Non-Lethal Sequential Individual Monitoring of Viremia in Relation to DNA Vaccination in Fish–Example Using a Salmon Alphavirus DNA Vaccine in Atlantic Salmon Salmo salar
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. DNA Vaccine
2.2. Ethical Statement
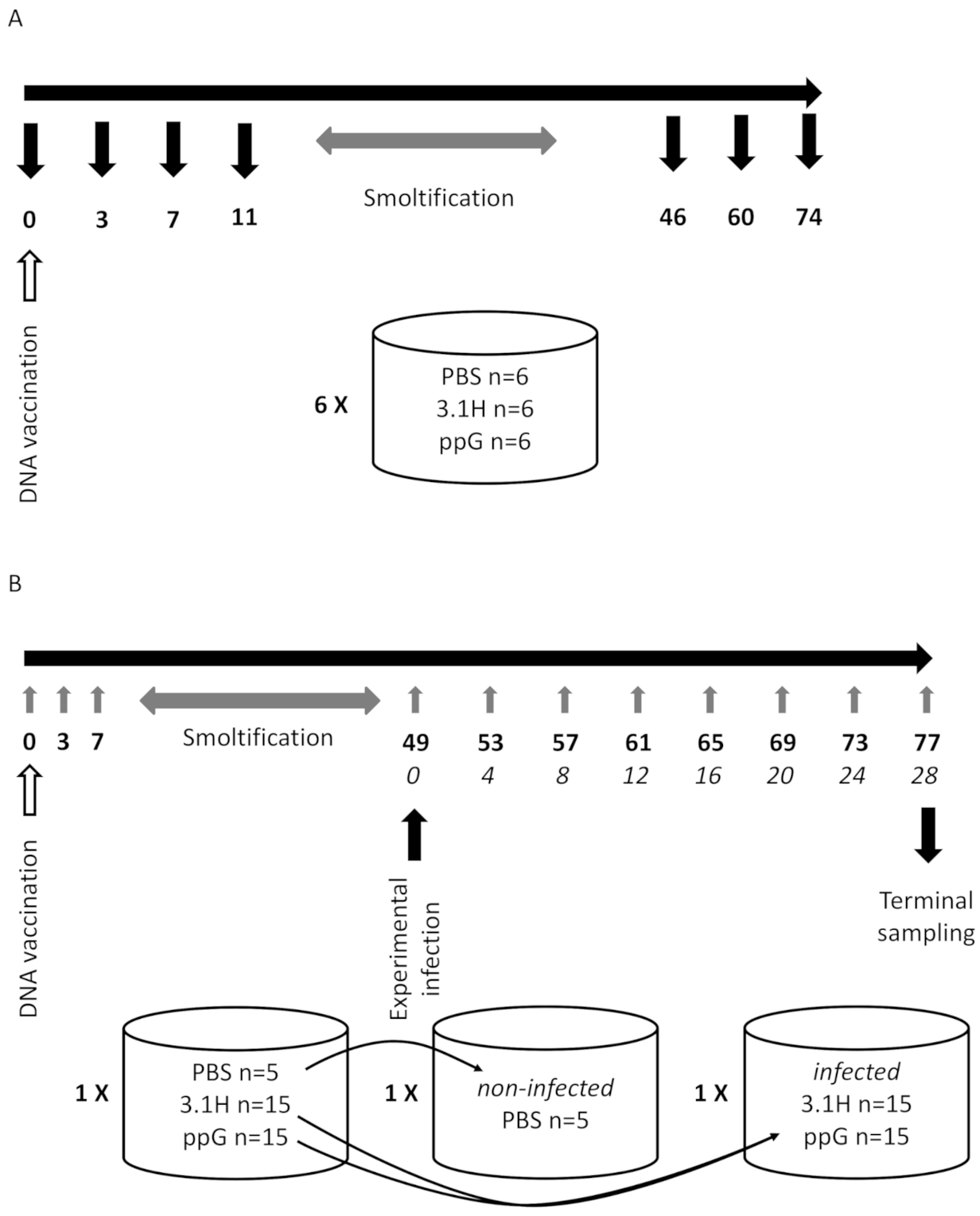
2.3. Experiment 1—Host Immune Response Following DNA Vaccination (Fish Not Challenged—Lethal Sampling)
2.4. Experiment 2—Non-Lethal Sampling, Vaccination Followed by Immersion Challenge
2.4.1. Vaccination
2.4.2. SPDv Challenge
2.5. Measurement of Viremia and Neutralising Antibodies by RTG-P1 Assay (Experiment 2)
2.6. SPDv Re-Isolation and Confirmation from Plasma Samples (Experiment 2)
2.7. Heart and Muscle Histopathology Scoring (Experiment 2)
2.8. RNA Extraction and Gene Expression (Immune Gene, Virus Load, Plasmid Load; Experiment 1 and/or 2)
2.9. Data and Statistical Analyses
3. Results
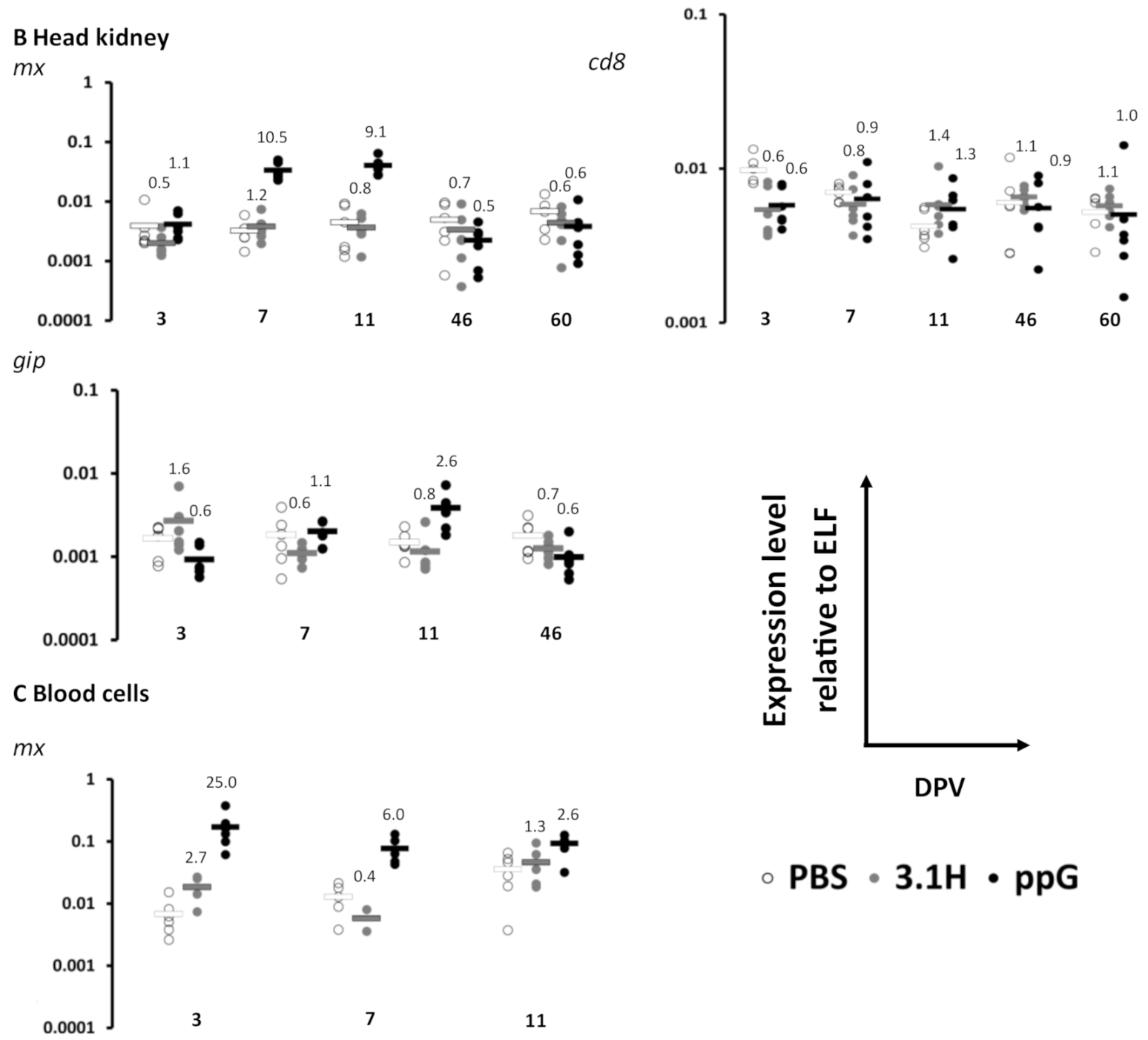
3.1. Immune Gene Expression Following Vaccination-Experiment 1 (Lethal Sampling)
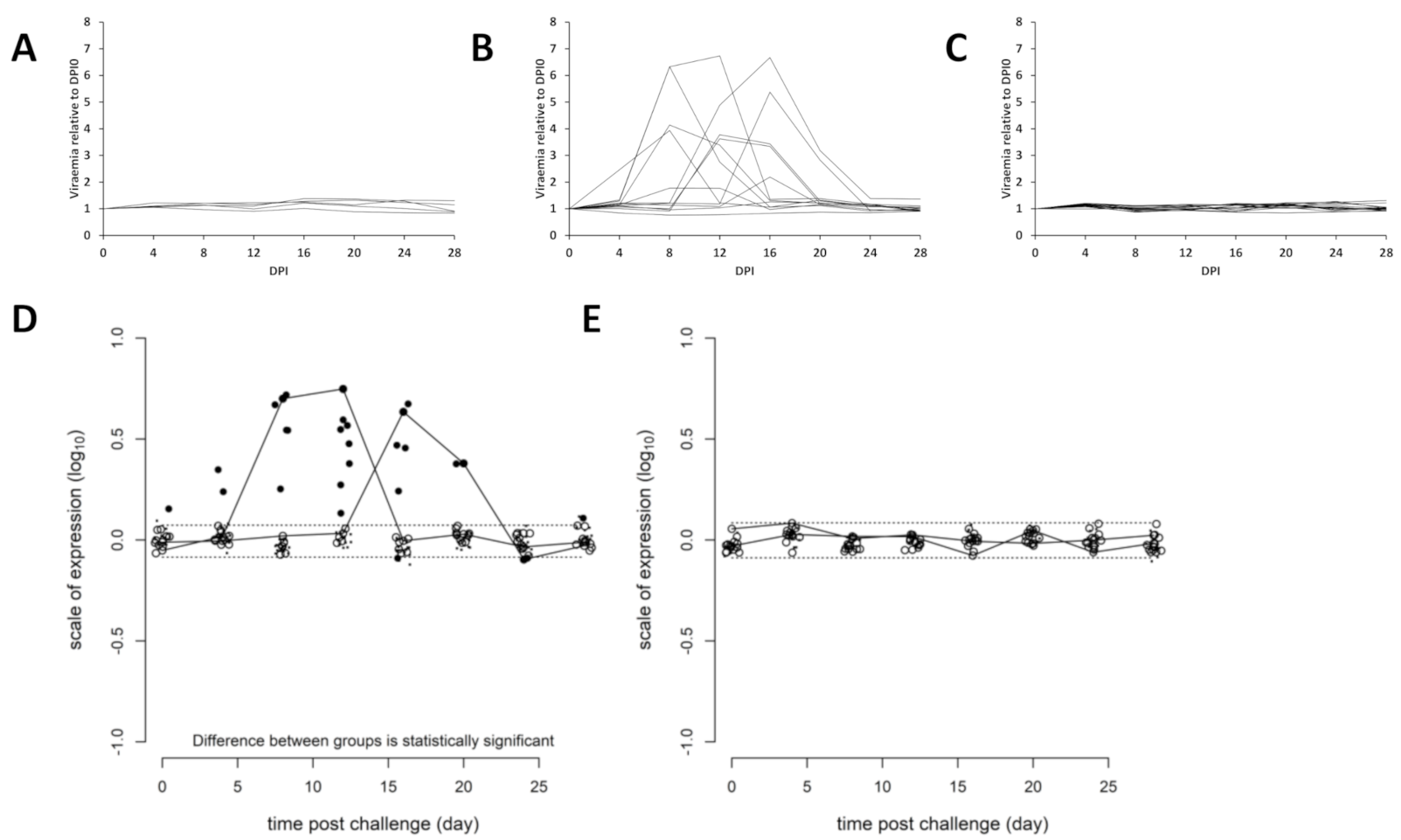
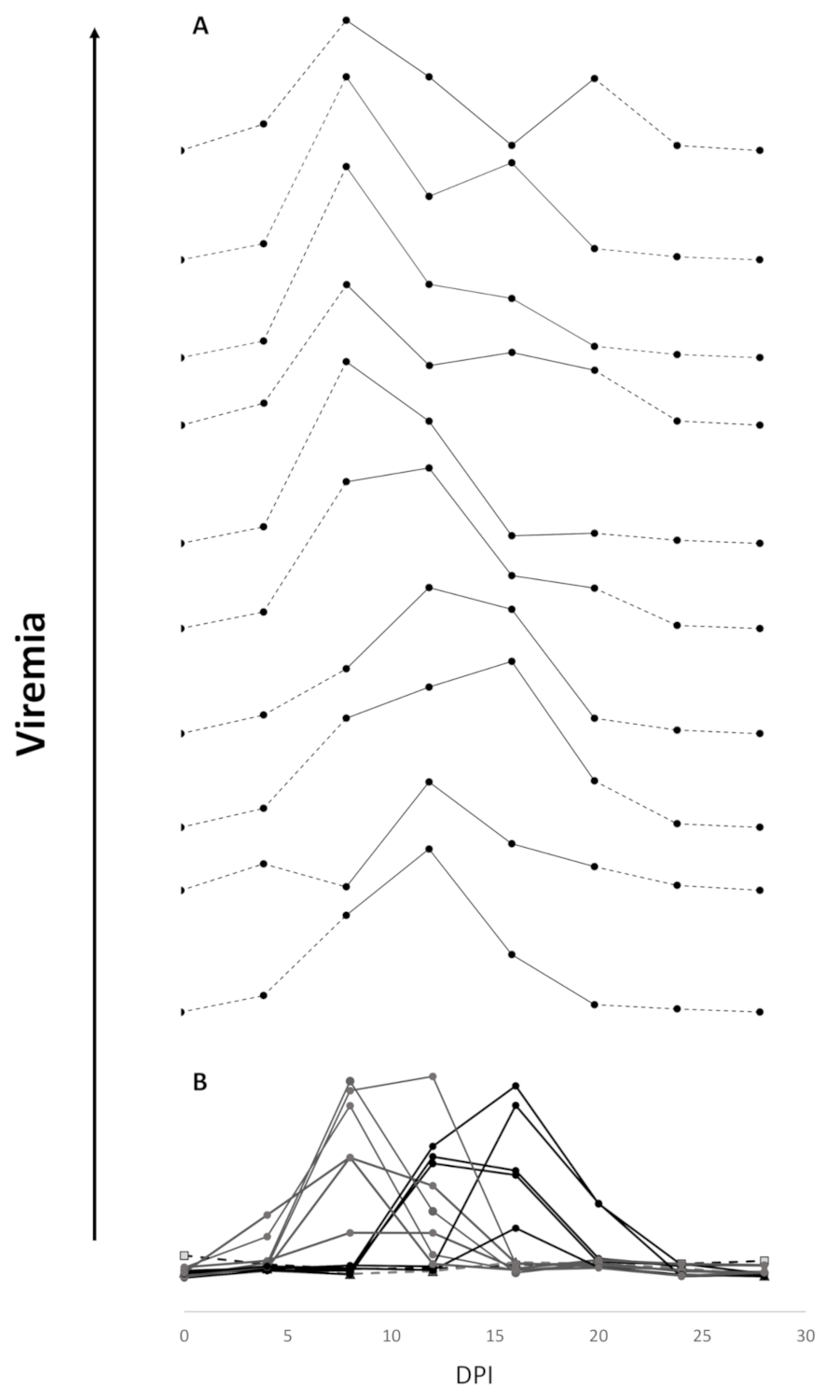
3.2. Efficacy of Sea Water Immersion Challenge and SPDv ppG DNA Vaccination–Experiment 2
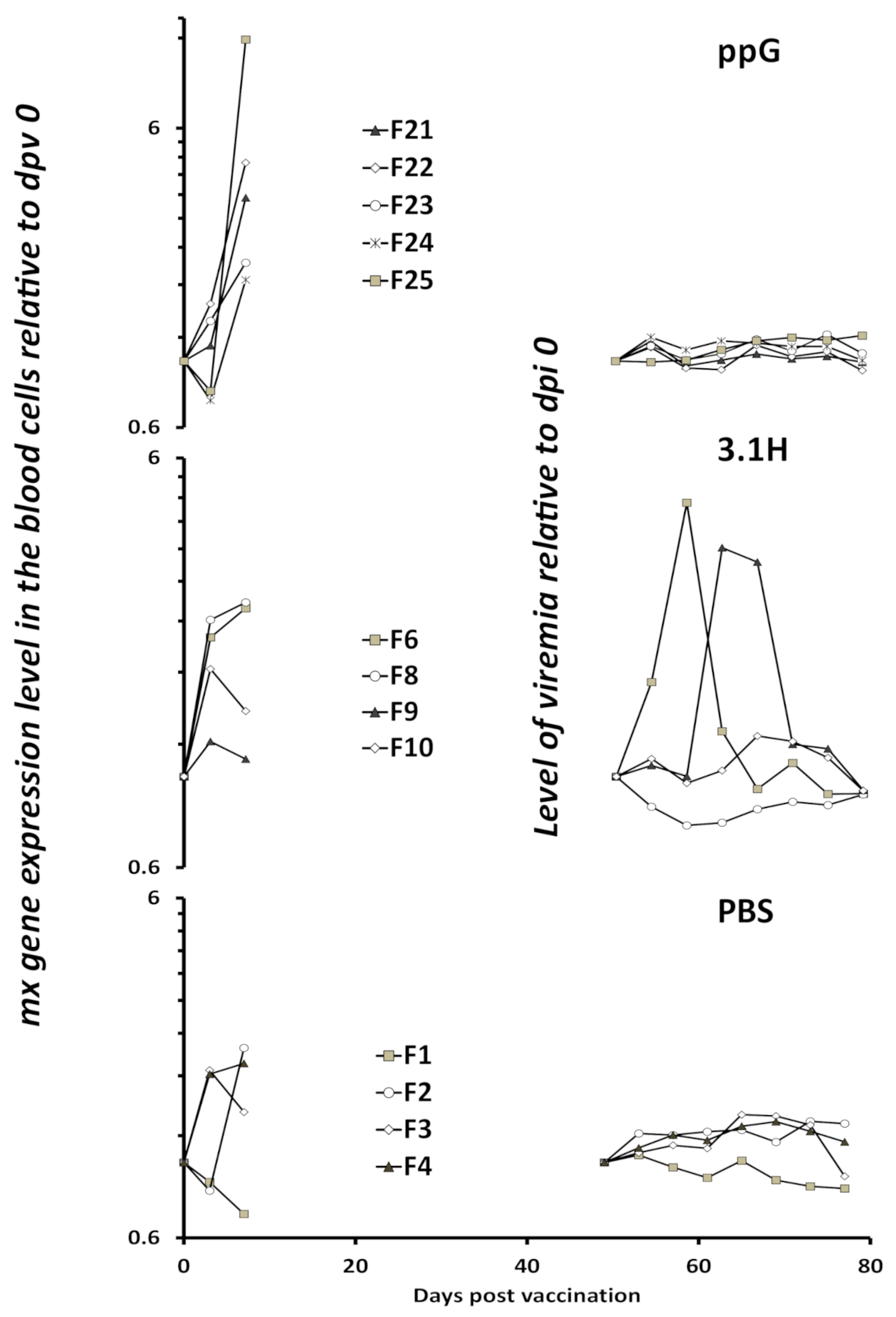
3.3. Viremia and Mx Gene Expression in Blood Cells–Experiment 2
3.4. Presence of SPDv Plasma Neutralising Antibodies—Experiment 2
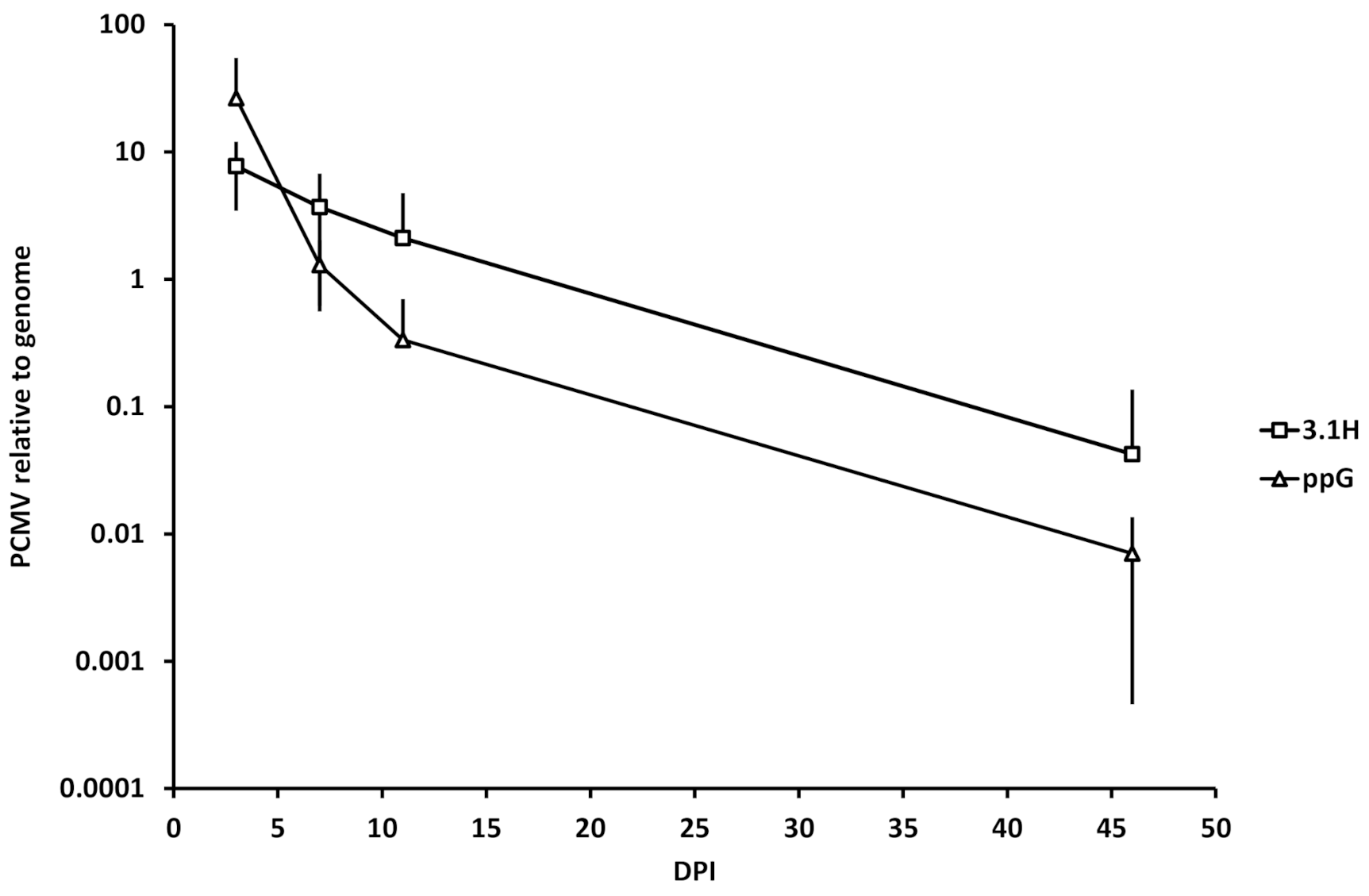
3.5. Kinetics of Plasmid Amount at the Site of Injection (Experiment 1)
4. Discussion
4.1. Viremia as a Proxy for Vaccine Efficacy
4.2. Viremia Kinetics
4.3. Plasma Neutralisation Levels
4.4. Plasmid Decay at the Site of Injection
4.5. Immersion SPDv Challenge
4.6. Early Type I Interferon and Later Vaccinal Protection
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jansen, M.D.; Jensen, B.B.; McLoughlin, M.F.; Rodger, H.D.; Taksdal, T.; Sindre, H.; Graham, D.A.; Lillehaug, A. The epidemiology of pancreas disease in salmonid aquaculture: Asummary of the current state of knowledge. J. Fish Dis. 2016, 40, 141–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brudeseth, B.E.; Wiulsrød, R.; Fredriksen, B.N.; Lindmo, K.; Løkling, K.-E.; Bordevik, M.; Steine, N.; Klevan, A.; Gravningen, K. Status and future perspectives of vaccines for industrialised fin-fish farming. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2013, 35, 1759–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evensen, Ø.; Leong, J.-A.C. DNA vaccines against viral diseases of farmed fish. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2013, 35, 1751–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hølvold, L.B.; Myhr, A.I.; Dalmo, R.A. Strategies and hurdles using DNA vaccines to fish. Veter. Res. 2014, 45, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lund, V.; Espelid, S.; Mikkelsen, H. Vaccine efficacy in spotted wolffish Anarhichas minor: Relationship to molecular variation in A-layer protein of atypical Aeromonas salmoncida. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2003, 56, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hikke, M.C.; Braaen, S.; Villoing, S.; Hodneland, K.; Geertsema, C.; Verhagen, L.; Frost, P.; Vlak, J.M.; Rimstad, E.; Pijlman, G. Salmonid alphavirus glycoprotein E2 requires low temperature and E1 for virion formation and induction of protective immunity. Vaccine 2014, 32, 6206–6212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, C.; Lorenzen, N.; Collet, B. DNA vaccination for finfish aquaculture. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019, 85, 106–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, M.; Collins, C.; Collet, B. The potential benefits of repeated measure experiments for fish disease-challenge host-pathogen investigations. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019, 85, 126–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collet, B.; Urquhart, K.; Monte, M.; Collins, C.; Perez, S.G.; Secombes, C.J.; Hall, M. Individual Monitoring of Immune Response in Atlantic Salmon Salmo salar following Experimental Infection with Infectious Salmon Anaemia Virus (ISAV). PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0137767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Monte, M.; Urquhart, K.; Evensen, Ø.; Secombes, C.J.; Collet, B. Individual monitoring of immune response in Atlantic salmon Salmo salar following experimental infection with piscine myocarditis virus (PMCV), agent of cardiomyopathy syndrome (CMS). Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2019, 99, 103406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teige, L.H.; Aksnes, I.; Røsæg, M.V.; Jensen, I.; Jørgensen, J.; Sindre, H.; Collins, C.; Collet, B.; Rimstad, E.; Dahle, M.K.; et al. Detection of specific Atlantic salmon antibodies against salmonid alphavirus using a bead-based immunoassay. Fish Shellfish. Immunol. 2020, 106, 374–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collet, B.; Urquhart, K.; Noguera, P.; Larsen, K.H.; Lester, K.; Smail, D.; Bruno, D. A method to measure an indicator of viraemia in Atlantic salmon using a reporter cell line. J. Virol. Methods 2013, 191, 113–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moriette, C.; Leberre, M.; Boscher, S.K.; Castric, J.; Brémont, M. Characterization and mapping of monoclonal antibodies against the Sleeping disease virus, an aquatic alphavirus. J. Gen. Virol. 2005, 86, 3119–3127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graham, D.A.; Frost, P.; McLaughlin, K.; Rowley, H.M.; Gabestad, I.; Gordon, A.; McLoughlin, M.F. A comparative study of marine salmonid alphavirus subtypes 1-6 using an experimental cohabitation challenge model. J. Fish Dis. 2011, 34, 273–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collet, B.; Collins, C. Comparative gene expression profile in two Atlantic salmon cell lines TO and SHK-1. Veter. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2009, 130, 92–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McBeath, A.J.; Snow, M.; Secombes, C.; Ellis, A.; Collet, B. Expression kinetics of interferon and interferon-induced genes in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) following infection with infectious pancreatic necrosis virus and infectious salmon anaemia virus. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2007, 22, 230–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodneland, K.; Endresen, C. Sensitive and specific detection of Salmonid alphavirus using real-time PCR (TaqMan®). J. Virol. Methods 2006, 131, 184–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruno, D.; Collet, B.; Turnbull, A.; Kilburn, R.; Walker, A.; Pendrey, D.; McIntosh, A.; Urquhart, K.; Taylor, G. Evaluation and development of diagnostic methods for Renibacterium salmoninarum causing bacterial kidney disease (BKD) in the UK. Aquaculture 2007, 269, 114–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjamini, Y.; Hochberg, Y. Controlling the False Discovery Rate—A Practical and Powerful Approach to Multiple Testing. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B Methodol. 1995, 57, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.J.; Gu, J.; Robertsen, B. Protective effect and antibody response of DNA vaccine against salmonid alphavirus 3 (SAV3) in Atlantic salmon. J. Fish Dis. 2017, 40, 1775–1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, C.-J.; Sun, B.; Robertsen, B. Adjuvant activity of fish type I interferon shown in a virus DNA vaccination model. Vaccine 2015, 33, 2442–2448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chang, C.-J.; Robertsen, C.; Sun, B.; Robertsen, B. Protection of Atlantic salmon against virus infection by intramuscular injection of IFNc expression plasmid. Vaccine 2014, 32, 4695–4702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Skjold, P.; Sommerset, I.; Frost, P.; Villoing, S. Vaccination against pancreas disease in Atlantic salmon, Salmo salar L., reduces shedding of salmonid alphavirus. Veter. Res. 2016, 47, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlsen, M.; Tingbø, T.; Solbakk, I.-T.; Evensen, Ø.; Furevik, A.; Aas-Eng, A. Efficacy and safety of an inactivated vaccine against Salmonid alphavirus (family Togaviridae). Vaccine 2012, 30, 5688–5694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- McLoughlin, M.F.; Nelson, R.; Rowley, H.; Cox, D.; Grant, A. Experimental pancreas disease in Atlantic salmon Salmo salar post-smolts induced by salmon pancreas disease virus (SPDV). Dis. Aquat. Org. 1996, 26, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jarungsriapisit, J.; Moore, L.J.; Taranger, G.L.; Nilsen, T.O.; Morton, H.C.; Fiksdal, I.U.; Stefansson, S.; Fjelldal, P.G.; Evensen, Ø.; Patel, S. Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.) post-smolts challenged two or nine weeks after seawater-transfer show differences in their susceptibility to salmonid alphavirus subtype 3 (SAV3). Virol. J. 2016, 13, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Urquhart, K.; Collins, C.; Monte, M.; Sokolowska, J.; Secombes, C.; Collet, B. Individual measurement of gene expression in blood cells from Rainbow trout Oncorhynchus mykiss (Walbaum). J. Exp. Appl. Anim. Sci. 2016, 2, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chance, R.J.; Cameron, G.A.; Fordyce, M.; Noguera, P.; Wang, T.; Collins, C.; Secombes, C.J.; Collet, B. Effects of repeated anaesthesia on gill and general health of Atlantic salmon, Salmo salar. J. Fish Biol. 2018, 93, 1069–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rosati, M.; Von Gegerfelt, A.; Roth, P.; Alicea, C.; Valentin, A.; Robert-Guroff, M.; Venzon, D.; Montefiori, D.C.; Markham, P.; Felber, B.K.; et al. DNA Vaccines Expressing Different Forms of Simian Immunodeficiency Virus Antigens Decrease Viremia upon SIVmac251 Challenge. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 8480–8492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Belisle, S.E.; Yin, J.; Shedlock, D.J.; Dai, A.; Yan, J.; Hirao, L.; Kutzler, M.A.; Lewis, M.G.; Andersen, H.; Lank, S.M.; et al. Long-Term Programming of Antigen-Specific Immunity from Gene Expression Signatures in the PBMC of Rhesus Macaques Immunized with an SIV DNA Vaccine. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e19681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Gao, N.; Song, Y.; Duan, S.; Wang, W.; Cong, Z.; Qin, C.; Jiang, C.; Yu, X.; Gao, F. Reduction of peak viremia by an integration-defective SIV proviral DNA vaccine in rhesus macaques. Microbiol. Immunol. 2020, 64, 52–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Rompay, K.K.A.; Keesler, R.I.; Ardeshir, A.; Watanabe, J.; Usachenko, J.; Singapuri, A.; Cruzen, C.; Bliss-Moreau, E.; Murphy, A.M.; Yee, J.L.; et al. DNA vaccination before conception protects Zika virus—Exposed pregnant macaques against prolonged viremia and improves fetal outcomes. Sci. Transl. Med. 2019, 11, eaay2736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munang’Andu, H.M.; Evensen, Ø. Correlates of protective immunity for fish vaccines. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019, 85, 132–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desvignes, L.; Quentel, C.; Lamour, F.; Le Ven, A. Pathogenesis and immune response in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.) parr experimentally infected with salmon pancreas disease virus (SPDV). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2002, 12, 77–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Christie, K.; Graham, D.; McLoughlin, M.; Villoing, S.; Todd, D.; Knappskog, D. Experimental infection of Atlantic salmon Salmo salar pre-smolts by i.p. injection with new Irish and Norwegian salmonid alphavirus (SAV) isolates: A comparative study. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2007, 75, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, D.A.; Jewhurst, V.A.; Rowley, H.M.; McLoughlin, M.F.; Rodger, H.D.; Todd, D. Longitudinal serological surveys of Atlantic salmon, Salmo salar L., using a rapid immunoperoxidase-based neutralization assay for salmonid alphavirus. J. Fish Dis. 2005, 28, 373–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graham, D.A.; Jewhurst, H.; McLoughlin, M.F.; Sourd, P.; Rowley, H.; Taylor, C.; Todd, D. Sub-clinical infection of farmed Atlantic salmon Salmo salar with salmonid alphavirus? A prospective longitudinal study. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2006, 72, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Graham, D.A.; Fringuelli, E.; Wilson, C.; Rowley, H.M.; Brown, A.; Rodger, H.D.; McLoughlin, M.F.; McManus, C.; Casey, E.; McCarthy, L.J.; et al. Prospective longitudinal studies of salmonid alphavirus infections on two Atlantic salmon farms in Ireland; evidence for viral persistence. J. Fish Dis. 2010, 33, 123–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, T.M.; Drinan, E.M.; Gannon, F. Studies with an experimental model for pancreas disease of Atlantic salmon Salmo Salar L. Aquac. Res. 1995, 26, 861–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houghton, G.; Ellis, A. Pancreas disease in Atlantic salmon: Serum neutralisation and passive immunisation. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 1996, 6, 465–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarzotti-Kelsoe, M.; Bailer, R.T.; Turk, E.; Lin, C.-L.; Bilska, M.; Greene, K.M.; Gao, H.; Todd, C.A.; Ozaki, D.A.; Seaman, M.S.; et al. Optimization and validation of the TZM-bl assay for standardized assessments of neutralizing antibodies against HIV-1. J. Immunol. Methods 2014, 409, 131–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Griffin, D.E. Roles and reactivities of antibodies to alphaviruses. Semin. Virol. 1995, 6, 249–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenberie, S.; Peñaranda, M.M.D.; Thim, H.L.; Styrvold, M.B.; Strandskog, G.; Jørgensen, J.B.; Jensen, I. Salmonid Alphavirus Subtype 3 Induces Prolonged Local B Cell Responses in Atlantic Salmon (Salmo salar) After Intraperitoneal Infection. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertsen, B.; Chang, C.-J.; Bratland, L. IFN-adjuvanted DNA vaccine against infectious salmon anemia virus: Antibody kinetics and longevity of IFN expression. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2016, 54, 328–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laylor, R.; Porakishvili, N.; De Souza, J.; Playfair, J.; Delves, P.; Lund, T. DNA vaccination favours memory rather than effector B cell responses. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 1999, 117, 106–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmaljohn, A.L.; Johnson, E.D.; Dalrymple, J.M.; Cole, G.A. Non-neutralizing monoclonal antibodies can prevent lethal alphavirus encephalitis. Nat. Cell Biol. 1982, 297, 70–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Excler, J.-L.; Ake, J.; Robb, M.L.; Kim, J.H.; Plotkin, S.A. Nonneutralizing Functional Antibodies: A New “Old” Paradigm for HIV Vaccines. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2014, 21, 1023–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Embregts, C.; Rigaudeau, D.; Veselý, T.; Pokorová, D.; Lorenzen, N.; Petit, J.; Houel, A.; Dauber, M.; Schütze, H.; Boudinot, P.; et al. Intramuscular DNA Vaccination of Juvenile Carp against Spring Viremia of Carp Virus Induces Full Protection and Establishes a Virus-Specific B and T Cell Response. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Heppell, J.; Lorenzen, N.; Armstrong, N.K.; Wu, T.; Lorenzen, E.; Einer-Jensen, K.; Schorr, J.; Davis, H.L. Development of DNA vaccines for fish: Vector design, intramuscular injection and antigen expression using viral haemorrhagic septicaemia virus genes as model. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 1998, 8, 271–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herath, T.K.; Ashby, A.J.; Jayasuriya, N.S.; Bron, J.E.; Taylor, J.F.; Adams, A.; Richards, R.H.; Weidmann, M.; Ferguson, H.W.; Taggart, J.B.; et al. Impact of Salmonid alphavirus infection in diploid and triploid Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.) fry. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0179192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cano, I.; Joiner, C.; Bayley, A.; Rimmer, G.; Bateman, K.; Feist, S.W.; Stone, D.; Paley, R. An experimental means of transmitting pancreas disease in Atlantic salmon Salmo salar L. fry in freshwater. J. Fish Dis. 2015, 38, 271–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLoughlin, M.F.; Graham, D.A. Alphavirus infections in salmonids? A review. J. Fish Dis. 2007, 30, 511–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Mutoloki, S. Evensen, Øystein Superior protection conferred by inactivated whole virus vaccine over subunit and DNA vaccines against salmonid alphavirus infection in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.). Vaccine 2012, 30, 3918–3928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tough, D.F. Type I Interferon as a Link Between Innate and Adaptive Immunity through Dendritic Cell Stimulation. Leuk. Lymphoma 2004, 45, 257–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, L.; Ohnemus, A.; Ong, L.C.; Gad, H.H.; Hartmann, R.; Lycke, N.; Staeheli, P. Type I and Type III Interferons Differ in Their Adjuvant Activities for Influenza Vaccines. J. Virol. 2019, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bracci, L.; Canini, I.; Venditti, M.; Spada, M.; Puzelli, S.; Donatelli, I.; Belardelli, F.; Proietti, E. Type I IFN as a vaccine adjuvant for both systemic and mucosal vaccination against influenza virus. Vaccine 2006, 24, S56–S57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagao, Y.; Yamashiro, K.; Hara, N.; Horisawa, Y.; Kato, K.; Uemura, A. Oral-Mucosal Administration of IFN-α Potentiates Immune Response in Mice. J. Interf. Cytokine Res. 1998, 18, 661–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Bon, A.; Durand, V.; Kamphuis, E.; Thompson, C.; Bulfone-Paus, S.; Rossmann, C.; Kalinke, U.; Tough, D.F. Direct Stimulation of T Cells by Type I IFN Enhances the CD8+T Cell Response during Cross-Priming. J. Immunol. 2006, 176, 4682–4689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mikalsen, A.B.; Sindre, H.; Torgersen, J.; Rimstad, E. Protective effects of a DNA vaccine expressing the infectious salmon anemia virus hemagglutinin-esterase in Atlantic salmon. Vaccine 2005, 23, 4895–4905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mosser, D.M.; Edwards, J.P. Exploring the full spectrum of macrophage activation. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2008, 8, 958–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boehm, U.; Klamp, T.; Groot, A.M.; Howard, J.C. Cellular responses to interferon-γ. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 1997, 15, 749–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vazirinejad, R.; Ahmadi, Z.; Arababadi, M.K.; Hassanshahi, G.; Kennedy, D. The Biological Functions, Structure and Sources of CXCL10 and Its Outstanding Part in the Pathophysiology of Multiple Sclerosis. Neuroimmunomodulation 2014, 21, 322–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sobhkhez, M.; Krasnov, A.; Robertsen, B. Transcriptome analyses of Atlantic salmon muscle genes induced by a DNA vaccine against salmonid alphavirus, the causative agent of salmon pancreas disease (PD). PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0204924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Utke, K.; Kock, H.; Schuetze, H.; Bergmann, S.M.; Lorenzen, N.; Einer-Jensen, K.; Köllner, B.; Dalmo, R.A.; Vesely, T.; Ototake, M.; et al. Cell-mediated immune responses in rainbow trout after DNA immunization against the viral hemorrhagic septicemia virus. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2008, 32, 239–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Metzemaekers, M.; Vanheule, V.; Janssens, R.; Struyf, S.; Proost, P. Overview of the Mechanisms that May Contribute to the Non-Redundant Activities of Interferon-Inducible CXC Chemokine Receptor 3 Ligands. Front. Immunol. 2018, 8, 1970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, R.; Martin, S.A.; Bird, S.; Lamas, J.; Secombes, C.J. Characterisation of γ-interferon responsive promoters in fish. Mol. Immunol. 2008, 45, 3454–3462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonheim, T.C.; Dalmo, R.A.; Bøgwald, J.; Seternes, T. Specific uptake of plasmid DNA without reporter gene expression in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.) kidney after intramuscular administration. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2008, 24, 90–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishii, K.J.; Kawagoe, T.; Koyama, S.; Matsui, K.; Kumar, H.; Kawai, T.; Uematsu, S.; Takeuchi, O.; Takeshita, F.; Coban, C.; et al. TANK-binding kinase-1 delineates innate and adaptive immune responses to DNA vaccines. Nat. Cell Biol. 2008, 451, 725–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishikawa, H.; Ma, Z.; Barber, G.N. STING regulates intracellular DNA-mediated, type I interferon-dependent innate immunity. Nat. Cell Biol. 2009, 461, 788–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Siegel, F.; Lu, M.; Roggendorf, M. Coadministration of Gamma Interferon with DNA Vaccine Expressing Woodchuck Hepatitis Virus (WHV) Core Antigen Enhances the Specific Immune Response and Protects against WHV Infection. J. Virol. 2001, 75, 5036–5042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Long, J.-E.; Huang, L.-N.; Qin, Z.-Q.; Wang, W.-Y.; Qu, D. IFN-γ increases efficiency of DNA vaccine in protecting ducks against infection. World J. Gastroenterol. 2005, 11, 4967–4973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarradas, J.; Argilaguet, J.; Rosell, R.; Nofrarías, M.; Crisci, E.; Córdoba, L.; Pérez-Martín, E.; Díaz, I.; Rodríguez, F.; Domingo, M.; et al. Interferon-gamma induction correlates with protection by DNA vaccine expressing E2 glycoprotein against classical swine fever virus infection in domestic pigs. Veter. Microbiol. 2010, 142, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, R.; Bourgine, M.; Zhang, X.M.; Bayard, F.; Deng, Q.; Michel, M.-L. Plasmid Vector-Linked Maturation of Natural Killer (NK) Cells Is Coupled to Antigen-Dependent NK Cell Activation during DNA-Based Immunization in Mice. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 10201–10212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bassity, E.; Clark, T.G. Functional Identification of Dendritic Cells in the Teleost Model, Rainbow Trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e33196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Granja, A.G.; Leal, E.; Pignatelli, J.; Castro, R.; Abós, B.; Kato, G.; Fischer, U.; Tafalla, C. Identification of Teleost Skin CD8α+ Dendritic-like Cells, Representing a Potential Common Ancestor for Mammalian Cross-Presenting Dendritic Cells. J. Immunol. 2015, 195, 1825–1837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mayer-Barber, K.D.; Yan, B. Clash of the Cytokine Titans: Counter-regulation of interleukin-1 and type I interferon-mediated inflammatory responses. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2017, 14, 22–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Braceland, M.; Bickerdike, R.; Tinsley, J.; Cockerill, D.; McLoughlin, M.; Graham, D.; Burchmore, R.; Weir, W.; Wallace, C.; Eckersall, P.D. The serum proteome of Atlantic salmon, Salmo salar, during pancreas disease (PD) following infection with salmonid alphavirus subtype 3 (SAV3). J. Proteom. 2013, 94, 423–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Andreassen, R.; Woldemariam, N.T.; Egeland, I.Ø.; Agafonov, O.; Sindre, H.; Høyheim, B. Identification of differentially expressed Atlantic salmon miRNAs responding to salmonid alphavirus (SAV) infection. BMC Genom. 2017, 18, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Attaya, A.; Jiang, Y.; Secombes, C.J.; Wang, T. Distinct response of immune gene expression in peripheral blood leucocytes modulated by bacterin vaccine candidates in rainbow trout Oncorhynchus mykiss: A potential in vitro screening and batch testing system for vaccine development in aquaculture. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019, 93, 631–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Tissue | Score | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Heart | 0 | Normal appearance |
| 1 | Focal myocardial degeneration ± inflammation (<7 fibres affected) | |
| 2 | Focal myocardial degeneration ± inflammation (<15% of heart affected) | |
| 3 | Multifocal myocardial degeneration ± inflammation (>15 and <50% of heart affected) | |
| 4 | Severe diffuse myocardial degeneration ± inflammation (<50% of heart affected) | |
| R | Repair | |
| Red and white skeletal muscle | 0 | Normal appearance |
| 1 | Focal myocytic degeneration ± inflammation | |
| 2 | Multifocal myocytic degeneration ± inflammation | |
| 3 | Severe diffuse myocytic degeneration ± inflammation | |
| R | Repair |
| Muscle (Site of Injection) | Head Kidney | Blood Cells | |||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| dpv | gene | Uncorrected p-Value | Corrected p-Value | Uncorrected p-Value | Corrected p-Value | Uncorrected p Value | Corrected p-Value | ||||||||||||
| PBS v 3.1H | PBS v ppG | 3.1H v ppG | PBS v 3.1H | PBS v ppG | 3.1H v ppG | PBS v 3.1H | PBS v ppG | 3.1H v ppG | PBS v 3.1H | PBS v ppG | 3.1H v ppG | PBS v 3.1H | PBS v ppG | 3.1H v ppG | PBS v 3.1H | PBS v ppG | 3.1H v ppG | ||
| 3 | mx | 0.8435 | 0.8401 | 0.9774 | ns | ns | ns | 0.2363 | 0.8740 | 0.0479 | ns | ns | ns | ||||||
| gIP | 0.2984 | 0.2016 | 0.1671 | ns | ns | ns | 0.3184 | 0.0491 | 0.1077 | ns | ns | ns | |||||||
| cd8 | 0.4611 | 0.3760 | 0.9204 | ns | ns | ns | 0.0046 | 0.0051 | 0.8038 | ns | ns | ns | |||||||
| cd83 | 0.5908 | 0.8532 | 0.6386 | ns | ns | ns | |||||||||||||
| il1b | 0.1822 | 0.0305 | 0.6475 | ns | ns | ns | |||||||||||||
| 7 | mx | 0.0131 | 0.0001 | 0.0002 | ns | * | * | 0.5843 | 0.0010 | 0.0011 | ns | * | * | 0.0810 | 0.0149 | 0.0194 | ns | ns | ns |
| gIP | 0.3994 | 0.0043 | 0.0086 | ns | ns | ns | 0.2039 | 0.7465 | 0.0071 | ns | ns | ns | |||||||
| cd8 | 0.5121 | 0.0017 | 0.0007 | ns | ns | * | 0.2387 | 0.6095 | 0.7348 | ns | ns | ns | |||||||
| cd83 | 0.0248 | 0.0219 | 0.0100 | ns | ns | ns | |||||||||||||
| il1b | 0.3671 | 0.6218 | 0.1698 | ns | ns | ns | |||||||||||||
| 11 | mx | 0.2075 | 0.0048 | 0.0050 | ns | ns | ns | 0.6453 | 0.0010 | 0.0011 | ns | * | * | 0.1288 | 0.0180 | 0.0130 | ns | ns | ns |
| gIP | 0.3259 | 0.0439 | 0.0534 | ns | ns | ns | 0.3677 | 0.0297 | 0.0172 | ns | ns | ns | |||||||
| cd8 | 0.7784 | 0.1697 | 0.1791 | ns | ns | ns | 0.1708 | 0.2485 | 0.7811 | ns | ns | ns | |||||||
| cd83 | 0.3940 | 0.8094 | 0.2950 | ns | ns | ns | |||||||||||||
| il1b | 0.9824 | 0.8759 | 0.8680 | ns | ns | ns | |||||||||||||
| 46 | mx | 0.4706 | 0.5430 | 0.1777 | ns | ns | ns | 0.4432 | 0.1412 | 0.4686 | ns | ns | ns | ||||||
| gIP | 0.5673 | 0.2851 | 0.1196 | ns | ns | ns | 0.2002 | 0.1227 | 0.3344 | ns | ns | ns | |||||||
| cd8 | 0.2869 | 0.9520 | 0.0669 | ns | ns | ns | 0.7191 | 0.7936 | 0.4058 | ns | ns | ns | |||||||
| 60 | mx | 0.3101 | 0.2542 | 0.7686 | ns | ns | ns | ||||||||||||
| cd8 | 0.5566 | 0.9337 | 0.7346 | ns | ns | ns | |||||||||||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Collins, C.; Lester, K.; Del-Pozo, J.; Collet, B. Non-Lethal Sequential Individual Monitoring of Viremia in Relation to DNA Vaccination in Fish–Example Using a Salmon Alphavirus DNA Vaccine in Atlantic Salmon Salmo salar. Vaccines 2021, 9, 163. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines9020163
Collins C, Lester K, Del-Pozo J, Collet B. Non-Lethal Sequential Individual Monitoring of Viremia in Relation to DNA Vaccination in Fish–Example Using a Salmon Alphavirus DNA Vaccine in Atlantic Salmon Salmo salar. Vaccines. 2021; 9(2):163. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines9020163
Chicago/Turabian StyleCollins, Catherine, Katherine Lester, Jorge Del-Pozo, and Bertrand Collet. 2021. "Non-Lethal Sequential Individual Monitoring of Viremia in Relation to DNA Vaccination in Fish–Example Using a Salmon Alphavirus DNA Vaccine in Atlantic Salmon Salmo salar" Vaccines 9, no. 2: 163. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines9020163
APA StyleCollins, C., Lester, K., Del-Pozo, J., & Collet, B. (2021). Non-Lethal Sequential Individual Monitoring of Viremia in Relation to DNA Vaccination in Fish–Example Using a Salmon Alphavirus DNA Vaccine in Atlantic Salmon Salmo salar. Vaccines, 9(2), 163. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines9020163






