Fabrication of Cellulose Acetate-Based Proton Exchange Membrane with Sulfonated SiO2 and Plasticizers for Microbial Fuel Cell Applications
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Sulfonated SiO2
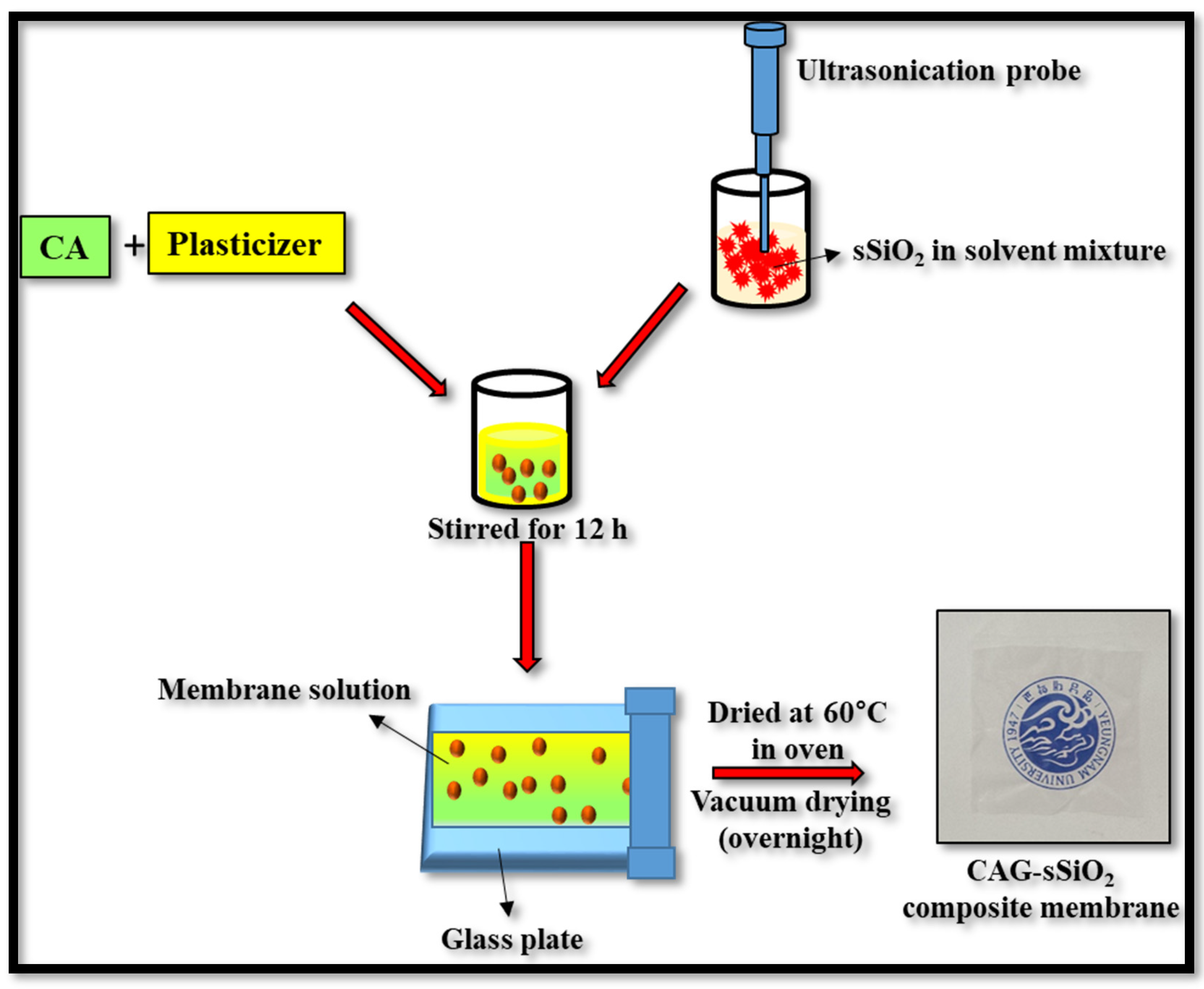
2.3. Membrane Fabrication
2.4. Membrane Characterization
Mechanical Properties
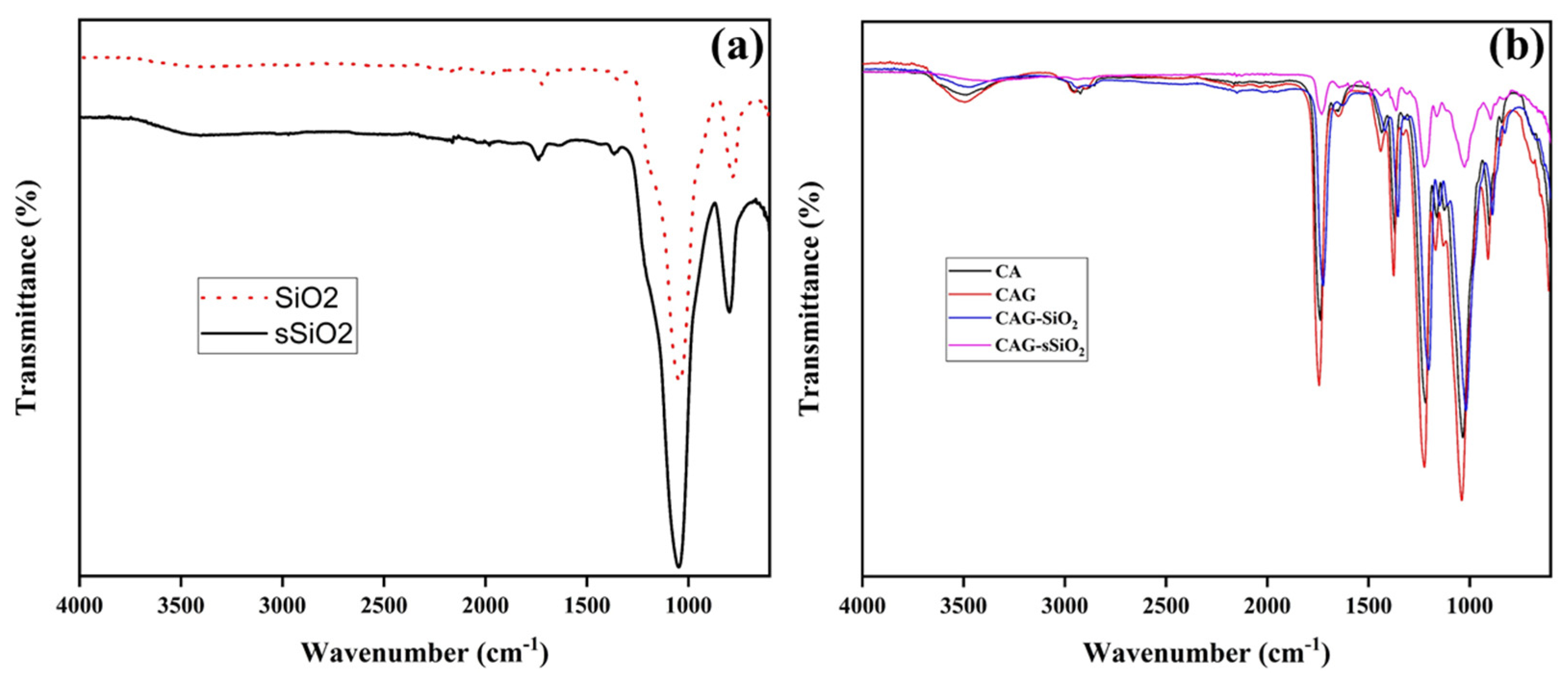
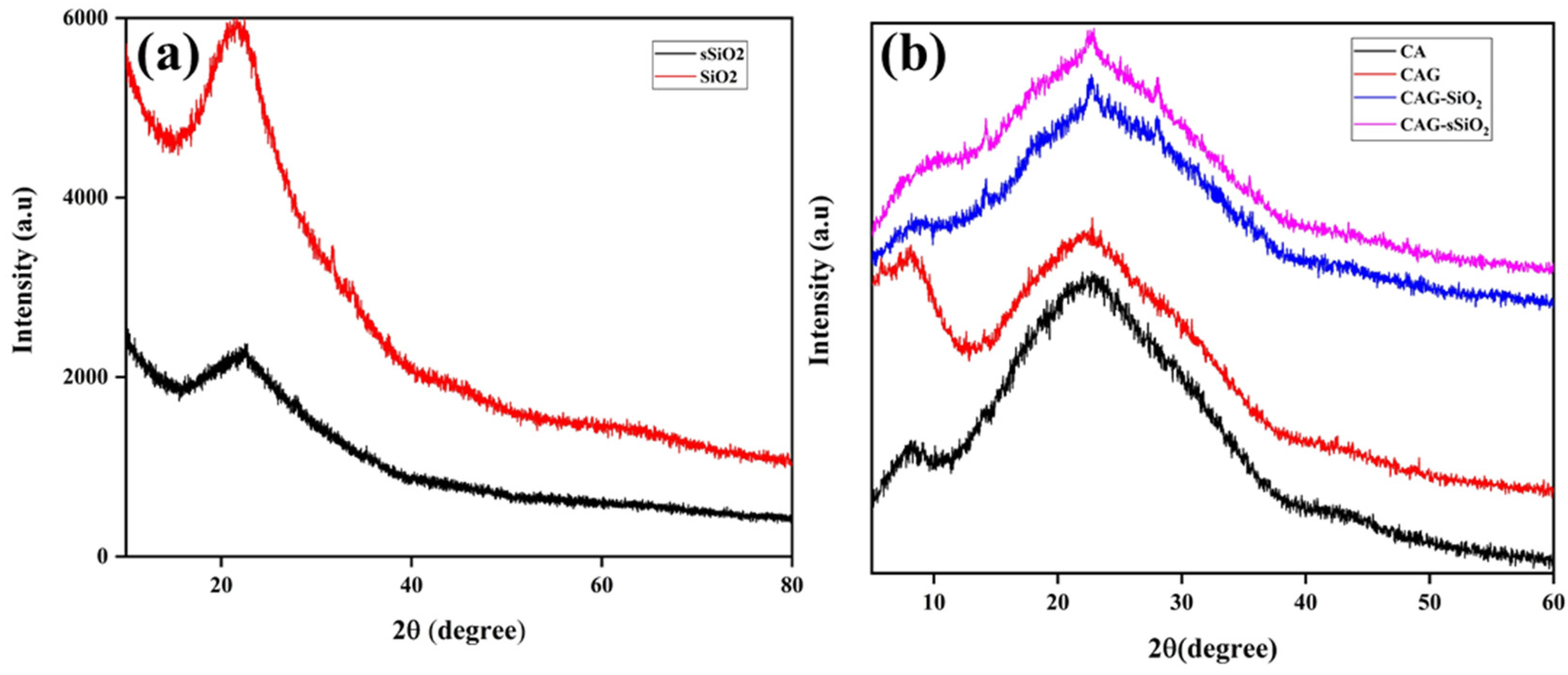
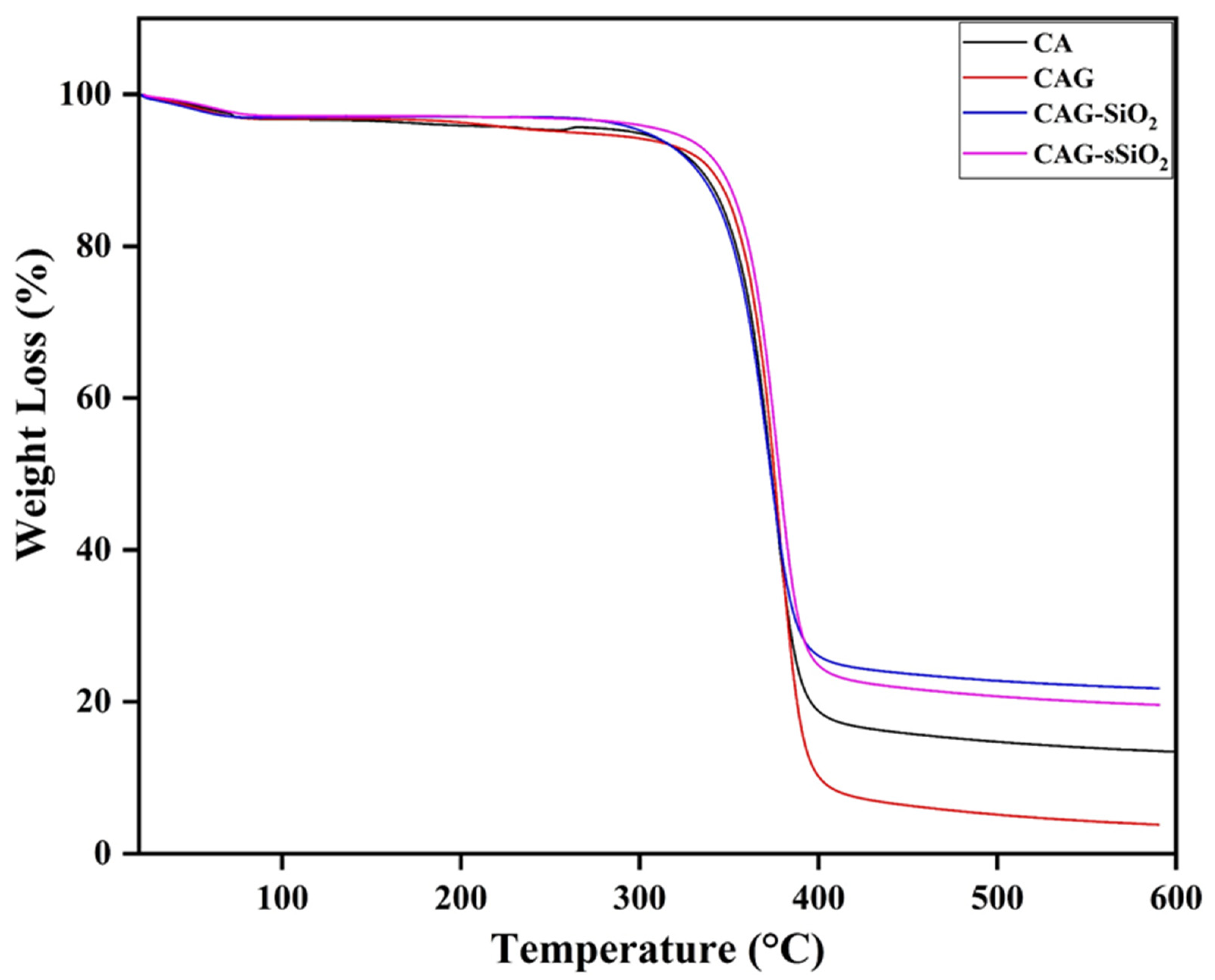
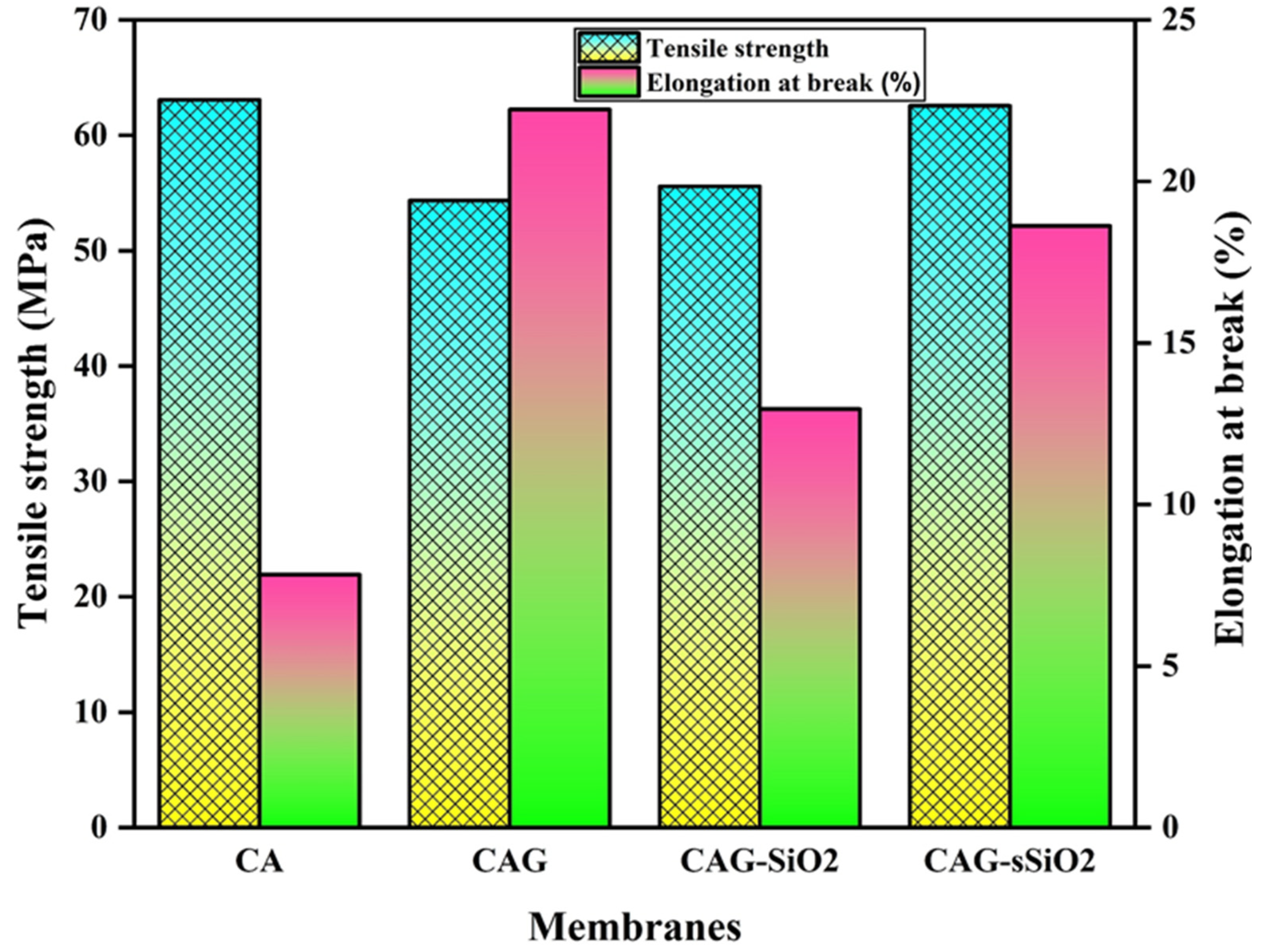
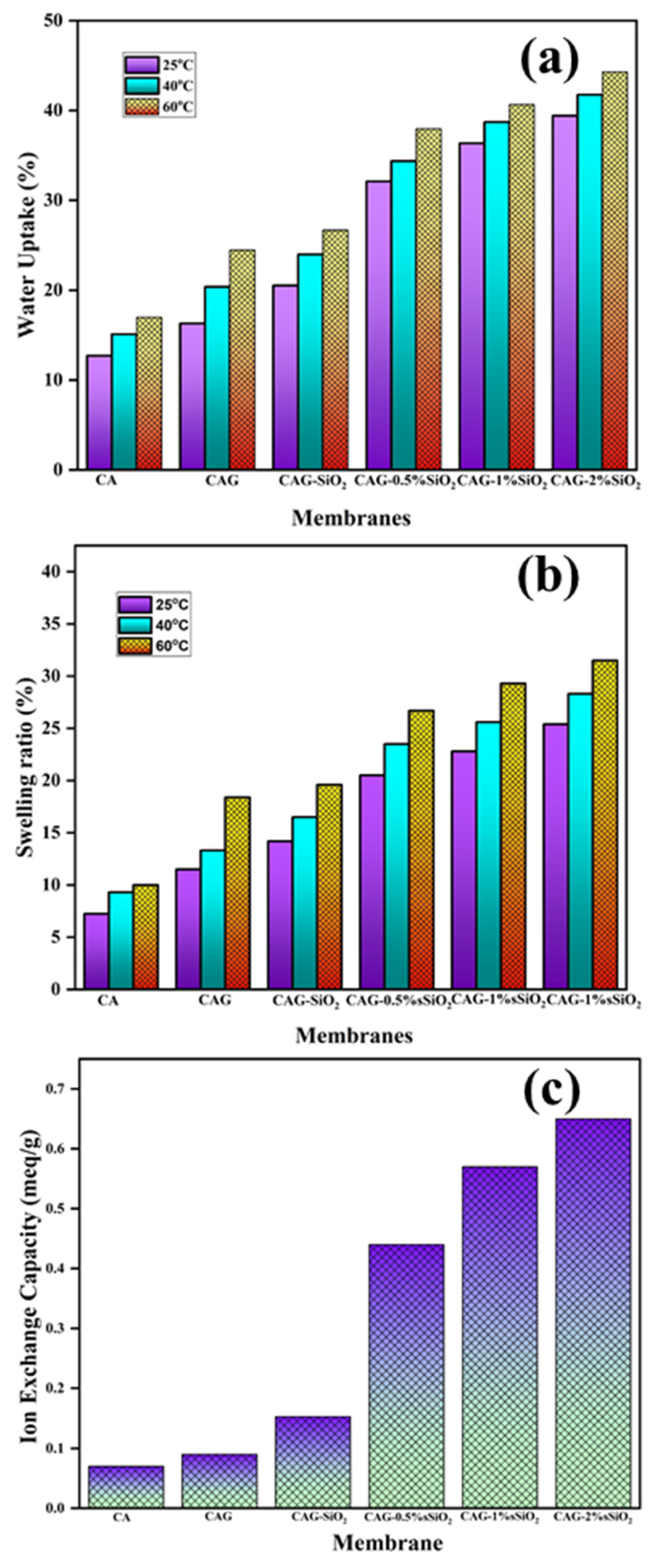
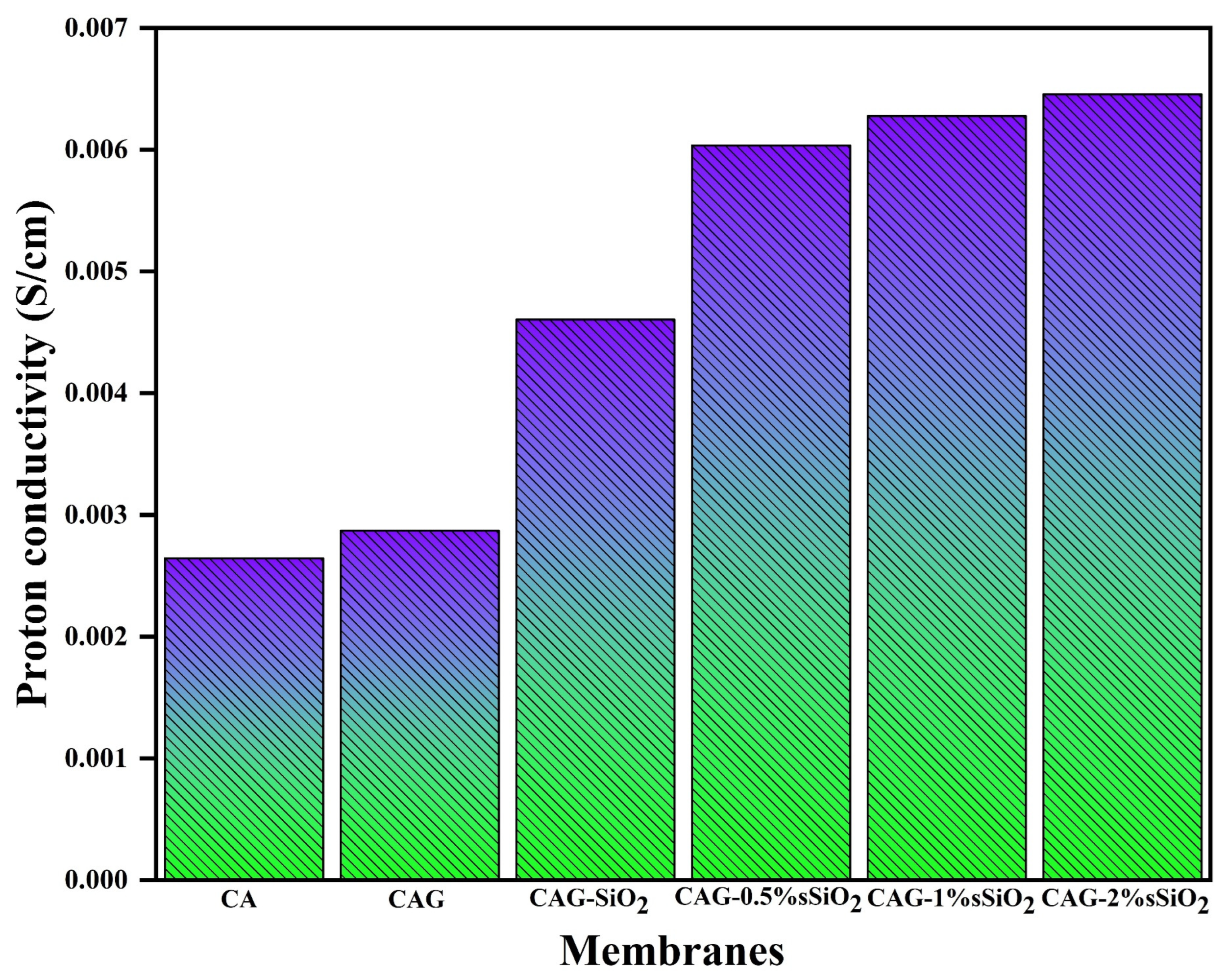
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Neethu, B.; Bhowmick, G.; Ghangrekar, M. A novel proton exchange membrane developed from clay and activated carbon derived from coconut shell for application in microbial fuel cell. Biochem. Eng. J. 2019, 148, 170–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.-H.; Lee, K.-Y. Optimization preparation of composite membranes as proton exchange membrane for gaseous acetone fed microbial fuel cells. J. Power Sources 2021, 509, 230368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caizán-Juanarena, L.; Borsje, C.; Sleutels, T.; Yntema, D.; Santoro, C.; Ieropoulos, I.; Soavi, F.; ter Heijne, A. Combination of bioelectrochemical systems and electrochemical capacitors: Principles, analysis and opportunities. Biotechnol. Adv. 2020, 39, 107456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sirajudeen, A.A.O.; Annuar, M.S.M.; Ishak, K.A.; Yusuf, H.; Subramaniam, R. Innovative application of biopolymer composite as proton exchange membrane in microbial fuel cell utilizing real wastewater for electricity generation. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 278, 123449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, J.K.; Shankar, U.; Samal, K. Fabrication and development of SPEEK/PVdF-HFP/SiO2 proton exchange membrane for microbial fuel cell application. Chem. Eng. J. Adv. 2023, 14, 100459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, S.; Nawaz, T.; Ali, A.; Orhan, M.F.; Samreen, A.; Kannan, A.M. An overview of proton exchange membranes for fuel cells: Materials and manufacturing. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2022, 47, 19086–19131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liew, K.B.; Leong, J.X.; Daud, W.R.W.; Ahmad, A.; Hwang, J.J.; Wu, W. Incorporation of silver graphene oxide and graphene oxide nanoparticles in sulfonated polyether ether ketone membrane for power generation in microbial fuel cell. J. Power Sources 2020, 449, 227490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Divya, K.; Saraswathi, M.S.S.A.; Alwarappan, S.; Nagendran, A.; Rana, D. Sulfonated poly (ether sulfone)/poly (vinyl alcohol) blend membranes customized with tungsten disulfide nanosheets for DMFC applications. Polymer 2018, 155, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, S.; Papiya, F.; Ash, S.N.; Kundu, P.P. Composite membrane of sulfonated polybenzimidazole and sulfonated graphene oxide for potential application in microbial fuel cell. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 104945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roshanravan, B.; Younesi, H.; Abdollahi, M.; Rahimnejad, M.; Pyo, S.-H. Application of proton-conducting sulfonated polysulfone incorporated MIL-100 (Fe) composite materials for polymer-electrolyte membrane microbial fuel cells. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 300, 126963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, T.; Kim, K.; Jung, B.-K.; Cha, S.-H.; Kim, S.-K.; Lee, J.-C. Cross-linked sulfonated poly (arylene ether sulfone) membranes formed by in situ casting and click reaction for applications in fuel cells. Macromolecules 2015, 48, 1104–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, G.; Park, B.J.; Kim, J.; Kang, D.; Yoon, H.H. Quaternized cellulose and graphene oxide crosslinked polyphenylene oxide based anion exchange membrane. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 9572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zuo, X.; Raut, A.; Isseroff, R.; Xue, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Sandhu, B.; Schein, T.; Zeliznyak, T.; Sharma, P.; et al. Operation of proton exchange membrane (PEM) fuel cells using natural cellulose fiber membranes. Sustain. Energy Fuels 2019, 3, 2725–2732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerqueira, D.A.; Valente, A.J.; Filho, G.R.; Burrows, H.D. Synthesis and properties of polyaniline–cellulose acetate blends: The use of sugarcane bagasse waste and the effect of the substitution degree. Carbohydr. Polym. 2009, 78, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, D.; Hu, J.; Zhang, M.; Li, M.; Wang, G.; Yao, H. Synthesis and characterization of camphorsulfonyl acetate of cellulose. Carbohydr. Res. 2004, 339, 1925–1931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monisha, S.; Mathavan, T.; Selvasekarapandian, S.; Benial, A.M.F.; Aristatil, G.; Mani, N.; Premalatha, M.; Pandi, D.V. Investigation of bio polymer electrolyte based on cellulose acetate-ammonium nitrate for potential use in electrochemical devices. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 157, 38–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madih, K.; El-Shazly, A.; Elkady, M.; Aziz, A.N.; Youssef, M.E.; Khalifa, R.E. A facile synthesis of cellulose acetate reinforced graphene oxide nanosheets as proton exchange membranes for fuel cell applications. J. Saudi Chem. Soc. 2022, 26, 101435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalifa, R.E.; Omer, A.M.; Elmageed, M.H.A.; Eldin, M.S.M. Titanium dioxide/phosphorous-functionalized cellulose acetate nanocomposite membranes for DMFC applications: Enhancing properties and performance. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 17194–17202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalifa, R.E.; Omer, A.M.; Tamer, T.M.; Salem, W.M.; Eldin, M.S.M. Removal of methylene blue dye from synthetic aqueous solutions using novel phosphonate cellulose acetate membranes: Adsorption kinetic, equilibrium, and thermodynamic studies. Desalination Water Treat. 2019, 144, 272–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shalaby, A.A.; Elmageed, M.H.A.; Malash, G.F.; Tamer, T.M.; Omer, A.M.; Mohy-Eldin, M.S.; Khalifa, R.E. Development of novel cellulose acetate-g-poly (sodium 4-styrenesulfonate) proton conducting polyelectrolyte polymer. J. Saudi Chem. Soc. 2021, 25, 101327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mesbah, F.; El Gayar, D.; Farag, H.; Tamer, T.M.; Omer, A.M.; Mohy-Eldin, M.S.; Khalifa, R.E. Development of highly ionic conductive cellulose acetate-g-poly (2-acrylamido-2-methylpropane sulfonic acid-co-methyl methacrylate) graft copolymer membranes. J. Saudi Chem. Soc. 2021, 25, 101318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Guo, K.; Li, H.; Du, Z.; Tian, J. Microfiltration Membrane Performance in Two-Chamber Microbial Fuel Cells. Biochem. Eng. J. 2010, 52, 194–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, A. Thermal and Dielectric Behaviour of Polymer Composites with Hybrid Fillers. Ph.D. Thesis, National Institute of Technology, Rourkela, India, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Shaari, N.; Kamarudin, S.K. Recent advances in additive-enhanced polymer electrolyte membrane properties in fuel cell applications: An overview. Int. J. Energy Res. 2019, 43, 2756–2794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kircheva, N.; Outin, J.; Perrier, G.; Ramousse, J.; Merlin, G.; Lyautey, E. Bio-electrochemical characterization of air-cathode microbial fuel cells with microporous polyethylene/silica membrane as separator. Bioelectrochemistry 2015, 106, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palanisamy, G.; Thangarasu, S.; Oh, T.H. Effect of Sulfonated Inorganic Additives Incorporated Hybrid Composite Polymer Membranes on Enhancing the Performance of Microbial Fuel Cells. Polymers 2023, 15, 1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Q.; Wang, L.; Li, C.; Wang, X.; Li, C.; Geng, Y. Study on improvement of the proton conductivity and anti-fouling of proton exchange membrane by doping SGO@ SiO2 in microbial fuel cell applications. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2019, 44, 15322–15332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisht, S.; Balaguru, S.; Ramachandran, S.K.; Gangasalam, A.; Kweon, J. Proton exchange composite membranes comprising SiO2, sulfonated SiO2, and metal–organic frameworks loaded in SPEEK polymer for fuel cell applications. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2021, 138, 50530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivasankaran, A.; Sangeetha, D. Influence of sulfonated SiO2 in sulfonated polyether ether ketone nanocomposite membrane in microbial fuel cell. Fuel 2015, 159, 689–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivasankaran, A.; Sangeetha, D.; Ahn, Y.-H. Nanocomposite membranes based on sulfonated polystyrene ethylene butylene polystyrene (SSEBS) and sulfonated SiO2 for microbial fuel cell application. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 289, 442–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terbish, N.; Lee, C.-H.; Popuri, S.R.; Nalluri, L.P. An investigation into polymer blending, plasticization and cross-linking effect on the performance of chitosan-based composite proton exchange membranes for microbial fuel cell applications. J. Polym. Res. 2020, 27, 280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadhasivam, T.; Kim, H.-T.; Park, W.-S.; Lim, H.; Ryi, S.-K.; Roh, S.-H.; Jung, H.-Y. Low permeable composite membrane based on sulfonated poly (phenylene oxide)(sPPO) and silica for vanadium redox flow battery. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2017, 42, 19035–19043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unnikrishnan, L.; Mohanty, S.; Nayak, S. Proton exchange membranes from sulfonated poly (ether ether ketone) reinforced with silica nanoparticles. High Perform. Polym. 2013, 25, 854–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Cid, P.; Rubio-Valle, J.F.; Jiménez-Rosado, M.; Pérez-Puyana, V.; Romero, A. Effect of Solution Properties in the Development of Cellulose Derivative Nanostructures Processed via Electrospinning. Polymers 2022, 14, 665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nodeh, H.R.; Ibrahim, W.A.W.; Ali, I.; Sanagi, M.M. Development of magnetic graphene oxide adsorbent for the removal and preconcentration of As(III) and As(V) species from environmental water samples. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 9759–9773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.H.; Kim, Y.S.; Kyung, S.J.; Lim, J.T.; Yeom, G.Y. Characteristics of SiOx thin films deposited by using direct-type pin-to-plate dielectric barrier discharge with PDMS/He/O2 gases at low temperature. J. Korean Phys. Soc. 2009, 54, 981–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massines, F.; Gherardi, N.; Fornelli, A.; Martin, S. Atmospheric pressure plasma deposition of thin films by Townsend dielectric barrier discharge. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2005, 200, 1855–1861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panwar, K.; Jassal, M.; Agrawal, A.K. In situ synthesis of Ag–SiO2 Janus particles with epoxy functionality for textile applications. Particuology 2015, 19, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Ouyang, J.; Wang, H.; Wang, W.; Chui, P.; Sun, K. Synthesis and characterization of core–shell structured SiO2@ YVO4: Yb3+, Er3+ microspheres. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2012, 258, 3689–3694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gui-Long, X.; Changyun, D.; Yun, L.; Pi-Hui, P.; Jian, H.; Zhuoru, Y. Preparation and characterization of Raspberry-like SiO2 particles by the sol-gel method. Nanomater. Nanotechnol. 2011, 1, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mojarrad, N.R.; Iskandarani, B.; Taşdemir, A.; Yürüm, A.; Gürsel, S.A.; Kaplan, B.Y. Nanofiber based hybrid sulfonated silica/P (VDF-TrFE) membranes for PEM fuel cells. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2021, 46, 13583–13593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, S.C.; Silva, R.R.A.; de Oliveira, T.V.; Stringheta, P.C.; Pinto, M.R.M.R.; Soares, N.D.F.F. Glycerol and triethyl citrate plasticizer effects on molecular, thermal, mechanical, and barrier properties of cellulose acetate films. Food Biosci. 2021, 42, 101202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Z.; Dai, W.; Li, X.; Wu, Y.; Zang, K.; Zeng, J.; Jian, J.; Zhou, H. Improvement of the functional properties of cellulose acetate film by incorporating with glycerol and n-propanol. Cellulose 2022, 29, 7823–7836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barud, H.S.; Júnior, A.M.D.A.; Santos, D.B.; de Assunção, R.M.; Meireles, C.S.; Cerqueira, D.A.; Filho, G.R.; Ribeiro, C.A.; Messaddeq, Y.; Ribeiro, S.J. Thermal behavior of cellulose acetate produced from homogeneous acetylation of bacterial cellulose. Thermochim. Acta 2008, 471, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filho, G.R.; da Cruz, S.F.; Pasquini, D.; Cerqueira, D.; Prado, V.D.S.; de Assunção, R.M.N. Water flux through cellulose triacetate films produced from heterogeneous acetylation of sugar cane bagasse. J. Membr. Sci. 2000, 177, 225–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daud, W.R.W.; Djuned, F.M. Cellulose acetate from oil palm empty fruit bunch via a one step heterogeneous acetylation. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 132, 252–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gontijo de Melo, P.; Fornazier Borges, M.; Afonso Ferreira, J.; Vicente Barbosa Silva, M.; Ruggiero, R. Bio-based cellulose acetate films reinforced with lignin and glycerol. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, C. Cellulose Acetate/Plasticizer Systems: Structure, Morphology and Dynamics; Université Claude Bernard-Lyon I: Villeurbanne, France, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, H.; Tong, H.; Lu, J.; Cheng, Y.; Qian, F.; Tao, Y.; Wang, H. Preparation of bio-based cellulose acetate/chitosan composite film with oxygen and water resistant properties. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 270, 118381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Wang, W.; Zhang, R.; Zhai, X.; Hou, H. Effect of gelatin bloom values on the physicochemical properties of starch/gelatin–beeswax composite films fabricated by extrusion blowing. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 113, 106466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samaniego, A.J.; Arabelo, A.K.; Sarker, M.; Mojica, F.; Madrid, J.; Chuang, P.-Y.A.; Ocon, J.; Espiritu, R. Fabrication of cellulose acetate-based radiation grafted anion exchange membranes for fuel cell application. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2021, 138, 49947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Ba, X.; Cui, N.; Ma, Z.; Wang, L.; Wang, Z.; Gao, X. Preparation, characterisation, and desalination performance study of cellulose acetate membranes with MIL-53 (Fe) additive. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 590, 117057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Zuo, X.; Bao, R.; Xu, X.; Wang, J.; Xu, J. Effect of SiO2 nanoparticle addition on the characteristics of a new organic–inorganic hybrid membrane. Polymer 2009, 50, 553–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, S.M.; dos Santos, D.C.; Motta, J.F.G.; dos Santos, R.R.; Chávez, D.W.H.; de Melo, N.R. Structure and functional properties of cellulose acetate films incorporated with glycerol. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 209, 190–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reyna-Valencia, A.; Kaliaguine, S.; Bousmina, M. Tensile mechanical properties of sulfonated poly (ether ether ketone)(SPEEK) and BPO4/SPEEK membranes. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2005, 98, 2380–2393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.S.M.; Soliman, M.M.; Kandil, S.H.; Ebrahim, S.; Khalil, M. Tailoring nanocomposite membranes of cellulose acetate/silica nanoparticles for desalination. J. Mater. 2022, 8, 1122–1130. [Google Scholar]
- Vinothkannan, M.; Kim, A.R.; Yoo, D.J. Sulfonated graphene oxide/Nafion composite membranes for high temperature and low humidity proton exchange membrane fuel cells. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 7494–7508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uma, T.; Mahalingam, T.; Stimming, U. Mixed phase solid polymer electrolytes based on poly (methylmethacrylate) systems. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2003, 82, 478–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhargav, P.B.; Mohan, V.M.; Sharma, A.K.; Rao, V.V.R.N. Structural, electrical and optical characterization of pure and doped poly (vinyl alcohol) (PVA) polymer electrolyte films. Int. J. Polym. Mater. 2007, 56, 579–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, S.B.; Hamsan, M.H.; Kadir, M.F.Z.; Woo, H.J. Design of polymer blends based on chitosan: POZ with improved dielectric constant for application in polymer electrolytes and flexible electronics. Adv. Polym. Technol. 2020, 2020, 8586136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosli, N.A.H.; Loh, K.S.; Wong, W.Y.; Lee, T.K.; Ahmad, A. Hybrid composite membrane of phosphorylated chitosan/poly (vinyl alcohol)/silica as a proton exchange membrane. Membranes 2021, 11, 675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.H.; Chu, J.Y.; Kim, A.R.; Yoo, D.J. Effect of functionalized SiO2 toward proton conductivity of composite membranes for PEMFC application. Int. J. Energy Res. 2019, 43, 5333–5345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Won, J.-H.; Lee, H.-J.; Yoon, K.-S.; Hong, Y.T.; Lee, S.-Y. Sulfonated SBA-15 mesoporous silica-incorporated sulfonated poly (phenylsulfone) composite membranes for low-humidity proton exchange membrane fuel cells: Anomalous behavior of humidity-dependent proton conductivity. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2012, 37, 9202–9211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, I.; Oh, K.-H.; Yun, M.; Kang, M.K.; Song, H.H.; Kim, H. Nanostructured composite membrane with cross-linked sulfonated poly (arylene ether ketone)/silica for high-performance polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cells under low relative humidity. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 549, 567–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martina, P.; Gayathri, R.; Pugalenthi, M.R.; Cao, G.; Liu, C.; Prabhu, M.R. Nanosulfonated silica incorporated SPEEK/SPVdF-HFP polymer blend membrane for PEM fuel cell application. Ionics 2020, 26, 3447–3458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kugarajah, V.; Sugumar, M.; Dharmalingam, S. Nanocomposite membrane and microbial community analysis for improved performance in microbial fuel cell. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2020, 140, 109606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Membrane | Proton Conductivity | Elongation at Break (%) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| NMPC/PVA-SiO2 (4 wt%) | 0.508 mS/cm at 100 °C | [61] | |
| sPEAK/f-SiO2-18 | 8.5 mS/cm | 10.7 | [62] |
| sGO@SiO2/PVDF-g-PSSA | 78 mS/cm | [27] | |
| SM-SiO2 + SPPSU | 5.9 mS/cm 80 °C and 50% RH | [63] | |
| CL-sPAEK/silica | 3.06 mS/cm, at 70 °C under 30% RH | 5.2 | [64] |
| 80 wt% sPEEK-20 wt% sPVdF-HFP-06 wt% sSiO2 | 79 mS/cm at RT | 35.8 | [65] |
| sPEEK/S-SiO2/MOF-5 | 3.69 mS/cm | 4.00 | [28] |
| 80 wt% sPEEK–20 wt% PVdF-HFP+7.5% SiO2 | 0.08 mS/cm | [5] | |
| sPEEK–7.5% sSiO2 | 10.18 mS/cm | [29] | |
| sPEEK+7.5 wt% sSiO2 | 12.4 mS/cm | [66] | |
| CAG–2% sSiO2 | 6.5 mS/cm | 22.23 | This study |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Palanisamy, G.; Im, Y.M.; Muhammed, A.P.; Palanisamy, K.; Thangarasu, S.; Oh, T.H. Fabrication of Cellulose Acetate-Based Proton Exchange Membrane with Sulfonated SiO2 and Plasticizers for Microbial Fuel Cell Applications. Membranes 2023, 13, 581. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes13060581
Palanisamy G, Im YM, Muhammed AP, Palanisamy K, Thangarasu S, Oh TH. Fabrication of Cellulose Acetate-Based Proton Exchange Membrane with Sulfonated SiO2 and Plasticizers for Microbial Fuel Cell Applications. Membranes. 2023; 13(6):581. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes13060581
Chicago/Turabian StylePalanisamy, Gowthami, Yeong Min Im, Ajmal P. Muhammed, Karvembu Palanisamy, Sadhasivam Thangarasu, and Tae Hwan Oh. 2023. "Fabrication of Cellulose Acetate-Based Proton Exchange Membrane with Sulfonated SiO2 and Plasticizers for Microbial Fuel Cell Applications" Membranes 13, no. 6: 581. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes13060581
APA StylePalanisamy, G., Im, Y. M., Muhammed, A. P., Palanisamy, K., Thangarasu, S., & Oh, T. H. (2023). Fabrication of Cellulose Acetate-Based Proton Exchange Membrane with Sulfonated SiO2 and Plasticizers for Microbial Fuel Cell Applications. Membranes, 13(6), 581. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes13060581







