Superwetting Stainless Steel Mesh Used for Both Immiscible Oil/Water and Surfactant-Stabilized Emulsion Separation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Underwater Super Oleophobic SSM
2.3. Preparation of Emulsions
2.4. Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
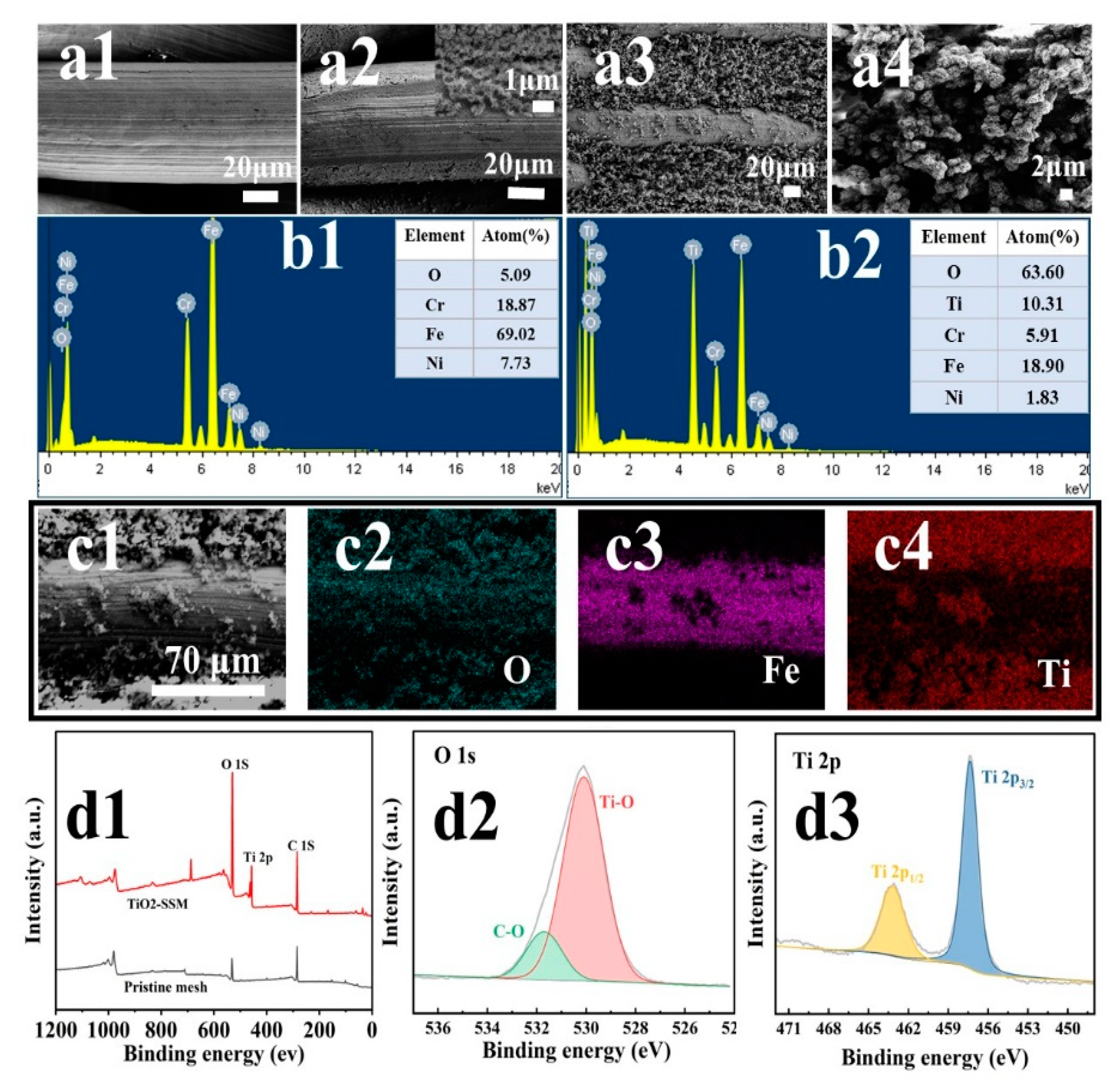
3.1. Characterization of Surface Structure and Composition
3.2. Surface Wettability of the SSM before and after Modification
3.3. Separation of Immiscible Mixtures of Light Oil–Water and Heavy Oil–Water
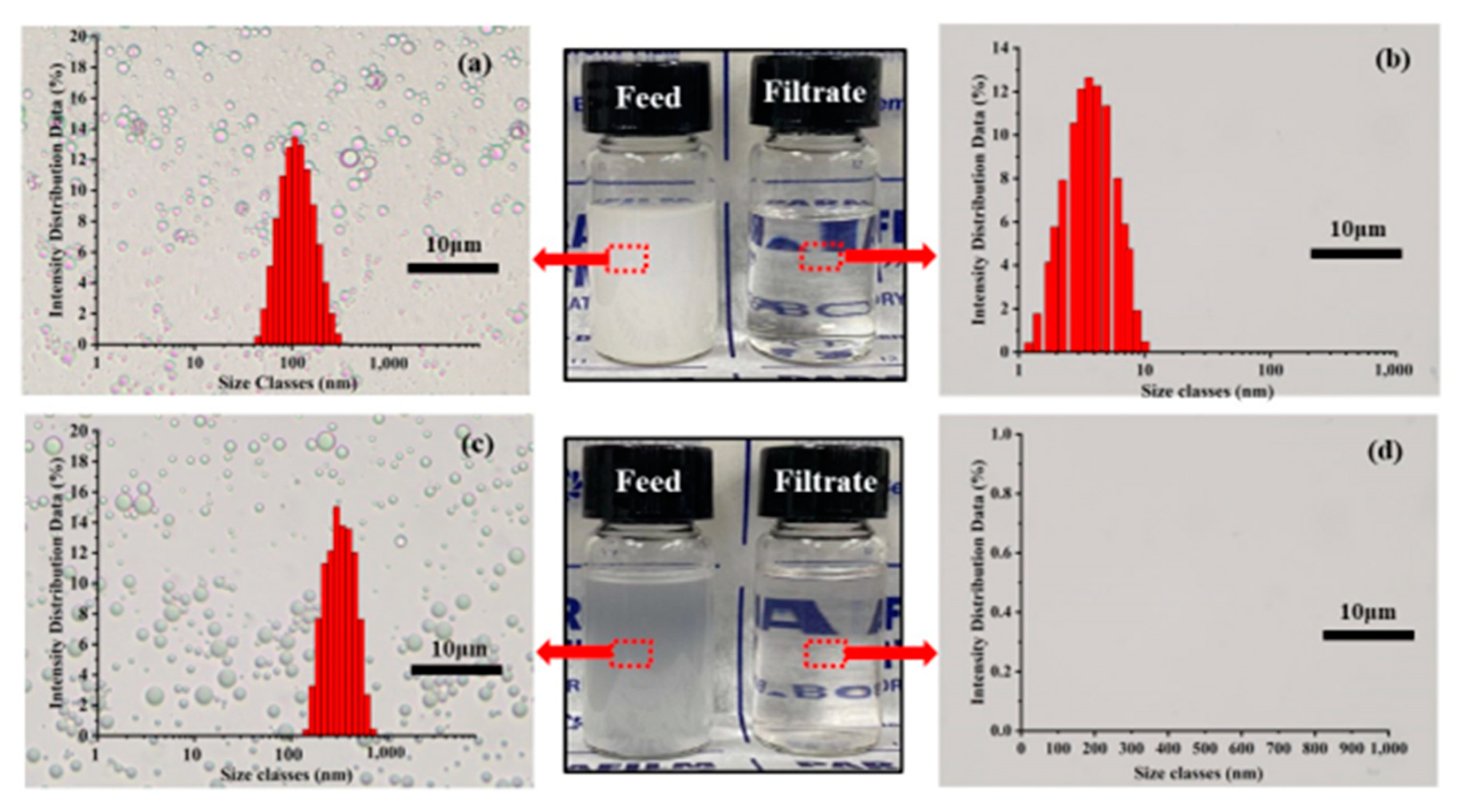
3.4. Emulsion Separation of Oil-in-Water and Water-in-Oil
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ferrer, C.; Isasi, J.; Arévalo, P.; Fernández-Ramos, M.; Rapp, M.; Alcolea, M.; Marco, J.F.; Martín-Hernández, F. Structural and magnetic studies of NiFe2O4 and NiFe2O4@SiO2-Silane agent samples useful for the removal of Cu2+ ions. J. Alloys Compd. 2022, 899, 163403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haleem, A.; Pan, J.M.; Shah, A.; Hussain, H.; He, W. A systematic review on new advancement and assessment of emerging polymeric cryogels for environmental sustainability and energy production. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 316, 123678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haleem, A.; Chen, J.; Guo, X.X.; Hou, S.C.; Chen, S.Q.; Siddiq, M.; He, W.D. Radiation-induced synthesis of hydrophobic cryogels with rapid and high absorption of organic solvents and oils. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2022, 330, 111486–111497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.P.; Yang, J.H.; Li, L.L.; Cui, C.X.; Li, Y.; Liu, S.Q.; Zhou, X.M.; Qu, L.B. Facile fabrication of superhydrophobic copper-foam and electrospinning polystyrene fiber for combinational oil-water separation. Polymers 2019, 11, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panda, S.K.; Singh, K.K.; Shenoy, K.T.; Buwa, V.V. Numerical simulations of liquid-liquid flow in a continuous gravity settler using OpenFOAM and experimental verification. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 310, 120–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, F.; Gao, M. Pore wettability for enhanced oil recovery, contaminant adsorption and oil/water separation: A review. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 289, 102377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghasemi Naghdi, F.; Schenk, P.M. Dissolved air flotation and centrifugation as methods for oil recovery from ruptured microalgal cells. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 218, 428–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Li, Q.; Yasir Akram, M.; Ali, S.; Nie, J.; Zhu, X. Decomposable Polyvinyl Alcohol-Based Super-Hydrophobic Three-Dimensional Porous Material for Effective Water/Oil Separation. Langmuir 2018, 34, 15700–15707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jun, B.-M.; Heo, J.; Taheri-Qazvini, N.; Park, C.M.; Yoon, Y. Adsorption of selected dyes on Ti3C2Tx MXene and Al-based metal-organic framework. Ceram. Int. 2020, 46, 2960–2968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, F.; Fang, W.; Jin, J. Membrane wettability manipulation via mixed-dimensional heterostructured surface towards highly efficient oil-in-water emulsion separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2023, 672, 121472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Wang, J.; Wu, J.; Wang, J.; Liu, F. Binary nanofibrous membranes with independent oil/water transport channels for durable emulsion separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2023, 673, 121484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanudjaja, H.J.; Hejase, C.A.; Tarabara, V.V.; Fane, A.G.; Chew, J.W. Membrane-based separation for oily wastewater: A practical perspective. Water Res. 2019, 156, 347–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dou, Y.L.; Yue, X.; Lv, C.J.; Yasin, A.; Hao, B.; Su, Y.; Ma, P.C. Dual-responsive polyacrylonitrile-based electrospun membrane for controllable oil-water separation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 438, 129565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, G.; Liu, Y.; Lin, Q.; Pu, S.; Zheng, S.; Ang, M.B.M.Y.; Chiao, Y.-H. Constructing composite membranes from functionalized metal organic frameworks integrated MXene intended for ultrafast oil/water emulsion separation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 293, 121052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Nian, P.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; Wang, Y.; Xu, N.; Wei, Y. Preparation of superhydrophobic superoleophilic ZnO nanoflower@SiC composite ceramic membranes for water-in-oil emulsion separation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 292, 121002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Gao, G.; Sheng, J.; Gao, X.; Wang, X.; Chen, S.; Yu, J. Renewable superhydrophobic PVB/SiO2 composite membranes with self-repairing for high-efficiency emulsion separation. Surf. Interfaces 2023, 36, 102543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, J.; Mao, H.; Zhou, S.; Zhou, L.; Wang, C.; Li, M.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, A.; Wu, Z. Self-cleaning catalytic membrane with super-wetting interface for high-efficiency oil-in-water emulsion separation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 312, 123381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Li, Y.; Li, H.; Zeng, X.; Pi, P.; Wen, X.; Xu, S.; Cheng, J. A self-cleaning titanium mesh with underwater superoleophobicity for oil/water separation and aqueous pollutant degradation. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2017, 313, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.P.; Sivalingam, K.; Shibu, M.A.; Peramaiyan, R.; Day, C.H.; Shen, C.Y.; Lai, C.H.; Chen, R.J.; Viswanadha, V.P.; Chen, Y.F.; et al. Protective effect of Fisetin against angiotensin II-induced apoptosis by activation of IGF-IR-PI3K-Akt signaling in H9c2 cells and spontaneous hypertension rats. Phytomedicine 2019, 57, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khashan, S.; Dagher, S.; Tit, N.; Alazzam, A.; Obaidat, I. Novel method for synthesis of Fe3O4@TiO2 core/shell nanoparticles. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2017, 322, 92–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Chen, Y.; Liu, N.; Cao, Y.; Xu, L.; Zhang, W.; Feng, L. In situ ultrafast separation and purification of oil/water emulsions by superwetting TiO2 nanocluster-based mesh. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 8525–8529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.; Bi, H.; Jia, H.; Su, S.; Dong, H.; Xie, X.; Sun, L. A low cost paper tissue-based PDMS/SiO2 composite for both high efficient oil absorption and water-in-oil emulsion separation. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 244, 118814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Chen, L.; Liu, S.; Hou, W.; Zhu, J.; Zhao, P.; Zhang, Q. Facile and sustainable fabrication of high-performance cellulose sponge from cotton for oil-in-water emulsion separation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 408, 124408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Kang, R.; Tang, X.; She, H.; Yang, Y.; Zha, F. Superhydrophobic meshes that can repel hot water and strong corrosive liquids used for efficient gravity-driven oil/water separation. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 7638–7645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, J.; Zhou, C.; Yang, Z.; Cheng, J.; Shen, Y.; Zeng, X.; Dong, L. Conversion of solid Cu2(OH)2CO3 into HKUST-1 metal-organic frameworks: Toward an under-liquid superamphiphobic surface. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2019, 363, 282–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, L.; Zhang, J.; Guo, Z.; Liu, W. Asymmetric superwetting stainless steel meshes for on-demand and highly effective oil-water emulsion separation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 273, 118994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Materials | Method | Wettability | Separation Target | Driving Force | Separation Efficiency | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TiO2@Cu mesh | Solvothermal method | Superamphiphilic | Water-in-oil Oil-in-water | Gravity | 99.97% | [21] |
| SiO2/PDMS composite | Immersing | Superhydrophobic | Water-in-oil | Gravity | >99.4% | [22] |
| Cellulose sponge | Dissolution and regeneration method | Superoleophobicity under water | Oil-in-water | Gravity | >99.2% | [23] |
| C@SiO2@SSM | Spraying | Superhydrophobic | Oil/water separation | Gravity | >99.0% | [24] |
| Copper mesh | In situ growth of MOF | Underwater superoleophobicity and underoil superhydrophobicity | Oil/water separation | Gravity | >97% | [25] |
| HDMS@SiO2@SSM | Spraying | Asymmetric wettability | Water-in-oil Oil-in-water | Gravity 4 Kpa | >98.6% >97.5% | [26] |
| TiO2@SSM | Solvothermal method | Superamphiphilic | Oil/water separation Water-in-oil Oil-in-water | Gravity Gravity Gravity | >98% >99.0% >99.0% | This work |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Y.-P.; Wang, Y.-N.; Wan, L.; Chen, X.-X.; Zhao, C.-H. Superwetting Stainless Steel Mesh Used for Both Immiscible Oil/Water and Surfactant-Stabilized Emulsion Separation. Membranes 2023, 13, 808. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes13100808
Zhang Y-P, Wang Y-N, Wan L, Chen X-X, Zhao C-H. Superwetting Stainless Steel Mesh Used for Both Immiscible Oil/Water and Surfactant-Stabilized Emulsion Separation. Membranes. 2023; 13(10):808. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes13100808
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Yu-Ping, Ya-Ning Wang, Li Wan, Xin-Xin Chen, and Chang-Hua Zhao. 2023. "Superwetting Stainless Steel Mesh Used for Both Immiscible Oil/Water and Surfactant-Stabilized Emulsion Separation" Membranes 13, no. 10: 808. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes13100808
APA StyleZhang, Y.-P., Wang, Y.-N., Wan, L., Chen, X.-X., & Zhao, C.-H. (2023). Superwetting Stainless Steel Mesh Used for Both Immiscible Oil/Water and Surfactant-Stabilized Emulsion Separation. Membranes, 13(10), 808. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes13100808





