Thermal Lamination of Electrospun Nanofiber Membrane with Woven Fabric and Yarn Embedding Effect
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Electrospinning
2.3. Laminations
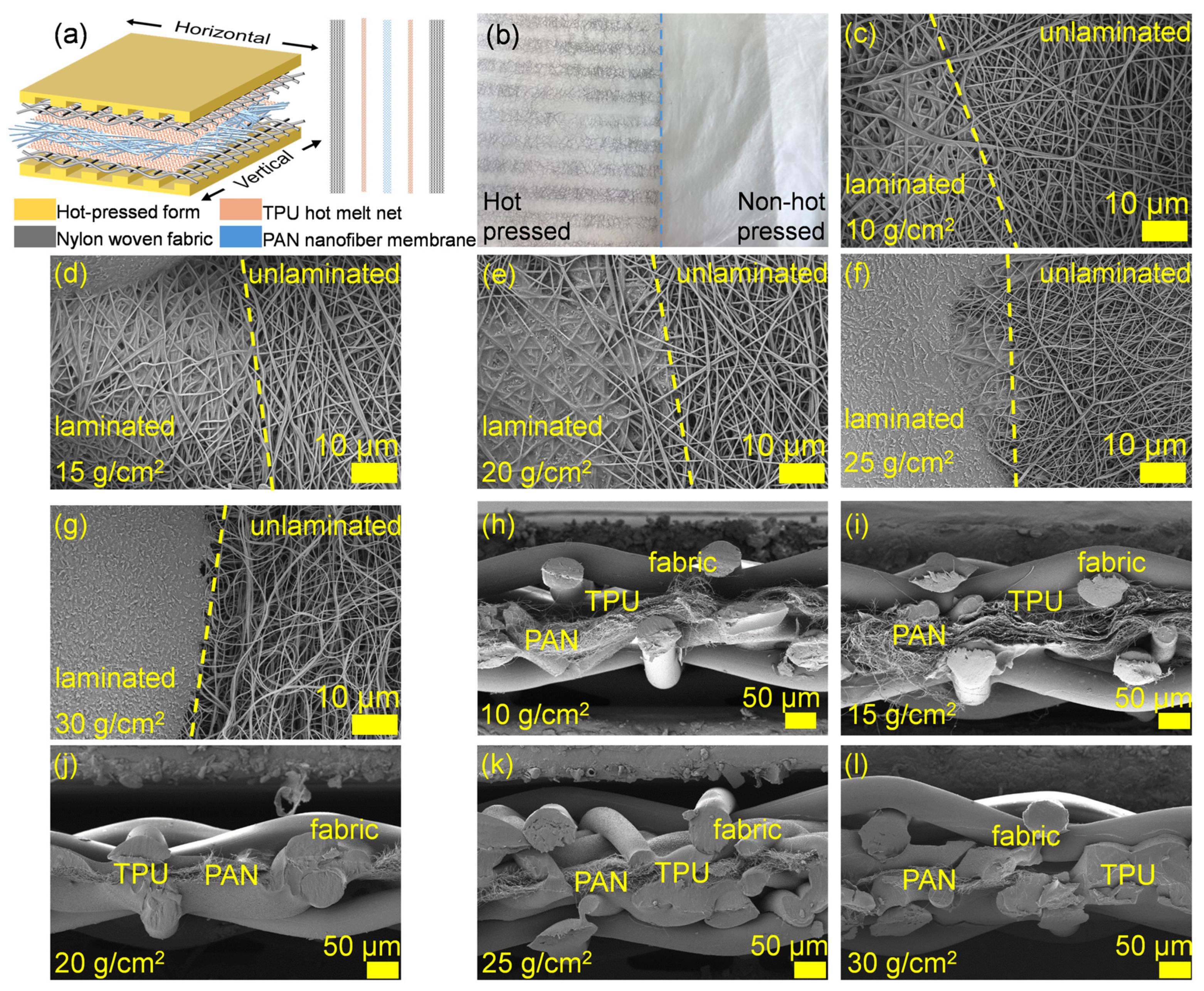
2.3.1. Hot-Press Lamination
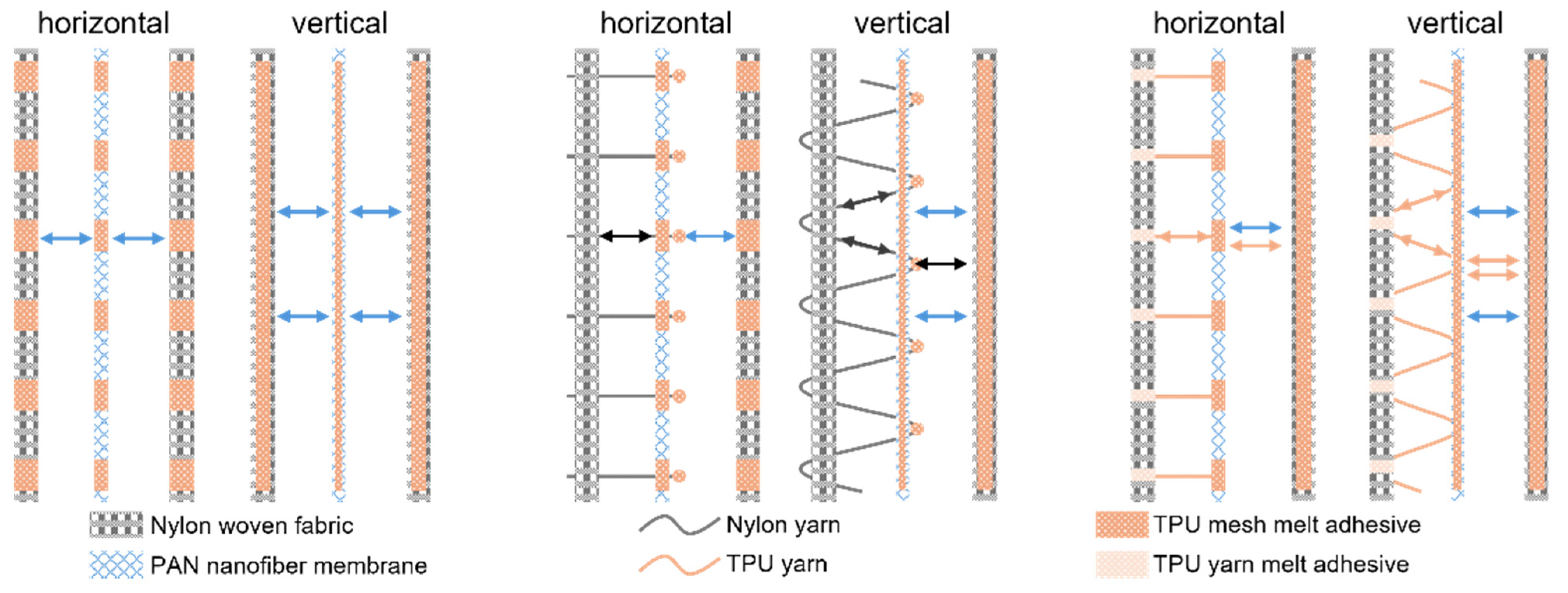
2.3.2. Lamination with Infusible Yarn Embedded
2.3.3. Lamination with TPU Fusible Yarn Embedded
2.4. Characterizations
3. Results
3.1. Preparation and Morphological Characterization of PAN Nanofiber Membranes
3.2. Lamination of Nanofiber Membrane with Nylon Fabric Using Method 1
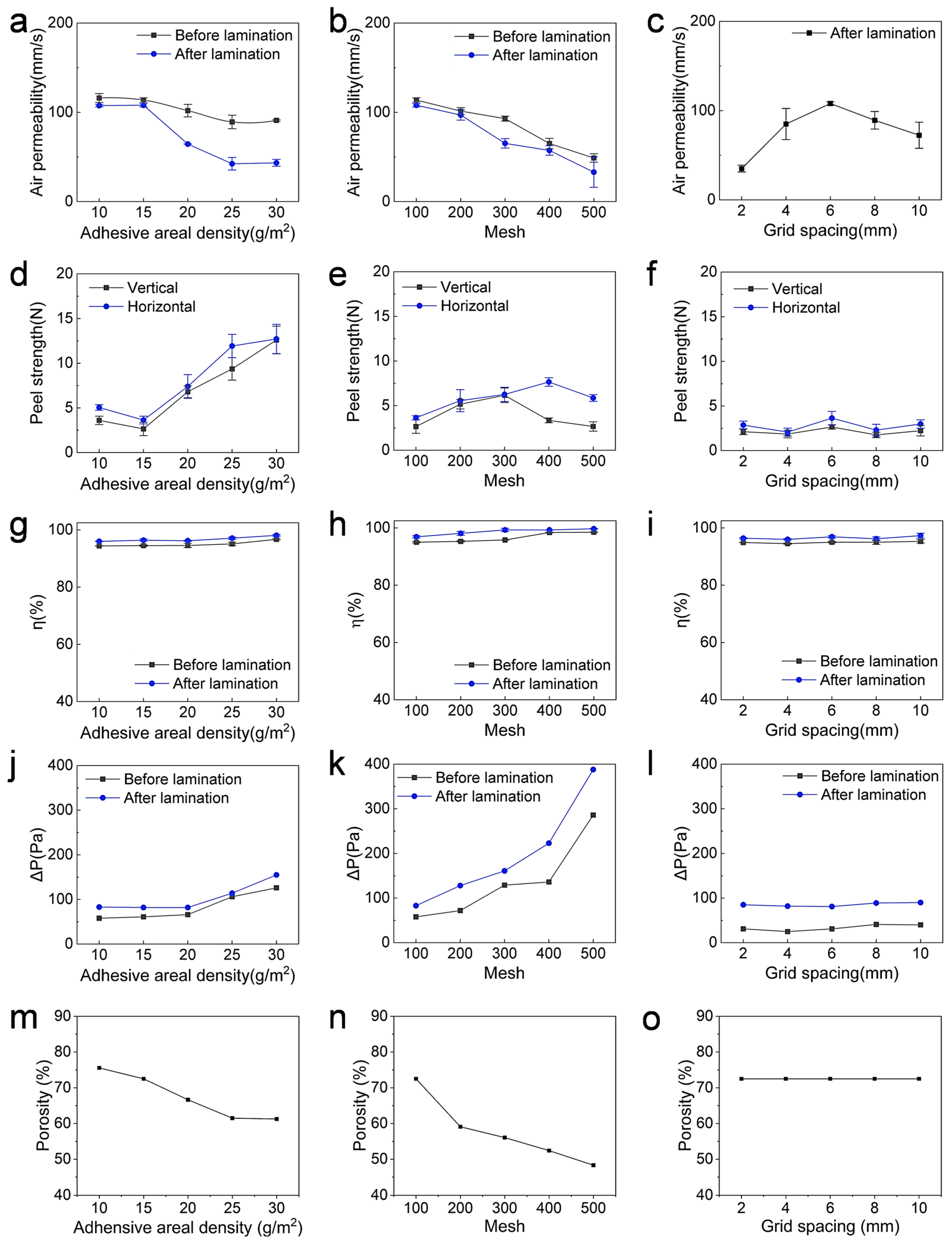
3.2.1. Air Permeability
3.2.2. Peel Strength
3.2.3. Oil Mist Filtration Properties
3.2.4. Porosity
3.3. Lamination of Nanofiber Membrane with Nylon Fabric Using Method 2
3.3.1. Incorporation of Infusible Yarns
3.3.2. Incorporation of Fusible TPU Yarns
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alshabanah, L.A.; Omran, N.; Elwakil, B.H.; Hamed, M.T.; Abdallah, S.M.; Al-Mutabagani, L.A.; Wang, D.; Liu, Q.; Shehata, N.; Hassanin, A.H.; et al. Elastic Nanofibrous Membranes for Medical and Personal Protection Applications: Manufacturing, Anti-COVID-19, and Anti-Colistin Resistant Bacteria Evaluation. Polymers 2021, 13, 3987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patnaik, A. Recent Developments in Application of Nanofibers. Processes 2024, 12, 1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koozekonan, A.G.; Esmaeilpour, M.R.M.; Kalantary, S.; Karimi, A.; Azam, K.; Moshiran, V.A.; Golbabaei, F. Fabrication and characterization of PAN/CNT, PAN/TiO2, and PAN/CNT/TiO2 nanofibers for UV protection properties. J. Text. Inst. 2020, 112, 946–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Li, Y.; Sheng, G. Nanodiamond-Reinforced Polyurethane Micro/Nanofiber Membrane for UV Protection in Multifunctional Textiles. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2024, 7, 12323–12333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Chen, W.; Wang, L.; Yao, J.; Zhu, G.; Guo, B.; Militky, J.; Venkataraman, M.; Zhang, M. Multifunctional nanofiber membrane with anti-ultraviolet and thermal regulation fabricated by coaxial electrospinning. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2022, 108, 449–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, Y.; Shi, S.; Hu, J. Applications of electrospinning in human health: From detection, protection, regulation to reconstruction. Nano Today 2023, 48, 101723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.; Gu, J.; Liu, X.; Ren, Y.; Mi, X.; Zhan, W.; Zhang, X.; Wang, H.; Ji, X.; Yue, Z.; et al. A Robust Core-Shell Nanofabric with Personal Protection, Health Monitoring and Physical Comfort for Smart Sportswear. Adv. Mater. 2024, 36, e2411131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Chang, Q.; Li, H.; Wang, J.; Guo, S.; Zhang, X. Multifunctional wearable Spider-Silk Inspired fabric for personal protection in extreme environments. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 491, 152011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.; Jiang, L.; Chen, G.; Ma, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, R. Electrospun porous polyacrylonitrile/polyvinylpyrrolidone nanofiber membrane with ultra-hydrophilic and high moisture-permeability for dust personal protection. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 113524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alharbi, H.F.; Luqman, M.; Khalil, K.A.; Elnakady, Y.A.; Abd-Elkader, O.H.; Rady, A.M.; Alharthi, N.H.; Karim, M.R. Fabrication of core-shell structured nanofibers of poly (lactic acid) and poly (vinyl alcohol) by coaxial electrospinning for tissue engineering. Eur. Polym. J. 2018, 98, 483–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Okaidy, H.S.; Waisi, B.I. The Effect of Electrospinning Parameters on Morphological and Mechanical Properties of PAN-based Nanofibers Membrane. Baghdad Sci. J. 2023, 20, 1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, N.; Qin, X.; Wang, L.; Yu, J. Electrospun nanofiber/cotton composite yarn with enhanced moisture management ability. Text. Res. J. 2021, 91, 1467–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalalah, M.; Ahmad, A.; Saleem, A.; Qadir, M.B.; Khaliq, Z.; Khan, M.Q.; Nazir, A.; Faisal, M.; Alsaiari, M.; Irfan, M.; et al. Electrospun Nanofiber/Textile Supported Composite Membranes with Improved Mechanical Performance for Biomedical Applications. Membranes 2022, 12, 1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suekawa, M.; Hashizume, Y.; Tanoue, S.; Uematsu, H.; Yamashita, Y. Infection Prevention Mask Consisting of Nanofiber Filter and Habutae Silk Fabrics. Materials 2021, 14, 7391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagherzadeh, R.; Latifi, M.; Najar, S.S.; Tehran, M.A.; Gorji, M.; Kong, L. Transport properties of multi-layer fabric based on electrospun nanofiber mats as a breathable barrier textile material. Text. Res. J. 2011, 82, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akduman, Ç.; Oğlakcıoğlu, N.; Çay, A. Enhanced thermoregulation performance of knitted fabrics using phase change material incorporated thermoplastic polyurethane and cellulose acetate nanofibers. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2024, 64, 5360–5374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, R.; Li, J.; Chen, M.; Zhang, S.; Cheng, Y.; Ning, X.; Wang, N. Tailoring moisture electroactive Ag/Zn@cotton coupled with electrospun PVDF/PS nanofibers for antimicrobial face masks. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 428, 128239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taheri, P.; Khajeh-Amiri, A. Antibacterial cotton fabrics via immobilizing silver phosphate nanoparticles onto the chitosan nanofiber coating. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 158, 282–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varesano, A.; Rombaldoni, F.; Tonetti, C.; Di Mauro, S.; Mazzuchetti, G. Chemical treatments for improving adhesion between electrospun nanofibers and fabrics. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2013, 131, 39766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Zhang, X.; Jiang, A.; Pan, Z. Adhesion and protective properties of polyvinyl alcohol nanofibrous composite fabrics. J. Text. Inst. 2018, 109, 1263–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herwan, J.; Al-Bahkali, E.; Khalil, K.A.; Souli, M. Load bearing enhancement of pin joined composite laminates using electrospun polyacrylonitrile nanofiber mats. Arab. J. Chem. 2016, 9, 262–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Chen, Y.; Wei, M.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, X.; Fu, Z.; Liu, Y. Autoclavable Nanofiber Laminated Fabrics with Waterproof and Breathability for Reusable Medical Protective Textiles. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2023, 6, 23496–23505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Zhang, Q.; Chadyagondo, T.T.; Li, G.; Gu, H.; Li, N. Designing Waterproof and Breathable Fabric Based on Polyurethane/Silica Dioxide Web Fabricated by Electrospinning. Fibers Polym. 2020, 21, 1444–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T5453; Test Method for Determination of Fabric Breathability. National standard of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 1995.
- FZ/T 6011-2016; Test Method for Peel Strength of Composite Fabrics. Textile Industry Standards of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2016.
- Shao, H.; Wang, H.; Cao, Y.; Ding, X.; Bai, R.; Chang, H.; Fang, J.; Jin, X.; Wang, W.; Lin, T. Single-layer piezoelectric nanofiber membrane with substantially enhanced noise-to-electricity conversion from endogenous triboelectricity. Nano Energy 2021, 89, 106427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, H.; Wang, H.; Cao, Y.; Ding, X.; Fang, J.; Niu, H.; Wang, W.; Lang, C.; Lin, T. Efficient conversion of sound noise into electric energy using electrospun polyacrylonitrile membranes. Nano Energy 2020, 75, 104956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karbownik, I.; Rac-Rumijowska, O.; Fiedot-Tobola, M.; Rybicki, T.; Teterycz, H. The Preparation and Characterization of Polyacrylonitrile-Polyaniline (PAN/PANI) Fibers. Materials 2019, 12, 664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Yarn | Count | Size (μm) | Strength (N) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nylon | 150D/3 | 180 | 35.6 |
| Cotton | 40S/2 | 120 | 11.8 |
| Polyester | 40S/2 | 50 | 12.0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gao, Z.; Xu, L.; Wang, H.; Wei, X.; Chen, K.; Wang, W.; Zhang, S.; Lin, T. Thermal Lamination of Electrospun Nanofiber Membrane with Woven Fabric and Yarn Embedding Effect. Membranes 2025, 15, 95. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes15030095
Gao Z, Xu L, Wang H, Wei X, Chen K, Wang W, Zhang S, Lin T. Thermal Lamination of Electrospun Nanofiber Membrane with Woven Fabric and Yarn Embedding Effect. Membranes. 2025; 15(3):95. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes15030095
Chicago/Turabian StyleGao, Ziyuan, Le Xu, Hongxia Wang, Xin Wei, Kaikai Chen, Wenyu Wang, Suzhen Zhang, and Tong Lin. 2025. "Thermal Lamination of Electrospun Nanofiber Membrane with Woven Fabric and Yarn Embedding Effect" Membranes 15, no. 3: 95. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes15030095
APA StyleGao, Z., Xu, L., Wang, H., Wei, X., Chen, K., Wang, W., Zhang, S., & Lin, T. (2025). Thermal Lamination of Electrospun Nanofiber Membrane with Woven Fabric and Yarn Embedding Effect. Membranes, 15(3), 95. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes15030095









