Congenital Tufting Enteropathy: Biology, Pathogenesis and Mechanisms
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Clinical Aspects of CTE
1.2. CTE Genetics
1.3. CTE Models
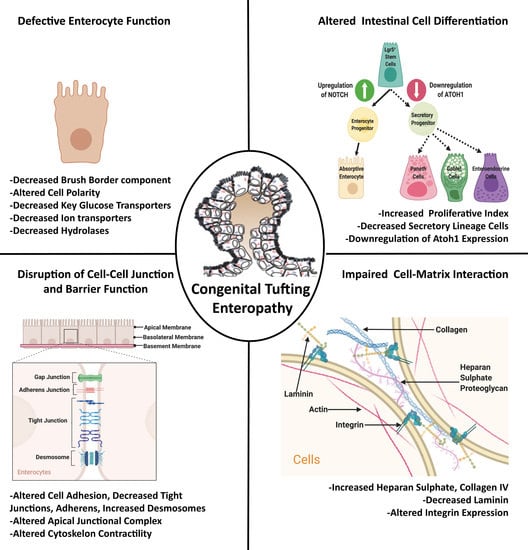
2. Role of Intestinal Homeostasis in CTE Pathogenesis
2.1. Role of Intestinal Cell Differentiation
2.2. Role of Defective Enterocyte Function
2.3. Role of Defective Barrier Function and Altered Cell–Cell Junction
2.4. Role of Cell-Matrix Adhesion
3. Probable Signaling Mechanisms in CTE Pathogenesis
3.1. Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress and Unfolded Protein Response
3.2. Novel Protein Kinase C (nPKC)-Mediated Signaling
3.3. Canonical Wnt Signaling
4. Candidate Therapeutics
5. Future Directions
6. Conclusions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Thiagarajah, J.R.; Kamin, D.S.; Acra, S.; Goldsmith, J.D.; Roland, J.T.; Lencer, W.I.; Muise, A.M.; Goldenring, J.R.; Avitzur, Y.; Martin, M.G.; et al. Advances in Evaluation of Chronic Diarrhea in Infants. Gastroenterology 2018, 154, 2045–2059.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Canani, R.B.; Castaldo, G.; Bacchetta, R.; Martin, M.G.; Goulet, O. Congenital diarrhoeal disorders: Advances in this evolving web of inherited enteropathies. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2015, 12, 293–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goulet, O.; Salomon, J.; Ruemmele, F.; de Serres, N.P.-M.; Brousse, N. Intestinal epithelial dysplasia (tufting enteropathy). Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2007, 2, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Reifen, R.M.; Cutz, E.; Griffiths, A.-M.; Ngan, B.Y.; Sherman, P.M. Tufting enteropathy: A newly recognized clinicopathological entity associated with refractory diarrhea in infants. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 1994, 18, 379–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Mayouf, S.M.; Alswaied, N.; Alkuraya, F.S.; AlMehaidib, A.; Faqih, M. Tufting enteropathy and chronic arthritis: A newly recognized association with a novel EpCAM gene mutation. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2009, 49, 642–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gambarara, M.; Diamanti, A.; Ferretti, F.; Papadatou, B.; Knafelz, D.; Pietrobattista, A.; Castro, M. Intractable diarrhea of infancy with congenital intestinal mucosa abnormalities: Outcome of four cases. Transplant. Proc. 2003, 35, 3052–3053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemale, J.; Coulomb, A.; Dubern, B.; Boudjemaa, S.; Viola, S.; Josset, P.; Tounian, P.; Girardet, J.P. Intractable diarrhea with tufting enteropathy: A favorable outcome is possible. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2011, 52, 734–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, N.S.; Kang, I.S.; Suh, Y.L. Protracted diarrhea: Results of the five-year survey in a tertiary hospital in Korea. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2001, 16, 736–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Davidson, G.P.; Cutz, E.; Hamilton, J.R.; Gall, D.G. Familial enteropathy: A syndrome of protracted diarrhea from birth, failure to thrive, and hypoplastic villus atrophy. Gastroenterology 1978, 75, 783–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivagnanam, M.; Mueller, J.L.; Lee, H.; Chen, Z.; Nelson, S.F.; Turner, D.; Zlotkin, S.H.; Pencharz, P.B.; Ngan, B.Y.; Libiger, O.; et al. Identification of EpCAM as the gene for congenital tufting enteropathy. Gastroenterology 2008, 135, 429–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pathak, S.J.; Mueller, J.L.; Okamoto, K.; Das, B.; Hertecant, J.; Greenhalgh, L.; Cole, T.; Pinsk, V.; Yerushalmi, B.; Gurkan, O.E.; et al. EPCAM mutation update: Variants associated with congenital tufting enteropathy and Lynch syndrome. Hum. Mutat. 2019, 40, 142–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cai, C.; Chen, Y.; Chen, X.; Ji, F. Tufting Enteropathy: A Review of Clinical and Histological Presentation, Etiology, Management, and Outcome. Gastroenterol. Res. Pract. 2020, 2020, 5608069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerada, J. Mucosal Inflammation as a Component of Tufting Enteropathy. Immunogastroenterology 2013, 2, 62–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salomon, J.; Espinosa-Parrilla, Y.; Goulet, O.; Guigue, P.; Canioni, D.; Bruneau, J.; Alzahrani, F.; Almuhsen, S.; Cerf-Bensussan, N.; Jeanpierre, M. A founder effect at the EPCAM locus in Congenital Tufting Enteropathy in the Arabic Gulf. Eur. J. Med. Gen. 2011, 54, 319–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Matary, W.; Dalzell, A.M.; Kokai, G.; Davidson, J.E. Tufting enteropathy and skeletal dysplasia: Is there a link? Eur. J. Pediatr. 2007, 166, 265–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salomon, J.; Goulet, O.; Canioni, D.; Brousse, N.; Lemale, J.; Tounian, P.; Coulomb, A.; Marinier, E.; Hugot, J.-P.; Ruemmele, F. Genetic characterization of congenital tufting enteropathy: Epcam associated phenotype and involvement of SPINT2 in the syndromic form. Hum. Gen. 2014, 133, 299–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terrin, G.; Tomaiuolo, R.; Passariello, A.; Elce, A.; Amato, F.; Di Costanzo, M.; Castaldo, G.; Canani, R.B. Congenital diarrheal disorders: An updated diagnostic approach. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 4168–4185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kahvecioglu, D.; Yildiz, D.; Kilic, A.; Ince-Alkan, B.; Erdeve, O.; Kuloglu, Z.; Atasay, B.; Ensari, A.; Yilmaz, R.; Arsan, S. A rare cause of congenital diarrhea in a Turkish newborn: Tufting enteropathy. Turk. J. Pediatr. 2014, 56, 440–443. [Google Scholar]
- Goulet, O.J.; Brousse, N.; Canioni, D.; Walker-Smith, J.A.; Schmitz, J.; Phillips, A.D. Syndrome of intractable diarrhoea with persistent villous atrophy in early childhood: A clinicopathological survey of 47 cases. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 1998, 26, 151–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haas, K.; Martin, B.; Martin, M.; Kerner, J. Intractable Diarrhea in Two Brothers: Late Diagnosis of Tufting Enteropathy in Adolescence. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2016, 61, 381–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Q.K.; Cardona, D.M.; Rehder, C.W.; McDonald, M.T. Identification of EPCAM mutation: Clinical use of microarray. Clin. Case Rep. 2017, 5, 980–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janecke, A.R.; Heinz-Erian, P.; Muller, T. Congenital Sodium Diarrhea: A Form of Intractable Diarrhea, with a Link to Inflammatory Bowel Disease. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2016, 63, 170–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cameron, D.J.S.; Barnes, G.L. Successful Pregnancy Outcome in Tufting Enteropathy. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2003, 36, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sivagnanam, M.; Janecke, A.R.; Muller, T.; Heinz-Erian, P.; Taylor, S.; Bird, L.M. Case of syndromic tufting enteropathy harbors SPINT2 mutation seen in congenital sodium diarrhea. Clin. Dysmorphol. 2010, 19, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roche, O.; Putterman, M.; Salomon, J.; Lacaille, F.; Brousse, N.; Goulet, O.; Dufier, J.L. Superficial punctate keratitis and conjunctival erosions associated with congenital tufting enteropathy. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2010, 150, 116–121.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heinz-Erian, P.; Muller, T.; Krabichler, B.; Schranz, M.; Becker, C.; Ruschendorf, F.; Nurnberg, P.; Rossier, B.; Vujic, M.; Booth, I.W.; et al. Mutations in SPINT2 cause a syndromic form of congenital sodium diarrhea. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2009, 84, 188–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bird, L.M.; Sivagnanam, M.; Taylor, S.; Newbury, R.O. A new syndrome of tufting enteropathy and choanal atresia, with ophthalmologic, hematologic and hair abnormalities. Clin. Dysmorphol. 2007, 16, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slae, M.A.; Saginur, M.; Persad, R.; Yap, J.; Lacson, A.; Salomon, J.; Canioni, D.; Huynh, H.Q. Syndromic congenital diarrhea because of the SPINT2 mutation showing enterocyte tufting and unique electron microscopy findings. Clin. Dysmorphol. 2013, 22, 118–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azzopardi, C.; Pullicino, E.; Coleiro, B.; Galea Soler, S. Congenital tufting enteropathy and chronic arthritis: A clinical and radiological perspective. BMJ Case Rep. 2016, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.Q.; Wu, G.S.; Kong, Y.M.; Zhang, X.Y.; Wang, C.L. New mutation in EPCAM for congenital tufting enteropathy: A case report. World J. Clin. Cases 2020, 8, 4975–4980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnell, U.; Kuipers, J.; Mueller, J.L.; Veenstra-Algra, A.; Sivagnanam, M.; Giepmans, B.N. Absence of cell-surface EpCAM in congenital tufting enteropathy. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2013, 22, 2566–2571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Szabo, R.; Bugge, T.H. Loss of HAI-2 in mice with decreased prostasin activity leads to an early-onset intestinal failure resembling congenital tufting enteropathy. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0194660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Szabo, R.; Callies, L.K.; Bugge, T.H. Matriptase drives early-onset intestinal failure in a mouse model of congenital tufting enteropathy. Development 2019, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.-J.; Feng, X.; Lu, M.; Morimura, S.; Udey, M.C. Matriptase-mediated cleavage of EpCAM destabilizes claudins and dysregulates intestinal epithelial homeostasis. J. Clin. Invest. 2017, 127, 623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawaguchi, M.; Yamamoto, K.; Takeda, N.; Fukushima, T.; Yamashita, F.; Sato, K.; Kitamura, K.; Hippo, Y.; Janetka, J.W.; Kataoka, H. Hepatocyte growth factor activator inhibitor-2 stabilizes Epcam and maintains epithelial organization in the mouse intestine. Commun. Biol. 2019, 2, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerra, E.; Lattanzio, R.; La Sorda, R.; Dini, F.; Tiboni, G.M.; Piantelli, M.; Alberti, S. mTrop1/Epcam knockout mice develop congenital tufting enteropathy through dysregulation of intestinal E-cadherin/β-catenin. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e49302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kozan, P.A.; McGeough, M.D.; Peña, C.A.; Mueller, J.L.; Barrett, K.E.; Marchelletta, R.R.; Sivagnanam, M. Mutation of EpCAM leads to intestinal barrier and ion transport dysfunction. J. Mol. Med. 2015, 93, 535–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mueller, J.L.; McGeough, M.D.; Pena, C.A.; Sivagnanam, M. Functional consequences of EpCam mutation in mice and men. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2014, 306, G278–G288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Das, B.; Okamoto, K.; Rabalais, J.; Kozan, P.A.; Marchelletta, R.R.; McGeough, M.D.; Durali, N.; Go, M.; Barrett, K.E.; Das, S.; et al. Enteroids expressing a disease-associated mutant of EpCAM are a model for congenital tufting enteropathy. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2019, 317, G580–G591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Z.; Maeda, T.; Tamura, A.; Nakamura, T.; Yamazaki, Y.; Shiratori, H.; Yashiro, K.; Tsukita, S.; Hamada, H. EpCAM contributes to formation of functional tight junction in the intestinal epithelium by recruiting claudin proteins. Dev. Biol. 2012, 371, 136–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Das, B.; Okamoto, K.; Rabalais, J.; Young, J.; Barrett, K.E.; Sivagnanam, M. Aberrant Epithelial Differentiation Contributes to Pathogenesis in a Murine Model of Congenital Tufting Enteropathy. bioRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patey, N.; Scoazec, J.Y.; Cuenod-Jabri, B.; Canioni, D.; Kedinger, M.; Goulet, O.; Brousse, N. Distribution of cell adhesion molecules in infants with intestinal epithelial dysplasia (tufting enteropathy). Gastroenterology 1997, 113, 833–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salomon, J.; Gaston, C.; Magescas, J.; Duvauchelle, B.; Canioni, D.; Sengmanivong, L.; Mayeux, A.; Michaux, G.; Campeotto, F.; Lemale, J.; et al. Contractile forces at tricellular contacts modulate epithelial organization and monolayer integrity. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 13998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noah, T.K.; Donahue, B.; Shroyer, N.F. Intestinal development and differentiation. Exp. Cell. Res. 2011, 317, 2702–2710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Overeem, A.W.; Posovszky, C.; Rings, E.H.; Giepmans, B.N.; van IJzendoorn, S.C. The role of enterocyte defects in the pathogenesis of congenital diarrheal disorders. Dis. Models Mech. 2016, 9, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martin, B.A.; Kerner, J.A.; Hazard, F.K.; Longacre, T.A. Evaluation of intestinal biopsies for pediatric enteropathy: A proposed immunohistochemical panel approach. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2014, 38, 1387–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engevik, A.C.; Goldenring, J.R. Trafficking Ion Transporters to the Apical Membrane of Polarized Intestinal Enterocytes. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2018, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Litvinov, S.V.; Bakker, H.A.; Gourevitch, M.M.; Velders, M.P.; Warnaar, S.O. Evidence for a role of the epithelial glycoprotein 40 (Ep-CAM) in epithelial cell-cell adhesion. Cell Adhes. Commun. 1994, 2, 417–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, L.; Yang, Y.; Yang, F.; Liu, S.; Zhu, Z.; Lei, Z.; Guo, J. Functions of EpCAM in physiological processes and diseases (Review). Int. J. Mol. Med. 2018, 42, 1771–1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bondow, B.J.; Faber, M.L.; Wojta, K.J.; Walker, E.M.; Battle, M.A. E-cadherin is required for intestinal morphogenesis in the mouse. Dev. Biol. 2012, 371, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tunggal, J.A.; Helfrich, I.; Schmitz, A.; Schwarz, H.; Gunzel, D.; Fromm, M.; Kemler, R.; Krieg, T.; Niessen, C.M. E-cadherin is essential for in vivo epidermal barrier function by regulating tight junctions. EMBO J. 2005, 24, 1146–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Litvinov, S.V.; Balzar, M.; Winter, M.J.; Bakker, H.A.; Briaire-de Bruijn, I.H.; Prins, F.; Fleuren, G.J.; Warnaar, S.O. Epithelial cell adhesion molecule (Ep-CAM) modulates cell–cell interactions mediated by classic cadherins. J. Cell Biol. 1997, 139, 1337–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Winter, M.J.; Nagtegaal, I.D.; van Krieken, J.H.J.; Litvinov, S.V. The epithelial cell adhesion molecule (Ep-CAM) as a morphoregulatory molecule is a tool in surgical pathology. Am. J. Pathol. 2003, 163, 2139–2148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Slanchev, K.; Carney, T.J.; Stemmler, M.P.; Koschorz, B.; Amsterdam, A.; Schwarz, H.; Hammerschmidt, M. The epithelial cell adhesion molecule EpCAM is required for epithelial morphogenesis and integrity during zebrafish epiboly and skin development. PLoS Genet. 2009, 5, e1000563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.J.; Mannan, P.; Lu, M.; Udey, M.C. Epithelial cell adhesion molecule (EpCAM) regulates claudin dynamics and tight junctions. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 12253–12268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maghzal, N.; Kayali, H.A.; Rohani, N.; Kajava, A.V.; Fagotto, F. EpCAM controls actomyosin contractility and cell adhesion by direct inhibition of PKC. Dev. Cell 2013, 27, 263–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nubel, T.; Preobraschenski, J.; Tuncay, H.; Weiss, T.; Kuhn, S.; Ladwein, M.; Langbein, L.; Zoller, M. Claudin-7 regulates EpCAM-mediated functions in tumor progression. Mol. Cancer Res. 2009, 7, 285–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tamura, A.; Hayashi, H.; Imasato, M.; Yamazaki, Y.; Hagiwara, A.; Wada, M.; Noda, T.; Watanabe, M.; Suzuki, Y.; Tsukita, S. Loss of claudin-15, but not claudin-2, causes Na+ deficiency and glucose malabsorption in mouse small intestine. Gastroenterology 2011, 140, 913–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gladden, A.B.; Hebert, A.M.; Schneeberger, E.E.; McClatchey, A.I. The NF2 tumor suppressor, Merlin, regulates epidermal development through the establishment of a junctional polarity complex. Dev. Cell 2010, 19, 727–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rusu, A.D.; Georgiou, M. The multifarious regulation of the apical junctional complex. Open Biol. 2020, 10, 190278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosveld, F.; Wang, Z.; Bellaiche, Y. Tricellular junctions: A hot corner of epithelial biology. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2018, 54, 80–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Resnik-Docampo, M.; Koehler, C.L.; Clark, R.I.; Schinaman, J.M.; Sauer, V.; Wong, D.M.; Lewis, S.; D’Alterio, C.; Walker, D.W.; Jones, D.L. Tricellular junctions regulate intestinal stem cell behaviour to maintain homeostasis. Nat. Cell Biol. 2017, 19, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Goulet, O.; Kedinger, M.; Brousse, N.; Cuenod, B.; Colomb, V.; Patey, N.; de Potter, S.; Mougenot, J.F.; Canioni, D.; Cerf-Bensussan, N.; et al. Intractable diarrhea of infancy with epithelial and basement membrane abnormalities. J. Pediatr. 1995, 127, 212–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon-Assmann, P.; Bouziges, F.; Vigny, M.; Kedinger, M. Origin and deposition of basement membrane heparan sulfate proteoglycan in the developing intestine. J. Cell Biol. 1989, 109, 1837–1848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simon-Assmann, P.; Duclos, B.; Orian-Rousseau, V.; Arnold, C.; Mathelin, C.; Engvall, E.; Kedinger, M. Differential expression of laminin isoforms and alpha 6-beta 4 integrin subunits in the developing human and mouse intestine. Dev. Dyn. 1994, 201, 71–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simon-Assmann, P.; Kedinger, M. Heterotypic cellular cooperation in gut morphogenesis and differentiation. Semin. Cell Biol. 1993, 4, 221–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaber, A.; Lenarcic, B.; Pavsic, M. Current View on EpCAM Structural Biology. Cells 2020, 9, 1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, B.; Okamoto, K.; Rabalais, J.; Marchelletta, R.R.; Barrett, K.E.; Das, S.; Niwa, M.; Sivagnanam, M. Congenital Tufting Enteropathy-Associated Mutant of Epithelial Cell Adhesion Molecule Activates the Unfolded Protein Response in a Murine Model of the Disease. Cells 2020, 9, 946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heijmans, J.; van Lidth de Jeude, J.F.; Koo, B.K.; Rosekrans, S.L.; Wielenga, M.C.; van de Wetering, M.; Ferrante, M.; Lee, A.S.; Onderwater, J.J.; Paton, J.C.; et al. ER stress causes rapid loss of intestinal epithelial stemness through activation of the unfolded protein response. Cell Rep. 2013, 3, 1128–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, X.; Sun, L.; Zha, W.; Studer, E.; Gurley, E.; Chen, L.; Wang, X.; Hylemon, P.B.; Pandak, W.M., Jr.; Sanyal, A.J.; et al. HIV protease inhibitors induce endoplasmic reticulum stress and disrupt barrier integrity in intestinal epithelial cells. Gastroenterology 2010, 138, 197–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reynaud, E.G.; Simpson, J.C. Navigating the secretory pathway: Conference on exocytosis membrane structure and dynamics. EMBO Rep. 2002, 3, 828–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Maghzal, N.; Vogt, E.; Reintsch, W.; Fraser, J.S.; Fagotto, F. The tumor-associated EpCAM regulates morphogenetic movements through intracellular signaling. J. Cell Biol. 2010, 191, 645–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ivanov, A.I.; Bachar, M.; Babbin, B.A.; Adelstein, R.S.; Nusrat, A.; Parkos, C.A. A unique role for nonmuscle myosin heavy chain IIA in regulation of epithelial apical junctions. PLoS ONE 2007, 2, e658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maetzel, D.; Denzel, S.; Mack, B.; Canis, M.; Went, P.; Benk, M.; Kieu, C.; Papior, P.; Baeuerle, P.A.; Munz, M.; et al. Nuclear signalling by tumour-associated antigen EpCAM. Nat. Cell Biol. 2009, 11, 162–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, F.Q.; Qi, Y.M.; Xu, H.; Wang, Q.Y.; Gao, X.S.; Guo, H.G. Expression of EpCAM and Wnt/ beta-catenin in human colon cancer. Genet. Mol. Res. 2015, 14, 4485–4494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mani, S.K.; Zhang, H.; Diab, A.; Pascuzzi, P.E.; Lefrancois, L.; Fares, N.; Bancel, B.; Merle, P.; Andrisani, O. EpCAM-regulated intramembrane proteolysis induces a cancer stem cell-like gene signature in hepatitis B virus-infected hepatocytes. J. Hepatol. 2016, 65, 888–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lu, H.; Ma, J.; Yang, Y.; Shi, W.; Luo, L. EpCAM is an endoderm-specific Wnt derepressor that licenses hepatic development. Dev. Cell 2013, 24, 543–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shi, F.; Cheng, Y.F.; Wang, X.L.; Edge, A.S. Beta-catenin up-regulates Atoh1 expression in neural progenitor cells by interaction with an Atoh1 3’ enhancer. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 392–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, Q.; Bermingham, N.A.; Finegold, M.J.; Zoghbi, H.Y. Requirement of Math1 for secretory cell lineage commitment in the mouse intestine. Science 2001, 294, 2155–2158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangalat, N.; Teckman, J. Pediatric Intestinal Failure Review. Children 2018, 5, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jeppesen, P.B.; Sanguinetti, E.L.; Buchman, A.; Howard, L.; Scolapio, J.S.; Ziegler, T.R.; Gregory, J.; Tappenden, K.A.; Holst, J.; Mortensen, P.B. Teduglutide (ALX-0600), a dipeptidyl peptidase IV resistant glucagon-like peptide 2 analogue, improves intestinal function in short bowel syndrome patients. Gut 2005, 54, 1224–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- O’Keefe, S.J.; Jeppesen, P.B.; Gilroy, R.; Pertkiewicz, M.; Allard, J.P.; Messing, B. Safety and efficacy of teduglutide after 52 weeks of treatment in patients with short bowel intestinal failure. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2013, 11, 815–823.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carter, B.A.; Cohran, V.C.; Cole, C.R.; Corkins, M.R.; Dimmitt, R.A.; Duggan, C.; Hill, S.; Horslen, S.; Lim, J.D.; Mercer, D.F.; et al. Outcomes from a 12-Week, Open-Label, Multicenter Clinical Trial of Teduglutide in Pediatric Short Bowel Syndrome. J. Pediatr. 2017, 181, 102–111.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Smith, H.L.; Mallucci, G.R. The unfolded protein response: Mechanisms and therapy of neurodegeneration. Brain 2016, 139, 2113–2121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Das, B.; Sivagnanam, M. Congenital Tufting Enteropathy: Biology, Pathogenesis and Mechanisms. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 19. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10010019
Das B, Sivagnanam M. Congenital Tufting Enteropathy: Biology, Pathogenesis and Mechanisms. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2021; 10(1):19. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10010019
Chicago/Turabian StyleDas, Barun, and Mamata Sivagnanam. 2021. "Congenital Tufting Enteropathy: Biology, Pathogenesis and Mechanisms" Journal of Clinical Medicine 10, no. 1: 19. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10010019
APA StyleDas, B., & Sivagnanam, M. (2021). Congenital Tufting Enteropathy: Biology, Pathogenesis and Mechanisms. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 10(1), 19. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10010019