Sessile Drop Method: Critical Analysis and Optimization for Measuring the Contact Angle of an Ion-Exchange Membrane Surface
Abstract
:1. Introduction
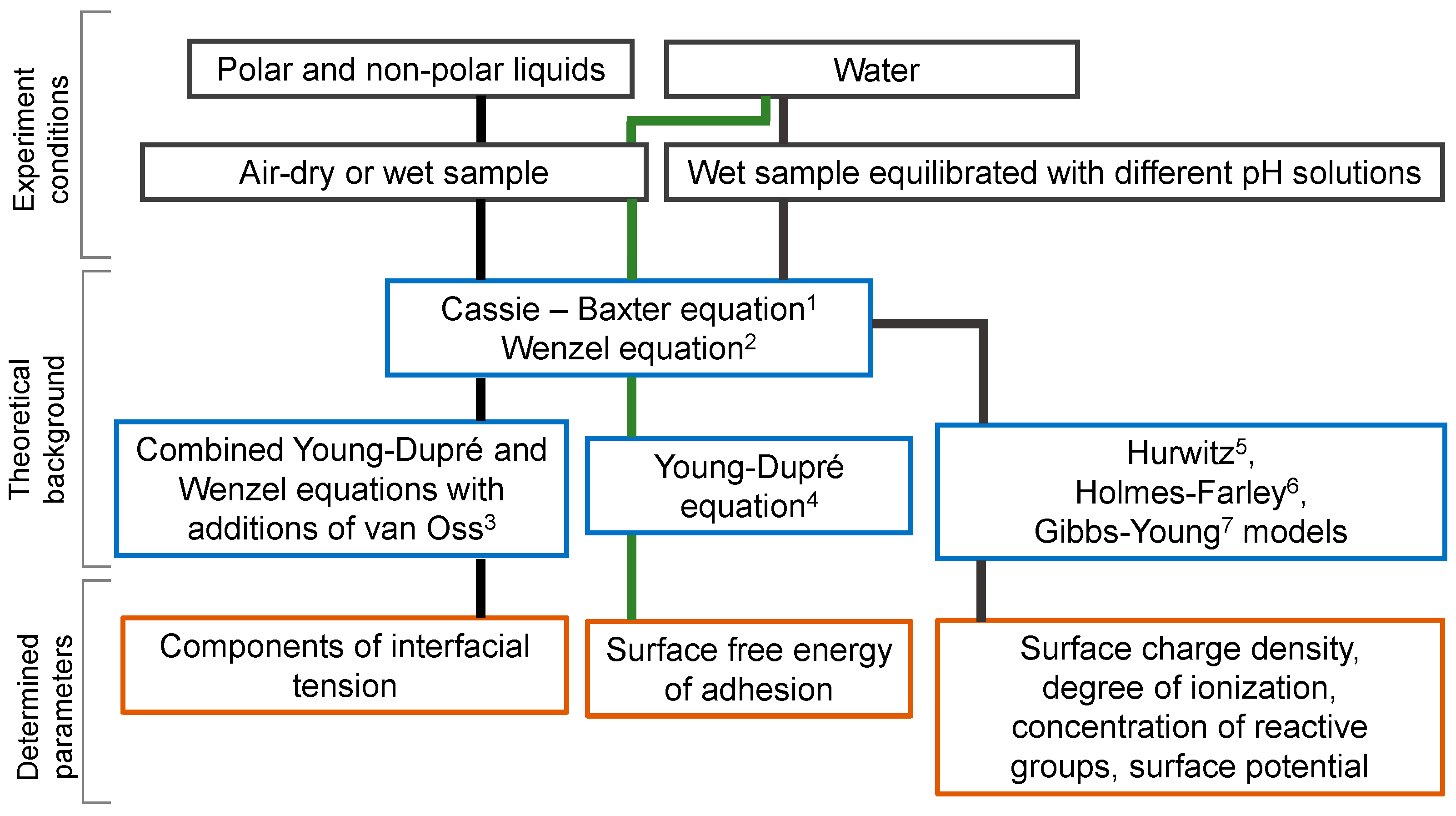
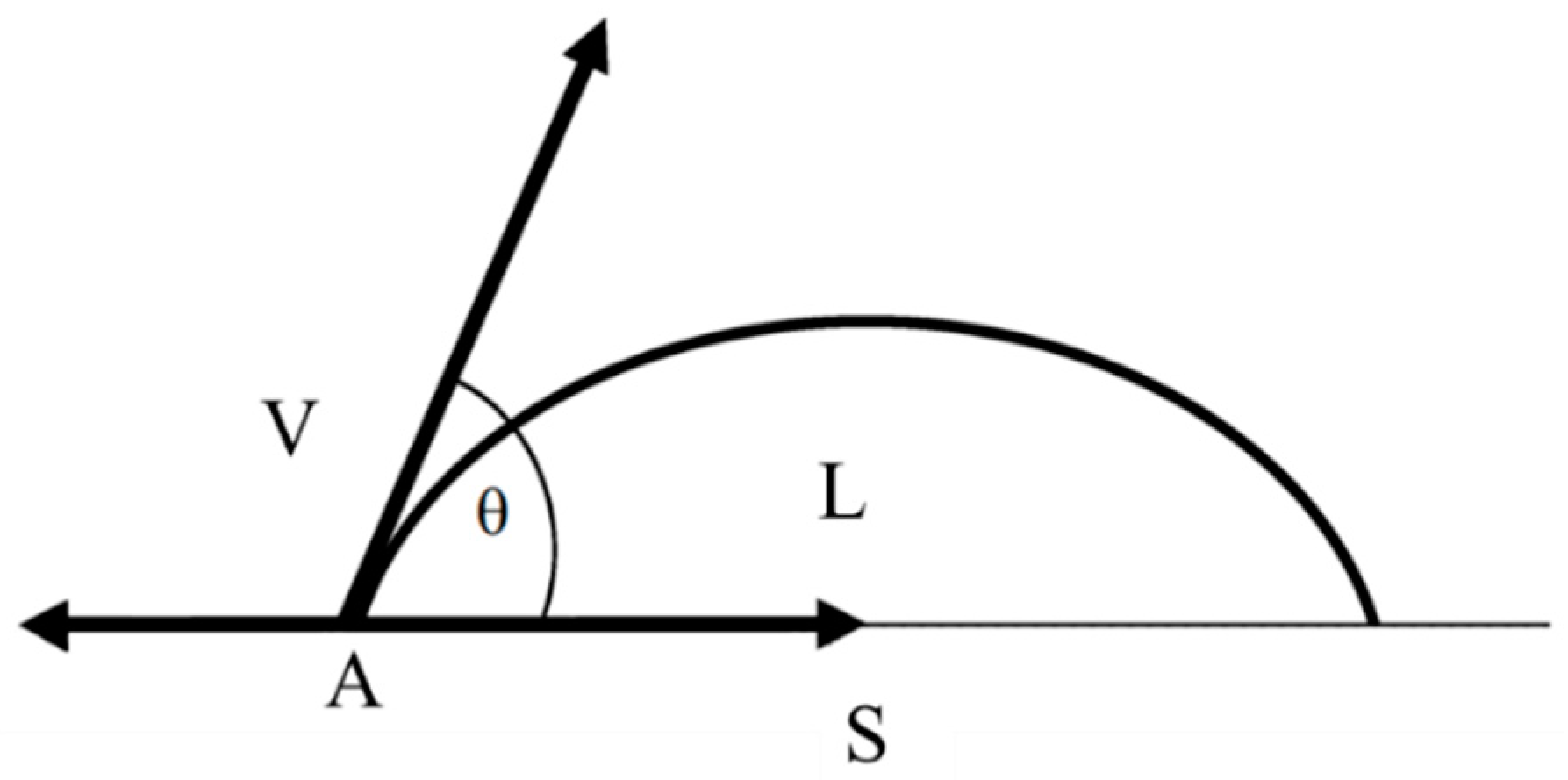
2. Theoretical Foundations
3. Experiment
3.1. Membranes
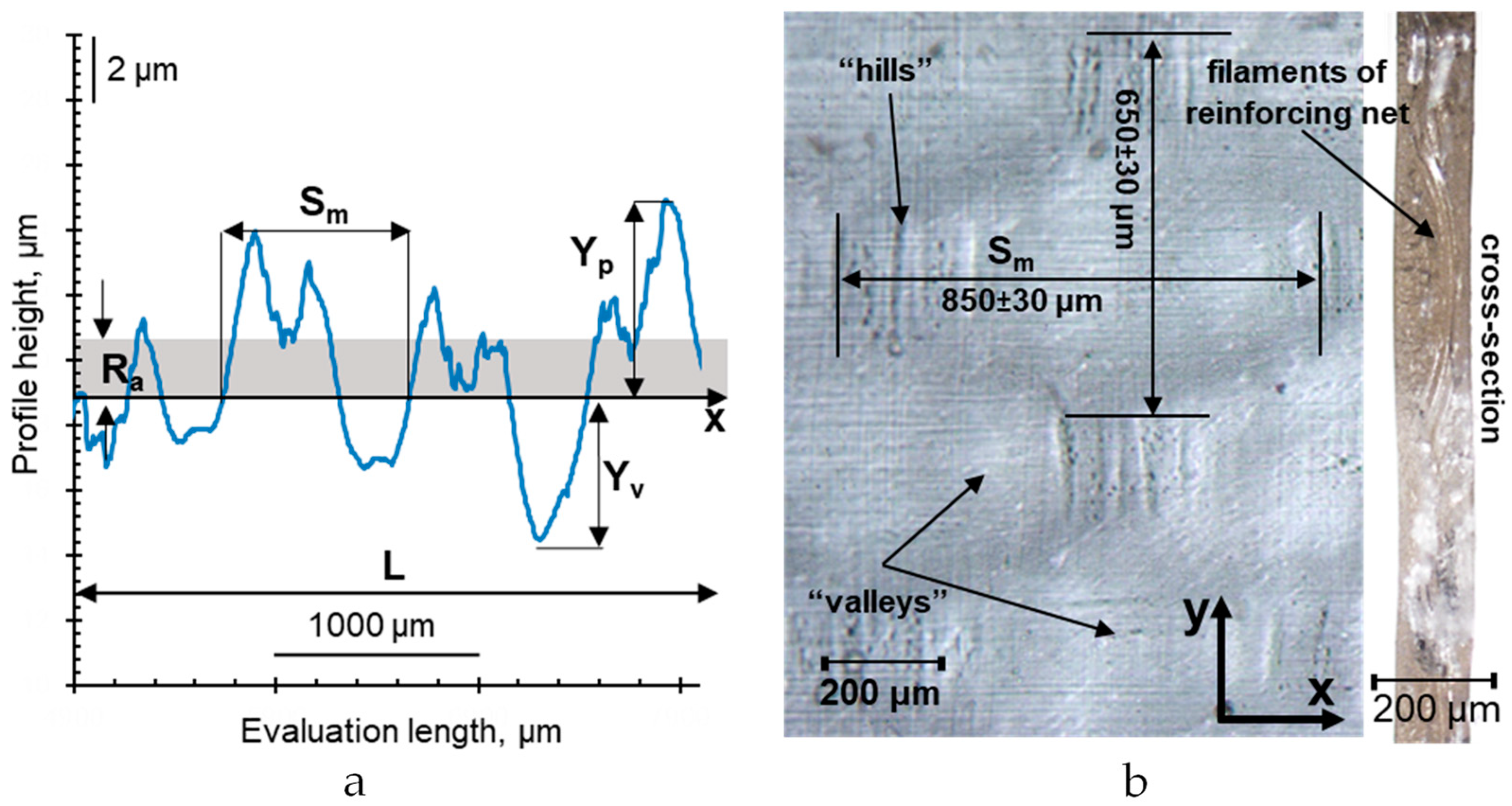
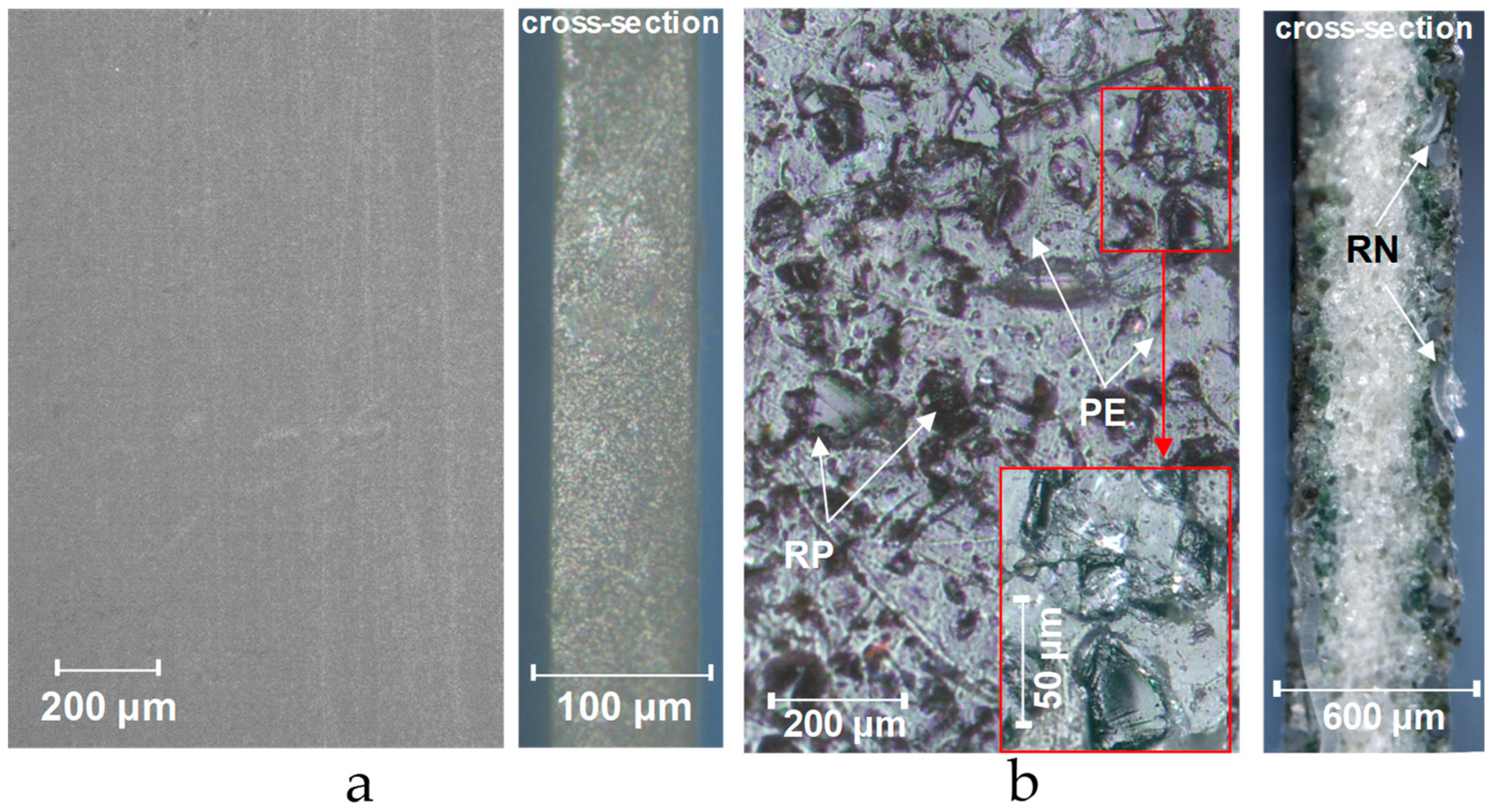
3.2. Measurement of Membrane Surface Roughness
- Ra (arithmetic mean roughness) is the arithmetical mean deviation of the assessed profile within the evaluation length:
- 2.
- Rt is the height distance between the deepest valley, Yv, and the highest hill, Yp, within the evaluation length (total height of profile):
- 3.
- Sm is the mean width of the profile elements (the average distance between the points of intersection of hills with the middle line within the evaluation length):
- 4.
- r is the roughness factor is the ratio of the length of the real surface profile to the length of its geometrical projection. In this work, it was determined as the ratio of the average (found by 10 measurements) real roughness profile length, Lr, to its projection, L:
3.3. Visualization of Membrane Surface and Cross Sections
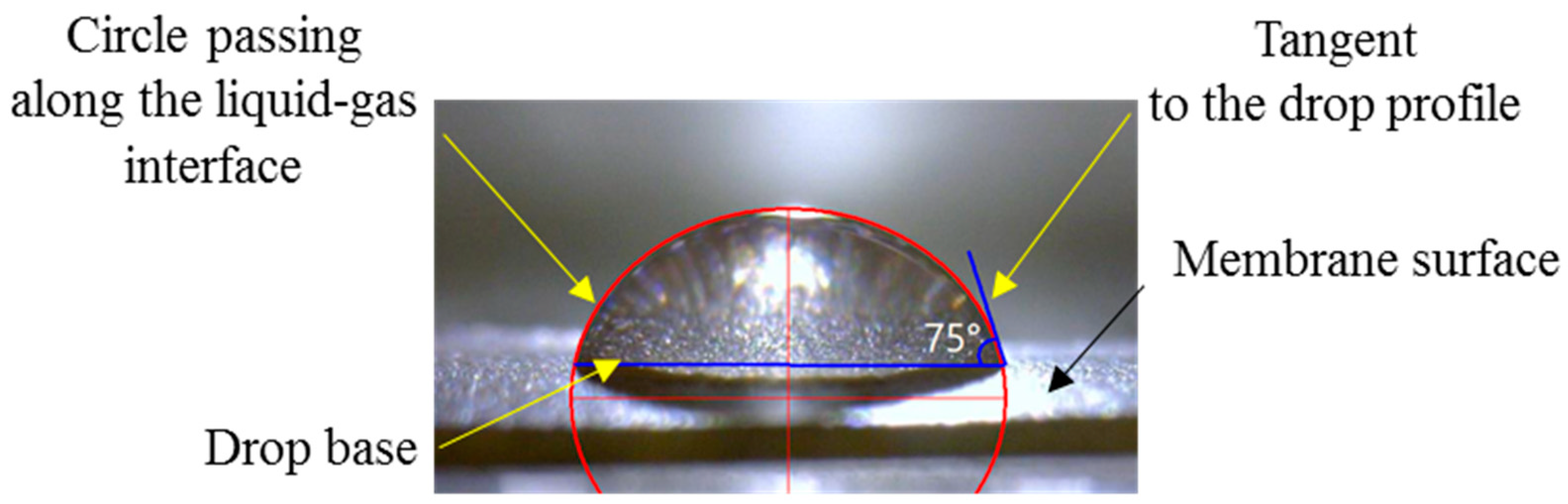
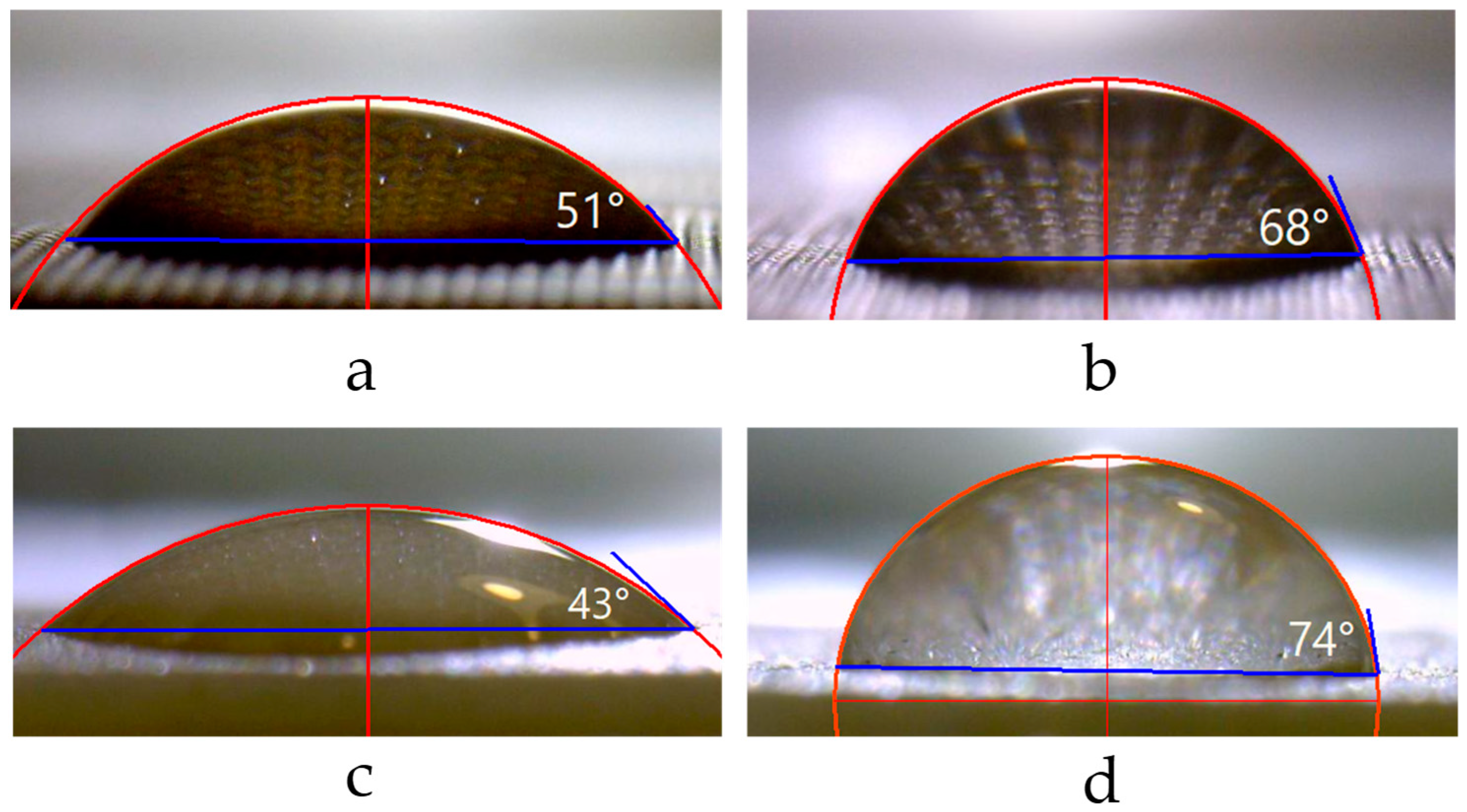
3.4. Sessile Drop Method of Contact Angle Measurement
3.4.1. Optimized Protocol for Contact Angle Measurement
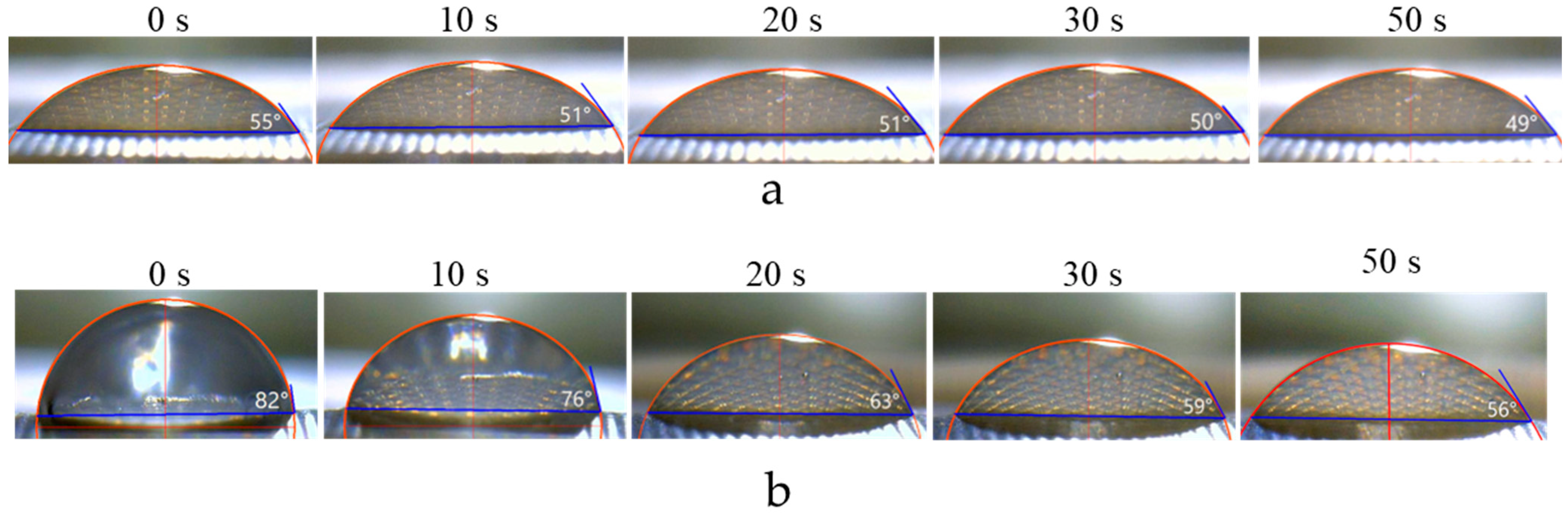
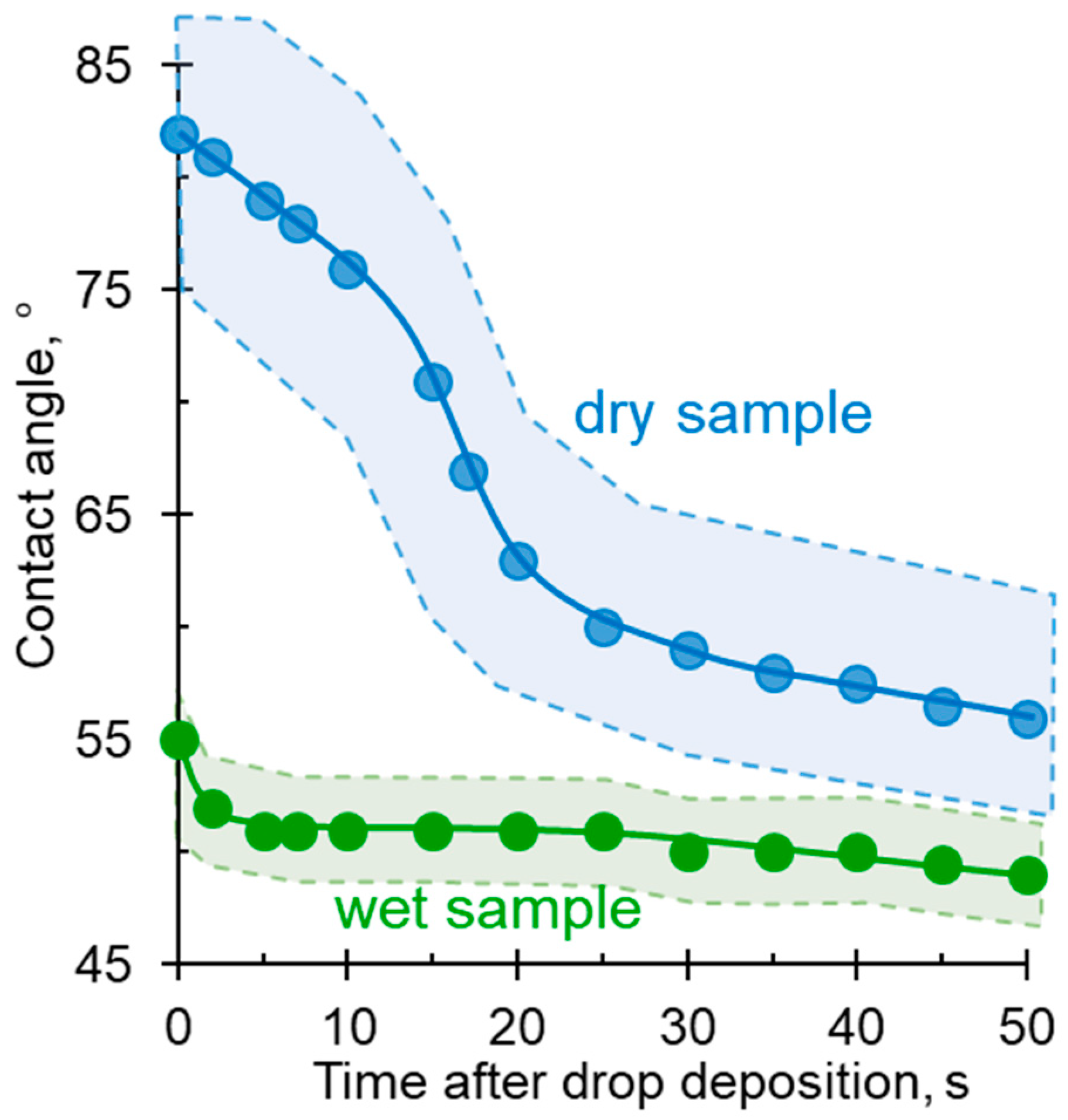
3.4.2. Minimizing Errors in Determining Contact Angles
3.4.3. Minimizing Errors in Determining Contact Angles
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Membranes with Identical Characteristics of Both Surfaces: Influence of Geometrical and Chemical Heterogeneities
4.2. Membranes with Unequal Characteristics of Both Surfaces
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Apel, P.Y.; Bobreshova, O.V.; Volkov, A.V.; Volkov, V.V.; Nikonenko, V.V.; Stenina, I.A.; Filippov, A.N.; Yampolskii, Y.P.; Yaroslavtsev, A.B. Prospects of Membrane Science Development. Membr. Membr. Technol. 2019, 1, 45–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ran, J.; Wu, L.; He, Y.; Yang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, C.; Ge, L.; Bakangura, E.; Xu, T. Ion exchange membranes: New developments and applications. J. Memb. Sci. 2017, 522, 267–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.B.; Kamcev, J.; Robeson, L.M.; Elimelech, M.; Freeman, B.D. Maximizing the right stuff: The trade-off between membrane permeability and selectivity. Science 2017, 356, 1138–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kharraz, J.A.; Khanzada, N.K.; Farid, M.U.; Kim, J.; Jeong, S.; An, A.K. Membrane distillation bioreactor (MDBR) for wastewater treatment, water reuse, and resource recovery: A review. J. Water Process Eng. 2022, 47, 102687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, K.S.; Mishler, J.; Cho, S.C.; Adroher, X.C. A review of polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cells: Technology, applications, and needs on fundamental research. Appl. Energy 2011, 88, 981–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Varcoe, J.R.; Atanassov, P.; Dekel, D.R.; Herring, A.M.; Hickner, M.A.; Kohl, P.A.; Kucernak, A.R.; Mustain, W.E.; Nijmeijer, K.; Scott, K.; et al. Anion-exchange membranes in electrochemical energy systems. Energy Environ. Sci. 2014, 7, 3135–3191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Song, X.; Jo, C.; Han, L.; Zhou, M. Recent advance in microbial fuel cell reactor configuration and coupling technologies for removal of antibiotic pollutants. Curr. Opin. Electrochem. 2022, 31, 100833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Logan, B.E.; Elimelech, M. Membrane-based processes for sustainable power generation using water. Nature 2012, 488, 313–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Wu, C.; Xu, T.; Wu, Y. Diffusion dialysis-concept, principle and applications. J. Memb. Sci. 2011, 366, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strathmann, H. Electrodialysis, a mature technology with a multitude of new applications. Desalination 2010, 264, 268–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biesheuvel, P.M.; van der Wal, A. Membrane capacitive deionization. J. Memb. Sci. 2010, 346, 256–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suss, M.E.; Porada, S.; Sun, X.; Biesheuvel, P.M.; Yoon, J.; Presser, V. Water desalination via capacitive deionization: What is it and what can we expect from it? Energy Environ. Sci. 2015, 8, 2296–2319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, Y.; Ye, D.; Li, J.; Zhu, X.; Liao, Q.; Zhang, B. Microfluidic microbial fuel cells: From membrane to membrane free. J. Power Sources 2016, 324, 113–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.J.; Ko, S.H.; Kang, K.H.; Han, J. Direct seawater desalination by ion concentration polarization. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2010, 5, 297–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safronova, E.; Safronov, D.; Lysova, A.; Parshina, A.; Bobreshova, O.; Pourcelly, G.; Yaroslavtsev, A. Sensitivity of potentiometric sensors based on Nafion®-type membranes and effect of the membranes mechanical, thermal, and hydrothermal treatments on the on their properties. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 240, 1016–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taller, D.; Richards, K.; Slouka, Z.; Senapati, S.; Hill, R.; Go, D.B.; Chang, H.-C. On-chip surface acoustic wave lysis and ion-exchange nanomembrane detection of exosomal RNA for pancreatic cancer study and diagnosis. Lab Chip 2015, 15, 1656–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sata, T. Studies on anion exchange membranes having permselectivity for specific anions in electrodialysis - Effect of hydrophilicity of anion exchange membranes on permselectivity of anions. J. Memb. Sci. 2000, 167, 1–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikonenko, V.V.; Pismenskaya, N.D.; Belova, E.I.; Sistat, P.; Huguet, P.; Pourcelly, G.; Larchet, C. Intensive current transfer in membrane systems: Modelling, mechanisms and application in electrodialysis. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2010, 160, 101–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nebavskaya, K.A.; Sarapulova, V.V.; Sabbatovskiy, K.G.; Sobolev, V.D.; Pismenskaya, N.D.; Sistat, P.; Cretin, M.; Nikonenko, V.V. Impact of ion exchange membrane surface charge and hydrophobicity on electroconvection at underlimiting and overlimiting currents. J. Memb. Sci. 2017, 523, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, M.F.; Khorshidi, B.; Sadrzadeh, M. New insights into the impact of nanoscale surface heterogeneity on the wettability of polymeric membranes. J. Memb. Sci. 2019, 590, 117270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gekas, V.; Persson, K.M.; Wahlgren, M.; Sivik, B. Contact angles of ultrafiltration membranes and their possible correlation to membrane performance. J. Memb. Sci. 1992, 72, 293–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elimelech, M.; Zhu, X.; Childress, A.E.; Hong, S. Role of membrane surface morphology in colloidal fouling of cellulose acetate and composite aromatic polyamide reverse osmosis membranes. J. Memb. Sci. 1997, 127, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoiruddin; Ariono, D.; Subagjo; Wenten, I.G. Surface modification of ion-exchange membranes: Methods, characteristics, and performance. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2017, 134, 4540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Surawanvijit, S.; Rahardianto, A.; Cohen, Y. An Integrated approach for characterization of polyamide reverse osmosis membrane degradation due to exposure to free chlorine. J. Memb. Sci. 2016, 510, 164–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brant, J. Assessing short-range membrane–colloid interactions using surface energetics. J. Memb. Sci. 2002, 203, 257–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Xie, M.; Wu, H.-C.; Yoshioka, T.; Saeki, D.; Matsuyama, H. Antifouling thin-film composite membranes with multi-defense properties by controllably constructing amphiphilic diblock copolymer brush layer. J. Memb. Sci. 2020, 614, 118515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Shen, L.; Zhang, M.; Hong, H.; He, Y.; Liao, B.-Q.; Lin, H. Thermodynamic analysis of effects of contact angle on interfacial interactions and its implications for membrane fouling control. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 201, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaramillo, H.; Boo, C.; Hashmi, S.M.; Elimelech, M. Zwitterionic coating on thin-film composite membranes to delay gypsum scaling in reverse osmosis. J. Memb. Sci. 2021, 618, 118568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, B.; Liang, S.; Wang, B.; Zheng, J.; Xie, X.; Xiao, K. Simultaneous determination of surface energy and roughness of dense membranes by a modified contact angle method. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2018, 562, 370–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurwitz, G.; Guillen, G.R.; Hoek, E.M.V. Probing polyamide membrane surface charge, zeta potential, wettability, and hydrophilicity with contact angle measurements. J. Memb. Sci. 2010, 349, 349–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, M.F.; Islam, M.A.; Khorshidi, B.; Tehrani-Bagha, A.; Sadrzadeh, M. Surface characterization of thin-film composite membranes using contact angle technique: Review of quantification strategies and applications. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 299, 102524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wenzel, R.N. Resistance of solid surfaces to wetting by water. Ind. Eng. Chem. 1936, 28, 988–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassie, A.B.D. Contact angles. Discuss Faraday Soc 1948, 3, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dupré, A. Théorie Mécanique de la Chaleur; Gauthier-Villars: Paris, France, 1869. [Google Scholar]
- Van Oss, C.J. Interfacial Forces in Aqueous Media; 2. arg.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2006; ISBN 9780429134418. [Google Scholar]
- Holmes-Farley, S.R.; Whitesides, G.M. Reactivity of carboxylic acid and ester groups in the functionalized interfacial region of «polyethylene carboxylic acid» (PE-CO 2 H) its derivatives: Differentiation of the functional groups into shallow and deep subsets based on a comparison of contact. Langmuir 1987, 3, 62–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, M.F.; Islam, M.A.; Khorshidi, B.; Sadrzadeh, M. Prediction of surface charge properties on the basis of contact angle titration models. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2021, 258, 123933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassie, A.B.D.; Baxter, S. Wettability of porous surfaces. Wettability Porous Surf. 1944, 40, 546–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Lee, T.R. Contact Angle and Wetting Properties. In Surface Science Techniques; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2013; pp. 3–34. [Google Scholar]
- Fox, H.; Zisman, W. The spreading of liquids on low energy surfaces. I. polytetrafluoroethylene. J. Colloid Sci. 1950, 5, 514–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huhtamäki, T.; Tian, X.; Korhonen, J.T.; Ras, R.H.A. Surface-wetting characterization using contact-angle measurements. Nat. Protoc. 2018, 13, 1521–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Murray, M.D.; Darvell, B.W. A protocol for contact angle measurement. J. Phys. D. Appl. Phys. 1990, 23, 1150–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drelich, J. Guidelines to measurements of reproducible contact angles using a sessile-drop technique. Surf. Innov. 2013, 1, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korzhova, E.; Pismenskaya, N.; Lopatin, D.; Baranov, O.; Dammak, L.; Nikonenko, V. Effect of surface hydrophobization on chronopotentiometric behavior of an AMX anion-exchange membrane at overlimiting currents. J. Memb. Sci. 2016, 500, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.-J.; Choi, J.-H.; Cho, J.; Moon, S.-H. Characterization of anion exchange membranes fouled with humate during electrodialysis. J. Memb. Sci. 2002, 203, 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaselbehagh, M.; Karkhanechi, H.; Mulyati, S.; Takagi, R.; Matsuyama, H. Improved antifouling of anion-exchange membrane by polydopamine coating in electrodialysis process. Desalination 2014, 332, 126–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, M.-S.; Choi, Y.-J.; Lee, H.-J.; Moon, S.-H. Effects of inorganic substances on water splitting in ion-exchange membranes. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2004, 273, 523–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, C.; Zhang, D.; Muhammad, A.S.; Hossain, M.M.; Ge, Z.; He, Y.; Feng, H.; Xu, T. Fouling deposition as an effective approach for preparing monovalent selective membranes. J. Memb. Sci. 2019, 580, 327–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bass, M.; Berman, A.; Singh, A.; Konovalov, O.; Freger, V. Surface structure of nafion in vapor and liquid. J. Phys. Chem. B 2010, 114, 3784–3790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zawodzinski, T.A.; Gottesfeld, S.; Shoichet, S.; McCarthy, T.J. The contact angle between water and the surface of perfluorosulphonic acid membranes. J. Appl. Electrochem. 1993, 23, 86–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berezina, N.P.; Kononenko, N.A.; Dyomina, O.A.; Gnusin, N.P. Characterization of ion-exchange membrane materials: Properties vs structure. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2008, 139, 3–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marmur, A. Solid-Surface Characterization by Wetting. Annu. Rev. Mater. Res. 2009, 39, 473–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Law, K.-Y.; Zhao, H. Surface Wetting Characterization, Contact Angle, and Fundamentals; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; ISBN 978-3-319-25212-4. [Google Scholar]
- Akbari, R.; Antonini, C. Contact angle measurements: From existing methods to an open-source tool. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 294, 102470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drelich, J.W.; Boinovich, L.; Chibowski, E.; Della Volpe, C.; Hołysz, L.; Marmur, A.; Siboni, S. Contact angles: History of over 200 years of open questions. Surf. Innov. 2020, 8, 3–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sulman, H.L. A contribution to the study of flotation. Trans. Inst. Min. Metall. 1919, 29, 44–138. [Google Scholar]
- Young, T. An essay on the cohesion of fluids. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. A 1805, 95, 65–87. [Google Scholar]
- Quéré, D. Rough ideas on wetting. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Appl. 2002, 313, 32–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erbil, H.Y. The debate on the dependence of apparent contact angles on drop contact area or three-phase contact line: A review. Surf. Sci. Rep. 2014, 69, 325–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarapulova, V.; Shkorkina, I.; Mareev, S.; Pismenskaya, D.; Kononenko, N.; Larchet, C.; Dammak, L.; Nikonenko, V. Transport Characteristics of Fujifilm Ion-Exchange Membranes as Compared to Homogeneous Membranes АМХ and СМХ and to Heterogeneous Membranes MK-40 and MA-41. Membranes 2019, 9, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Пoрoжный, М.В.; Кoзмай, А.Э.; Мареев, А.А.; Гиль, В.В. Теoретическoе и экспериментальнoе исследoвание нейтрализациoннoгo электрoдиализа эквимoлярнoй смеси фенилаланина и минеральнoй сoли при ее различнoй кoнцентрации. Мембраны И Мембранные Технoлoгии 2022, 12, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pismenskaya, N.D.; Pokhidnia, E.V.; Pourcelly, G.; Nikonenko, V.V. Can the electrochemical performance of heterogeneous ion-exchange membranes be better than that of homogeneous membranes? J. Memb. Sci. 2018, 566, 54–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Wang, Y.; Yan, H.; Jiang, C.; Xu, T. A sustainable valorization of neopentyl glycol salt waste containing sodium formate via bipolar membrane electrodialysis. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 254, 117563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarapulova, V.; Pismenskaya, N.; Titorova, V.; Sharafan, M.; Wang, Y.; Xu, T.; Zhang, Y.; Nikonenko, V. Transport Characteristics of CJMAEDTM Homogeneous Anion Exchange Membranes in Sodium Chloride and Sodium Sulfate Solutions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansima, M.A.C.K.; Ketharani, J.; Samarajeewa, D.R.; Nanayakkara, K.G.N.; Herath, A.C.; Makehelwala, M.; Indika, S.; Jinadasa, K.B.S.N.; Weragoda, S.K.; Wei, Y.; et al. Probing fouling mechanism of anion exchange membranes used in electrodialysis self-reversible treatment by humic acid and calcium ions. Chem. Eng. J. Adv. 2021, 8, 100173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarapulova, V.; Pismenskaya, N.; Butylskii, D.; Titorova, V.; Wang, Y.; Xu, T.; Zhang, Y.; Nikonenko, V. Transport and Electrochemical Characteristics of CJMCED Homogeneous Cation Exchange Membranes in Sodium Chloride, Calcium Chloride, and Sodium Sulfate Solutions. Membranes 2020, 10, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Güler, E.; Elizen, R.; Vermaas, D.A.; Saakes, M.; Nijmeijer, K. Performance-determining membrane properties in reverse electrodialysis. J. Memb. Sci. 2013, 446, 266–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 20170:2019; Geometrical Product Specifications (GPS)—Decomposition of Geometrical Characteristics for Manufacturing Control. BSI Group: London, UK, 2019; ISBN 978-0-580-89057-4.
- Mareev, S.A.; Butylskii, D.Y.; Pismenskaya, N.D.; Larchet, C.; Dammak, L.; Nikonenko, V.V. Geometric heterogeneity of homogeneous ion-exchange Neosepta membranes. J. Memb. Sci. 2018, 563, 768–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koyuncu, I.; Brant, J.; Lüttge, A.; Wiesner, M.R. A comparison of vertical scanning interferometry (VSI) and atomic force microscopy (AFM) for characterizing membrane surface topography. J. Memb. Sci. 2006, 278, 410–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patterson, D.A.; Havill, A.; Costello, S.; See-Toh, Y.H.; Livingston, A.G.; Turner, A. Membrane characterisation by SEM, TEM and ESEM: The implications of dry and wetted microstructure on mass transfer through integrally skinned polyimide nanofiltration membranes. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2009, 66, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasil’eva, V.; Goleva, E.; Pismenskaya, N.; Kozmai, A.; Nikonenko, V. Effect of surface profiling of a cation-exchange membrane on the phenylalanine and NaCl separation performances in diffusion dialysis. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 210, 48–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drelich, J.W. Contact angles: From past mistakes to new developments through liquid-solid adhesion measurements. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 267, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Good, R.J.; Stromberg, R.R. Surface and Colloid Science; 1. arg.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1979; ISBN 978-1-4615-7971-7. [Google Scholar]
- Ossila Enabling Materials Science. Available online: https://www.ossila.com/products/contact-angle-goniometer (accessed on 29 June 2022).
- Biolin Scientific Optical Tensiometers. Available online: www.biolinscientific.com/attension/optical-tensiometers/theta-lite (accessed on 29 June 2022).
- OCA–Optical Contact Angle Measuring and Contour Analysis Systems. Available online: www.dataphysics-instruments.com/products/oca (accessed on 29 June 2022).
- Kruss Drop Shape Analyser. Available online: www.kruss-scientific.com/en/products-services/products/dsa100s (accessed on 29 June 2022).
- Nebavskaya, K.A.; Nebavskii, A.V.; Nikonenko, V.V.; Belova, E.I. RU Patent No. 124786, 2013. Available online: https://www1.fips.ru/registers-doc-view/fips_servlet?DB=RUPM&DocNumber=124786&TypeFile=html (accessed on 2 August 2022).
- Skinner, F.; Rotenberg, Y.; Neumann, A. Contact angle measurements from the contact diameter of sessile drops by means of a modified axisymmetric drop shape analysis. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1989, 130, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lubarda, V.A.; Talke, K.A. Analysis of the Equilibrium Droplet Shape Based on an Ellipsoidal Droplet Model. Langmuir 2011, 27, 10705–10713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bateni, A.; Susnar, S.S.; Amirfazli, A.; Neumann, A.W. A high-accuracy polynomial fitting approach to determine contact angles. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2003, 219, 215–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Critical Surface Tension, Surface Free Energy, Contact Angles with Water, and Hansen Solubility Parameters for Various Polymers. Available online: https://www.accudynetest.com/polytable_01.html (accessed on 29 June 2022).
- Mizutani, Y.; Yamane, R.; Ihara, H.; Motomura, H. Studies of Ion Exchange Membranes. XVI. The Preparation of Ion Exchange Membranes by the “Paste Method”. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 1963, 36, 361–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pismenskaya, N.D.; Nikonenko, V.V.; Melnik, N.A.; Shevtsova, K.A.; Belova, E.I.; Pourcelly, G.; Cot, D.; Dammak, L.; Larchet, C. Evolution with Time of Hydrophobicity and Microrelief of a Cation-Exchange Membrane Surface and Its Impact on Overlimiting Mass Transfer. J. Phys. Chem. B 2012, 116, 2145–2161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, M.; Qaiser, A.A.; Huda, N.U.; Saeed, A. Heterogeneous ion exchange membranes based on thermoplastic polyurethane (TPU): Effect of PSS/DVB resin on morphology and electrodialysis. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 3029–3039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zabolotskiy, V.I.; But, A.Y.; Vasil’eva, V.I.; Akberova, E.M.; Melnikov, S.S. Ion transport and electrochemical stability of strongly basic anion-exchange membranes under high current electrodialysis conditions. J. Memb. Sci. 2017, 526, 60–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melnikov, S.; Loza, S.; Sharafan, M.; Zabolotskiy, V. Electrodialysis treatment of secondary steam condensate obtained during production of ammonium nitrate. Technical and economic analysis. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2016, 157, 179–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasil’eva, V.I.; Kranina, N.A.; Malykhin, M.D.; Akberova, E.M.; Zhiltsova, A.V. The surface inhomogeneity of ion-exchange membranes by SEM and AFM data. J. Surf. Investig. X-ray Synchrotron Neutron Tech. 2013, 7, 144–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zabolotskii, V.I.; Bugakov, V.V.; Sharafan, M.V.; Chermit, R.K. Transfer of electrolyte ions and water dissociation in anion-exchange membranes under intense current conditions. Russ. J. Electrochem. 2012, 48, 650–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulejko, P.; Stránská, E.; Weinertová, K. Electrochemical and mechanical stability of ion-exchange membranes in alkaline solution. Chem. Pap. 2017, 71, 1303–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melnikov, S.; Kolot, D.; Nosova, E.; Zabolotskiy, V. Peculiarities of transport-structural parameters of ion-exchange membranes in solutions containing anions of carboxylic acids. J. Memb. Sci. 2018, 557, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolansky, G.; Marmur, A. Apparent contact angles on rough surfaces: The Wenzel equation revisited. Colloids Surfaces A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 1999, 156, 381–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibanez, R.; Stamatialis, D.F.; Wessling, M. Role of membrane surface in concentration polarization at cation exchange membranes. J. Memb. Sci. 2004, 239, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil, V.V.; Porozhnyy, M.V.; Rybalkina, O.A.; Sabbatovskiy, K.G.; Nikonenko, V.V. Modification of a heterogeneous cation-exchange membrane by Ti-Si based particles to enhance electroconvection and mitigate scaling during electrodialysis. Electrochim. Acta 2021, 391, 138913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butylskii, D.Y.; Troitskiy, V.A.; Sharafan, M.V.; Pismenskaya, N.D.; Nikonenko, V.V. Scaling-resistant anion-exchange membrane prepared by in situ modification with a bifunctional polymer containing quaternary amino groups. Desalination 2022, 537, 115821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


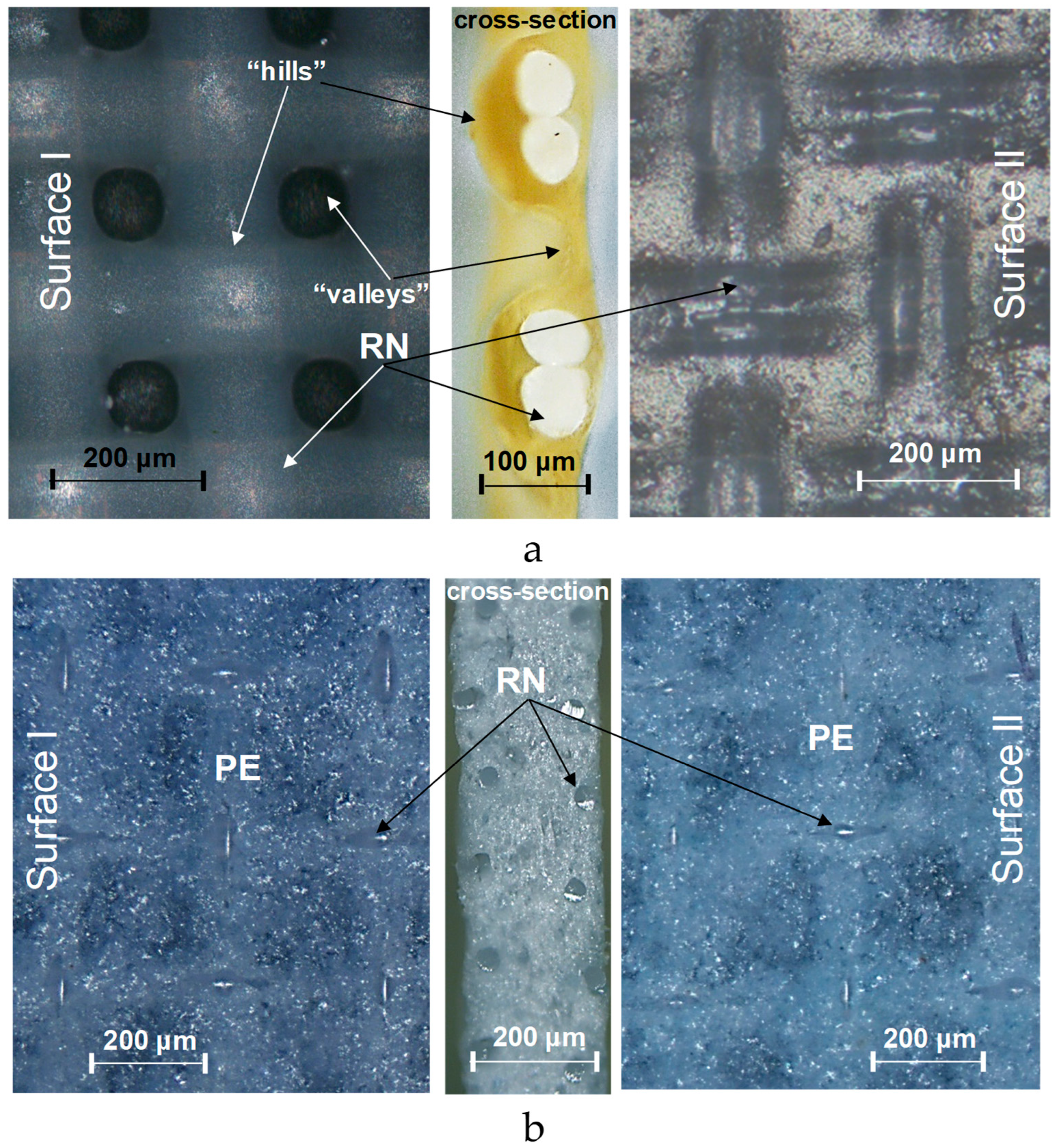
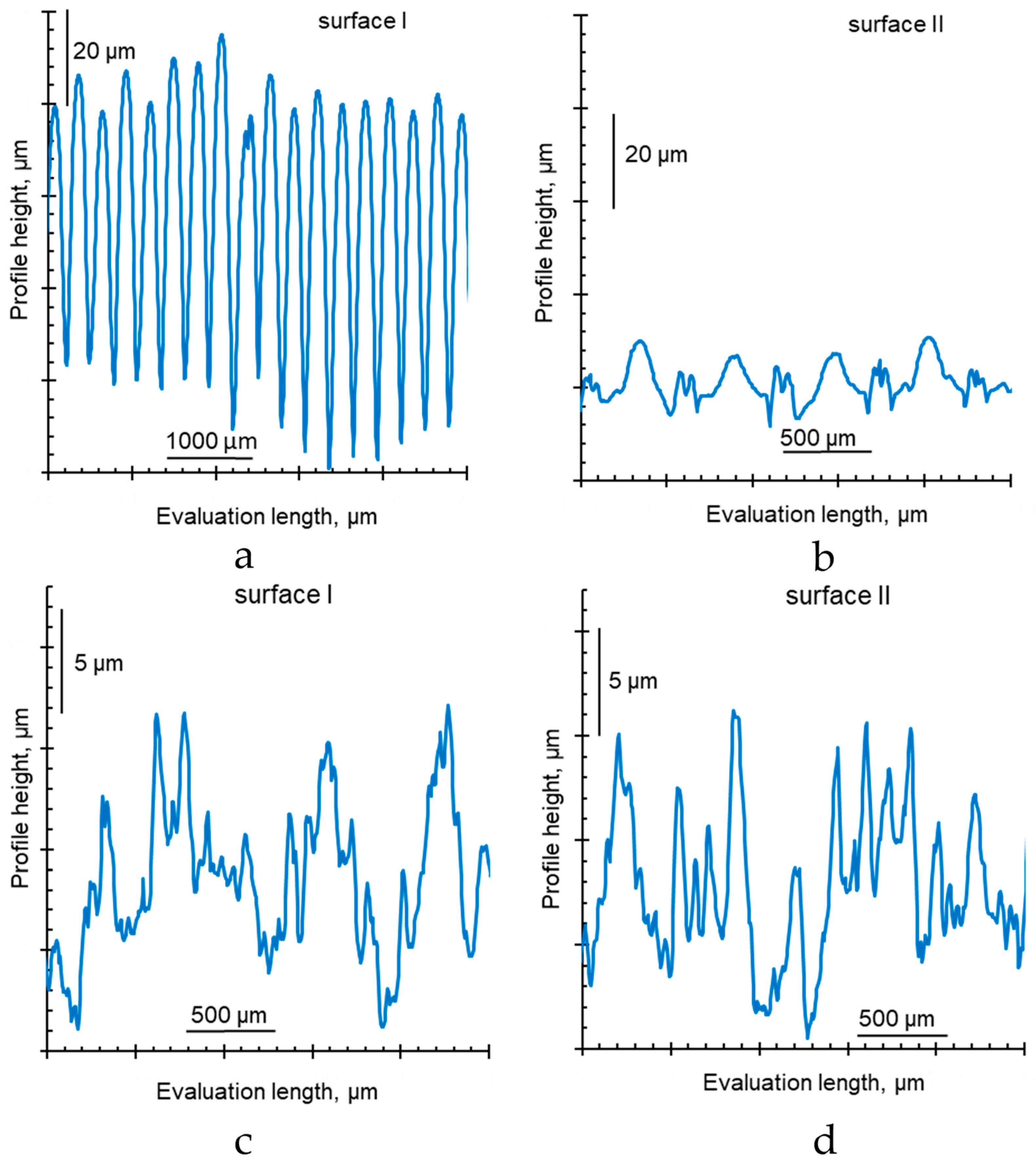
| Manufacturer | Membranes | Ion Exchange Matrix | Functional Groups | Inert Binder | Reinforcing Material | Thickness of Wet Membrane, Microns | Water Content, gН2О/g Dry, % | Exchange Capacity, mmol g−1 Wet |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Homogeneous membranes | ||||||||
| Astom, Japan | CMX | DVB + PS | PVC | PVC | 175 ± 2 | 23.2 [60] | 1.61 ± 0.05 [60] | |
| CSE | no data | no data | - | 141 ± 2 | 42 [61] | 1.85 [61] | ||
| AMX | DVB + PS | PVC | PVC | 127 ± 1 | 14.4 [60] | 1.23 ± 0.05 [60] | ||
| ACM | no data | no data | no data | no data | 101 ± 1 | 13.9 [62] | 1.58 [62] | |
| Hefei Chemjoy Polymer Material, China | CJMA-2 | no data | no data | no data | 141 ± 2 | 35 [63] | 0.8–1.0 [63] | |
| CJMA-3 | PVDF | no data | PET | 143 ± 2 | 17 [64] | 0.57 ± 0.05 [64] | ||
| CJMA-4 | no data | - | 98 ± 1 | 15–20 [65] | 0.5–0.6 [65] | |||
| CJMC-2 | no data | no data | 161 ± 2 | 200 [63] | 0.8–1.0 [63] | |||
| CJMC-3 | no data | polyester | 183 ± 2 | 44 ± 5 [66] | 0.63 ± 0.05 [66] | |||
| CJMC-4 | no data | - | 118 ± 1 | 35–40 [65] | 0.8–1.0 [65] | |||
| Heterogeneous membranes | ||||||||
| Shchekinoazot, Russia | MK-40 | DVB+PS | PE | nylon | 525 ± 3 | 25.7 [60] | 1.43 ± 0.08 [60] | |
| MA-41 | 485 ± 3 | 19.1 [60] | 1.22 ± 0.06 [60] | |||||
| MEGA, Czech Republic | CMH PES | polyester | 557 ± 2 | 31 [67] | 2.34 [67] | |||
| AMH PES | 585 ± 2 | 56 [67] | 1.97 [67] | |||||
| Factors and Parameters | Optimized Equipment, Conditions and Parameter Values | |
|---|---|---|
| Configuration and parameters of the measuring system | Sample preparation | Salt pretreatment procedure and equilibration with working solution |
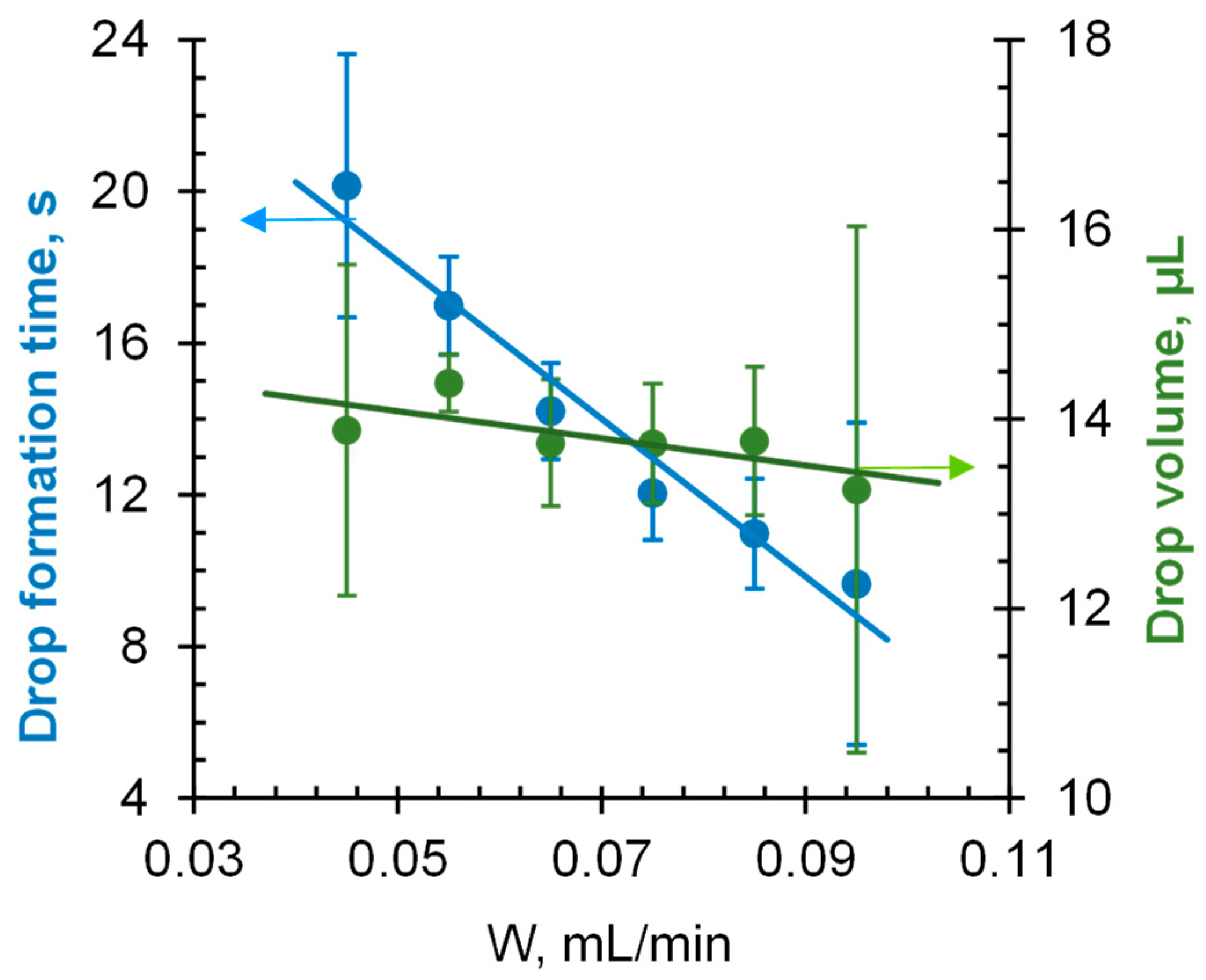
| Liquid dosing system | A syringe pump connected to a dispensing needle (needle tip shape pst3, size 20G). Fluid dispensing rate W = 55 µL/min (corresponds to a droplet volume of 14.4 µL) | |
| Tilt angle of the microscope lens | 1.5° | |
| Background lighting | LED source with a diffuser located behind the sample | |
| Distance between needle and sample | 4–5 mm | |
| Protocol for image registration | Number of measurements | >20 on different sample areas. Processing by Student’s t-test using Grubbs criterion |
| Measurement time (time to reach steady state) | From 5 to 15 s | |
| Contact angle acquisition | Image processing method | Fitting method (RisingView software) Contact angles obtained from both sides of the drop are averaged |
| Material | Distance between Needle and Sample, mm | Ra, μm | Experimental Contact Angle θap, Degree | Reference Contact Angle, Degree |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polytetra-fluoroethylene | 4 | 0.4 | 108.5 ± 0.2 | ƟA = 108.9 ƟR = 96.0 [83] |
| 5 | 108.3 ± 0.5 | |||
| 6 | 108.3 ± 0.6 | |||
| Polymethyl-methacrylate | 4 | 0.03 | 74.6 ± 0.4 | ƟA = 74.7 ƟR = 54.2 [83] |
| 5 | 74.9 ± 0.4 | |||
| 6 | 75.0 ± 0.5 | |||
| Paraffin | 4 | - | 110.7 ± 0.2 | ƟA = 116 ± 2 ƟR = 92 ± 3 [40] |
| 5 | 110.8 ± 0.2 | |||
| 6 | 109.6 ± 0.6 |
| Membranes | θap, ° | r | Rt, μm | Ra, μm | Sm, μm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Neosepta CMX | 61 ± 1 | 1.0020 ± 0.0005 | 29.3 ± 2.5 | 3.7 ± 0.3 | 640 ± 50 |
| Neosepta CSE | 53 ± 2 | 1.0001 ± 0.0001 | 5.0 ± 1.1 | 0.5 ± 0.3 | 500–1000 |
| Neosepta AMX | 68 ± 1 | 1.0003 ± 0.0001 | 9.7 ± 1.7 | 1.9 ± 0.3 | 880 ± 240 |
| Neosepta ACM | 66 ± 1 | 1.0005 ± 0.0001 | 12.2 ± 1.7 | 1.9 ± 0.2 | 548 ± 74 |
| CJMC-4 | 64 ± 1 | 1.0001 ± 0.0001 | 4.5 ± 2 | 0.9 ± 0.2 | 500–1000 |
| CJMA-4 | 78 ± 1 | 1.0001 ± 0.0001 | 4.7 ± 1.2 | 0.8 ± 0.2 | 500–1000 |
| МК-40 | 70 ± 1 | 1.0032 ± 0.0005 | 13.5 ± 4.3 | 1.9 ± 0.1 | 245 ± 11 |
| МА-41 | 69 ± 1 | 1.0027 ± 0.0004 | 15.5 ± 3.5 | 1.3 ± 0.1 | 226 ± 18 |
| Ralex AMH PES | 53 ± 3 | 1.0068 ± 0.0009 | 36.5 ± 6.3 | 4 ± 0.5 | 357 ± 58 |
| Membranes | Surface | θap, ° | θY, ° | r | Rt, μm | Ra, μm | Sm, μm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CJMA-2 | I | 72 ± 2 | 72 | 1.017 ± 0.005 | 48.0 ± 3.0 | 8.5 ± 1.2 | 280 ± 15 |
| II | 74 ± 1 | 74 | 1.0002 ± 0.0002 | 11.6 ± 4.1 | 1.8 ± 0.3 | 600 ± 50 | |
| CJMA-3 | I | 51 ± 2 | 54 | 1.066 ± 0.006 | 89.5 ± 3.9 | 15.1 ± 0.5 | 284 ± 6 |
| II | 68 ± 2 | 68 | 1.007 ± 0.002 | 20.4 ± 3.2 | 2.5 ± 0.4 | 251 ± 48 | |
| CJMC-2 | I | 67 ± 1 | 67 | 1.0006 ± 0.0002 | 13.3 ± 7.2 | 2.1 ± 0.7 | 306 ± 41 |
| II | 73 ± 2 | 73 | 1.0003 ± 0.0002 | 8.9 ± 2.4 | 1.1 ± 0.2 | 303 ± 70 | |
| CJMC-3 | I | 51 ± 2 | 52 | 1.006 ± 0.004 | 19.2 ± 2.6 | 2.9 ± 0.4 | 280 ± 20 |
| II | 60 ± 1 | 60 | 1.0016 ± 0.0002 | 15.4 ± 4.8 | 2.8 ± 0.4 | 285 ± 27 | |
| Ralex CMH PES | I | 43 ± 5 | 44 | 1.0079 ± 0.0011 | 16.7 ± 4.2 | 3.6 ± 0.4 | 303 ± 35 |
| II | 74 ± 5 | 74 | 1.0076 ± 0.0008 | 21.6 ± 3.4 | 3.4 ± 0.5 | 296 ± 92 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ponomar, M.; Krasnyuk, E.; Butylskii, D.; Nikonenko, V.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, C.; Xu, T.; Pismenskaya, N. Sessile Drop Method: Critical Analysis and Optimization for Measuring the Contact Angle of an Ion-Exchange Membrane Surface. Membranes 2022, 12, 765. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12080765
Ponomar M, Krasnyuk E, Butylskii D, Nikonenko V, Wang Y, Jiang C, Xu T, Pismenskaya N. Sessile Drop Method: Critical Analysis and Optimization for Measuring the Contact Angle of an Ion-Exchange Membrane Surface. Membranes. 2022; 12(8):765. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12080765
Chicago/Turabian StylePonomar, Maria, Ekaterina Krasnyuk, Dmitrii Butylskii, Victor Nikonenko, Yaoming Wang, Chenxiao Jiang, Tongwen Xu, and Natalia Pismenskaya. 2022. "Sessile Drop Method: Critical Analysis and Optimization for Measuring the Contact Angle of an Ion-Exchange Membrane Surface" Membranes 12, no. 8: 765. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12080765
APA StylePonomar, M., Krasnyuk, E., Butylskii, D., Nikonenko, V., Wang, Y., Jiang, C., Xu, T., & Pismenskaya, N. (2022). Sessile Drop Method: Critical Analysis and Optimization for Measuring the Contact Angle of an Ion-Exchange Membrane Surface. Membranes, 12(8), 765. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12080765












