Mixed-Matrix Membranes Comprising of Polysulfone and Porous UiO-66, Zeolite 4A, and Their Combination: Preparation, Removal of Humic Acid, and Antifouling Properties
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of MOF (UiO-66)
2.3. Preparation of Membranes
2.4. Characterization of UiO-66 and Membranes
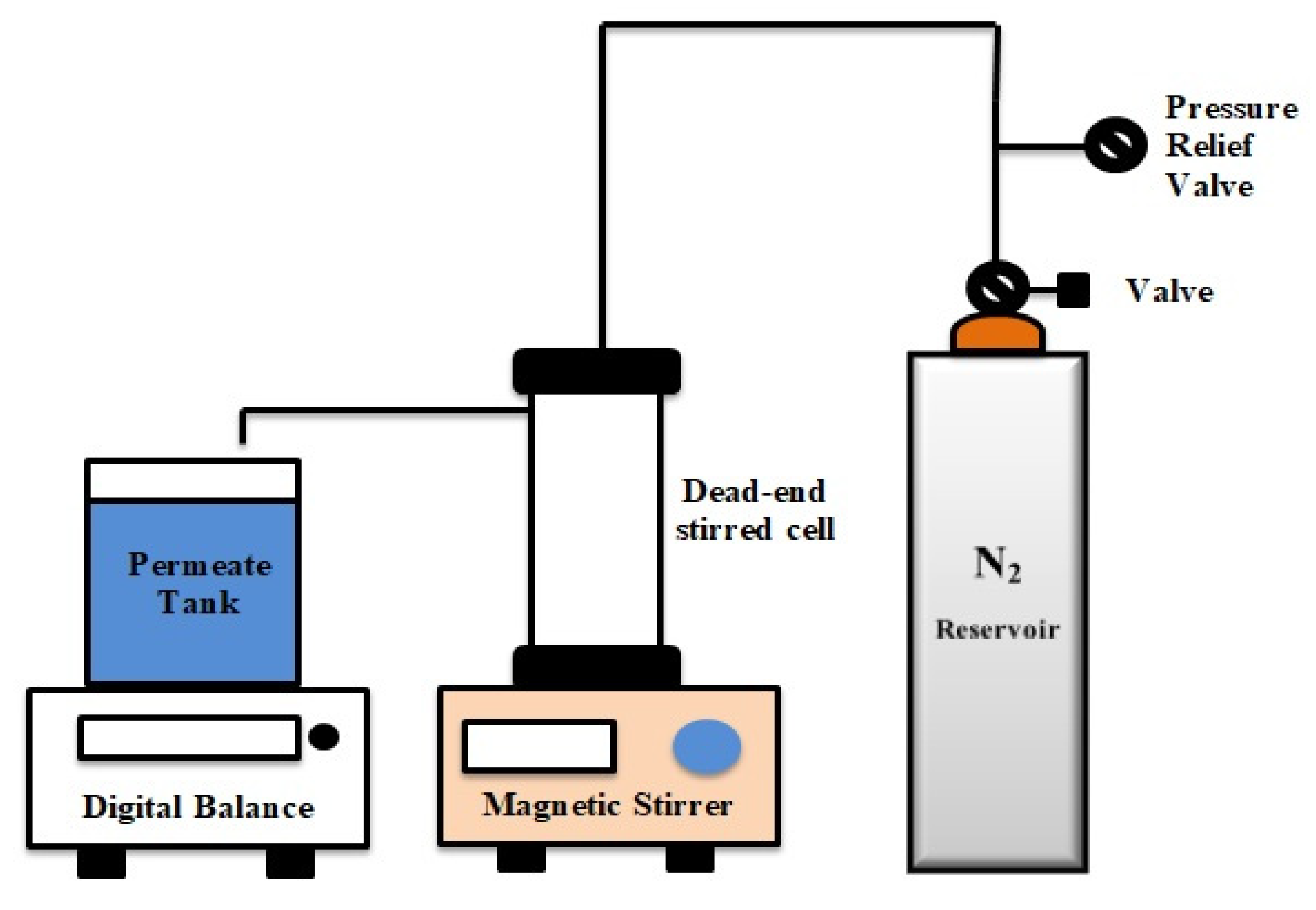
2.5. Membrane Performance
2.5.1. Permeation and Rejection
2.5.2. Antifouling Properties of Membranes
Static Humic Acid Adsorption
Flux Recovery Ratio (FRR)
Reversible and Irreversible Fouling
3. Results and Discussion
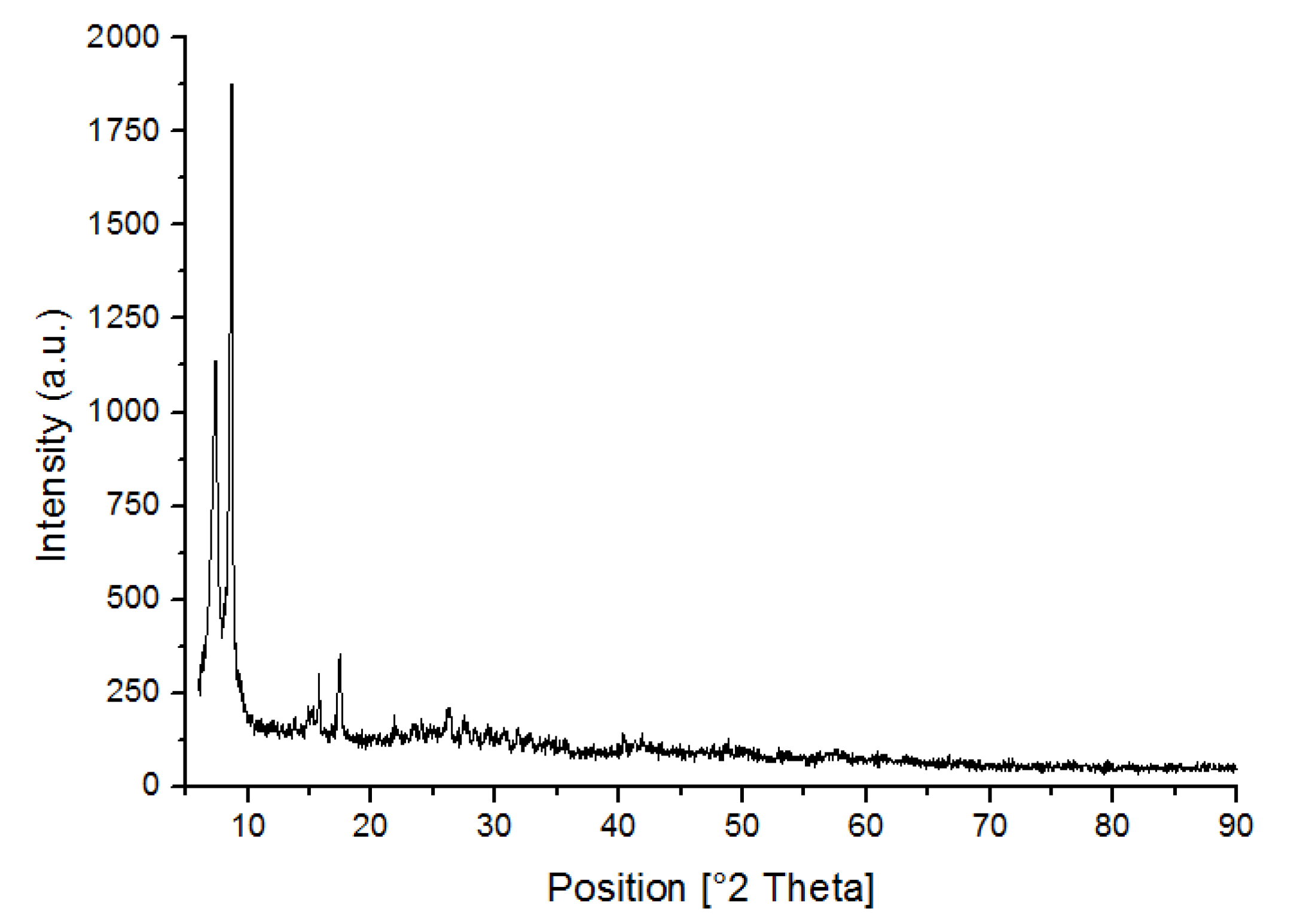
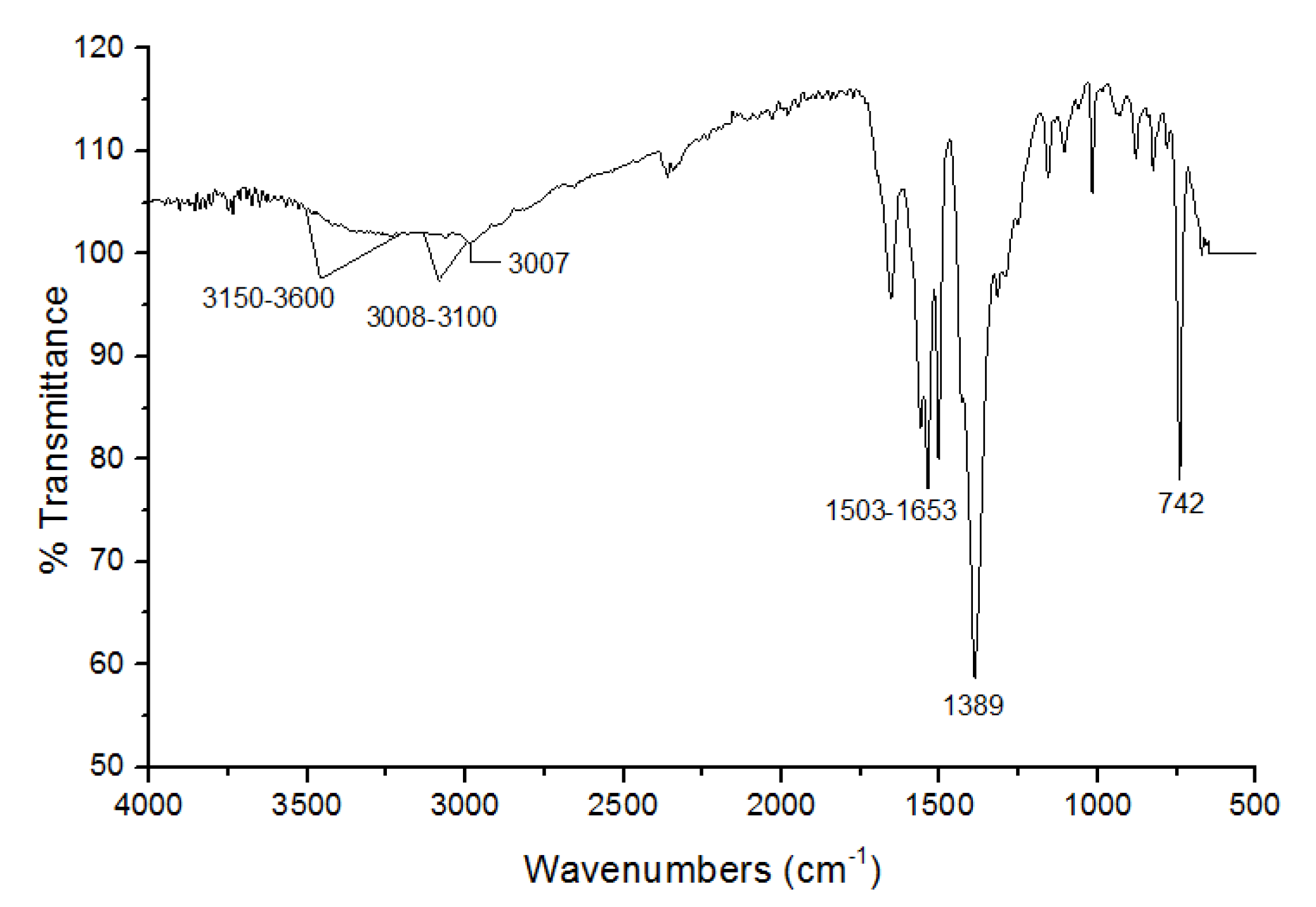
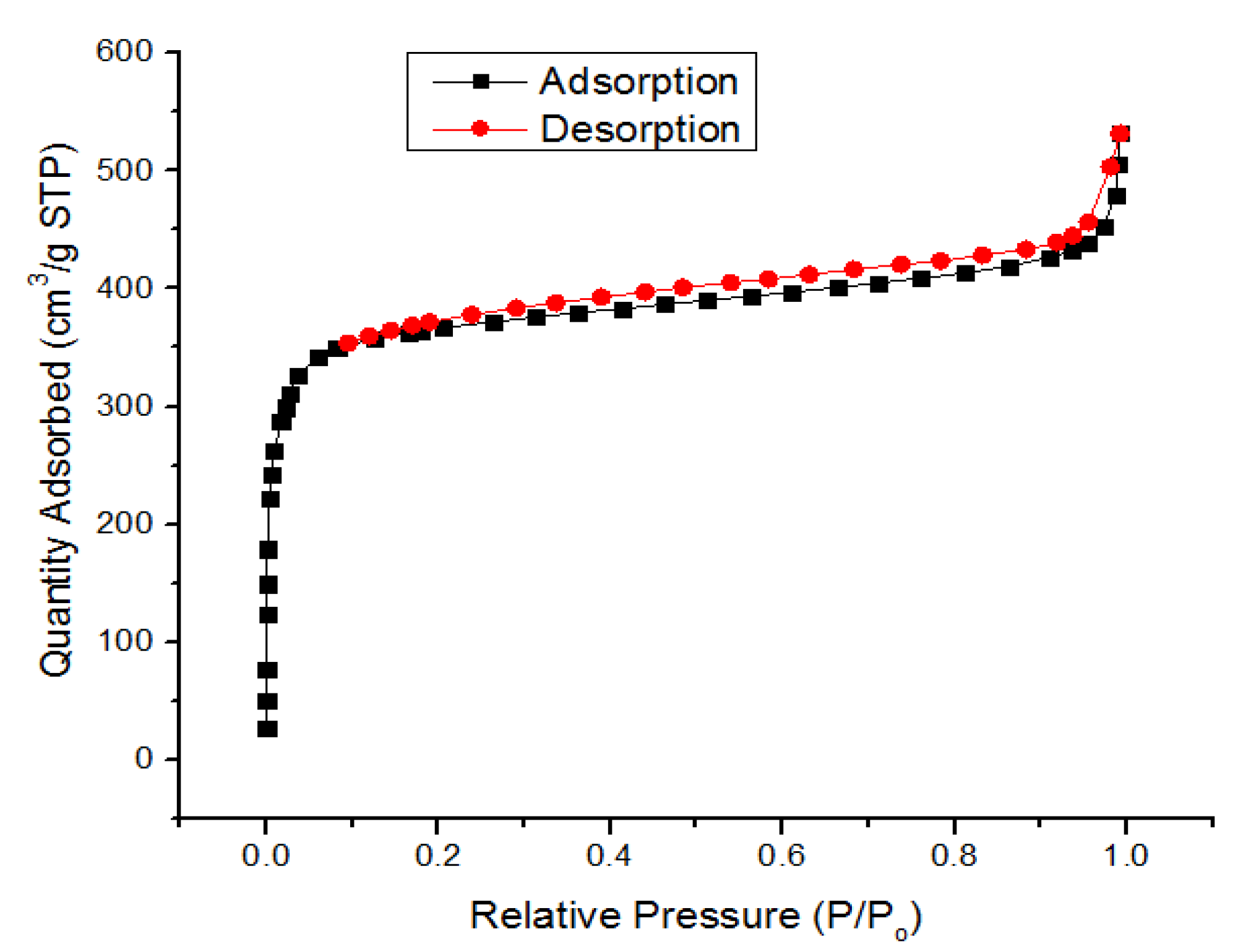
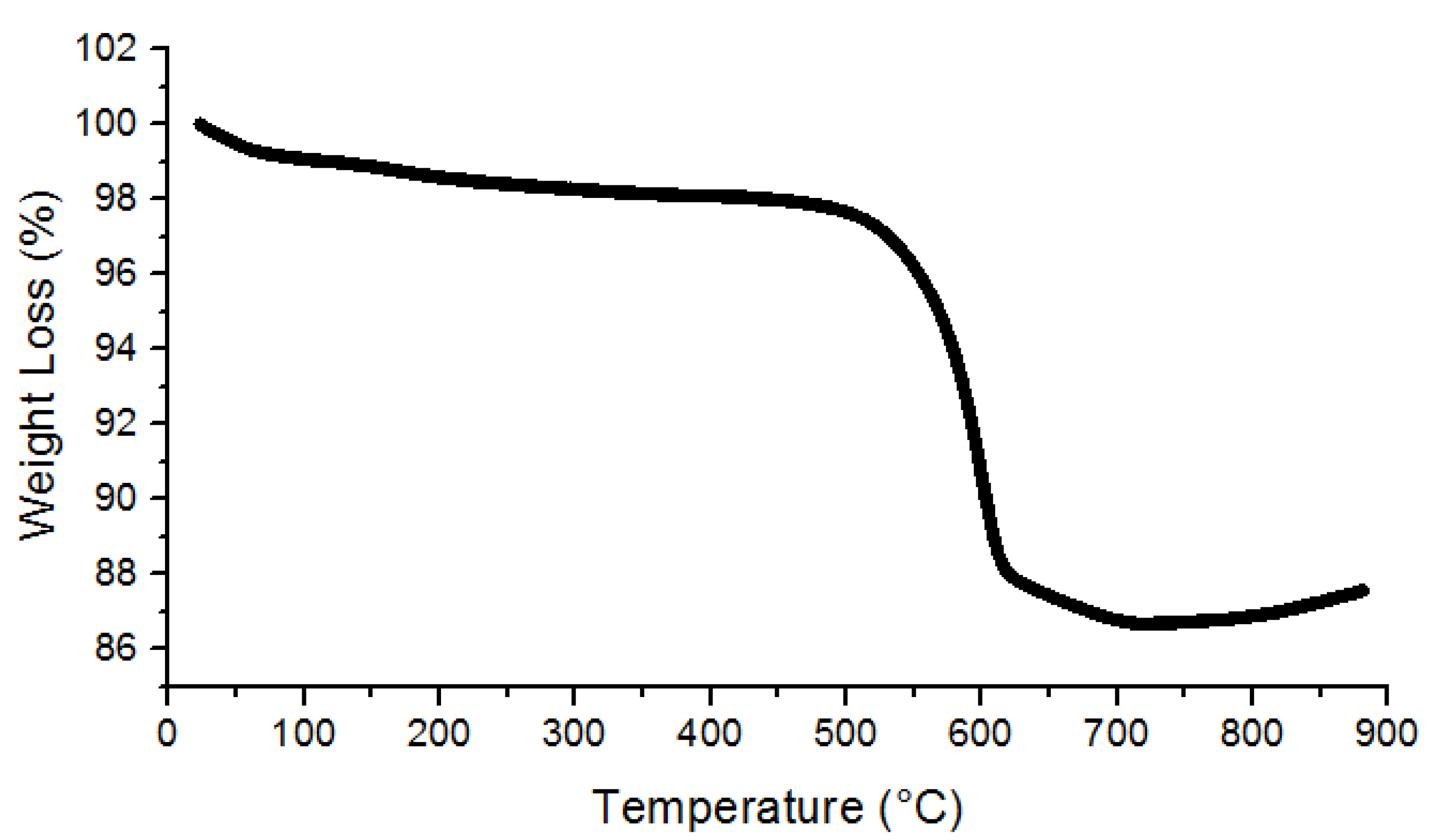
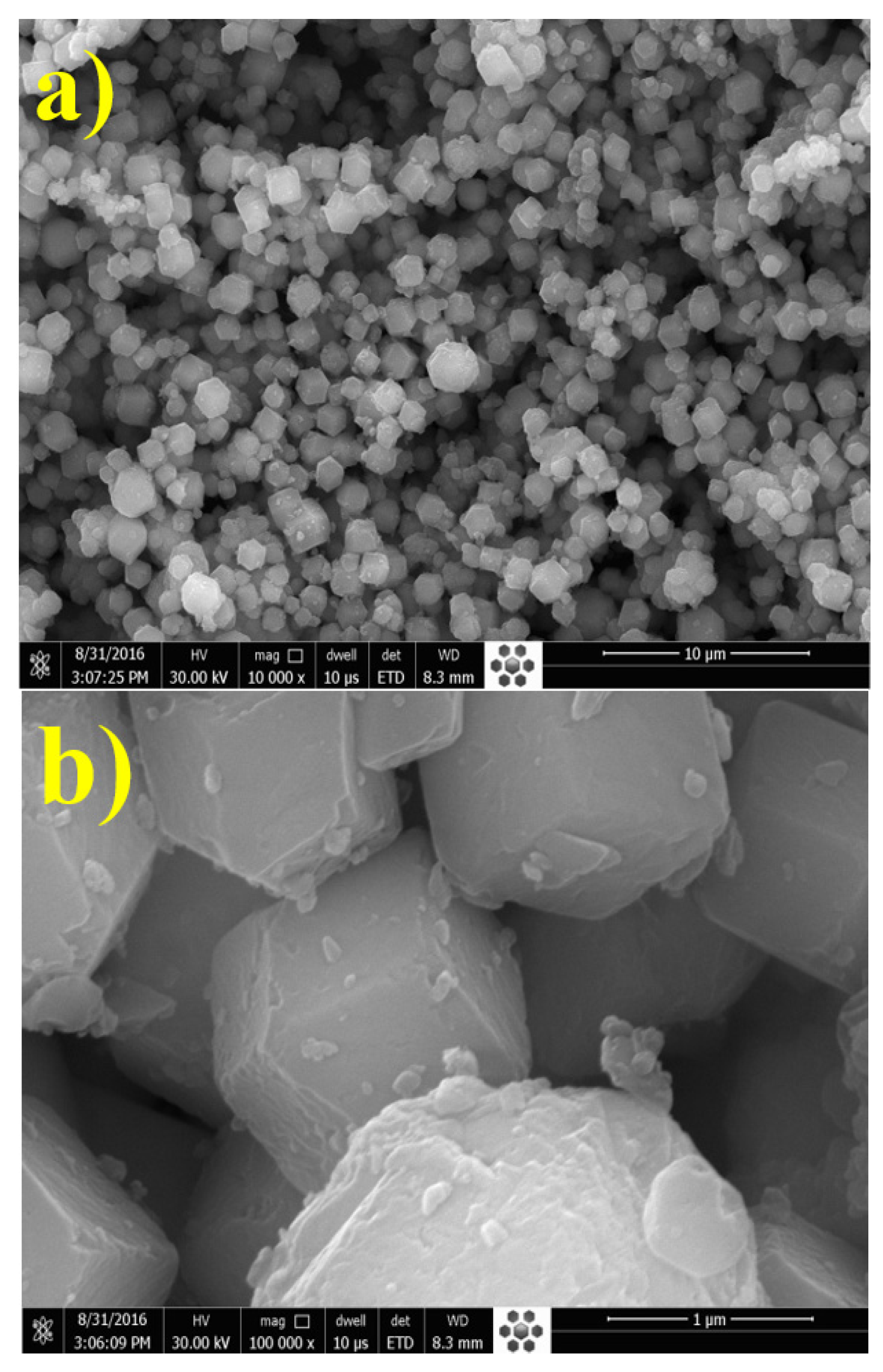
3.1. Characterization of UiO-66
3.2. Characterization of Membranes
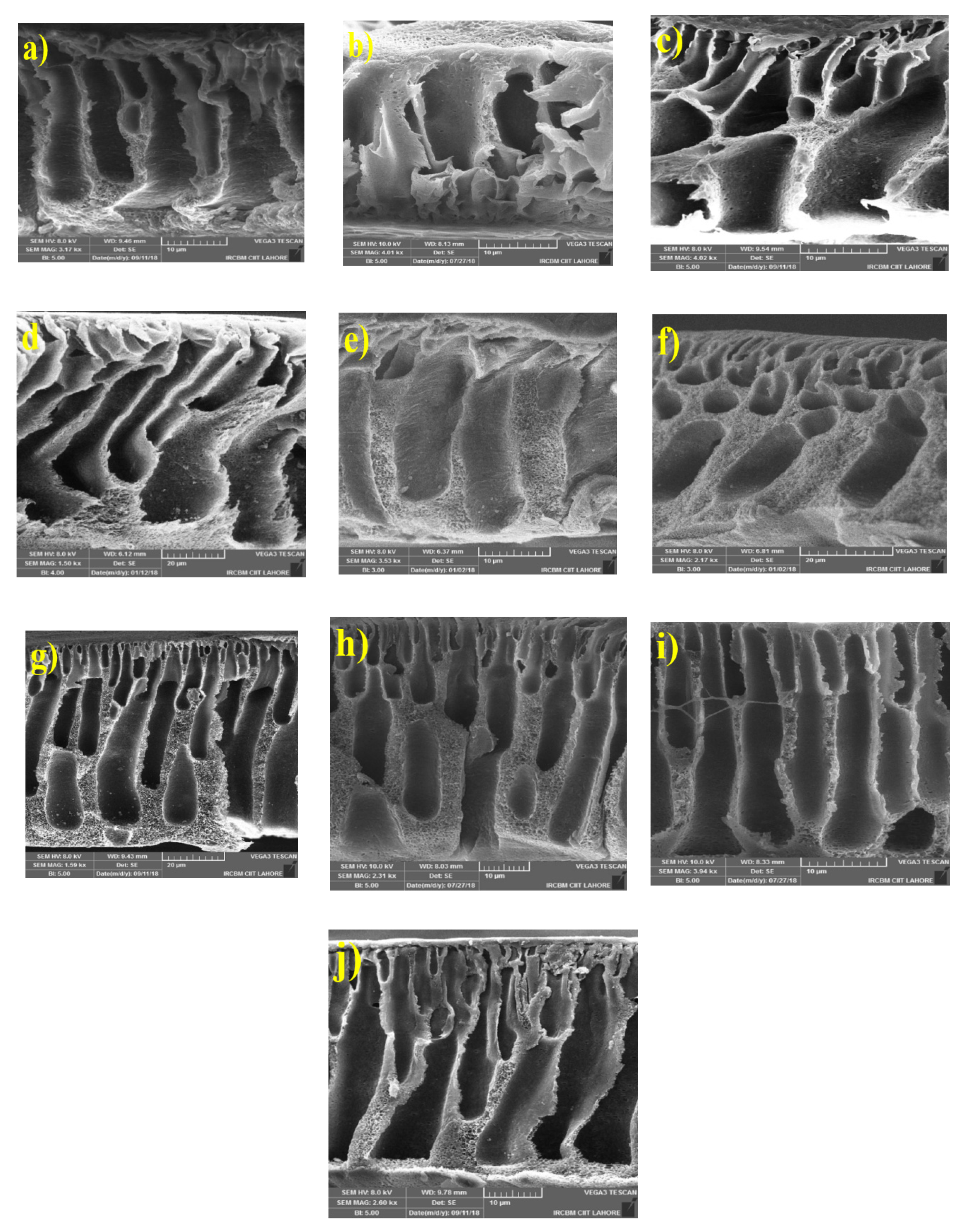
3.2.1. Morphology of MMMs
3.2.2. Static Water Contact Angle
3.2.3. Equilibrium Water Content (EWC)
3.3. Membrane Performance
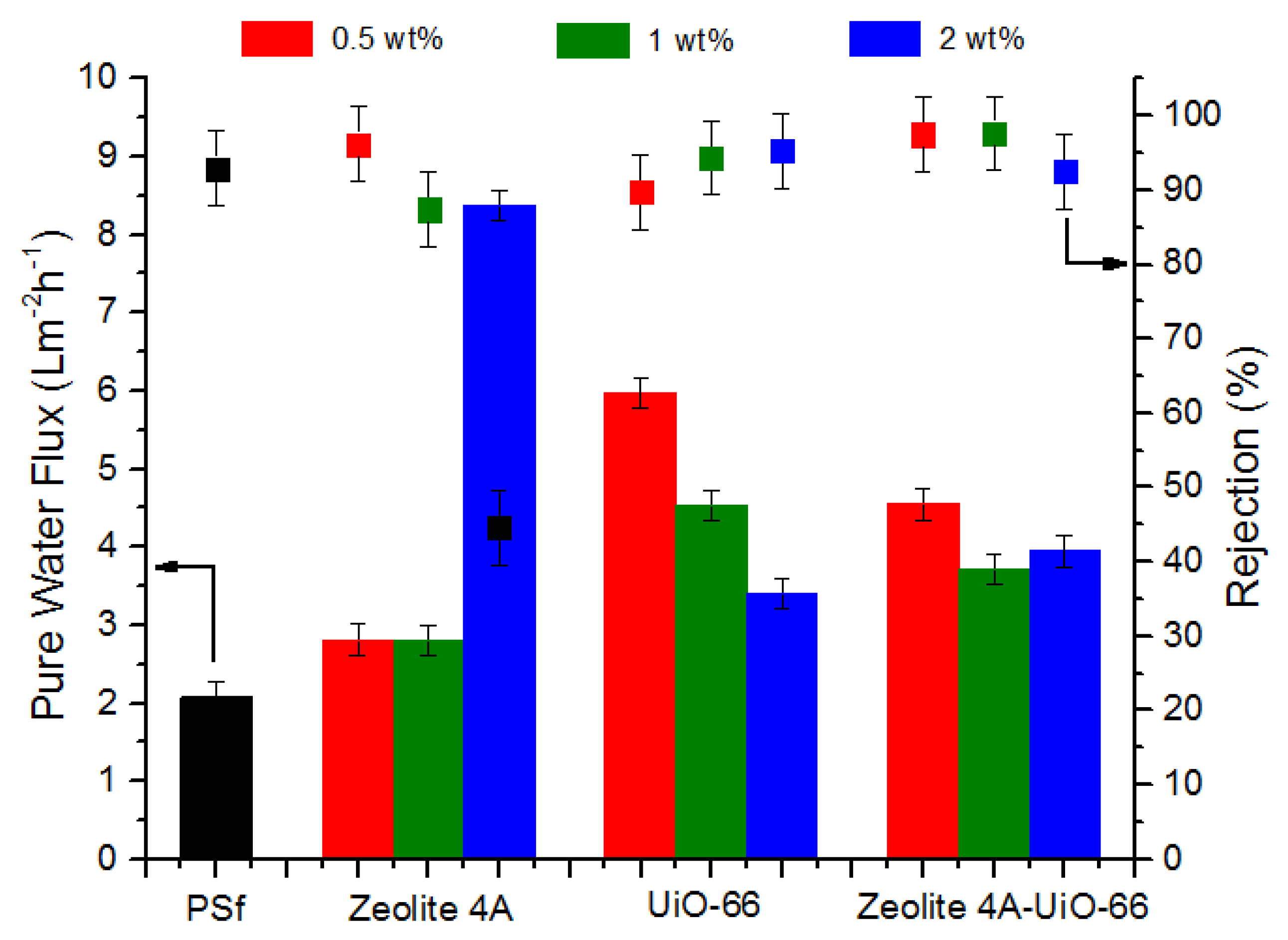
3.3.1. Permeation and Rejection
3.3.2. Antifouling Properties of Membranes
Static Humic Acid Adsorption
Flux Recovery Ratio (FRR)
Reversible and Irreversible Fouling
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Farahani, M.H.D.A.; Vatanpour, V. A comprehensive study on the performance and antifouling enhancement of the PVDF mixed matrix membranes by embedding different nanoparticulates: Clay, functionalized carbon nanotube, SiO2 and TiO2. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2018, 197, 372–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Der Bruggen, B.; Vandecasteele, C.; Van Gestel, T.; Doyen, W.; Leysen, R. A review of pressure-driven membrane processes in wastewater treatment and drinking water production. Environ. Prog. 2003, 22, 46–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kellenberger, C.; Luechinger, N.A.; Lamprou, A.; Rossier, M.; Grass, R.N.N.; Stark, W.J. Soluble nanoparticles as removable pore templates for the preparation of polymer ultrafiltration membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2012, 387, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabiee, H.; Farahani, M.H.D.A.; Vatanpour, V. Preparation and characterization of emulsion poly (vinyl chloride)(EPVC)/TiO2 nanocomposite ultrafiltration membrane. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 472, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelrasoul, A.; Doan, H.; Lohi, A.; Cheng, C.-H. Morphology control of polysulfone membranes in filtration processes: A critical review. ChemBioEng Rev. 2015, 2, 22–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Shan, L.; Tu, Z.; Zhang, Y. Preparation and characterization of novel Ce-doped nonstoichiometric nanosilica/polysulfone composite membranes. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2008, 63, 207–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Xuan, H.; Chen, Y.; He, C. Preparation and characterization of superior antifouling PVDF membrane with extremely ordered and hydrophilic surface layer. J. Membr. Sci. 2015, 494, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutzkover-Gutman, I.; Hasson, D.; Semiat, R. Humic substances fouling in ultrafiltration processes. Desalination 2010, 261, 218–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, H.-J.; Kim, H.; Lee, Y.; Yang, J.-W. Removal of anionic contaminants by surfactant modified powdered activated carbon (SM-PAC) combined with ultrafiltration. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 170, 1242–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Zhang, Z.; Fang, L.; Su, L. Study on ultrafiltration for surface water by a polyvinylchloride hollow fiber membrane. Desalination 2009, 238, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vatanpour, V.; Madaeni, S.; Khataee, A.R.; Salehi, E.; Zinadini, S.; Monfared, H.A. TiO2 embedded mixed matrix PES nanocomposite membranes: Influence of different sizes and types of nanoparticles on antifouling and performance. Desalination 2012, 292, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xueli, G.; Haizeng, W.; Jian, W.; Xing, H.; Congjie, G. Surface-modified PSf UF membrane by UV-assisted graft polymerization of capsaicin derivative moiety for fouling and bacterial resistance. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 445, 146–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahimpour, A. UV photo-grafting of hydrophilic monomers onto the surface of nano-porous PES membranes for improving surface properties. Desalination 2011, 265, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razmjou, A.; Mansouri, J.; Chen, V.; Lim, M.; Amal, R. Titania nanocomposite polyethersulfone ultrafiltration membranes fabricated using a low temperature hydrothermal coating process. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 380, 98–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Du, C.-H.; Zhu, B.-K.; Xu, Y.-Y. Surface immobilization of polymer brushes onto porous poly(vinylidene fluoride) membrane by electron beam to improve the hydrophilicity and fouling resistance. Polymer 2007, 48, 2910–2918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razmjou, A.; Mansouri, J.; Chen, V. The effects of mechanical and chemical modification of TiO2 nanoparticles on the surface chemistry, structure and fouling performance of PES ultrafiltration membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 378, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokhtari, S.; Rahimpour, A.; Shamsabadi, A.A.; Habibzadeh, S.; Soroush, M. Enhancing performance and surface antifouling properties of polysulfone ultrafiltration membranes with salicylate-alumoxane nanoparticles. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 393, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.Y.; Kim, H.S.; Kim, D.; Kim, S.-S.; Lee, P.-S. Preparation of mixed matrix membranes containing ZIF-8 and UiO-66 for multicomponent light gas separation. Crystals 2018, 9, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Gan, S.; Cui, L.; Xu, Y. Preparation and characterization of PES/TiO2 composite membranes. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2008, 254, 7080–7086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balta, S.; Sotto, A.; Luis, P.; Benea, L.; Van Der Bruggen, B.; Kim, J. A new outlook on membrane enhancement with nanoparticles: The alternative of ZnO. J. Membr. Sci. 2012, 389, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.-N.; Ruan, H.-M.; Wu, L.; Gao, C.-J. Preparation and characterization of PES–SiO2 organic–inorganic composite ultrafiltration membrane for raw water pretreatment. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 168, 1272–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esfahani, M.R.; Tyler, J.L.; Stretz, H.A.; Wells, M.J. Effects of a dual nanofiller, nano-TiO2 and MWCNT, for polysulfone-based nanocomposite membranes for water purification. Desalination 2015, 372, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celik, E.; Liu, L.; Choi, H. Protein fouling behavior of carbon nanotube/polyethersulfone composite membranes during water filtration. Water Res. 2011, 45, 5287–5294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Xu, Z.; Mai, W.; Min, C.; Zhou, B.; Shan, M.; Li, Y.; Yang, C.; Wang, Z.; Qian, X. Improved hydrophilicity, permeability, antifouling and mechanical performance of PVDF composite ultrafiltration membranes tailored by oxidized low-dimensional carbon nanomaterials. J. Mater. Chem. A 2013, 1, 3101–3111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maximous, N.; Nakhla, G.; Wan, W.; Wong, K. Preparation, characterization and performance of Al2O3/PES membrane for wastewater filtration. J. Membr. Sci. 2009, 341, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leo, C.; Kamil, N.A.; Junaidi, M.U.M.; Kamal, S.; Ahmad, A.L. The potential of SAPO-44 zeolite filler in fouling mitigation of polysulfone ultrafiltration membrane. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2013, 103, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leo, C.; Lee, W.C.; Ahmad, A.; Mohammad, A. Polysulfone membranes blended with ZnO nanoparticles for reducing fouling by oleic acid. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2012, 89, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S.; Xiao, K.; Mo, Y.; Huang, X. A novel ZnO nanoparticle blended polyvinylidene fluoride membrane for anti-irreversible fouling. J. Membr. Sci. 2012, 394, 184–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zirehpour, A.; Rahimpour, A.; Khoshhal, S.; Firouzjaei, M.D.; Ghoreyshi, A.A. The impact of MOF feasibility to improve the desalination performance and antifouling properties of FO membranes. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 70174–70185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prince, J.; Bhuvana, S.; Anbharasi, V.; Ayyanar, N.; Boodhoo, K.V.K.; Singh, G. Self-cleaning Metal Organic Framework (MOF) based ultra filtration membranes—A solution to bio-fouling in membrane separation processes. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 6555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhao, X.; He, C. Enhanced antifouling performance of hybrid PVDF ultrafiltration membrane with the dual-mode SiO2-g-PDMS nanoparticles. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2016, 166, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Mansouri, J.; Chen, V. Silica nanoparticles as carriers of antifouling ligands for PVDF ultrafiltration membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 433, 135–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zinadini, S.; Zinatizadeh, A.A.; Rahimi, M.; Vatanpour, V.; Zangeneh, H. Preparation of a novel antifouling mixed matrix PES membrane by embedding graphene oxide nanoplates. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 453, 292–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Wu, L.; Zhou, Z.; Zhang, L.; Chen, H. Improving the antifouling property of polysulfone ultrafiltration membrane by incorporation of isocyanate-treated graphene oxide. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2013, 15, 9084–9092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gun’Ko, V.; Voronin, E.; Pakhlov, E.; Zarko, V.; Turov, V.; Guzenko, N.; Leboda, R.; Chibowski, E. Features of fumed silica coverage with silanes having three or two groups reacting with the surface. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2000, 166, 187–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, R.; Zhang, S.; Liu, C.; Wang, Y.; Jian, X. Effect of NaA zeolite particle addition on poly(phthalazinone ether sulfone ketone) composite ultrafiltration (UF) membrane performance. J. Membr. Sci. 2009, 345, 5–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Yu, H.; Xia, J.; Zhang, F.; Li, F.; Xia, Y.; Li, Y. Novel GO-blended PVDF ultrafiltration membranes. Desalination 2012, 299, 50–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, G.; He, Y.; Yu, Z.; Zhan, Y.; Ma, L.; Zhang, L. Preparation and characterization of a novel PVDF ultrafiltration membrane by blending with TiO2-HNTs nanocomposites. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 371, 624–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, Y.T.; Mahmoudi, E.; Mohammad, A.W.; Benamor, A.; Johnson, D.; Hilal, N. Development of polysulfone-nanohybrid membranes using ZnO-GO composite for enhanced antifouling and antibacterial control. Desalination 2017, 402, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Guo, X.; Ying, Y.; Liu, D.; Zhong, C. Composite ultrafiltration membrane tailored by MOF@GO with highly improved water purification performance. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 313, 890–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valero, M.; Zornoza, B.; Téllez, C.; Coronas, J. Mixed matrix membranes for gas separation by combination of silica MCM-41 and MOF NH2-MIL-53(Al) in glassy polymers. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2014, 192, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, M.; Janakiram, S.; Dai, Z.; Ansaloni, L.; Deng, L. Performance of mixed matrix membranes containing porous two-dimensional (2D) and three-dimensional (3D) fillers for CO2 separation: A review. Membranes 2018, 8, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anjum, M.W.; Vermoortele, F.; Khan, A.L.; Bueken, B.; De Vos, D.E.; Vankelecom, I.F. Modulated UiO-66-based mixed-matrix membranes for CO2 separation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 25193–25201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, D.; Han, G.; Peh, S.B.; Chen, S.B. Water-stable metal–organic framework UiO-66 for performance enhancement of forward osmosis membranes. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2017, 56, 12773–12782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zornoza, B.; Téllez, C.; Coronas, J. Mixed matrix membranes comprising glassy polymers and dispersed mesoporous silica spheres for gas separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 368, 100–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Ma, B.-R.; Zhou, D.; Xiang, Y.-H.; Xue, L. Breaking through tradeoff of Polysulfone ultrafiltration membranes by zeolite 4A. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2014, 186, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, L.-L.; Tseng, H.-H.; Chen, J.-C. Fabrication of polyphenylsulfone/polyetherimide blend membranes for ultrafiltration applications: The effects of blending ratio on membrane properties and humic acid removal performance. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 384, 72–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, S.J.D.; Ladewig, B.P.; Hill, A.J.; Lau, C.H.; Hill, M.R. Post-synthetic Ti Exchanged UiO-66 metal-organic frameworks that deliver exceptional gas permeability in mixed matrix membranes. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 7823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Liu, M.; Li, K.; Zuo, Y.; Wei, Y.; Xu, S.; Zhang, G.; Song, C.; Zhang, Z.; Guo, X. Facile synthesis of morphology and size-controlled zirconium metal–organic framework UiO-66: The role of hydrofluoric acid in crystallization. CrystEngComm 2015, 17, 6434–6440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, R.T.; Lee, J.S.; Bae, T.-H.; Ward, J.K.; Johnson, J.; Jones, C.W.; Nair, S.; Koros, W.J. CO2–CH4 permeation in high zeolite 4A loading mixed matrix membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 367, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Ye, W.; Zhong, K.; Shen, J.; Jullok, N.; Sotto, A.; Van Der Bruggen, B. Enhancement of polyethersulfone (PES) membrane doped by monodisperse stobersilica for water treatment. Chem. Eng. Process. Process. Intensif. 2016, 107, 194–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Guan, H.-M.; Tan, W.L.; Qiao, X.-Y.; Kulprathipanja, S. Pervaporation study of aqueous ethanol solution through zeolite-incorporated multilayer poly(vinyl alcohol) membranes: Effect of zeolites. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 276, 260–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Wang, P.; Zheng, Q. Preparation and properties of polysulfone/TiO2 composite ultrafiltration membranes. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 2006, 44, 879–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Gholamvand, Z.; Morrissey, A.; Nolan, K.; Ulbricht, M.; Lawler, J. Preparation and characterization of low fouling novel hybrid ultrafiltration membranes based on the blends of GO−TiO2 nanocomposite and polysulfone for humic acid removal. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 506, 38–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pieracci, J.; Crivello, J.V.; Belfort, G. Increasing membrane permeability of UV-modified poly(ether sulfone) ultrafiltration membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2002, 202, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Membrane | Nanofiller Composition | |
|---|---|---|
| Zeolite 4A (wt%) | UiO-66 (wt%) | |
| Neat PSf | - | - |
| Zeolite 4A (0.5 wt%) | 0.5 | - |
| Zeolite 4A (1 wt%) | 1.0 | - |
| Zeolite 4A (2 wt%) | 2.0 | - |
| UiO-66 (0.5 wt%) | - | 0.5 |
| UiO-66 (1 wt%) | - | 1.0 |
| UiO-66 (2 wt%) | - | 2.0 |
| Zeolite 4A-UiO-66 (0.5 wt%) | 0.25 | 0.25 |
| Zeolite 4A-UiO-66 (1 wt%) | 0.5 | 0.5 |
| Zeolite 4A-UiO-66 (2 wt%) | 1.0 | 1.0 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Anjum, T.; Tamime, R.; Khan, A.L. Mixed-Matrix Membranes Comprising of Polysulfone and Porous UiO-66, Zeolite 4A, and Their Combination: Preparation, Removal of Humic Acid, and Antifouling Properties. Membranes 2020, 10, 393. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes10120393
Anjum T, Tamime R, Khan AL. Mixed-Matrix Membranes Comprising of Polysulfone and Porous UiO-66, Zeolite 4A, and Their Combination: Preparation, Removal of Humic Acid, and Antifouling Properties. Membranes. 2020; 10(12):393. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes10120393
Chicago/Turabian StyleAnjum, Tanzila, Rahma Tamime, and Asim Laeeq Khan. 2020. "Mixed-Matrix Membranes Comprising of Polysulfone and Porous UiO-66, Zeolite 4A, and Their Combination: Preparation, Removal of Humic Acid, and Antifouling Properties" Membranes 10, no. 12: 393. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes10120393
APA StyleAnjum, T., Tamime, R., & Khan, A. L. (2020). Mixed-Matrix Membranes Comprising of Polysulfone and Porous UiO-66, Zeolite 4A, and Their Combination: Preparation, Removal of Humic Acid, and Antifouling Properties. Membranes, 10(12), 393. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes10120393







