Isolation of Carboxylic Acids and NaOH from Kraft Black Liquor with a Membrane-Based Process Sequence
Abstract
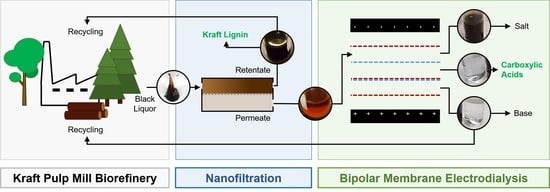
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. BL Feed Pretreatment by NF
2.3. EDBM Experiments
2.3.1. EDBM Treatment of BL Permeate
2.3.2. EDBM Treatment of BL Model Solution
2.4. Analyses
2.4.1. DM, Ash and pH Value
2.4.2. Lignin Content
2.4.3. Carboxylic Acid Content
2.5. Evaluation of EDBM Experiments
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. BL Feed Pretreatment by NF
3.2. EDBM Treatment of BL Permeate
3.3. EDBM Treatment of BL Model Solution
3.4. Evaluation of EDBM Experiments
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Van Heiningen, A. Converting a kraft pulp mill into an interated forest biorefinery. Pulp Pap. Can. 2006, 6, 141–146. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, H. Novel Concepts on the Recovery of By-Products from Alkaline Pulping; Research Report No. 198; University of Jyväskylä: Jyväskylä, Finland, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Alén, R. Combustion Behaviour of Black Liquors from Different Delignification Conditions. In 40 Years Recovery Boiler Co-Operation in Finland; Suomen Soodakattilayhdistys Finnish Recovery Boiler Committee: Porvoo, Finland, 2004; pp. 31–42. [Google Scholar]
- Sixta, H.; Potthast, A.; Krotschek, A. Chemical Pulping Processes. In Handbook of Pulp; Sixta, H., Ed.; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2006; Volume 1, pp. 109–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajpai, P. Pulping Fundamentals. In Biermann’s Handbook of Pulp and Paper Vol. 1 Raw Material and Pulp Making; Bajpai, P., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 295–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Liu, J.; Du, X.; Hu, Z.; Chang, H.-M.; Jameel, H. Phenolation to Improve Lignin Reactivity toward Thermosets Application. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 5504–5512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teguia, C.D.; Albers, R.; Stuart, P. Analysis of economically viable lignin-based biorefinery strategies implemented within a kraft pulp mill. TAPPI J. 2017, 16, 157–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubbe, M.; Alén, R.; Paleologou, M.; Kannangara, M.; Kihlman, J. Lignin recovery from spent alkaline pulping liquors using acidification, membrane separation, and related processing steps: A review. Bioresources 2019, 14, 2300–2351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sjöström, E. Wood Chemistry: Fundamentals and Applications, 2nd ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Bharate, S.S. Carboxylic Acid Counterions in FDA-Approved Pharmaceutical Salts. Pharm. Res. 2021, 38, 1307–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sengun, I.Y.; Karabiyikli, S. Importance of acetic acid bacteria in food industry. Food Control 2011, 22, 647–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Datta, R.; Henry, M. Lactic acid: Recent advances in products, processes and technologies—A review. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2006, 81, 1119–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alén, R.; Sjöström, E.; Suominen, S. Application of ion-exclusion chromatography to alkaline pulping liquors; separation of hydroxy carboxylic acids from inorganic solids. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 1991, 51, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, H.; Alén, R. Partial Recovery of Aliphatic Carboxylic Acids and Sodium Hydroxide from Hardwood Black Liquor by Electrodialysis. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2014, 53, 9464–9470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, H.; Alén, R. Recovery of aliphatic low-molecular-mass carboxylic acids from hardwood kraft black liquor. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2015, 142, 293–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mänttäri, M.; Lahti, J.; Hatakka, H.; Louhi-Kultanen, M.; Kallioinen, M. Separation phenomena in UF and NF in the recovery of organic acids from kraft black liquor. J. Membr. Sci. 2015, 490, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niemi, H.; Lahti, J.; Hatakka, H.; Kärki, S.; Rovio, S.; Kallioinen, M.; Mänttäri, M.; Louhi-Kultanen, M. Fractionation of Organic and Inorganic Compounds from Black Liquor by Combining Membrane Separation and Crystallization. Chem. Eng. Technol. 2011, 34, 593–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes, L.; Nikitine, C.; Vilcocq, L.; Fongarland, P. Green is the new black—A review of technologies for carboxylic acid recovery from black liquor. Green Chem. 2020, 22, 8097–8115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddad, M.; Bazinet, L.; Savadogo, O.; Paris, J. A feasibility study of a novel electro-membrane based process to acidify Kraft black liquor and extract lignin. Process. Saf. Environ. Prot. 2016, 106, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, A.; Bhattacharya, P. Alkaline black liquor treatment by continuous electrodialysis. J. Membr. Sci. 1987, 33, 83–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowe, J.; Gregor, H. Membrane Processes for Separation of Organic Acids from Kraft Black Liquors. U.S. Patent 4,584,057, 22 April 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, C.; Xu, T.; Zhang, Y.; Xue, Y.; Chen, G. Application of electrodialysis to the production of organic acids: State-of-the-art and recent developments. J. Membr. Sci. 2007, 288, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Mou, H.; Wang, L.; Matsuura, T. Membrane Filtration. In Handbook of Environmental Engineering, Vol. 4: Advanced Physicochemical Treatment Processes; Wang, L., Hung, Y., Shammas, N., Eds.; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2006; pp. 203–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R. Membrane Technology and Engineering for Water Purification: Application, Systems Design and Operation; Butterworth-Heinemann: Oxford, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Bazinet, L.; Lamarche, F.; Ippersiel, D. Bipolar-membrane electrodialysis: Applications of electrodialysis in the food industry. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 1998, 9, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Linden, N.; Bandinu, G.L.; Vermaas, D.A.; Spanjers, H.; van Lier, J.B. Bipolar membrane electrodialysis for energetically competitive ammonium removal and dissolved ammonia production. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 259, 120788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, C.A.E.; Pinto, P.C.R.; Rodrigues, A.E. Lignin fractionation from E. Globulus kraft liquor by ultrafiltration in a three stage membrane sequence. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2017, 192, 140–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaime-Ferrer, J.; Couallier, E.; Viers, P.; Durand, G.; Rakib, M. Three-compartment bipolar membrane electrodialysis for splitting of sodium formate into formic acid and sodium hydroxide: Role of diffusion of molecular acid. J. Membr. Sci. 2008, 325, 528–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moon, P.J.; Parulekar, S.J.; Tsai, S.-P. Competitive anion transport in desalting of mixtures of organic acids by batch electrodialysis. J. Membr. Sci. 1998, 141, 75–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lide, D. (Ed.) Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, 84th ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Samjeské, G.; Miki, A.; Ye, S.; Yamakata, A.; Mukouyama, Y.; Okamoto, H.; Osawa, M. Potential Oscillations in Galvanostatic Electrooxidation of Formic Acid on Platinum: A Time-Resolved Surface-Enhanced Infrared Study. J. Phys. Chem. B 2005, 109, 23509–23516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, J.R.; Chen, Y.; Baygents, J.C.; Farrell, J. Production of Acids and Bases for Ion Exchange Regeneration from Dilute Salt Solutions Using Bipolar Membrane Electrodialysis. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2015, 3, 2337–2342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Chen, G.Q.; Lin, L.; Li, X.; Kentish, S.E. Purification of organic acids using electrodialysis with bipolar membranes (EDBM) combined with monovalent anion selective membranes. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 279, 119739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Parameter | |
|---|---|
| Wood source | Hardwood |
| pH | 12.1 |
| Dry matter (DM) [%] | 29.1 |
| Sum measured carboxylic acids [g/kg] | 65.6 |
| Formic acid [g/kg] | 19.9 |
| Acetic acid [g/kg] | 34.0 |
| Glycolic acid [g/kg] | 2.4 |
| Lactic acid [g/kg] | 9.3 |
| lignin [g/kg] | 45 |
| Permeate cP/cFeed | Retentate cR/cFeed | |
|---|---|---|
| Lignin | 0.28 | 1.41 |
| Carboxylic Acids | 1.23 | 0.87 |
| DM | 0.78 | 1.18 |
| Ash | 0.88 | 1.09 |
| EDBM Treatment Time [h] | Electrical Energy Requirement [kWh/kgAcid] | |
|---|---|---|
| BL permeate | 1 | 1.8 |
| 9 | 2.6 | |
| BL model solution | 1 | 1.5 |
| 9 | 1.7 | |
| 25 | 2.5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Maitz, S.; Wernsperger, L.; Kienberger, M. Isolation of Carboxylic Acids and NaOH from Kraft Black Liquor with a Membrane-Based Process Sequence. Membranes 2023, 13, 92. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes13010092
Maitz S, Wernsperger L, Kienberger M. Isolation of Carboxylic Acids and NaOH from Kraft Black Liquor with a Membrane-Based Process Sequence. Membranes. 2023; 13(1):92. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes13010092
Chicago/Turabian StyleMaitz, Silvia, Lukas Wernsperger, and Marlene Kienberger. 2023. "Isolation of Carboxylic Acids and NaOH from Kraft Black Liquor with a Membrane-Based Process Sequence" Membranes 13, no. 1: 92. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes13010092
APA StyleMaitz, S., Wernsperger, L., & Kienberger, M. (2023). Isolation of Carboxylic Acids and NaOH from Kraft Black Liquor with a Membrane-Based Process Sequence. Membranes, 13(1), 92. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes13010092