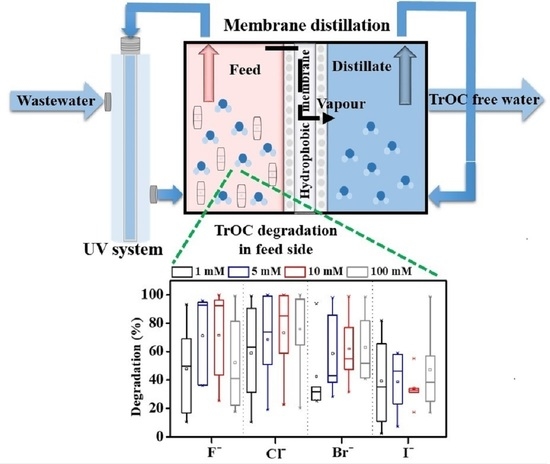
Impact of Inorganic Ions and Organic Matter on the Removal of Trace Organic Contaminants by Combined Direct Contact Membrane Distillation–UV Photolysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Sample Preparation
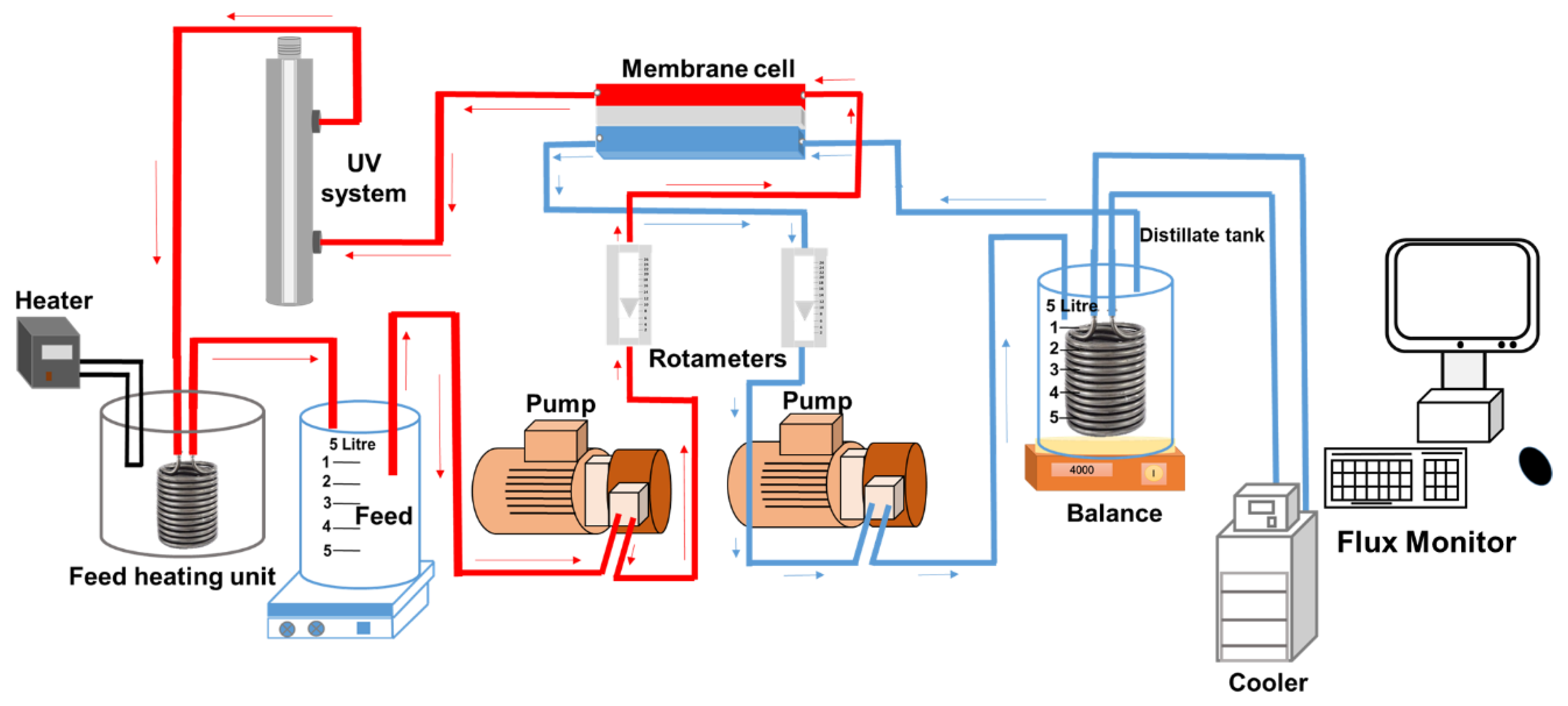
2.3. DCMD and UV Setup and Operation Protocol
2.4. TrOC Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Results and Discussion
TrOC Removal by DCMD
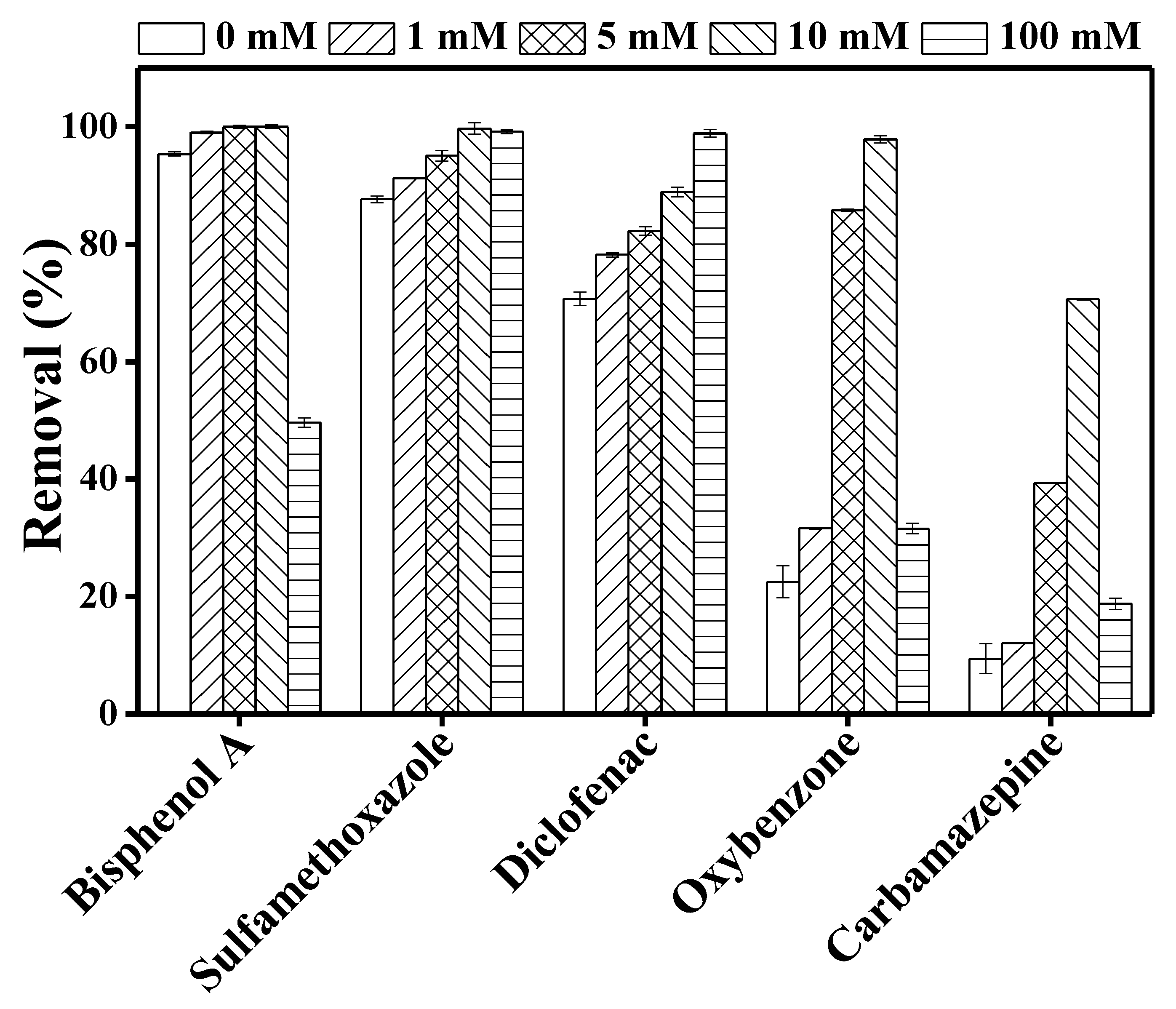
3.2. Fate of TrOCs in DCMD–UV Photolysis Process
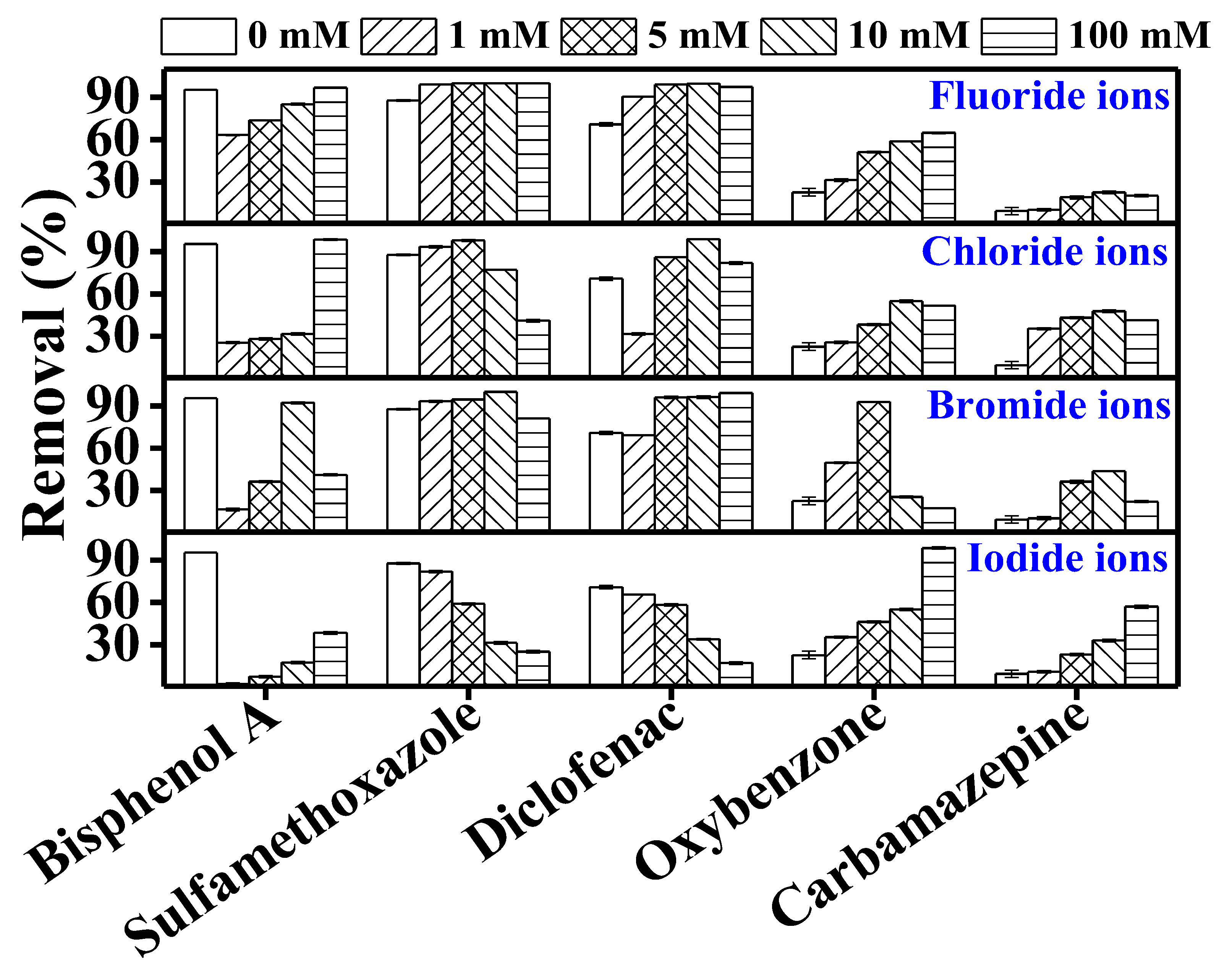
3.3. Effect of Inorganic Ions on the TrOC Removal by DCMD–UV Photolysis
3.3.1. Effect of Nitrate Ion
3.3.2. Effect of Halide Ions
3.3.3. Effect of Bicarbonate Ion
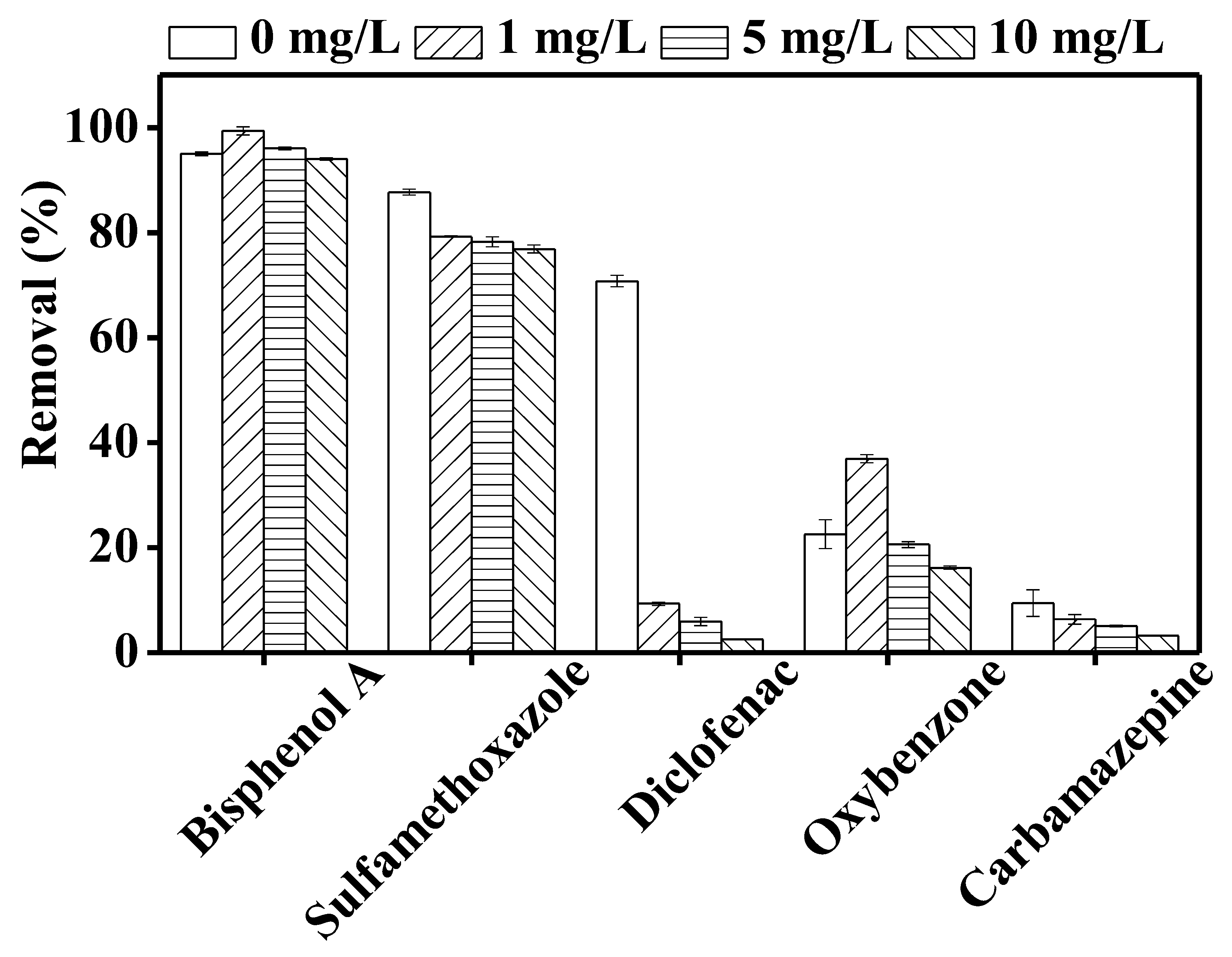
3.4. Effect of Humic Acid on TrOC Removal by DCMD–UV Photolysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Luo, Y.; Guo, W.; Ngo, H.H.; Nghiem, L.D.; Hai, F.I.; Zhang, J.; Liang, S.; Wang, X.C. A review on the occurrence of micropollutants in the aquatic environment and their fate and removal during wastewater treatment. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 473–474, 619–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jelić, A.; Gros, M.; Petrović, M.; Ginebreda, A.; Barceló, J. Occurrence and Elimination of Pharmaceuticals during Conventional Wastewater Treatment. Emerg. Prior. Pollut. Rivers 2012, 24, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hai, F.I.; Nghiem, L.D.; Khan, S.J.; Asif, M.B.; Price, W.E.; Yamamoto, K. Removal of Emerging Trace Organic Contaminants (TrOC) by MBR. In Membrane Biological Reactors: Theory, Modeling, Design, Management and Applications to Wastewater Reuse; IWA Publishing: London, UK, 2019; pp. 413–468. [Google Scholar]
- Bayen, S. Occurrence, bioavailability and toxic effects of trace metals and organic contaminants in mangrove ecosystems: A review. Environ. Int. 2012, 48, 84–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadkaew, N.; Hai, F.I.; McDonald, J.A.; Khan, S.J.; Nghiem, L.D. Removal of trace organics by MBR treatment: The role of molecular properties. Water Res. 2011, 45, 2439–2451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijekoon, K.C.; Hai, F.I.; Kang, J.; Price, W.E.; Guo, W.; Ngo, H.H.; Nghiem, L.D. The fate of pharmaceuticals, steroid hormones, phytoestrogens, UV-filters and pesticides during MBR treatment. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 144, 247–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikhlaq, A.; Kazmi, M.; Tufail, A.; Fatima, H.; Joya, K.S. Application of peanut shell ash as a low-cost support for Fenton-like catalytic removal of methylene blue in wastewater. Desalin. Water Treat. 2018, 111, 338–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chew, N.G.P.; Zhang, Y.; Goh, K.; Ho, J.S.; Xu, R.; Wang, R. Hierarchically Structured Janus Membrane Surfaces for Enhanced Membrane Distillation Performance. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 25524–25534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Vanangamudi, A.; Wang, J.; Jegatheesan, J.; Mishra, V.; Sharma, R.; Gray, S.R.; Kujawa, J.; Kujawski, W.; Wicaksana, F.; et al. Direct contact membrane distillation for effective concentration of perfluoroalkyl substances—Impact of surface fouling and material stability. Water Res. 2020, 182, 116010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Couto, C.F.; Amaral, M.C.S.; Lange, L.C.; Santos, L.V.D.S. Effect of humic acid concentration on pharmaceutically active compounds (PhACs) rejection by direct contact membrane distillation (DCMD). Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 212, 920–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkhudhiri, A.; Darwish, N.A.; Hilal, N. Membrane distillation: A comprehensive review. Desalination 2012, 287, 2–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijekoon, K.C.; Hai, F.I.; Kang, J.; Price, W.E.; Guo, W.; Ngo, H.H.; Cath, T.Y.; Nghiem, L.D. A novel membrane distillation–thermophilic bioreactor system: Biological stability and trace organic compound removal. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 159, 334–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chew, N.G.P.; Zhao, S.; Wang, R. Recent advances in membrane development for treating surfactant- and oil-containing feed streams via membrane distillation. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 273, 102022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeszhanov, A.; Korolkov, I.V.; Gorin, Y.G.; Dosmagambetova, S.S.; Zdorovets, M.V. Membrane distillation of pesticide solutions using hydrophobic track-etched membranes. Chem. Pap. 2020, 74, 3445–3453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chew, N.G.P.; Zhao, S.; Loh, C.H.; Permogorov, N.; Wang, R. Surfactant effects on water recovery from produced water via direct-contact membrane distillation. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 528, 126–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asif, M.B.; Hai, F.I.; Kang, J.; Van De Merwe, J.P.; Leusch, F.D.; Price, W.E.; Nghiem, L.D. Biocatalytic degradation of pharmaceuticals, personal care products, industrial chemicals, steroid hormones and pesticides in a membrane distillation-enzymatic bioreactor. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 247, 528–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wijekoon, K.C.; Hai, F.I.; Kang, J.; Price, W.E.; Cath, T.Y.; Nghiem, L.D. Rejection and fate of trace organic compounds (TrOCs) during membrane distillation. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 453, 636–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tufail, A.; Alharbi, S.; Alrifai, J.; Ansari, A.; Price, W.E.; Hai, F.I. Combining enzymatic membrane bioreactor and ultraviolet photolysis for enhanced removal of trace organic contaminants: Degradation efficiency and by-products formation. Process. Saf. Environ. Prot. 2021, 145, 110–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alharbi, S.K.; Price, W.E. Degradation and Fate of Pharmaceutically Active Contaminants by Advanced Oxidation Processes. Curr. Pollut. Rep. 2017, 3, 268–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tufail, A.; Price, W.E.; Hai, F.I. A critical review on advanced oxidation processes for the removal of trace organic contaminants: A voyage from individual to integrated processes. Chemosphere 2020, 260, 127460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tufail, A.; Price, W.E.; Mohseni, M.; Pramanik, B.K.; Hai, F.I. A critical review of advanced oxidation processes for emerging trace organic contaminant degradation: Mechanisms, factors, degradation products, and effluent toxicity. J. Water Process. Eng. 2020, 101778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mozia, S.; Darowna, D.; Przepiórski, J.; Morawski, A.W. Evaluation of Performance of Hybrid Photolysis-DCMD and Photocatalysis-DCMD Systems Utilizing UV-C Radiation for Removal of Diclofenac Sodium Salt from Water. Pol. J. Chem. Technol. 2013, 15, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanzada, N.K.; Farid, M.U.; Kharraz, J.A.; Choi, J.; Tang, C.Y.; Nghiem, L.D.; Jang, A.; An, A.K. Removal of organic micropollutants using advanced membrane-based water and wastewater treatment: A review. J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 598, 117672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapple, A.; Nguyen, L.N.; Hai, F.I.; Dosseto, A.; Rashid, M.H.O.; Oh, S.; Price, W.E.; Nghiem, L.D. Impact of inorganic salts on degradation of bisphenol A and diclofenac by crude extracellular enzyme from Pleurotus ostreatus. Biocatal. Biotransform. 2019, 37, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Qiao, X.; Zhang, Y.-N.; Zhou, C.; Xie, H.; Chen, J. Effects of halide ions on photodegradation of sulfonamide antibiotics: Formation of halogenated intermediates. Water Res. 2016, 102, 405–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Lu, X.; Jiang, J.; Ma, J.; Liu, G.; Cao, Y.; Liu, W.; Li, J.; Pang, S.; Kong, X.; et al. Degradation of sulfamethoxazole by UV, UV/H2O2 and UV/persulfate (PDS): Formation of oxidation products and effect of bicarbonate. Water Res. 2017, 118, 196–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, D.; Huang, B.; Xiong, D.; He, H.; Meng, X.; Pan, X. Photodegradation of 17α-ethynylestradiol in dissolved humic substances solution: Kinetics, mechanism and estrogenicity variation. J. Environ. Sci. 2017, 54, 196–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, R.R.; Charpentier, P.A.; Ray, M.B. Photodegradation of 17β-estradiol in aquatic solution under solar irradiation: Kinetics and influencing water parameters. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2011, 219, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Liu, L.; Su, J.; Liang, J.; Wu, B.; Zuo, J.; Zuo, Y. Role of humic substances in the photodegradation of naproxen under simulated sunlight. Chemosphere 2017, 187, 261–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asif, M.B.; Fida, Z.; Tufail, A.; Van De Merwe, J.P.; Leusch, F.D.; Pramanik, B.K.; Price, W.E.; Hai, F.I. Persulfate oxidation-assisted membrane distillation process for micropollutant degradation and membrane fouling control. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 222, 321–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lekkerkerker-Teunissen, K.; Benotti, M.J.; Snyder, S.A.; Van Dijk, H.C. Transformation of atrazine, carbamazepine, diclofenac and sulfamethoxazole by low and medium pressure UV and UV/H2O2 treatment. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2012, 96, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gago-Ferrero, P.; Badia-Fabregat, M.; Olivares, A.; Piña, B.; Blánquez, P.; Vicent, T.; Caminal, G.; Díaz-Cruz, M.S.; Barceló, D. Evaluation of fungal- and photo-degradation as potential treatments for the removal of sunscreens BP3 and BP1. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 427–428, 355–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mozia, S.; Tsumura, T.; Toyoda, M.; Morawski, A.W. Degradation of Ibuprofen Sodium Salt in a Hybrid Photolysis—Membrane Distillation System Utilizing Germicidal UVC Lamp. J. Adv. Oxid. Technol. 2011, 14, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mozia, S. Photocatalytic membrane reactors (PMRs) in water and wastewater treatment. A review. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2010, 73, 71–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Z.; Guo, C.; Lv, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, J. Kinetic and mechanistic study of sulfadimidine photodegradation under simulated sunlight irradiation. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2019, 31, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koumaki, E.; Mamais, D.; Noutsopoulos, C.; Nika, M.-C.; Bletsou, A.A.; Thomaidis, N.S.; Eftaxias, A.; Stratogianni, G. Degradation of emerging contaminants from water under natural sunlight: The effect of season, pH, humic acids and nitrate and identification of photodegradation by-products. Chemosphere 2015, 138, 675–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, N.; Liu, G.; Liu, H.; Wang, Y.; He, Z.; Wang, G. Diclofenac photodegradation under simulated sunlight: Effect of different forms of nitrogen and Kinetics. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 192, 411–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Zhao, H.; Quan, X.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, S. Formation of Chlorinated Intermediate from Bisphenol A in Surface Saline Water under Simulated Solar Light Irradiation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 7712–7717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, A.R.L.; Moreira, N.F.; Puma, G.L.; Silva, A.M. Impact of water matrix on the removal of micropollutants by advanced oxidation technologies. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 363, 155–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, R.; Li, M.; Wang, C.; Zhang, M.; Khan, M.A.N.; Sun, X.; Shen, J.; Han, W.; Wang, L.; Li, J. Singlet oxygen-dominated non-radical oxidation process for efficient degradation of bisphenol A under high salinity condition. Water Res. 2019, 148, 416–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grebel, J.E.; Pignatello, J.J.; Mitch, W.A. Impact of Halide Ions on Natural Organic Matter-Sensitized Photolysis of 17β-Estradiol in Saline Waters. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 7128–7134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Kong, Q.; Chen, P.; Chen, M.; Liu, G.; Lv, W.; Yao, K. Effect of halide ions on the photodegradation of ibuprofen in aqueous environments. Chemosphere 2017, 166, 412–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.-M.; Lee, G.; Kim, M.-K.; Zoh, K.-D. Kinetics and degradation mechanism of Benzophenone-3 in chlorination and UV/chlorination reactions. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 393, 124780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.-M.; Lee, G.; Zoh, K.-D. Benzophenone-3 degradation via UV/H2O2 and UV/persulfate reactions. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 403, 123591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazellier, P.; Busset, C.; Delmont, A.; De Laat, J. A comparison of fenuron degradation by hydroxyl and carbonate radicals in aqueous solution. Water Res. 2007, 41, 4585–4594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merouani, S.; Hamdaoui, O.; Saoudi, F.; Chiha, M.; Pétrier, C. Influence of bicarbonate and carbonate ions on sonochemical degradation of Rhodamine B in aqueous phase. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 175, 593–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Bianco, A.; Brigante, M.; Mailhot, G. UVA-UVB activation of hydrogen peroxide and persulfate for advanced oxidation processes: Efficiency, mechanism and effect of various water constituents. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 347, 279–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, H.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, Y.L. Degradation of Acid Pharmaceuticals in the UV/H 2 O 2 Process: Effects of Humic Acid and Inorganic Salts. Clean Soil Air Water 2012, 41, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calza, P.; Vione, D.; Minero, C. The role of humic and fulvic acids in the phototransformation of phenolic compounds in seawater. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 493, 411–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhao, F.; Wang, F.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, Q.; Han, X.; Geng, H. Molecular characteristics of leonardite humic acid and the effect of its fractionations on sulfamethoxazole photodegradation. Chemosphere 2020, 246, 125642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Roddick, F.A.; Fan, L. Direct and indirect photolysis of seven micropollutants in secondary effluent from a wastewater lagoon. Chemosphere 2017, 185, 297–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chianese, S.; Iovino, P.; Leone, V.; Musmarra, D.; Prisciandaro, M. Photodegradation of Diclofenac Sodium Salt in Water Solution: Effect of HA, NO3—and TiO2 on Photolysis Performance. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2017, 228, 270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trovó, A.G.; Nogueira, R.F.; Agüera, A.; Sirtori, C.; Fernández-Alba, A.R. Photodegradation of sulfamethoxazole in various aqueous media: Persistence, toxicity and photoproducts assessment. Chemosphere 2009, 77, 1292–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
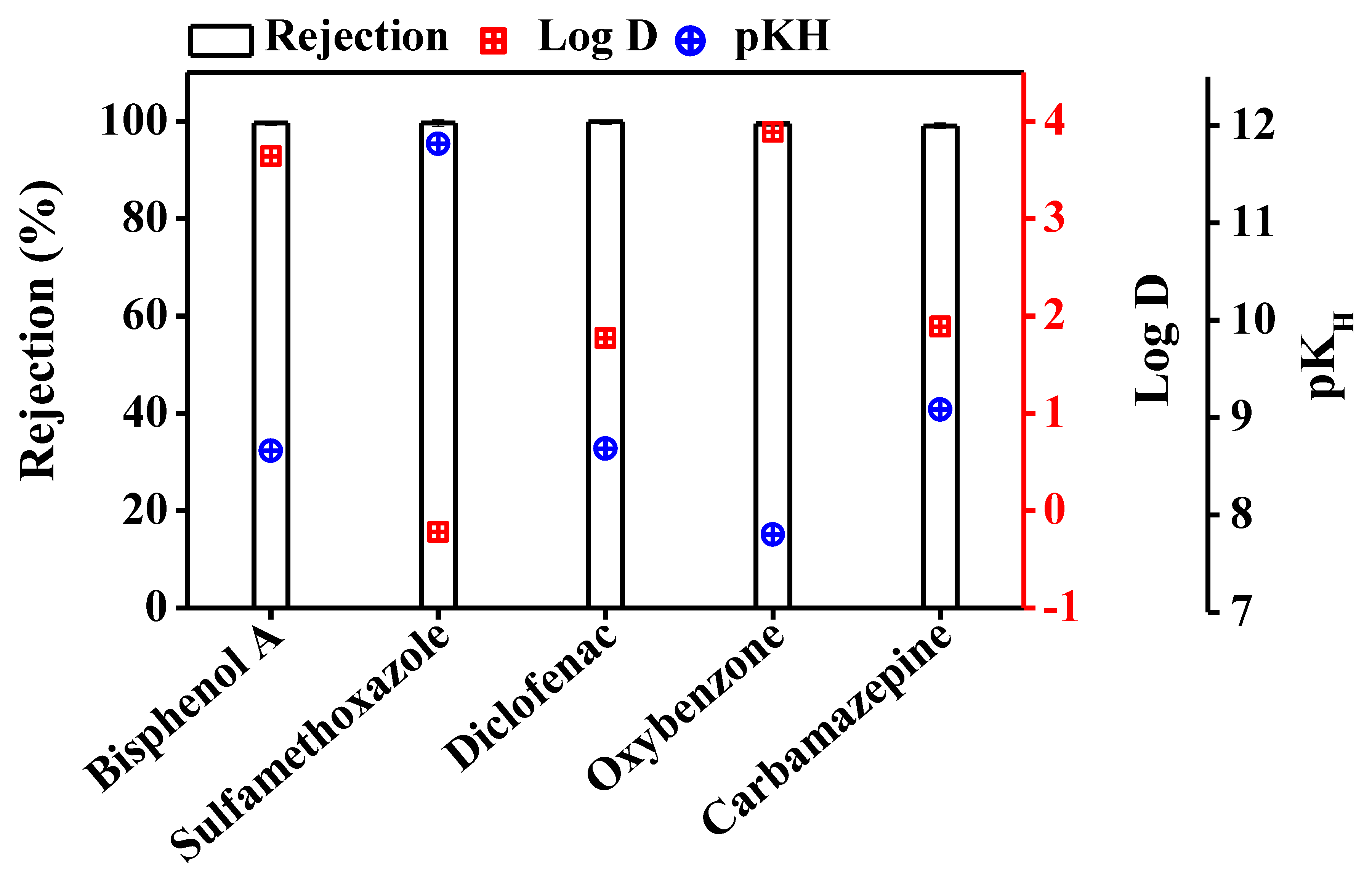


| Compound | Molecular Weight (g/mol) | Log D at pH 7 | Vapour Pressure (mmHg) | pKH at pH 7 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Bisphenol A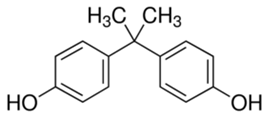 | 228.29 | 3.64 | 5.34 × 10−7 | 8.66 |
Sulfamethoxazole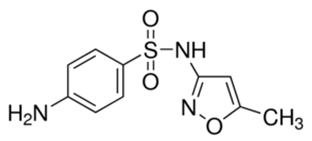 | 253.28 | −0.22 | 1.52 × 10−12 | 11.81 |
Diclofenac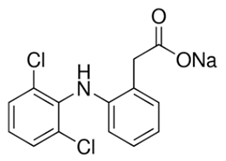 | 296.15 | 1.77 | 1.59 × 10−7 | 8.68 |
Oxybenzone | 228.24 | 3.89 | 5.26 × 10−6 | 7.80 |
Carbamazepine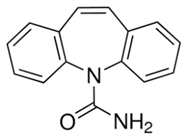 | 236.27 | 1.89 | 5.78 × 10−7 | 9.08 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tufail, A.; Price, W.E.; Hai, F.I. Impact of Inorganic Ions and Organic Matter on the Removal of Trace Organic Contaminants by Combined Direct Contact Membrane Distillation–UV Photolysis. Membranes 2020, 10, 428. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes10120428
Tufail A, Price WE, Hai FI. Impact of Inorganic Ions and Organic Matter on the Removal of Trace Organic Contaminants by Combined Direct Contact Membrane Distillation–UV Photolysis. Membranes. 2020; 10(12):428. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes10120428
Chicago/Turabian StyleTufail, Arbab, William E. Price, and Faisal I. Hai. 2020. "Impact of Inorganic Ions and Organic Matter on the Removal of Trace Organic Contaminants by Combined Direct Contact Membrane Distillation–UV Photolysis" Membranes 10, no. 12: 428. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes10120428
APA StyleTufail, A., Price, W. E., & Hai, F. I. (2020). Impact of Inorganic Ions and Organic Matter on the Removal of Trace Organic Contaminants by Combined Direct Contact Membrane Distillation–UV Photolysis. Membranes, 10(12), 428. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes10120428