Composite Membrane for Sodium Polysulfide Hybrid Redox Flow Batteries
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experiments
2.1. Materials
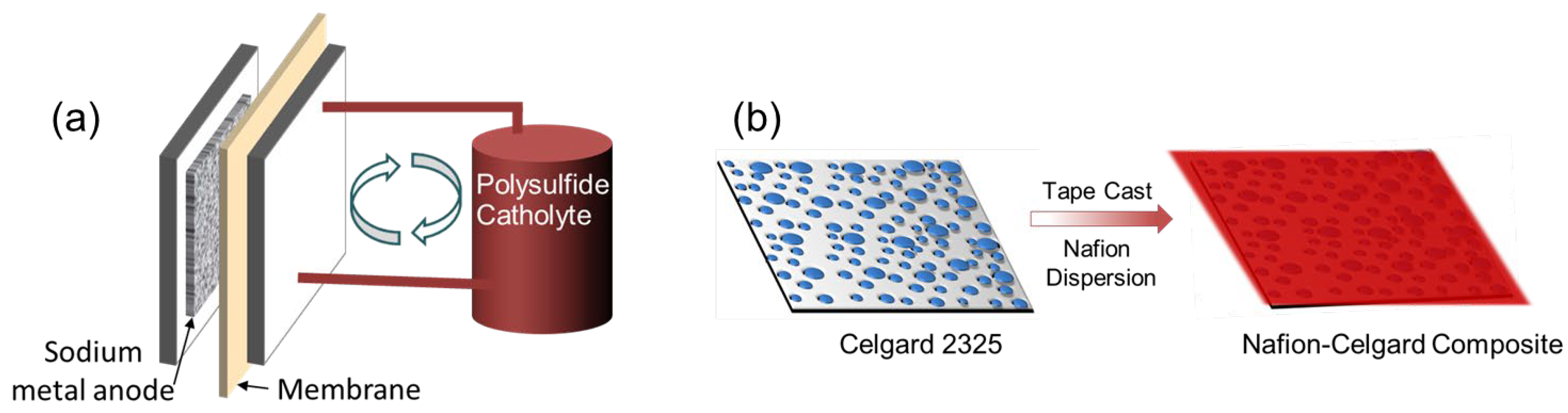
2.2. Membrane Fabrication
2.3. Characterizations
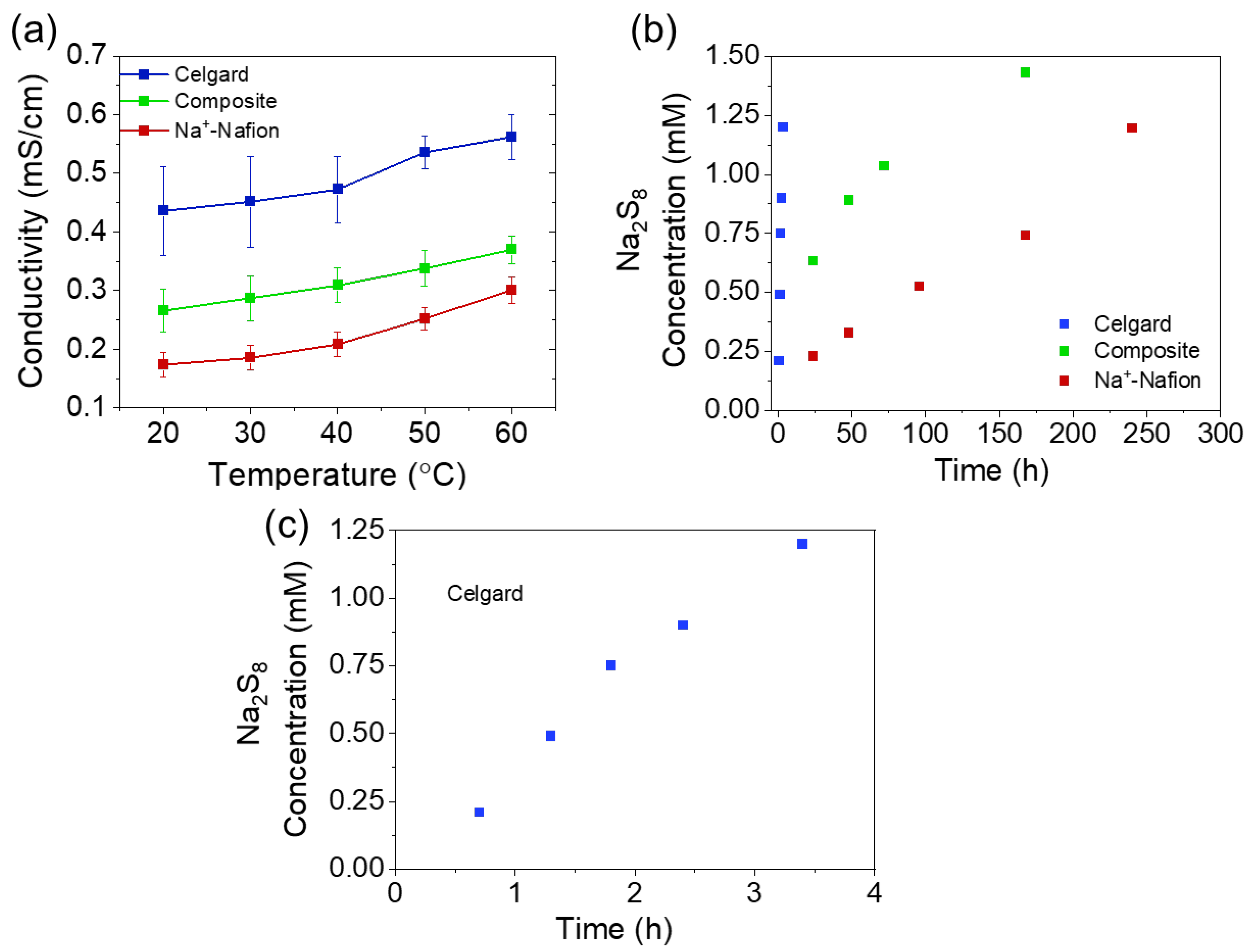
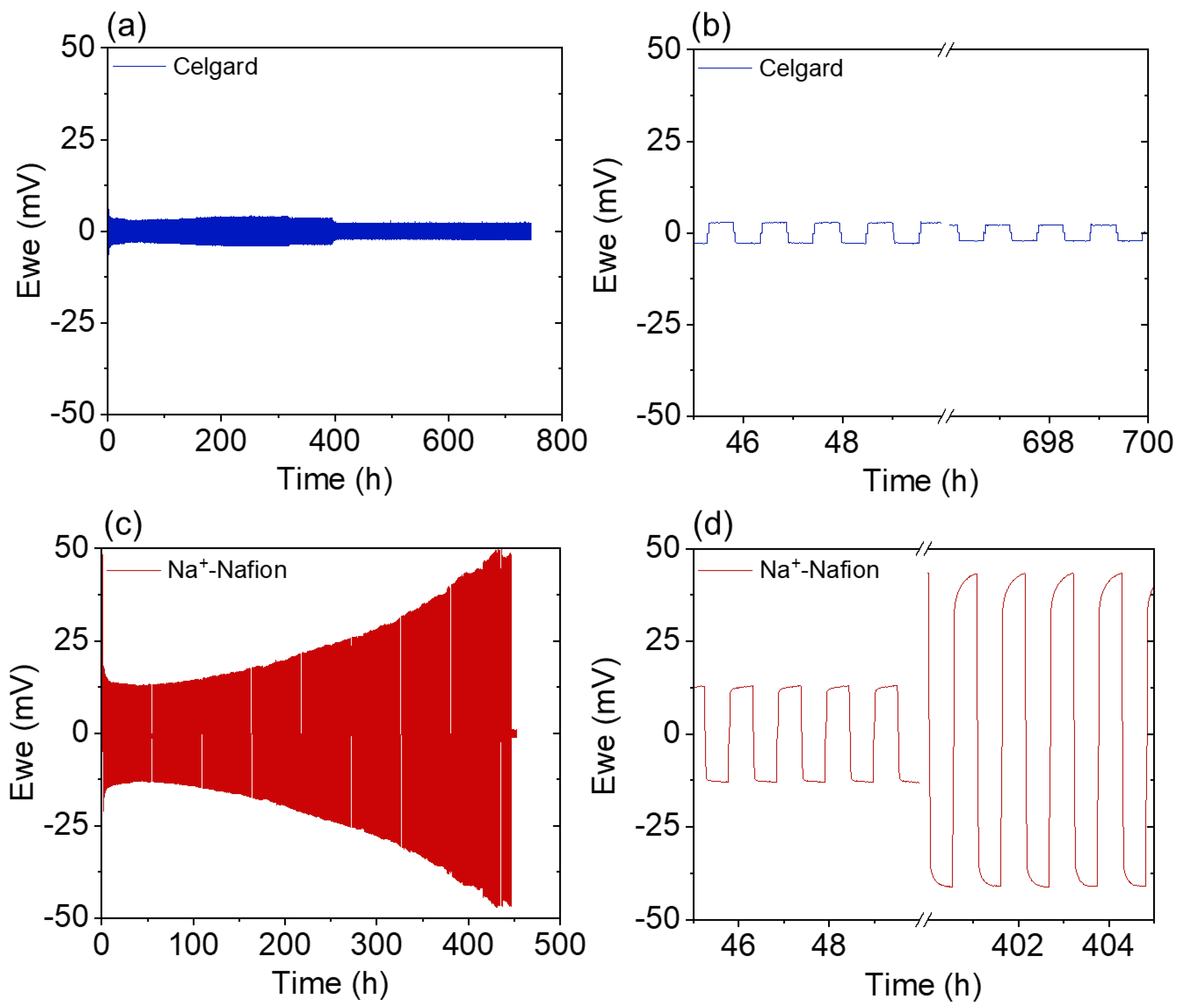
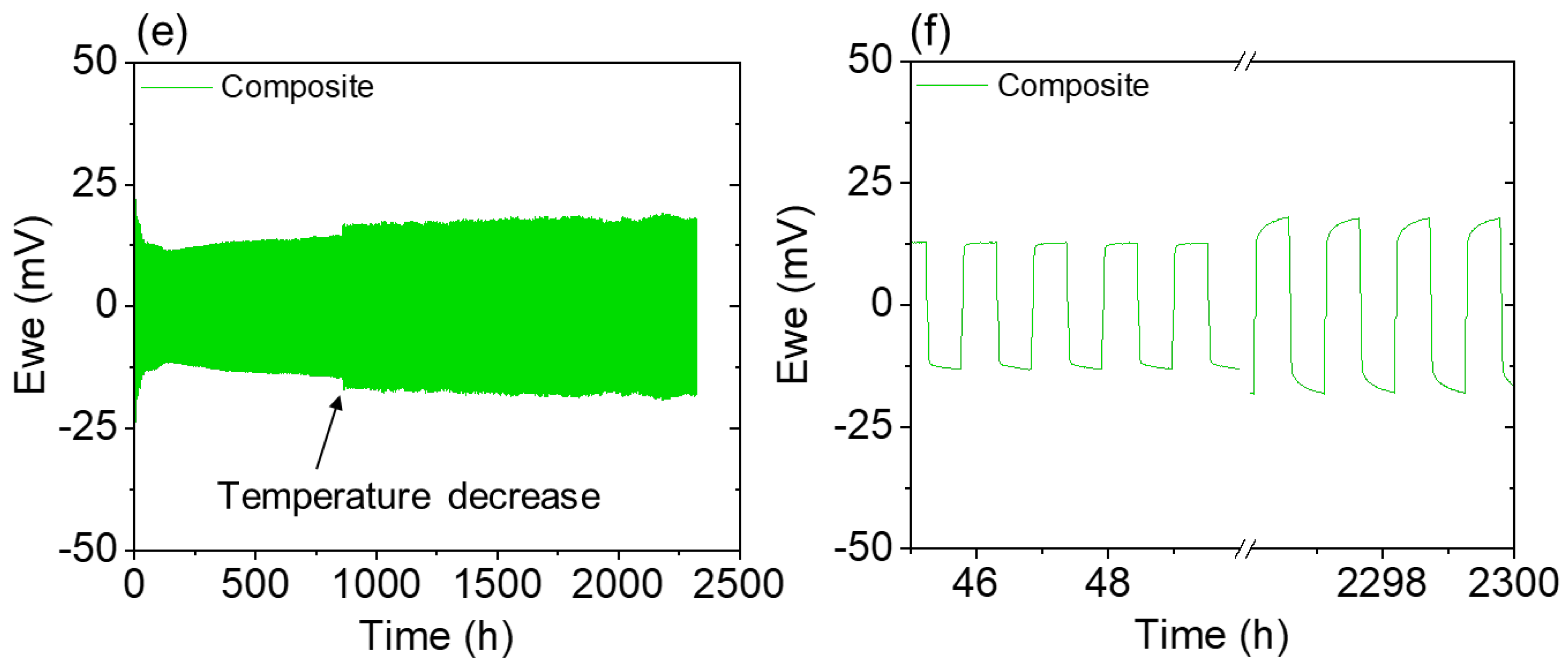
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sun, C.; Negro, E.; Vezzù, K.; Pagot, G.; Cavinato, G.; Nale, A.; Bang, Y.H.; Di Noto, V. Hybrid inorganic-organic proton-conducting membranes based on SPEEK doped with WO3 nanoparticles for application in vanadium redox flow batteries. Electrochim. Acta 2019, 309, 311–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, M.L.; Tyler, L.; Self, E.C.; Yang, G.; Nanda, J.; Saito, T. Membrane design for non-aqueous redox flow batteries: Current status and path forward. Chem 2022, 8, 1611–1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, K.; Fang, Q.; Gu, S.; Li, S.F.Y.; Yan, Y. Nonaqueous redox-flow batteries: Organic solvents, supporting electrolytes, and redox pairs. Energy Environ. Sci. 2015, 8, 3515–3530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shin, S.-H.; Yun, S.-H.; Moon, S.-H. A review of current developments in non-aqueous redox flow batteries: Characterization of their membranes for design perspective. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 9095–9116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zheng, G.; Cui, Y. A membrane-free lithium/polysulfide semi-liquid battery for large-scale energy storage. Energy. Environ. Sci. 2013, 6, 1552–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Guo, W.; Yang, F.; Zheng, P.; Qiao, R.; Li, Z. Recent progress in polysulfide redox-flow batteries. Batter. Supercaps 2019, 2, 627–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyler, J.L.; Sacci, R.L.; Lehmann, M.L.; Yang, G.; Zawodzinski, T.A.; Nanda, J. Nafion Inhibits Polysulfide Crossover in Hybrid Nonaqueous Redox Flow Batteries. J. Phys. Chem. C 2022, 126, 21188–21195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhang, H.; Mai, Z.; Zhang, H.; Vankelecom, I. Ion exchange membranes for vanadium redox flow battery (VRB) applications. Energy. Environ. Sci. 2011, 4, 1147–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prifti, H.; Parasuraman, A.; Winardi, S.; Lim, T.M.; Skyllas-Kazacos, M. Membranes for redox flow battery applications. Membranes 2012, 2, 275–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bladwin, R.S. A Review of State-of-the-Art Separator Materials for Advanced Lithium-Based Batteries for Future Aerospace Missions; NASA: Washington, DC, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Page, K.A.; Cable, K.M.; Moore, R.B. Molecular origins of the thermal transitions and dynamic mechanical relaxations in perfluorosulfonate ionomers. Macromolecules 2005, 38, 6472–6484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCormack, P.M.; Koenig, G.M., Jr.; Geise, G.M. Thermodynamic Interactions as a Descriptor of Cross-Over in Nonaqueous Redox Flow Battery Membranes. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 2021, 13, 49331–49339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCormack, P.M.; Luo, H.; Geise, G.M.; Koenig, G.M., Jr. Conductivity, permeability, and stability properties of chemically tailored poly (Phenylene oxide) membranes for Li+ conductive non-aqueous redox flow battery separators. J. Power Sources 2020, 460, 228107–228117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, J.; Teng, X.; Song, Y.; Ren, J. Effect of casting solvent and annealing temperature on recast Nafion membranes for vanadium redox flow battery. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 522, 56–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Self, E.C.; Tyler, J.L.; Nanda, J. Ambient Temperature Sodium Polysulfide Catholyte for Nonaqueous Redox Flow Batteries. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2021, 168, 080540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Chen, Y.; Jie, Y.; Lang, S.; Song, J.; Lei, Z.; Wang, S.; Ren, X.; Wang, D.; Li, X. Stable sodium metal batteries via manipulation of electrolyte solvation structure. Small Methods 2020, 4, 1900856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Xue, L.; Goodenough, J.B.; Manthiram, A. All-Solid-State Sodium Batteries with a Polyethylene Glycol Diacrylate–Na3Zr2Si2PO12 Composite Electrolyte. Adv. Energy Sustain. Res. 2021, 2, 2000061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casas, X.; Niederberger, M.; Lizundia, E. A sodium-ion battery separator with reversible voltage response based on water-soluble cellulose derivatives. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 2020, 12, 29264–29274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Song, X.; Lu, X.; Zhang, Z.; Onyianta, A.J.; Wang, M.; Titirici, M.M.; Eichhorn, S.J. Stable Sodium-Metal Batteries in Carbonate Electrolytes Achieved by Bifunctional, Sustainable Separators with Tailored Alignment. Adv. Mater. 2022, 34, 2206367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, X.B.; Zhang, R.; Zhao, C.Z.; Zhang, Q. Toward Safe Lithium Metal Anode in Rechargeable Batteries: A Review. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 10403–10473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lehmann, M.L.; Yang, G.; Gilmer, D.; Han, K.S.; Self, E.C.; Ruther, R.E.; Ge, S.; Li, B.; Murugesan, V.; Sokolov, A.P.; et al. Tailored Crosslinking of Poly (Ethylene oxide) Enables Mechanical Robustness and Improved Sodium-Ion Conductivity. Energy Stor. Mater. 2019, 21, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruther, R.E.; Yang, G.; Delnick, F.M.; Tang, Z.J.; Lehmann, M.L.; Saito, T.; Meng, Y.J.; Zawodzinski, T.A.J.; Nanda, J. Mechanically Robust, Sodium-Ion Conducting Membranes for Nonaqueous Redox Flow Batteries. ACS Energy Lett. 2018, 3, 1640–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.D.; Li, Y.T.; Xin, S.; Goodenough, J.B. Rechargeable Sodium All-Solid-State Battery. ACS Cent. Sci. 2017, 3, 52–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ansari, Y.; Guo, B.; Cho, J.H.; Park, K.; Song, J.; Ellison, C.J.; Goodenough, J.B. Low-cost, dendrite-blocking polymer-Sb2O3 separators for lithium and sodium batteries. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2014, 161, A1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Sample | Na2S8 Permeability (cm2/s) | Conductivity (mS/cm, 20 °C) | Area Specific Resistance (Ω cm2, 20 °C) | Storage Modulus (MPa, 25 °C) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Celgard | 2.2 × 10−6 | 0.44 | 5.2 | 584 |
| Na+-Nafion | 3.1 × 10−8 | 0.17 | 19.5 | 318 |
| Composite | 1.4 × 10−7 | 0.26 | 23.7 | 935 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lehmann, M.L.; Self, E.C.; Saito, T.; Yang, G. Composite Membrane for Sodium Polysulfide Hybrid Redox Flow Batteries. Membranes 2023, 13, 700. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes13080700
Lehmann ML, Self EC, Saito T, Yang G. Composite Membrane for Sodium Polysulfide Hybrid Redox Flow Batteries. Membranes. 2023; 13(8):700. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes13080700
Chicago/Turabian StyleLehmann, Michelle L., Ethan C. Self, Tomonori Saito, and Guang Yang. 2023. "Composite Membrane for Sodium Polysulfide Hybrid Redox Flow Batteries" Membranes 13, no. 8: 700. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes13080700
APA StyleLehmann, M. L., Self, E. C., Saito, T., & Yang, G. (2023). Composite Membrane for Sodium Polysulfide Hybrid Redox Flow Batteries. Membranes, 13(8), 700. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes13080700






