Incorporation of Lipids into Wheat Bran Cellulose/Wheat Gluten Composite Film Improves Its Water Resistance Properties
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Wheat Bran Cellulose
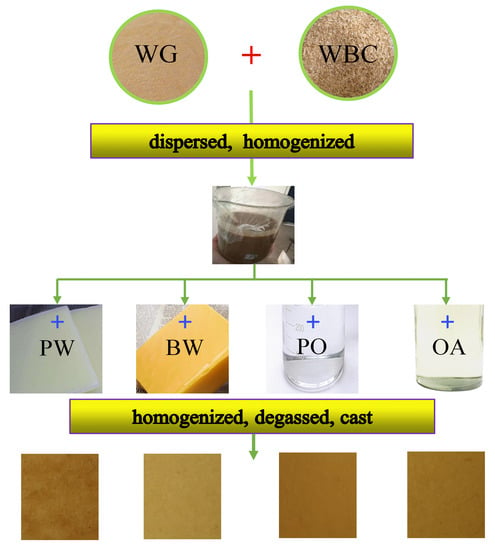
2.3. Preparation of Film-Forming Dispersions
2.4. Preparation of Films
2.5. Characterization of Films
2.5.1. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
2.5.2. Fourier Transform Infrared (FT-IR) Spectroscopy
2.5.3. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
2.5.4. Determination of Water Solubility
2.5.5. Water Vapor Permeability (WVP)
2.5.6. Water Contact Angle (WCA)
2.5.7. Mechanical Properties
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Film Morphology
3.2. FT-IR Spectra
3.3. Thermal Properties of Film
3.4. Water-Resistance Properties
3.4.1. Water Solubility
3.4.2. Water Vapor Permeability (WVP)
3.4.3. Water Contact Angle (WCA)
3.5. Mechanical Properties
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Guerreiro, T.M.; de Oliveira, D.N.; Melo, C.; Lima, E.D.; Catharino, R.R. Migration from plastic packaging into meat. Food Res. Int. 2018, 109, 320–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deya, A.; Pandey, G.; Rawtania, D. Functionalized nanomaterials driven antimicrobial food packaging: A technological advancement in food science. Food Control 2022, 131, 108469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgos, N.; Valdes, A.; Jimenez, A. Valorization of agricultural wastes for the production of protein-based biopolymers. J. Renew. Mater. 2016, 4, 165–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Delcour, J.A.; Joye, I.J.; Pareyt, B.; Wilderjans, E.; Brijs, K.; Lagrain, B. Wheat gluten functionality as a quality determinant in cereal-based food products. Annu. Rev. Food Sci. Technol. 2012, 3, 469–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, B.; Chatha, S.A.S.; Hussain, A.I.; Zia, K.M.; Akhtar, N. Recent advances on polysaccharides, lipids and protein based edible films and coatings: A review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 109, 1095–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocca-Smith, J.R.; Marcuzzo, E.; Karbowiak, T.; Centa, J.; Giacometti, M.; Scapin, F.; Venir, E.; Sensidoni, A.; Debeaufort, F. Effect of lipid incorporation on functional properties of wheat gluten based edible films. J. Cereal Sci. 2016, 69, 275–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labuza, T.P.; Hyman, C.R. Moisture migration and control in multi-domain foods. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 1998, 9, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cazon, P.; Vazquez, M.; Velazquez, G. Composite films of regenerate cellulose with chitosan and polyvinyl alcohol: Evaluation of water adsorption, mechanical and optical properties. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 117, 235–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mastromatteo, M.; Chillo, S.; Buonocore, G.G.; Massaro, A.; Conte, A.; Del Nobile, M.A. Effects of spelt and wheat bran on the performances of wheat gluten films. J. Food Eng. 2008, 88, 202–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nataraj, D.; Sakkara, S.; Meenakshi, H.N.; Reddy, N. Properties and applications of citric acid crosslinked banana fibre-wheat gluten films. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2018, 124, 265–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G.; Xiao, L.; Wu, H.; Li, S.; Luo, Q.; Liu, X.; Chen, A.; Shen, G.; Zhang, Z. Influence of alkaline-ethanol filming system for wheat gluten-based films containing wheat-bran cellulose. Food Mach. 2018, 34, 12–18. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.; Wang, S.; Wang, W.; Qin, C.; Wu, M. Facile preparation of reactive hydrophobic cellulose nanofibril film for reducing water vapor permeability (WVP) in packaging applications. Cellulose 2019, 26, 3271–3284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wihodo, M.; Moraru, C.I. Physical and chemical methods used to enhance the structure and mechanical properties of protein films: A review. J. Food Eng. 2013, 114, 292–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, T.L.; Song, K.B. Development of bioactive Bombacaceae gum films containing cinnamon leaf essential oil and their application in packaging of fresh salmon fillets. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 131, 109647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalczyk, D.; Gustaw, W.; Zieba, E.; Lisiecki, S.; Stadnik, J.; Baraniak, B. Microstructure and functional properties of sorbitol-plasticized pea protein isolate emulsion films: Effect of lipid type and concentration. Food Hydrocoll. 2016, 60, 353–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nurul Syahida, S.; Ismail-Fitry, M.R.; Ainun, Z.M.A.; Nur Hanani, Z.A. Effects of palm wax on the physical, mechanical and water barrier properties of fish gelatin films for food packaging application. Food Packag. Shelf. 2020, 23, 100437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cecchini, J.P.; Spotti, M.J.; Piagentini, A.M.; Milt, V.G.; Carrara, C.R. Development of edible films obtained from submicron emulsions based on whey protein concentrate, oil/beeswax and brea gum. Food Sci. Technol. Int. 2017, 23, 371–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Simpson, B.K.; Dumont, M.J. Effect of beeswax and carnauba wax addition on properties of gelatin films: A comparative study. Food Biosci. 2018, 26, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, K.; Zhou, L.; Xu, J.; Jiang, F.; Zhong, Z.; Zou, L.; Liu, W. Carboxymethyl cellulose-based water barrier coating regulated postharvest quality and ROS metabolism of pakchoi (Brassica chinensis, L.). Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2022, 185, 111804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Sun, X.X.; Lian, Z.X.; Wang, X.X.; Zhou, J.; Ma, Z.S. The effects of ultrasonic/microwave assisted treatment on the properties of soy protein isolate/microcrystalline wheat-bran cellulose film. J. Food Eng. 2013, 114, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM. Standard test methods for water vapor transmission of materials. In Annual Book of ASTM Standards; ASTM: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Aline, O.E.S.I.; Stoll, L.; Belle, A.S.; Bellé, A.S.; Hertz, P.F.; Rios, A.O.; Rahier, H.; Flôres, S.H. Gelatin capsule residue-based films crosslinked with the natural agent genipin. Packag. Technol. Sci. 2020, 33, 15–26. [Google Scholar]
- Beneventi, D.; Pugh, R.J.; Carré, B.; Gandini, A. Surface rheology and foaming properties of sodium oleate and C12(EO)6 aqueous solutions. J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 2003, 268, 221–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Xiao, D.; Lu, J.; Jiao, C.; Li, S.; Lei, Y.; Liu, D.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, Y.; et al. Effect of high-pressure homogenization on microstructure and properties of pomelo peel flour film-forming dispersions and their resultant films. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 102, 105628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Wang, W.T.; Zhang, H.; Dai, Y.Y.; Dong, H.Z.; Hou, H.X. Effects of hydrophobic agents on the physicochemical properties of edible agar/maltodextrin films. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 88, 283–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Yu, J.; He, K.; Wang, N. The effects of different plasticizers on the properties of thermoplastic starch as solid polymer electrolytes. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2007, 292, 503–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, L.; Li, Y.; Zhang, A.; Zhang, H. Characterization and physical properties of electrospun gelatin nanofibrous films by incorporation of nano-hydroxyapatite. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 103, 105640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chawla, P.; Najda, A.; Bains, A.; Nurzyńska-Wierdak, R.; Kaushik, R.; Tosif, M.M. Potential of gum arabic functionalized iron hydroxide nanoparticles embedded cellulose paper for packaging of Paneer. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tosif, M.M.; Najda, A.; Bains, A.; Zawiślak, G.; Maj, G.; Chawla, P. Starch–mucilage composite films: An inclusive on physicochemical and biological perspective. Polymers 2021, 13, 2588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamróz, E.; Juszczak, L.; Kucharek, M. Investigation of the physical properties, antioxidant and antimicrobial activity of ternary potato starch-furcellaran-gelatin films incorporated with lavender essential oil. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 114, 1094–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanzadi, M.; Jafari, S.M.; Mirzaei, H.; Chegini, F.K.; Maghsoudlou, Y.; Dehnad, D. Physical and mechanical properties in biodegradable films of whey protein concentrate–pullulan by application of beeswax. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 118, 24–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wicochea-Rodríguez, J.D.; Chalier, P.; Ruiz, T.; Gastaldi, E. Active food packaging based on biopolymers and aroma compounds: How to design and control the release. Front. Chem. 2019, 7, 398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Park, I.; Seo, J.; Han, H.; Jang, W. Effects of the paraffin wax (PW) content on the thermal and permeation properties of the LDPE/PW composite films. J. Polym. Res. 2015, 22, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, H.; Wang, C.; Gong, S.; Mei, Y.; Li, H.; Ma, W. Investigation on contact angle measurement methods and wettability transition of porous surfaces. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2016, 292, 72–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabra, M.J.; Talens, P.; Chiralt, A. Tensile properties and water vapor permeability of sodium caseinate films containing oleic acid-beeswax mixtures. J. Food Eng. 2008, 85, 393–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morillon, V.; Debeaufort, F.; Blond, G.; Capelle, M.; Voilley, A. Factors affecting the moisture permeability of lipid-based edible films: A review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2002, 42, 67–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valizadeh, S.; Naseri, M.; Babaei, S.; Hosseini, S.M.H.; Imani, A. Development of bioactive composite films from chitosan and carboxymethyl cellulose using glutaraldehyde, cinnamon essential oil and oleic acid. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 134, 604–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Lipid Type | Lipid Concentration (%) | WS (%) | WVP (10−12 g/cm·s·Pa) | WCA (°) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Air-Side | PMMA-Side | ||||
| Control | 0 | 22.59 ± 0.26 a | 1.63 ± 0.01 a | 55.78 ± 3.27 e | 73.89 ± 3.00 e |
| PW | 5 | 21.64 ± 0.18 b | 1.14 ± 0.08 def | 68.86 ± 3.56 cd | 73.60 ± 2.79 e |
| 10 | 21.06 ± 0.36 bcd | 1.02 ± 0.03 gh | 56.60 ± 4.83 e | 74.28 ± 2.92 e | |
| 15 | 19.91 ± 0.45 ef | 0.78 ± 0.06 ij | 56.17 ± 3.60 e | 84.88 ± 5.31 b | |
| 20 | 18.88 ± 0.52 gh | 1.01 ± 0.05 h | 54.81 ± 0.72 e | 95.46 ± 2.01 a | |
| BW | 5 | 21.31 ± 0.44 bcd | 1.23 ± 0.03 cd | 73.70 ± 4.06 bc | 75.34 ± 2.87 de |
| 10 | 20.80 ± 0.32 cd | 1.12 ± 0.05 ef | 67.50 ± 2.91 cd | 80.58 ± 3.54 bcd | |
| 15 | 19.82 ± 0.62 efg | 0.76 ± 0.02 j | 66.68 ± 2.46 d | 86.18 ± 1.20 b | |
| 20 | 18.50 ± 0.25 h | 1.02 ± 0.06 gh | 57.96 ± 0.65 e | 85.62 ± 2.53 b | |
| PO | 5 | 21.54 ± 0.34 bc | 1.39 ± 0.04 b | 66.95 ± 3.74 d | 75.02 ± 0.55 de |
| 10 | 20.46 ± 0.48 def | 1.17 ± 0.04 def | 76.68 ± 3.32 b | 77.72 ± 1.60 cde | |
| 15 | 19.77 ± 0.57 efg | 0.85 ± 0.03 i | 91.21 ± 3.50 a | 81.90 ± 4.53 bc | |
| 20 | 19.29 ± 0.26 gh | 1.10 ± 0.04 fg | 86.30 ± 4.94 a | 84.84 ± 3.31 b | |
| OA | 5 | 20.76 ± 0.39 bc | 1.28 ± 0.05 c | 51.43 ± 3.87 ef | 64.87 ± 1.09 f |
| 10 | 19.44 ± 0.55 fgh | 1.20 ± 0.10 cde | 46.80 ± 2.39 fg | 63.99 ± 0.89 f | |
| 15 | 18.82 ± 0.60 gh | 1.09 ± 0.02 fgh | 41.04 ± 1.44 g | 62.56 ± 4.29 f | |
| 20 | n.a. | n.a. | n.a. | n.a. | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shen, G.; Yu, G.; Wu, H.; Li, S.; Hou, X.; Li, M.; Li, Q.; Liu, X.; Zhou, M.; Chen, A.; et al. Incorporation of Lipids into Wheat Bran Cellulose/Wheat Gluten Composite Film Improves Its Water Resistance Properties. Membranes 2022, 12, 18. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12010018
Shen G, Yu G, Wu H, Li S, Hou X, Li M, Li Q, Liu X, Zhou M, Chen A, et al. Incorporation of Lipids into Wheat Bran Cellulose/Wheat Gluten Composite Film Improves Its Water Resistance Properties. Membranes. 2022; 12(1):18. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12010018
Chicago/Turabian StyleShen, Guanghui, Guoxian Yu, Hejun Wu, Shanshan Li, Xiaoyan Hou, Meiliang Li, Qingye Li, Xingyan Liu, Man Zhou, Anjun Chen, and et al. 2022. "Incorporation of Lipids into Wheat Bran Cellulose/Wheat Gluten Composite Film Improves Its Water Resistance Properties" Membranes 12, no. 1: 18. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12010018
APA StyleShen, G., Yu, G., Wu, H., Li, S., Hou, X., Li, M., Li, Q., Liu, X., Zhou, M., Chen, A., & Zhang, Z. (2022). Incorporation of Lipids into Wheat Bran Cellulose/Wheat Gluten Composite Film Improves Its Water Resistance Properties. Membranes, 12(1), 18. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12010018