Serological Response in Lung Transplant Recipients after Two Doses of SARS-CoV-2 mRNA Vaccines
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
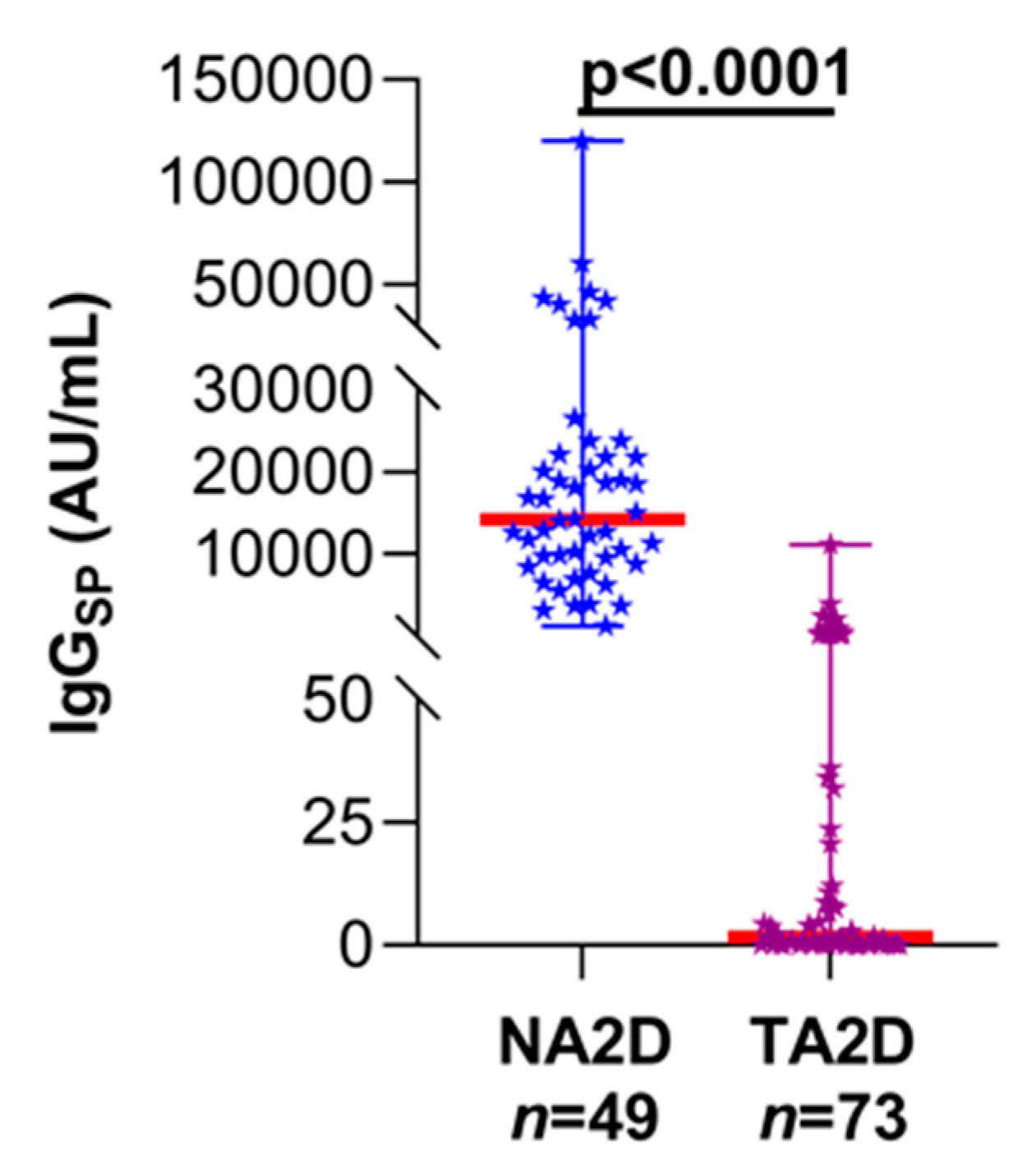
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Boyarsky, B.J.; Werbel, W.A.; Avery, R.K.; Tobian, A.A.; Massie, A.B.; Segev, D.L.; Garonzik-Wang, J.M. Immunogenicity of a Single Dose of SARS-CoV-2 Messenger RNA Vaccine in Solid Organ Transplant Recipients. JAMA 2021, 325, 1784–1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyarsky, B.J.; Werbel, W.A.; Avery, R.K.; Tobian, A.A.; Massie, A.B.; Segev, D.L.; Garonzik-Wang, J.M. Antibody Response to 2-Dose SARS-CoV-2 mRNA Vaccine Series in Solid Organ Transplant Recipients. JAMA 2021, 325, 2204–2206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Havlin, J.; Svorcova, M.; Dvorackova, E.; Lastovicka, J.; Lischke, R.; Kalina, T.; Hubacek, P. Immunogenicity of BNT162b2 mRNA COVID-19 vaccine and SARS-CoV-2 infection in lung transplant recipients. J. Heart Lung Transpl. 2021, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- SARS-CoV-2 Vaccination in Heart and Lung Transplantation: Recommendations from the ISHLT COVID-19 Task Force. Available online: https://ishlt.org/ishlt/media/Documents/COVID19_Vaccine-Recommendations_3-15-2021.pdf (accessed on 7 June 2021).
- Narasimhan, M.; Mahimainathan, L.; Araj, E.; Clark, A.E.; Markantonis, J.; Green, A.; Xu, J.; SoRelle, J.A.; Alexis, C.; Fankhauser, K.; et al. Clinical evaluation of the Abbott Alinity SARS-CoV-2 spike-specific quantitative IgG and IgM assays in infected, recovered, and vaccinated groups. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2021, 59, e0038821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phipps, W.S.; SoRelle, J.A.; Li, Q.Z.; Mahimainathan, L.; Araj, E.; Markantonis, J.; Lacelle, C.; Balani, J.; Parikh, H.; Solow, E.B.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 antibody responses do not predict COVID-19 disease severity. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2020, 154, 459–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Premkumar, L.; Segovia-Chumbez, B.; Jadi, R.; Martinez, D.R.; Raut, R.; Markmann, A.; Cornaby, C.; Bartelt, L.; Weiss, S.; Park, Y.; et al. The receptor binding domain of the viral spike protein is an immunodominant and highly specific target of antibodies in SARS-CoV-2 patients. Sci. Immunol. 2020, 5, eabc8413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebinger, J.E.; Fert-Bober, J.; Printsev, I.; Wu, M.; Sun, N.; Prostko, J.C.; Frias, E.C.; Stewart, J.L.; Van Eyk, J.E.; Braun, J.G.; et al. Antibody responses to the BNT162b2 mRNA vaccine in individuals previously infected with SARS-CoV-2. Nat. Med. 2021, 27, 981–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kowalski, R.J.; Post, D.R.; Mannon, R.B.; Sebastian, A.; Wright, H.I.; Sigle, G. Assessing relative risks of infection and rejection: A meta—Analysis using an immune function assay. Transplantation 2006, 82, 663–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husain, S.; Raza, K.; Pilewski, J.M.; Zaldonis, D.; Crespo, M.; Toyoda, Y. Experience with immune monitoring in lung transplant recipients: Correlation of low immune function with infection. Transplantation 2009, 87, 1852–1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, W.; Zhu, Z.J.; Sun, L.Y.; Wei, L.; Liu, Y.; Zeng, Z.G. Correlation between survival interval and CD4+ T-cell intracellular ATP levels in liver transplant recipients. Transpl. Proc. 2017, 49, 316–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quaglia, M.; Cena, T.; Fenoglio, R.; Museti, C.; Cagna, D.; Radin, E.; Roggero, S.; Amoroso, A.; Magnani, C.; Stratta, P. Immune function assay (immunknow) drop over first 6 months after renal transplant: A predictor of opportunistic viral infections? Transpl. Proc. 2014, 46, 2220–2223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gralla, J.; Huskey, J.; Wiseman, A.C. Trends in immune function assay (ImmuKnow; Cylex™) results in the first year post-transplant and relationship to BK virus infection. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2012, 27, 2565–2570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Hsieh, C.L.; Goldsmith, J.A.; Schaub, J.M.; DiVenere, A.M.; Kuo, H.C.; Javanmardi, K.; Le, K.C.; Wrapp, D.; Lee, A.G.; Liu, Y.; et al. Structure-based design of prefusion-stabilized SARS-CoV-2 spikes. Science 2020, 369, 1501–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corbett, K.S.; Edwards, D.K.; Leist, S.R.; Abiona, O.M.; Boyoglu-Barnum, S.; Gillespie, R.A.; Himansu, S.; Schäfer, A.; Ziwawo, C.T.; DiPiazza, A.T.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccine design enabled by prototype pathogen preparedness. Nature 2020, 586, 567–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bavaro, D.F.; Laghetti, P.; Milano, E.; Brindicci, G.; Volpe, A.; Lagioia, A.; Saracino, A.; Monno, L. Anti-spike S1 receptor-binding domain antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 persist several months after infection regardless of disease severity. J. Med. Virol. 2021, 93, 3158–3164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, M.S.; Case, J.B.; Franks, C.E.; Chen, R.E.; Anderson, N.W.; Henderson, J.P.; Diamond, M.S.; Gronowski, A.M.; Farnsworth, C.W. Association between SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibodies and commercial serological assays. Clin. Chem. 2020, 66, 1538–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagin, D.; Freund, T.; Navon, M.; Halperin, T.; Adir, D.; Marom, R.; Levi, I.; Benor, S.; Alcalay, Y.; Freund, N.T. Immunogenicity of Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine in patients with inborn errors of immunity. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2021, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruckner, H.W.; Mokyr, M.B.; Mitchell, M.S. Effect of imidazole-4-carboxamide, 5-(3,3-dimethyl-1-triazeno) on immunity in patients with malignant melanoma. Cancer Res. 1974, 34, 181–183. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mombelli, M.; Rettby, N.; Perreau, M.; Pascual, M.; Pantaleo, G.; Manuel, O. Immunogenicity and safety of double versus standard dose of the seasonal influenza vaccine in solid-organ transplant recipients: A randomized controlled trial. Vaccine 2018, 36, 6163–6169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, T.; Klemis, V.; Schub, D.; Schneitler, S.; Reichert, M.C.; Wilkens, H.; Sester, U.; Sester, M.; Mihm, J. Cellular immunity predominates over humoral immunity after the first dose of COVID-19 vaccines in solid organ transplant recipients. medRxiv 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Information | IgGSP | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Total n (%) | Positive n (%) | Negative n (%) | |
| 2D-vaccine-administered total LT subjects | 73 (100) | ||
| Age (Years) | |||
| 20–39 | 10 (14) | 2 (20) | 8 (80) |
| 40–59 | 17 (23) | 9 (53) | 8 (47) |
| ≥60 | 46 (63) | 7 (15) | 39 (85) |
| Sex | |||
| Female | 26 (36) | 7 (27) | 19 (73) |
| Male | 47 (64) | 11 (23) | 36 (77) |
| Race | |||
| White | 55 (75) | 13 (24) | 42 (76) |
| Non-White | 18 (25) | 5 (28) | 13 (72) |
| TSTS a (Months) | |||
| 1–50 | 47 (64) | 12 (26) | 35 (74) |
| 51–100 | 23 (32) | 5 (22) | 18 (78) |
| >100 | 3 (4) | 1 (33) | 2 (67) |
| DMR b | |||
| ON anti-metabolite c | 72 (99) | 18 (25) | 54 (75) |
| OFF anti-metabolite | 1 (1) | 0 | 1 (100) |
| Vaccine | |||
| BNT162b2 (Pfizer-BioNTech) | 48 (66) | 9 (19) | 39 (81) |
| mRNA-1273 (Moderna) | 25 (34) | 9 (36) | 16 (64) |
| Information | n (%) | Cylex ImmuKnow Assay Levels | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low n (%) | Moderate n (%) | Strong n (%) | ||
| 2D-vaccine-administered LT subjects that had Cylex results | 56/73 (77) | 22/56 (39.3) | 26/56 (46.4) | 8/56 (14.3) |
| IgGSP serology results | ||||
| BNT162b2 (Pfizer-BioNTech) | + | 3/15 (20) | 3/17 (18) | 0/6 (--) |
| − | 12/15 (80) | 14/17 (82) | 6/6 (100) | |
| mRNA-1273 (Moderna) | + | 1/7 (14) | 4/9 (44) | 1/2 (50) |
| − | 6/7 (86) | 5/9 (56) | 1/2 (50) | |
| IgMSP serology results | ||||
| BNT162b2 (Pfizer-BioNTech) | + | 1/15 (7) | 1/17 (6) | 0/6 (--) |
| − | 14/15 (93) | 16/17 (94) | 6/6 (100) | |
| mRNA-1273 (Moderna) | + | 0/7 (--) | 0/9 (--) | 0/2 (--) |
| − | 7/7 (100) | 9/9 (100) | 2/2 (100) | |
| IgGNC serology results | ||||
| BNT162b2 (Pfizer-BioNTech) | + | 0/15 (--) | 1/17 (6) | 0/6 (--) |
| − | 15/15 (100) | 16/17 (94) | 6/6 (100) | |
| mRNA-1273 (Moderna) | + | 0/7 (--) | 0/9 (--) | 0/2 (--) |
| − | 7/7 (100) | 9/9 (100) | 2/2 (100) | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Narasimhan, M.; Mahimainathan, L.; Clark, A.E.; Usmani, A.; Cao, J.; Araj, E.; Torres, F.; Sarode, R.; Kaza, V.; Lacelle, C.; et al. Serological Response in Lung Transplant Recipients after Two Doses of SARS-CoV-2 mRNA Vaccines. Vaccines 2021, 9, 708. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines9070708
Narasimhan M, Mahimainathan L, Clark AE, Usmani A, Cao J, Araj E, Torres F, Sarode R, Kaza V, Lacelle C, et al. Serological Response in Lung Transplant Recipients after Two Doses of SARS-CoV-2 mRNA Vaccines. Vaccines. 2021; 9(7):708. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines9070708
Chicago/Turabian StyleNarasimhan, Madhusudhanan, Lenin Mahimainathan, Andrew E Clark, Amena Usmani, Jing Cao, Ellen Araj, Fernando Torres, Ravi Sarode, Vaidehi Kaza, Chantale Lacelle, and et al. 2021. "Serological Response in Lung Transplant Recipients after Two Doses of SARS-CoV-2 mRNA Vaccines" Vaccines 9, no. 7: 708. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines9070708
APA StyleNarasimhan, M., Mahimainathan, L., Clark, A. E., Usmani, A., Cao, J., Araj, E., Torres, F., Sarode, R., Kaza, V., Lacelle, C., & Muthukumar, A. (2021). Serological Response in Lung Transplant Recipients after Two Doses of SARS-CoV-2 mRNA Vaccines. Vaccines, 9(7), 708. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines9070708





