Newcastle Disease Virus-Like Particles Displaying Prefusion-Stabilized SARS-CoV-2 Spikes Elicit Potent Neutralizing Responses
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Line
2.2. Preparation of Plasmids
2.3. Preparation of HEK293T Cell Pool Stably Expressing the SARS-CoV-2 Spike (S2P)
2.4. Live Cell-Surface Staining
2.5. Production and Purification of SARS-CoV-2 S2P-NDVLP
2.6. Negative-Staining Electron Microscopy
2.7. Preparation of Prefusion-Stabilized SARS-CoV-2 Spike Glycoprotein (S2P Trimer) and RBD Glycoprotein
2.8. Preparation of Antibodies
2.9. Antigenic Analysis
2.10. Quantitation of SARS-CoV-2 Spikes of SARS-CoV-2 S2P-NDVLP
2.11. Mouse Immunization and Ethics Statement
2.12. Serum IgG Assay
2.13. Pseudovirus Neutralization Assay
2.14. Serum Anti-RBD or Anti-S2P Titer Assay
2.15. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
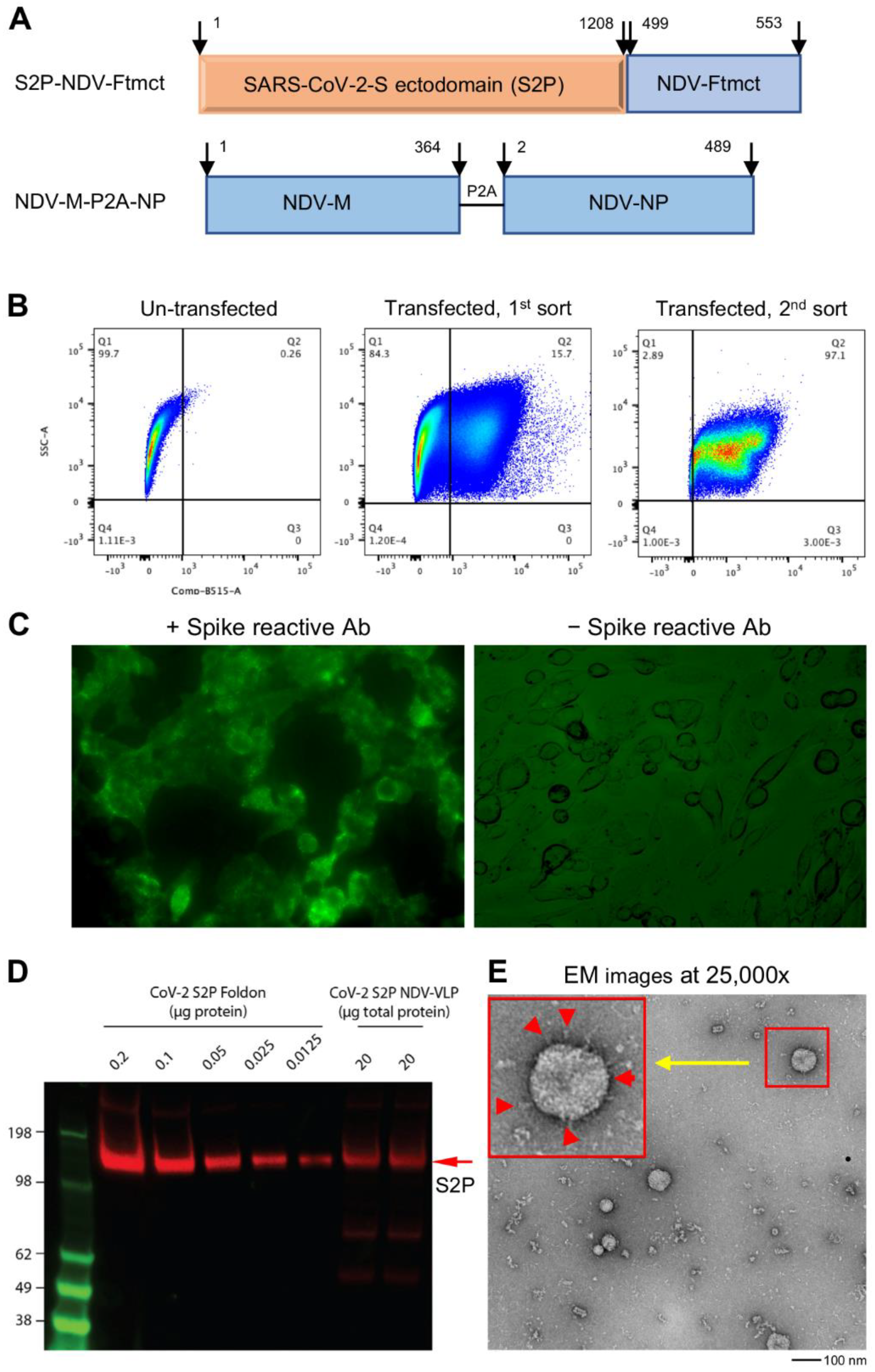
3.1. Design of S2P-NDVLP Constructs and Generation of S2P-NDVLP
3.2. S2P-NDVLP Was Specifically Recognized by SARS-CoV-2-Neutralizing Antibodies
3.3. Immunogenicity Assessments of S2P-NDVLP in Mice
4. Discussion
5. Patents
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Corey, L.; Mascola, J.R.; Fauci, A.S.; Collins, F.S. A strategic approach to COVID-19 vaccine R & D. Science 2020, 368, 948–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, W.; Yang, Y.; Rao, Y.; Rao, X. The outbreak of SARS-CoV-2 pneumonia calls for viral vaccines. NPJ Vaccines 2020, 5, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Walsh, E.E.; Frenck, R.; Falsey, A.R.; Kitchin, N.; Absalon, J.; Gurtman, A.; Lockhart, S.; Neuzil, K.; Mulligan, M.J.; Bailey, R.; et al. RNA-Based COVID-19 Vaccine BNT162b2 Selected for a Pivotal Efficacy Study. medRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corbett, K.S.; Flynn, B.; Foulds, K.E.; Francica, J.R.; Boyoglu-Barnum, S.; Werner, A.P.; Flach, B.; O’Connell, S.; Bock, K.W.; Minai, M.; et al. Evaluation of the mRNA-1273 Vaccine against SARS-CoV-2 in Nonhuman Primates. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 1544–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, F.C.; Li, Y.H.; Guan, X.H.; Hou, L.H.; Wang, W.J.; Li, J.X.; Wu, S.P.; Wang, B.S.; Wang, Z.; Wang, L.; et al. Safety, tolerability, and immunogenicity of a recombinant adenovirus type-5 vectored COVID-19 vaccine: A dose-escalation, open-label, non-randomised, first-in-human trial. Lancet 2020, 395, 1845–1854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polack, F.P.; Thomas, S.J.; Kitchin, N.; Absalon, J.; Gurtman, A.; Lockhart, S.; Perez, J.L.; Perez Marc, G.; Moreira, E.D.; Zerbini, C.; et al. Safety and Efficacy of the BNT162b2 mRNA Covid-19 Vaccine. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurup, D.; Wirblich, C.; Ramage, H.; Schnell, M.J. Rabies virus-based COVID-19 vaccine CORAVAX induces high levels of neutralizing antibodies against SARS-CoV-2. NPJ Vaccines 2020, 5, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hennrich, A.A.; Banda, D.H.; Oberhuber, M.; Schopf, A.; Pfaffinger, V.; Wittwer, K.; Sawatsky, B.; Riedel, C.; Pfaller, C.K.; Conzelmann, K.-K. Safe and effective two-in-one replicon-and-VLP minispike vaccine for COVID-19. bioRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; McCroskery, S.; Liu, W.C.; Leist, S.R.; Liu, Y.; Albrecht, R.A.; Slamanig, S.; Oliva, J.; Amanat, F.; Schäfer, A.; et al. A Newcastle Disease Virus (NDV) Expressing a Membrane-Anchored Spike as a Cost-Effective Inactivated SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine. Vaccines 2020, 8, 771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walls, A.C.; Fiala, B.; Schäfer, A.; Wrenn, S.; Pham, M.N.; Murphy, M.; Tse, L.V.; Shehata, L.; O’Connor, M.A.; Chen, C.; et al. Elicitation of Potent Neutralizing Antibody Responses by Designed Protein Nanoparticle Vaccines for SARS-CoV-2. Cell 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Chao, C.W.; Tsybovsky, Y.; Abiona, O.M.; Hutchinson, G.B.; Moliva, J.I.; Olia, A.S.; Pegu, A.; Phung, E.; Stewart-Jones, G.B.E.; et al. A platform incorporating trimeric antigens into self-assembling nanoparticles reveals SARS-CoV-2-spike nanoparticles to elicit substantially higher neutralizing responses than spike alone. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 18149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Zhong, G.; Zhang, J.; Shuai, L.; Zhang, Z.; Wen, Z.; Wang, B.; Zhao, Z.; Song, X.; Chen, Y.; et al. A single dose of an adenovirus-vectored vaccine provides protection against SARS-CoV-2 challenge. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 4081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, L.; Lin, X.; Wang, Y.; Abraham, C.; Sou, C.; Ngo, T.; Zhang, Y.; Wilson, I.A.; Zhu, J. Self-assembling nanoparticles presenting receptor binding domain and stabilized spike as next-generation COVID-19 vaccines. bioRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poland, G.A.; Ovsyannikova, I.G.; Kennedy, R.B. SARS-CoV-2 immunity: Review and applications to phase 3 vaccine candidates. Lancet 2020, 396, 1595–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krammer, F. SARS-CoV-2 vaccines in development. Nature 2020, 586, 516–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marian, A.J. Current state of vaccine development and targeted therapies for COVID-19: Impact of basic science discoveries. Cardiovasc. Pathol. 2020, 50, 107278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callaway, E. The race for coronavirus vaccines: A graphical guide. Nature 2020, 580, 576–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, J.; Wan, Y.; Luo, C.; Ye, G.; Geng, Q.; Auerbach, A.; Li, F. Cell entry mechanisms of SARS-CoV-2. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 11727–11734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Zhang, J.; Xiao, T.; Peng, H.; Sterling, S.M.; Walsh, R.M., Jr.; Rawson, S.; Rits-Volloch, S.; Chen, B. Distinct conformational states of SARS-CoV-2 spike protein. Science 2020, 369, 1586–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, H.; Song, Y.; Chen, Y.; Wu, N.; Xu, J.; Sun, C.; Zhang, J.; Weng, T.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, Z.; et al. Molecular Architecture of the SARS-CoV-2 Virus. Cell 2020, 183, 730–738.e13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corbett, K.S.; Edwards, D.K.; Leist, S.R.; Abiona, O.M.; Boyoglu-Barnum, S.; Gillespie, R.A.; Himansu, S.; Schafer, A.; Ziwawo, C.T.; DiPiazza, A.T.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccine design enabled by prototype pathogen preparedness. Nature 2020, 586, 567–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Q.; Bao, L.; Mao, H.; Wang, L.; Xu, K.; Yang, M.; Li, Y.; Zhu, L.; Wang, N.; Lv, Z.; et al. Development of an inactivated vaccine candidate for SARS-CoV-2. Science 2020, 369, 77–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackson, L.A.; Anderson, E.J.; Rouphael, N.G.; Roberts, P.C.; Makhene, M.; Coler, R.N.; McCullough, M.P.; Chappell, J.D.; Denison, M.R.; Stevens, L.J.; et al. An mRNA Vaccine against SARS-CoV-2—Preliminary Report. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, J.; Tostanoski, L.H.; Peter, L.; Mercado, N.B.; McMahan, K.; Mahrokhian, S.H.; Nkolola, J.P.; Liu, J.; Li, Z.; Chandrashekar, A.; et al. DNA vaccine protection against SARS-CoV-2 in rhesus macaques. Science 2020, 369, 806–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zost, S.J.; Gilchuk, P.; Case, J.B.; Binshtein, E.; Chen, R.E.; Nkolola, J.P.; Schafer, A.; Reidy, J.X.; Trivette, A.; Nargi, R.S.; et al. Potently neutralizing and protective human antibodies against SARS-CoV-2. Nature 2020, 584, 443–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vashishtha, V.M.; Kumar, P. Development of SARS-CoV-2 vaccines: Challenges, risks, and the way forward. Hum. Vaccines Immunother. 2020, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zeng, G.; Pan, H.; Li, C.; Hu, Y.; Chu, K.; Han, W.; Chen, Z.; Tang, R.; Yin, W.; et al. Safety, tolerability, and immunogenicity of an inactivated SARS-CoV-2 vaccine in healthy adults aged 18–59 years: A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 1/2 clinical trial. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S.; Ghani, K.; de Campos-Lima, P.O.; Caruso, M. Efficient production of Moloney murine leukemia virus-like particles pseudotyped with the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2) spike protein. bioRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Case, J.B.; Rothlauf, P.W.; Chen, R.E.; Kafai, N.M.; Fox, J.M.; Smith, B.K.; Shrihari, S.; McCune, B.T.; Harvey, I.B.; Keeler, S.P.; et al. Replication-Competent Vesicular Stomatitis Virus Vaccine Vector Protects against SARS-CoV-2-Mediated Pathogenesis in Mice. Cell Host Microbe 2020, 28, 465–474.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yahalom-Ronen, Y.; Tamir, H.; Melamed, S.; Politi, B.; Shifman, O.; Achdout, H.; Vitner, E.B.; Israeli, O.; Milrot, E.; Stein, D.; et al. A single dose of recombinant VSV-ΔG-spike vaccine provides protection against SARS-CoV-2 challenge. bioRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erasmus, J.H.; Khandhar, A.P.; Walls, A.C.; Hemann, E.A.; O’Connor, M.A.; Murapa, P.; Archer, J.; Leventhal, S.; Fuller, J.; Lewis, T.; et al. Single-dose replicating RNA vaccine induces neutralizing antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 in nonhuman primates. bioRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrett, J.R.; Belij-Rammerstorfer, S.; Dold, C.; Ewer, K.J.; Folegatti, P.M.; Gilbride, C.; Halkerston, R.; Hill, J.; Jenkin, D.; Stockdale, L.; et al. Phase 1/2 trial of SARS-CoV-2 vaccine ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 with a booster dose induces multifunctional antibody responses. Nat. Med. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ewer, K.J.; Barrett, J.R.; Belij-Rammerstorfer, S.; Sharpe, H.; Makinson, R.; Morter, R.; Flaxman, A.; Wright, D.; Bellamy, D.; Bittaye, M.; et al. T cell and antibody responses induced by a single dose of ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 (AZD1222) vaccine in a phase 1/2 clinical trial. Nat. Med. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nichols, W.W.; Ledwith, B.J.; Manam, S.V.; Troilo, P.J. Potential DNA vaccine integration into host cell genome. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1995, 772, 30–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauch, S.; Jasny, E.; Schmidt, K.E.; Petsch, B. New Vaccine Technologies to Combat Outbreak Situations. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mohsen, M.O.; Zha, L.; Cabral-Miranda, G.; Bachmann, M.F. Major findings and recent advances in virus-like particle (VLP)-based vaccines. Semin. Immunol. 2017, 34, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boson, B.; Legros, V.; Zhou, B.; Mathieu, C.; Cosset, F.-L.; Lavillette, D.; Denolly, S. The SARS-CoV-2 Envelope and Membrane proteins modulate maturation and retention of the Spike protein, allowing optimal formation of VLPs in presence of Nucleoprotein. bioRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGinnes, L.W.; Morrison, T.G. Newcastle disease virus-like particles: Preparation, purification, quantification, and incorporation of foreign glycoproteins. Curr. Protoc. Microbiol. 2013, 30, 18.2.1–18.2.21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pantua, H.D.; McGinnes, L.W.; Peeples, M.E.; Morrison, T.G. Requirements for the assembly and release of Newcastle disease virus-like particles. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 11062–11073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schmidt, M.R.; McGinnes-Cullen, L.W.; Kenward, S.A.; Willems, K.N.; Woodland, R.T.; Morrison, T.G. Modification of the respiratory syncytial virus f protein in virus-like particles impacts generation of B cell memory. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 10165–10176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, T.; Teng, I.T.; Olia, A.S.; Cerutti, G.; Gorman, J.; Nazzari, A.; Shi, W.; Tsybovsky, Y.; Wang, L.; Wang, S.; et al. Structure-Based Design with Tag-Based Purification and In-Process Biotinylation Enable Streamlined Development of SARS-CoV-2 Spike Molecular Probes. Cell Rep. 2020, 33, 108322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wrapp, D.; Wang, N.; Corbett, K.S.; Goldsmith, J.A.; Hsieh, C.L.; Abiona, O.; Graham, B.S. McLellan, J.S. Cryo-EM structure of the 2019-nCoV spike in the prefusion conformation. Science 2020, 367, 1260–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, Z.; Chen, O.; Wall, J.B.J.; Zheng, M.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, L.; Vaseghi, H.R.; Qian, L.; Liu, J. Systematic comparison of 2A peptides for cloning multi-genes in a polycistronic vector. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 2193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pallesen, J.; Wang, N.; Corbett, K.S.; Wrapp, D.; Kirchdoerfer, R.N.; Turner, H.L.; Cottrell, C.A.; Becker, M.M.; Wang, L.; Shi, W.; et al. Immunogenicity and structures of a rationally designed prefusion MERS-CoV spike antigen. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, E7348–E7357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ni, L.; Ye, F.; Cheng, M.L.; Feng, Y.; Deng, Y.Q.; Zhao, H.; Wei, P.; Ge, J.; Gou, M.; Li, X.; et al. Detection of SARS-CoV-2-Specific Humoral and Cellular Immunity in COVID-19 Convalescent Individuals. Immunity 2020, 52, 971–977.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robbiani, D.F.; Gaebler, C.; Muecksch, F.; Lorenzi, J.C.C.; Wang, Z.; Cho, A.; Agudelo, M.; Barnes, C.O.; Gazumyan, A.; Finkin, S.; et al. Convergent antibody responses to SARS-CoV-2 in convalescent individuals. Nature 2020, 584, 437–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, Z.; Oton, J.; Qu, K.; Cortese, M.; Zila, V.; McKeane, L.; Nakane, T.; Zivanov, J.; Neufeldt, C.J.; Cerikan, B.; et al. Structures and distributions of SARS-CoV-2 spike proteins on intact virions. Nature 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Wang, P.; Nair, M.S.; Yu, J.; Rapp, M.; Wang, Q.; Luo, Y.; Chan, J.F.; Sahi, V.; Figueroa, A.; et al. Potent neutralizing antibodies against multiple epitopes on SARS-CoV-2 spike. Nature 2020, 584, 450–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Wang, F.; Shen, C.; Peng, W.; Li, D.; Zhao, C.; Li, Z.; Li, S.; Bi, Y.; Yang, Y.; et al. A noncompeting pair of human neutralizing antibodies block COVID-19 virus binding to its receptor ACE2. Science 2020, 368, 1274–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, B.; Zhang, Q.; Ge, J.; Wang, R.; Sun, J.; Ge, X.; Yu, J.; Shan, S.; Zhou, B.; Song, S.; et al. Human neutralizing antibodies elicited by SARS-CoV-2 infection. Nature 2020, 584, 115–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolles, M.; Deming, D.; Long, K.; Agnihothram, S.; Whitmore, A.; Ferris, M.; Funkhouser, W.; Gralinski, L.; Totura, A.; Heise, M.; et al. A double-inactivated severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus vaccine provides incomplete protection in mice and induces increased eosinophilic proinflammatory pulmonary response upon challenge. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 12201–12215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Czub, M.; Weingartl, H.; Czub, S.; He, R.; Cao, J. Evaluation of modified vaccinia virus Ankara based recombinant SARS vaccine in ferrets. Vaccine 2005, 23, 2273–2279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deming, D.; Sheahan, T.; Heise, M.; Yount, B.; Davis, N.; Sims, A.; Suthar, M.; Harkema, J.; Whitmore, A.; Pickles, R.; et al. Vaccine efficacy in senescent mice challenged with recombinant SARS-CoV bearing epidemic and zoonotic spike variants. PLoS Med. 2006, 3, e525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Premkumar, L.; Segovia-Chumbez, B.; Jadi, R.; Martinez, D.R.; Raut, R.; Markmann, A.; Cornaby, C.; Bartelt, L.; Weiss, S.; Park, Y.; et al. The receptor binding domain of the viral spike protein is an immunodominant and highly specific target of antibodies in SARS-CoV-2 patients. Sci. Immunol. 2020, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuenmayor, J.; Godia, F.; Cervera, L. Production of virus-like particles for vaccines. New Biotechnol. 2017, 39, 174–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plummer, E.M.; Manchester, M. Viral nanoparticles and virus-like particles: Platforms for contemporary vaccine design. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Nanomed. Nanobiotechnol. 2011, 3, 174–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laczko, D.; Hogan, M.J.; Toulmin, S.A.; Hicks, P.; Lederer, K.; Gaudette, B.T.; Castano, D.; Amanat, F.; Muramatsu, H.; Oguin, T.H., 3rd; et al. A Single Immunization with Nucleoside-Modified mRNA Vaccines Elicits Strong Cellular and Humoral Immune Responses against SARS-CoV-2 in Mice. Immunity 2020, 53, 724–732 e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, Y.; Shi, W.; Abiona, O.M.; Nazzari, A.; Olia, A.S.; Ou, L.; Phung, E.; Stephens, T.; Tsybovsky, Y.; Verardi, R.; et al. Newcastle Disease Virus-Like Particles Displaying Prefusion-Stabilized SARS-CoV-2 Spikes Elicit Potent Neutralizing Responses. Vaccines 2021, 9, 73. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines9020073
Yang Y, Shi W, Abiona OM, Nazzari A, Olia AS, Ou L, Phung E, Stephens T, Tsybovsky Y, Verardi R, et al. Newcastle Disease Virus-Like Particles Displaying Prefusion-Stabilized SARS-CoV-2 Spikes Elicit Potent Neutralizing Responses. Vaccines. 2021; 9(2):73. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines9020073
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Yongping, Wei Shi, Olubukola M. Abiona, Alexandra Nazzari, Adam S. Olia, Li Ou, Emily Phung, Tyler Stephens, Yaroslav Tsybovsky, Raffaello Verardi, and et al. 2021. "Newcastle Disease Virus-Like Particles Displaying Prefusion-Stabilized SARS-CoV-2 Spikes Elicit Potent Neutralizing Responses" Vaccines 9, no. 2: 73. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines9020073





