Immunogenicity and Safety of Inactivated Sabin-Strain Polio Vaccine “PoliovacSin”: Clinical Trials Phase I and II
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cells and Viruses
2.2. Biosafety and Biosecurity Measures
2.3. Vaccine
2.3.1. Upstream Processes
2.3.2. Downstream Processes
2.3.3. PoliovacSin Composition
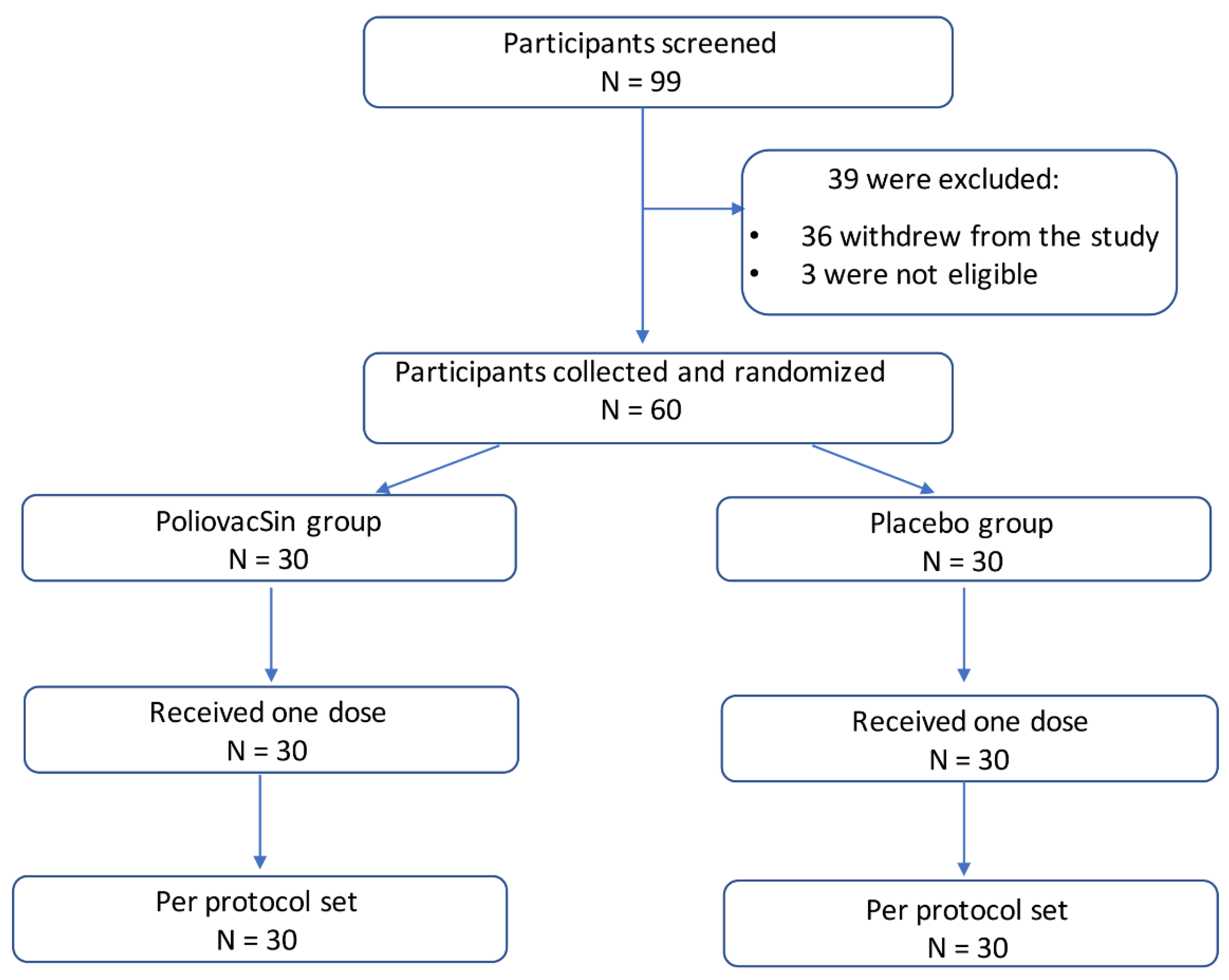
2.4. Study Design and Participants
2.5. Randomization
2.6. Safety Assessment
2.7. Blood Sampling
2.8. Neutralization Test (NT)
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Safety Assessments—Phase I
3.2. Safety Assessments—Phase II
3.3. Immunogenicity Assessment—Phase II
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Peter, F.; Wright, R.J.; Kim-Farley, C.A.; de Quadros, S.E.; Robertson, R.M.N.; Scott, N.A. Ward and Ralph, H. Henderson. Strategies for the global eradication of poliomyelitis by the year 2000. N. Engl. J. Med. 1991, 325, 1774–1779. [Google Scholar]
- Dowdle, W.R.; de Gourville, E.; Kew, O.M.; Pallansch, M.A.; Wood, D.J. Polio eradication: The OPV paradox. Med. Virol. 2003, 13, 277–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burns, C.C.; Diop, O.M.; Sutter, R.W.; Kew, O.M. Vaccine-Derived Polioviruses. J. Infect. Dis. 2014, 210, 283–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sutter, R.W.; Kew, O.M.; Cochi, S.L.; Aylward, R.B. Poliovirus vaccine—Live. In Vaccines, 7th ed.; Plotkin, S.A., Orenstein, W.A., Offit, P.A., Edwards, K.M., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 866–916. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization (WHO). Transmission of wild poliovirus type 2—Apparent global interruption. Wkly. Epidemiol. Rec. 2001, 76, 95–97. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization (WHO). Report from the Twentieth Meeting of the Global Commission for Certification of Poliomyelitis Eradication; World Health Organization (WHO): Geneva, Switzerland, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Certification of poliomyelitis eradication—The Americas, 1994. MMWR Morb. Mortal Wkly. Rep. 1994, 43, 720–722. [Google Scholar]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Certification of poliomyelitis eradication—The Western Pacific region, October 2000. MMWR Morb. Mortal Wkly. Rep. 2001, 50, 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Certification of poliomyelitis eradication—European Region, June 2002. MMWR Morb. Mortal Wkly. Rep. 2002, 51, 572–574. [Google Scholar]
- Bahl, S.; Kumar, R.; Menabde, N.; Thapa, A.; McFarland, J.; Swezy, V.; Tangermann, R.H.; Jafari, H.S.; Elsner, L.; Wassilak, S.G.F.; et al. Polio-free certification and lessons learned—South-East Asia. MMWR Morb. Mortal Wkly. Rep. 2014, 63, 941–946. [Google Scholar]
- Sáez-Llorens, X.; Clemens, R.; Leroux-Roels, G.; Jimeno, J.; Clemens, S.A.C.; Weldon, W.C.; Oberste, M.S.; Molina, N.; Bandyopadhyay, A.S. Immunogenicity and safety of a novel monovalent high-dose inactivated poliovirus type 2 vaccine in infants: A comparative, observer-blind, randomised, controlled trial. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2016, 16, 321–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://www.who.int/news/item/25-08-2020-global-polio-eradication-initiative-applauds-who-african-region-for-wild-polio-free-certification (accessed on 18 May 2021).
- Available online: https://polioeradication.org/wp-content/uploads/2021/05/weekly-polio-analyses-WPV-20210518.pdf (accessed on 18 May 2021).
- Available online: https://polioeradication.org/wp-content/uploads/2021/05/weekly-polio-analyses-cVDPV-20210518.pdf (accessed on 18 May 2021).
- Yakovenko, M.L.; Gmyl, A.P.; Ivanova, O.E.; Eremeeva, T.P.; Ivanov, A.P.; Prostova, M.A.; Baykova, O.Y.; Isaeva, O.V.; Lipskaya, G.Y.; Shakaryan, A.K.; et al. The 2010 outbreak of poliomyelitis in Tajikistan: Epidemiology and lessons learnt. Eurosurveillance 2014, 19, 20706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puligedda, R.D.; Kouiavskaia, D.; Al-Saleem, F.H.; Kattala, C.D.; Nabi, U.; Yaqoob, H.; Bhagavathula, V.S.; Sharma, R.; Chumakov, K.; Dessain, S.K. Characterization of human monoclonal antibodies that neutralize multiple poliovirus serotypes. Vaccine 2017, 35, 5455–5462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomassen, Y.E.; van Sprang, E.N.; van der Pol, L.A.; Bakker, W.A. Multivariate Data Analysis on Historical IPV Production Data for Better Process Understanding and Future Improvements. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2010, 107, 96–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomassen, Y.E.; van’t Oever, A.G.; Vinke, M.; Spiekstra, A.; Wijffels, R.H.; van der Pol, L.A.; Bakker, W.A. Scale-Down of the Inactivated Polio Vaccine Production Process. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2013, 110, 1354–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanders, B.P.; Oakes Ide, L.; van Hoek, V.; Liu, Y.; Marissen, W.; Minor, P.D.; Wimmer, E.; Schuitemaker, H.; Custers, J.H.; Macadam, A.; et al. Production of high titer attenuated poliovirus strains on the serum-free PER.C6(®) cell culture platform for the generation of safe and affordable next generation IPV. Vaccine 2015, 33, 6611–6616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verdijk, P.; Rots, N.Y.; Bakker, W.A. Clinical development of a novel inactivated poliomyelitis vaccine based on attenuated Sabin poliovirus strains. Expert Rev. Vaccines 2011, 10, 635–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, W.J.; Hara, D.; Gbormittah, F.; Chang, H.; Chang, B.S.; Jung, J.U. Development of Thermostable Lyophilized Sabin Inactivated Poliovirus Vaccine. Mbio 2018, 9, e02287-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okayasu, H.; Sein, C.; Hamidi, A.; Bakker, W.A.; Sutter, R.W. Development of inactivated poliovirus vaccine from Sabin strains: A progress report. Biologicals 2016, 44, 581–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torisu, T.; Shikama, S.; Nakamura, K.; Enomoto, K.; Maruno, T.; Mori, A.; Uchiyama, S.; Satou, T. Physicochemical Characterization of Sabin Inactivated Poliovirus Vaccine for Process Development. J. Pharm. Sci. 2021, 110, 2121–2129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hotta, C.; Ogawa, T.; Shirasawa, H. Surveillance of immunity acquired from poliovirus immunization including vaccination with the Sabin strain-derived inactivated vaccine. Hum. Vaccines Immunother. 2019, 15, 1154–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivanov, A.P.; Kozlov, V.G.; Klebleeva, T.D.; Ivanova, O.E.; Kiktenko, A.V. An ELISA system based on the specific class Y (IgY) antibodies from egg yolks for the quantitative determination of D-antigen in inactivated poliovirus vaccines. Vopr. Virususologii 2014, 59, 39–42. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization (WHO). Manual for Virological Investigation of Poliomyelitis; WHO/EPI/GEN/97.1; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- UNICEF. Inactivated Polio Vaccine (IPV): Supply Update; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Sutter, R.W.; Okayasu, H.; Kieny, M.P. Next Generation Inactivated Poliovirus Vaccine: The Future Has Arrived. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2017, 64, 1326–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, R.; Liu, X.; Sun, X.; Wang, J.; Huang, Z.; Li, C.; Li, Z.; Zhou, J.; Pu, Y.; Ying, Z.; et al. Immunogenicity and safety of the inactivated poliomyelitis vaccine made from Sabin strains in a phase IV clinical trial for the vaccination of a large population. Vaccine 2021, 39, 1463–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimizu, H. Development and introduction of inactivated poliovirus vaccines derived from Sabin strains in Japan. Vaccine 2016, 34, 1975–1985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.; Li, C.; Xu, W.; Liao, G.; Li, R.; Zhou, J.; Li, Y.; Cai, W.; Yan, D.; Che, Y.; et al. Immune Serum from Sabin Inactivated Poliovirus Vaccine Immunization Neutralizes Multiple Individual Wild and Vaccine-Derived Polioviruses. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2017, 64, 1317–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivanova, O.E.; Eremeeva, T.P.; Morozova, N.; Shakaryan, A.K.; Gmyl, A.P.; Yakovenko, M.L.; Korotkova, E.A.; Chernjavskaja, O.P.; Baykova, O.Y.; Silenova, O.V.; et al. Vaccine-associated paralytic poliomyelitis in Russian Federation during the period of changes in vaccination schedule (2006–2013 yy.). Vopr. Virusol. 2016, 61, 9–15. [Google Scholar]
- Ivanov, A.P.; Klebleeva, T.D.; Ivanova, O.E.; Ipatova, E.G.; Gmyl, L.V.; Ishmuhametov, A.A. Experimental Approaches to the Development of Inactivated Poliovirus Vaccine Based on Sabin Strains. Epidemiol. Vaccinal Prev. 2016, 15, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]


| Characteristics | PoliovacSin Group | Placebo Group |
|---|---|---|
| Participants, no | 30 | 30 |
| Female/Male, no | 16/14 | 11/19 |
| Age, years, mean ± SD | 37.4 ± 11.4 * | 32.5 ± 11.4 * |
| Height, m, mean ± SD | 1.72 ± 0.09 * | 1.75 ± 0.11 * |
| Weight, kg, mean ± SD | 74.6 ± 10.7 * | 77.4 ± 9.5 * |
| Group | Participants, No | Adverse Events Registered from 0 to 7 Day After Vaccination | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Local | Systemic | ||||||||||||
| Grade 1 | Grade 2 | Grade 3 | Grade 1 | Grade 2 | Grade 3 | ||||||||
| N | % | N | % | N | % | N | % | N | % | N | % | ||
| PoliovacSin | 30 | 2 | 6.67 | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| Placebo | 30 | – * | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | 1 | 3.33 | – | – |
| Total | 60 | 2 | 3.33 | – | – | – | – | – | – | 1 | 1.67 | – | – |
| Characteristics | PoliovacSin Group * | Imovax Group * |
|---|---|---|
| Participants, no | 100 | 100 |
| Female/Male, no | 59/41 | 61/39 |
| Age, years, mean ± SD | 32.1 ± 9.3 | 31.7 ± 9.1 |
| Female/Male 45 + years of age, no | 8/8 | 6/4 |
| Height, m, mean ± SD | 1.71 ± 0.08 | 1.69 ± 0.08 |
| Weight, kg, mean ± SD | 73.4 ± 13.8 | 69.0 ± 12.1 |
| Group | Participants, No | Adverse Events Registered from 0 to 7 Day After Vaccination | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Local | Systemic | ||||||||||||
| Grade 1 | Grade 2 | Grade 3 | Grade 1 | Grade 2 | Grade 3 | ||||||||
| N | % | N | % | N | % | N | % | N | % | N | % | ||
| PoliovacSin | 100 | 7 | 7.0 | 1 | 1.0 | – | – | 7 | 7.0 | 1 | 0.5 | – | – |
| Imovax Polio | 100 | 5 | 5.0 | – * | – | – | – | 5 | 5.0 | – | – | – | – |
| Total | 200 | 12 | 6.0 | 1 | 0.5 | – | – | 12 | 6.0 | 1 | 0.5 | – | – |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Piniaeva, A.; Ignatyev, G.; Kozlovskaya, L.; Ivin, Y.; Kovpak, A.; Ivanov, A.; Shishova, A.; Antonova, L.; Khapchaev, Y.; Feldblium, I.; et al. Immunogenicity and Safety of Inactivated Sabin-Strain Polio Vaccine “PoliovacSin”: Clinical Trials Phase I and II. Vaccines 2021, 9, 565. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines9060565
Piniaeva A, Ignatyev G, Kozlovskaya L, Ivin Y, Kovpak A, Ivanov A, Shishova A, Antonova L, Khapchaev Y, Feldblium I, et al. Immunogenicity and Safety of Inactivated Sabin-Strain Polio Vaccine “PoliovacSin”: Clinical Trials Phase I and II. Vaccines. 2021; 9(6):565. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines9060565
Chicago/Turabian StylePiniaeva, Anastasia, Georgy Ignatyev, Liubov Kozlovskaya, Yury Ivin, Anastasia Kovpak, Alexander Ivanov, Anna Shishova, Liliia Antonova, Yusuf Khapchaev, Irina Feldblium, and et al. 2021. "Immunogenicity and Safety of Inactivated Sabin-Strain Polio Vaccine “PoliovacSin”: Clinical Trials Phase I and II" Vaccines 9, no. 6: 565. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines9060565
APA StylePiniaeva, A., Ignatyev, G., Kozlovskaya, L., Ivin, Y., Kovpak, A., Ivanov, A., Shishova, A., Antonova, L., Khapchaev, Y., Feldblium, I., Ivanova, O., Siniugina, A., & Ishmukhametov, A. (2021). Immunogenicity and Safety of Inactivated Sabin-Strain Polio Vaccine “PoliovacSin”: Clinical Trials Phase I and II. Vaccines, 9(6), 565. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines9060565






