Simulation Study on Direct Contact Membrane Distillation Modules for High-Concentration NaCl Solution
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Theoretical Background
3. Methodology
3.1. Geometry and Governing Equations
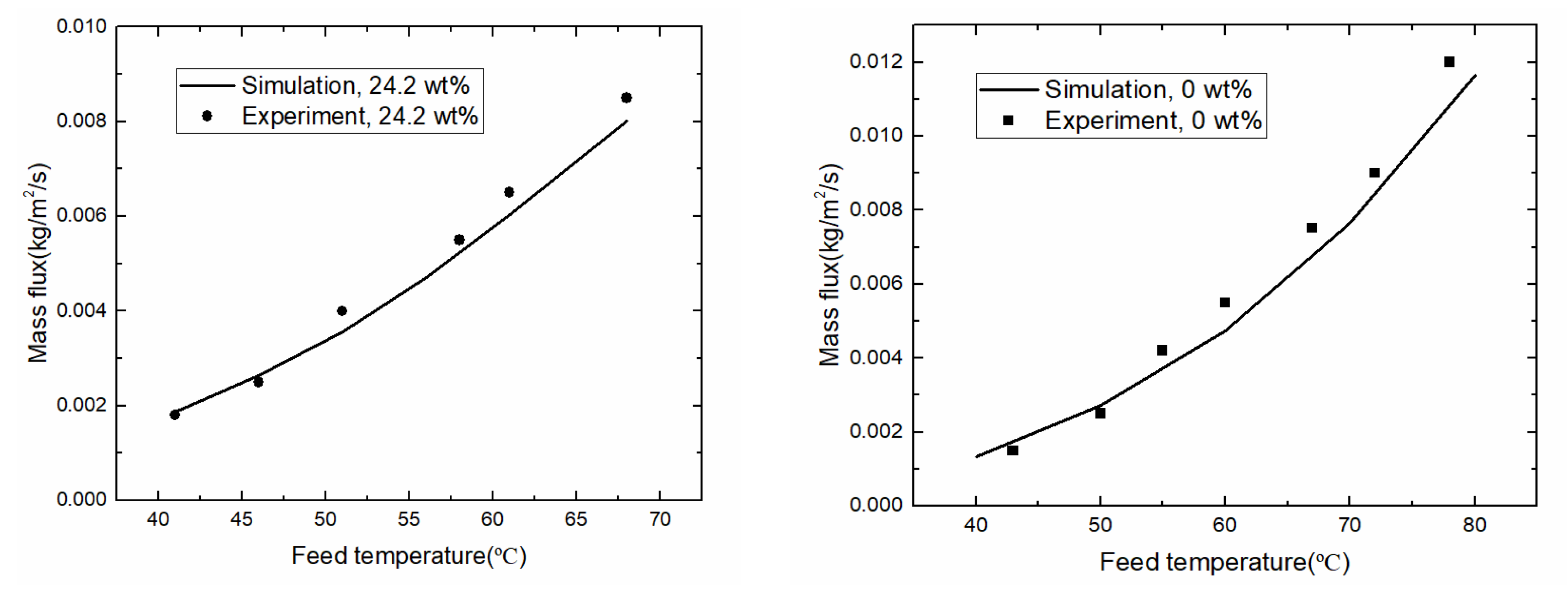
3.2. Model Validation
4. Results and Discussion
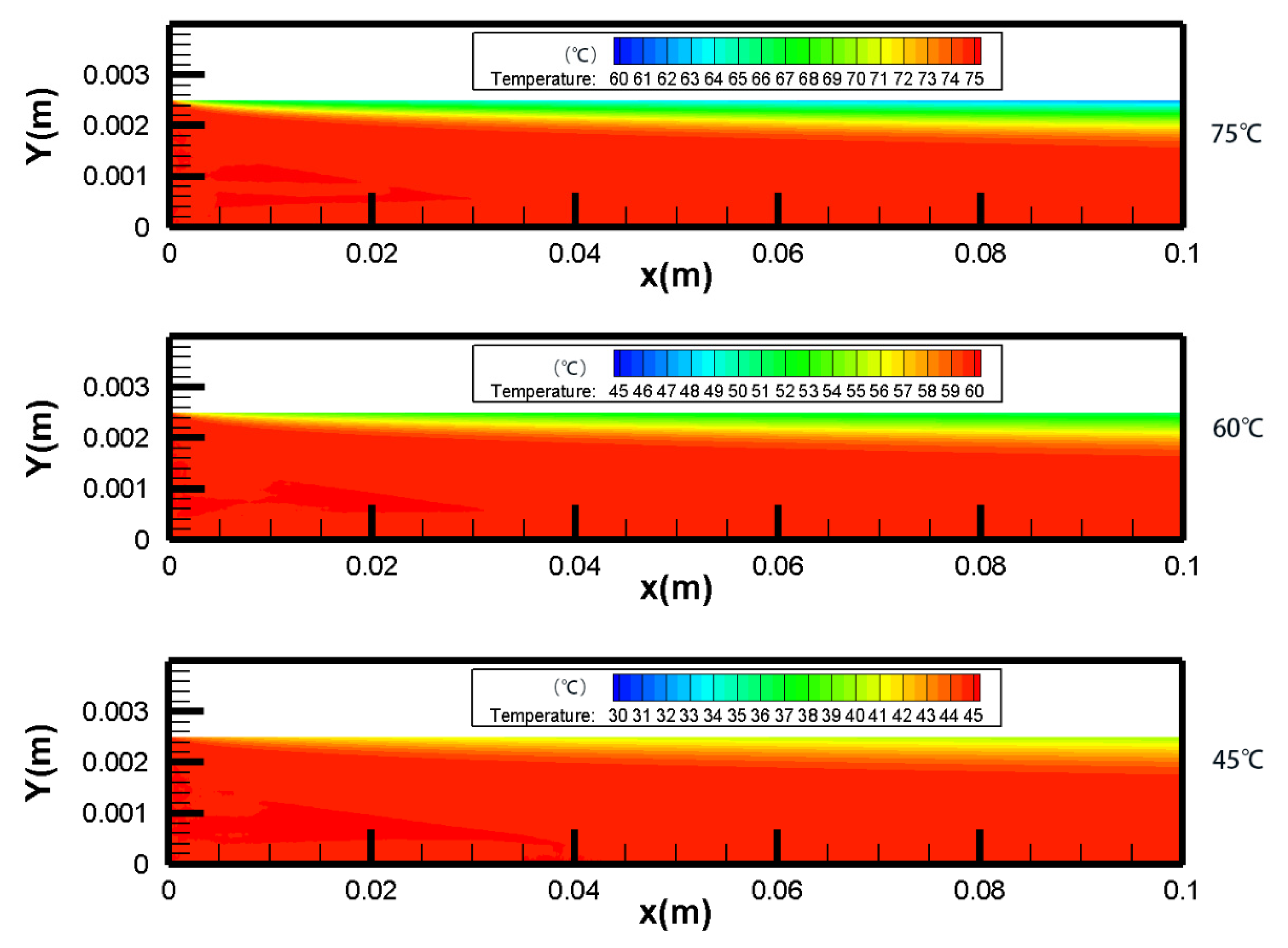
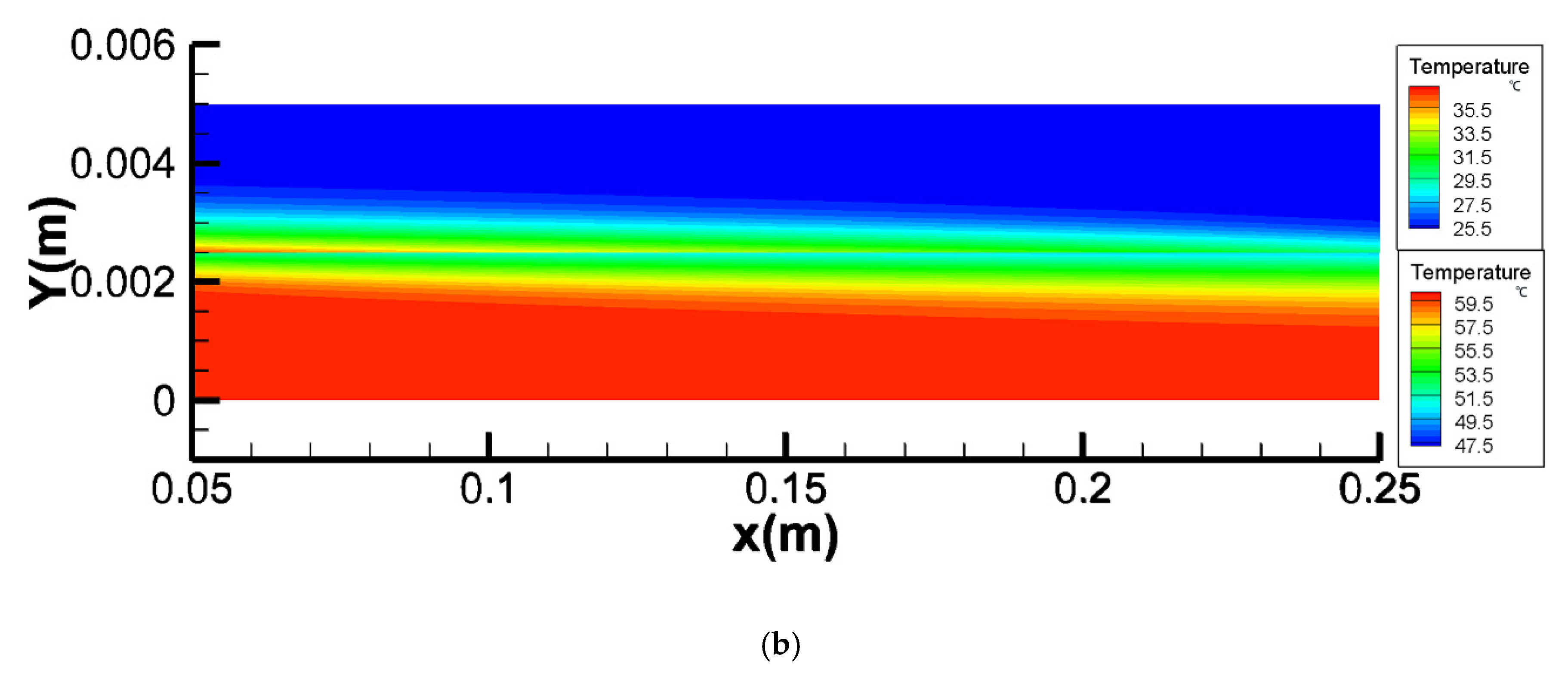
4.1. Temperature Polarization
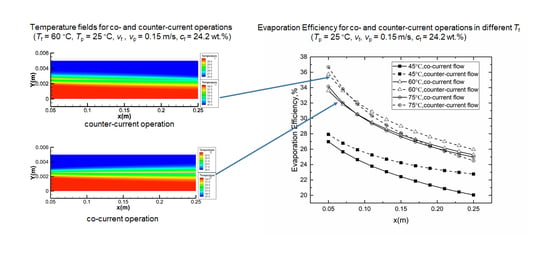
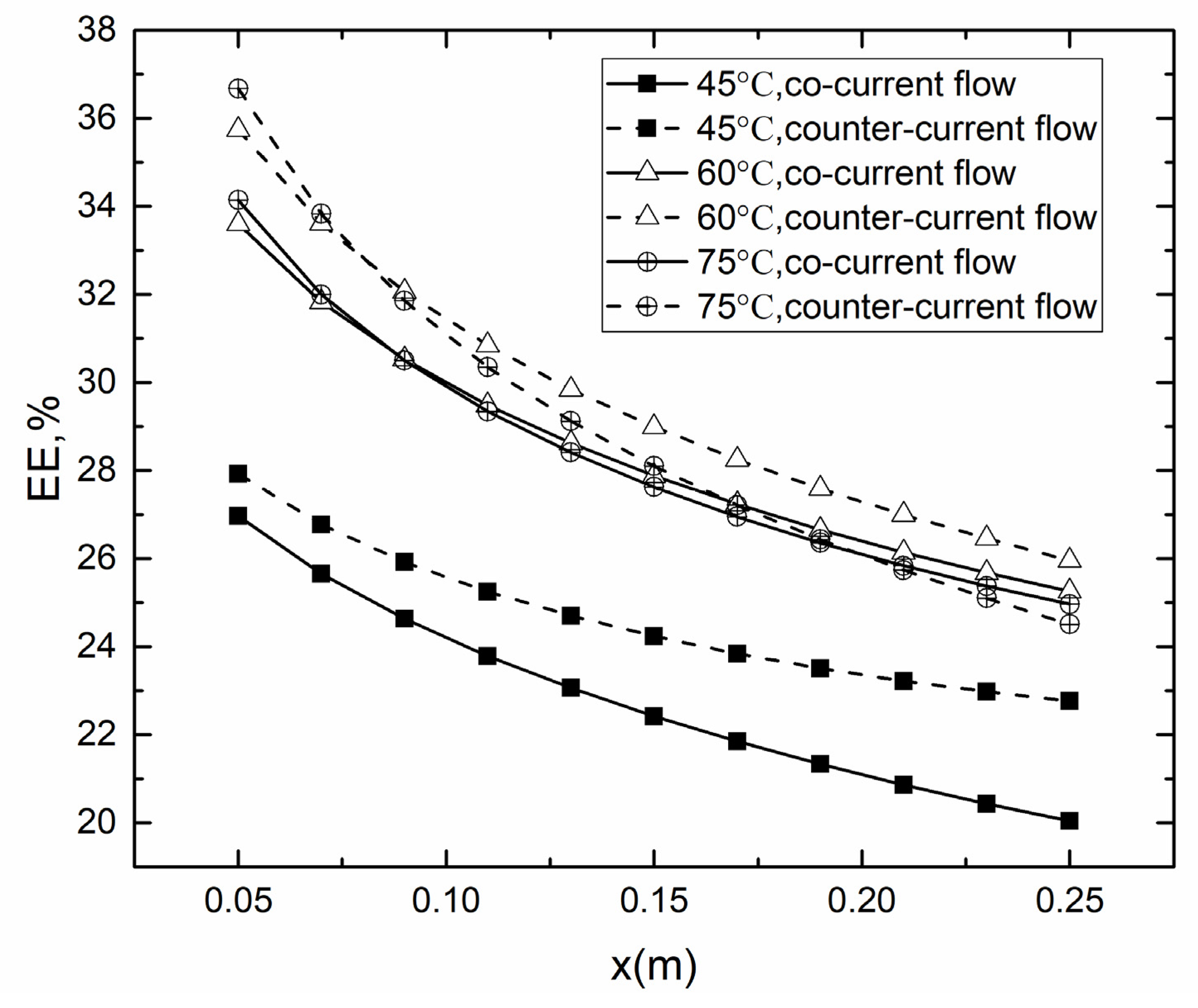
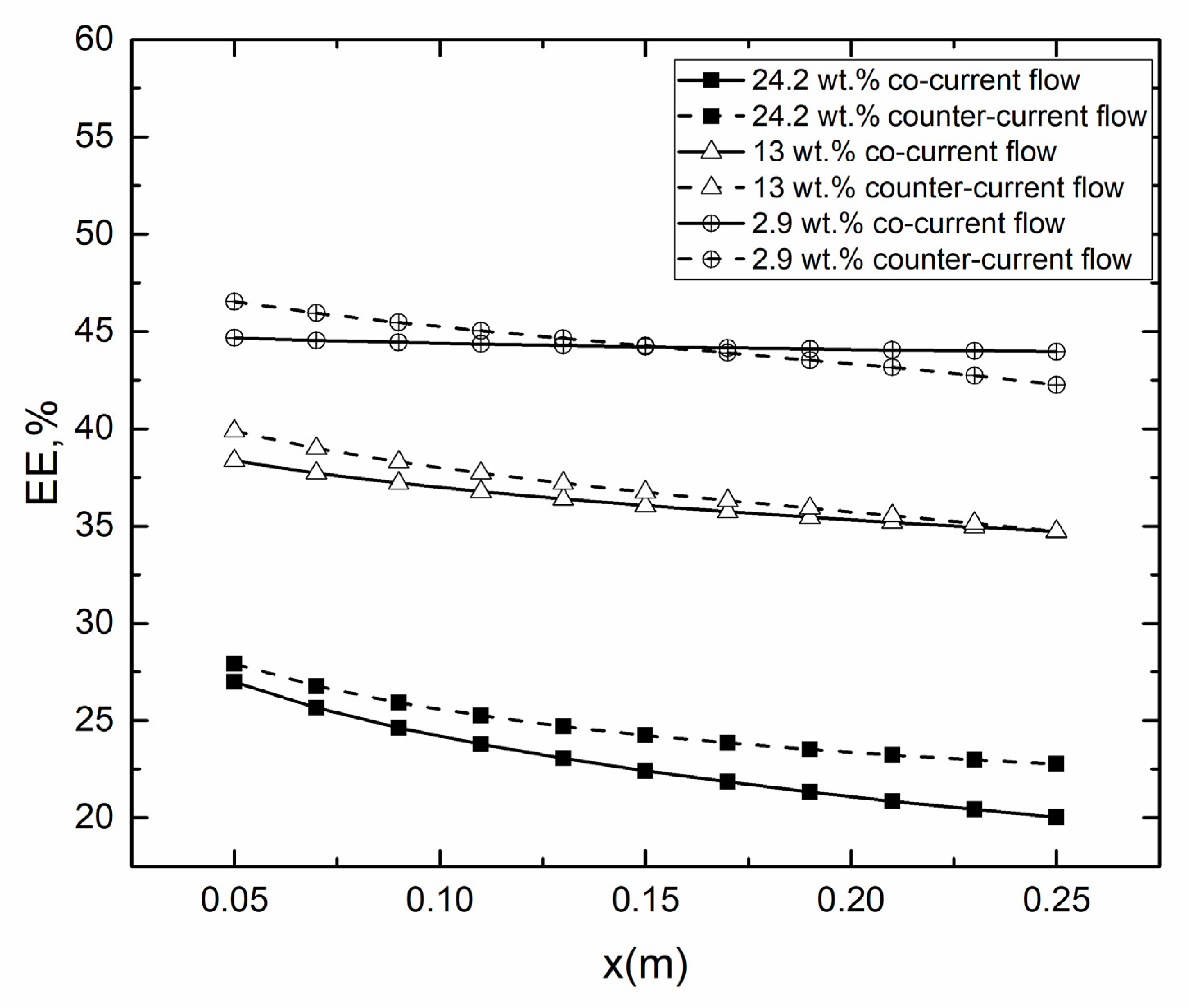
4.2. Co- and Counter-Current Operations
4.2.1. Temperature Fields
4.2.2. Evaporation Efficiency for Co- and Counter-Current Operations
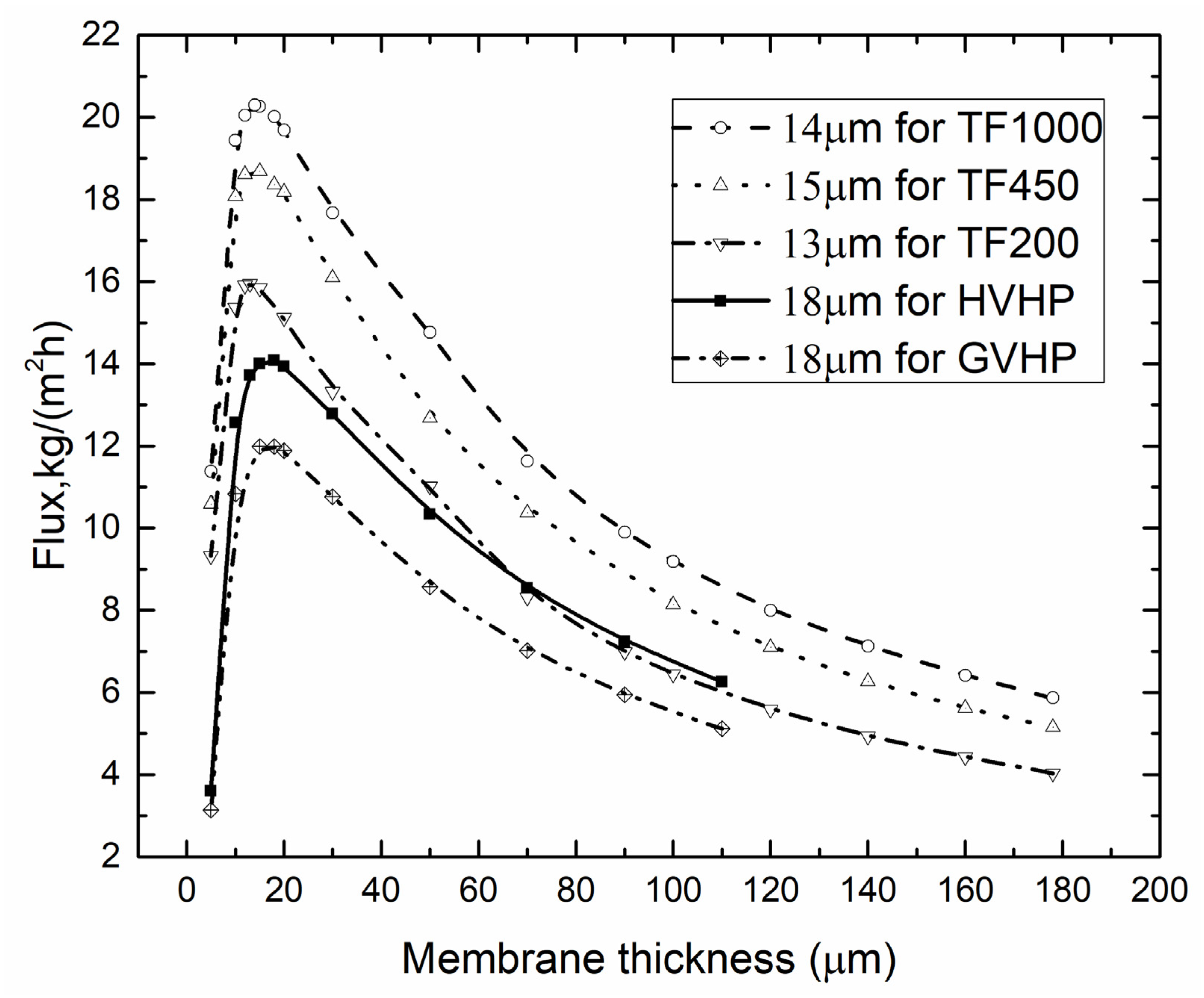
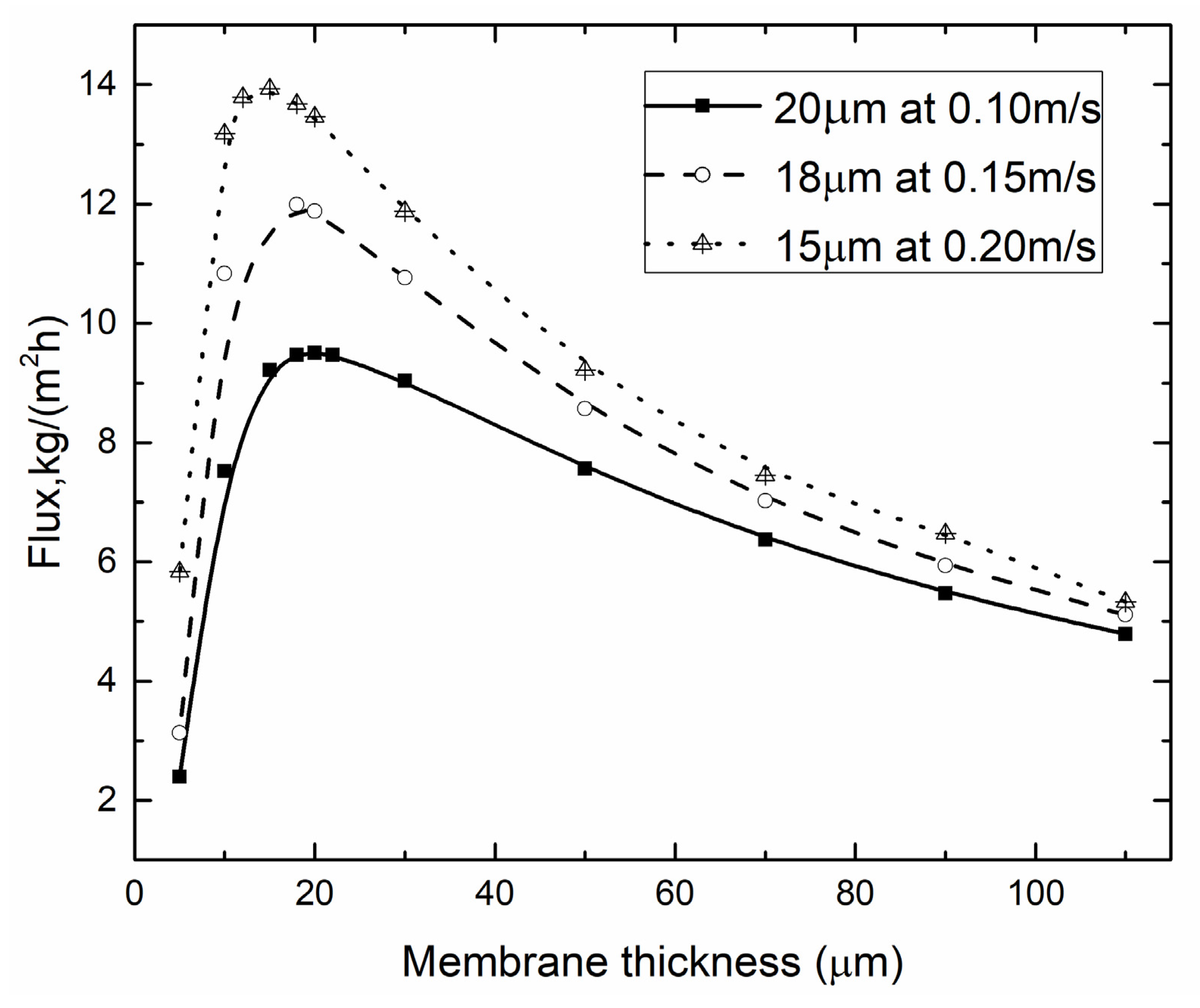
4.3. Optimal Membrane Thickness
4.3.1. Optimal Membrane Thickness for Different Tf
4.3.2. Optimal Membrane Thickness for Different vf, vp
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
| Nomenclature | |
| Q | Heat flux, W∙m−2 |
| h | Convective heat transfer coefficient, W∙m−2∙K−1 |
| T | Temperature, K |
| v | Velocity, m∙s−1 |
| dm | Hydraulic radius, m |
| ΔH | Latent heat of water, J∙kg−1 |
| N | Mass flow across membrane, kg∙m−2∙s−1 |
| k | Thermal conductivity, W∙m−1∙K−1 |
| km | Membrane thermal conductivity, W∙m−1∙K−1 |
| kg | Thermal conductivity of air, W∙m−1∙K−1 |
| ks | Thermal conductivity of membrane materials, W∙m−1∙K−1 |
| Dw-a | Diffusivity of water vapor-air mixture, m2∙s−2 |
| Dkn | Knudsen diffusion coefficient, m2∙s−1 |
| P | Vapor pressure, Pa |
| PT | Total pressure, Pa |
| R | Gas constant (8.314 J∙mol−1∙K−2) |
| xs | Molar fraction of solute |
| mw | Molecular weight of water |
| b | Height of first grid, m |
| Sw | Source, kg∙m−3∙s−1 |
| u | Velocity vector, m∙s−1 |
| p | Pressure, Pa |
| x,y | Cartesian coordinates, m |
| cp | Specific heat capacity, J∙kg−1∙K−1 |
| D | Mass diffusivity, m2∙s−1 |
| c | concentration, g∙L−1 |
| EE | Evaporation Efficiency, % |
| CPC | Concentration polarization coefficient, % |
| t | Time, s |
| Greek Symbols | |
| δ | Membrane thickness, m |
| ε | Membrane porosity |
| λ | Membrane tortuosity |
| γw | Activity coefficient of water |
| Density, kg∙m−3 | |
| Viscous stress tensor | |
| Dynamic viscosity, Pa∙s | |
| ϑNa | The equivalent limiting ionic conductance of the sodium |
| ϑCl | The equivalent limiting ionic conductance of the chloride |
| Subscripts | |
| f | The bulk of the feed |
| fm | Membrane surface of the feed |
| p | The bulk of the permeate |
| pm | Membrane surface of the permeate |
| m | Membrane |
| N | Flux |
| C | Conduction |
| Abbreviations | |
| DCMD | Direct contact membrane distillation |
| FGD | Flue gas desulfurization |
| MD | Membrane Distillation |
| CFD | Computational fluid dynamics |
| CPC | Concentration polarization coefficient |
| TPC | Temperature polarization coefficient |
| UDF | User-defined function |
| EE | Evaporation efficiency |
References
- Chen, M.; Zhu, L.; Dong, Y.; Li, L.; Liu, J. Engineering, Waste-to-resource strategy to fabricate highly porous whisker-structured mullite ceramic membrane for simulated oil-in-water emulsion wastewater treatment. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 2098–2106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Ma, L.; Tang, C.Y.; Yang, F.; Quan, X.; Jassby, D.; Zaworotko, M.J.; Guiver, M.D. Stable superhydrophobic ceramic-based carbon nanotube composite desalination membranes. Nano Lett. 2018, 18, 5514–5521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, J.; Dong, Y.; Dong, X.; Hampshire, S.; Zhu, L.; Zhu, Z.; Li, L. Feasible recycling of industrial waste coal fly ash for preparation of anorthite-cordierite based porous ceramic membrane supports with addition of dolomite. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2016, 36, 1059–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Chen, M.; Dong, Y.; Tang, C.Y.; Huang, A.; Li, L. A low-cost mullite-titania composite ceramic hollow fiber microfiltration membrane for highly efficient separation of oil-in-water emulsion. Water Res. 2016, 90, 277–285. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.; Zhu, L.; Chen, J.; Yang, F.; Tang, C.Y.; Guiver, M.D.; Dong, Y. Spinel-based ceramic membranes coupling solid sludge recycling with oily wastewater treatment. Water Res. 2020, 169, 115180. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, M.; Jin, W.; Yang, F.; Duke, M.C.; Dong, Y.; Tang, C.Y. Engineering Nano-Composite Interlayer for Novel Ceramic-based Forward Osmosis Membrane with Enhanced Performance. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 7715–7724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, Y.; Sun, C.; Li, D.; Yang, F.; Tang, C.Y.; Quan, X.; Dong, Y.; Guiver, M.D. Flexible Superhydrophobic Metal-based Carbon Nanotube Membrane for Electrochemically Enhanced Water Treatment. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 9074–9082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phattaranawik, J.; Jiraratananon, R.; Fane, A.G. Heat transport and membrane distillation coefficients in direct contact membrane distillation. J. Membr. Sci. 2003, 212, 177–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshmukh, A.; Boo, C.; Karanikola, V.; Lin, S.; Straub, A.P.; Tong, T.; Warsinger, D.M.; Elimelech, M. Membrane distillation at the water-energy nexus: Limits, opportunities, and challenges. Energy Environ. Sci. 2018, 11, 1177–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomaszewska, M. Direct Contact Membrane Distillation (DCMD) Applications. In Encyclopedia of Membranes; Drioli, E., Giorno, L., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Bouchrit, R.; Boubakri, A.; Hafiane, A.; Bouguecha, S.A.-T. Direct contact membrane distillation: Capability to treat hyper-saline solution. Desalination 2015, 376, 117–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christie, K.S.S.; Horseman, T.; Lin, S. Energy efficiency of membrane distillation: Simplified analysis, heat recovery, and the use of waste-heat. Environ. Int. 2020, 138, 105588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshmukh, A.; Elimelech, M. Understanding the impact of membrane properties and transport phenomena on the energetic performance of membrane distillation desalination. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 539, 458–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardikar, M.; Marquez, I.; Achilli, A. Emerging investigator series: Membrane distillation and high salinity: Analysis and implications. Environ. Sci. Water Res. Technol. 2020, 6, 1538–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, S.T.; Cheng, K.T.; Chiou, J.S. Seawater desalination by direct contact membrane distillation. Desalination 2002, 143, 279–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schofield, R.W.; Fane, A.G.; Fell, C.J.D.; Macoun, R. Factors affecting flux in membrane distillation. Desalination 1990, 77, 279–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khayet, M.; Velázquez, A.; Mengual, J.I. Direct contact membrane distillation of humic acid solutions. J. Membr. Sci. 2004, 240, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, Y.; Ma, R.; Zhang, W.; Fane, A.G.; Li, J. Direct contact membrane distillation mechanism for high concentration NaCl solutions. Desalination 2006, 188, 251–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakaib, M.; Hasani, S.M.F.; Ahmed, I.; Yunus, R.M. A CFD study on the effect of spacer orientation on temperature polarization in membrane distillation modules. Desalination 2012, 284, 332–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayer, H.; Bakhtiari, O.; Mohammadi, T. Simulation of momentum, heat and mass transfer in direct contact membrane distillation: A computational fluid dynamics approach. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2015, 21, 1379–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, H.; Hsu, J.-A.; Chang, C.-L.; Ho, C.-D.; Cheng, T.-W. Simulation study of transfer characteristics for spacer-filled membrane distillation desalination modules. Appl. Energy 2017, 185, 2045–2057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, J.; Vanneste, J.; Decaluwe, S.C.; Cath, T.Y.; Tilton, N. Computational fluid dynamics simulations of polarization phenomena in Direct Contact Membrane Distillation. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 591, 117150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hitsov, I.; Maere, T.; De Sitter, K.; Dotremont, C.; Nopens, I. Modelling approaches in membrane distillation: A critical review. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2015, 142, 48–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Sharif, S.; Albeirutty, M.; Cipollina, A.; Micale, G. Modelling flow and heat transfer in spacer-filled membrane distillation channels using open source CFD code. Desalination 2013, 311, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, M.; Dutta, S.K.; Sikder, J.; Mandal, M.K. Computational and experimental study of chromium (VI) removal in direct contact membrane distillation. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 450, 447–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janajreh, I.; Suwwan, D.; Hashaikeh, R. Assessment of direct contact membrane distillation under different configurations, velocities and membrane properties. Appl. Energy 2017, 185, 2058–2073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponzio, F.N.; Tamburini, A.; Cipollina, A.; Micale, G.; Ciofalo, M. Experimental and computational investigation of heat transfer in channels filled by woven spacers. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2017, 104, 163–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Taamneh, Y.; Bataineh, K. Improving the performance of direct contact membrane distillation utilizing spacer-filled channel. Desalination 2017, 408, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Yang, X.; Wang, R.; Fane, A.G. Numerical simulation of heat and mass transfer in direct membrane distillation in a hollow fiber module with laminar flow. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 384, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Yu, H.; Wang, R.; Fane, A.G. Analysis of the effect of turbulence promoters in hollow fiber membrane distillation modules by computational fluid dynamic (CFD) simulations. J. Membr. Sci. 2012, 415–416, 758–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yazgan-Birgi, P.; Hassan Ali, M.I.; Arafat, H.A. Comparative performance assessment of flat sheet and hollow fiber DCMD processes using CFD modeling. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 212, 709–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabassud, C.; Wirth, D. Membrane distillation for water desalination: How to chose an appropriate membrane? Desalination 2003, 157, 307–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drioli, E.; Ali, A.; Macedonio, F. Membrane distillation: Recent developments and perspectives. Desalination 2015, 356, 56–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawson, K.W.; Hall, M.S.; Lloyd, D.R. Compaction of microporous membranes used in membrane distillation. I. Effect on gas permeability. J. Membr. Sci. 1995, 101, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eykens, L.; Hitsov, I.; De Sitter, K.; Dotremont, C.; Pinoy, L.; Nopens, I.; Van der Bruggen, B. Influence of membrane thickness and process conditions on direct contact membrane distillation at different salinities. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 498, 353–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaulsky, E.; Karanikola, V.; Straub, A.P.; Deshmukh, A.; Zucker, I.; Elimelech, M. Asymmetric membranes for membrane distillation and thermo-osmotic energy conversion. Desalination 2019, 452, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martınez-Dıez, L.; Vázquez-González, M.I. Temperature and concentration polarization in membrane distillation of aqueous salt solutions. J. Membr. Sci. 1999, 156, 265–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phattaranawik, J.; Jiraratananon, R.; Fane, A.G. Effect of pore size distribution and air flux on mass transport in direct contact membrane distillation. J. Membr. Sci. 2003, 215, 75–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, S.S.; Alsalhy, Q.F. Modeling and simulation for direct contact membrane distillation in hollow fiber modules. Aiche J. 2013, 59, 589–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schofield, R.W.; Fane, A.G.; Fell, C.J.D. Gas and vapour transport through microporous membranes. I. Knudsen-Poiseuille transition. J. Membr. Sci. 1990, 53, 159–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuangchen, M.; Jin, C.; Gongda, C.; Weijing, Y.; Sijie, Z. Research on desulfurization wastewater evaporation: Present and future perspectives. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 58, 1143–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.; Macedonio, F.; Drioli, E.; Aljlil, S.; Alharbi, O.A. Experimental and theoretical evaluation of temperature polarization phenomenon in direct contact membrane distillation. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2013, 91, 1966–1977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, H.J.; He, K.; Gray, S.; Zhang, J.; Moon, I.S. Direct contact membrane distillation (DCMD): Experimental study on the commercial PTFE membrane and modeling. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 371, 90–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Swaminathan, J.; Chung, H.W.; Warsinger, D.M.; Lienhard, V.J.H. Energy efficiency of membrane distillation up to high salinity: Evaluating critical system size and optimal membrane thickness. Appl. Energy 2018, 211, 715–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.Y.; Wang, R.; Field, R.W. Direct contact membrane distillation: An experimental and analytical investigation of the effect of membrane thickness upon transmembrane flux. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 470, 257–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, L.; Rodríguez-Maroto, J.M. Membrane thickness reduction effects on direct contact membrane distillation performance. J. Membr. Sci. 2008, 312, 143–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Membrane Type | Producer | Material | dp (μm) | δ (μm) | km (W∙m−1∙K−1) | ε | λ | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GVHP | Millipore | PVDF | 0.22 | 120 | 0.041 | 0.75 | 2 | [18] |
| HVHP | Millipore | PVDF | 0.45 | 110 | 0.041 | 0.75 | 2 | [18] |
| TF200 | Gelman | PTFE | 0.20 | 178 | 0.031 | 0.80 | 1.8 | [33] |
| TF450 | Gelman | PTFE | 0.45 | 178 | 0.031 | 0.80 | 1.8 | [33] |
| TF1000 | Gelman | PTFE | 1.00 | 178 | 0.031 | 0.80 | 1.8 | [33] |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ni, W.; Li, Y.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, G.; Du, X.; Dong, Y. Simulation Study on Direct Contact Membrane Distillation Modules for High-Concentration NaCl Solution. Membranes 2020, 10, 179. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes10080179
Ni W, Li Y, Zhao J, Zhang G, Du X, Dong Y. Simulation Study on Direct Contact Membrane Distillation Modules for High-Concentration NaCl Solution. Membranes. 2020; 10(8):179. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes10080179
Chicago/Turabian StyleNi, Weiming, Yongli Li, Juezhen Zhao, Gaoyuan Zhang, Xiaoze Du, and Yingchao Dong. 2020. "Simulation Study on Direct Contact Membrane Distillation Modules for High-Concentration NaCl Solution" Membranes 10, no. 8: 179. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes10080179
APA StyleNi, W., Li, Y., Zhao, J., Zhang, G., Du, X., & Dong, Y. (2020). Simulation Study on Direct Contact Membrane Distillation Modules for High-Concentration NaCl Solution. Membranes, 10(8), 179. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes10080179