Attenuation of Antibody Titers from 3 to 6 Months after the Second Dose of the BNT162b2 Vaccine Depends on Sex, with Age and Smoking Risk Factors for Lower Antibody Titers at 6 Months
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Population and Study Design
2.2. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Study Population
3.2. Distribution of Ab Titers against the SARS-CoV-2 Spike Sntigen 6 Sonths after the Second Dose of the BNT162b2 COVID-19 Vaccine by Age and Sex
3.3. Relationship between the Ab Titers against the SARS-CoV-2 Spike Antigen 6 Months after Vaccination and Risk Factors
3.4. Distribution of the Percentage Change in Ab Titers from 3 to 6 Months after the Second Dose of the BNT162b2 COVID-19 Vaccine by Age and Sex
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Nomura, Y.; Sawahata, M.; Nakamura, Y.; Kurihara, M.; Koike, R.; Katsube, O.; Hagiwara, K.; Niho, S.; Masuda, N.; Tanaka, T.; et al. Age and smoking predict antibody titres at 3 months after the second dose of the BNT162b2 COVID-19 vaccine. Vaccines 2021, 9, 1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perkmann, T.; Perkmann-Nagele, N.; Breyer, M.K.; Breyer-Kohansal, R.; Burghuber, O.C.; Hartl, S.; Aletaha, D.; Sieghart, D.; Quehenberger, P.; Marculescu, R.; et al. Side-by-side comparison of three fully automated SARS-CoV-2 antibody assays with a focus on specificity. Clin. Chem. 2020, 66, 1405–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kageyama, T.; Ikeda, K.; Tanaka, S.; Taniguchi, T.; Igari, H.; Onouchi, Y.; Kaneda, A.; Matsushita, K.; Hanaoka, H.; Nakada, T.; et al. Antibody responses to BNT162b2 mRNA COVID-19 vaccine and their predictors among healthcare workers in a tertiary referral hospital in Japan. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2021, 27, 1861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callegaro, A.; Borleri, D.; Farina, C.; Napolitano, G.; Valenti, D.; Rizzi, M.; Maggiolo, F. Antibody response to SARS-CoV-2 vaccination is extremely vivacious in subjects with previous SARS-CoV-2 infection. J. Med. Virol. 2021, 93, 4612–4615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller, L.; Andrée, M.; Moskorz, W.; Drexler, I.; Walotka, L.; Grothmann, R.; Ptok, J.; Hillebrandt, J.; Ritchie, A.; Rabl, D.; et al. Age-dependent immune response to the Biontech/Pfizer BNT162b2 COVID-19 vaccination. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2021, 73, 2065–2072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terpos, E.; Trougakos, I.P.; Apostolakou, F.; Charitaki, I.; Sklirou, A.D.; Mavrianou, N.; Papanagnou, E.-D.; Liacos, C.-I.; Gumeni, S.; Rentziou, G.; et al. Age-dependent and gender-dependent antibody responses against SARS-CoV-2 in health workers and octogenarians after vaccination with the BNT162b2 mRNA vaccine. Am. J. Hematol. 2021, 96, 257–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kennedy, N.A.; Lin, S.; Goodhand, J.R.; Chanchlani, N.; Hamilton, B.; Bewshea, C.; Nice, R.; Chee, D.; Cummings, J.F.; Fraser, A.; et al. Infliximab is associated with attenuated immunogenicity to BNT162b2 and ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 SARS-CoV-2 vaccines in patients with IBD. Gut 2021, 70, 1884–1893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, J.; Stoesser, N.; Matthews, P.C.; Ayoubkhani, D.; Studley, R.; Bell, I.; Bell, J.I.; Newton, J.N.; Farrar, J.; Diamond, I.; et al. COVID-19 Infection Survey team. Antibody responses to SARS-CoV-2 vaccines in 45,965 adults from the general population of the United Kingdom. Nat. Microbiol. 2021, 6, 1140–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ledford, H. How obesity could create problems for a COVID vaccine. Nature 2020, 586, 488–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watanabe, M.; Balena, A.; Tuccinardi, D.; Tozzi, R.; Risi, R.; Masi, D.; Caputi, A.; Rossetti, R.; Spoltore, M.E.; Filippi, V.; et al. Central obesity, smoking habit, and hypertension are associated with lower antibody titres in response to COVID-19 mRNA vaccine. Diabetes Metab. Res. Rev. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collier, D.A.; Ferreira, I.A.T.M.; Kotagiri, P.; Datir, R.P.; Lim, E.Y.; Touizer, E.; Meng, B.; Abdullahi, A.; Elmer, A.; Kingston, N.; et al. Age-related immune response heterogeneity to SARS-CoV-2 vaccine BNT162b2. Nature 2021, 596, 417–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monin-Aldama, L.; Laing, A.G.; Muñoz-Ruiz, M.; McKenzie, D.R.; del Molino del Barrio, I.; Alaguthurai, T.; Domingo-Vila, C.; Hayday, T.S.; Graham, C.; Cooper, J.; et al. Interim results of the safety and immune-efficacy of 1 versus 2 doses of COVID-19 vaccine BNT162b2 for cancer patients in the context of the UK vaccine priority guidelines. medRxiv 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergwerk, M.; Gonen, T.; Lustig, Y.; Amit, S.; Lipsitch, M.; Cohen, C.; Mandelboim, M.; Levin, E.G.; Rubin, C.; Indenbaum, V.; et al. Covid-19 Breakthrough Infections in Vaccinated Health Care Workers. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 1474–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- L’Huillier, A.G.; Meyer, B.; Andrey, D.O.; Vernez, I.A.; Baggio, S.; Didierlaurent, A.; Eberhardt, C.S.; Eckerle, I.; Salomon, C.G.; Huttner, A.; et al. Antibody persistence in the first 6 months following SARS-CoV-2 infection among hospital workers: A prospective longitudinal study. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2021, 27, 784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naaber, P.; Tserel, L.; Kangro, K.; Sepp, E.; Jürjenson, V.; Adamson, A.; Haljasmägi, L.; Rumm, A.P.; Maruste, R.; Maruste, R.; et al. Dynamics of antibody response to BNT162b2 vaccine after six months: A longitudinal prospective study. Lancet Reg. Health Eur. 2021, 10, 100208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacKenzie, J.S.; MacKenzie, I.H.; Holt, P.G. The effect of cigarette smoking on susceptibility to epidemic influenza and on serological responses to live attenuated and killed subunit influenza vaccines. J. Hyg. 1976, 77, 409–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zimmermann, P.; Curtis, N. Factors that influence the immune response to vaccination. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2019, 32, e00084-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
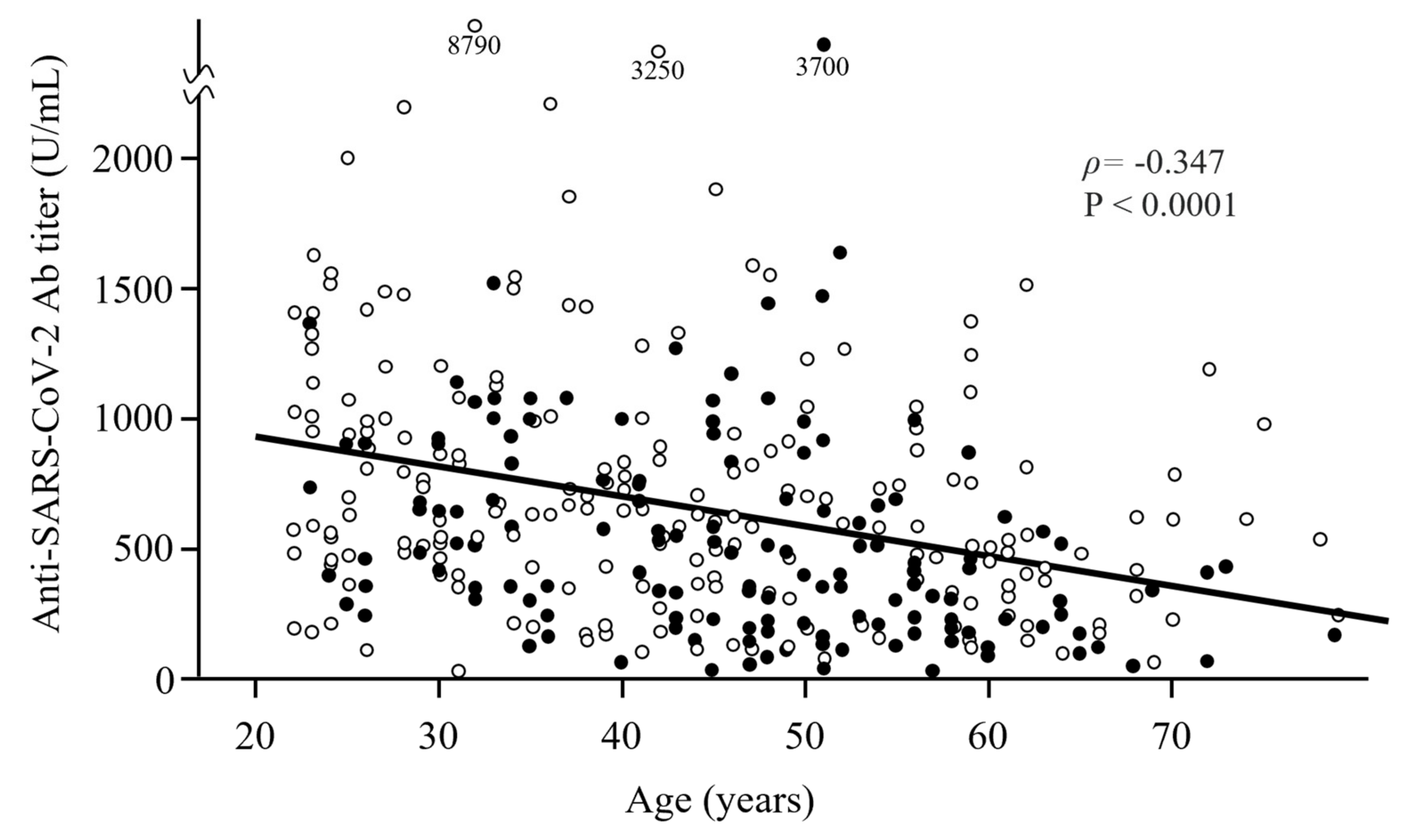

| Variable | Total | Ab Titer at 6 Months, Median (IQR), U/mL | Correlation Coefficient ρ | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age, median (IQR), y | 44 (32–54) | −0.347 | <0.0001 # | |
| Sex (M/F), n | 115/250 | 482 (305 to 865)/572 (316 to 884) | 0.1970 * | |
| Body mass index, median (IQR), kg/m2 | 22.4 (20.2–24.8) | −0.017 | 0.7446 # | |
| Smoking (ever/never), n | 149/216 | 406 (213 to 688)/614 (405 to 957) | <0.0001 * | |
| Current smoker/ex-smoker/unknown | 90/45/14 | 354 (174 to 564)/436 (225 to 894) §§ | 0.0609 * | |
| ex-smoker vs. never-smoker | 0.0014 * | |||
| current smoker vs. never-smoker | <0.0001 * | |||
| Brinkman Index §§, §§§, n | 129 | −0.197 | 0.0258 # | |
| Drinking, n | 228/134/3 § | 544 (299 to 881)/536 (348 to 868) §§ | 0.7697 * | |
| Allergy, n | ||||
| Food | 38/292/35 § | 515 (307 to 925)/544 (318 to 807) §§ | 0.7697 * | |
| Drug | 37/293/35 § | 517 (287 to 759)/549 (321 to 833) §§ | 0.5858 * | |
| Allergic disease, n | ||||
| Allergic rhinitis including pollinosis | 167/175/23 § | 546 (258 to 895)/523 (320 to 792) §§ | 0.8242 * | |
| Bronchial asthma | 43/299/23 § | 582 (360 to 885)/522 304 to 837) §§ | 0.5643 * | |
| Skin allergy including atopic dermatitis | 47/295/23 § | 641(380 to 1005)/522(303 to 815) §§ | 0.0710 * | |
| Diabetes mellitus, n | 12/340/13 § | 331 (149 to 589)/540 (318 to878) §§ | 0.0512 * | |
| Hypertension, n | 27/325/13 § | 356 (195 to 566)/553 (321to 872) §§ | 0.0327 * | |
| Dyslipidemia, n | 18/334/13 § | 351 (205to 698)/544 (317 to 877) §§ | 0.0834 * | |
| Collagen disease, n | 13/332/20 § | 303 (126 to 840)/544 (324 to 843) §§ | 0.2695 * |
| Variable | Ab Titer at 6 Months, Median (IQR), U/mL | Correlation Coefficient ρ | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Male/female | −15 (−246 to 241)/8 (−209 to 290) | 0.2851 * | |
| Body mass index, median (IQR), kg/m2 | 0.023 | 0.6647 # | |
| Smoking (ever/never) | −97 (−277 to 184)/56 (−182 to 342) | <0.0001 * | |
| Current smoker/ex-smoker | −205 (−320 to 7)/−72 (−264 to 256) | 0.0255 * | |
| ex-smoker vs. never-smoker | 0.0203 * | ||
| current smoker vs. never-smoker | <0.0001 * | ||
| Brinkman Index §§, §§§ | 0.012 | 0.8935 # | |
| Drinking | 3 (−242 to 296)/5 (−205 to 249) §, §§ | 0.6475 * | |
| Allergy | |||
| Food | 18 (−250 to 235)/−2 (−223 to 256) §, §§ | 0.9604 * | |
| Drug | −4 (−131 to 271)/−1 (−238 to 251) §, §§ | 0.5858 * | |
| Allergic disease | |||
| Allergic rhinitis including pollinosis | −7 (−240 to 271)/−1 (−223 to 253) §, §§ | 0.8473 * | |
| Bronchial asthma | 30 (−223 to 254)/−8 (−239 to 263) §, §§ | 0.7390 * | |
| Skin allergy including atopic dermatitis | 61 (−166 to 421)/−9 (−240 to 248) §, §§ | 0.1638 * | |
| Diabetes mellitus | −60 (−269 to 77)/0 (−225 to 272) §, §§ | 0.4696 * | |
| Hypertension | −69 (−247 to 183)/0 (−225 to 271) §, §§ | 0.6409 * | |
| Dyslipidemia | −56 (−220 to 259)/0 (−232 to 268) §, §§ | 0.7392 * | |
| Collagen disease | −227 (−368 to 290)/0 (−222 to 261) §, §§ | 0.3021 * |
| Variable | Percentage Change in Ab Titers, Median (IQR), % § | Correlation Coefficient ρ | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age | −0.028 | 0.5876 # | |
| Male/female | −25.1 (−36.8 to −12.0)/−31.6 (−42.0 to −20.2) | 0.0005 * | |
| Body mass index, median (IQR), kg/m2 | 0.025 | 0.6274 # | |
| Smoking (ever/never) | −28.4 (−39.7 to −15.5)/−30.3 (−40.7 to −19.0) | 0.3051 * | |
| Current smoker/ex-smoker | −31.7 (−40.6 to −18.3)/−27.4 (−40.1 to −16.1) §§ | 0.3853 * | |
| ex-smoker vs. never-smoker | 0.2914 * | ||
| current smoker vs. never-smoker | 0.8809 * | ||
| Brinkman Index §§, §§§ | −0.034 | 0.6990 # | |
| Drinking | −29.1(−41.0 to −17.8)/−30.5(−39.1 to −18.1) §, §§ | 0.777 * | |
| Allergy | |||
| Food | −29.4 (−37.1 to −16.5)/−29.4 (−39.9 to −18.6) §, §§ | 0.7821 * | |
| Drug | −28.8 (−40.7 to −22.6)/−29.7 (−39.3 to −18.3) §, §§ | 0.7469 * | |
| Allergic disease | |||
| Allergic rhinitis including pollinosis | −29.2 (−40.9 to −18.1)/−29.6 (−39.6 to −18.0) §, §§ | 0.8606 * | |
| Bronchial asthma | −31.7 (−40.5 to −19.4)/−29.1 (−40.5 to −17.6) §, §§ | 0.5521 * | |
| Skin allergy including atopic dermatitis | −30.3 (−44.6 to −25.1)/−29.1 (−39.7 to −17.6) §, §§ | 0.1677 * | |
| Diabetes mellitus | −27.6 (−32.8 to −11.4)/−29.4 (−40.5 to −18.0) §, §§ | 0.3617 * | |
| Hypertension | −24.0 (−32.1 to −12.3)/−29.7 (−40.8 to −18.0) §, §§ | 0.0679 * | |
| Dyslipidemia | −31.7 (−39.2 to −22.8)/−29.3 (−40.5 to −17.7) §, §§ | 0.7178 * | |
| Collagen disease | −27.0 (−48.6 to −19.1)/−29.6 (−40.3 to −17.9) §, §§ | 0.889 * |
| Variable | Male n, Ab, Median (IQR), U/mL Percentage Change, Median (IQR), % | Female n, Ab, Median (IQR), U/mL Percentage Change, Median (IQR), % | p-Value for Ab Titer Percentage Change |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ever-smokers | 70 | 79 | |
| −120 (−266 to 152) | −68 (−278 to 193) | 0.5709 * | |
| −25.9% (−38.0 to −12.0) | −30.5% (−42.0 to −18.7) | 0.0400 * | |
| Never-smokers | 45 | 171 | |
| 115 (−181 to 519) | 46 (−181 to 332) | 0.4700 * | |
| −24.0% (−34.0 to −12.1) | −31.7% (−42.1 to −20.9) | 0.0050 * | |
| p-value for | |||
| Ab titer | 0.0040 * | 0.0120 * | |
| Percentage change | 0.7613 * | 0.7018 * |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nomura, Y.; Sawahata, M.; Nakamura, Y.; Koike, R.; Katsube, O.; Hagiwara, K.; Niho, S.; Masuda, N.; Tanaka, T.; Sugiyama, K. Attenuation of Antibody Titers from 3 to 6 Months after the Second Dose of the BNT162b2 Vaccine Depends on Sex, with Age and Smoking Risk Factors for Lower Antibody Titers at 6 Months. Vaccines 2021, 9, 1500. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines9121500
Nomura Y, Sawahata M, Nakamura Y, Koike R, Katsube O, Hagiwara K, Niho S, Masuda N, Tanaka T, Sugiyama K. Attenuation of Antibody Titers from 3 to 6 Months after the Second Dose of the BNT162b2 Vaccine Depends on Sex, with Age and Smoking Risk Factors for Lower Antibody Titers at 6 Months. Vaccines. 2021; 9(12):1500. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines9121500
Chicago/Turabian StyleNomura, Yushi, Michiru Sawahata, Yosikazu Nakamura, Ryousuke Koike, Otohiro Katsube, Koichi Hagiwara, Seiji Niho, Norihiro Masuda, Takaaki Tanaka, and Kumiya Sugiyama. 2021. "Attenuation of Antibody Titers from 3 to 6 Months after the Second Dose of the BNT162b2 Vaccine Depends on Sex, with Age and Smoking Risk Factors for Lower Antibody Titers at 6 Months" Vaccines 9, no. 12: 1500. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines9121500
APA StyleNomura, Y., Sawahata, M., Nakamura, Y., Koike, R., Katsube, O., Hagiwara, K., Niho, S., Masuda, N., Tanaka, T., & Sugiyama, K. (2021). Attenuation of Antibody Titers from 3 to 6 Months after the Second Dose of the BNT162b2 Vaccine Depends on Sex, with Age and Smoking Risk Factors for Lower Antibody Titers at 6 Months. Vaccines, 9(12), 1500. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines9121500






