Addressing Contaminants of Emerging Concern in Aquaculture: A Vacuum Membrane Distillation Approach
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials, Reagents, Standards, and Solutions
2.2. Sample Preparation for Permeation Tests
2.3. Vacuum Membrane Distillation Process
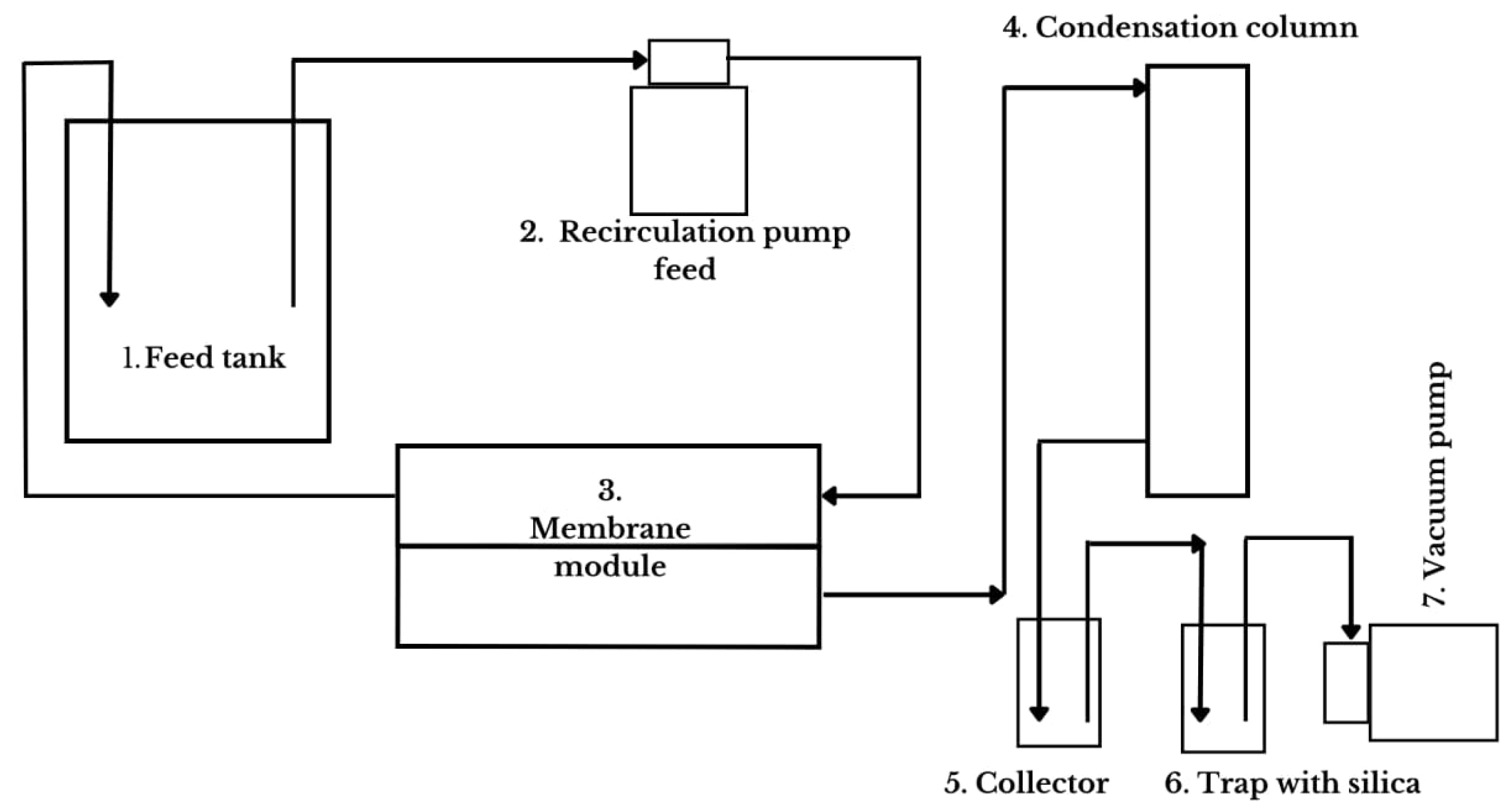
2.3.1. Equipment, Membrane Specification, and General Description
- Feed Tank: double-jacketed borosilicate glass feed tank; it is heated, and samples are added to initiate the process, serving as the initial feed point;
- Recirculation pump feed (SFDPA2-015-060, Seaflo, Xiamen, China): This pump is responsible for recirculating the solution between the feed and the membrane module. The pump uses a Variac transformer to control the flow rate of the recirculation system, which can be visualized using a rotameter that measures the flow rate;
- Membrane module: A support structure that holds the membrane through which the solution recirculates at the selected temperature. Above the membrane, a hot aqueous solution flows, and what permeates the membrane—a solution/solvent in a vapor state—flows to the Serpentine Graham condenser;
- Condensation column (Serpentine Graham): using a 40% ethylene glycol solution at 0 °C, the condenser is responsible for precipitating the solution/solvent so it can be collected in the collector;
- Collector: where the permeate or distilled solution is collected;
- Trap with silica: a vacuum pump buffer container containing silica to retain vapor;
- Vacuum pump (Q-355B, Quimis, São Paulo, Brazil): responsible for creating negative pressure in the system (−640 mmHg).
2.3.2. Determining VMD Membrane Performance
- J is the permeate flux (L·h−1·m−2);
- V is the collected permeate volume (L);
- t is the sample collection time (h);
- A is the area in m2.
- Cinitial is the initial concentration of the analyte or particles in the feed solution;
- Cfinal is the final concentration of the analyte or particles in the solution (permeate).
2.4. Antimicrobial Quantification
2.4.1. Sample Preparation by Solid Phase Extraction (SPE)
2.4.2. Analysis by LC-MS/MS
2.5. Plant Ecotoxicity Test with Lactuca sativa L.
- Control A and control B (distilled water);
- Sulfamethoxazole A and sulfamethoxazole B;
- Ciprofloxacin A and ciprofloxacin B;
- Azithromycin A and azithromycin B;
- Clindamycin A and clindamycin B;
- Mixture A and mixture B.
- RSG: Relative seed germination
- RGR: Relative growth of the radicle
- NGI: Normalized Residual Germination Percentage Index
- Germy is the average percentage of germinated seeds in each sample;
- Germcontrol is the percentage of germinated seeds in the control.
- NGR: Normalized Residual Radical Elongation Percentage Index
- alongy is the average radicle length of the germinated seeds in each sample;
- alongcontrol is the average radicle length of the germinated seeds in the control.
- 0 to −0.25: low toxicity;
- −0.25 to −0.5: moderate toxicity;
- −0.5 to −0.75: high toxicity;
- −0.75 to −1.0: very high toxicity.
2.6. CECS Human Risk Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Permeation Tests
3.1.1. Preliminary Tests for Temperature Process Definition
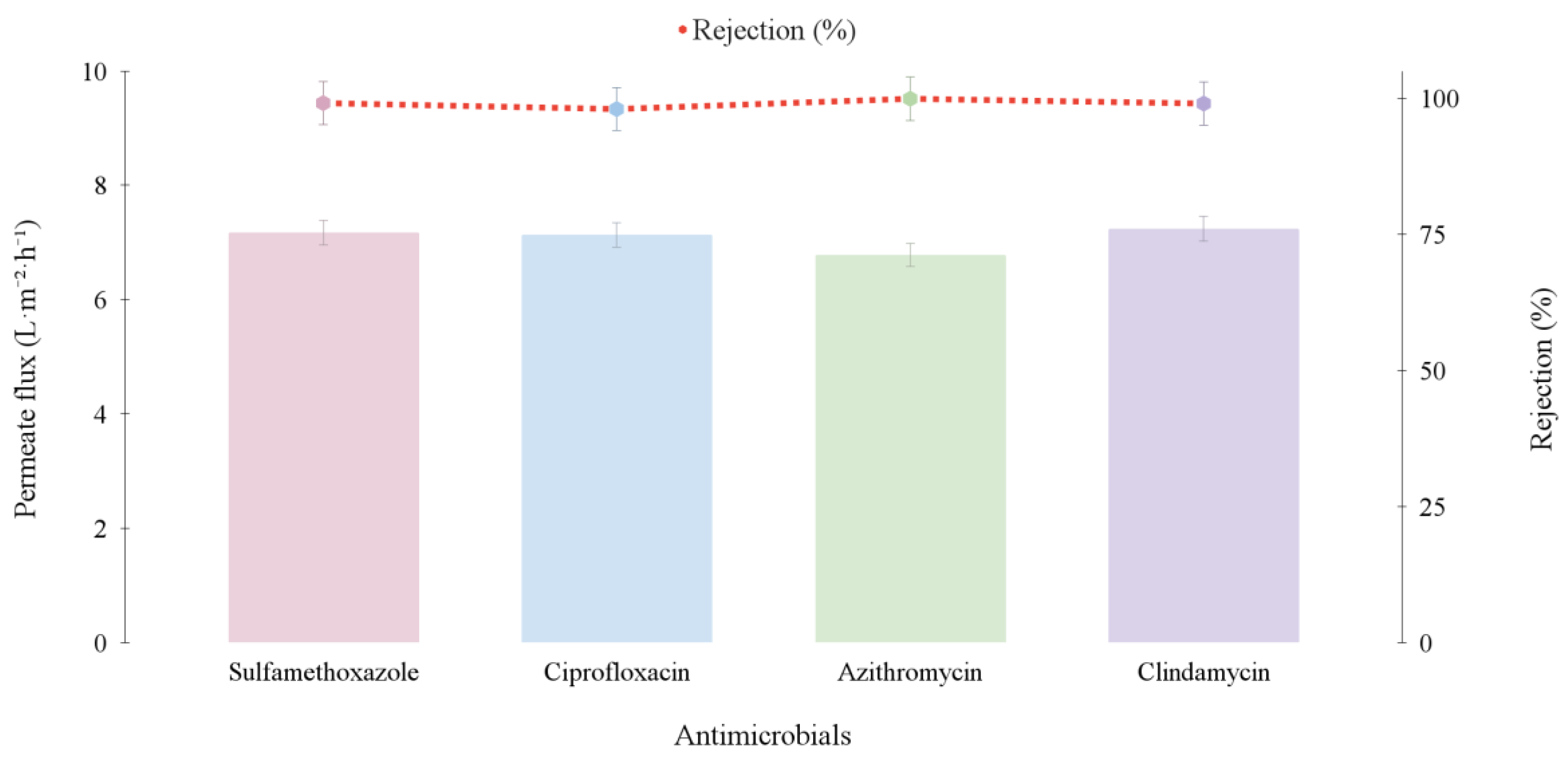
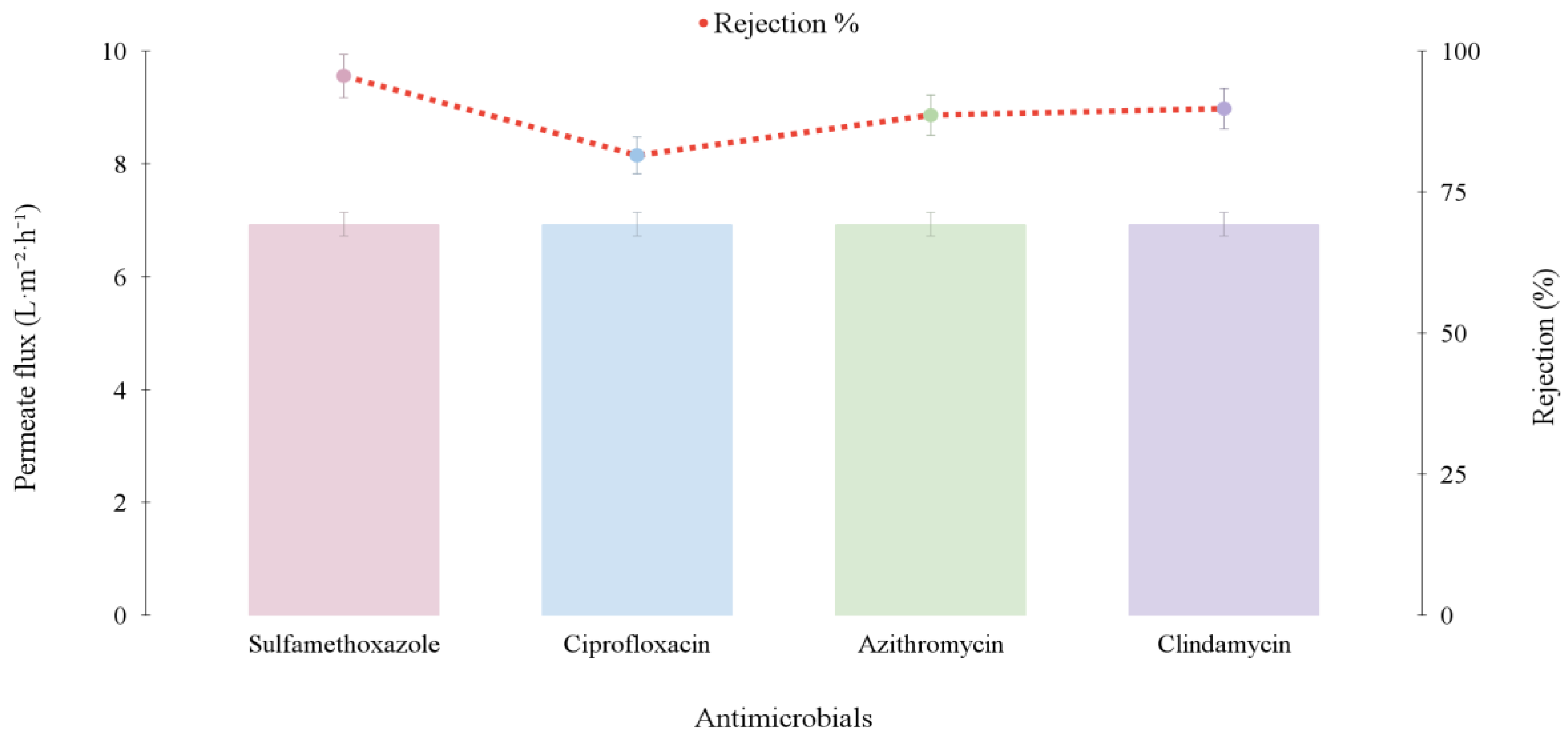
3.1.2. Individual and Mixture Antimicrobials Tests
3.2. Plant Ecotoxicity Test
3.3. Human Risk Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Falda, L.P.; Assunção, E.G.; Kuroda, E.K. Concepções de biofiltração aplicada ao pré-tratamento de águas de abastecimento para remoção de contaminantes emergentes. Eng. Sanit. E Ambiental 2023, 28, e20220174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil, M.L.; Melgaço, S.; da Cunha, D.L.; Bila, D.M.; da Fonseca, E.M. Contaminantes emergentes e indicadores de contaminação em ambientes costeiros brasileiros: Ocorrência, distribuição geográfica e procedimentos analíticos utilizados. Pesquisa Em Geociências 2023, 50, e131523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brasil. Ministério da Saúde do Brasil; Saúde Única. Conceito sobre Saúde Única: Brasília, Brasil, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Rios, M.C.F.A. Percepção da Qualidade Ambiental da Lagoa da Conceição pelos Pescadores Artesanais e sua Relação com a Pesca: Ilha de Santa Catarina, Brasil. Trab. De Conclusão De Curso De Oceanogr.-UFSC. 2017. Available online: https://biogeoqmar.paginas.ufsc.br/files/2018/03/percepção-da-qualidade-ambiental-da-lagoa-da-conceição-pelos-pescadores-artesanais-e-sua-relação-com-a-pesca-ilha-de-santa-catarina-brasil.-tcc-maria-clara-rios-2017.pdf (accessed on 11 March 2025).
- Da Silva, A.C.; de Oliveira, L.V.; Alexandre, L.A.; Ribas, M.R.; Dal Pizzol, J.L.; Rocha, G.; Palmeiro, J.K.; Perin, M.; Hoff, R.; Verruck, S. Suspect screening and quantitative analysis of 165 contaminants of emerging concern in water, sediments, and biota using LC-MS/MS: Ecotoxicological and human health risk assessment. Sci. Total Environ. 2025, 963, 178434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, T.; Kang, G.; Zhou, M.; Li, M.; Cao, Y. Investigation of flux attenuation and crystallization behavior in submerged vacuum membrane distillation (SVMD) for SWRO brine concentration. Chem. Eng. Process.-Process Intensif. 2019, 143, 107567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woldemariam, D.; Kullab, A.; Fortkamp, U.; Magner, J.; Royen, H.; Martin, A. Membrane distillation pilot plant trials with pharmaceutical residues and energy demand analysis. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 306, 471–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Côté, P.; Siverns, S.; Monti, S. Comparison of membrane-based solutions for water reclamation and desalination. Desalination 2005, 182, 251–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsheghri, A.; Sharief, S.A.; Rabbani, S.; Aitzhan, N.Z. Design and cost analysis of a solar photovoltaic powered reverse osmosis plant for Masdar Institute. Energy Procedia 2015, 75, 319–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Ji, Z.; Yan, H.; Wu, B.; Guo, Y.; Wang, H.; Li, C. Water recovery from cleaning wastewater of traditional Chinese medicine processing via vacuum membrane distillation: Parameters optimization and membrane fouling investigation. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2022, 188, 555–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omi, F.R.; Rastgar, M.; Mohseni, M.; Singh, U.; Dilokekunakul, W.; Keller, R.; Wishart, D.; Wessling, M.; Vecitis, C.D.; Sadrzadeh, M. Removal of emerging contaminants from water using novel electroconductive membranes in a hybrid membrane distillation and electro-Fenton process. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2025, 357, 130083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kern, P.; de Liz Arcari, T.; Franco, D.; Uda, P.K. In Proceedings of the XXIII Simpósio Brasileiro De Recursos Hídricos, Foz do Iguaçu, Brazil, 24–28 November 2019.
- Lisboa, L.K.; Teive, L.F.; Petrucio, M.M. Lagoa da Conceição: Uma revisão da disponibilidade de dados ecológicos visando o direcionamento de novas pesquisas no ecossistema. Biotemas 2008, 21, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Li, C.; Liu, W.; Mao, J.; Hu, L.; Yun, Y.; Li, B. Superhydrophobic PVDF membrane modified by dopamine self-polymerized nanoparticles for vacuum membrane distillation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 304, 122182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jank, L.; Hoff, R.B.; da Costa, F.J.; Pizzolato, T.M. Simultaneous determination of eight antibiotics from distinct classes in surface and wastewater samples by solid-phase extraction and high-performance liquid chromatography–electrospray ionisation mass spectrometry. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2014, 94, 1013–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoff, R.; Vogelmann, E.S.; de Melo, A.P.Z.; Deolindo, C.T.P.; Medeiros, B.M.d.S.; Daguer, H. Reacqua: A low-cost solar still system for the removal of antibiotics from contaminated effluents. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 106488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobrero, M.C.; Ronco, A. Ensayo de toxicidad aguda con semillas de lechuga Lactuca sativa L. In Ensayos Toxicológicos y Métodos de Evaluación de Calidad de Aguas: Estandarización, Intercalibración, Resultados y Aplicaciones; Instituto Mexicano de Tecnología del Agua: Progreso, Mexico, 2004; pp. 63–70. [Google Scholar]
- Marcu, D.; Keyser, S.; Petrik, L.; Fuhrimann, S.; Maree, L. Contaminants of emerging concern (CECs) and male reproductive health: Challenging the future with a double-edged sword. Toxics 2023, 11, 330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Andrade, J.C.; Galvan, D.; Kato, L.S.; Conte-Junior, C.A. Consumption of fruits and vegetables contaminated with pesticide residues in Brazil: A systematic review with health risk assessment. Chemosphere 2023, 322, 138244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucchesi, I.; Fisberg, R.M.; Sales, C.H. A qualidade da dieta está associada com a ingestão de água em residentes de São Paulo, Brasil. Ciência Saúde Coletiva 2021, 26, 3875–3883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alawad, S.M.; Shamet, O.; Khalifa, A.E.; Lawal, D. Enhancing productivity and energy efficiency in vacuum membrane distillation systems. Energy Convers. Manag. X 2024, 22, 100593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martıánez-Dıáez, L.; Vázquez-González, M.I. Temperature and concentration polarization in membrane distillation of aqueous salt solutions. J. Membr. Sci. 1999, 156, 265–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freitas, R.L.M. Efeito da Temperatura de Resfriamento Sobre as Propriedades de Polímeros Amorfos e Semicristalinos. Rio de Janeiro: UFRJ—Escola Politécnica, 2014. XII, 53 p. Trab. De Conclusão De Curso Em Eng. De Mater. Univ. Fed. Do Rio De Janeiro. Rio de Janeiro. 2014. Available online: https://monografias.poli.ufrj.br/monografias/monopoli10011617.pdf (accessed on 11 March 2025).
- Mahlangu, O.T.; Motsa, M.M.; Hai, F.I.; Mamba, B.B. Role of Membrane–Solute Affinity Interactions in Carbamazepine Rejection and Resistance to Organic Fouling by Nano-Engineered UF/PES Membranes. Membranes 2023, 13, 744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, F.C.; dos Santos, C.R.; Amaral, M.C. Trace organic contaminants removal by membrane distillation: A review on mechanisms, performance, applications, and challenges. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 464, 142461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramlow, H.; Correa, V.H.M.; Machado, R.A.F.; Bierhalz, A.C.K.; Marangoni, C. Intensification of water reclamation from textile dyeing wastewater using thermal membrane technologies–Performance comparison of vacuum membrane distillation and thermopervaporation. Chem. Eng. Process.-Process Intensif. 2019, 146, 107695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, D.; Sarma, S.S.; Kumar, D.; Ingole, P.G. Amine functionalized TiO2-based eco-friendly thin-film nanocomposite membranes for efficient pharmaceutical micropollutant removal. Chem. Eng. J. 2025, 504, 158695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Yang, J.; Yu, X.; Zhao, G.; Zhao, Q.; Wang, N.; Jiang, Y.; Jiang, F.; He, G.; Chen, Y.; et al. Exposure of adults to antibiotics in a Shanghai suburban area and health risk assessment: A biomonitoring-based study. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 13942–13950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burmaster, D.E.; Anderson, P.D. Principles of good practice for the use of Monte Carlo techniques in human health and ecological risk assessments. Risk Anal. 1994, 14, 477–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drakvik, E.; Altenburger, R.; Aoki, Y.; Backhaus, T.; Bahadori, T.; Barouki, R.; Brack, W.; Cronin, M.T.; Demeneix, B.; Bennekou, S.H.; et al. Statement on advancing the assessment of chemical mixtures and their risks for human health and the environment. Environ. Int. 2020, 134, 105267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Characteristics | |
|---|---|
| Polymer | PTFE |
| Pore size (µm) | 0.22 |
| Air flow (L·min−1·cm−2) | 5 |
| Water flow (mL·min·cm−2) | 24 |
| Porosity (%) | 85 |
| Thickness (µm) | 150 |
| Maximum Temperature (°C) | 130 |
| Wettability | Hydrophobic |
| Saline Solution | Lagoa da Conceição Water | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 65 °C | 75 °C | 65 °C | 75 °C | |
| Rejection (%) | 99.7 ± 0.3 | 99.8 ± 0.2 | 99.8 ± 0.2 | 99.9 ± 0.1 |
| Permeate flux reduction (%) | 6 | 22 | 11 | 36 |
| Permeate flux (L·m2·h−1) | 2.9 ± 0.2 | 7.9 ± 0.3 | 3.3 ± 0.2 | 8.2 ± 0.1 |
| Conductivity (µ·Scm−1) | 27,800 | 29,900 | ||
| Concentration (g·L−1) | 27.14 | 30.01 | ||
| Sample (Root) | Control (H2O) | Sulfamethoxazole | Ciprofloxacin | Azithromycin | Clindamycin | Mixing |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Average size (cm) | 26.52 ± 9.15 | 22.78 ± 5.60 | 22.24 ± 4.89 | 22.92 ± 6.09 | 10.68 ± 6.02 | 21.36 ± 4.95 |
| Average number of ungerminated seeds | 19 | 20 | 18 | 18 | 17.50 | 17.50 |
| % Germination | 95 | 95 | 90 | 90 | 87.50 | 87.50 |
| GI% | - | 90.40 | 79.42 | 81.88 | 37.10 | 74.16 |
| NGI | - | 0 | −0.051 | 0 | −0.028 | 0 |
| RSG | - | 105.26 | 94.74 | 94.74 | 92.11 | 92.11 |
| RGR | - | 85.87 | 83.84 | 86.43 | 40.28 | 80.52 |
| NGR | - | −0.14 | −0.16 | −0.14 | −0.60 | −0.19 |
| Toxicity | Control ◎ | Low ◉ | Low ◉ | Low ◉ | High ◉ | Low ◉ |
| Sulfametoxazol | Ciprofloxacino | Azitromicina | Clindamicina | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ADD (ng·kg−1/bw·day−1) | ND | 226.65 ± 45.32 | ND | 211.5 ± 42.3 |
| HI (ng·kg−1/bw·day−1) | ND | 3.18 × 10−4 | ND | 3.53 × 10−3 |
| Risk level | ++ | +++ |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Malaghini, C.M.E.; Garcez, J.; Hoff, R.; Ambrosi, A.; Rezzadori, K. Addressing Contaminants of Emerging Concern in Aquaculture: A Vacuum Membrane Distillation Approach. Membranes 2025, 15, 127. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes15050127
Malaghini CME, Garcez J, Hoff R, Ambrosi A, Rezzadori K. Addressing Contaminants of Emerging Concern in Aquaculture: A Vacuum Membrane Distillation Approach. Membranes. 2025; 15(5):127. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes15050127
Chicago/Turabian StyleMalaghini, Claudio Marcos Eugênio, Jussara Garcez, Rodrigo Hoff, Alan Ambrosi, and Katia Rezzadori. 2025. "Addressing Contaminants of Emerging Concern in Aquaculture: A Vacuum Membrane Distillation Approach" Membranes 15, no. 5: 127. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes15050127
APA StyleMalaghini, C. M. E., Garcez, J., Hoff, R., Ambrosi, A., & Rezzadori, K. (2025). Addressing Contaminants of Emerging Concern in Aquaculture: A Vacuum Membrane Distillation Approach. Membranes, 15(5), 127. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes15050127








