Screening of Porcine Innate Immune Adaptor Signaling Revealed Several Anti-PRRSV Signaling Pathways
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cells, Virus and Reagents
2.2. Subcloning of Porcine Innate Immune Signaling Adaptor Gene ORFs
2.3. Preparation of Polyclonal Antibody against N Protein of PRRSV
2.4. Construction of Full-Length cDNA Clones of HP-PRRSV XJ17-5 Carrying EGFP
2.5. RNA Interference by siRNA
2.6. Quantitative Reverse Transcription Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-qPCR)
2.7. Western Blot Analysis
2.8. Flow Cytometry
2.9. Virus TCID50 Titration
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
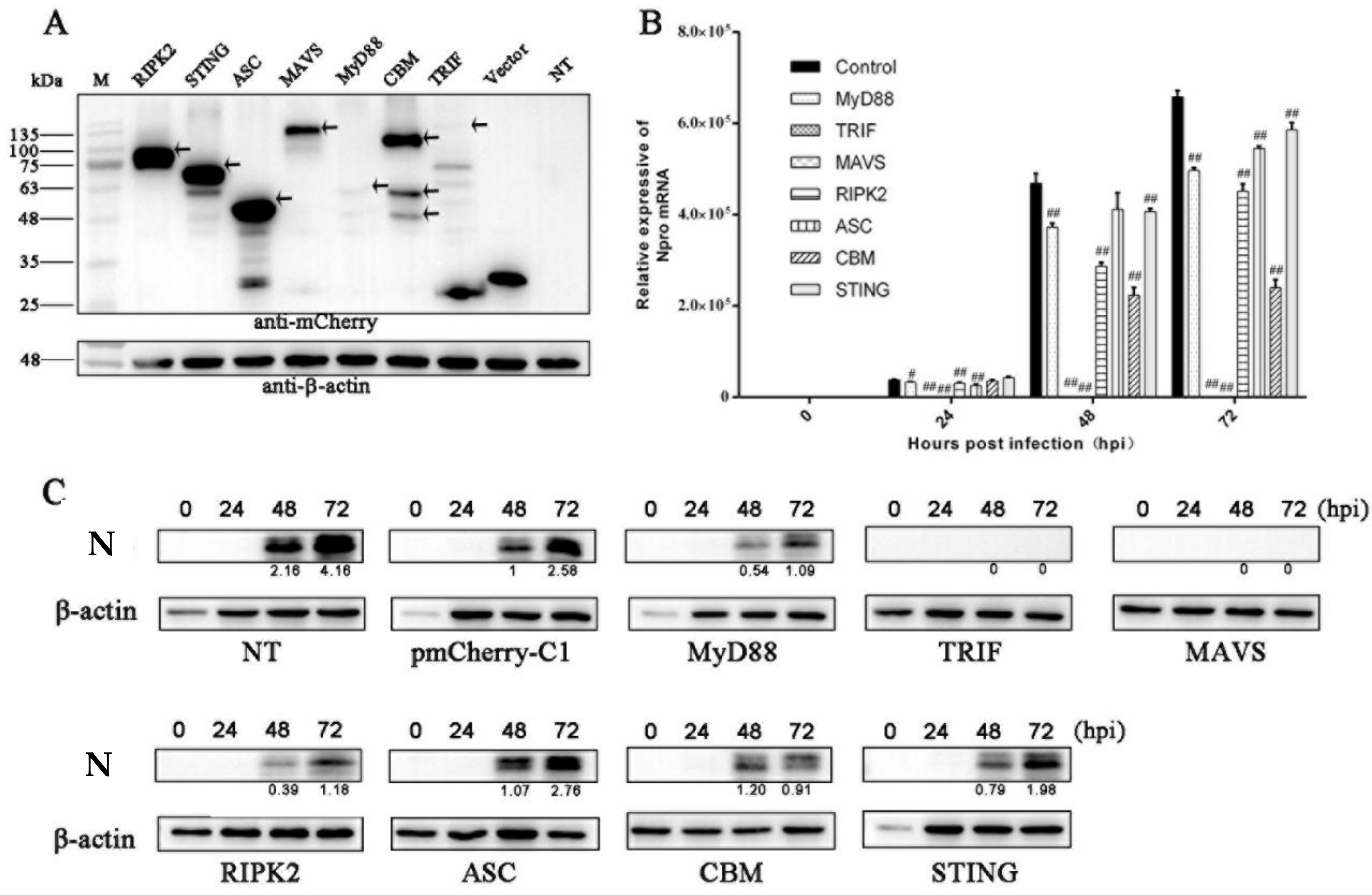
3.1. The Antiviral Activities of Ectopic Porcine Innate Signaling Adaptor Proteins against PRRSV Infection
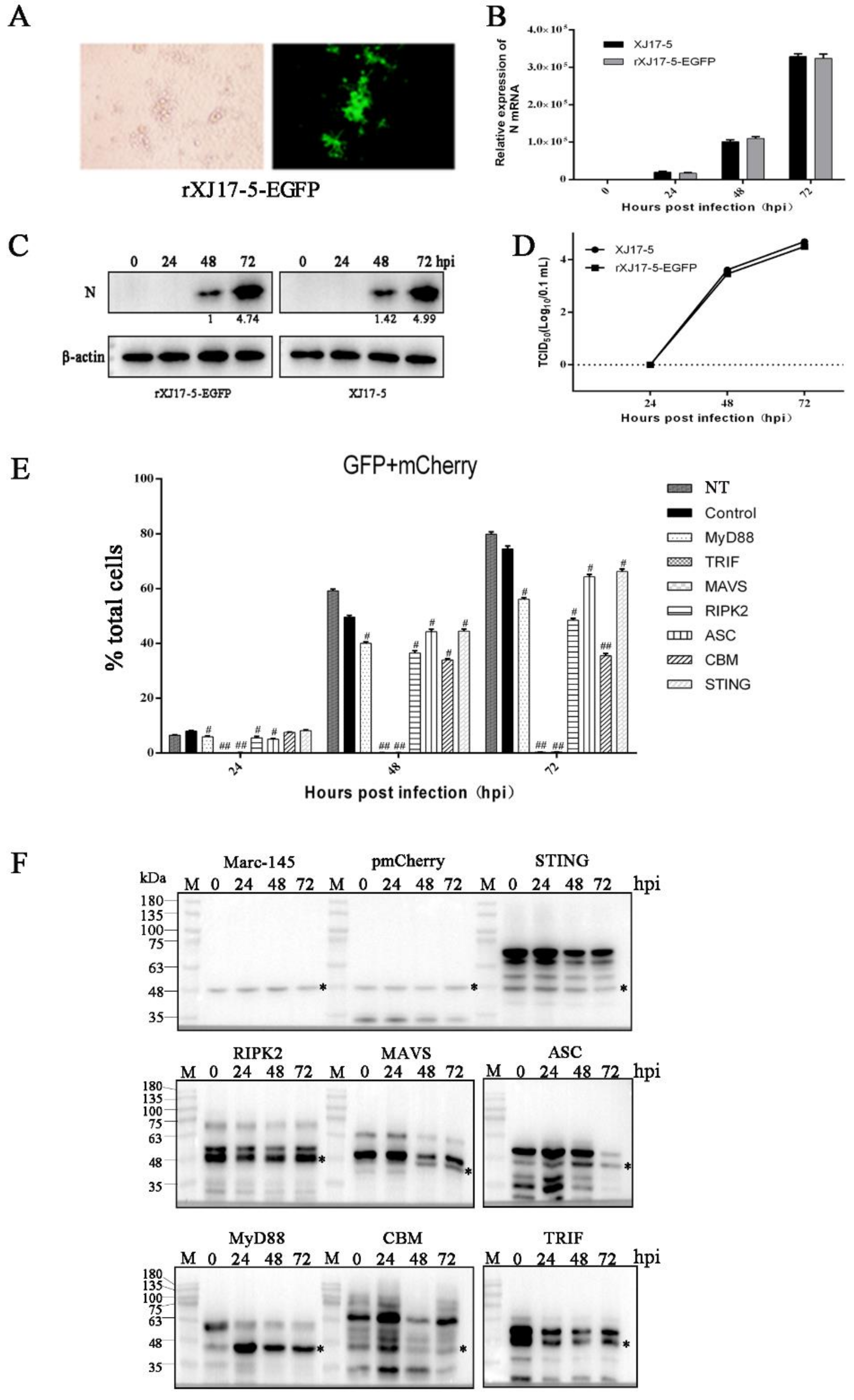
3.2. The Antiviral Activities of Ectopic Porcine Innate Signaling Adaptor Proteins against PRRSV-EGFP Infection
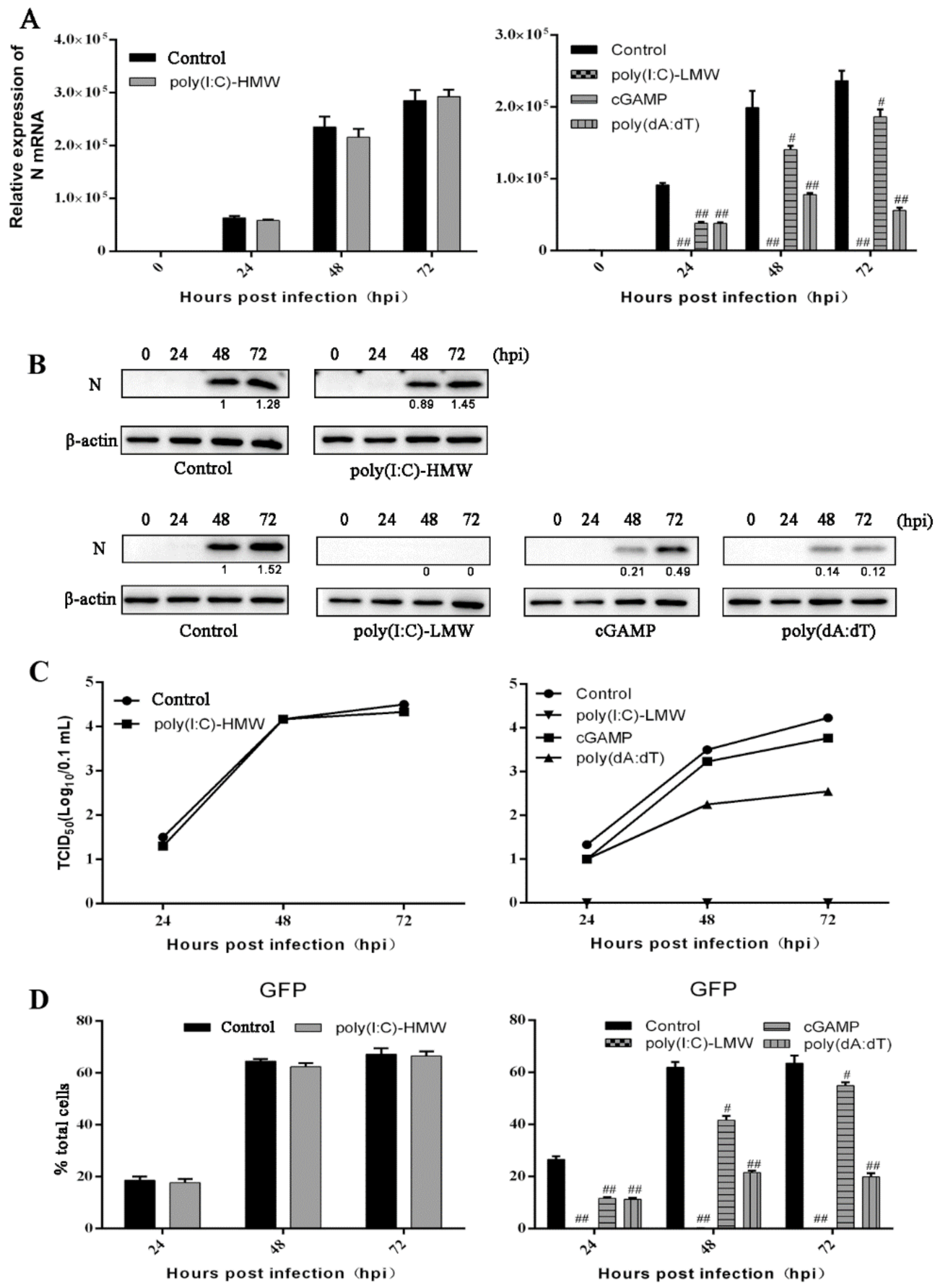
3.3. The Antiviral Activities of Endogenous TRIF, MAVS and STING Signaling against PRRSV Replication
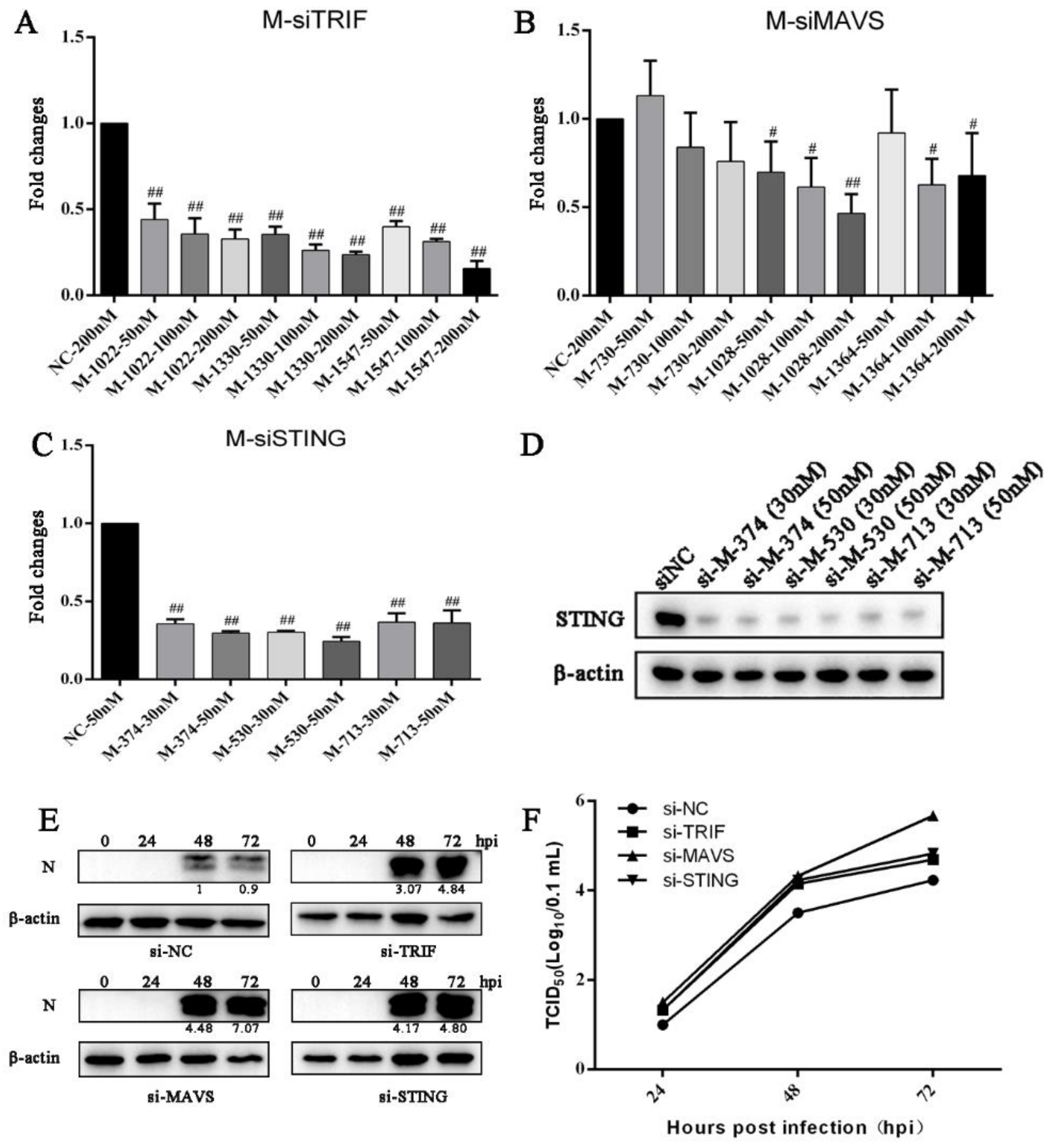
3.4. Knockdown of Endogenous TRIF, MAVS and STING Enhances PRRSV Replication
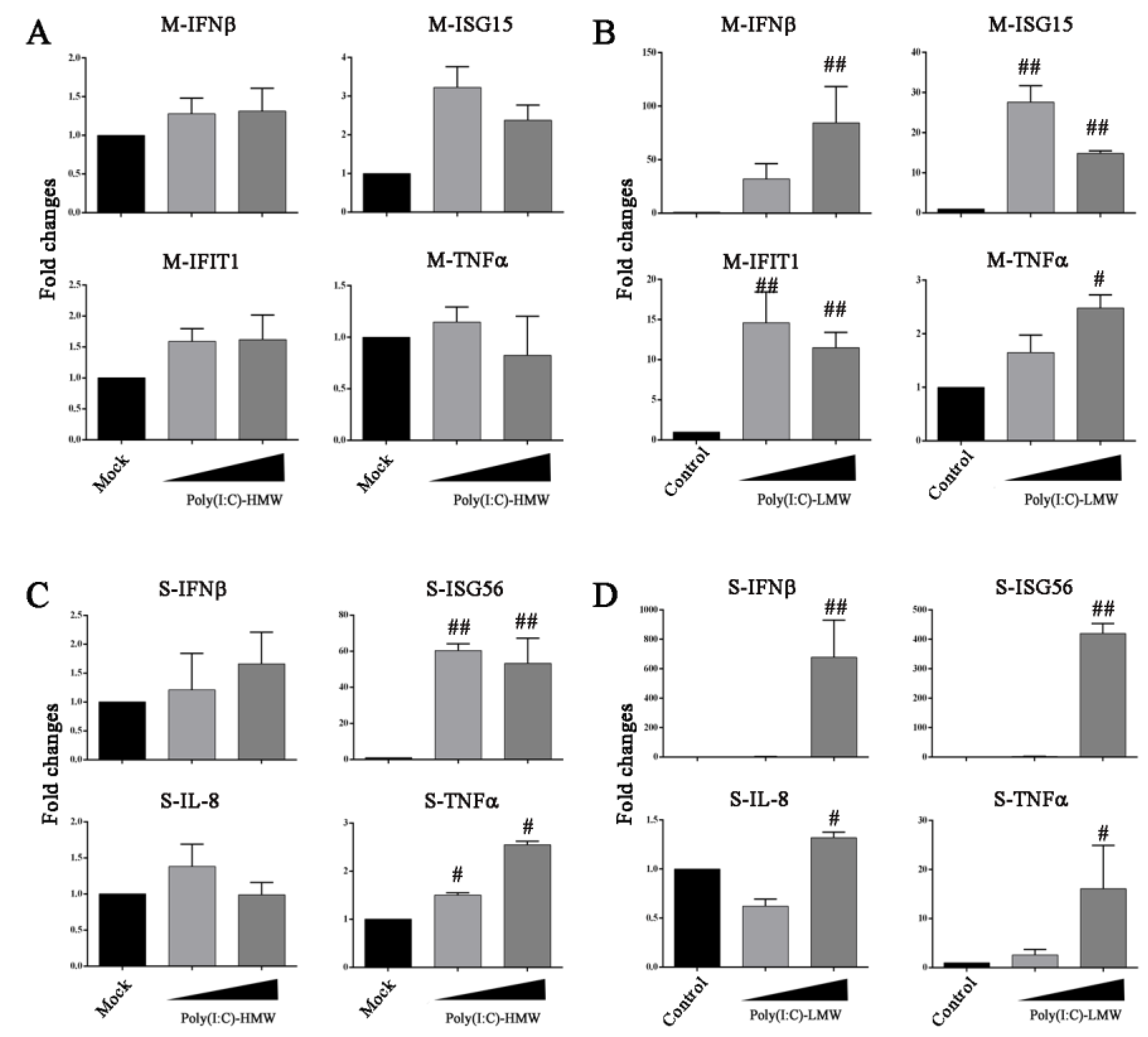
3.5. Innate TLR3-TRIF Signaling Plays a Differential Role in Marc-145 Cells and Porcine Macrophages
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Balasuriya, U.B.; Carossino, M. Reproductive effects of arteriviruses: Equine arteritis virus and porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus infections. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2017, 27, 57–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lunney, J.K.; Fang, Y.; Ladinig, A.; Chen, N.; Li, Y.; Rowland, B.; Renukaradhya, G.J. Porcine Reproductive and Respiratory Syndrome Virus (PRRSV): Pathogenesis and Interaction with the Immune System. Annu. Rev. Anim. Biosci. 2016, 4, 129–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kappes, M.A.; Faaberg, K.S. PRRSV structure, replication and recombination: Origin of phenotype and genotype diversity. Virology 2015, 479–480, 475–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, N.; Xia, P.; Li, S.; Zhang, T.; Wang, T.T.; Zhu, J. RNA sensors of the innate immune system and their detection of pathogens. Iubmb Life 2017, 69, 297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mair, K.H.; Sedlak, C.; KäSer, T.; Pasternak, A.; Levast, B.; Gerner, W.; Saalmüller, A.; Summerfield, A.; Gerdts, V.; Wilson, H.L. The porcine innate immune system: An update. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2014, 45, 321–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beutler, B. Innate immunity: An overview. Mol. Immunol. 2004, 40, 845–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawai, T.; Akira, S. TLR signaling. Semin. Immunol. 2007, 19, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loo, Y.M.; Gale, M. Immune Signaling by RIG-I-like Receptors. Immunity 2011, 34, 680–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Platnich, J.M.; Muruve, D.A. NOD-like receptors and inflammasomes: A review of their canonical and non-canonical signaling pathways. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2019, 670, 4–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geijtenbeek, T.B.; Gringhuis, S.I. Signalling through C-type lectin receptors: Shaping immune responses. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2009, 9, 465–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Wu, J.; Du, F.; Chen, X.; Chen, Z.J. Cyclic GMP-AMP synthase is a cytosolic DNA sensor that activates the type I interferon pathway. Science 2013, 339, 786–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Overend, C.; Mitchell, R.; He, D.; Rompato, G.; Grubman, M.J.; Garmendia, A.E. Recombinant swine beta interferon protects swine alveolar macrophages and MARC-145 cells from infection with Porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus. J. Gen. Virol. 2007, 88 Pt 3, 925–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Han, M.; Kim, C.; Calvert, J.G.; Yoo, D. Interplay between interferon-mediated innate immunity and porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus. Viruses 2012, 4, 424–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- An, T.Q.; Li, J.N.; Su, C.M.; Yoo, D. Molecular and Cellular Mechanisms for PRRSV Pathogenesis and Host Response to Infection. Virus Res. 2020, 286, 197980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Zhang, Y.J. Antagonizing interferon-mediated immune response by porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 315470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huang, C.; Zhang, Q.; Feng, W.H. Regulation and evasion of antiviral immune responses by porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus. Virus Res. 2015, 202, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Liu, J.; Bai, J.; Du, Y.; Wang, X.; Liu, X.; Jiang, P. Poly(I:C) inhibits porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus replication in MARC-145 cells via activation of IFIT3. Antivir. Res. 2013, 99, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, P.; Shabir, N.; Khatun, A.; Seo, B.J.; Gu, S.; Lee, S.M.; Lim, S.K.; Kim, K.S.; Kim, W.I. Effect of polymorphisms in the GBP1, Mx1 and CD163 genes on host responses to PRRSV infection in pigs. Vet. Microbiol. 2016, 182, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Liang, S.; Liu, H.; Sun, Y.; Kang, L.; Jiang, Y. Identification of a short interspersed repetitive element insertion polymorphism in the porcine MX1 promoter associated with resistance to porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus infection. Anim. Genet. 2015, 46, 437–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Song, Z.; Bai, J.; Liu, X.; Nauwynck, H.; Jiang, P. ZAP, a CCCH-Type Zinc Finger Protein, Inhibits Porcine Reproductive and Respiratory Syndrome Virus Replication and Interacts with Viral Nsp9. J. Virol. 2019, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jing, H.; Song, T.; Cao, S.; Sun, Y.; Wang, J.; Dong, W.; Zhang, Y.; Ding, Z.; Wang, T.; Xing, Z.; et al. Nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain-like receptor X1 restricts porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus-2 replication by interacting with viral Nsp9. Virus Res. 2019, 268, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, J.; Wang, H.; Bai, J.; Zhang, Q.; Li, Y.; Liu, F.; Jiang, P. Monkey Viperin Restricts Porcine Reproductive and Respiratory Syndrome Virus Replication. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0156513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chang, X.; Shi, X.; Zhang, X.; Wang, L.; Li, X.; Wang, A.; Deng, R.; Zhou, E.; Zhang, G. IFI16 Inhibits Porcine Reproductive and Respiratory Syndrome Virus 2 Replication in a MAVS-Dependent Manner in MARC-145 Cells. Viruses 2019, 11, 1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ke, W.; Fang, L.; Jing, H.; Tao, R.; Wang, T.; Li, Y.; Long, S.; Wang, D.; Xiao, S. Cholesterol 25-Hydroxylase Inhibits Porcine Reproductive and Respiratory Syndrome Virus Replication through Enzyme Activity-Dependent and -Independent Mechanisms. J. Virol. 2017, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sang, Y.; Rowland, R.R.; Blecha, F. Interaction between innate immunity and porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus. Anim. Health Res. Rev. 2011, 12, 149–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, N.; Ye, M.; Huang, Y.; Li, S.; Xiao, Y.; Li, X.; Li, S.; Li, X.; Yu, X.; Tian, K.; et al. Identification of Two Porcine Reproductive and Respiratory Syndrome Virus Variants Sharing High Genomic Homology but with Distinct Virulence. Viruses 2019, 11, 875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ao, D.; Li, S.; Jiang, S.; Luo, J.; Chen, N.; Meurens, F.; Zhu, J. Inter-relation analysis of signaling adaptors of porcine innate immune pathways. Mol. Immunol. 2020, 121, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Ao, D.; Ni, J.; Chen, N.; Meurens, F.; Zhu, J. The signaling relations between three adaptors of porcine C-type lectin receptor pathway. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2020, 104, 103555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, N.; Li, S.; Li, X.; Ye, M.; Xiao, Y.; Yan, X.; Li, X.; Zhu, J. The infectious cDNA clone of commercial HP-PRRS JXA1-R-attenuated vaccine can be a potential effective live vaccine vector. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2020, 67, 1820–1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murtaugh, M.P.; Genzow, M. Immunological solutions for treatment and prevention of porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome (PRRS). Vaccine 2011, 29, 8192–8204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loving, C.L.; Osorio, F.A.; Murtaugh, M.P.; Zuckermann, F.A. Innate and adaptive immunity against Porcine Reproductive and Respiratory Syndrome Virus. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2015, 167, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ullah, M.O.; Sweet, M.J.; Mansell, A.; Kellie, S.; Kobe, B. TRIF-dependent TLR signaling, its functions in host defense and inflammation, and its potential as a therapeutic target. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2016, 100, 27–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, M.; Sato, S.; Hemmi, H.; Hoshino, K.; Kaisho, T.; Sanjo, H.; Takeuchi, O.; Sugiyama, M.; Okabe, M.; Takeda, K.; et al. Role of adaptor TRIF in the MyD88-independent toll-like receptor signaling pathway. Science 2003, 301, 640–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, Y.; Du, T.; Shi, Y.; Zhang, A.; Zhang, C.; Diao, Y.; Jin, G.; Zhou, E.M. Synthetic Toll-like receptor 7 ligand inhibits porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus infection in primary porcine alveolar macrophages. Antivir. Res. 2016, 131, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sumpter, R., Jr.; Loo, Y.M.; Foy, E.; Li, K.; Yoneyama, M.; Fujita, T.; Lemon, S.M.; Gale, M., Jr. Regulating intracellular antiviral defense and permissiveness to hepatitis C virus RNA replication through a cellular RNA helicase, RIG-I. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 2689–2699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- He, D.; Overend, C.; Ambrogio, J.; Maganti, R.J.; Grubman, M.J.; Garmendia, A.E. Marked differences between MARC-145 cells and swine alveolar macrophages in IFNbeta-induced activation of antiviral state against PRRSV. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2011, 139, 57–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Xu, S.; Wang, J.; Luo, R.; Wang, D.; Xiao, S.; Fang, L.; Chen, H.; Jiang, Y. Porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus 3C protease cleaves the mitochondrial antiviral signalling complex to antagonize IFN-beta expression. J. Gen. Virol. 2015, 96, 3049–3058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, Y.; Ke, H.; Han, M.; Chen, N.; Fang, W.; Yoo, D. Nonstructural Protein 11 of Porcine Reproductive and Respiratory Syndrome Virus Suppresses Both MAVS and RIG-I Expression as One of the Mechanisms to Antagonize Type I Interferon Production. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0168314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iampietro, M.; Dumont, C.; Mathieu, C.; Spanier, J.; Robert, J.; Charpenay, A.; Dupichaud, S.; Dhondt, K.P.; Aurine, N.; Pelissier, R.; et al. Activation of cGAS/STING pathway upon paramyxovirus infection. iScience 2021, 24, 102519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Yang, J.; Zhu, Y.; Ji, X.; Wang, K.; Jiang, S.; Luo, J.; Wang, H.; Zheng, W.; Chen, N.; et al. Chicken DNA Sensing cGAS-STING Signal Pathway Mediates Broad Spectrum Antiviral Functions. Vaccines 2020, 8, 369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heim, V.J.; Stafford, C.A.; Nachbur, U. NOD Signaling and Cell Death. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2019, 7, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stehlik, C.; Fiorentino, L.; Dorfleutner, A.; Bruey, J.M.; Ariza, E.M.; Sagara, J.; Reed, J.C. The PAAD/PYRIN-family protein ASC is a dual regulator of a conserved step in nuclear factor kappaB activation pathways. J. Exp. Med. 2002, 196, 1605–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ruland, J.; Hartjes, L. CARD-BCL-10-MALT1 signalling in protective and pathological immunity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2019, 19, 118–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Primer Names | Primer Sequences (5′-3′) |
|---|---|
| PRRSV-N-F | CATGCCATGGATGCCAAATAACAACGGCAAGC |
| PRRSV-N-R | CCGCTCGAGTACTGAGGGTGATGCTGTGGC |
| Primer Names | Primer Sequences (5′-3′) * |
|---|---|
| XJ17-5 -PacI-F1 | AGCTCGTTAATTAATACATGACGTATAGGTGTTGGCT |
| XJ17-5 -AflII-R1 | CATAGGTGCTTAAGTTCATTACCACCTGTAACGGAT |
| XJ17-5 -AflII-F2 | ATCCGTTACAGGTGGTAATGAACTTAAGCACCTATG |
| XJ17-5 -AscI-R2 | CCTTTCTGGCGCGCCCGAAAC |
| XJ17-5 -AscI-F3 | GTTTCGGGCGCGCCAGAAAGG |
| XJ17-5 -1R3 | AGCGAGGAGGCTGGGACCATGCCGGCCTTTTTTTTT TTTTTTTTTTTTAATTACGGCCGCATGGTTCT |
| XJ17-5 -NotI-2R3 | ACAGGCGGCCGCGTCCCATTCGCCATTACCGAGGGG ACGGTCCCCTCGGAATGTTGCCCAGCCGGCGCCAGC GAGGAGGCTGGGACCAT # |
| siRNA Name | Primer Sequences (5′-3′) |
|---|---|
| TRIF-1022-F | CCACCUCUCCAAAUACCAATT |
| TRIF-1022-R | UUGGUAUUUGGAGAGGUGGTT |
| TRIF-1330-F | GCGAUAGACCACUCAGCUUTT |
| TRIF-1330-R | AAGCUGAGUGGUCUAUCGCTT |
| TRIF-1547-F | CCCAGAUCUUCGCUAGGAATT |
| TRIF-1547-R | UUCCUAGCGAAGAUCUGGGTT |
| MAVS-730-F | GCAGGGUCAGUUGUAUCUATT |
| MAVS-730-R | UAGAUACAACUGACCCUGCTT |
| MAVS-1028-F | CCAAUCCAGCACCAUCCAATT |
| MAVS-1028-R | UUGGAUGGUGCUGGAUUGGTT |
| MAVS-1364-F | GCCCAGAGGAGAAUGAGUATT |
| MAVS-1364-R | UACUCAUUCUCCUCUGGGCTT |
| STING-374-F | GCCUUUCGCAGGCACUGAATT |
| STING-374-R | UUCAGUGCCUGCGAAAGGCTT |
| STING-530-F | CCCGGAUUCAAACUUACAATT |
| STING-530-R | UUGUAAGUUUGAAUCCGGGTT |
| STING-713-F | GGGUUUACAGCAACAGCAUTT |
| STING-713-R | AUGCUGUUGCUGUAAACCCTT |
| NC-F | UUCUCCGAACGUGUCACG UTT |
| NC-R | ACGUGACACGUUCGGAGAATT |
| Primer Names | Primer Sequences (5′-3′) |
|---|---|
| PRRSV N-F | ATAACAACGGCAAGCAGCAG |
| PRRSV N-R | CTCTGGACTGGTTTTGTTG |
| M-MyD88-F | TCTCTCCAGGTGCCCATCAGAAG |
| M-MyD88-R | GCAAGGCGAGTCCAGAACCAAG |
| M-TRIF-F | AGTCGCCACTGCAACTTTCTGTAG |
| M-TRIF-R | GGCTGATGAAGGAGGAGGAGGAG |
| M-MAVS-F | CCCGAAAGTGCCTGCCAACC |
| M-MAVS-R | TTGGATGGTGCTGGATTGGTGAAC |
| M-RIPK2-F | CCCTGCCAGTTCCTCAAGACAATG |
| M-RIPK2-R | AGCCCTTTGAGACGCAGAAATGG |
| M-ASC-F | GATGCCATCGACCTCACTGACAAG |
| M-ASC-R | TCCGCCACCTCCTTCATGCC |
| M-CARD9-F | ACTTCCACTTCCGTCTGCCTCTC |
| M-CARD9-R | CCACAGTCCCGCCAGTCCTC |
| M-BCL10-F | CCAGATGGAGCCACGAACAACC |
| M-BCL10-R | GGATGGTACATGACAGTGGATGCC |
| M-MALT1-F | CGAGGTTTGGGAAGGAAGACTTGC |
| M-MALT1-R | GTGATAATGCCCTGCTGCTCCTG |
| M-STING-F | TCGCTGTCCCAAGAGGTTCTCC |
| M-STING-R | GGGCACCGCTGAGTTCTTCAAG |
| M-β-actin-F | AGAAGATGACCCAGATCATGTTTGA |
| M-β-actin-R | TCCATCACGATGCCAGTGGTA |
| M-IFN-β-F | ATGGAGAAAGGACATTCTAACTGCAA |
| M-IFN-β-R | AGAAGCACAACAGGAGAGCAATTT |
| M-ISG15-F | CTCTGAGCATCCTGGTGAGGAA |
| M-ISG15-R | CGAAGGTCAGCCAGAACAGGT |
| M-IFIT1-F | TCAGGTCAAGGATAGTCTGGAGCA |
| M-IFIT1-R | TGTCTAGGAATTCAATCTGGTCCAA |
| M-TNF-α-F | CATGTTGTAGCAAACCCTCAAGC |
| M-TNF-α-R | ATGGCACCACCAGCTGGTTAT |
| S-IFN-β-F | TGAGCATTCTGCAGTACCTGA |
| S-IFN-β-R | CCGGAGGTAATCTGTAAGTCTGT |
| S-ISG56-F | ATGGGAGTTGGTCATTCAAGA |
| S-ISG56-R | CAGGTGTTTCACATAGGCCA |
| S-IL-8-F | CTGCAGTTCTGGCAAGAGTAAGT |
| S-IL-8-R | CACTCTCAATCACTCTCAGTTCCT |
| S-TNF-α-F | ATCGCCGTCTCCTACCAGA |
| S-TNF-α-R | TCGATCATCCTTCTCCAGCT |
| S-β-actin-F | ATGAAGATCAAGATCATCGCG |
| S-β-actin-R | TCGTACTCCTGCTTGCTGATC |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, Y.; Ye, M.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, S.; Luo, J.; Jiang, S.; Zhang, J.; Liu, X.; Shao, Q.; Cao, Q.; et al. Screening of Porcine Innate Immune Adaptor Signaling Revealed Several Anti-PRRSV Signaling Pathways. Vaccines 2021, 9, 1176. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines9101176
Xu Y, Ye M, Zhang Y, Sun S, Luo J, Jiang S, Zhang J, Liu X, Shao Q, Cao Q, et al. Screening of Porcine Innate Immune Adaptor Signaling Revealed Several Anti-PRRSV Signaling Pathways. Vaccines. 2021; 9(10):1176. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines9101176
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Yulin, Mengxue Ye, Youwen Zhang, Shaohua Sun, Jia Luo, Sen Jiang, Jiajia Zhang, Xueliang Liu, Qi Shao, Qi Cao, and et al. 2021. "Screening of Porcine Innate Immune Adaptor Signaling Revealed Several Anti-PRRSV Signaling Pathways" Vaccines 9, no. 10: 1176. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines9101176
APA StyleXu, Y., Ye, M., Zhang, Y., Sun, S., Luo, J., Jiang, S., Zhang, J., Liu, X., Shao, Q., Cao, Q., Zheng, W., Meurens, F., Chen, N., & Zhu, J. (2021). Screening of Porcine Innate Immune Adaptor Signaling Revealed Several Anti-PRRSV Signaling Pathways. Vaccines, 9(10), 1176. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines9101176









