrick, R.P.; Muir, D.G.; Parham, P. CK-1, a putative chemokine of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Immunol. Rev. 1998, 166, 341–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montero, J.; Coll, J.; Sevilla, N.; Cuesta, A.; Bols, N.C.; Tafalla, C. Interleukin 8 and CK-6 chemokines specifically attract rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) RTS11 monocyte-macrophage cells and have variable effects on their immune functions. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2008, 32, 1374–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montero, J.; Ordas, M.C.; Alejo, A.; Gonzalez-Torres, L.; Sevilla, N.; Tafalla, C. CK12, a rainbow trout chemokine with lymphocyte chemo-attractant capacity associated to mucosal tissues. Mol. Immunol. 2011, 48, 1102–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Farrell, C.; Vaghefi, N.; Cantonnet, M.; Buteau, B.; Boudinot, P.; Benmansour, A. Survey of transcript expression in rainbow trout leukocytes reveals a major contribution of interferon-responsive genes in the early response to a rhabdovirus infection. J. Virol. 2002, 76, 8040–8049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, J.; Yaneva, Y.R.; Cresswell, P. Viperin: A multifunctional, interferon-inducible protein that regulates virus replication. Cell Host Microbe 2011, 10, 534–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boudinot, P.; Salhi, S.; Blanco, M.; Benmansour, A. Viral haemorrhagic septicaemia virus induces vig-2, a new interferon-responsive gene in rainbow trout. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2001, 11, 383–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najib, A.; Kim, M.S.; Choi, S.H.; Kang, Y.J.; Kim, K.H. Changes in microRNAs expression profile of olive flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus) in response to viral hemorrhagic septicemia virus (VHSV) infection. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2016, 51, 384–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laxman, N.; Rubin, C.J.; Mallmin, H.; Nilsson, O.; Pastinen, T.; Grundberg, E.; Kindmark, A. Global miRNA expression and correlation with mRNA levels in primary human bone cells. Rna 2015, 21, 1433–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Estepa, A.; Coll, J. Innate Multigene Family Memories Are Implicated in the Viral-Survivor Zebrafish Phenotype. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0135483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Encinas, P.; Garcia-Valtanen, P.; Chinchilla, B.; Gomez-Casado, E.; Estepa, A.; Coll, J. Identification of multipath genes differentially expressed in pathway-targeted microarrays in zebrafish infected and surviving spring viremia carp virus (SVCV) suggest preventive drug candidates. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e73553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).