Synthesis and Characterization of Novel Integral Asymmetric Monophasic Cellulose–Acetate/Silica/Titania and Cellulose–Acetate/Titania Membranes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
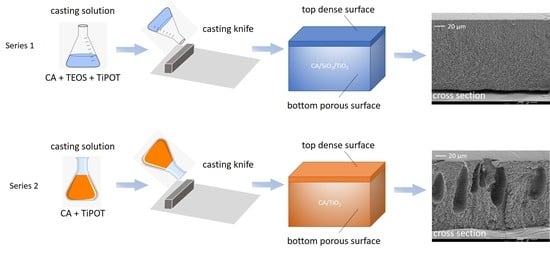
2.2. Membrane Synthesis
2.2.1. Series 1: CA/SiO2/TiO2 Membranes
2.2.2. Series 2: CA/TiO2 Membranes
2.3. Membrane Drying
2.4. Membrane Characterization
2.4.1. FEG-SEM: Surface Morphology and Cross-Section Structure
2.4.2. ICP-OES: Quantification of Titanium
2.4.3. ICP-OES: Quantification of Leached Titanium
2.4.4. ATR-FTIR: Chemical Bonding
2.5. Permeation Properties
2.5.1. Hydraulic Permeability
2.5.2. Molecular Weight Cut-Off
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Membrane Structure and Surface Morphology
3.2. Titanium Quantification
3.2.1. Titanium Incorporated in the Membranes
3.2.2. Titanium Leached from the Membranes
3.3. Chemical Composition and Hybrid Bonding
3.3.1. Series 1 Membranes
3.3.2. Series 2 Membranes
3.4. Permeation Properties
Hydraulic Permeability and MWCO
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
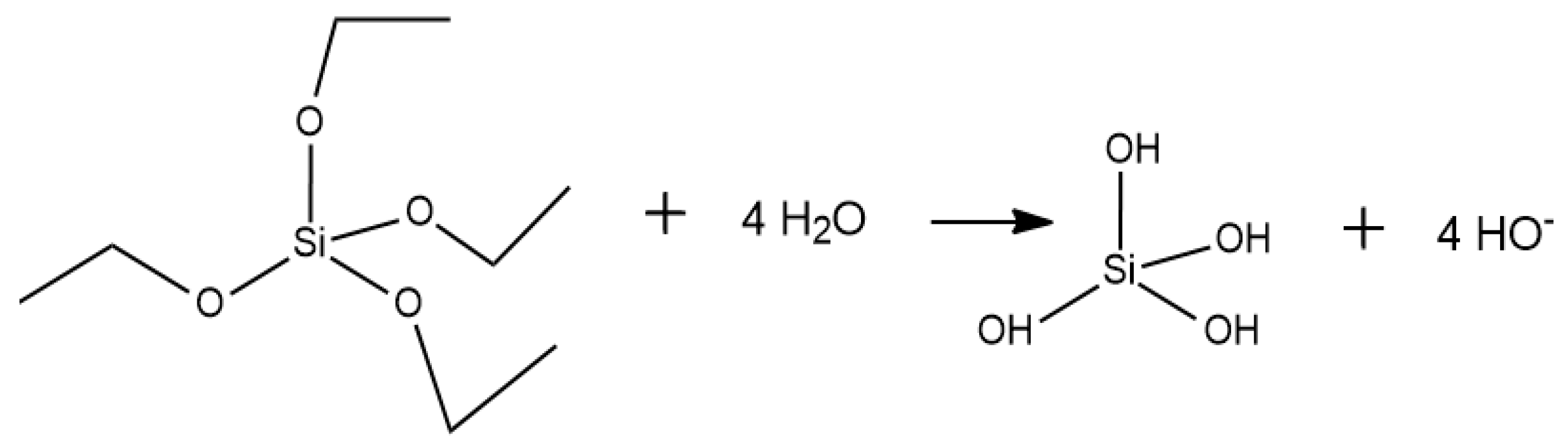
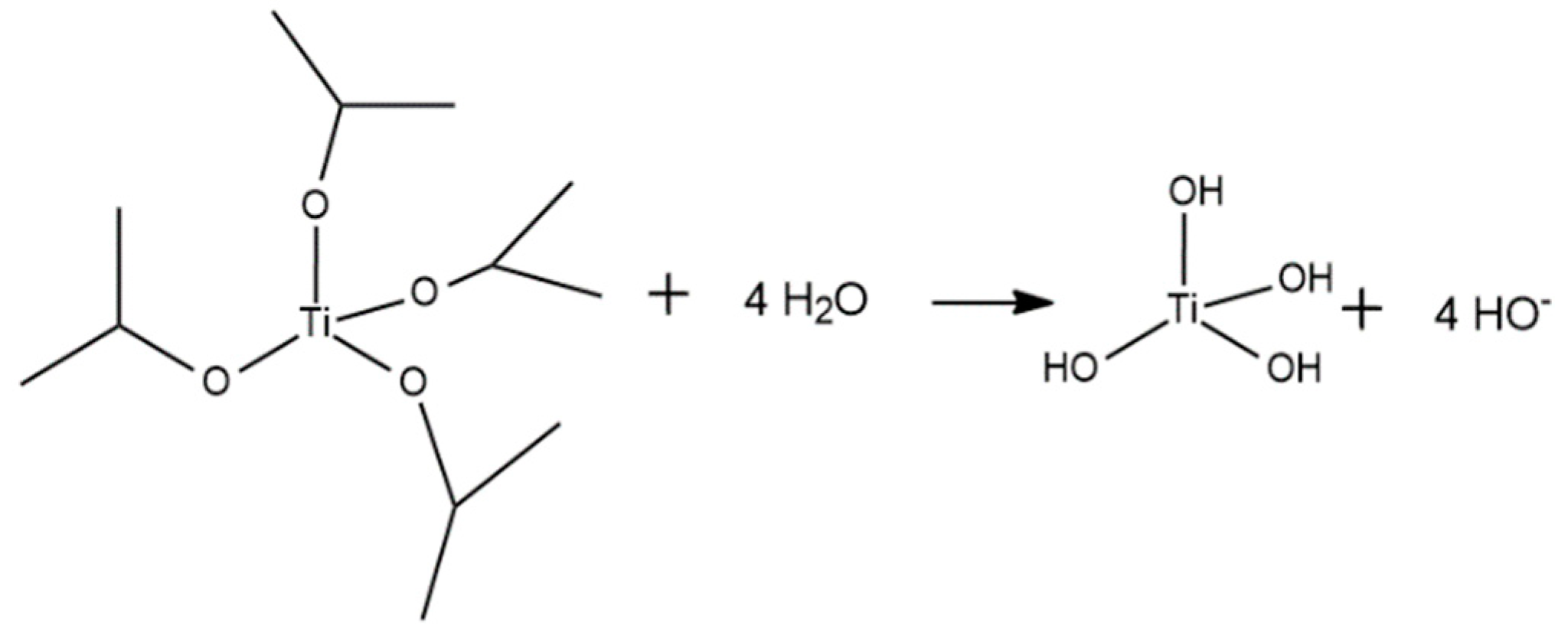
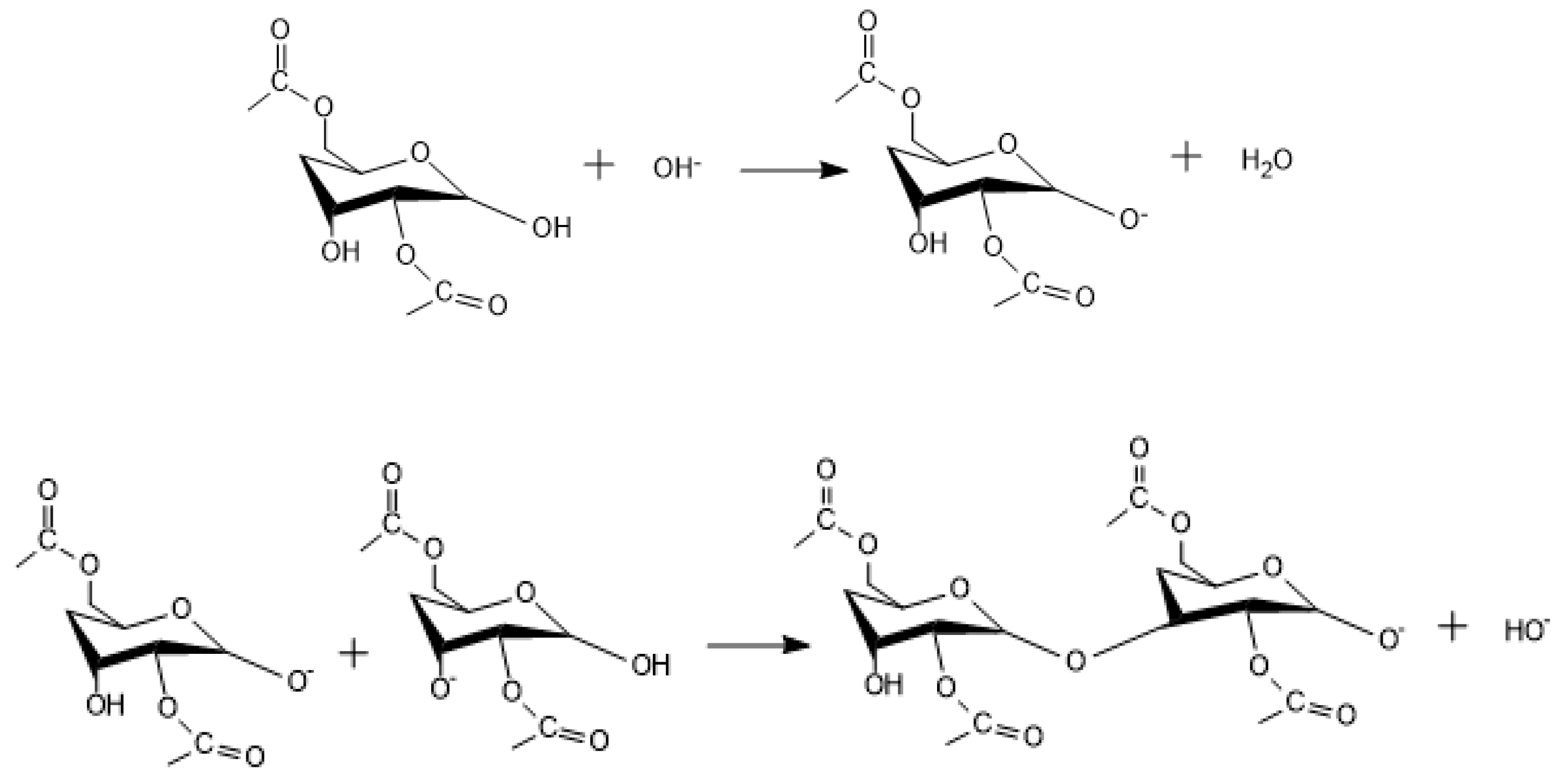
Appendix A. Acid Catalyzed Sol-Gel Hydrolysis and Condensation Reactions


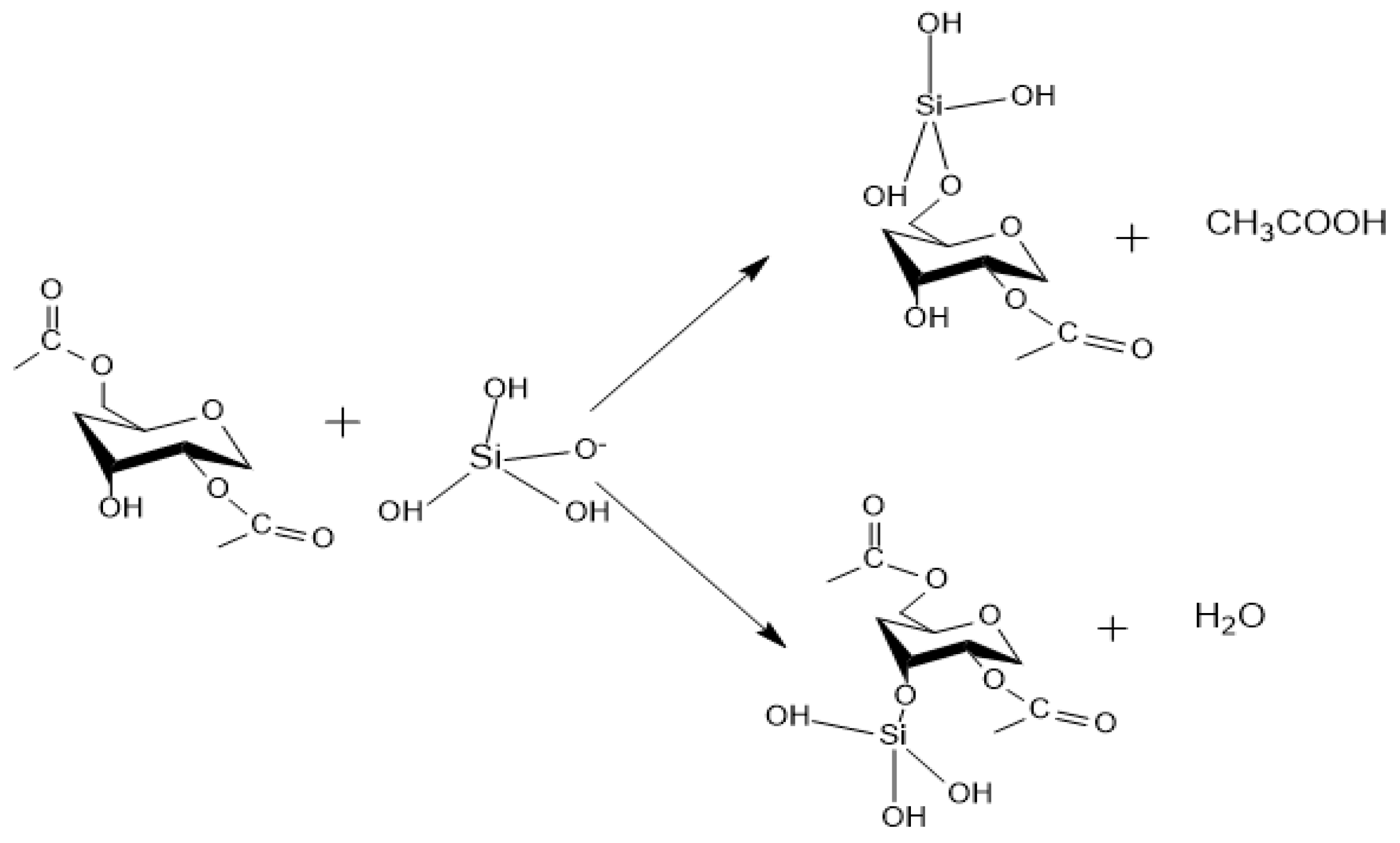
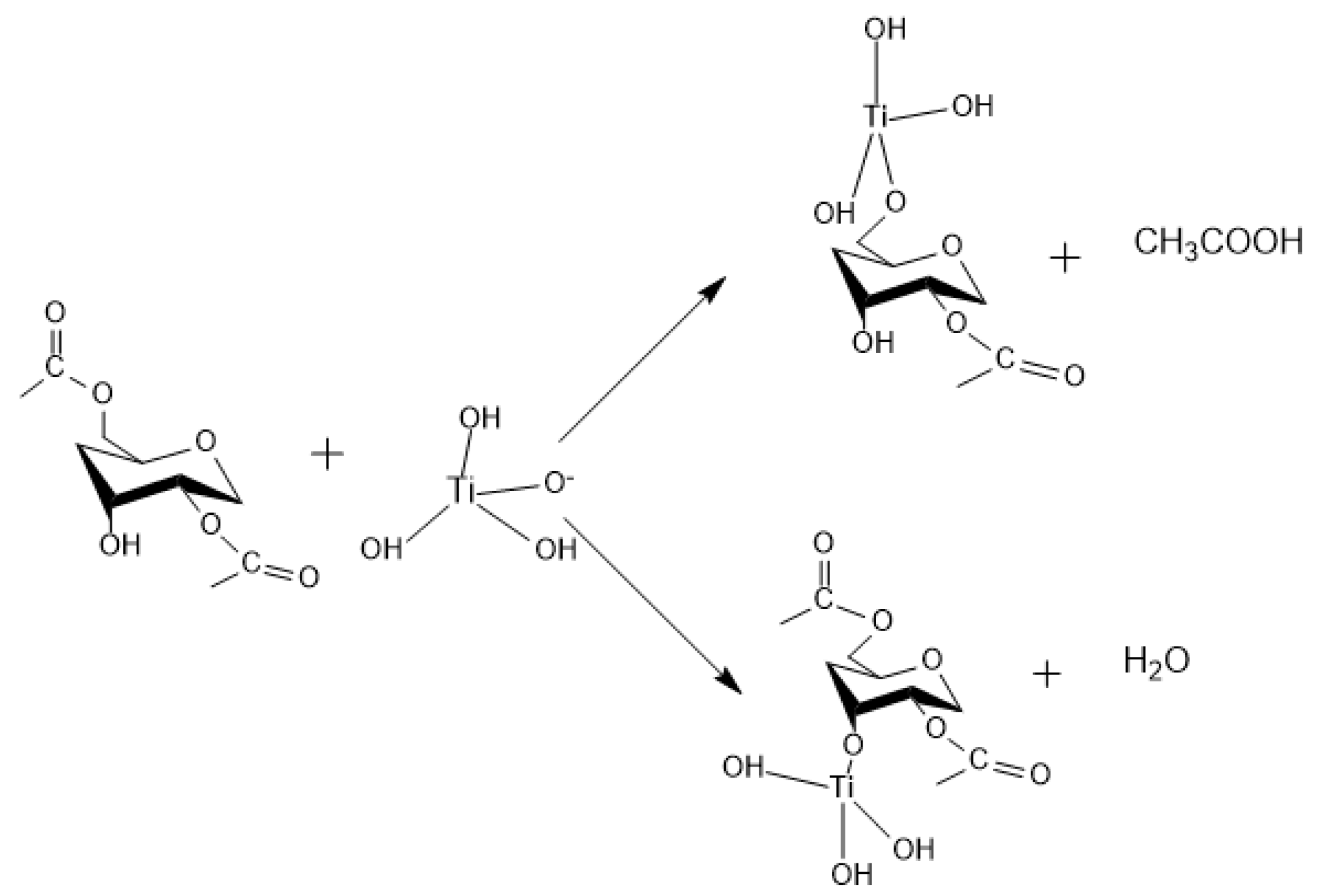
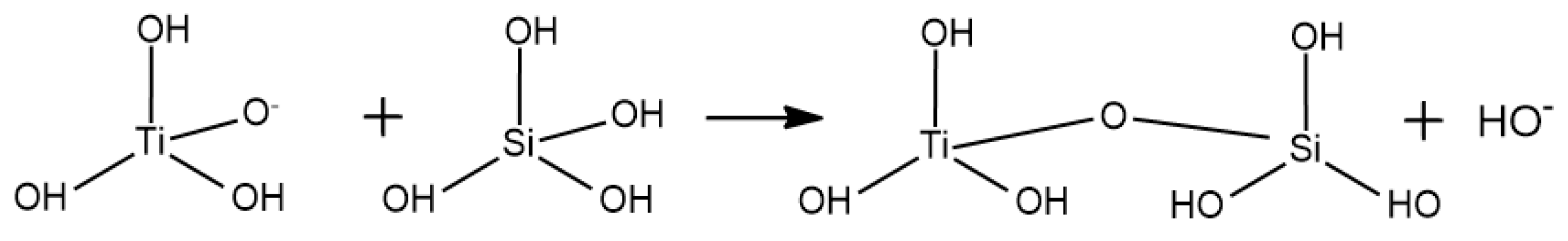

Appendix B
| Calculation base: 100 g casting solution |
| M (TEOS) = 208.33 gmol−1 M(SiO2) = 60.0843 gmol−1 |
| M(TiPOT) = 284.22 gmol−1 M(TiO2) = 79.8658 gmol−1 |
| ACRONYM | Casting Solution Composition (wt%) | |||||
| CA/SiO2/TiO2 | TEOS | SiO2 | TiPOT | TiO2 | CA | (CA + SiO2 + TiO2) |
| 95/5/0 | 3 | 0.865228 | 0 | 0 | 16.4 | 17.26523 |
| 95/4.5/0.5 | 2.7 | 0.778705 | 0.32 | 0.08992 | 16.4 | 17.26863 |
| 95/4/1 | 2.4 | 0.692182 | 0.64 | 0.17984 | 16.4 | 17.27202 |
| 95/3/2 | 2.1 | 0.605659 | 0.96 | 0.269761 | 16.4 | 17.27542 |
| 95/2/3 | 0.93 | 0.268221 | 2.07 | 0.581671 | 16.4 | 17.24989 |
| ACRONYM | Casting Solution Composition (wt%) | |||||
| CA/TiO2 | TiPOT | TiO2 | CA | (CA + TiO2) | ||
| 100 | 0 | 0 | 17 | 17 | ||
| 99.5/0.5 | 0.32 | 0.08992 | 16.4 | 16.48992 | ||
| 98/2 | 0.96 | 0.269761 | 16.4 | 16.66976 | ||
| 97/3 | 2.07 | 0.581671 | 16.4 | 16.98167 | ||
| 95/5 | 3 | 0.843002 | 16.4 | 17.243 | ||
Appendix C
| Stage | Solution | Time (h) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | H2Od | 24 |
| 2 | Aqueous solution of Isopropanol (25% V/V) | |
| 3 | Aqueous solution of Isopropanol (50% V/V) | |
| 4 | Aqueous solution of Isopropanol (75% V/V) | |
| 5 | Solution of Isopropanol (100% V/V) | |
| 6 | Solution of Isopropanol (75% V/V) + n–Hexane (25% V/V) | |
| 7 | Solution of Isopropanol (50% V/V) + n–Hexane (50% V/V) | |
| 8 | Solution of Isopropanol (25% V/V) + n–Hexane (75% V/V) | |
| 9 | Solution of n–Hexane (100% V/V) | |
| 10 | Desiccator |
Appendix D. Estimation of the Dense Layer Thickness from FEG-SEM cross Section Images and ImageJ Software
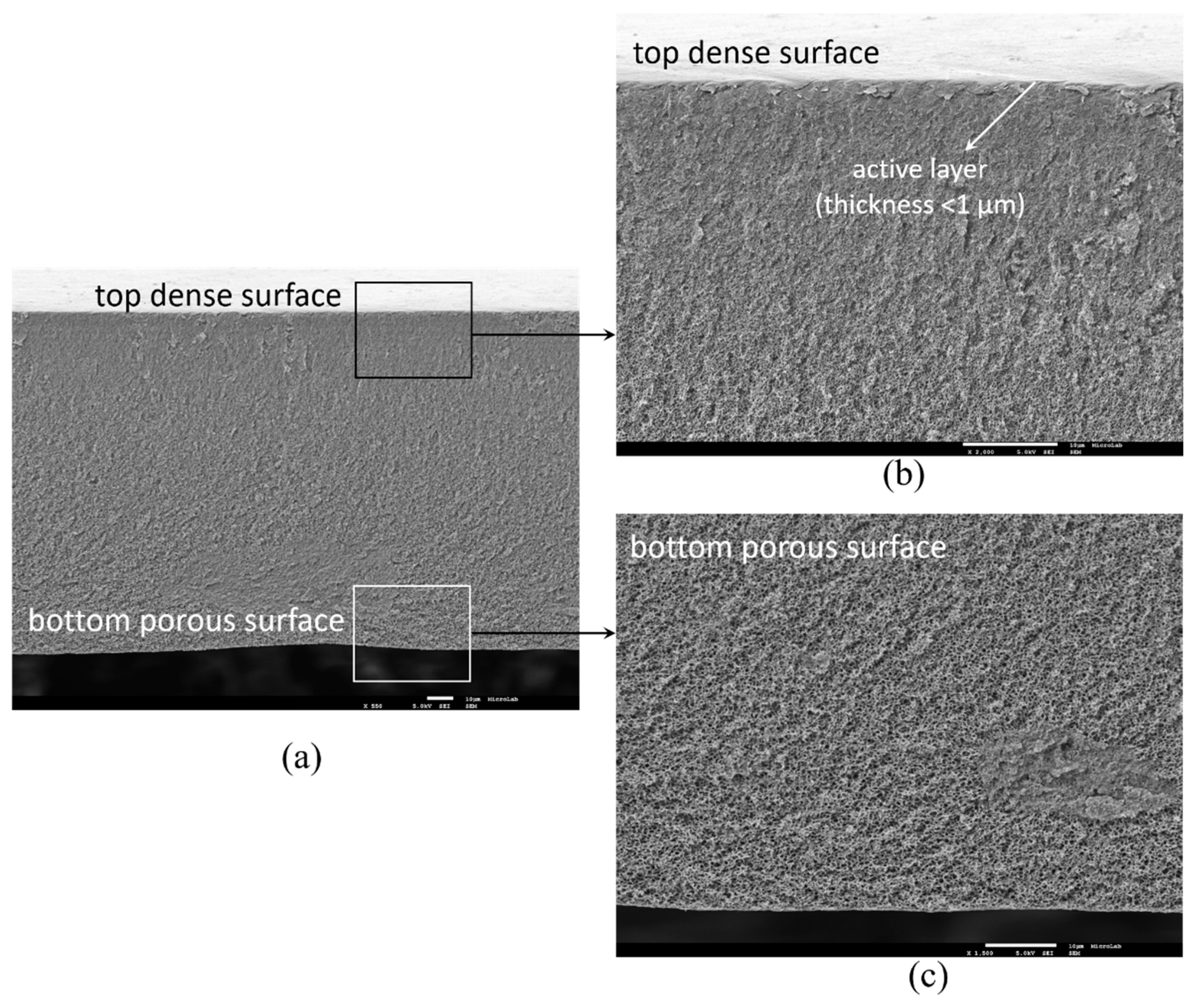
Appendix E. Titanium Leached from the Membranes
| Series 1 | H2Od Sample | [Ti] (mg/L) |
| CA/SiO2/TiO2 (95/2/3) | Initial | <0.010 ± 0.000 |
| Final permeate | <0.010 ± 0.000 | |
| Final concentrate | <0.010 ± 0.000 | |
| Series 2 | H2Od Sample | [Ti] (mg/L) |
| CA/TiO2 (95/5) | Initial | <0.010 ± 0.000 |
| Final permeate | <0.010 ± 0.000 | |
| Final concentrate | <0.010 ± 0.000 |
References
- Qiu, X.; Hu, S. “Smart” Materials Based on Cellulose: A Review of the Preparations, Properties, and Applications. Mater. Basel Switz. 2013, 6, 738–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puls, J.; Wilson, S.A.; Hölter, D. Degradation of Cellulose Acetate-Based Materials: A Review. J. Polym. Environ. 2011, 19, 152–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitrijevich, S.D.; Tatarko, M.; Gracy, R.W.; Wise, G.E.; Oakford, L.X.; Linsky, C.B.; Kamp, L. In vivo degradation of oxidized, regenerated cellulose. Carbohydr. Res. 1990, 198, 331–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokunaga, Y.; Kojima, T.; Naruse, T. Antitumor effect of oxycellulose as a hemostatic during operation. Cancer Biother. Radiopharm. 1998, 13, 437–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Credou, J.; Berthelot, T. Cellulose: From biocompatible to bioactive material. J. Mater. Chem. B 2014, 2, 4767–4788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cellulose Acetate: Properties, Uses and Preparation; Nova Science Publishers, Inc.: Hauppauge, NY, USA, 2018.
- Beisl, S.; Monteiro, S.; Santos, R.; Figueiredo, A.S.; Sánchez-Loredo, M.G.; Lemos, M.A.; Lemos, F.; Minhalma, M.; de Pinho, M.N. Synthesis and bactericide activity of nanofiltration composite membranes—Cellulose acetate/silver nanoparticles and cellulose acetate/silver ion exchanged zeolites. Water Res. 2019, 149, 225–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Yuan, Q. Gas permeability of a novel cellulose membrane. J. Membr. Sci. 2002, 204, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faria, M.; Moreira, C.; Eusébio, T.; Brogueira, P.; de Pinho, M.N. Hybrid flat sheet cellulose acetate/silicon dioxide ultrafiltration membranes for uremic blood purification. Cellulose 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, M.; Hosoya, N.; Saruhashi, M. Vitamin E modified cellulose membrane. Artif. Organs 2000, 24, 779–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, J.-J.; Li, Y.; Lee, L.-S.; Lee, H. Cellulose acetate hollow fiber ultrafiltration membranes made from CA/PVP 360 K/NMP/water. J. Membr. Sci. 2003, 218, 173–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.; Yang, Q.; Teo, J.F.; Chung, T.-S. Cellulose acetate nanofiltration hollow fiber membranes for forward osmosis processes. J. Membr. Sci. 2010, 355, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinnau, I.; Freeman, B.D. Chapter I Formation and Modification of Polymeric Membranes: Overview. Am. Chem. Soc. 1999, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabsch-Korbutowicz, M.; Majewska-Nowak, K.; Winnicki, T. Analysis of membrane fouling in the treatment of water solutions containing humic acids and mineral salts. Desalination 1999, 126, 179–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orooji, Y.; Faghih, M.; Razmjou, A.; Hou, J.; Moazzam, P.; Emami, N.; Aghababaie, M.; Nourisfa, F.; Chen, V.; Jin, W. Nanostructured mesoporous carbon polyethersulfone composite ultrafiltration membrane with significantly low protein adsorption and bacterial adhesion. Carbon 2017, 111, 689–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Uliana, A.; Zhu, J.; Liu, J.; Van der Bruggen, B. Zeolitic Imidazolate Framework/Graphene Oxide Hybrid Nanosheets Functionalized Thin Film Nanocomposite Membrane for Enhanced Antimicrobial Performance. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 25508–25519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duval, J.-M.; Kemperman, A.J.B.; Folkers, B.; Mulder, M.H.V.; Desgrandchamps, G.; Smolders, C.A. Preparation of zeolite filled glassy polymer membranes. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1994, 54, 409–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwang-Il, L.; Il-Wun, S.; Sun-Tak, H. The effects of transition metal complexes on the permeation of small gas molecules through cellulose acetate membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 1991, 60, 207–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonawane, S.H.; Terrien, A.; Figueiredo, A.S.; Clara Gonçalves, M.; De Pinho, M.N. The role of silver nanoparticles on mixed matrix Ag/cellulose acetate asymmetric membranes. Polym. Compos. 2017, 38, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polyakova, A. Covalent and non-covalently coupled polyester-inorganic composite materials. Polymer 2002, 43, 6101–6114. [Google Scholar]
- Dasgupta, J.; Chakraborty, S.; Sikder, J.; Kumar, R.; Pal, D.; Curcio, S.; Drioli, E. The effects of thermally stable titanium silicon oxide nanoparticles on structure and performance of cellulose acetate ultrafiltration membranes. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2014, 133, 55–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina, A.; Faria, M.; Delgado, G.J.L.; de Pinho, M.N.; Sánchez Loredo, M.G. Synthesis of Calcium Fluoride Ultrafine Particles for the Preparation of Integral Asymmetric Cellulose Acetate/Calcium Fluoride Membranes. J. Membr. Sci. Res. 2020, 6, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghadassi, A.R.; Rajabi, Z.; Hosseini, S.M.; Mohammadi, M. Fabrication and modification of cellulose acetate based mixed matrix membrane: Gas separation and physical properties. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2014, 20, 1050–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendes, G.; Faria, M.; Carvalho, A.; Gonçalves, M.C.; de Pinho, M.N. Structure of water in hybrid cellulose acetate-silica ultrafiltration membranes and permeation properties. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 189, 342–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matos, J.C.; Oliveira, C.; Gonçalves, M.C. Daylight Bactericidal Titania Textiles: A Contribution to Nosocomial Infections Control. Mol. Basel Switz. 2019, 24, 1891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, M.C.; Pereira, J.C.; Matos, J.C.; Vasconcelos, H.C. Photonic Band Gap and Bactericide Performance of Amorphous Sol-Gel Titania: An Alternative to Crystalline TiO2. Molecules 2018, 23, 1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fagan, R.; McCormack, D.E.; Dionysiou, D.D.; Pillai, S.C. A review of solar and visible light active TiO2 photocatalysis for treating bacteria, cyanotoxins and contaminants of emerging concern. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2016, 42, 2–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunst, B.; Sourirajan, S. An approach to the development of cellulose acetate ultrafiltration membranes. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1974, 18, 3423–3434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brinker, J.; Scherer, G. Sol-Gel Science: The Physics and Chemistry of Sol-Gel Processing Presents the Physical and Chemical Principles of the Sol-Gel Process; Gulf Professional Publishing: Houston, TX, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Lui, A.; Talbot, F.D.F.; Matsuura, T.; Sourirajan, S. Studies on the solvent exchange technique for making dry cellulose acetate membranes for the separation of gaseous mixtures. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1988, 36, 1809–1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kline, S.J.; Mcclintock, F.A. Describing uncertainties in single-sample experiments. Mech. Eng. 1953, 75, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, J.R. An introduction to Error Analysis; University Science Books: Sausalito, CA, USA, 1982; Volume 45–60, ISBN 9788578110796. [Google Scholar]
- Baird, D.C. An Introduction to Measurement Theory and Experiment Design; Prentice Hall: Skokie, IL, USA, 1988; ISBN 0133032981. [Google Scholar]
- Jensen, H.; Soloviev, A.; Li, Z.; Søgaard, E.G. XPS and FTIR investigation of the surface properties of different prepared titania nano-powders. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2005, 246, 239–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, M.T.; Singhal, A.; Look, J.L.; Smith-Kristensen, J.R.; Lin, J.S.; Toth, L.M. FTIR Spectroscopy, SAXS and Electrical Conductivity Studies of the Hydrolysis and Condensation of Zirconium and Titanium Alkoxides. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 1997, 8, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velasco, M.J.; Rubio, F.; Rubio, J.; Oteo, J.L. Hydrolysis of Titanium Tetrabutoxide. Study by FT-IR Spectroscopy. Spectrosc. Lett. 1999, 32, 289–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lui, G.; Liao, J.-Y.; Duan, A.; Zhang, Z.; Fowler, M.; Yu, A. Graphene-wrapped hierarchical TiO2 nanoflower composites with enhanced photocatalytic performance. J. Mater. Chem. A 2013, 1, 12255–12262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smolders, C.A.; Reuvers, A.J.; Boom, R.M.; Wienk, I.M. Microstructures in phase-inversion membranes. Part 1. Formation of macrovoids. J. Membr. Sci. 1992, 73, 259–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, D.; de Pinho, M.N. An ATR-FTIR study of water in cellulose acetate membranes prepared by phase inversion. J. Membr. Sci. 1995, 106, 245–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, A.; Waheed, S.; Khan, S.M.; e-Gul, S.; Shafiq, M.; Farooq, M.; Sanaullah, K.; Jamil, T. Effect of silica on the properties of cellulose acetate/polyethylene glycol membranes for reverse osmosis. Desalination 2015, 355, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minhas, F.T.; Farrukh, S.; Hussain, A.; Mujahid, M. Comparison of silica and novel functionalized silica-based cellulose acetate hybrid membranes in gas permeation study. J. Polym. Res. 2015, 22, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naghsh, M.; Sadeghi, M.; Moheb, A.; Chenar, M.P.; Mohagheghian, M. Separation of ethylene/ethane and propylene/propane by cellulose acetate–silica nanocomposite membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2012, 423, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikonenko, N.A.; Buslov, D.K.; Sushko, N.I.; Zhbankov, R.G. Investigation of stretching vibrations of glycosidic linkages in disaccharides and polysaccharides with use of IR spectra deconvolution. Biopolymers 2000, 57, 257–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wojciechowska, P.; Foltynowicz, Z.; Nowicki, M. Cellulose acetate butyrate nanocomposites synthesized via sol-gel method. Polimery 2013, 58, 543–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wojciechowska, P.; Foltynowicz, Z.; Nowicki, M. Synthesis and Characterization of Modified Cellulose Acetate Propionate Nanocomposites via Sol-Gel Process. J. Spectrosc. 2013, 2013, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Oweini, R.; El-Rassy, H. Synthesis and characterization by FTIR spectroscopy of silica aerogels prepared using several Si(OR)4 and R″Si(OR′)3 precursors. J. Mol. Struct. 2009, 919, 140–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Z.F.; Jiang, Y.; Field, R.W. Fundamentals of Pressure-Driven Membrane Separation Processes, 1st ed.; Elsevier Ltd.: Oxford, UK, 2010; ISBN 9781856176323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
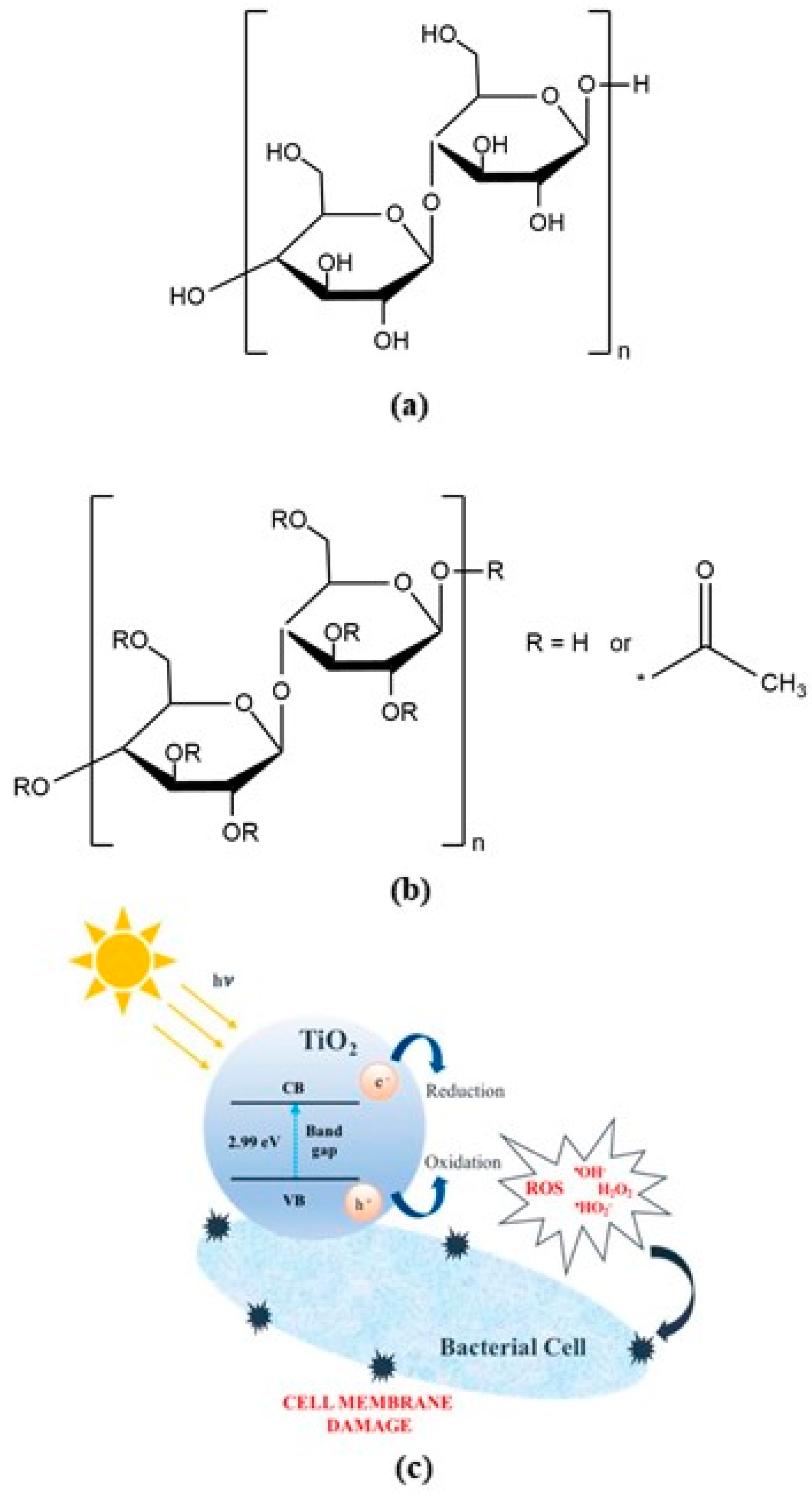


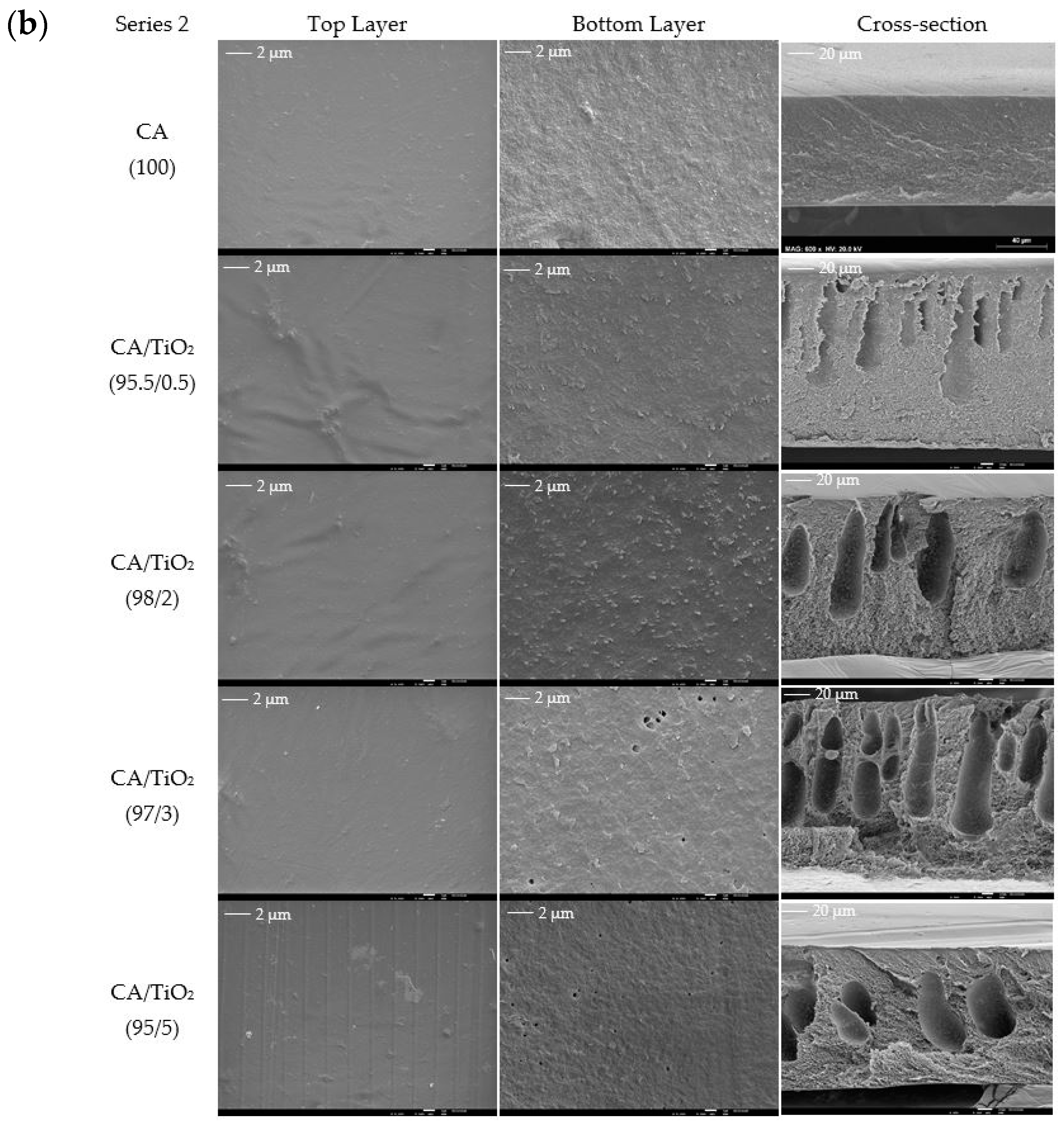

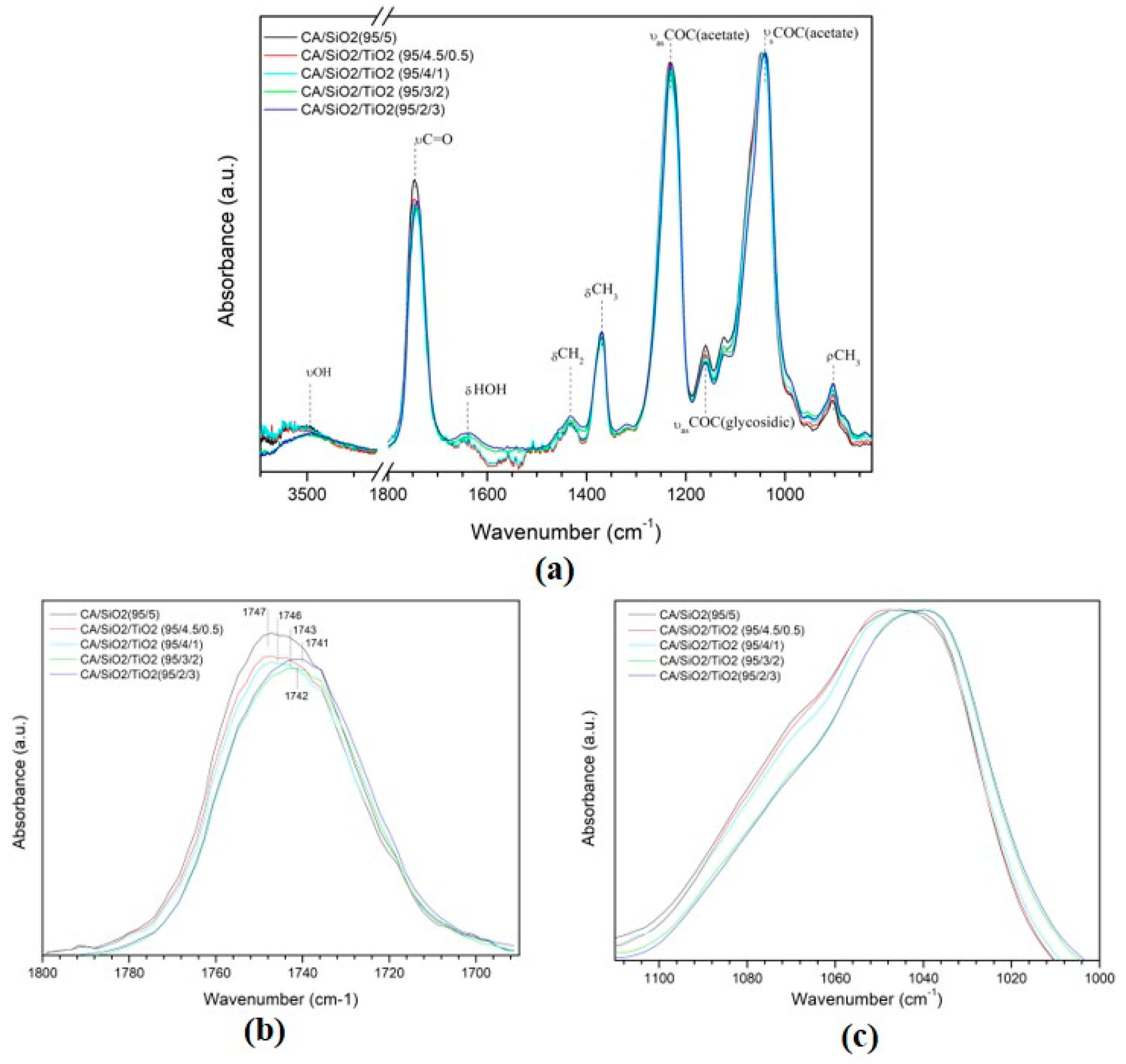


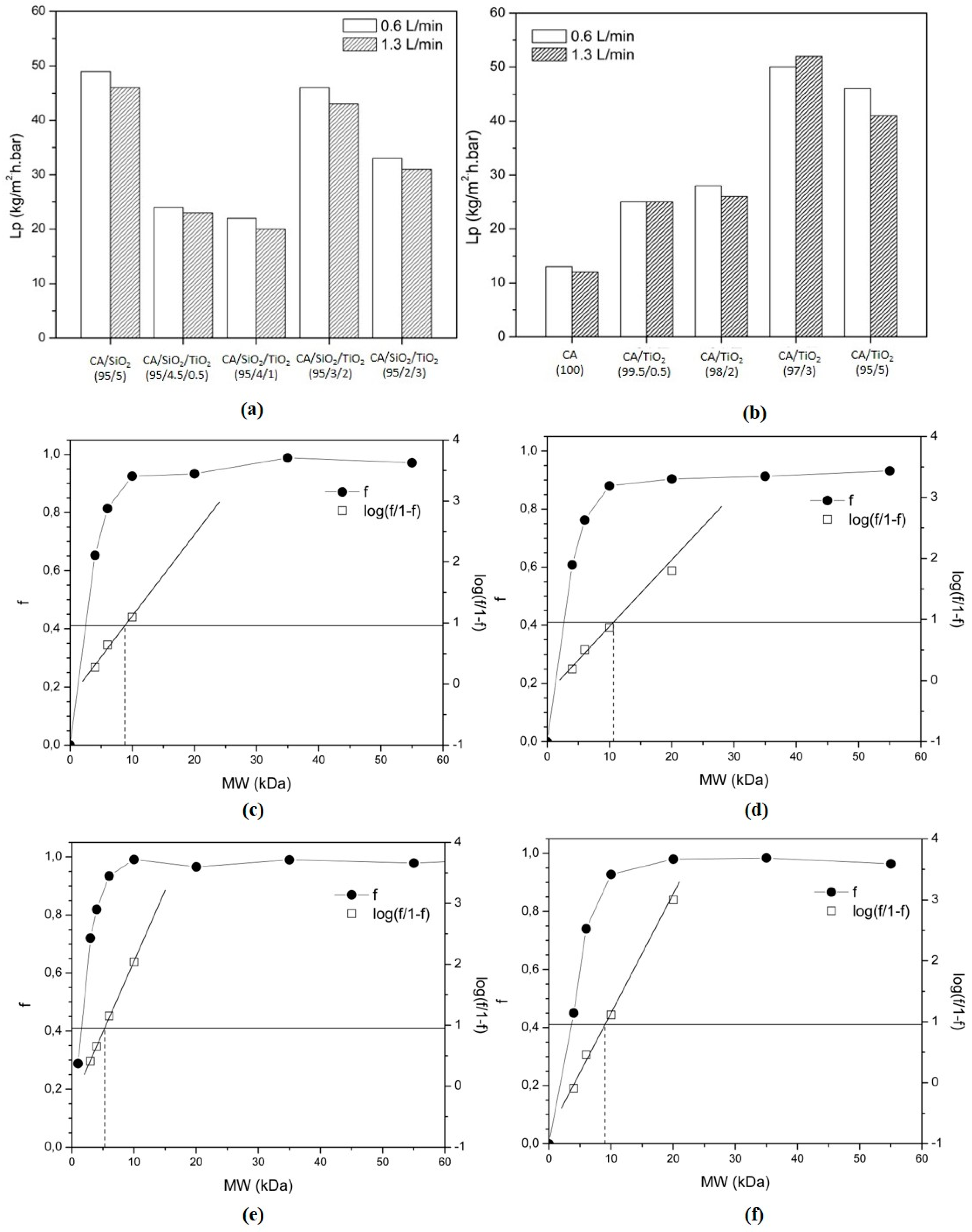
| Acronyms/Compounds | Series 1 | ||||
| CA/SiO2 (95/5) | CA/SiO2/TiO2 (95/4.5/0.5) | CA/SiO2/TiO2 (95/4/1) | CA/SiO2/TiO2 (95/3/2) | CA/SiO2/TiO2 (95/2/3) | |
| CA | 16.40 | 16.40 | 16.40 | 16.40 | 16.40 |
| Formamide | 29.00 | 29.00 | 29.00 | 29.00 | 29.00 |
| Acetone | 51.10 | 51.10 | 51.10 | 51.10 | 51.10 |
| TEOS | 3.00 | 2.70 | 2.40 | 2.10 | 0.93 |
| TiPOT | 0.00 | 0.32 | 0.64 | 0.96 | 2.07 |
| DI | 0.50 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 |
| HNO3 | 3 drops (pH 1.5–2) | ||||
| Acronyms/Compounds | Series 2 | ||||
| CA (100) | CA/TiO2 (99.5/0.5) | CA/TiO2 (98/2) | CA/TiO2 (97/3) | CA/TiO2 (95/5) | |
| CA | 17.00 | 16.40 | 16.40 | 16.40 | 16.40 |
| Formamide | 30.00 | 29.00 | 29.00 | 29.00 | 29.00 |
| Acetone | 53.00 | 51.10 | 51.10 | 51.10 | 51.10 |
| TEOS | - | - | - | - | - |
| TiPOT | 0.00 | 0.32 | 0.96 | 2.07 | 3.00 |
| DI | 0.00 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 |
| HNO3 | 3 drops (pH 1.5–2) | ||||
| Casting Conditions | |||||
| Temperature (°C): 19–23 | |||||
| Solvent evaporation time (s): 30 | |||||
| Coagulation medium: Deionized water at 0 °C during 1–2 h | |||||
| Series 1 | Ti(theoretical) (mg) | Ti(exp) (mg) |
| CA/SiO2 (95/5) | 0.00 ± 0.01 | 0.00 ± 0.10 |
| CA/SiO2/TiO2 (95/4.5/0.5) | 0.20 ± 0.01 | 0.20 ± 0.10 |
| CA/SiO2/TiO2 (95/4/1) | 0.44 ± 0.01 | 0.40 ± 0.10 |
| CA/SiO2/TiO2 (95/3/2) | 0.62 ± 0.01 | 0.70 ± 0.10 |
| CA/SiO2/TiO2 (95/2/3) | 1.28 ± 0.01 | 1.20 ± 0.20 |
| Series 2 | Ti(theoretical) (mg) | Ti(exp) (mg) |
| CA (100) | 0.00 ± 0.01 | 0.00 ± 0.10 |
| CA/TiO2 (99.5/0.5) | 0.31 ± 0.01 | 0.50 ± 0.10 |
| CA/TiO2 (98/2) | 0.76 ± 0.01 | 1.30 ± 0.30 |
| CA/TiO2 (97/3) | 1.66 ± 0.01 | 1.30 ± 0.50 |
| CA/TiO2 (95/5) | 2.39 ± 0.01 | 2.00 ± 0.20 |
| Wavenumber/cm−1 | Assignment | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CA/SiO2 (95/5) | CA/SiO2/TiO2 (95/4.5/0.5) | CA/SiO2/TiO2 (95/4/1) | CA/SiO2/TiO2 (95/3.5/1.5) | CA/SiO2/TiO2 (95/2/3) | |
| 3487 br | 3490 | 3491 | 3489 | 3490 | νOH (H bonded) |
| 1741 S | 1742 | 1743 | 1736 | 1747 | νC=O |
| 1637 w | 1637 | 1637 | 1637 | 1638 | δHOH (H2O) |
| 1433 w | 1432 | 1432 | 1431 | 1432 | δCH2 |
| 1369 m | 1369 | 1369 | 1369 | 1369 | δsCH3 |
| 1232 VS | 1232 | 1232 | 1233 | 1232 | νasCOC (acetate) |
| 1161 w | 1161 | 1161 | 1161 | 1161 | νasCOC (glycosidic) |
| 1122 w,sh | 1122 | 1122 | 1122 | 1122 | νasCOC (glycosidic) |
| 1065 w | 1065 | 1065 | 1065 | 1065 | νasCOC (glycosidic), ν(Si–O–Si) |
| 1045 VS | 1045 | 1045 | 1045 | 1045 | νsCOC (acetate) |
| 903 w | 904 | 903 | 903 | 904 | ρCH3 |
| Components | CA/SiO2 (95/5) | CA/SiO2/TiO2 (95/4.5/0.5) | CA/SiO2/TiO2 (95/4/1) | CA/SiO2/TiO2 (95/3.5/1.5) | CA/SiO2/TiO2 (95/2/3) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| /cm−1 | A | /cm−1 | A | /cm−1 | A | /cm−1 | A | /cm−1 | A | |
| 1741 | 27.67 | 1742 | 23.87 | 1743 | 23.30 | 1746 | 22.80 | 1747 | 23.40 | |
| Components | CA/SiO2 (95/5) | CA/SiO2/TiO2 (95/4.5/0.5) | CA/SiO2/TiO2 (95/4/1) | CA/SiO2/TiO2 (95/3.5/1.5) | CA/SiO2/TiO2 (95/2/3) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| /cm−1 | A (%) | /cm−1 | A (%) | /cm−1 | A (%) | /cm−1 | A (%) | /cm−1 | A (%) | |
| 1039 | 51 | 1040 | 53 | 1040 | 57 | 1039 | 63 | 1039 | 64 | |
| 1066 | 49 | 1067 | 47 | 1068 | 43 | 1068 | 37 | 1067 | 36 | |
| Wavenumber/cm−1 | Assignment | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CA(100) | CA/TiO2 (99.5/0.5) | CA/TiO2 (98/2) | CA/TiO2 (97/3) | CA/TiO2 (95/5) | |
| 3490 br | 3488 | 3494 | 3500 | 3500 | νOH (H bonded) |
| 1739 S | 1744 | 1745 | 1749 | 1749 | νC=O |
| 1635 w | 1639 | 1636 | 1639 | 1639 | δHOH (H2O) |
| 1435 w | 1437 | 1430 | 1433 | 1433 | δCH2 |
| 1368 m | 1379 | 1369 | 1379 | 1373 | δsCH3 |
| 1233 VS | 1234 | 1234 | 1234 | 1228 | νasCOC (acetate) |
| 1165 w | 1163 | 1163 | 1163 | 1163 | νasCOC (glycosidic) |
| 1037 VS | 1043 | 1043 | 1043 | 1043 | νsCOC (acetate) |
| 898 w | 903 | 903 | 897 | 903 | ρCH3 |
| Components | CA (100) | CA/TiO2 (99.5/0.5) | CA/TiO2 (98/2) | CA/TiO2 (97/3) | CA/TiO2 (95/5) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| /cm−1 | A | /cm−1 | A | /cm−1 | A | /cm−1 | A | /cm−1 | A | |
| 1739 | 18.69 | 1744 | 22.35 | 1745 | 22.41 | 1749 | 22.80 | 1749 | 23.09 | |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Peixoto, I.; Faria, M.; Gonçalves, M.C. Synthesis and Characterization of Novel Integral Asymmetric Monophasic Cellulose–Acetate/Silica/Titania and Cellulose–Acetate/Titania Membranes. Membranes 2020, 10, 195. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes10090195
Peixoto I, Faria M, Gonçalves MC. Synthesis and Characterization of Novel Integral Asymmetric Monophasic Cellulose–Acetate/Silica/Titania and Cellulose–Acetate/Titania Membranes. Membranes. 2020; 10(9):195. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes10090195
Chicago/Turabian StylePeixoto, Inês, Mónica Faria, and M. Clara Gonçalves. 2020. "Synthesis and Characterization of Novel Integral Asymmetric Monophasic Cellulose–Acetate/Silica/Titania and Cellulose–Acetate/Titania Membranes" Membranes 10, no. 9: 195. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes10090195
APA StylePeixoto, I., Faria, M., & Gonçalves, M. C. (2020). Synthesis and Characterization of Novel Integral Asymmetric Monophasic Cellulose–Acetate/Silica/Titania and Cellulose–Acetate/Titania Membranes. Membranes, 10(9), 195. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes10090195