Chemical Cleaning Techniques for Fouled RO Membranes: Enhancing Fouling Removal and Assessing Microbial Composition
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Methodology
3.1. RO Membrane Cutting
3.2. Cleaning Procedures for Membranes
3.2.1. Cleaning A
3.2.2. Cleaning B
3.2.3. Cleaning C (Proposed by the Membrane Manufacturer)
3.3. Analysis and Characterization of RO Membranes
3.3.1. SEM
3.3.2. ATR-FTIR
3.3.3. Thermal Stability Using TGA and DSC
3.3.4. Surface Wettability
3.4. Microbial Characterization
Total Bacterial Count
3.5. Bacterial Community Analysis
3.5.1. Culture-Dependent Techniques
3.5.2. 16S rDNA Analysis
3.6. Statistical Analysis
4. Results
4.1. Characterization of RO Membranes
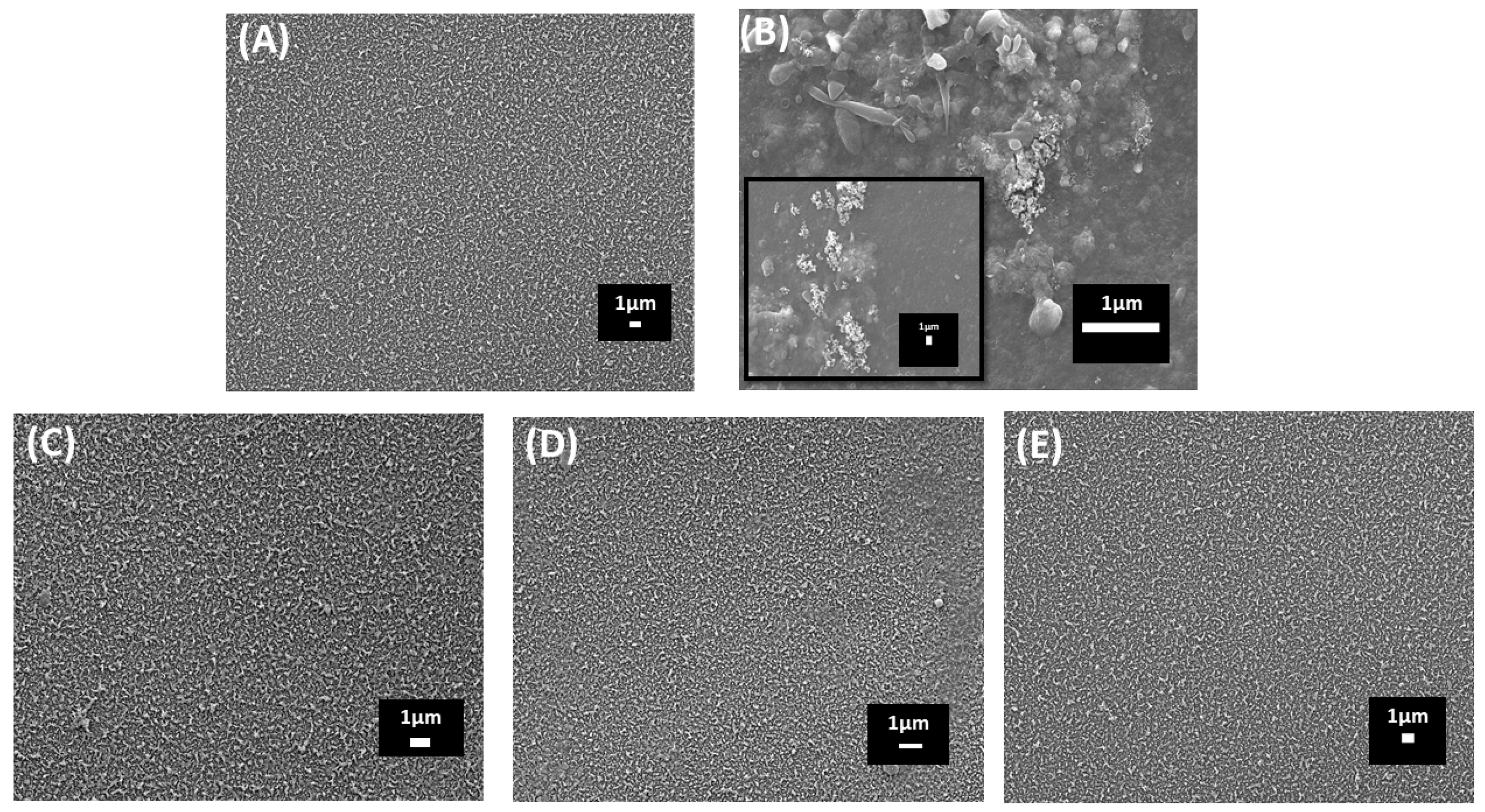
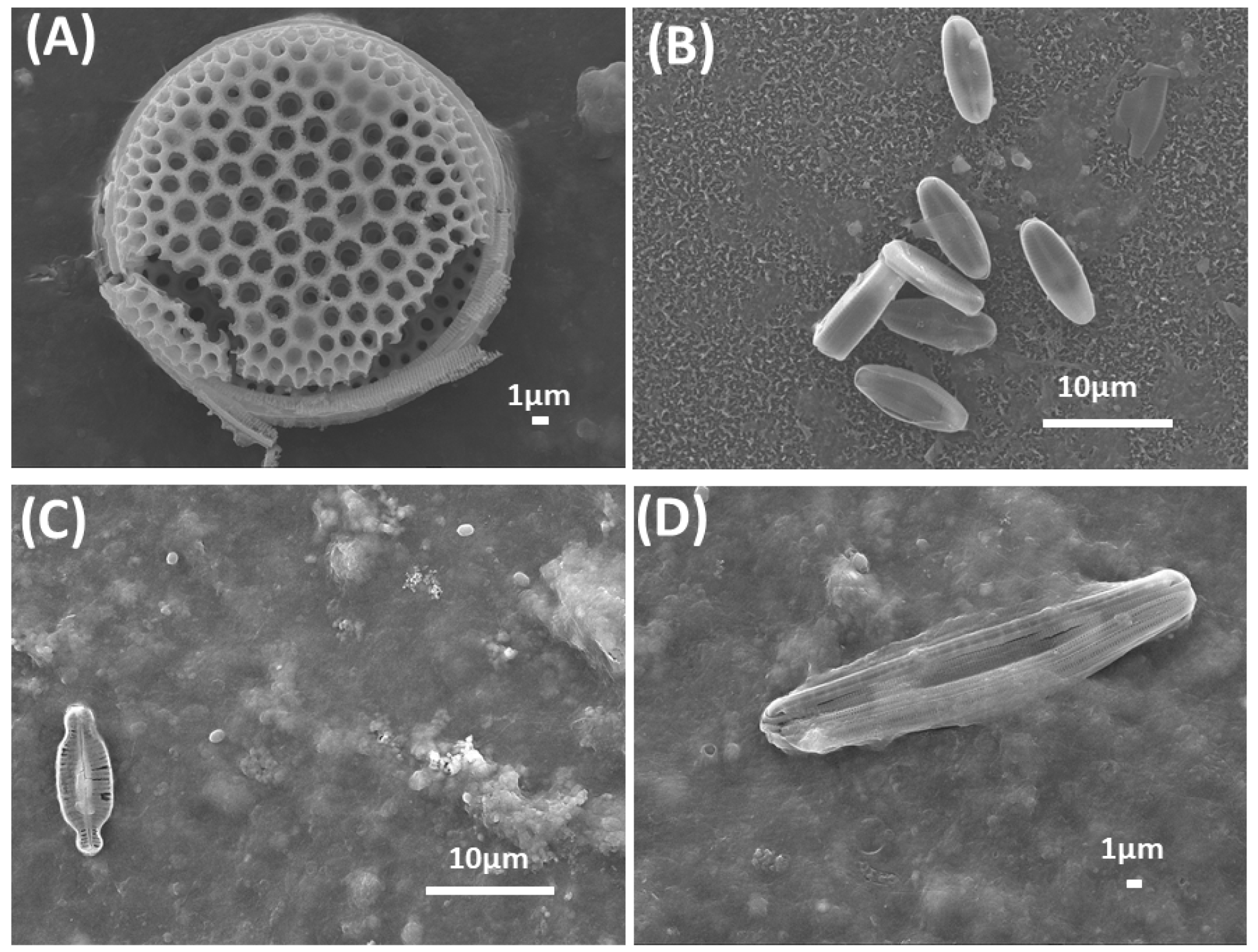
4.1.1. Surface Morphology Analysis
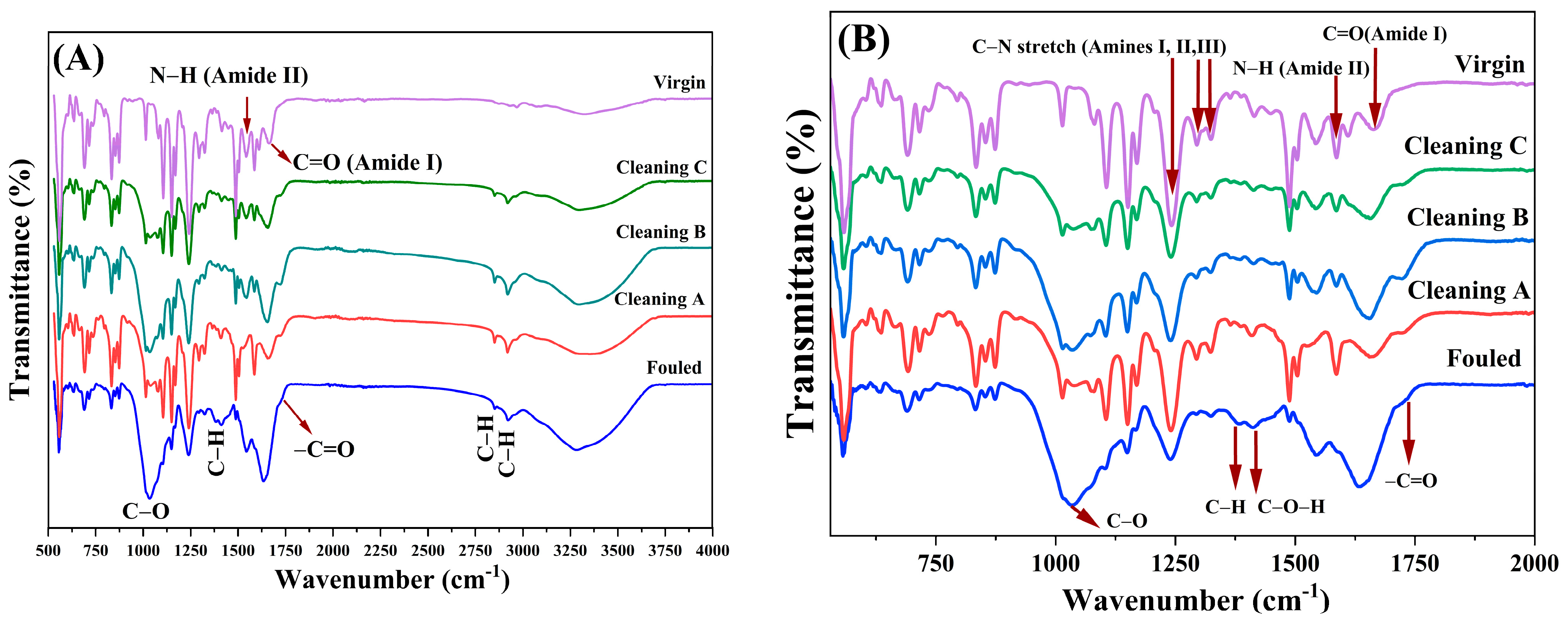
4.1.2. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy Analysis (FTIR)
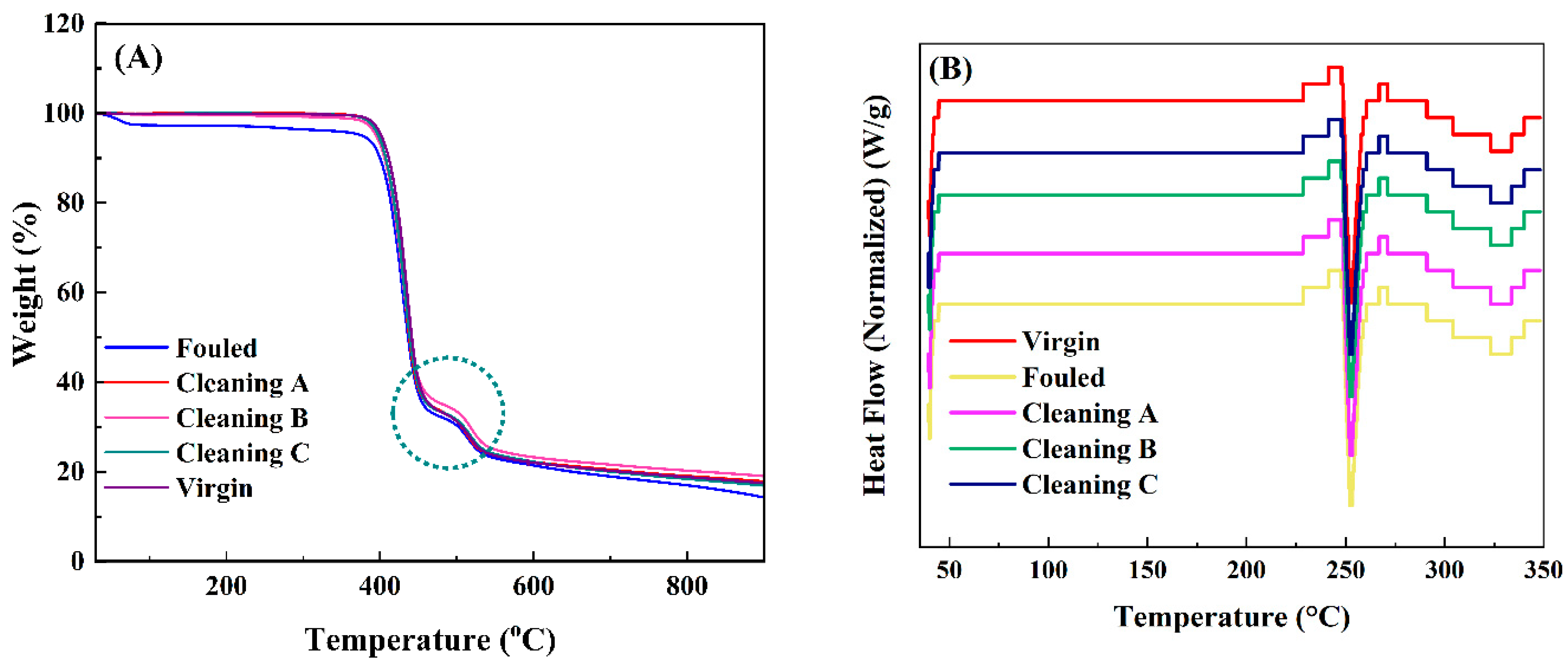
4.1.3. Thermogravimetric Analysis
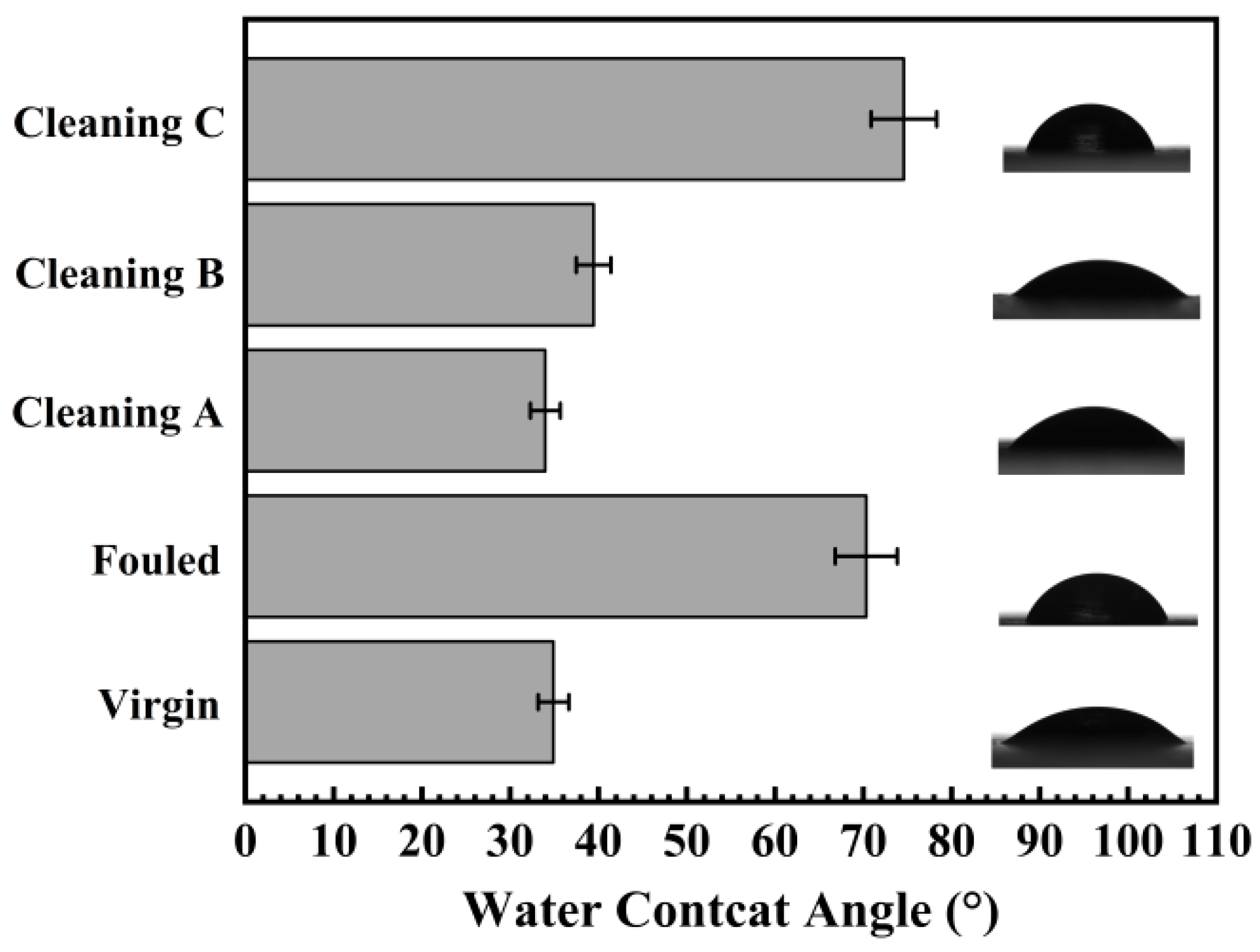
4.1.4. Surface Wettability
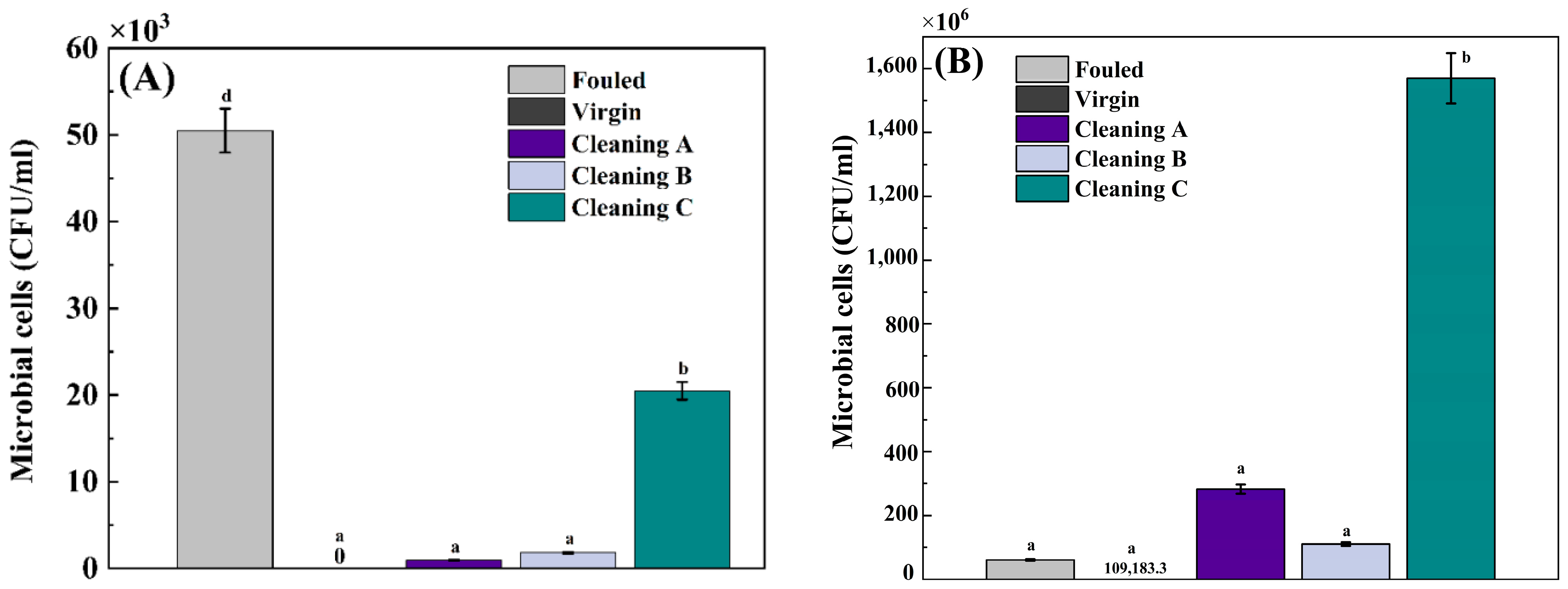
4.2. Microbial Characterization
4.3. Bacterial Community Analysis
4.3.1. Culture-Dependent Techniques
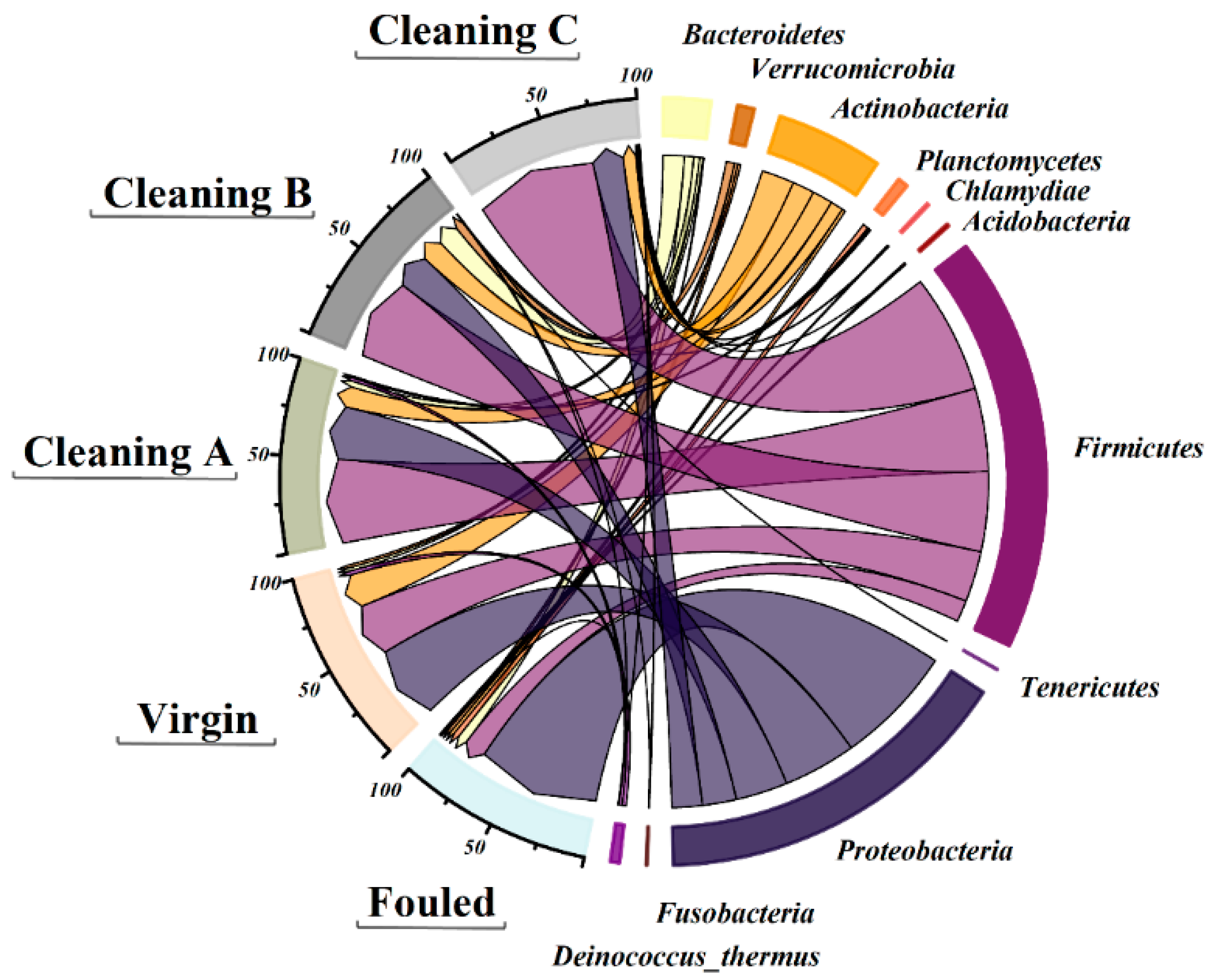
4.3.2. 16S rRNA Analysis
Bacteria
4.3.3. Operational Taxonomic Units and Principal Component Analysis
4.3.4. Archaea Community Composition
5. Discussion
5.1. Surface Morphology Analysis by SEM
5.2. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy Analysis (FTIR)
5.3. Thermal Gravimetric Analysis (TGA)
5.4. Surface Wettability
5.5. Microbial Counts
5.6. Bacterial Community Analysis
5.6.1. Culture-Dependent Techniques
5.6.2. 16S rRNA Analysis
Bacteria
Operational Taxonomic Units and Principal Component Analysis
Archaea
6. Limitations and Future Work Directions
7. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shannon, M.A.; Bohn, P.W.; Elimelech, M.; Georgiadis, J.G.; Mariñas, B.J.; Mayes, A.M. Science and technology for water purification in the coming decades. Nature 2008, 452, 301–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Li, X.; Liu, H.; Zhou, T.; Wang, Z.; Nghiem, L.D.; Wang, Q. Biofouling control of reverse osmosis membrane using free ammonia as a cleaning agent. J. Membr. Sci. 2024, 694, 122414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AlSawaftah, N.; Abuwatfa, W.; Darwish, N.; Husseini, G.A. A review on membrane biofouling: Prediction, characterization, and mitigation. Membranes 2022, 12, 1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- UN-Water. Summary Progress Update 2021: SDG 6—Water and Sanitation for All; United Nations: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021; Available online: https://www.unwater.org/sites/default/files/app/uploads/2021/12/SDG-6-Summary-Progress-Update-2021_Version-July-2021a.pdf (accessed on 22 September 2024).
- Kesieme, U.K.; Milne, N.; Aral, H.; Cheng, C.Y.; Duke, M. Economic analysis of desalination technologies in the context of carbon pricing, and opportunities for membrane distillation. Desalination 2013, 323, 66–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ang, W.S.; Yip, N.Y.; Tiraferri, A.; Elimelech, M. Chemical cleaning of RO membranes fouled by wastewater effluent: Achieving higher efficiency with dual-step cleaning. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 382, 100–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nthunya, L.N.; Bopape, M.F.; Mahlangu, O.T.; Mamba, B.B.; Van der Bruggen, B.; Quist-Jensen, C.A.; Richards, H. Fouling, performance and cost analysis of membrane-based water desalination technologies: A critical review. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 301, 113922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qasim, M.; Badrelzaman, M.; Darwish, N.N.; Darwish, N.A.; Hilal, N. Reverse osmosis desalination: A state-of-the-art review. Desalination 2019, 459, 59–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamaly, S.; Darwish, N.; Ahmed, I.; Hasan, S. A short review on reverse osmosis pretreatment technologies. Desalination 2014, 354, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qasim, M.; Darwish, N.A.; Sarp, S.; Hilal, N. Water desalination by forward (direct) osmosis phenomenon: A comprehensive review. Desalination 2015, 374, 47–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenlee, L.F.; Lawler, D.F.; Freeman, B.D.; Marrot, B.; Moulin, P. Reverse osmosis desalination: Water sources, technology, and today’s challenges. Water Res. 2009, 43, 2317–2348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivnitsky, H.; Minz, D.; Kautsky, L.; Preis, A.; Ostfeld, A.; Semiat, R.; Dosoretz, C.G. Biofouling formation and modeling in nanofiltration membranes applied to wastewater treatment. J. Membr. Sci. 2010, 360, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasmore, M.; Todd, P.; Smith, S.; Baker, D.; Silverstein, J.; Coons, D.; Bowman, C.N. Effects of ultrafiltration membrane surface properties on Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm initiation for the purpose of reducing biofouling. J. Membr. Sci. 2001, 194, 15–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gul, A.; Hruza, J.; Yalcinkaya, F. Fouling and chemical cleaning of microfiltration membranes: A mini-review. Polymers 2021, 13, 846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, G.D.; Cao, Y.M. Development of antifouling reverse osmosis membranes for water treatment: A review. Water Res. 2012, 46, 584–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matin, A.; Khan, Z.; Zaidi, S.M.J.; Boyce, M.C. Biofouling in reverse osmosis membranes for seawater desalination: Phenomena and prevention. Desalination 2011, 281, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Creber, S.A.; Vrouwenvelder, J.S.; Van Loosdrecht, M.C.M.; Johns, M.L. Chemical cleaning of biofouling in reverse osmosis membranes evaluated using magnetic resonance imaging. J. Membr. Sci. 2010, 362, 202–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burn, S.; Gray, S. Efficient Desalination by Reverse Osmosis: A Guide to RO Practice; IWA Publishing: London, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, X.; Wen, J.; Shi, L.; Cheng, R.; Zhang, Z. A top-down approach to estimate global RO desalination water production considering uncertainty. Desalination 2020, 488, 114523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Liu, X.P.; Li, H.Q. A review of forward osmosis membrane fouling: Types, research methods and future prospects. Environ. Technol. Rev. 2017, 6, 26–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boo, C.; Lee, S.; Elimelech, M.; Meng, Z.; Hong, S. Colloidal fouling in forward osmosis: Role of reverse salt diffusion. J. Membr. Sci. 2012, 390–391, 277–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yiantsios, S.; Sioutopoulos, D.; Karabelas, A. Colloidal fouling of RO membranes: An overview of key issues and efforts to develop improved prediction techniques. Desalination 2005, 183, 257–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Ashhab, A.; Herzberg, M.; Gillor, O. Biofouling of reverse-osmosis membranes during tertiary wastewater desalination: Microbial community composition. Water Res. 2014, 50, 341–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, W.; Ahn, C.H.; Hong, S.; Kim, S.; Lee, S.; Baek, Y.; Yoon, J. Evaluation of surface properties of reverse osmosis membranes on the initial biofouling stages under no filtration condition. J. Membr. Sci. 2010, 351, 112–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Luo, J.; Chen, X.; Feng, S.; Wan, Y. How do chemical cleaning agents act on polyamide nanofiltration membrane and fouling layer? Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2020, 59, 17653–17670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bereschenko, L.; Stams, A.; Euverink, G.; Van Loosdrecht, M. Biofilm formation on reverse osmosis membranes is initiated and dominated by Sphingomonas spp. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 76, 2623–2632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, T.; Meng, L.; Zhao, Q.B.; Shi, Y.; Hu, H.Y.; Lu, Y. Effects of chemical cleaning on RO membrane inorganic, organic and microbial foulant removal in a full-scale plant for municipal wastewater reclamation. Water Res. 2017, 113, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gul, A.; Hruza, J.; Dvorak, L.; Yalcinkaya, F. Chemical cleaning process of polymeric nanofibrous membranes. Polymers 2022, 14, 1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Shuili, Y.; Youbing Zhu, Y.; Gao, S.; Shi, W.; Tay, J. Efficiencies and mechanisms of the chemical cleaning of fouled polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) membranes during the microfiltration of alkali/surfactant/polymer flooding oilfield wastewater. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 36940–36950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.X.; Dong, B.Z.; Sheng, Y.G.; Wang, J.P. Identifying membrane foulants in chemical cleaning solutions. Adv. Mater. Res. 2013, 726, 1872–1878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.M.; Kim, S.J.; Kim, Y.S.; Lee, S.; Kim, I.S.; Kim, J.H. Overview of systems engineering approaches for a large-scale seawater desalination plant with a reverse osmosis network. Desalination 2009, 238, 312–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paugam, L.; Delaunay, D.; Diagne, N.W.; Rabiller-Baudry, M. Cleaning of skim milk PES ultrafiltration membrane: On the real effect of nitric acid step. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 428, 275–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dowd, S.E.; Callaway, T.R.; Wolcott, R.D.; Sun, Y.; McKeehan, T.; Hagevoort, R.G.; Edrington, T.S. Evaluation of the bacterial diversity in the feces of cattle using 16S rDNA bacterial tag-encoded FLX amplicon pyrosequencing (bTEFAP). BMC Microbiol. 2008, 8, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Yu, P.; Luo, Y. Fouling mechanisms and primary foulant constituents in reverse osmosis membrane reclamation of a petrochemical secondary effluent. Desalination Water Treat. 2015, 54, 3200–3210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Abri, M.; Kyaw, H.H.; Al-Ghafri, B.; Myint, M.T.Z.; Dobretsov, S. Autopsy of Used Reverse Osmosis Membranes from the Largest Seawater Desalination Plant in Oman. Membranes 2022, 12, 671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, M.M.; Al-Sulaimi, S.; Farooque, A.M. Characterization of new and fouled SWRO membranes by ATR/FTIR spectroscopy. Appl Water Sci. 2018, 8, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.U.H.; Khan, Z.; Aljundi, I.H. Improved hydrophilicity and anti-fouling properties of polyamide TFN membrane comprising carbide derived carbon. Desalination 2017, 420, 125–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dilshad, M.R.; Islam, A.; Hamidullah, U.; Jamshaid, F.; Ahmad, A.; Butt, M.T.Z.; Ijaz, A. Effect of alumina on the performance and characterization of cross-linked PVA/PEG 600 blended membranes for CO2/N2 separation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 210, 627–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manawi, Y.; Kochkodan, V.; Ismail, A.F.; Mohammad, A.W.; Ali Atieh, M. Performance of acacia gum as a novel additive in thin film composite polyamide RO membranes. Membranes 2019, 9, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shon, H.; Vigneswaran, S.; Zareie, M.; Aim, R.B.; Lee, E.; Lee, J.; Cho, J.; Kim, I.S. Physico-chemical pretreatment to seawater reverse osmosis (SWRO): Organic characterization and membrane autopsy. Desalination 2009, 236, 282–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO E. 4833-1: 2013; Microbiology of the Food Chain—Horizontal Method for the Enumeration of Microorganisms—Part 1: Colony Count at 30 C by the Pour Plate Technique. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2020.
- Tian, J.Y.; Chen, Z.L.; Yang, Y.L.; Liang, H.; Nan, J.; Li, G.B. Consecutive chemical cleaning of fouled PVC membrane using NaOH and ethanol during ultrafiltration of river water. Water Res. 2010, 44, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zondervan, E.; Roffel, B. Evaluation of different cleaning agents used for cleaning ultra filtration membranes fouled by surface water. J. Membr. Sci. 2007, 304, 40–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguiar, A.; Andrade, L.; Grossi, L.; Pires, W.; Amaral, M. Acid mine drainage treatment by nanofiltration: A study of membrane fouling, chemical cleaning, and membrane ageing. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2018, 192, 185–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, T.; Madaeni, S.; Moghadam, M. Investigation of membrane fouling. Desalination 2003, 153, 155–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unal, B.O. Membrane autopsy study to characterize fouling type of RO membrane used in an industrial zone wastewater reuse plant. Desalination 2022, 529, 115648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustafa, Z.; Rao, N.; Johnston-Hall, G.; Henderson, R.; Leslie, G.; Le-Clech, P. Membrane fouling during algal blooms: Impact of extracellular algal organic matter feed and membrane surface properties. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 108749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villacorte, L.; Ekowati, Y.; Calix-Ponce, H.; Kisielius, V.; Kleijn, J.; Vrouwenvelder, J.S.; Schippers, J.C.; Kennedy, M. Biofouling in capillary and spiral wound membranes facilitated by marine algal bloom. Desalination 2017, 424, 74–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villacorte, L.O. Algal Blooms and Membrane Based Desalination Technology; IHE Delft Institute for Water Education: Delft, The Netherlands, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Villacorte, L.O.; Tabatabai, S.A.A.; Anderson, D.M.; Amy, G.L.; Schippers, J.C.; Kennedy, M.D. Seawater reverse osmosis desalination and (harmful) algal blooms. Desalination 2015, 360, 61–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashiba, K.; Nakai, S.; Ohno, M.; Nishijima, W.; Gotoh, T.; Iizawa, T. Deterioration mechanism of a tertiary polyamide reverse osmosis membrane by hypochlorite. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 9109–9117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Do, V.T.; Tang, C.Y.; Reinhard, M.; Leckie, J.O. Effects of Chlorine Exposure Conditions on Physiochemical Properties and Performance of a Polyamide Membrane-Mechanisms and Implications. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 13184–13192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashiba, K.; Nakai, S.; Nishijima, W.; Ohno, M.; Gotoh, T. Degradation of secondary polyamide reverse osmosis membrane by hypochlorite in the presence of calcium ions. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2020, 181, 109351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, A.; Price, W.E.; Nghiem, L.D. Effects of chemical cleaning on the nanofiltration of pharmaceutically active compounds (PhACs). Sep. Purif. Technol. 2012, 88, 208–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, K.L.; Chivas, A.R.; Nghiem, L.D. Chemical cleaning effects on properties and separation efficiency of an RO membrane. Membr. Water Treat. 2015, 6, 141–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.K.; Kim, J.H.; Roh, I.J.; Kim, J.J. The changes of membrane performance with polyamide molecular structure in the reverse osmosis process. J. Membr. Sci. 2000, 165, 189–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flemming, H.C. Biofouling in water systems—Cases, causes and countermeasures. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2002, 59, 629–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rabin, N.; Zheng, Y.; Opoku-Temeng, C.; Du, Y.; Bonsu, E.; Sintim, H.O. Agents that inhibit bacterial biofilm formation. Future Med. Chem. 2015, 7, 647–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, P.; Singh, N.; Anand, S. A competitive exclusion study reveals the emergence of Bacillus subtilis as a predominant constitutive microorganism of a whey reverse osmosis membrane biofilm matrix. J. Dairy Sci. 2021, 104, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahto, K.U.; Priyadarshanee, M.; Samantaray, D.P.; Das, S. Bacterial biofilm and extracellular polymeric substances in the treatment of environmental pollutants: Beyond the protective role in survivability. J. Clean Prod. 2022, 379, 134759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobretsov, S.; Rittschof, D. “Omics” Techniques Used in Marine Biofouling Studies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 10518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vries, H.J.; Beyer, F.; Jarzembowska, M.; Lipińska, J.; Van Den Brink, P.; Zwijnenburg, A.; Timmers, P.H.A.; Stams, A.J.M.; Plugge, C.M. Isolation and characterization of Sphingomonadaceae from fouled membranes. NPJ Biofilms Microbiomes 2019, 5, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Ding, W.; Li, Y.X.; Tam, C.; Bougouffa, S.; Wang, R.; Pei, B.; Chiang, H.; Leung, P.; Lu, Y. Marine biofilms constitute a bank of hidden microbial diversity and functional potential. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chun, Y.; Ha, P.T.; Powell, L.; Lee, J.; Kim, D.; Choi, D.; Lovitt, R.W.; Kim, I.S.; Mitra, S.S.; Chang, I.S. Exploring microbial communities and differences of cartridge filters (CFs) and reverse osmosis (RO) membranes for seawater desalination processes. Desalination 2012, 298, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forbes, S.; Knight, C.G.; Cowley, N.L.; Amézquita, A.; McClure, P.; Humphreys, G.; McBain, A.J. Variable effects of exposure to formulated microbicides on antibiotic susceptibility in firmicutes and proteobacteria. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 82, 3591–3598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pazouki, P.; Sidhu, J.; Ipe, D.; Pype, M.; Wohlsen, T.; Helfer, F.; Bertone, E.; Stewart, R. Seawater dilution desalination with hybrid FO-RO and UF-RO: Characterisation and assessment of pathogen removal efficacy. Desalination 2022, 525, 115509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setlow, P. Spore resistance properties. In The Bacterial Spore: From Molecules to Systems; Driks, A., Eichenberger, P., Eds.; ASM Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2016; pp. 201–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agulló-Barceló, M.; Polo-López, M.I.; Lucena, F.; Jofre, J.; Fernández-Ibánez, P. Solar advanced oxidation processes as disinfection tertiary treatments for real wastewater: Implications for water reclamation. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2013, 136, 341–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brazier, J.; Levett, P.; Stannard, A.; Phillips, K.; Willis, A. Antibiotic susceptibility of clinical isolates of clostridia. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 1985, 15, 181–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sebald, M. Genetic basis for antibiotic resistance in anaerobes. Clin. Infect. Dis. 1994, 18 (Suppl. S4), S297–S304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauge, I.H.; Sandegren, V.; Winther, A.R.; Bøe, C.A.; Salehian, Z.; Håvarstein, L.S.; Kjos, M.; Straume, D. A novel proteinaceous molecule produced by Lysinibacillus sp. OF-1 depends on the Ami oligopeptide transporter to kill Streptococcus pneumoniae. Microbiology 2023, 169, 001313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, M.; Li, X.; Liu, H.; Miller, S.J.; Wang, G.; Rensing, C. Characterization and genomic analysis of a highly chromate resistant and reducing bacterial strain Lysinibacillus fusiformis ZC1. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 185, 682–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menezes, H.S.G.; Nascimento, N.A.; Paiva-Cavalcanti, M.; da Costa-Latgé, S.G.; Genta, F.A.; Oliveira, C.M.; Romão, T.P.; Silva-Filha, M.H.N. Molecular and biological features of Culex quinquefasciatus homozygous larvae for two cqm1 alleles that confer resistance to Lysinibacillus sphaericus larvicides. Pest Manag. Sci. 2021, 77, 3135–3144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wirth, M.C.; Walton, W.E.; Federici, B.A. Evolution of resistance in Culex quinquefasciatus (Say) selected with a recombinant Bacillus thuringiensis strain-producing Cyt1Aa and Cry11Ba, and the binary toxin, Bin, from Lysinibacillus sphaericus. J. Med. Entomol. 2015, 52, 1028–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Zhou, H.; Li, L.; Wang, E.; Zhou, X.; Gu, Y.; Wu, X.; Shen, L.; Zeng, W. Whole genome sequencing and comparative genomic analyses of Lysinibacillus pakistanensis LZH-9, a halotolerant strain with excellent COD removal capability. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuevas, J.P.; Moraga, R.; Sánchez-Alonzo, K.; Valenzuela, C.; Aguayo, P.; Smith, C.T.; García, A.; Fernandez, Í.; Campos, V.L. Characterization of the bacterial biofilm communities present in reverse-osmosis water systems for haemodialysis. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiarini, L.; Bevivino, A.; Dalmastri, C.; Tabacchioni, S.; Visca, P. Burkholderia cepacia complex species: Health hazards and biotechnological potential. Trends Microbiol. 2006, 14, 277–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eberl, L.; Vandamme, P. Members of the genus Burkholderia: Good and bad guys. F1000Research 2016, 5, F1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morya, R.; Salvachúa, D.; Thakur, I.S. Burkholderia: An untapped but promising bacterial genus for the conversion of aromatic compounds. Trends Biotechnol. 2020, 38, 963–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avelino-Jiménez, I.; Hernández-Maya, L.; Larios-Serrato, V.; Quej-Ake, L.; Castelán-Sánchez, H.; Herrera-Díaz, J.; Garibay-Febles, V.; Rivera-Olvera, J.; Zavala-Olivares, G.; Zapata-Peñasco, I. Biofouling and biocorrosion by microbiota from a marine oil pipeline: A metagenomic and proteomic approach. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 109413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajala, P.; Sohlberg, E.; Priha, O.; Tsitko, I.; Väisänen, H.; Tausa, M.; Carpén, L. Biofouling on coated carbon steel in cooling water cycles using brackish seawater. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2016, 4, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Ma, Y.; Duan, J.; Li, X.; Wang, J.; Hou, B. Analysis of marine microbial communities colonizing various metallic materials and rust layers. Biofouling 2019, 35, 429–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calderón, K.; González-Martínez, A.; Gómez-Silván, C.; Osorio, F.; Rodelas, B.; González-López, J. Archaeal diversity in biofilm technologies applied to treat urban and industrial wastewater: Recent advances and future prospects. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 18572–18598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.; Zhou, J.; Hong, P.Y. Attached-growth configuration outperforms continuously stirred tank anaerobic membrane bioreactors in alleviating membrane biofouling. Environ. Res. 2021, 199, 111272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palacios, P.A.; Snoeyenbos-West, O.; Löscher, C.R.; Thamdrup, B.; Rotaru, A.E. Baltic Sea methanogens compete with acetogens for electrons from metallic iron. ISME J. 2019, 13, 3011–3023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Sample | Bacterial Species Identified | Mean Score Value |
|---|---|---|
| Bacteria Test—STANDARD | Escherichia coli | 2.30 |
| Fouled | Bacillus cereus | 2.42 |
| Fouled | Citrobacter koseri | 2.57 |
| Fouled | Citrobacter farmer | 2.35 |
| Fouled | Bacillus cereus | 2.32 |
| Fouled | Bacillus licheniformis | 2.08 |
| Cleaning C | Bacillus licheniformis | 2.11 |
| Cleaning C | Burkholderia cepacia | 2.33 |
| Cleaning A | Bacillus licheniformis | 2.43 |
| Cleaning B | Burkholderia cepacia | 2.05 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Al-Balushi, M.A.; Kyaw, H.H.; Myint, M.T.Z.; Al-Abri, M.; Dobretsov, S. Chemical Cleaning Techniques for Fouled RO Membranes: Enhancing Fouling Removal and Assessing Microbial Composition. Membranes 2024, 14, 204. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes14100204
Al-Balushi MA, Kyaw HH, Myint MTZ, Al-Abri M, Dobretsov S. Chemical Cleaning Techniques for Fouled RO Membranes: Enhancing Fouling Removal and Assessing Microbial Composition. Membranes. 2024; 14(10):204. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes14100204
Chicago/Turabian StyleAl-Balushi, Mohammed A., Htet Htet Kyaw, Myo Tay Zar Myint, Mohammed Al-Abri, and Sergey Dobretsov. 2024. "Chemical Cleaning Techniques for Fouled RO Membranes: Enhancing Fouling Removal and Assessing Microbial Composition" Membranes 14, no. 10: 204. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes14100204
APA StyleAl-Balushi, M. A., Kyaw, H. H., Myint, M. T. Z., Al-Abri, M., & Dobretsov, S. (2024). Chemical Cleaning Techniques for Fouled RO Membranes: Enhancing Fouling Removal and Assessing Microbial Composition. Membranes, 14(10), 204. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes14100204









