Immuno-Informatics Analysis of Pakistan-Based HCV Subtype-3a for Chimeric Polypeptide Vaccine Design
Abstract
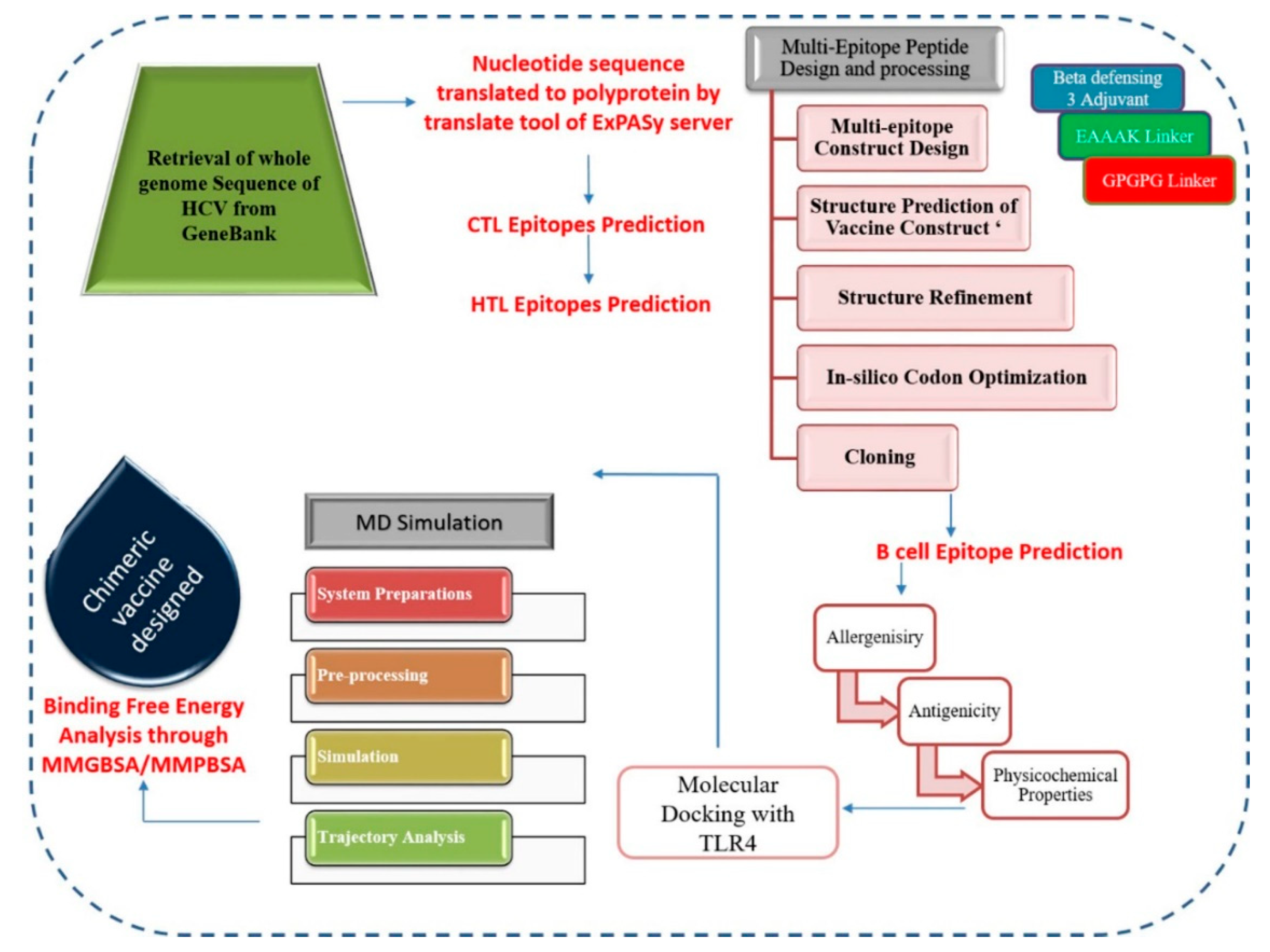
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sequence Retrieval
2.2. CTL Epitopes Prediction
2.3. HTL Epitopes Prediction
2.4. Chimeric Polypeptide Vaccine Construction and Structure Prediction
2.5. Codon Adaptation and In-Silico Cloning
2.6. B-Cell Epitopes Prediction
2.7. Antigenicity and Allergenicity Prediction
2.8. Physiochemical Properties Assessment
2.9. Molecular Docking and Dynamics Simulations
2.10. Estimation of MM/GB-PBSA Binding Energy
2.11. Immune Simulation
3. Results
3.1. Sequence Retrieval
3.2. CTL Epitopes Prediction
3.3. HTL Epitopes Prediction
3.4. Chimeric Polypeptide Vaccine Construction
3.5. Tertiary Structure Prediction, Refinement, and Validation
3.6. In-Silico Cloning and Codon Adaptation
3.7. B-Cell Epitopes Mapping
3.8. Vaccine Antigenicity and Allergenicity
3.9. Vaccine Physicochemical Properties
3.10. Molecular Docking
3.11. Molecular Dynamics Simulation
3.12. Estimation of MM/GB-PBSA Binding Energy
3.13. Host Immune System Dynamics to Vaccine
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Williams, R. Global Challenges in Liver Disease. Hepatology 2006, 44, 521–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashfaq, U.A.; Jalil, A.; Tahir ul Qamar, M. Antiviral Phytochemicals Identification from Azadirachta Indica Leaves against HCV NS3 Protease: An in Silico Approach. Nat. Prod. Res. 2016, 30, 1866–1869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogo, L.D.; Akogwu, S.; Umar, U.Z.; Aliyu, A.M.; Aminu, B.M. The Genetic and Molecular Studies of Hepatitis C Virus: A Review. Bayero J. Pure Appl. Sci. 2011, 4, 72–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Csete, J.; Elliott, R.; Fischer, B. “Viral Time Bomb”: Health and Human Rights Challenges in Addressing Hepatitis C in Canada; Canadian HIV/AIDS Legal Network, Centre for Addictions Research of BC and Centre for Applied Research in Mental Health and Addiction: Victoria, BC, Canada, 2008; ISBN 1926789083. [Google Scholar]
- Razavi, H. Global Epidemiology of Viral Hepatitis. Gastroenterol. Clin. 2020, 49, 179–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.L.; Morgan, T.R. The Natural History of Hepatitis C Virus (HCV) Infection. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2006, 3, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Houghton, M. The Long and Winding Road Leading to the Identification of the Hepatitis C Virus. J. Hepatol. 2009, 51, 939–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Memon, M.I.; Memon, M.A. Hepatitis C: An Epidemiological Review. J. Viral Hepat. 2002, 9, 84–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thrift, A.P.; El-Serag, H.B.; Kanwal, F. Global Epidemiology and Burden of HCV Infection and HCV-related Disease. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 14, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Messina, J.P.; Humphreys, I.; Flaxman, A.; Brown, A.; Cooke, G.S.; Pybus, O.G.; Barnes, E. Global Distribution and Prevalence of Hepatitis C Virus Genotypes. Hepatology 2015, 61, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rajhi, M.; Haddad-Boubaker, S.; Chouikha, A.; Bourquain, D.; Michel, J.; Hammami, W.; Sadraoui, A.; Touzi, H.; Ghedira, K.; Triki, H. Identification of Two Novel Hepatitis C Virus Subtype 2 from Tunisia (2v and 2w). PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0248249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.-L.; Kao, J.-H. The Clinical Implications of Hepatitis B Virus Genotype: Recent Advances. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2011, 26, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petruzziello, A.; Marigliano, S.; Loquercio, G.; Cozzolino, A.; Cacciapuoti, C. Global Epidemiology of Hepatitis C Virus Infection: An Up-date of the Distribution and Circulation of Hepatitis C Virus Genotypes. World J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 22, 7824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, G.L.; Wong, J.B.; McHutchison, J.G.; Manns, M.P.; Harvey, J.; Albrecht, J. Early Virologic Response to Treatment with Peginterferon Alfa-2b Plus Ribavirin in Patients with Chronic Hepatitis C. Hepatology 2003, 38, 645–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yau, A.H.L.; Yoshida, E.M. Hepatitis C Drugs: The End of the Pegylated Interferon Era and the Emergence of All-oral, Interferon-free Antiviral Regimens: A Concise Review. Can. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2014, 28, 445–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ford, N.; Kirby, C.; Singh, K.; Mills, E.J.; Cooke, G.; Kamarulzaman, A.; duCros, P. Chronic Hepatitis C Treatment Outcomes in Low-and Middle-income Countries: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Bull. World Health Organ. 2012, 90, 540–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jayasekera, C.R.; Barry, M.; Roberts, L.R.; Nguyen, M.H. Treating Hepatitis C in Lower-income Countries. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 370, 1869–1871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mittal, S.; El-Serag, H.B. Epidemiology of HCC: Consider the Population. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2013, 47, S2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Probst, A.; Dang, T.; Bochud, M.; Egger, M.; Negro, F.; Bochud, P.-Y. Role of Hepatitis C Virus Genotype 3 in Liver Fibrosis Progression–A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. J. Viral Hepat. 2011, 18, 745–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Waheed, Y.; Shafi, T.; Safi, S.Z.; Qadri, I. Hepatitis C Virus in Pakistan: A Systematic Review of Prevalence, Genotypes and Risk Factors. World J. Gastroenterol. WJG 2009, 15, 5647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al Kanaani, Z.; Mahmud, S.; Kouyoumjian, S.P.; Abu-Raddad, L.J. The Epidemiology of Hepatitis C Virus in Pakistan: Systematic Review and Meta-analyses. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ali, S.A.; Donahue, R.M.J.; Qureshi, H.; Vermund, S.H. Hepatitis B and Hepatitis C in Pakistan: Prevalence and Risk Factors. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2009, 13, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wei, Y.; Li, J.; Qing, J.; Huang, M.; Wu, M.; Gao, F.; Li, D.; Hong, Z.; Kong, L.; Huang, W.; et al. Discovery of Novel Hepatitis C Virus NS5B Polymerase Inhibitors by Combining Random Forest, Multiple e-Pharmacophore Modeling and Docking. PLoS ONE 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarrazin, C.; Zeuzem, S. Resistance to Direct Antiviral Agents in Patients with Hepatitis C Virus Infection. Gastroenterology 2010, 138, 447–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Roohvand, F.; Kossari, N. Advances in Hepatitis C Virus Vaccines, Part One: Advances in Basic Knowledge for Hepatitis C Virus Vaccine Design. Expert Opin. Ther. Pat. 2011, 21, 1811–1830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Center, R.J.; Boo, I.; Phu, L.; McGregor, J.; Poumbourios, P.; Drummer, H.E. Enhancing the Antigenicity and Immunogenicity of Monomeric Forms of Hepatitis C Virus E2 for Use as a Preventive Vaccine: EDITORS’PICK: Multimerization of HCV E2 Enhances Immunogenicity. J. Biol. Chem. 2020, 295, 7179–7192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Akache, B.; Deschatelets, L.; Harrison, B.A.; Dudani, R.; Stark, F.C.; Jia, Y.; Landi, A.; Law, J.L.M.; Logan, M.; Hockman, D. Effect of Different Adjuvants on the Longevity and Strength of Humoral and Cellular Immune Responses to the HCV Envelope Glycoproteins. Vaccines 2019, 7, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Beaumont, E.; Patient, R.; Hourioux, C.; Dimier-Poisson, I.; Roingeard, P. Chimeric Hepatitis B Virus/Hepatitis C Virus Envelope Proteins Elicit Broadly Neutralizing Antibodies and Constitute a Potential Bivalent Prophylactic Vaccine. Hepatology 2013, 57, 1303–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Frey, S.E.; Houghton, M.; Coates, S.; Abrignani, S.; Chien, D.; Rosa, D.; Pileri, P.; Ray, R.; Di Bisceglie, A.M.; Rinella, P. Safety and Immunogenicity of HCV E1E2 Vaccine Adjuvanted with MF59 Administered to Healthy Adults. Vaccine 2010, 28, 6367–6373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Forns, X.; Payette, P.J.; Ma, X.; Satterfield, W.; Eder, G.; Mushahwar, I.K.; Govindarajan, S.; Davis, H.L.; Emerson, S.U.; Purcell, R.H. Vaccination of Chimpanzees with Plasmid DNA Encoding the Hepatitis C Virus (HCV) Envelope E2 Protein Modified the Infection after Challenge with Homologous Monoclonal HCV. Hepatology 2000, 32, 618–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijesundara, D.K.; Gummow, J.; Li, Y.; Yu, W.; Quah, B.J.; Ranasinghe, C.; Torresi, J.; Gowans, E.J.; Grubor-Bauk, B. Induction of Genotype Cross-reactive, Hepatitis C Virus-specific, Cell-mediated Immunity in DNA-vaccinated Mice. J. Virol. 2018, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Masavuli, M.G.; Wijesundara, D.K.; Underwood, A.; Christiansen, D.; Earnest-Silveira, L.; Bull, R.; Torresi, J.; Gowans, E.J.; Grubor-Bauk, B. A Hepatitis C Virus DNA Vaccine Encoding a Secreted, Oligomerized Form of Envelope Proteins is Highly Immunogenic and Elicits Neutralizing Antibodies in Vaccinated Mice. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Filskov, J.; Andersen, P.; Agger, E.M.; Bukh, J. HCV p7 as a Novel Vaccine-target Inducing Multifunctional CD4+ and CD8+ T-cells Targeting Liver Cells Expressing the Viral Antigen. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dawood, R.M.; Moustafa, R.I.; Abdelhafez, T.H.; El-Shenawy, R.; El-Abd, Y.; El Din, N.G.B.; Dubuisson, J.; El Awady, M.K. A Multiepitope Peptide Vaccine against HCV Stimulates Neutralizing Humoral and Persistent Cellular Responses in Mice. BMC Infect. Dis. 2019, 19, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Marín, M.Q.; Pérez, P.; Ljungberg, K.; Sorzano, C.Ó.S.; Gómez, C.E.; Liljeström, P.; Esteban, M.; García-Arriaza, J. Potent Anti-hepatitis C Virus (HCV) T Cell Immune Responses Induced in Mice Vaccinated with DNA-launched RNA Replicons and Modified Vaccinia Virus Ankara-HCV. J. Virol. 2019, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Serviddio, G. Practical Management of Chronic Viral Hepatitis; BoD–Books on Demand: Norderstedt, Germany, 2013; ISBN 9535111094. [Google Scholar]
- Shehzadi, A.; ur Rehman, S.; Idrees, M. Promiscuous Prediction and Conservancy Analysis of CTL Binding Epitopes of HCV 3a Viral Proteome from Punjab Pakistan: An in silico Approach. Virol. J. 2011, 8, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Memarnejadian, A.; Roohvand, F.; Arashkia, A.; Rafati, S.; Shokrgozar, M.A. Polytope DNA Vaccine Development against Hepatitis C Virus: A Streamlined Approach from in silico Design to in vitro and Primary in vivo Analyses in BALB/c Mice. Protein Pept. Lett. 2009, 16, 842–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikram, A.; Zaheer, T.; Awan, F.M.; Obaid, A.; Naz, A.; Hanif, R.; Paracha, R.Z.; Ali, A.; Naveed, A.K.; Janjua, H.A. Exploring NS3/4A, NS5A and NS5B Proteins to Design Conserved Subunit Multi-epitope Vaccine against HCV Utilizing Immunoinformatics Approaches. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sabet, L.P.; Taheri, T.; Memarnejadian, A.; Azad, T.M.; Asgari, F.; Rahimnia, R.; Alavian, S.M.; Rafati, S.; Rad, K.S. Immunogenicity of Multi-epitope DNA and Peptide Vaccine Candidates Based on Core, E2, NS3 and NS5B HCV Epitopes in BALB/c Mice. Hepat. Mon. 2014, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Benson, D.A.; Karsch-Mizrachi, I.; Lipman, D.J.; Ostell, J.; Sayers, E.W. GenBank. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010, 39, D32–D37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larsen, M.V.; Lundegaard, C.; Lamberth, K.; Buus, S.; Lund, O.; Nielsen, M. Large-scale Validation of Methods for Cytotoxic T-lymphocyte Epitope Prediction. BMC Bioinform. 2007, 8, 424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vita, R.; Mahajan, S.; Overton, J.A.; Dhanda, S.K.; Martini, S.; Cantrell, J.R.; Wheeler, D.K.; Sette, A.; Peters, B. The Immune Epitope Database (IEDB): 2018 Update. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 47, D339–D343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Doytchinova, I.A.; Flower, D.R. VaxiJen: A Server for Prediction of Protective Antigens, Tumour Antigens and Subunit Vaccines. BMC Bioinform. 2007, 8, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dimitrov, I.; Flower, D.R.; Doytchinova, I. AllerTOP-a Server for in silico Prediction of Allergens. BMC Bioinform. 2013, 14, S4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shahid, F.; Ashfaq, U.A.; Javaid, A.; Khalid, H. Immunoinformatics Guided Rational Design of a Next Generation Multi Epitope Based Peptide (MEBP) Vaccine by Exploring Zika Virus Proteome. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2020, 80, 104199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugiarto, H.; Yu, P.-L. Avian Antimicrobial Peptides: The Defense Role of $β$-defensins. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2004, 323, 721–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y. I-TASSER Server for Protein 3D Structure Prediction. BMC Bioinform. 2008, 9, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Heo, L.; Park, H.; Seok, C. GalaxyRefine: Protein Structure Refinement Driven by Side-chain Repacking. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, W384–W388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grote, A.; Hiller, K.; Scheer, M.; Münch, R.; Nörtemann, B.; Hempel, D.C.; Jahn, D. JCat: A Novel Tool to Adapt Codon Usage of a Target Gene to Its Potential Expression Host. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005, 33, W526–W531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jespersen, M.C.; Peters, B.; Nielsen, M.; Marcatili, P. BepiPred-2.0: Improving Sequence-based B-cell Epitope Prediction Using Conformational Epitopes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, W24–W29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cheng, J.; Randall, A.Z.; Sweredoski, M.J.; Baldi, P. SCRATCH: A Protein Structure and Structural Feature Prediction Server. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005, 33, W72–W76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- ProtParam, E. ExPASy-ProtParam Tool. 2017. Available online: https://web.expasy.org/protparam/ (accessed on 3 March 2021).
- Kozakov, D.; Hall, D.R.; Xia, B.; Porter, K.A.; Padhorny, D.; Yueh, C.; Beglov, D.; Vajda, S. The ClusPro Web Server for Protein-Protein Docking. Nat. Protoc. 2017, 12, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Case, D.; Ben-Shalom, I.; Brozell, S.; Cerutti, D.; Cheatham III, T.; Cruzeiro, V.; Darden, T.; Duke, R.; Ghoreishi, D.; Gilson, M.; et al. Amber 18 Reference Manual; University of California: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Dickson, C.J.; Rosso, L.; Betz, R.M.; Walker, R.C.; Gould, I.R. GAFFlipid: A General Amber Force Field for the Accurate Molecular Dynamics Simulation of Phospholipid. Soft Matter 2012, 8, 9617–9627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feller, S.E.; Zhang, Y.; Pastor, R.W.; Brooks, B.R. Constant Pressure Molecular Dynamics Simulation: The Langevin Piston Method. J. Chem. Phys. 1995, 103, 4613–4621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kräutler, V.; Van Gunsteren, W.F.; Hünenberger, P.H. A Fast SHAKE Algorithm to Solve Distance Constraint Equations for Small Molecules in Molecular Dynamics Simulations. J. Comput. Chem. 2001, 22, 501–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roe, D.R.; Cheatham III, T.E. PTRAJ and CPPTRAJ: Software for Processing and Analysis of Molecular Dynamics Trajectory Data. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2013, 9, 3084–3095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, B.R.; McGee, T.D.; Swails, J.M.; Homeyer, N.; Gohlke, H.; Roitberg, A.E. MMPBSA.py: An Efficient Program for End-state Free Energy Calculations. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2012, 8, 3314–3321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genheden, S.; Ryde, U. The MM/PBSA and MM/GBSA Methods to Estimate Ligand-binding Affinities. Expert Opin. Drug Discov. 2015, 10, 449–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rapin, N.; Lund, O.; Castiglione, F. C-ImmSim 10.1 Server. PLoS Pathog. 2012, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, M.E.; Varga, S.M. The CD8 T Cell Response to Respiratory Virus Infections. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Luckheeram, R.V.; Zhou, R.; Verma, A.D.; Xia, B. CD4+ T Cells: Differentiation and Functions. Clin. Dev. Immunol. 2012, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Angov, E. Codon Usage: Nature’s Roadmap to Expression and Folding of Proteins. Biotechnol. J. 2011, 6, 650–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sanchez-Trincado, J.L.; Gomez-Perosanz, M.; Reche, P.A. Fundamentals and Methods for T-and B-cell Epitope Prediction. J. Immunol. Res. 2017, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Manns, M.P.; Buti, M.; Gane, E.; Pawlotsky, J.M.; Razavi, H.; Terrault, N.; Younossi, Z. Hepatitis C Virus Infection. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Joshi, M.D.; Singhania, S.; Ramsey, K.H.; Murthy, A.K. Peptide Vaccine: Progress and Challenges. Vaccines 2014, 2, 515–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, L. Multi-epitope Vaccines: A Promising Strategy against Tumors and Viral Infections. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2018, 15, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- María, R.R.; Arturo, C.J.; Alicia, J.; Paulina, M.G.; Gerardo, A. The Impact of Bioinformatics on Vaccine Design and Development; InTech: Rijeka, Croatia, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Sayed, S.B.; Nain, Z.; Khan, M.S.A.; Abdulla, F.; Tasmin, R.; Adhikari, U.K. Exploring Lassa Virus Proteome to Design a Multi-epitope Vaccine through Immunoinformatics and Immune Simulation Analyses. Int. J. Pept. Res. Ther. 2020, 26, 2089–2107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, M.; Pandey, R.K.; Khatoon, N.; Narula, A.; Mishra, A.; Prajapati, V.K. Exploring Dengue Genome to Construct a Multi-epitope Based Subunit Vaccine by Utilizing Immunoinformatics Approach to Battle against Dengue Infection. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodman, A.G.; Heinen, P.P.; Guerra, S.; Vijayan, A.; Sorzano, C.O.S.; Gomez, C.E.; Esteban, M. A Human Multi-epitope Recombinant Vaccinia Virus as a Universal T Cell Vaccine Candidate against Influenza Virus. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e25938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ashfaq, U.A.; Saleem, S.; Masoud, M.S.; Ahmad, M.; Nahid, N.; Bhatti, R.; Almatroudi, A.; Khurshid, M. Rational Design of Multi Epitope-based Subunit Vaccine by Exploring MERS-COV Proteome: Reverse Vaccinology and Molecular Docking Approach. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0245072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tahir Ul Qamar, M.; Saleem, S.; Ashfaq, U.A.; Bari, A.; Anwar, F.; Alqahtani, S. Epitope-based Peptide Vaccine Design and Target Site Depiction Against Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus: An Immune-informatics Study. J. Transl. Med. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qamar, M.T.U.; Shokat, Z.; Muneer, I.; Ashfaq, U.A.; Javed, H.; Anwar, F.; Bari, A.; Zahid, B.; Saari, N. Multiepitope-based Subunit Vaccine Design and Evaluation against Respiratory Syncytial Virus Using Reverse Vaccinology Approach. Vaccines 2020, 8, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enayatkhani, M.; Hasaniazad, M.; Faezi, S.; Gouklani, H.; Davoodian, P.; Ahmadi, N.; Einakian, M.A.; Karmostaji, A.; Ahmadi, K. Reverse Vaccinology Approach to Design a Novel Multi-epitope Vaccine Candidate Against COVID-19: An in silico Study. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2020, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tahir ul Qamar, M.; Shahid, F.; Aslam, S.; Ashfaq, U.A.; Aslam, S.; Fatima, I.; Fareed, M.M.; Zohaib, A.; Chen, L.-L. Reverse Vaccinology Assisted Designing of Multiepitope-based Subunit Vaccine Against SARS-CoV-2. Infect. Dis. Poverty 2020, 9, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Tahir ul Qamar, M.; Rehman, A.; Tusleem, K.; Ashfaq, U.A.; Qasim, M.; Zhu, X.; Fatima, I.; Shahid, F.; Chen, L.L. Designing of a Next Generation Multiepitope Based Vaccine (MEV) against SARS-COV-2: Immunoinformatics and in silico Approaches. PLoS ONE 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tahir Ul Qamar, M.; Bari, A.; Adeel, M.M.; Maryam, A.; Ashfaq, U.A.; Du, X.; Muneer, I.; Ahmad, H.I.; Wang, J. Peptide Vaccine against Chikungunya Virus: Immuno-informatics Combined with Molecular Docking Approach. J. Transl. Med. 2018, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Regenmortel, M.H. V Mapping Epitope Structure and Activity: From One-dimensional Prediction to Four-dimensional Description of Antigenic Specificity. Methods 1996, 9, 465–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shamriz, S.; Ofoghi, H.; Moazami, N. Effect of Linker Length and Residues on the Structure and Stability of a Fusion Protein with Malaria Vaccine Application. Comput. Biol. Med. 2016, 76, 24–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Valtanen, P.; Martinez-Lopez, A.; Ortega-Villaizan, M.; Perez, L.; Coll, J.M.; Estepa, A. In Addition to Its Antiviral and Immunomodulatory Properties, the Zebrafish β-defensin 2 (zfBD2) is a Potent Viral DNA Vaccine Molecular Adjuvant. Antiviral Res. 2014, 101, 136–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mittal, A.; Sasidharan, S.; Raj, S.; Balaji, S.N.; Saudagar, P. Exploring the Zika Genome to Design a Potential Multiepitope Vaccine Using an Immunoinformatics Approach. Int. J. Pept. Res. Ther. 2020, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojha, R.; Gupta, N.; Naik, B.; Singh, S.; Verma, V.K.; Prusty, D.; Prajapati, V.K. High Throughput and Comprehensive Approach to Develop Multiepitope Vaccine against Minacious COVID-19. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2020, 151, 105375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meza, B.; Ascencio, F.; Sierra-Beltrán, A.P.; Torres, J.; Angulo, C. A Novel Design of a Multi-antigenic, Multistage and Multi-epitope Vaccine against Helicobacter Pylori: An in silico Approach. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2017, 49, 309–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Nguyen, M.T. Recent Advances of Vaccine Adjuvants for Infectious Diseases. Immune Netw. 2015, 15, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Arai, R.; Ueda, H.; Kitayama, A.; Kamiya, N.; Nagamune, T. Design of the Linkers Which Effectively Separate Domains of a Bifunctional Fusion Protein. Protein Eng. 2001, 14, 529–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durdagi, S.; Tahir ul Qamar, M.; Salmas, R.E.; Tariq, Q.; Anwar, F.; Ashfaq, U.A. Investigating the Molecular Mechanism of Staphylococcal DNA Gyrase Inhibitors: A Combined Ligand-based and Structure-based Resources Pipeline. J. Mol. Graph. Model. 2018, 85, 122–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, L.S.; Eddy, S.R.; Portugaly, E. Hidden Markov Model Speed Heuristic and Iterative HMM Search Procedure. BMC Bioinform. 2010, 11, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Machida, K.; Cheng, K.T.H.; Sung, V.M.-H.; Levine, A.M.; Foung, S.; Lai, M.M.C. Hepatitis C Virus Induces Toll-like Receptor 4 Expression, Leading to Enhanced Production of Beta Interferon and Interleukin-6. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 866–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gori, A.; Longhi, R.; Peri, C.; Colombo, G. Peptides for Immunological Purposes: Design, Strategies and Applications. Amino Acids 2013, 45, 257–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, R.K.; Ojha, R.; Aathmanathan, V.S.; Krishnan, M.; Prajapati, V.K. Immunoinformatics Approaches to Design a Novel Multi-epitope Subunit Vaccine against HIV Infection. Vaccine 2018, 36, 2262–2272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R. Bacterial Expression Systems for Recombinant Protein Production: E. coli and Beyond. Biotechnol. Adv. 2012, 30, 1102–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosano, G.L.; Ceccarelli, E.A. Recombinant Protein Expression in Escherichia coli: Advances and Challenges. Front. Microbiol. 2014, 5, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]





| Sr. No. | NETCTL | Score | IEDB Immunogenicity Score |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | FSGVDAVTY | 2.044 | 0.1684 |
| 2 | LMTTVLLAY | 2.158 | 0.0949 |
| 3 | VTTGANLTY | 3.078 | 0.092 |
| 4 | LTLSLRWIY | 2.662 | 0.1325 |
| Sr. No. | IEBD (HTL Peptide) | Percentile Rank |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | LRAWRHRARAVRAML | 0.17 |
| 2 | ITSLVVPPPPWPVLL | 0.29 |
| 3 | TSLVVPPPPWPVLLG | 0.29 |
| 4 | IITSLVVPPPPWPVL | 0.36 |
| 5 | SLVVPPPPWPVLLGR | 0.37 |
| Sr. No. | Start | End | Peptide | Length |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 24 | 50 | LPKEEQIGKCSTRGRKCCRRKKFSGVD | 27 |
| 3 | 102 | 105 | VPPP | 4 |
| 4 | 115 | 119 | VVPPP | 5 |
| 5 | 132 | 138 | VPPPPWP | 7 |
| 6 | 143 | 151 | VVPPPPWPV | 9 |
| Energy Component | Binding Free Energy (kcal/mol) |
|---|---|
| ΔEvdw | −234.48 |
| ΔEele | −85.16 |
| Epolar.solv | 59.14 |
| Enon-polar.solv | −21.7 |
| ΔGgas (GBSA) | −319.64 |
| ΔGsol (GBSA) | 37.44 |
| ΔGbind (GBSA) | −282.2 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ahmad, S.; Shahid, F.; Tahir ul Qamar, M.; Rehman, H.u.; Abbasi, S.W.; Sajjad, W.; Ismail, S.; Alrumaihi, F.; Allemailem, K.S.; Almatroudi, A.; et al. Immuno-Informatics Analysis of Pakistan-Based HCV Subtype-3a for Chimeric Polypeptide Vaccine Design. Vaccines 2021, 9, 293. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines9030293
Ahmad S, Shahid F, Tahir ul Qamar M, Rehman Hu, Abbasi SW, Sajjad W, Ismail S, Alrumaihi F, Allemailem KS, Almatroudi A, et al. Immuno-Informatics Analysis of Pakistan-Based HCV Subtype-3a for Chimeric Polypeptide Vaccine Design. Vaccines. 2021; 9(3):293. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines9030293
Chicago/Turabian StyleAhmad, Sajjad, Farah Shahid, Muhammad Tahir ul Qamar, Habib ur Rehman, Sumra Wajid Abbasi, Wasim Sajjad, Saba Ismail, Faris Alrumaihi, Khaled S. Allemailem, Ahmad Almatroudi, and et al. 2021. "Immuno-Informatics Analysis of Pakistan-Based HCV Subtype-3a for Chimeric Polypeptide Vaccine Design" Vaccines 9, no. 3: 293. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines9030293
APA StyleAhmad, S., Shahid, F., Tahir ul Qamar, M., Rehman, H. u., Abbasi, S. W., Sajjad, W., Ismail, S., Alrumaihi, F., Allemailem, K. S., Almatroudi, A., & Ullah Saeed, H. F. (2021). Immuno-Informatics Analysis of Pakistan-Based HCV Subtype-3a for Chimeric Polypeptide Vaccine Design. Vaccines, 9(3), 293. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines9030293









