AP205 VLPs Based on Dimerized Capsid Proteins Accommodate RBM Domain of SARS-CoV-2 and Serve as an Attractive Vaccine Candidate
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Mice
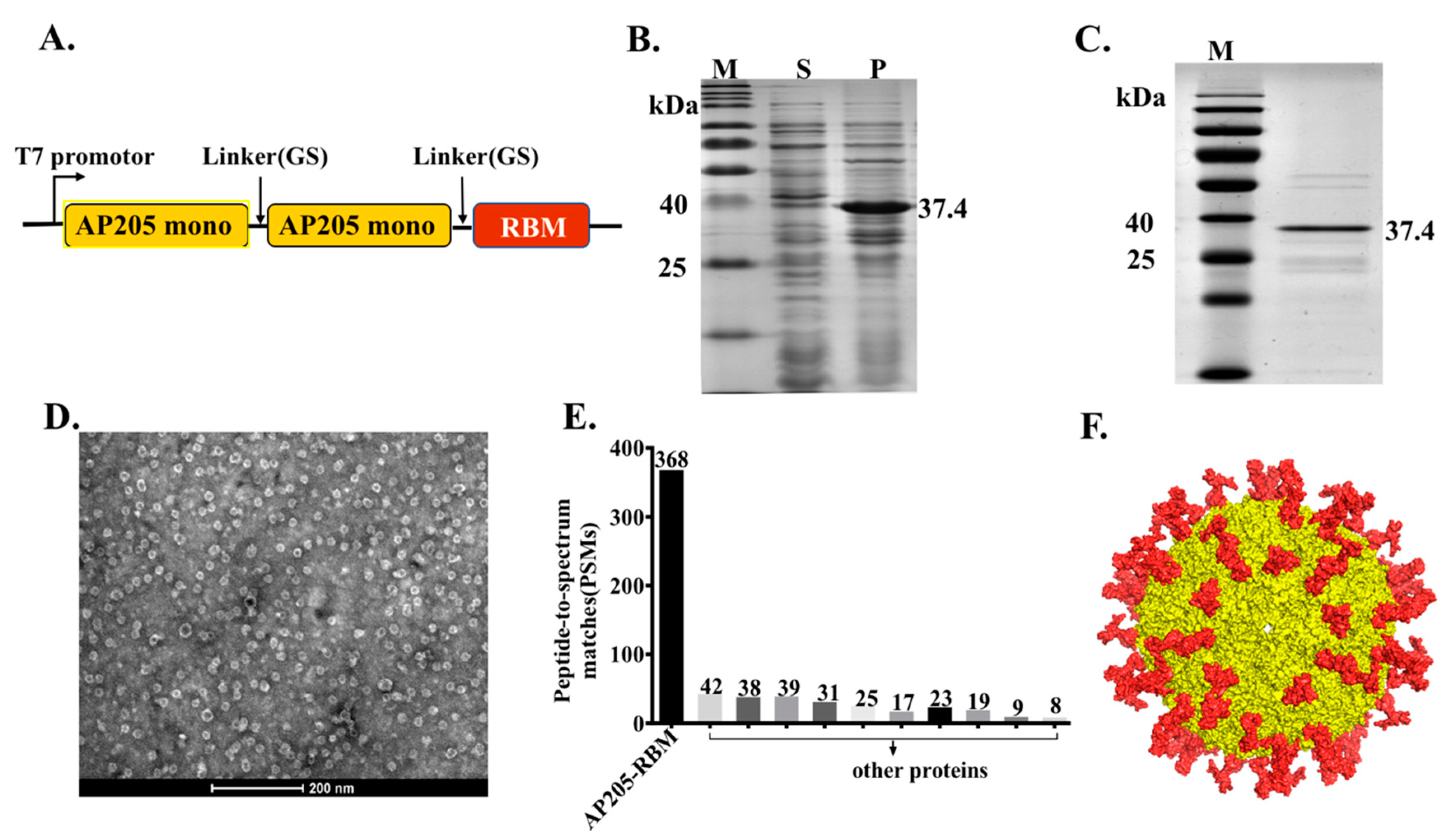
2.2. AP205-RBM Vaccine Cloning, Expression, and Production
2.3. Protein Refolding and Purifying
2.4. Electron Microscopy
2.5. Mass Spectrometry
2.6. Vaccination Regimen
2.7. The Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
2.8. Antibody Avidity Measurement
2.9. Neutralization Assay
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. The Bacteriophage AP205-VLPs Can Be Used Efficiently for Generating a Fusion Vaccine Against SARS-CoV-2
3.2. Vaccination with AP205-RBM Vaccine Induces High Titers of RBD and Spike-Specific IgG Abs
3.3. AP205-RBM Vaccine Promotes IgA Production and IgG Responses Dominated by IgG2a
3.4. The Induced IgG Antibodies against RBD and Spike Protein by AP205-RBM Vaccine Are of High Avidity
3.5. The AP205-RBM Vaccine Candidate Induces Antibodies Neutralizing SARS-CoV2
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Guan, W.J.; Ni, Z.Y.; Hu, Y.; Liang, W.H.; Ou, C.Q.; He, J.X.; Liu, L.; Shan, H.; Lei, C.L.; Hui, D.S.C.; et al. Clinical Characteristics of Coronavirus Disease 2019 in China. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 1708–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, X.; Lau, E.H.Y.; Wu, P.; Deng, X.; Wang, J.; Hao, X.; Lau, Y.C.; Wong, J.Y.; Guan, Y.; Tan, X.; et al. Temporal dynamics in viral shedding and transmissibility of COVID-19. Nat. Med. 2020, 26, 672–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cheng, V.C.; Wong, S.C.; Chen, J.H.; Yip, C.C.; Chuang, V.W.; Tsang, O.T.; Sridhar, S.; Chan, J.F.W.; Ho, P.-L.; Yuen, K.-Y. Escalating infection control response to the rapidly evolving epidemiology of the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) due to SARS-CoV-2 in Hong Kong. Infect. Control Hosp. Epidemiol. 2020, 41, 493–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Salathé, M.; Althaus, C.L.; Neher, R.; Stringhini, S.; Hodcroft, E.; Fellay, J.; Zwahlen, M.; Senti, G.; Battegay, M.; Wilder-Smith, A.; et al. COVID-19 epidemic in Switzerland: On the importance of testing, contact tracing and isolation. Swiss Med. Wkly. 2020, 150, w20225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, R.M.; Heesterbeek, H.; Klinkenberg, D.; Hollingsworth, T.D. How will country-based mitigation measures influence the course of the COVID-19 epidemic? Lancet 2020, 395, 931–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Ulitzky, L.; Silberstein, E.; Taylor, D.R.; Viscidi, R. Immunogenicity and Protection Efficacy of Monomeric and Trimeric Recombinant SARS Coronavirus Spike Protein Subunit Vaccine Candidates. Viral Immunol. 2013, 26, 126–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, J.; Zeng, H.; Gu, J.; Li, H.; Zheng, L.; Zou, Q. Progress and Prospects on Vaccine Development against SARS-CoV-2. Vaccines (Basel) 2020, 8, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, Y.; Guo, Y.; Pan, Y.; Zhao, Z.J. Structure analysis of the receptor binding of 2019-nCoV. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2020, 525, 135–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zinkhan, S.; Ogrina, A.; Balke, I.; Reseviča, G.; Zeltins, A.; de Brot, S.; Lipp, C.; Chang, X.; Zha, L.; Vogel, M.; et al. The impact of size on particle drainage dynamics and antibody response. J. Control. Release 2021, 331, 296–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohsen, M.O.; Augusto, G.; Bachmann, M.F. The 3Ds in virus-like particle based-vaccines: “Design, Delivery and Dynamics”. Immunol. Rev. 2020, 296, 155–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohsen, M.O.; Gomes, A.C.; Vogel, M.; Bachmann, M.F. Interaction of Viral Capsid-Derived Virus-Like Particles (VLPs) with the Innate Immune System. Vaccines 2018, 6, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bachmann, M.F.; Jennings, G.T. Vaccine delivery: A matter of size, geometry, kinetics and molecular patterns. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2010, 10, 787–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shishovs, M.; Rumnieks, J.; Diebolder, C.; Jaudzems, K.; Andreas, L.B.; Stanek, J.; Kazaks, A.; Kotelovica, S.; Akopjana, I.; Pintacuda, G.; et al. Structure of AP205 Coat Protein Reveals Circular Permutation in ssRNA Bacteriophages. J. Mol. Biol. 2016, 428, 4267–4279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whitt, M.A. Generation of VSV pseudotypes using recombinant ΔG-VSV for studies on virus entry, identification of entry inhibitors, and immune responses to vaccines. J. Virol. Methods 2010, 169, 365–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tissot, A.C.; Renhofa, R.; Schmitz, N.; Cielens, I.; Meijerink, E.; Ose, V.; Jennings, G.T.; Saudan, P.; Pumpens, P.; Bachmann, M.F. Versatile Virus-Like Particle Carrier for Epitope Based Vaccines. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e9809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hazenbos, W.L.; Heijnen, I.A.; Meyer, D.; Hofhuis, F.M.; De Lavalette, C.R.R.; Schmidt, R.E.; Capel, P.J.; Van De Winkel, J.G.; Gessner, J.E.; Berg, T.K.V.D.; et al. Murine IgG1 complexes trigger immune effector functions predominantly via Fc gamma RIII (CD16). J. Immunol. 1998, 161, 3026–3032. [Google Scholar]
- Oishi, K.; Koles, N.L.; Guelde, G.; Pollack, M. Antibacterial and Protective Properties of Monoclonal Antibodies Reactive with Escherichia coli O111:B4 Lipopolysaccharide: Relation to Antibody Isotype and Complement-Fixing Activity. J. Infect. Dis. 1992, 165, 34–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polack, F.P.; Hoffman, S.J.; Crujeiras, G.; Griffin, D.E. A role for nonprotective complement-fixing antibodies with low avidity for measles virus in atypical measles. Nat. Med. 2003, 9, 1209–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klasse, P.J. How to assess the binding strength of antibodies elicited by vaccination against HIV and other viruses. Expert Rev. Vaccines 2016, 15, 295–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zha, L.; Zhao, H.; Mohsen, M.O.; Hong, L.; Zhou, Y.; Li, Z.; Chen, H.; Liu, X.; Chang, X.; Zhang, J.; et al. Development of a vaccine against the newly emerging COVID-19 virus based on the receptor binding domain displayed on virus-like particles. Vaccines 2021, 9, 395. [Google Scholar]
- Mohsen, M.O.; Gomes, A.C.; Cabral-Miranda, G.; Krueger, C.C.; Leoratti, F.M.; Stein, J.V.; Bachmann, M.F. Delivering adjuvants and antigens in separate nanoparticles eliminates the need of physical linkage for effective vaccination. J. Control. Release 2017, 251, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mohsen, M.O.; Zha, L.; Cabral-Miranda, G.; Bachmann, M.F. Major findings and recent advances in virus–like particle (VLP)-based vaccines. Semin. Immunol. 2017, 34, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomes, A.C.; Flace, A.; Saudan, P.; Zabel, F.; Cabral-Miranda, G.; El Turabi, A.; Manolova, V.; Bachmann, M.F. Adjusted Particle Size Eliminates the Need of Linkage of Antigen and Adjuvants for Appropriated T Cell Responses in Virus-Like Particle-Based Vaccines. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cabral-Miranda, G.; Lim, S.M.; Mohsen, M.O.; Pobelov, I.V.; Roesti, E.S.; Heath, M.D.; Skinner, M.A.; Kramer, M.F.; Martina, B.E.E.; Bachmann, M.F. Correction: Zika Virus-Derived E-DIII Protein Displayed on Immunologically Optimized VLPs Induces Neutralizing Antibodies without Causing Enhancement of Dengue Virus Infection. Vaccines 2019, 7, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gilfillan, C.B.; Wang, C.; Mohsen, M.O.; Rufer, N.; Hebeisen, M.; Allard, M.; Verdeil, G.; Irvine, D.J.; Bachmann, M.F.; Speiser, D.E. Murine CD8 T-cell functional avidity is stable in vivo but not in vitro: Independence from homologous prime/boost time interval and antigen density. Eur. J. Immunol. 2020, 50, 505–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Morita, M.; Aizawa, M.; Toi, H.; Fukuhara, E.; Hashimoto, K. Continuous flow ultracentrifuge system for production of infection prevention vaccines. Hitachi Rev. 2011, 60, 257–261. [Google Scholar]
- Grant, O.C.; Montgomery, D.; Ito, K.; Woods, R.J. Analysis of the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein glycan shield: Implications for immune recognition. bioRxiv 2020, 9, 2754. [Google Scholar]
- Gudbjartsson, D.F.; Norddahl, G.L.; Melsted, P.; Gunnarsdottir, K.; Holm, H.; Eythorsson, E.; Arnthorsson, A.O.; Helgason, D.; Bjarnadottir, K.; Ingvarsson, R.F.; et al. Humoral Immune Response to SARS-CoV-2 in Iceland. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 1724–1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isho, B.; Abe, K.T.; Zuo, M.; Jamal, A.J.; Rathod, B.; Wang, J.H.; Li, Z.; Chao, G.; Rojas, O.L.; Bang, Y.M.; et al. Persistence of serum and saliva antibody responses to SARS-CoV-2 spike antigens in COVID-19 patients. Sci. Immunol. 2020, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachmann, M.F.; Mohsen, M.O.; Zha, L.; Vogel, M.; Speiser, D.E. SARS-CoV-2 structural features may explain limited neutralizing-antibody responses. NPJ Vaccines 2021, 6, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachmann, M.F.; Rohrer, U.H.; Kündig, T.M.; Burki, K.; Hengartner, H.; Zinkernagel, R.M. The influence of antigen organization on B cell responsiveness. Science 1993, 262, 1448–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chackerian, B.; Lowy, D.R.; Schiller, J.T. Conjugation of a self-antigen to papillomavirus-like particles allows for efficient induction of protective autoantibodies. J. Clin. Investig. 2001, 108, 415–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Link, A.; Zabel, F.; Schnetzler, Y.; Titz, A.; Brombacher, F.; Bachmann, M.F. Innate Immunity Mediates Follicular Transport of Particulate but Not Soluble Protein Antigen. J. Immunol. 2012, 188, 3724–3733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vogel, M.; Chang, X.Y.; Augusto, G.S.; Mohsen, M.O.; Speiser, D.E.; Bachmann, M.F. SARS-CoV-2 variant with higher affinity to ACE2 shows reduced sera neutralization susceptibility. bioRxiv 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, X.; Augusto, G.S.; Liu, X.; Kündig, T.M.; Vogel, M.; Mohsen, M.O.; Bachmann, M.F. BNT162b2 mRNA COVID-19 vaccine induces antibodies of broader cross-reactivity than natural infection but recognition of mutant viruses is up to 10-fold reduced. bioRxiv 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coutelier, J.-P.; Van Der Logt, J.T.M.; Heessen, F.W.A.; Warnier, G.; Van Snick, J. IgG2a restriction of murine antibodies elicited by viral infections. J. Exp. Med. 1987, 165, 64–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markine-Goriaynoff, D.; Coutelier, J.-P. Increased Efficacy of the Immunoglobulin G2a Subclass in Antibody-Mediated Protection against Lactate Dehydrogenase-Elevating Virus-Induced Polioencephalomyelitis Revealed with Switch Mutants. J. Virol. 2002, 76, 432–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Heusser, C.H.; Anderson, C.L.; Grey, H.M. Receptors for IgG: Subclass specificity of receptors on different mouse cell types and the definition of two distinct receptors on a macrophage cell line. J. Exp. Med. 1977, 145, 1316–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Klaus, G.G.; Pepys, M.B.; Kitajima, K.; Askonas, B.A. Activation of mouse complement by different classes of mouse antibody. Immunology 1979, 38, 687–695. [Google Scholar]
- Kipps, T.J.; Parham, P.; Punt, J.; Herzenberg, L.A. Importance of Immunoglobulin Isotype in Human Antibody-Dependent, Cell-Mediated Cyto-Toxicity Directed by Murine Monoclonal-Antibodies. J. Exp. Med. 1985, 161, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schmitz, N.; Beerli, R.R.; Bauer, M.; Jegerlehner, A.; Dietmeier, K.; Maudrich, M.; Pumpens, P.; Saudan, P.; Bachmann, M.F. Universal vaccine against influenza virus: Linking TLR signaling to anti-viral protection. Eur. J. Immunol. 2012, 42, 863–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bessa, J.; Schmitz, N.; Hinton, H.J.; Schwarz, K.; Jegerlehner, A.; Bachmann, M.F. Efficient induction of mucosal and systemic immune responses by virus-like particles administered intranasally: Implications for vaccine design. Eur. J. Immunol. 2008, 38, 114–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, A.C.; Roesti, E.S.; El-Turabi, A.; Bachmann, M.F. Type of RNA Packed in VLPs Impacts IgG Class Switching—Implications for an Influenza Vaccine Design. Vaccines 2019, 7, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bessa, J.; Jegerlehner, A.; Hinton, H.J.; Pumpens, P.; Saudan, P.; Schneider, P.; Bachmann, M.F. Alveolar Macrophages and Lung Dendritic Cells Sense RNA and Drive Mucosal IgA Responses. J. Immunol. 2009, 183, 3788–3799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Skibinski, D.A.G.; Hanson, B.J.; Lin, Y.; Von Messling, V.; Jegerlehner, A.; Tee, J.B.S.; Chye, D.H.; Wong, S.K.K.; Ng, A.A.P.; Lee, H.Y.; et al. Enhanced Neutralizing Antibody Titers and Th1 Polarization from a Novel Escherichia coli Derived Pandemic Influenza Vaccine. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e76571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabral-Miranda, G.; Heath, M.D.; Mohsen, M.O.; Gomes, A.C.; Engeroff, P.; Flaxman, A.; Leoratti, F.M.S.; El-Turabi, A.; Reyes-Sandoval, A.; Skinner, M.A.; et al. Virus-Like Particle (VLP) Plus Microcrystalline Tyrosine (MCT) Adjuvants Enhance Vaccine Efficacy Improving T and B Cell Immunogenicity and Protection against Plasmodium berghei/vivax. Vaccines 2017, 5, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomes, A.C.; Mohsen, M.O.; Mueller, J.E.; Leoratti, F.M.S.; Cabral-Miranda, G.; Bachmann, M.F. Early Transcriptional Signature in Dendritic Cells and the Induction of Protective T Cell Responses upon Immunization with VLPs Containing TLR Ligands—A Role for CCL2. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]




Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, X.; Chang, X.; Rothen, D.; Derveni, M.; Krenger, P.; Roongta, S.; Wright, E.; Vogel, M.; Tars, K.; Mohsen, M.O.; et al. AP205 VLPs Based on Dimerized Capsid Proteins Accommodate RBM Domain of SARS-CoV-2 and Serve as an Attractive Vaccine Candidate. Vaccines 2021, 9, 403. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines9040403
Liu X, Chang X, Rothen D, Derveni M, Krenger P, Roongta S, Wright E, Vogel M, Tars K, Mohsen MO, et al. AP205 VLPs Based on Dimerized Capsid Proteins Accommodate RBM Domain of SARS-CoV-2 and Serve as an Attractive Vaccine Candidate. Vaccines. 2021; 9(4):403. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines9040403
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Xuelan, Xinyue Chang, Dominik Rothen, Mariliza Derveni, Pascal Krenger, Salony Roongta, Edward Wright, Monique Vogel, Kaspars Tars, Mona O. Mohsen, and et al. 2021. "AP205 VLPs Based on Dimerized Capsid Proteins Accommodate RBM Domain of SARS-CoV-2 and Serve as an Attractive Vaccine Candidate" Vaccines 9, no. 4: 403. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines9040403
APA StyleLiu, X., Chang, X., Rothen, D., Derveni, M., Krenger, P., Roongta, S., Wright, E., Vogel, M., Tars, K., Mohsen, M. O., & Bachmann, M. F. (2021). AP205 VLPs Based on Dimerized Capsid Proteins Accommodate RBM Domain of SARS-CoV-2 and Serve as an Attractive Vaccine Candidate. Vaccines, 9(4), 403. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines9040403






