Comparison of Physicochemical Properties of Two Types of Polyepichlorohydrin-Based Anion Exchange Membranes for Reverse Electrodialysis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Homogeneous AEMs
2.3. Membrane Characterization
2.3.1. Thickness of the PECH Membranes
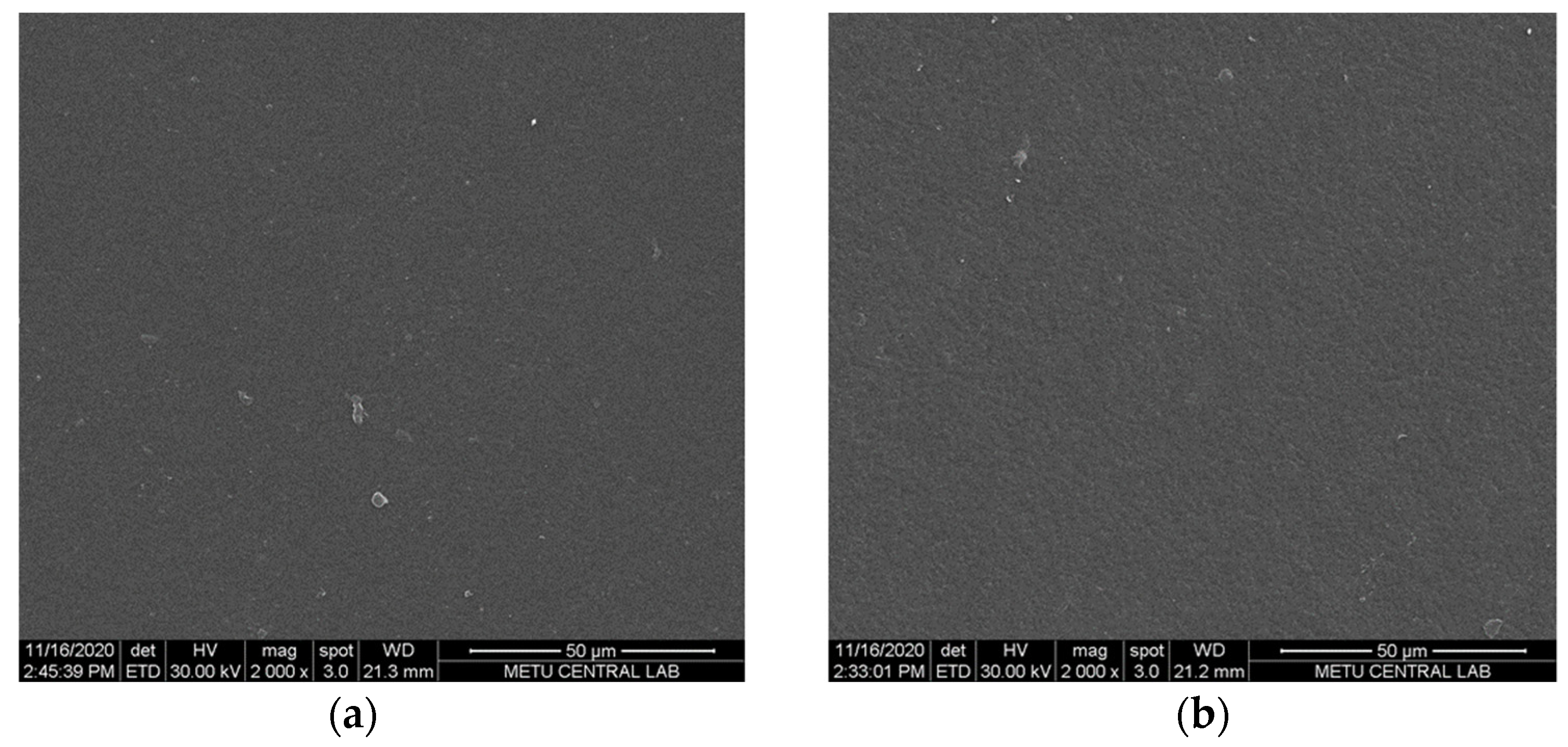
2.3.2. Scanning Electron Microscopy
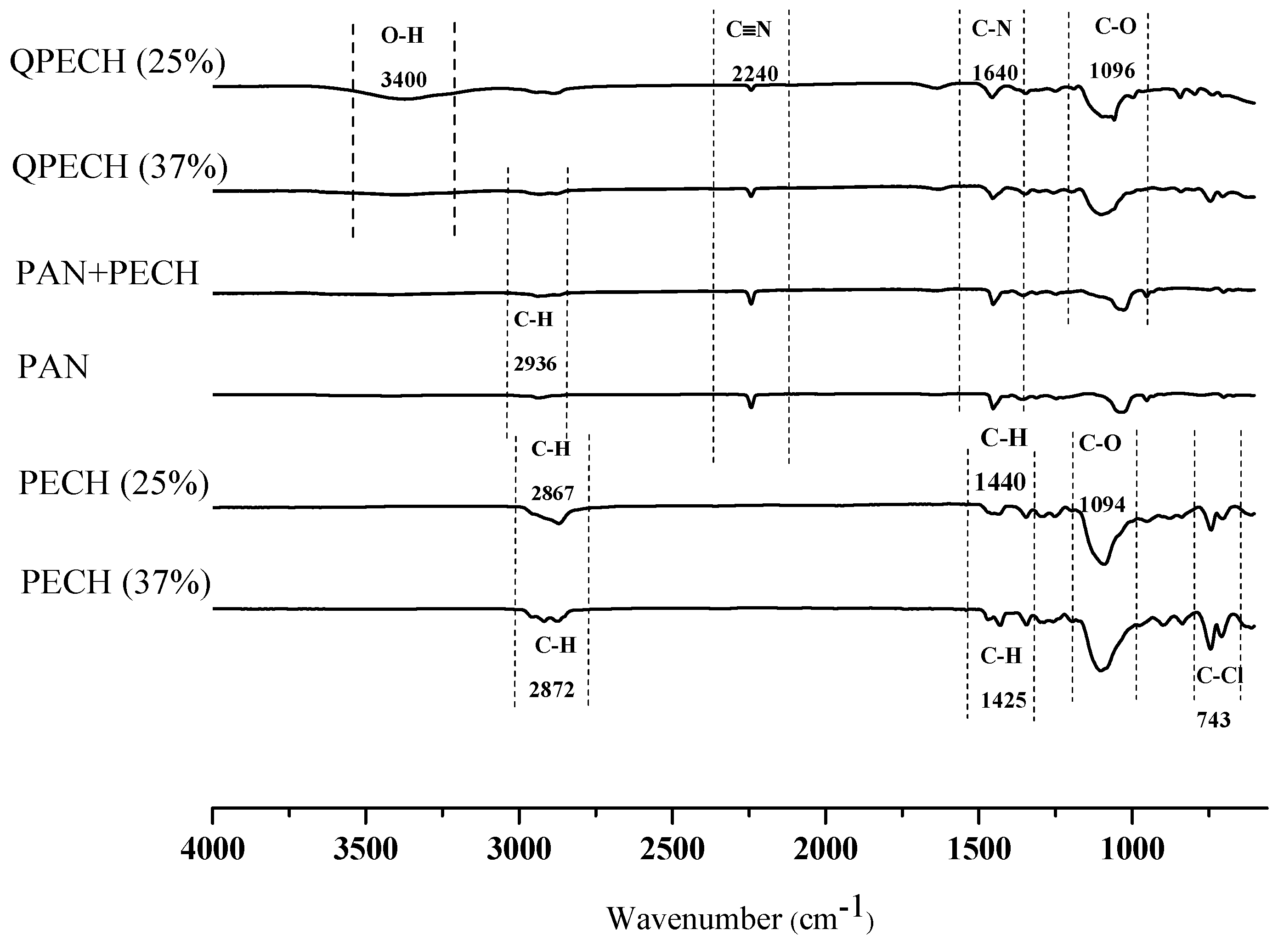
2.3.3. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy
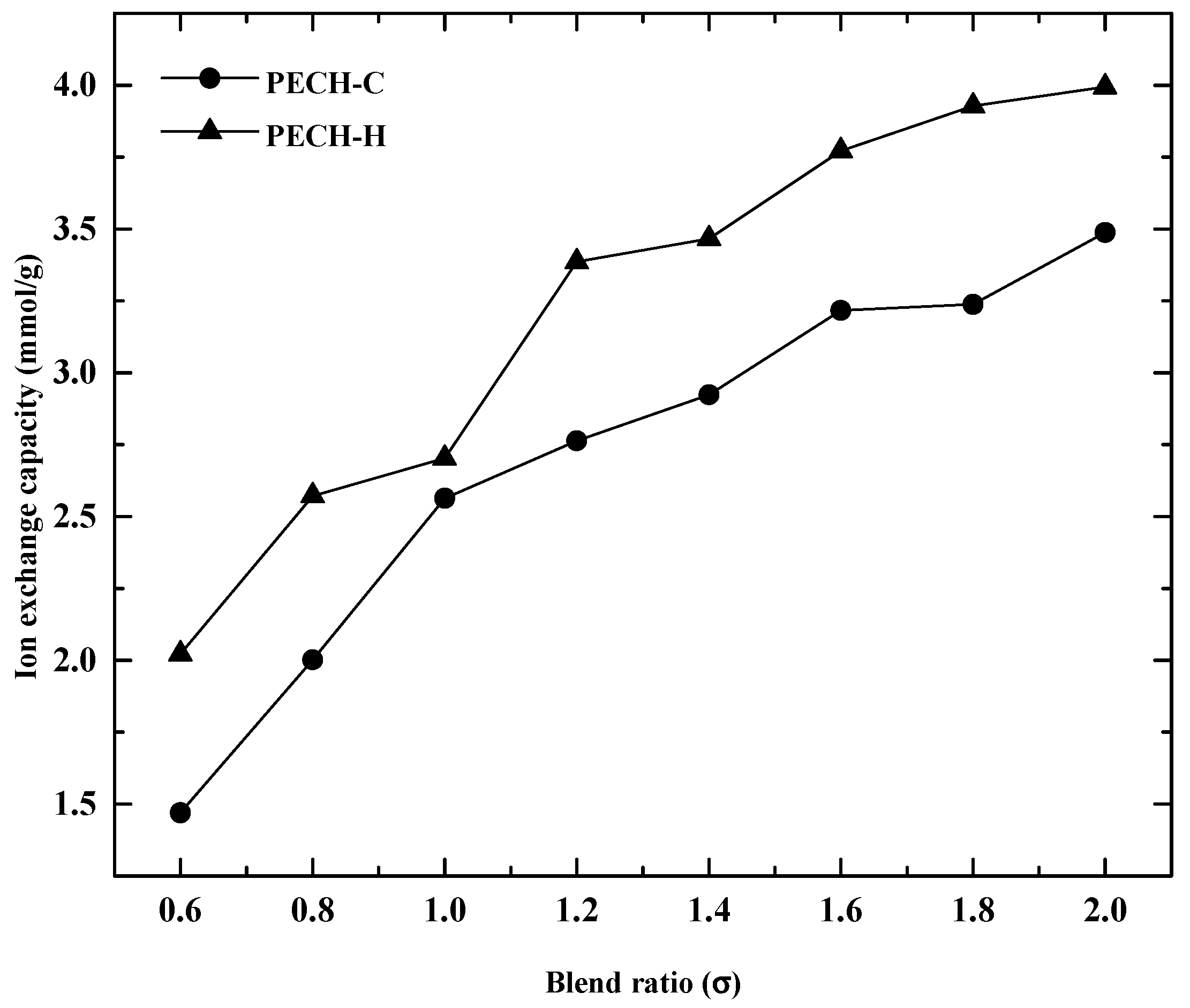
2.3.4. Ion Exchange Capacity
2.3.5. Swelling Degree
2.3.6. Fixed Charge Density
2.3.7. Differential Scanning Calorimetry
2.4. RED Tests
2.4.1. The RED System
2.4.2. Electrochemical Measurements
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Membrane Thickness and Morphology
3.2. FTIR Analysis
3.3. Effect of Blend Ratio on Membrane Characteristics
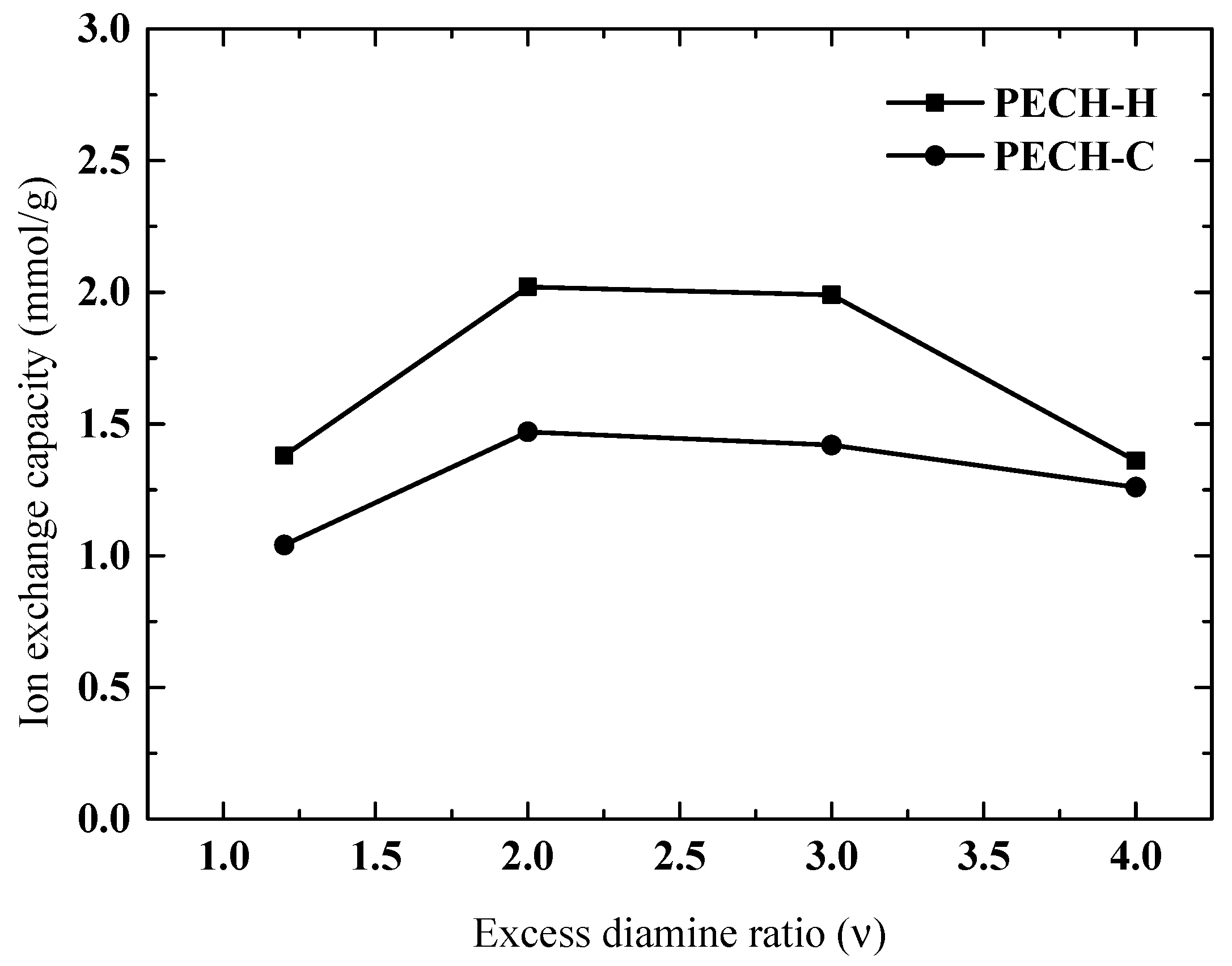
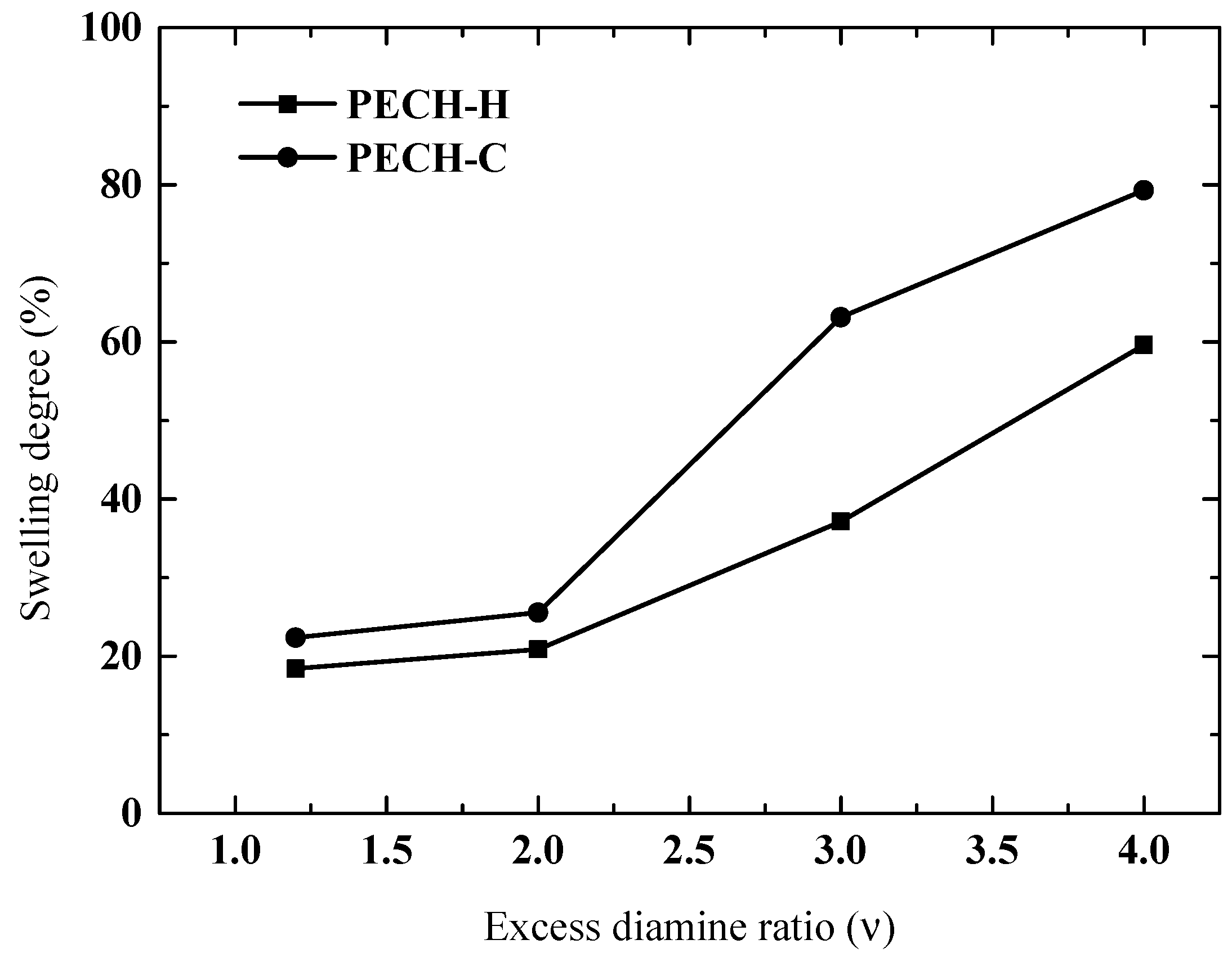
3.4. Effect of Excess Diamine Ratio on Membrane Characteristics
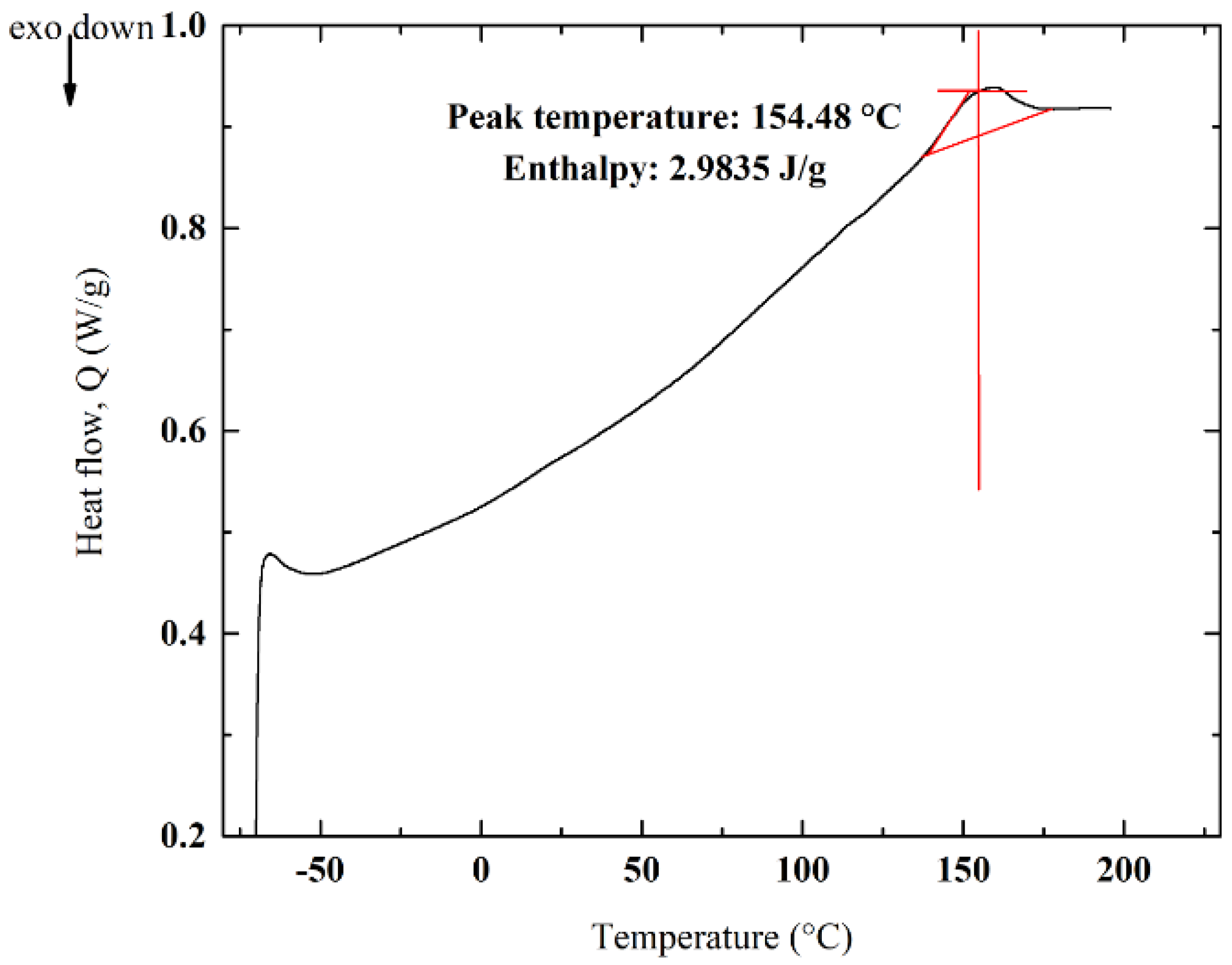
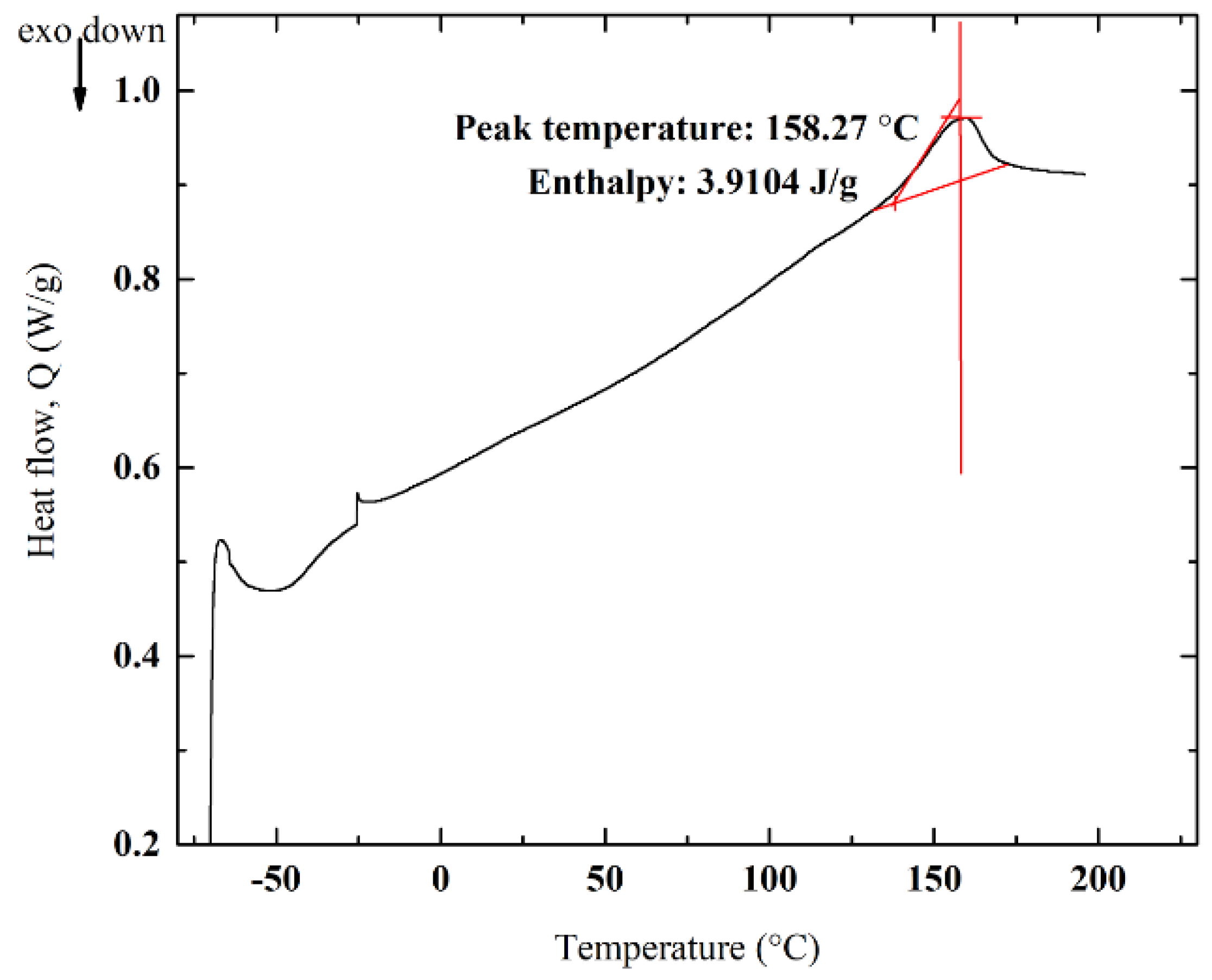
3.5. DSC Analyses and Impact of Crystallinity
3.6. Benchmarking of Membrane Properties
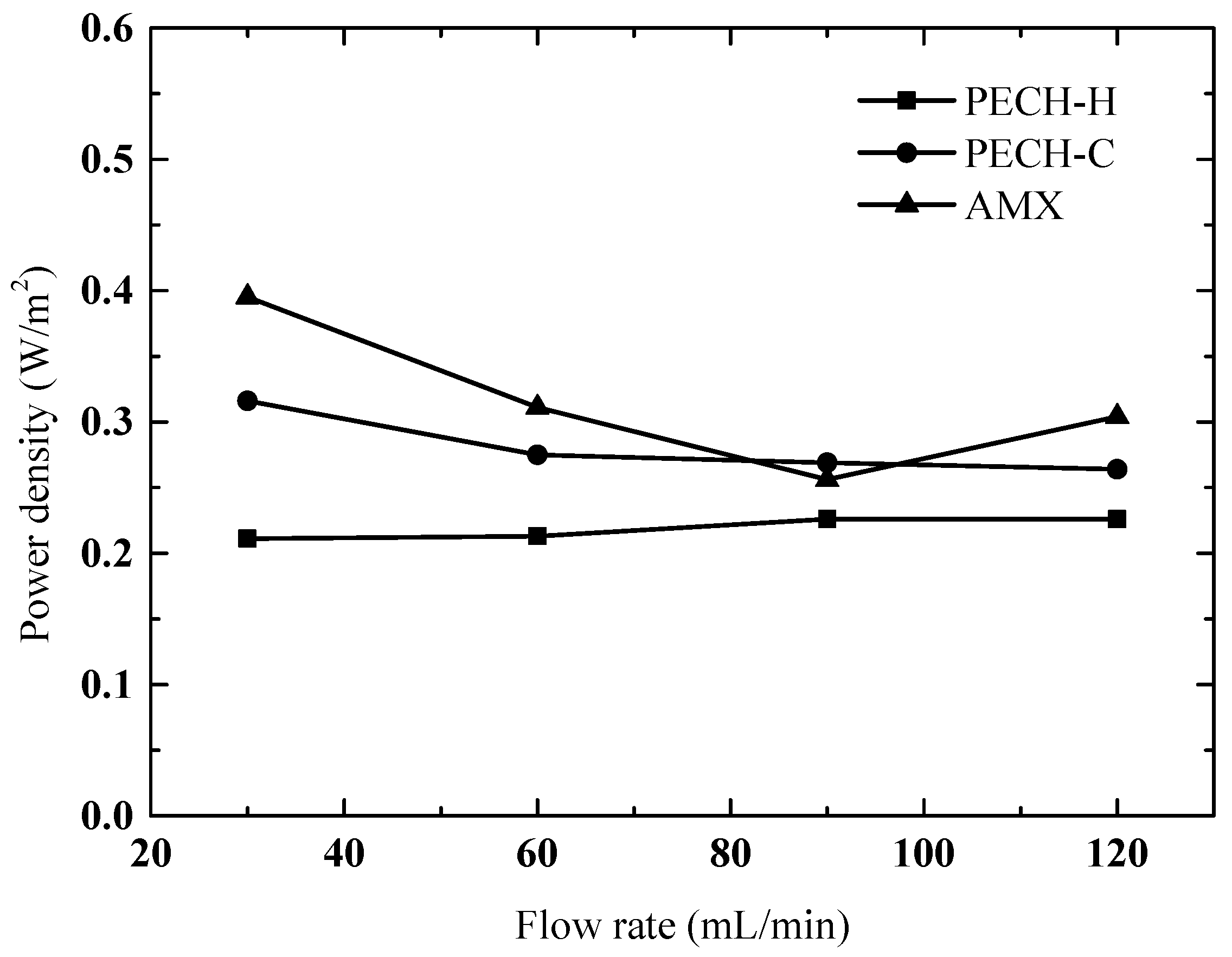
3.7. RED Performance
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shadravan, A.; Amani, M. Recent Advances of Nanomaterials in Membranes for Osmotic Energy Harvesting by Pressure Retarded Osmosis. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2112.01428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luque Di Salvo, J.; Cosenza, A.; Tamburini, A.; Micale, G.; Cipollina, A. Long-run operation of a reverse electrodialysis system fed with wastewaters. J. Environ. Manage. 2018, 217, 871–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alvarez-Silva, O.A.; Osorio, A.F.; Winter, C. Practical global salinity gradient energy potential. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 60, 1387–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniilidis, A.; Herber, R.; Vermaas, D.A. Upscale potential and financial feasibility of a reverse electrodialysis power plant. Appl. Energy 2014, 119, 257–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guler, E.; Zhang, Y.; Saakes, M.; Nijmeijer, K. Tailor-made anion-exchange membranes for salinity gradient power generation using reverse electrodialysis. ChemSusChem 2012, 5, 2262–2270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yip, N.Y.; Vermaas, D.A.; Nijmeijer, K.; Elimelech, M. Thermodynamic, energy efficiency, and power density analysis of reverse electrodialysis power generation with natural salinity gradients. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 4925–4936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Cerva, M.L.; Di Liberto, M.; Gurreri, L.; Tamburini, A.; Cipollina, A.; Micale, G.; Ciofalo, M. Coupling CFD with a one-dimensional model to predict the performance of reverse electrodialysis stacks. J. Memb. Sci. 2017, 541, 595–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brogioli, D.; Ziano, R.; Rica, R.A.; Salerno, D.; Mantegazza, F. Capacitive mixing for the extraction of energy from salinity differences: Survey of experimental results and electrochemical models. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2013, 407, 457–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Micale, G.; Cipollina, A.; Tamburini, A. 1—Salinity Gradient Energy; Cipollina, A., Micale, G.B.T.-S.E., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; pp. 1–17. ISBN 978-0-08-100312-1. [Google Scholar]
- Othman, N.H.; Kabay, N.; Guler, E. Principles of reverse electrodialysis and development of integrated-based system for power generation and water treatment: A review. Rev. Chem. Eng. 2021, 1–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altıok, E.; Kaya, T.Z.; Güler, E.; Kabay, N.; Bryjak, M. Performance of reverse electrodialysis system for salinity gradient energy generation by using a commercial ion exchange membrane pair with homogeneous bulk structure. Water 2021, 13, 814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tedesco, M.; Cipollina, A.; Tamburini, A.; Micale, G.; Helsen, J.; Papapetrou, M. REAPower: Use of desalination brine for power production through reverse electrodialysis. Desalin. Water Treat. 2015, 53, 3161–3169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bryjak, M.; Kabay, N.; Güler, E.; Tomaszewska, B. Concept for energy harvesting from the salinity gradient on the basis of geothermal water. WEENTECH Proc. Energy 2018, 4, 88–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tedesco, M.; Scalici, C.; Vaccari, D.; Cipollina, A.; Tamburini, A.; Micale, G. Performance of the first reverse electrodialysis pilot plant for power production from saline waters and concentrated brines. J. Memb. Sci. 2016, 500, 33–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kwon, K.; Park, B.H.; Kim, D.H.; Kim, D. Parametric study of reverse electrodialysis using ammonium bicarbonate solution for low-grade waste heat recovery. Energy Convers. Manag. 2015, 103, 104–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kingsbury, R.S.; Chu, K.; Coronell, O. Energy storage by reversible electrodialysis: The concentration battery. J. Memb. Sci. 2015, 495, 502–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Egmond, W.J.; Saakes, M.; Porada, S.; Meuwissen, T.; Buisman, C.J.N.; Hamelers, H.V.M. The concentration gradient flow battery as electricity storage system: Technology potential and energy dissipation. J. Power Sources 2016, 325, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altıok, E.; Kaya, T.Z.; Othman, N.H.; Kınalı, O.; Kitada, S.; Güler, E.; Kabay, N. Investigations on the effects of operational parameters in reverse electrodialysis system for salinity gradient power generation using central composite design (CCD). Desalination 2022, 525, 115508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brogioli, D. Extracting renewable energy from a salinity difference using a capacitor. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2009, 103, 31–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caprarescu, S.; Corobea, M.C.; Purcar, V.; Spataru, C.I.; Ianchis, R.; Vasilievici, G.; Vuluga, Z. San copolymer membranes with ion exchangers for Cu(II) removal from synthetic wastewater by electrodialysis. J. Environ. Sci. 2015, 35, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Amshawee, S.; Yunus, M.Y.B.M.; Azoddein, A.A.M.; Hassell, D.G.; Dakhil, I.H.; Hasan, H.A. Electrodialysis desalination for water and wastewater: A review. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 380, 122231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eti, M.; Othman, N.H.; Güler, E.; Kabay, N. Ion Exchange Membranes for Reverse Electrodialysis (RED) Applications-Recent Developments Article info. J. Membr. Sci. Res. 2021, 7, 260–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tufa, R.A.; Pawlowski, S.; Veerman, J.; Bouzek, K.; Fontananova, E.; di Profio, G.; Velizarov, S.; Goulão Crespo, J.; Nijmeijer, K.; Curcio, E. Progress and prospects in reverse electrodialysis for salinity gradient energy conversion and storage. Appl. Energy 2018, 225, 290–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Vasquez, W.; Ghalloussi, R.; Dammak, L.; Larchet, C.; Nikonenko, V.; Grande, D. Structure and properties of heterogeneous and homogeneous ion-exchange membranes subjected to ageing in sodium hypochlorite. J. Memb. Sci. 2014, 452, 104–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandu, T.; Chiriac, A.L.; Tsyntsarski, B.; Stoycheva, I.; Căprărescu, S.; Damian, C.M.; Iordache, T.V.; Pătroi, D.; Marinescu, V.; Sârbu, A. Advanced hybrid membranes for efficient nickel retention from simulated wastewater. Polym. Int. 2021, 70, 866–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gally, C.R.; Benvenuti, T.; Da Trindade, C.D.M.; Rodrigues, M.A.S.; Zoppas-Ferreira, J.; Pérez-Herranz, V.; Bernardes, A.M. Electrodialysis for the tertiary treatment of municipal wastewater: Efficiency of ion removal and ageing of ion exchange membranes. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 5855–5869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.Y.; Jeong, Y.J.; Chae, S.R.; Yeon, K.H.; Lee, Y.; Kim, C.S.; Jeong, N.J.; Park, J.S. Porous carbon-coated graphite electrodes for energy production from salinity gradient using reverse electrodialysis. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 2016, 91, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Gao, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J. Revised spacer design to improve hydrodynamics and anti-fouling behavior in reverse electrodialysis processes. Desalin. Water Treat. 2016, 57, 28176–28186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, J.Y.; Jwa, E.; Eom, H.; Kim, H.; Hwang, K.; Jeong, N. Enhanced energy recovery using a cascaded reverse electrodialysis stack for salinity gradient power generation. Water Res. 2021, 200, 117255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Krantz, W.B.; Cornelissen, E.R.; Post, J.W.; Verliefde, A.R.D.; Tang, C.Y. A novel hybrid process of reverse electrodialysis and reverse osmosis for low energy seawater desalination and brine management. Appl. Energy 2013, 104, 592–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, Y.; Tang, C.Y. Recent developments and future perspectives of reverse electrodialysis technology: A review. Desalination 2018, 425, 156–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villafaña-López, L.; Reyes-Valadez, D.M.; González-Vargas, O.A.; Suárez-Toriello, V.A.; Jaime-Ferrer, J.S. Custom-made ion exchange membranes at laboratory scale for reverse electrodialysis. Membranes 2019, 9, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jung, D.H.; Han, E.D.; Kim, B.H.; Seo, Y.H. Ultra-thin ion exchange film on the ceramic supporter for output power improvement of reverse electrodialysis. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reyes-Aguilera, J.A.; Villafaña-López, L.; Rentería-Martínez, E.C.; Anderson, S.M.; Jaime-Ferrer, J.S. Electrospinning of polyepychlorhydrin and polyacrylonitrile anionic exchange membranes for reverse electrodialysis. Membranes 2021, 11, 717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guler, E. Anion Exchange Membrane Design for Reserve Electrodialysis. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Twente, Enschede, The Netherlands, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Güler, E.; Elizen, R.; Vermaas, D.A.; Saakes, M.; Nijmeijer, K. Performance-determining membrane properties in reverse electrodialysis. J. Memb. Sci. 2013, 446, 266–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontananova, E.; Messana, D.; Tufa, R.A.; Nicotera, I.; Kosma, V.; Curcio, E.; van Baak, W.; Drioli, E.; Di Profio, G. Effect of solution concentration and composition on the electrochemical properties of ion exchange membranes for energy conversion. J. Power Sources 2017, 340, 282–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Righetti, M.C. Crystallization of polymers investigated by temperature-modulated DSC. Materials 2017, 10, 442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stenina, I.; Golubenko, D.; Nikonenko, V. Selectivity of Transport Processes in Ion-Exchange Membranes: Relationship with the Structure and Methods for Its Improvement. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulder, M. Basic Principles of Membrane Technology, 2nd ed.; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1997; ISBN 0792342488. [Google Scholar]
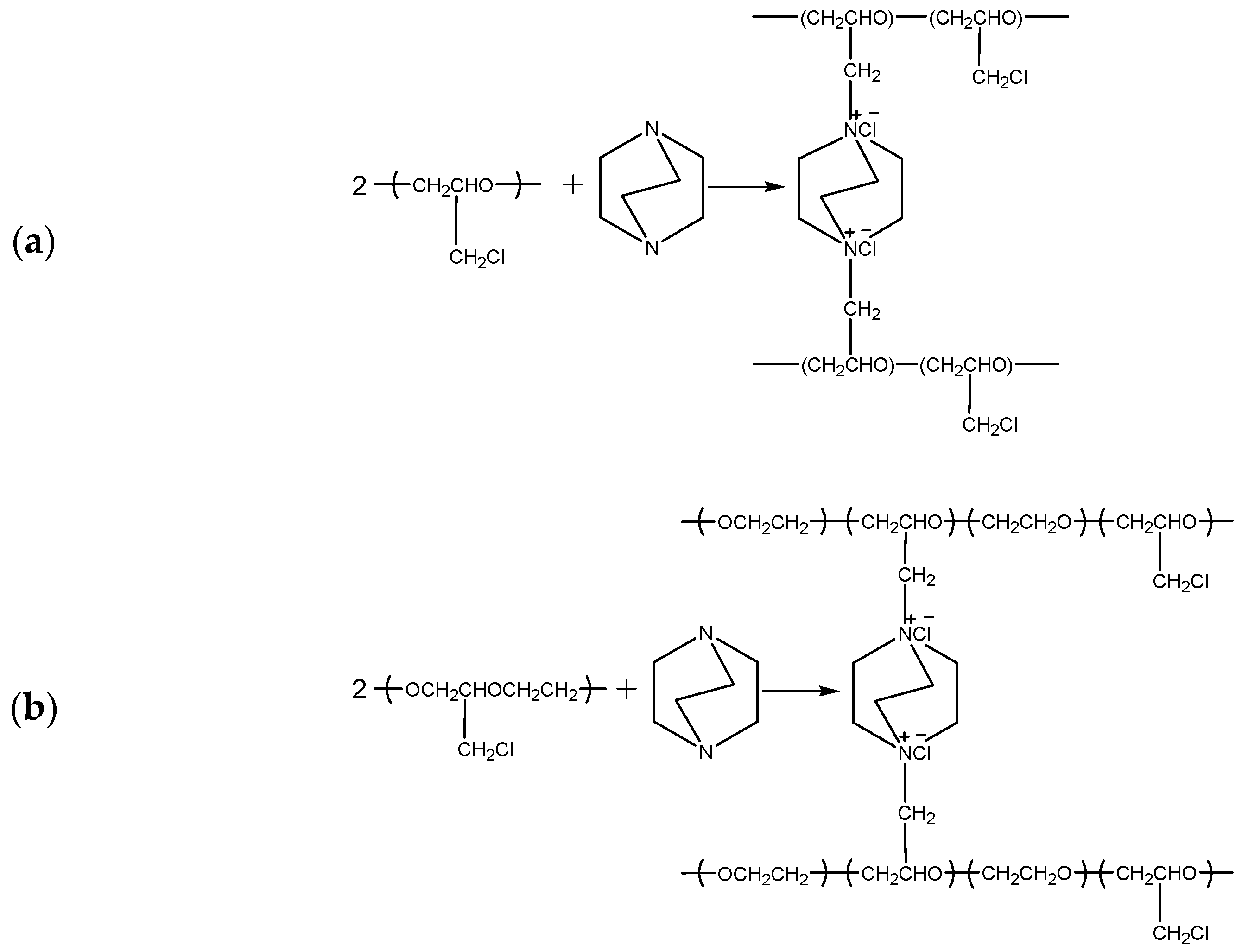



| Membrane | Thickness (µm) | IEC (mmol/g) | SD (%) | Cfix (mmol/g H2O) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PECH-H AEM | 154 | 2.02 | 20.88 | 9.70 |
| PECH-C AEM | 160 | 1.47 | 25.56 | 5.70 |
| Neosepta AMX | 134 | 1.40 | 26.00 | 5.40 |
| Neosepta CMX | 158 | 1.62 | 18.00 | 9.00 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Karakoç, E.; Güler, E. Comparison of Physicochemical Properties of Two Types of Polyepichlorohydrin-Based Anion Exchange Membranes for Reverse Electrodialysis. Membranes 2022, 12, 257. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12030257
Karakoç E, Güler E. Comparison of Physicochemical Properties of Two Types of Polyepichlorohydrin-Based Anion Exchange Membranes for Reverse Electrodialysis. Membranes. 2022; 12(3):257. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12030257
Chicago/Turabian StyleKarakoç, Ezgi, and Enver Güler. 2022. "Comparison of Physicochemical Properties of Two Types of Polyepichlorohydrin-Based Anion Exchange Membranes for Reverse Electrodialysis" Membranes 12, no. 3: 257. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12030257
APA StyleKarakoç, E., & Güler, E. (2022). Comparison of Physicochemical Properties of Two Types of Polyepichlorohydrin-Based Anion Exchange Membranes for Reverse Electrodialysis. Membranes, 12(3), 257. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12030257







