Nitrate-Selective Anion Exchange Membranes Prepared using Discarded Reverse Osmosis Membranes as Support
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemical Reagents
2.2. Recycled Membrane Support and Commercial Membranes
2.3. Anion Exchange Membrane Preparation
2.4. Membrane Characterization
2.4.1. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) and Energy-Dispersive X-ray Spectroscopy (EDX)
2.4.2. Thickness, Ion Exchange Capacity, Water Content
2.4.3. Electrochemical Properties
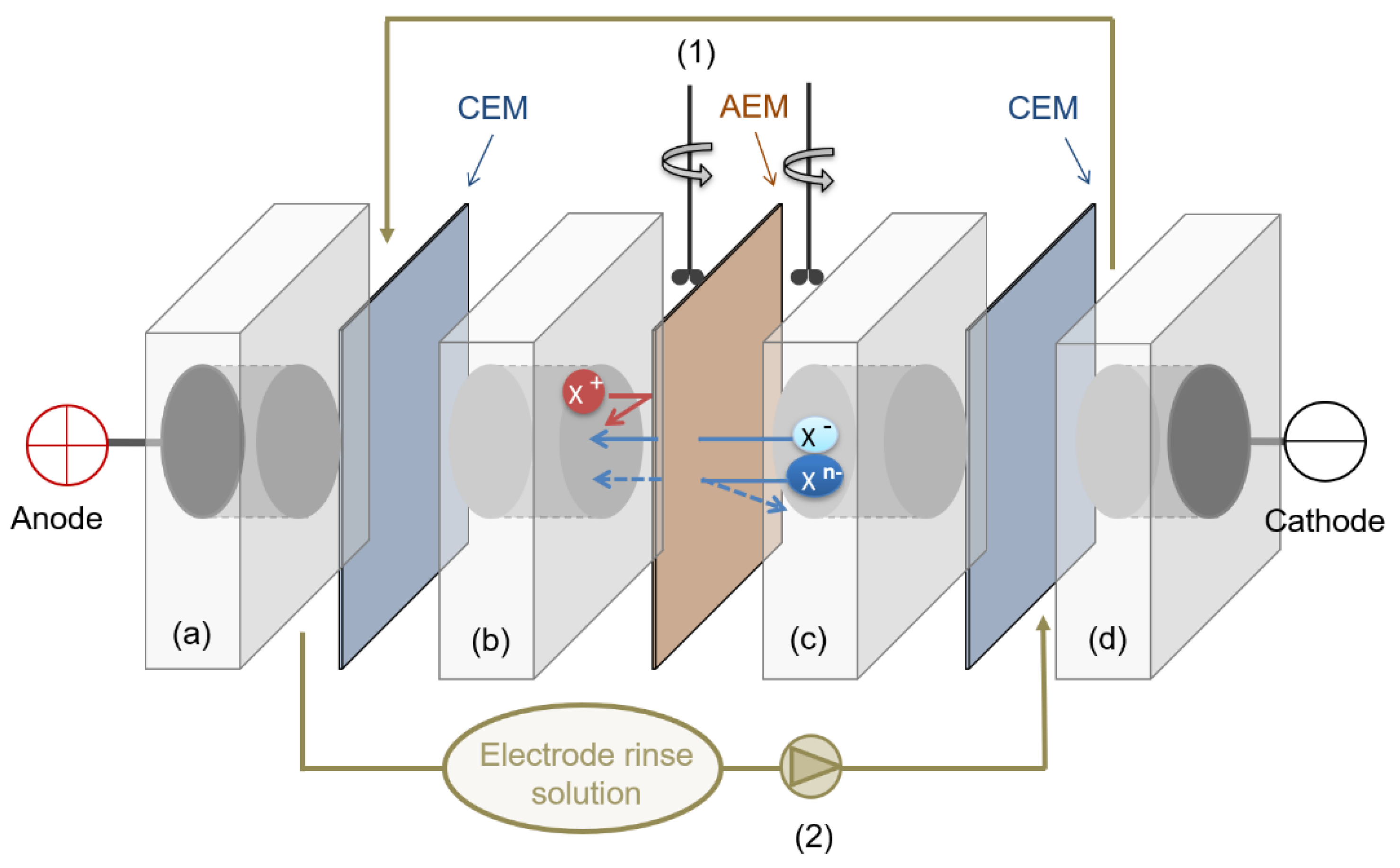
2.5. Evaluation of the Selective Ion Transport Properties
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Membrane Characterization
3.1.1. Main Characteristics of the Recycled Membrane Support
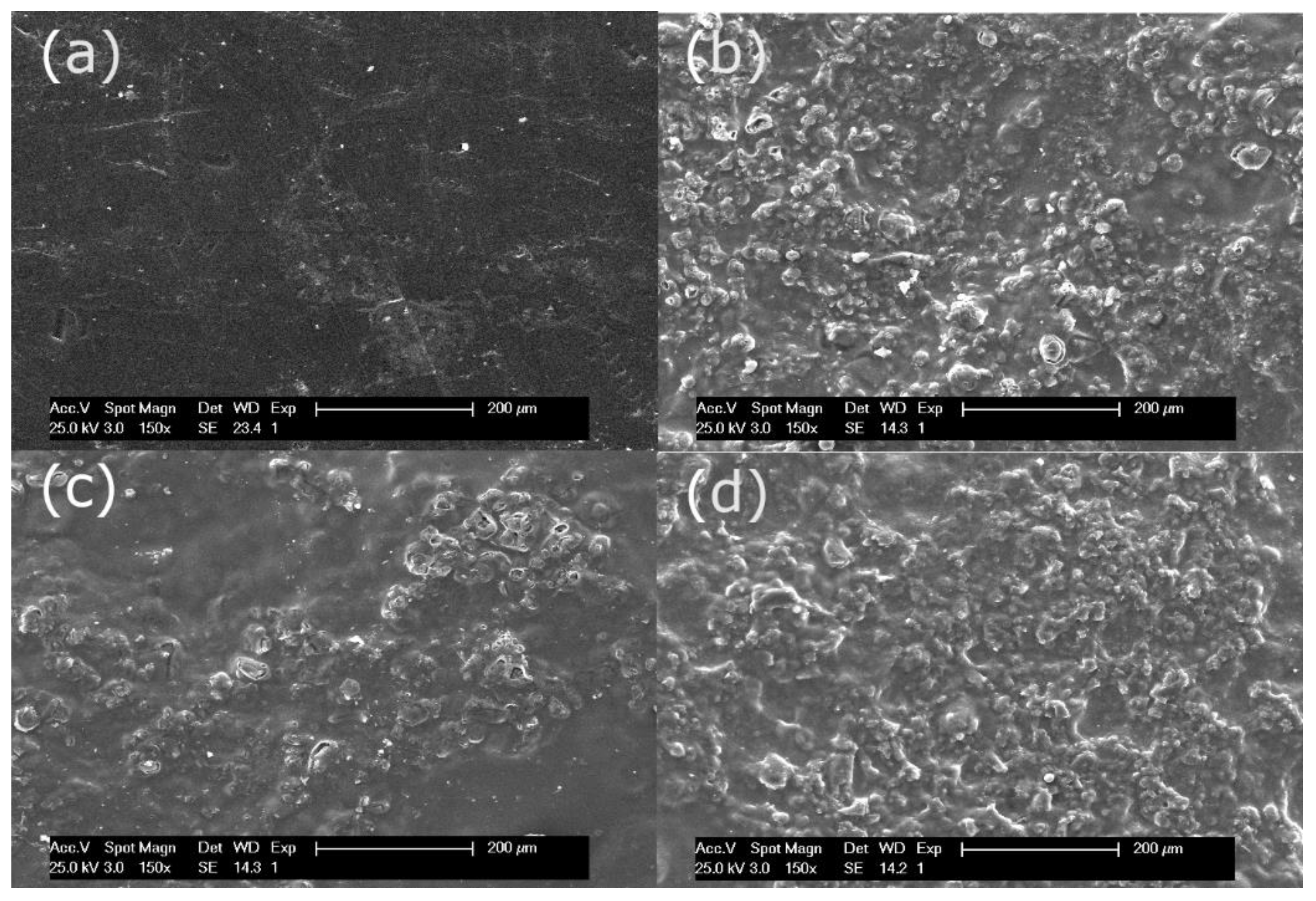
3.1.2. Anion Exchange Membrane Morphology and Elemental Composition
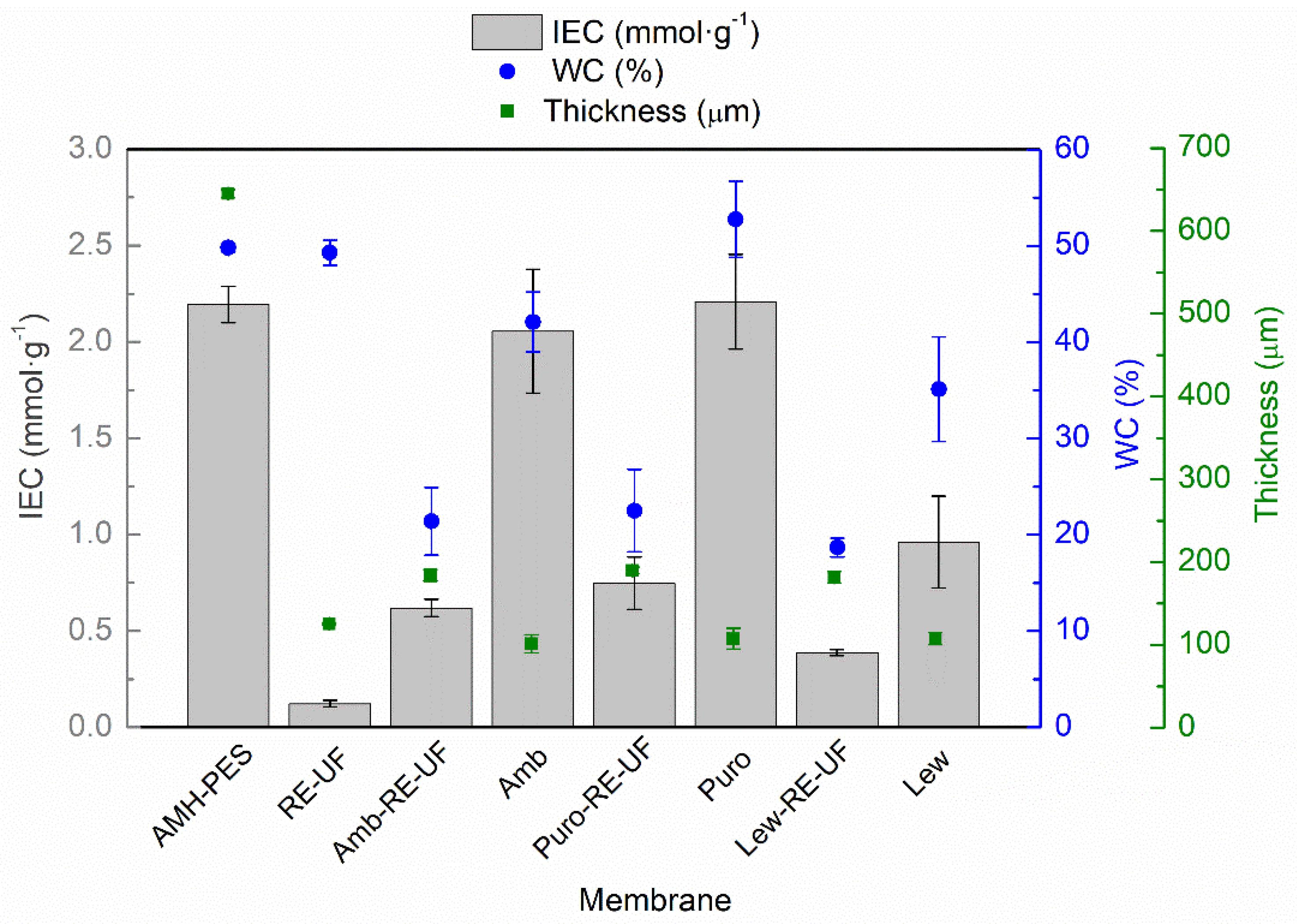
3.1.3. Thickness, Ion Exchange Capacity, Water Content
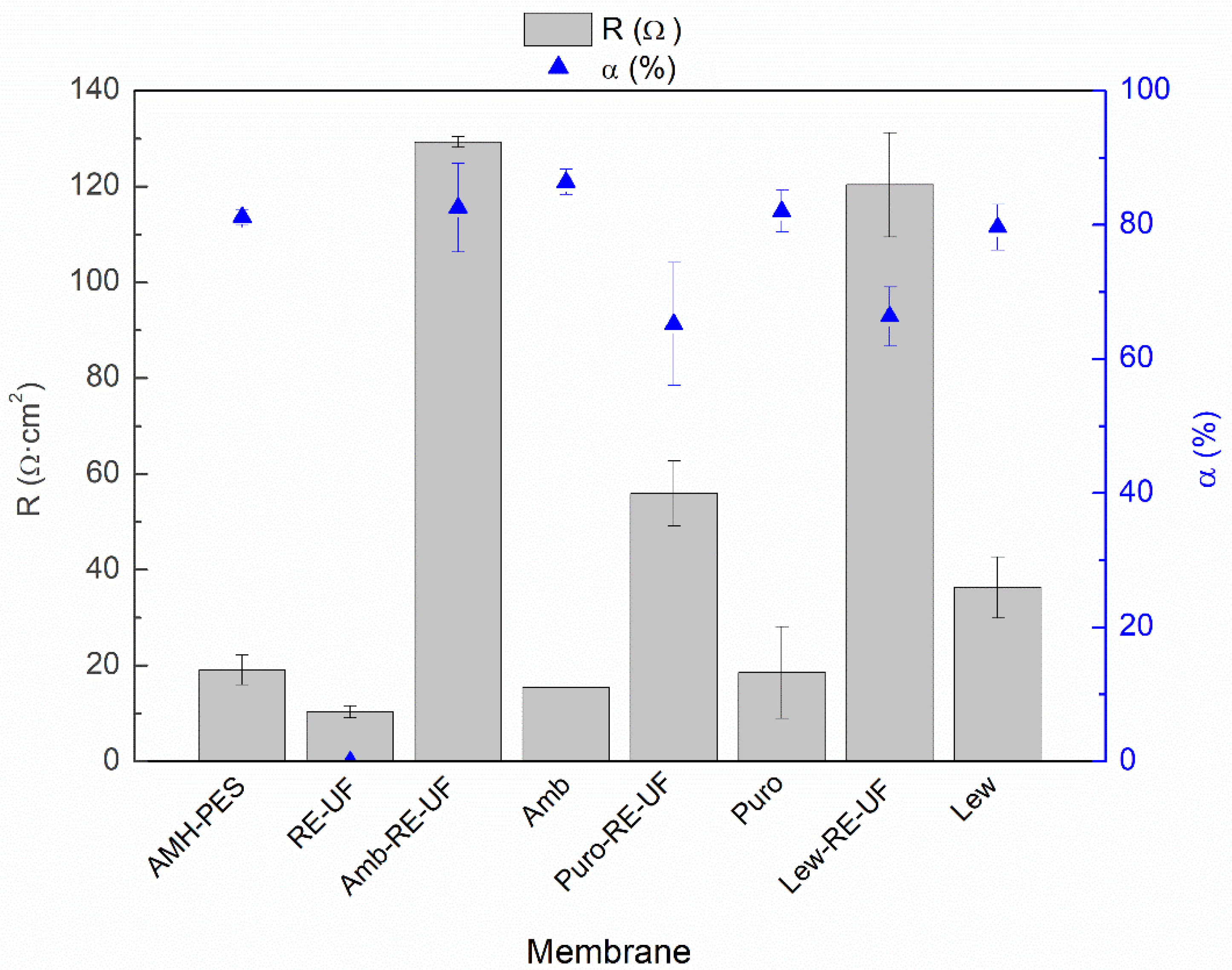
3.1.4. Electrochemical Properties
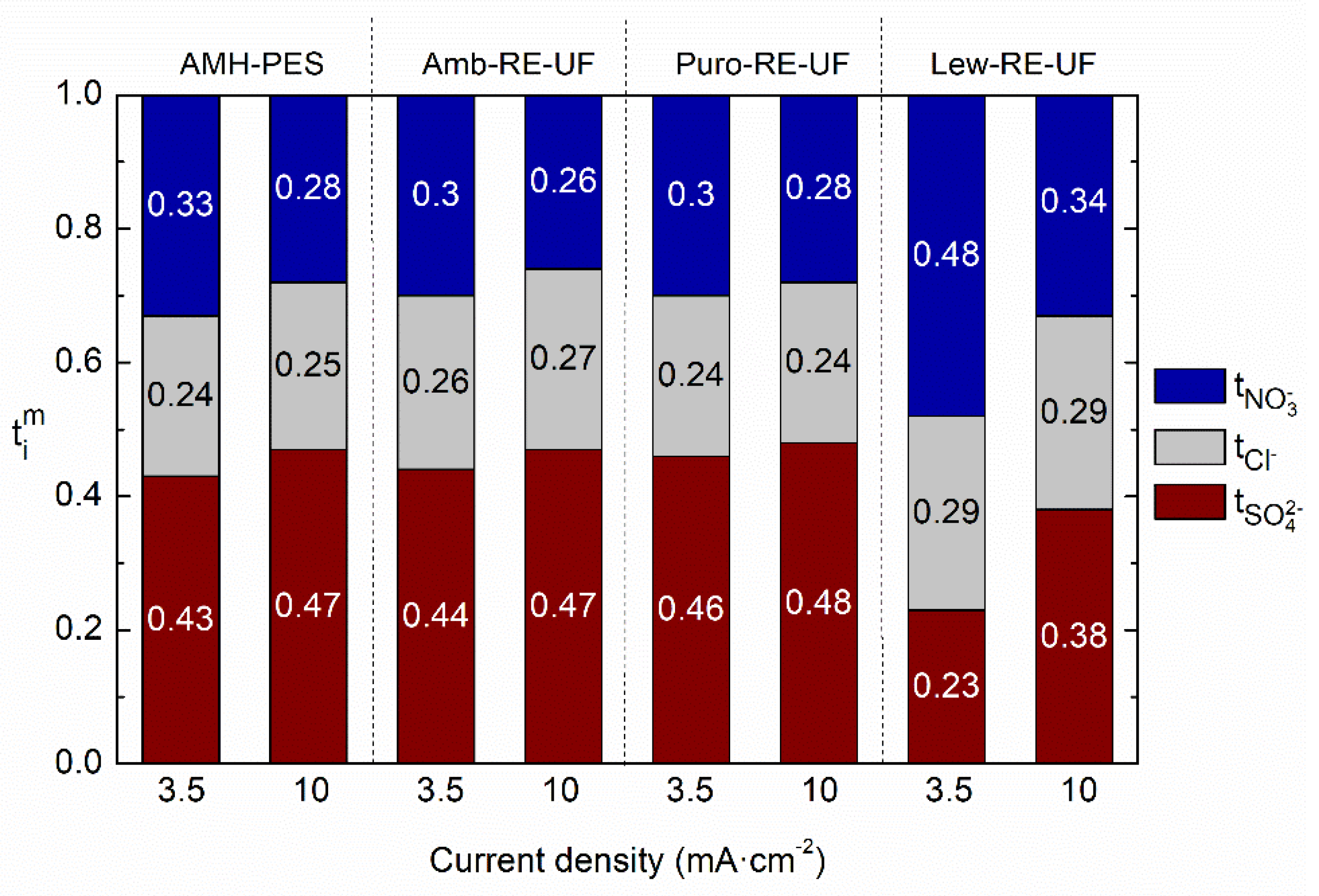
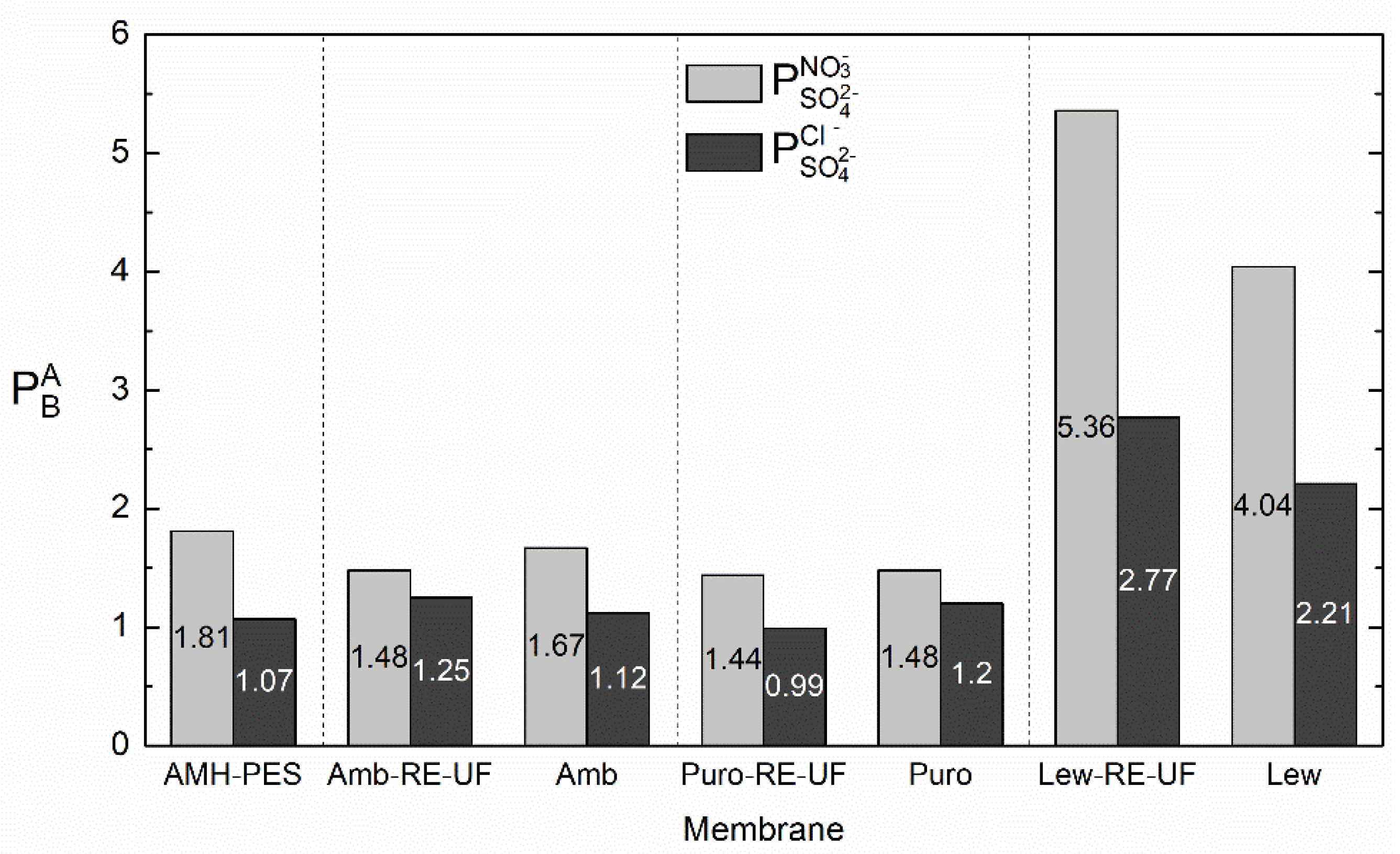
3.2. Evaluation of the Selective Ion Transport Properties
4. Conclusions
- Anion exchange membranes were prepared by casting method using a recycled pressure filtration membrane (RE-UF) as support. Homogeneous distribution of the ionic resin on the membrane surface was obtained. Despite differences in anion exchange resin distribution across the membrane section were found;
- The use of an anion exchanger to strengthen hydrophobicity in the functional groups increased the transport of less solvated ions (i.e., nitrates), while highly hydrated ions were repulsed by hydrophobic forces (i.e., sulfates);
- The use of a relatively low current density during the experiment further enhanced the transport of ions with lower charge (monovalent);
- The use of a recycled pressure filtration membrane (RE-UF) as support increased the transport number of nitrates while decreased the transport number of sulfates in the case of membranes containing nitrate selective anion exchange resin. Moreover, the use of recycled membranes as support material provided mechanical stability, and it is an attempt to face the waste management challenge of reverse osmosis desalination. In this line, another type of discarded membranes could be tested as mechanical support.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Turner, R.E.; Rabalais, N.N.; Justic, D.; Dortch, Q. Global patterns of dissolved N, P and Si in large rivers. Biogeochemistry 2003, 64, 297–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, M.H.; Jones, R.R.; Brender, J.D.; de Kok, T.M.; Weyer, P.J.; Nolan, B.T.; Villanueva, C.M.; van Breda, S.G. Drinking water nitrate and human health: An updated review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fan, A.M.; Steinberg, V.E. Health implications of nitrate and nitrite in drinking water: An update on methemoglobinemia occurrence and reproductive and developmental toxicity. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 1996, 23, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Commission. Council Directive 98/83/EC of 3 November 1998 on the quality of water intended for human consumption. Off. J. Eur. Communities 1998, 330, 32–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huno, S.K.M.; Rene, E.R.; Van Hullebusch, E.D.; Annachhatre, A.P. Nitrate removal from groundwater: A review of natural and engineered processes. J. Water Supply Res. Technol. Aqua 2018, 67, 885–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Strathmann, H. Ion-Exchange Membrane Separation Processes; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2004; ISBN 044450236X. [Google Scholar]
- Onoue, Y.; Mizutani, Y.; Yamame, R. Selectivity of cation exchange membranes for NaCl-MgCl2 systems. J. Electrochem. Soc. Jpn. 1959, 27, 482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, T.; Abdu, S.; Wessling, M. Selectivity of ion exchange membranes: A review. J. Memb. Sci. 2018, 555, 429–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotoka, F.; Merino-Garcia, I.; Velizarov, S. Surface Modifications of Anion Exchange Membranes for an Improved Reverse Electrodialysis Process Performance: A Review. Membranes 2020, 10, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sata, T. Studies on ion exchange membranes with permselectivity for specific ions in electrodialysis. J. Memb. Sci. 1994, 93, 117–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Wang, G.; Yu, D.; Sheng, F.; Shehzad, M.A.; He, T.; Xu, T.; Ren, X.; Cao, M.; Wu, B.; et al. Cross-linked anion exchange membranes with hydrophobic side-chains for anion separation. J. Memb. Sci. 2019, 581, 150–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; Ding, J.; Zheng, Y.; Gao, C.; Bruggen, B. Van Der One-pot approach to prepare internally cross-linked monovalent selective anion exchange membranes. J. Memb. Sci. 2018, 553, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stair, J.L.; Harris, J.J.; Bruening, M.L. Enhancement of the ion-transport selectivity of layered polyelectrolyte membranes through cross-linking and hybridization. Chem. Mater. 2001, 13, 2641–2648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lejarazu-Larrañaga, A.; Zhao, Y.; Molina, S.; García-Calvo, E.; Van der Bruggen, B. Alternating current enhanced deposition of a monovalent selective coating for anion exchange membranes with antifouling properties. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 229, 115807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Xiao, P.; Ruan, H.; Liao, J.; Gao, C.; Van der Bruggen, B.; Shen, J. Mussel-inspired surface functionalization of AEM for simultaneously improved monovalent anion selectivity and antibacterial property. Membranes 2019, 9, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nebavskaya, X.; Sarapulova, V.; Butylskii, D.; Larchet, C.; Pimenskaya, N. Electrochemical Properties of Homogeneous and Heterogeneous Anion Exchange Membranes Coated with Cation Exchange Polyelectrolyte. Membranes 2019, 9, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, H.; Ruan, H.; Zhao, Y.; Pan, J.; Sotto, A.; Gao, C.; van der Bruggen, B.; Shen, J. A facile avenue to modify polyelectrolyte multilayers on anion exchange membranes to enhance monovalent selectivity and durability simultaneously. J. Memb. Sci. 2017, 543, 310–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, R.; Lang, Q.; Tan, M.; Zhang, Y. Composite anion exchange membrane made by layer-by-layer method for selective ion separation and water migration control. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2018, 192, 278–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Liu, Y.; Liao, J.; Liu, H.; Jiang, Y.; Van Der Bruggen, B.; Shen, J.; Gao, C. Codeposition modification of cation exchange membranes with dopamine and crown ether to achieve high K+ electrodialysis selectivity. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 17730–17741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sata, T.; Yamaguchi, T.; Matsusaki, K. Effect of hydrophobicity of ion exchange groups of anion exchange membranes on permselectivity between two anions. J. Phys. Chem. 1995, 99, 12875–12882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mubita, T.; Porada, S.; Aerts, P.; Van Der Wal, A. Heterogeneous anion exchange membranes with nitrate selectivity and low electrical resistance. J. Memb. Sci. 2020, 607, 118000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sata, T. Studies on anion exchange membranes having permselectivity for specific anions in electrodialysis—Effect of hydrophilicity of anion exchange membranes on permselectivity of anions. J. Memb. Sci. 2000, 167, 1–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhou, C.; Wang, J.; Liu, H.; Xu, Y.; Seo, J.W.; Shen, J.; Gao, C.; Van der Bruggen, B. Formation of morphologically confined nanospaces via self-assembly of graphene and nanospheres for selective separation of lithium. J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 18859–18864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghadassi, A.R.; Koranian, P.; Hosseini, S.M.; Askari, M.; Madaeni, S.S. Surface modification of heterogeneous cation exchange membrane through simultaneous using polymerization of PAA and multi walled carbon nano tubes. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2014, 20, 2710–2718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Gonzalez, C.; Zhang, B.; Dominguez-Ramos, A.; Ibañez, R.; Irabien, A.; Chen, Y. Enhancing fouling resistance of polyethylene anion exchange membranes using carbon nanotubes and iron oxide nanoparticles. Desalination 2017, 411, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Patel, S.K.; Ritt, C.L.; Deshmukh, A.; Wang, Z.; Qin, M.; Epsztein, R.; Elimelech, M. The relative insignificance of advanced materials in enhancing the energy efficiency of desalination technologies. Energy Environ. Sci. 2020, 13, 1694–1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saracco, G.; Zanetti, M.C.; Onofrio, M. Novel application of monovalent-ion-permselective membranes to the recovery treatment of an industrial wastewater by electrodialysis. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 1993, 32, 657–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saracco, G.; Zanetti, M.C. Ion transport through monovalent-anion-permselective membranes. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 1994, 96–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saracco, G. Transport properties of monovalent-ion-permselective membranes. Chem. Eng. Sci. 1997, 52, 3019–3031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, L.; Wu, B.; Li, Q.; Wang, Y.; Yu, D.; Wu, L.; Pan, J.; Miao, J.; Xu, T. Electrodialysis with nanofiltration membrane (EDNF) for high-efficiency cations fractionation. J. Memb. Sci. 2016, 498, 192–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazinet, L.; Poulin, J.F.; Amiot, J. Effect of conditioning ultrafiltration membranes on their performances in electrodialysis with ultrafiltration membrane. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2007, 42, 2501–2518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaulieu, M.; Perreault, V.; Mikhaylin, S.; Bazinet, L. How overlimiting current condition influences lactic acid recovery and demineralization by electrodialysis with nanofiltration membrane: Comparison with conventional electrodialysis. Membranes 2020, 10, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lejarazu-Larrañaga, A.; Molina, S.; Ortiz, J.M.; Navarro, R.; García-Calvo, E. Circular economy in membrane technology: Using end-of-life reverse osmosis modules for preparation of recycled anion exchange membranes and validation in electrodialysis. J. Memb. Sci. 2020, 593, 117423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lejarazu-Larrañaga, A.; Molina, S.; Ortiz, J.M.; Riccardelli, G.; García-Calvo, E. Influence of acid/base activation treatment in the performance of recycled electromembrane for fresh water production by electrodialysis. Chemosphere 2020, 248, 126027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landaburu-Aguirre, J.; García-Pacheco, R.; Molina, S.; Rodríguez-Sáez, L.; Rabadán, J.; García-Calvo, E. Fouling prevention, preparing for re-use and membrane recycling. Towards circular economy in RO desalination. Desalination 2016, 393, 16–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senán-Salinas, J.; García-Pacheco, R.; Landaburu-Aguirre, J.; García-Calvo, E. Recycling of end-of-life reverse osmosis membranes: Comparative LCA and cost-effectiveness analysis at pilot scale. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2019, 150, 104423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos Pozuelo, E.; Terrero Rodríguez, P.; Zarzo Martínez, D.; Molina Serrano, F.J.; Calzada Garzón, M.; García Pacheco, R.; Molina Martínez, S.; Rodríguez Sáez, L.; Rabadán, F.J.; Landaburu Aguirre, J.; et al. Transformation of Spiral Wound Polyamide Membranes after Its Industrial Lifespan. Spanish Patent PCT/EP2016/30931, 8 July 2016. [Google Scholar]
- García-Pacheco, R.; Landaburu-Aguirre, J.; Terrero-Rodríguez, P.; Campos, E.; Molina-Serrano, F.; Rabadán, J.; Zarzo, D.; García-Calvo, E. Validation of recycled membranes for treating brackish water at pilot scale. Desalination 2018, 433, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Pacheco, R.; Landaburu-Aguirre, J.; Molina, S.; Rodríguez-Sáez, L.; Teli, S.B.; García-Calvo, E. Transformation of end-of-life RO membranes into NF and UF membranes: Evaluation of membrane performance. J. Memb. Sci. 2015, 495, 305–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina, S.; Landaburu-Aguirre, J.; Rodríguez-Sáez, L.; García-Pacheco, R.; de la Campa, J.G.; García-Calvo, E. Effect of sodium hypochlorite exposure on polysulfone recycled UF membranes and their surface characterization. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2018, 150, 46–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karas, F.; Hnát, J.; Paidar, M.; Schauer, J.; Bouzek, K. Determination of the ion-exchange capacity of anion-selective membranes. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2014, 39, 5054–5062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Güler, E.; Elizen, R.; Vermaas, D.A.; Saakes, M.; Nijmeijer, K. Performance-determining membrane properties in reverse electrodialysis. J. Memb. Sci. 2013, 446, 266–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lide, D.R. CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, 84th ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Ortiz, J.M.; Exposito, E.; Gallud, F.; García-García, V.; Montiel, V.; Aldaz, A. Desalination of underground brackish waters using an electrodialysis system powered directly by photovoltaic energy. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2008, 92, 1677–1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sata, T. Ion Exchange Membranes: Preparation, Characterization, Modification and Application; Royal Society of Chemistry: Cambridge, UK, 2004; ISBN 0854045902. [Google Scholar]
- Van der Bruggen, B.; Koninckx, A.; Vandecasteele, C. Separation of monovalent and divalent ions from aqueous solution by electrodialysis and nanofiltration. Water Res. 2004, 38, 1347–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brožová, L.; Křivčík, J.; Neděla, D.; Kysela, V.; Žitka, J. The influence of activation of heterogeneous ion-exchange membranes on their electrochemical properties. Desalin. Water Treat. 2015, 56, 3228–3232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vyas, P.V.; Shah, B.G.; Trivedi, G.S.; Ray, P.; Adhikary, S.K.; Rangarajan, R. Characterization of heterogeneous anion-exchange membrane. J. Memb. Sci. 2001, 187, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, S.M.; Gholami, A.; Madaeni, S.S.; Moghadassi, A.R.; Hamidi, A.R. Fabrication of (polyvinyl chloride/cellulose acetate) electrodialysis heterogeneous cation exchange membrane: Characterization and performance in desalination process. Desalination 2012, 306, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awasthi, A.; Datta, D. Application of Amberlite XAD-7HP resin impregnated with Aliquat 336 for the removal of Reactive Blue—13 dye: Batch and fixed-bed column studies. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 103502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, S.M.; Madaeni, S.S.; Khodabakhshi, A.R. Preparation and characterization of heterogeneous cation exchange membranes based on S-poly vinyl chloride and polycarbonate. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2011, 46, 794–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nightingale, E.R. Phenomenological theory of ion solvation. Effective radii of hydrated ions. J. Phys. Chem. 1959, 63, 1381–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, D.W. Ionic hydration enthalpies. J. Chem. Educ. 1977, 54, 540–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, H.; Sotto, A.; Gao, C.; Shen, J. A durable and antifouling monovalent selective anion exchange membrane modified by polydopamine and sulfonated reduced graphene oxide. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2018, 207, 116–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamcev, J.; Paul, D.R.; Freeman, B.D. Effect of fixed charge group concentration on equilibrium ion sorption in ion exchange membranes. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 4638–4650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurreri, L.; Tamburini, A.; Cipollina, A.; Micale, G. Electrodialysis applications in wastewater treatment for environmental protection and resources recovery: A systematic review on progress and perspectives. Membranes 2020, 10, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Anion Exchange Resin | Amberlite® IRA-402 | Purolite® A600/9413 | Lewatit® Sybron Ionac® SR-7 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Matrix | Styrene–divinyl benzene cross-linked copolymer | Styrene–divinyl benzene cross-linked copolymer | Styrene–divinyl benzene cross-linked copolymer |
| IEC (equiv.·L−1) * | 1.2 | 1.6 | 0.8 |
| Ion exchange group | R–(CH3)3 N+ | R–(CH3)3 N+ | R–(C3H7)3 N+ |
| Ionic form | Cl− | Cl− | Cl− |
| Membrane | Anion Exchange Resin | Mechanical Support |
|---|---|---|
| Commercial AMH-PES | Unspecified (ion exchange group, R–(CH3)3N+) | Polyester |
| Recycled ultrafiltration-like membrane (RE-UF) | None | Polyester |
| Amb-RE-UF | Amberlite® IRA-402 | RE-UF |
| Amb | Without support | |
| Puro-RE-UF | Purolite® A600E/9149 | RE-UF |
| Puro | Without support | |
| Lew-RE-UF | Lewatit® Sybron Ionac® SR-7 | RE-UF |
| Lew | Without support |
| Casting Layer | ||||||
| Amb-RE-UF | Puro-RE-UF | Lew-RE-UF | ||||
| Element | % weight | % atomic | % weight | % atomic | % weight | % atomic |
| C | 57.63 | 77.53 | 51.84 | 74.00 | 52.48 | 72.96 |
| N | 0.04 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.06 | 0.23 | 0.27 |
| O | 5.69 | 5.74 | 4.58 | 4.90 | 7.89 | 8.23 |
| S | 0.60 | 0.30 | 0.64 | 0.34 | 0.51 | 0.27 |
| Cl | 36.04 | 16.39 | 42.90 | 20.70 | 38.89 | 18.27 |
| Support Layer | ||||||
| Amb-RE-UF | Puro-RE-UF | Lew-RE-UF | ||||
| Element | % weight | % atomic | % weight | % atomic | % weight | % atomic |
| C | 74.78 | 82.34 | 64.80 | 71.62 | 62.52 | 69.13 |
| N | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.01 |
| O | 17.81 | 14.71 | 33.38 | 27.67 | 36.98 | 30.67 |
| S | 4.64 | 1.92 | 0.85 | 0.35 | 0.24 | 0.10 |
| Cl | 2.77 | 1.03 | 0.96 | 0.36 | 0.24 | 0.09 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lejarazu-Larrañaga, A.; Ortiz, J.M.; Molina, S.; Zhao, Y.; García-Calvo, E. Nitrate-Selective Anion Exchange Membranes Prepared using Discarded Reverse Osmosis Membranes as Support. Membranes 2020, 10, 377. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes10120377
Lejarazu-Larrañaga A, Ortiz JM, Molina S, Zhao Y, García-Calvo E. Nitrate-Selective Anion Exchange Membranes Prepared using Discarded Reverse Osmosis Membranes as Support. Membranes. 2020; 10(12):377. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes10120377
Chicago/Turabian StyleLejarazu-Larrañaga, Amaia, Juan Manuel Ortiz, Serena Molina, Yan Zhao, and Eloy García-Calvo. 2020. "Nitrate-Selective Anion Exchange Membranes Prepared using Discarded Reverse Osmosis Membranes as Support" Membranes 10, no. 12: 377. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes10120377
APA StyleLejarazu-Larrañaga, A., Ortiz, J. M., Molina, S., Zhao, Y., & García-Calvo, E. (2020). Nitrate-Selective Anion Exchange Membranes Prepared using Discarded Reverse Osmosis Membranes as Support. Membranes, 10(12), 377. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes10120377










