Elucidating the Efficacy of Vaccination against Vibriosis in Lates calcarifer Using Two Recombinant Protein Vaccines Containing the Outer Membrane Protein K (r-OmpK) of Vibrio alginolyticus and the DNA Chaperone J (r-DnaJ) of Vibrio harveyi
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Fish Maintenance
2.2. Preparation of Recombinant Cell as Formalin-Killed Vaccine
2.3. Bacterial Strain and Culture Condition
2.4. Experimental Design
2.5. Serum Bactericidal Assay
2.6. Agglutination Test
2.7. Semi Quantitative PCR Detection of Bacteria from Water Samples
2.8. Quantitative Detection of Recombinant Vaccines by Real Time qPCR
2.9. Total RNA Isolation, cDNA Synthesis, and RT-qPCR
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
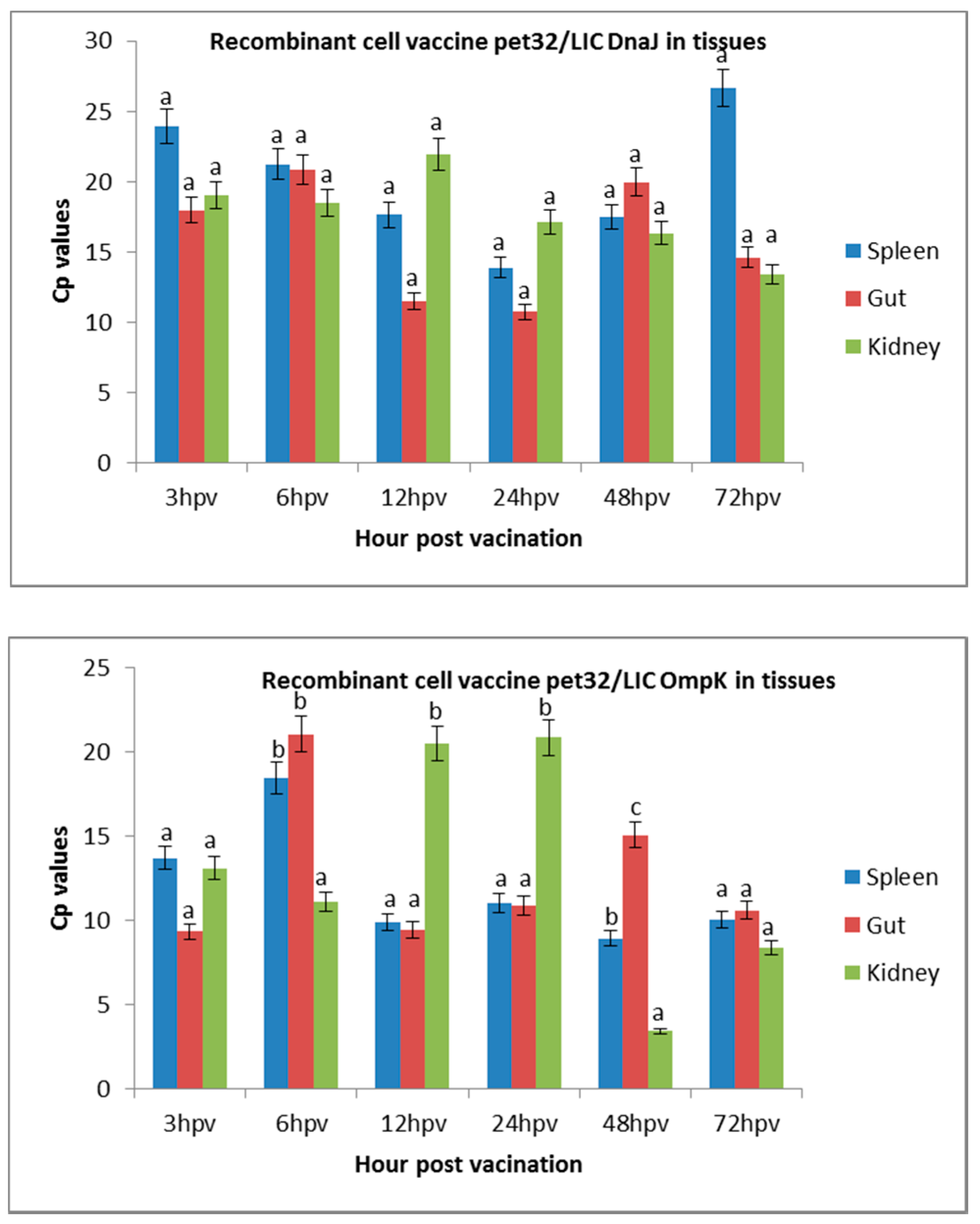
3.1. Quantification of Targeted r-OmpK and r-DnaJ in Vaccinated Juvenile Seabass
3.2. Agglutinating Antibody Levels
3.3. Gene Expression Profilings
3.3.1. Gene Expression in the Kidney
3.3.2. Gene Expression in the Intestine
3.3.3. Gene Expression in the Spleen
3.4. Clinical Symptoms of Infected Fish
3.5. Relative Percentage Mortality
3.6. Bacterial Isolation
3.7. Serum Bactericidal Activity
3.8. Pathogen Shedding
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAQ). The State of World Fisheries and Aquaculture. Meeting the Sustainable Development Goals; Licence: CC BY-NC-SA 3.0 IGO; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2018; ISBN 978-92-5-130562-1. [Google Scholar]
- National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration Fisheries: Office of Science and Technology. Available online: https://www.fisheries.noaa.gov/about/office-science-and-technology (accessed on 10 November 2019).
- Pridgeon, J.W.; Klesius, P.H. Major bacterial diseases in aquaculture and their vaccine development. Anim. Sci. Rev. 2012, 7, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Defoirdt, T.; Boon, N.; Sorgeloos, P.; Verstraete, W.; Bossier, P. Alternatives to antibiotics to control bacterial infections: Luminescent vibriosis in aquaculture as an example. Trends Biotechnol. 2007, 10, 472–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cabello, F.C. Antibióticos y acuicultura en Chile: Consecuencias para la salud humana y animal [Antibiotics and aquaculture in Chile: Implications for human and animal health]. Rev. Med. Chile 2007, 132, 1001–1006. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, L.Y.; Wang, K.Y.; Xiao, D.; Chen, D.F.; Geng, Y.; Wang, J.; He, Y.; Wang, E.L.; Huang, J.L.; Xiao, G.Y. Safety and immunogenicity of an oral DNA vaccine encoding Sip of Streptococcus agalactiae from Nile tilapia Oreochromis niloticus delivered by live attenuated Salmonella typhimurium. Fish. Shellfish. Immunol. 2014, 38, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muktar, Y.; Tesfaye, S.; Tesfaye, B. Present Status and Future Prospects of Fish Vaccination: A Review. J. Vet. Sci. Technol. 2016, 7, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Sikand, P.; Ma, C.; Tang, Z.X.; Han, L.; Li, Z.; Sun, S.; LaMotte, R.H.; Dong, X.Z. Mechanisms of itch evoked by β-alanine. J. Neurosci. 2012, 32, 14532–14537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, Z.; Yu, L.; You, Z.; Wei, Y.; Liu, Y. Expression and Immunogenicity Analysis of Two Iron-regulated Outer Membrane Proteins of Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Acta Biochim. Biophys. Sin. 2007, 39, 763–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jun, L.; Siyuan, M.; Norman, Y.S.W. Vaccination of Silver Sea Bream (Sparus sarba) against Vibrio alginolyticus: Protective Evaluation of Different Vaccinating Modalities. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 40. [Google Scholar]
- Rosli, N.; Ina-Salwany, M.Y.; Zulperi, Z. Antigenicity Analysis and Molecular Characterization of Two Outer Membrane Proteins of Vibrio alginolyticus Strain VA2 as Vaccine Candidates in Tiger Grouper Culture. J. Biol. Sci. 2016, 16, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Geng, Y.; Liu, D.; Han, S.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, K.Y.; Huang, X.; Chen, D.; Peng, X.; Lai, W.M. Outbreaks of vibriosis associated with Vibrio mimicus in freshwater catfish in China. Aquaculture 2014, 433, 82–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biller-Takahashi, J.D.; Takahashi, L.S.; Pilarski, F.; Sebastião, F.A.; Urbinati, E.C. Serum bactericidal activity as indicator of innate immunity in pacu Piaractus mesopotamicus (Holmberg, 1887). Arq. Bras. Med. Vet. Zootec. 2013, 5, 1745–1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Biller-Takahashi, J.D.; Montassier, H.J.; Takahashi, L.S.; Urbinati, E.C. Proposed method for agglutinating antibody titer analysis and its use as indicator of acquired immunity in pacu, Piaractus mesopotamicus. Braz. J. Biol. 2014, 74, 238–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jiang, J.; Miyata, M.; Chan, C.; Ngoh, S.Y.; Liew, W.C.; Saju, J.M.; Ng, K.S.; Wong, F.S.; Lee, Y.S.; Chang, S.F.; et al. Differential Transcriptomic Response in the Spleen and Head Kidney Following Vaccination and Infection of Asian Seabass with Streptococcus iniae. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e99128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.S.; Wetzel, K.; Buckley, T.; Wozniak, D.; Lee, J. Rapid and sensitive detection of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in chlorinated water and aerosols targeting gyrB gene using real-time PCR. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2011, 111, 893–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Qian, R.; Xiao, Z.; Zhang, C.; Chu, W.; Mao, Z.; Yu, L. Expression and purification of two major outer membrane proteins from Vibrio alginolyticus. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2008, 24, 245–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghamollaei, H.; Moghaddam, M.M.; Kooshki, H.; Heiat, M.; Mirnejad, R.; Barzi, N.S. Detection of Pseudomonas aeruginosa by a triplex polymerase chain reaction assay based on lasI/R and gyrB genes. J. Infect. Public Health 2015, 8, 314–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Joseph, A.W.; Nick, B.R.; Michael, A.W. A method for the absolute quantification of cDNA using real-time PCR. J. Immunol. Methods 2003, 278, 261–269. [Google Scholar]
- Paria, A.; Dong, J.; Babu, P.P.; Makesh, M.; Chaudhari, A.; Thirunavukkarasu, A.R.; Purushothaman, C.S.; Rajendran, K.V. Evaluation of candidate reference genes for quantitative expression studies in Asian seabass (Lates calcarifer) during ontogenesis and in tissues of healthy and infected fishes. I JEB 2016, 54, 597–605. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, D.; Liu, Q.; Ni, C.; Li, S.; Wu, H.; Wang, Q.; Xiao, J.; Zhang, Y. Gene expression profiling in live attenuated Edwardsiella tarda vaccine immunized and challenged zebrafish: Insights into the basic mechanisms of protection seen in immunized fish. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2013, 40, 132–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes-López, F.E.; Aerts, J.; Vallejos-Vidal, E.; Ampe, B.; Dierckens, K.; Tort, L.; Bossier, P. Modulation of innate immune-related genes and glucocorticoid synthesis in gnotobiotic full-sibling European sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax) larvae challenged with Vibrio anguillarum. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Harun, N.O.; Wang, T.; Secombes, C.J. Gene expression profiling in naïve and vaccinated rainbow trout after Yersinia ruckeri infection: Insights into the mechanisms of protection seen in vaccinated fish. Vaccine 2011, 29, 4388–4399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ina-Salwany, M.Y.; Al-saari, N.; Mohamad, A.; Mursidi, F.A.; Mohd-Aris, A.; Amal, M.N.A.; Kesai, H.; Mino, S.; Sawabe, T.; Zamri-Saad, M. Vibriosis in Fish: A Review on Disease Development and Prevention. J. Aquat. Anim. Health 2019, 31, 3–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zorrilla, M.; Chabrillon, A.S.; Rosales, P.D.; Manzanares, E.M.; Balebona, M.; Morinigo, M. Bacteria recovered from diseased cultured gilthead sea bream. Sparus Aurata L. In South Western Spain. Aquaculture 2003, 218, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, S.A.; Abou-Akkada, A.S.; El-Hoshy, S.M. Molecular studies on vibrio species isolated from imported frozen fish. Glob. Vet. 2014, 12, 782–789. [Google Scholar]
- Chu, W.H. Adjuvant effect of propolis on immunisation by inactivated Aeromonas hydrophila in carp (Carassius auratus gibelio). Fish. Shellfish Immunol. 2006, 21, 113–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gravningen, K.; Sakai, M.M.; Fujimoto, T. The efficacy and safety of an oil-based vaccine against Photobacterium damsela subsp. piscicida in yellowtail (Seriola quinqueradiata): A field study. Fish. Shellfish Immunol. 2008, 24, 523–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, J.; Zhang, J.; Ma, L.; Li, L.; Zhang, W.; Li, J. Identification of fish source Vibrio alginolyticus and evaluation of its bacterial ghosts vaccine immune effects. MicrobiologyOpen 2017, 7, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hordvik, I. Identification of a novel immunoglobulin d transcript and comparative analysis of the genes encoding IgD in Atlantic salmon and Atlantic halibut. Mol. Immunol. 2002, 39, 80–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Findly, R.C.; Dickerson, H.W. Cutaneous antibody-secreting cells and B cells in a teleost fish. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2008, 32, 500–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thorarinsson, R.; Powell, D.B. Effects of disease risk, vaccine efficacy, and market price on the economics of fish vaccination. Aquaculture 2006, 256, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefaan, V.; Frans, O.; Renaat, K.; Armand, M. Mucosal response in African catfish after administration of Vibrio anguillarum O2 antigens via different routes. Fish. Shellfish Immunol. 2005, 18, 125–133. [Google Scholar]
- Raida, M.; Buchmann, K. Development of adaptive immunity in trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss Walbaum) surviving an infection with Yersinia ruckeri. Fish. Shellfish Immunol. 2008, 25, 533–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jault, C.; Pichon, L.; Chluba, J. Toll-like receptor gene family and TIR-domain adapters in Danio rerio. Mol. Immunol. 2004, 40, 759–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roach, J.C.; Glusman, G.; Rowen, L.; Kaur, A.; Purcell, M.K.; Smith, K.D.; Hood, L.E.; Aderem, A. The evolution of vertebrate Toll-like receptors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 9577–9582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Patil, V.K.; David, M. Behavioral and morphological endpoints: As an early response to sublethal malathion intoxication in the freshwater fish, Labeo rohita. Drug Chem. Toxicol. 2010, 33, 160–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baoprasertkul, P.; Xu, P.; Peatman, E.; Kucuktas, H.; Liu, Z. Divergent toll-like receptors in catfish (Ictalurus punctatus): TLR5S, TLR20, TLR21. Fish. Shellfish Immunol. 2008, 23, 1218–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fink, J.; Schoenfeld, B.; Kikuchi, N.; Nakazato, K. Acute and Long-term Responses to Different Rest Intervals in Low-load Resistance Training. Int. J. Sports Med. 2016, 38, 118–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samanta, A.K.; Jayapal, N.; Chikkerur, J.; Roy, S.; Kolte, A.; Senani, S.; Sridhar, M. Xylooligosaccharides as prebiotics from agricultural by-products: Production and applications. Bioact. Carbohydr. Diet. Fibre 2015, 5, 62–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Pei, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Li, Y.; Liao, L.; Zhu, Z.; Wang, Y. Global gene expression patterns of grass carp following compensatory growth. BMC Genom. 2015, 16, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wei, L.; Zhu, S.; Ruan, G.; Hou, L.; Wang, J.; Wang, B.; Liu, J. Infectious bursal disease virus-induced activation of JNK signaling pathway is required for virus replication and correlates with virus-induced apoptosis. Virology 2011, 420, 156–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fan, Z.J.; Jia, Q.J.; Yao, C.L. Characterization and expression analysis of Toll-like receptor 2 gene in large yellow croaker, Larimichthys crocea. Fish. Shellfish Immunol. 2015, 44, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, R.; Sun, Y.; Sun, D.; Xu, T. Characterization of the miiuy croaker (Miichthys miiuy) transcriptome and development of immune-relevant genes and molecular markers. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e94046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Cheng, S.; Chang, Y.; Li, K.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Y. Identification and expression analysis of a TLR11 family gene in the sea urchin Strongylocentrotus intermedius. Immunogenetics 2018, 70, 337–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirono, I.; Takami, M.; Miyata, M.; Miyazaki, T.; Han, H.J.; Takano, T.; Endo, M.; Aoki, T. Characterization of gene structure and expression of two toll-like receptors from Japanese flounder, Paralichthys olivaceus. Immunogenetics 2004, 56, 38–46. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Z.; Gatesoupe, F.J.; Li, T.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Q.; Feng, D.; Feng, Y.; Chen, H.; Li, A. Corrigendum: Significant improvement of intestinal microbiota of gibel carp (Carassius auratus gibelio ) after traditional Chinese medicine feeding. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2018, 124, 829–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Platt, C.D.; Ma, J.K.; Chalouni, C.; Ebersold, M.; Bou-Reslan, H.; Carano, R.A.D.; Mellam, I.; Delamarre, L. Mature dendritic cells use endocytic receptors to capture and present antigens. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 4287–4292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, L.; Udaka, K.; Mamitsuka, H.; Zhu, S. Toward more accurate pan-specific MHC-peptide binding prediction: A review of current methods and tools. Brief. Bioinform. 2012, 13, 350–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Toze, S. PCR and the detection of microbial pathogens in water and wastewater. Water Res. 1999, 33, 3545–3556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Treatment Groups | Vaccines | Dosages |
|---|---|---|
| Group 1 | Recombinant cell pet32/LIC OmpK vaccine (r-OmpK) | 107 cfu/mL |
| Group 2 | Recombinant cell pet32/LIC DnaJ vaccine (r-DnaJ) | 107 cfu/mL |
| Group 3 | Whole cells-killed V. harveyi vaccine (VH), positive control | 107 cfu/mL |
| Group 4 | BL21 (DE2) vaccine (BL21), negative control | 107 cfu/mL |
| Group 5 | Phosphate buffered saline (PBS), control | 0.01 M |
| No. | Vaccines | Forward Primer (5′–3′) | Reverse Primer (5′–3′) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | r-OmpK | GACGACGACAAGATGCGTAAATCACT | GAGGAGAAGCCCGGTTAGAACTTGTA | Qian et al. [17] |
| 2 | r-DnaJ | GACCACGACAAGATGCATATTTTTGGC | GAGGAGAAGCCCGGTTATTTAAAGCC |
| No. | Genes | Forward Primer (5′–3′) | Reverse Primer (5′–3′) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | ACTB * | taccaccggtatcgtcatgga | Ccacgctctgtcaggatcttc | Paria et al. [20] |
| 2 | GAPDH * | cgcttcctgcacaaccaact | Gtggcagtgatggcatgaac | |
| 3 | TLR-2 | Tctccgtcttggtttcac | Ggtcccacagttgagtatg | Dahai Yang et al. [21] |
| 4 | MHC I | ggctgtttttgccgctct g | Gtggacaggtctggataaag | |
| 5 | Myd88 | Aacaacttcgctggataa | Gttactggaatcgcctca | |
| 6 | IL-8 | Cttccctccaagcccacag | Gatccgggcattcatgg | Reyes-López et al. [22] |
| 7 | IL-1B | Atctggaggtggtggacaaa | Agggtgctgatgttcaaacc | |
| 8 | IL-10 | Cgaccagctcaagagtgatg | Agaggctgcatggtttctgt | |
| 9 | CCL4 | Tcctcgtctcactctgtctgt | Gacctgccactgtcttcagc |
| Challenged Bacteria | V. harveyi (108 CFU/mL) | V. alginolyticus (108 CFU/mL) | V. parahaemolyticus (108 CFU/mL) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vaccination Treatment | Survival (%) | Mortality (%) | RPS (%) | Survival (%) | Mortality (%) | RPS (%) | Survival (%) | Mortality (%) | RPS (%) |
| r-OmpK | 87 | 13 | 87 | 100 | 0 | 100 | 100 | 0 | 100 |
| r-DnaJ | 33 | 67 | 33 | 33 | 63 | 23 | 33 | 67 | 17 |
| VH | 93 | 7 | 93 | 100 | 0 | 100 | 100 | 0 | 100 |
| E. coli BL21(DE3) | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 |
| PBS | 0 | 100 | n.a | 13 | 87 | n.a | 20 | 80 | n.a |
| Treatments | Vibrio harveyi (108 cfu/mL) | Vibrio alginolyticus (108 cfu/mL) | Vibrio parahaemolyticus (108 cfu/mL) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Spleen | Kidney | Intestine | Spleen | Kidney | Intestine | Spleen | Kidney | Intestine | |
| PBS | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | ++ | +++ | + | - |
| r-OmpK | +++ | +++ | - | ++ | - | - | + | - | - |
| r-DnaJ | +++ | +++ | - | ++ | ++ | + | + | - | - |
| VH | ++ | - | - | + | - | - | + | - | - |
| E.coli BL21 (DE3) | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | ++ | ++ | + | + |
| Treatments | V. harveyi | V. alginolyticus | V. parahaemolyticus | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 24hpc | 48hpc | 72hpc | 24hpc | 48hpc | 72hpc | 24hpc | 48hpc | 72hpc | |
| +ve control * | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ |
| PBS | ++ | ++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | + | +++ | +++ |
| r-OmpK | + | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | - | - | ++ |
| r-DnaJ | + | ++ | +++ | ++ | +++ | +++ | - | +++ | +++ |
| VH | + | - | ++ | + | ++ | ++ | - | - | - |
| -ve control * | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Silvaraj, S.; Md Yasin, I.S.; A. Karim, M.M.; Saad, M.Z. Elucidating the Efficacy of Vaccination against Vibriosis in Lates calcarifer Using Two Recombinant Protein Vaccines Containing the Outer Membrane Protein K (r-OmpK) of Vibrio alginolyticus and the DNA Chaperone J (r-DnaJ) of Vibrio harveyi. Vaccines 2020, 8, 660. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines8040660
Silvaraj S, Md Yasin IS, A. Karim MM, Saad MZ. Elucidating the Efficacy of Vaccination against Vibriosis in Lates calcarifer Using Two Recombinant Protein Vaccines Containing the Outer Membrane Protein K (r-OmpK) of Vibrio alginolyticus and the DNA Chaperone J (r-DnaJ) of Vibrio harveyi. Vaccines. 2020; 8(4):660. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines8040660
Chicago/Turabian StyleSilvaraj, Santha, Ina Salwany Md Yasin, Murni Marlina A. Karim, and Mohd Zamri Saad. 2020. "Elucidating the Efficacy of Vaccination against Vibriosis in Lates calcarifer Using Two Recombinant Protein Vaccines Containing the Outer Membrane Protein K (r-OmpK) of Vibrio alginolyticus and the DNA Chaperone J (r-DnaJ) of Vibrio harveyi" Vaccines 8, no. 4: 660. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines8040660
APA StyleSilvaraj, S., Md Yasin, I. S., A. Karim, M. M., & Saad, M. Z. (2020). Elucidating the Efficacy of Vaccination against Vibriosis in Lates calcarifer Using Two Recombinant Protein Vaccines Containing the Outer Membrane Protein K (r-OmpK) of Vibrio alginolyticus and the DNA Chaperone J (r-DnaJ) of Vibrio harveyi. Vaccines, 8(4), 660. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines8040660





