Predictive Factors of Radiation-Induced Changes Following Single-Session Gamma Knife Radiosurgery for Arteriovenous Malformations
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patient Characteristics
2.2. Gamma Knife Radiosurgery
2.3. Neuroimaging Follow-Up and Outcome Assessment
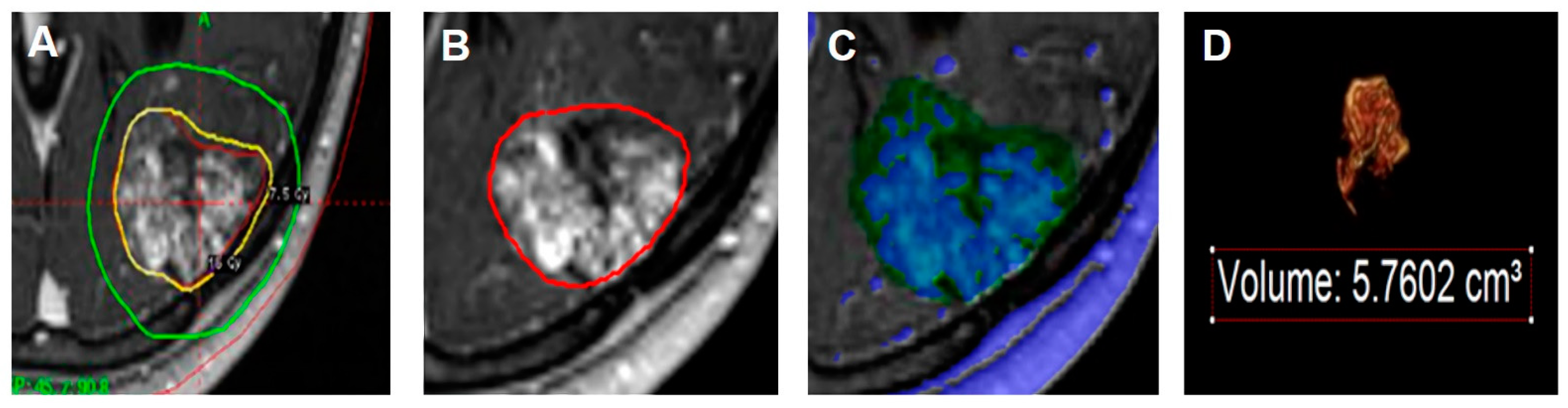
2.4. Volumetric Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patient Demographics, AVM Characteristics, and Radiosurgical Parameters
3.2. Treatment Outcomes
3.3. Radiation-Induced Change
4. Discussion
Study Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lunsford, L.D.; Kondziolka, D.; Flickinger, J.C.; Bissonette, D.J.; Jungreis, C.A.; Maitz, A.H.; Horton, J.A.; Coffey, R.J. Stereotactic radiosurgery for arteriovenous malformations of the brain. J. Neurosurg. 1991, 75, 512–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pan, D.H.; Guo, W.Y.; Chung, W.Y.; Shiau, C.Y.; Chang, Y.C.; Wang, L.W. Gamma knife radiosurgery as a single treatment modality for large cerebral arteriovenous malformations. J. Neurosurg. 2000, 93 (Suppl. 3), 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, H.K. Long-term results of Gamma Knife surgery for arteriovenous malformations: 10- to 15-year follow up in patients treated with lower doses. J. Neurosurg. 2006, 105 (Suppl.), 64–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Flickinger, J.C.; Kondziolka, D.; Lunsford, L.D.; Pollock, B.E.; Yamamoto, M.; Gorman, D.A.; Schomberg, P.J.; Sneed, P.; Larson, D.; Smith, V.; et al. A multi-institutional analysis of complication outcomes after arteriovenous malformation radiosurgery. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 1999, 44, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izawa, M.; Hayashi, M.; Chernov, M.; Nakaya, K.; Ochiai, T.; Murata, N.; Takasu, Y.; Kubo, O.; Hori, T.; Takakura, K. Long-term complications after gamma knife surgery for arteriovenous malformations. J. Neurosurg. 2005, 102 (Suppl.), 34–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, M.; Hara, M.; Ide, M.; Ono, Y.; Jimbo, M.; Saito, I. Radiation-related adverse effects observed on neuro-imaging several years after radiosurgery for cerebral arteriovenous malformations. Surg. Neurol. 1998, 49, 385–397; discussion 397–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yen, C.P.; Matsumoto, J.A.; Wintermark, M.; Schwyzer, L.; Evans, A.J.; Jensen, M.E.; Shaffrey, M.E.; Sheehan, J.P. Radiation-induced imaging changes following Gamma Knife surgery for cerebral arteriovenous malformations. J. Neurosurg. 2013, 118, 63–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrato-Avila, J.L.; da Costa, M.D.S.; Stávale, J.N.; Lima, J.V.F.; Carrasco-Hernandez, J.P.; Alejandro, S.A.; Chaddad-Neto, F. Microsurgical Resection of a Left Supramarginal Gyrus AVM Causing Radionecrosis. World Neurosurg. 2020, 138, 317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, D.; Starke, R.M.; Sheehan, J.P. Radiosurgery for the management of cerebral arteriovenous malformations. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 2017, 143, 69–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kano, H.; Flickinger, J.C.; Tonetti, D.; Hsu, A.; Yang, H.C.; Flannery, T.J.; Niranjan, A.; Lunsford, L.D. Estimating the Risks of Adverse Radiation Effects After Gamma Knife Radiosurgery for Arteriovenous Malformations. Stroke 2017, 48, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flickinger, J.C.; Kondziolka, D.; Lunsford, L.D.; Kassam, A.; Phuong, L.K.; Liscak, R.; Pollock, B. Development of a model to predict permanent symptomatic postradiosurgery injury for arteriovenous malformation patients. Arteriovenous Malformation Radiosurgery Study Group. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2000, 46, 1143–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flickinger, J.C.; Kondziolka, D.; Pollock, B.E.; Maitz, A.H.; Lunsford, L.D. Complications from arteriovenous malformation radiosurgery: Multivariate analysis and risk modeling. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 1997, 38, 485–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flickinger, J.C.; Lunsford, L.D.; Kondziolka, D.; Maitz, A.H.; Epstein, A.H.; Simons, S.R.; Wu, A. Radiosurgery and brain tolerance: An analysis of neurodiagnostic imaging changes after gamma knife radiosurgery for arteriovenous malformations. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 1992, 23, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilyas, A.; Chen, C.J.; Ding, D.; Buell, T.J.; Raper, D.M.S.; Lee, C.C.; Xu, Z.; Sheehan, J.P. Radiation-Induced Changes After Stereotactic Radiosurgery for Brain Arteriovenous Malformations: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Neurosurgery 2018, 83, 365–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.J.; Kearns, K.N.; Ding, D.; Kano, H.; Mathieu, D.; Kondziolka, D.; Feliciano, C.; Rodriguez-Mercado, R.; Grills, I.S.; Barnett, G.H.; et al. Stereotactic radiosurgery for arteriovenous malformations of the basal ganglia and thalamus: An international multicenter study. J. Neurosurg. 2019, 132, 122–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganz, J.C.; Reda, W.A.; Abdelkarim, K. Adverse radiation effects after Gamma Knife Surgery in relation to dose and volume. Acta Neurochir. (Wien.) 2009, 151, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.H.; Kim, D.G.; Chung, H.T.; Park, C.K.; Paek, S.H.; Kim, J.E.; Jung, H.W.; Han, D.H. Clinical and neuroimaging outcome of cerebral arteriovenous malformations after Gamma Knife surgery: Analysis of the radiation injury rate depending on the arteriovenous malformation volume. J. Neurosurg. 2008, 109, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liscak, R.; Vladyka, V.; Simonova, G.; Urgosik, D.; Novotny, J., Jr.; Janouskova, L.; Vymazal, J. Arteriovenous malformations after Leksell gamma knife radiosurgery: Rate of obliteration and complications. Neurosurgery 2007, 60, 1005–1014; discussion 1015–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuleasca, C.; Peciu-Florianu, I.; Leroy, H.A.; Vermandel, M.; Faouzi, M.; Reyns, N. Biologically effective dose and prediction of obliteration of unruptured arteriovenous malformations treated by upfront Gamma Knife radiosurgery: A series of 149 consecutive cases. J. Neurosurg. 2020, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.J.; Lee, C.C.; Wu, H.M.; Lin, C.J.; Shiau, C.Y.; Guo, W.Y.; Pan, D.H.; Liu, K.D.; Chung, W.Y.; Yang, H.C. Fully automated tissue segmentation of the prescription isodose region delineated through the Gamma knife plan for cerebral arteriovenous malformation (AVM) using fuzzy C-means (FCM) clustering. Neuroimage Clin. 2019, 21, 101608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganz, J.C.; Reda, W.A.; Abdelkarim, K.; Hafez, A. A simple method for predicting imaging-based complications following gamma knife surgery for cerebral arteriovenous malformations. J. Neurosurg. 2005, 102 (Suppl.), 4–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayhurst, C.; Monsalves, E.; van Prooijen, M.; Cusimano, M.; Tsao, M.; Menard, C.; Kulkarni, A.V.; Schwartz, M.; Zadeh, G. Pretreatment predictors of adverse radiation effects after radiosurgery for arteriovenous malformation. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2012, 82, 803–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.J.; Park, S.H.; Park, K.Y.; Jung, H.H.; Chang, J.H.; Chang, J.W.; Lee, J.W.; Chang, W.S. Gamma Knife Radiosurgery Followed by Flow-Reductive Embolization for Ruptured Arteriovenous Malformation. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.C.; Chen, C.J.; Ball, B.; Schlesinger, D.; Xu, Z.; Yen, C.P.; Sheehan, J. Stereotactic radiosurgery for arteriovenous malformations after Onyx embolization: A case-control study. J. Neurosurg. 2015, 123, 126–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hung, Y.C.; Mohammed, N.; Eluvathingal Muttikkal, T.J.; Kearns, K.N.; Li, C.E.; Narayan, A.; Schlesinger, D.; Xu, Z.; Sheehan, J.P. The impact of preradiosurgery embolization on intracranial arteriovenous malformations: A matched cohort analysis based on de novo lesion volume. J. Neurosurg. 2019, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Todnem, N.; Ward, A.; Nahhas, M.; Vender, J.R.; Alleyne, C.H.; Rahimi, S.Y. A Retrospective Cohort Analysis of Hemorrhagic Arteriovenous Malformations Treated with Combined Endovascular Embolization and Gamma Knife Stereotactic Radiosurgery. World Neurosurg. 2019, 122, e713–e722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blamek, S.; Tarnawski, R.; Miszczyk, L. Linac-based stereotactic radiosurgery for brain arteriovenous malformations. Clin. Oncol. (R. Coll. Radiol.) 2011, 23, 525–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, H.K.; Kohga, H.; Hirato, M.; Nakamura, M.; Ohye, C. Neurobiologic effects of radiosurgery: Histologic, immunohistochemical and electron-microscopic studies of a rat model. Stereotact. Funct. Neurosurg. 1994, 63, 280–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen-Inbar, O.; Lee, C.C.; Xu, Z.; Schlesinger, D.; Sheehan, J.P. A quantitative analysis of adverse radiation effects following Gamma Knife radiosurgery for arteriovenous malformations. J. Neurosurg. 2015, 123, 945–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Flickinger, J.C.; Kondziolka, D.; Maitz, A.H.; Lunsford, L.D. An analysis of the dose-response for arteriovenous malformation radiosurgery and other factors affecting obliteration. Radiother Oncol. 2002, 63, 347–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flickinger, J.C.; Kondziolka, D.; Maitz, A.H.; Lunsford, L.D. Analysis of neurological sequelae from radiosurgery of arteriovenous malformations: How location affects outcome. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 1998, 40, 273–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levegrün, S.; Hof, H.; Essig, M.; Schlegel, W.; Debus, J. Radiation-induced changes of brain tissue after radiosurgery in patients with arteriovenous malformations: Correlation with dose distribution parameters. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2004, 59, 796–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganz, J.C.; Reda, W.A. Radionecrosis following Gamma Knife treatment for mesial temporal lobe epilepsy. Br. J. Neurosurg. 2011, 25, 649–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.C.; Yang, H.C.; Lin, C.J.; Chen, C.J.; Wu, H.M.; Shiau, C.Y.; Guo, W.Y.; Hung-Chi Pan, D.; Liu, K.D.; Chung, W.Y.; et al. Intervening Nidal Brain Parenchyma and Risk of Radiation-Induced Changes After Radiosurgery for Brain Arteriovenous Malformation: A Study Using an Unsupervised Machine Learning Algorithm. World Neurosurg. 2019, 125, e132–e138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, D.; Yen, C.P.; Xu, Z.; Starke, R.M.; Sheehan, J.P. Radiosurgery for low-grade intracranial arteriovenous malformations. J. Neurosurg. 2014, 121, 457–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Quigg, M.; Yen, C.P.; Chatman, M.; Quigg, A.H.; McNeill, I.T.; Przybylowski, C.J.; Yan, G.; Sheehan, J.P. Risks of history of diabetes mellitus, hypertension, and other factors related to radiation-induced changes following Gamma Knife surgery for cerebral arteriovenous malformations. J. Neurosurg. 2012, 117 (Suppl.), 144–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ding, D.; Yen, C.P.; Starke, R.M.; Xu, Z.; Sheehan, J.P. Effect of prior hemorrhage on intracranial arteriovenous malformation radiosurgery outcomes. Cereb. Dis. 2015, 39, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohr, J.P.; Parides, M.K.; Stapf, C.; Moquete, E.; Moy, C.S.; Overbey, J.R.; Al-Shahi Salman, R.; Vicaut, E.; Young, W.L.; Houdart, E.; et al. Medical management with or without interventional therapy for unruptured brain arteriovenous malformations (ARUBA): A multicentre, non-blinded, randomised trial. Lancet 2014, 383, 614–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wedderburn, C.J.; van Beijnum, J.; Bhattacharya, J.J.; Counsell, C.E.; Papanastassiou, V.; Ritchie, V.; Roberts, R.C.; Sellar, R.J.; Warlow, C.P.; Al-Shahi Salman, R. Outcome after interventional or conservative management of unruptured brain arteriovenous malformations: A prospective, population-based cohort study. Lancet Neurol. 2008, 7, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Shahi Salman, R.; White, P.M.; Counsell, C.E.; du Plessis, J.; van Beijnum, J.; Josephson, C.B.; Wilkinson, T.; Wedderburn, C.J.; Chandy, Z.; St George, E.J.; et al. Outcome after conservative management or intervention for unruptured brain arteriovenous malformations. Jama 2014, 311, 1661–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]


| Total (n = 180) | |
|---|---|
| Median age | 34 (22, 46) |
| Sex | |
| Male | 98 (54.4%) |
| Female | 82 (45.6%) |
| Median FU, month | 47 (35, 73.5) |
| Median marginal dose, Gy | 16 (15,17) |
| Meadian target volume, cc | 3.65 (1.50, 9.09) |
| Median measured volume within 50% isodense line, cc | 4.18 (1.74, 10.17) |
| Median nidus volume within 50% isodense line, cc | 1.54 (0.62, 4.19) |
| Median parenchyma volume within 50% isodense line, cc | 2.41 (0.94, 5.94) |
| VRAS | |
| 0 | 12 (6.7%) |
| 1 | 38 (21.1%) |
| 2 | 60 (33.3%) |
| 3 | 57 (31.7%) |
| 4 | 13 (7.2%) |
| Pollock–Flickinger score | |
| <1 | 59 (32.8%) |
| 1.01–1.50 | 55 (30.6%) |
| 1.51–2.00 | 35 (19.4%) |
| >2 | 31 (17.2%) |
| SM grade | |
| 1 | 42 (23.3%) |
| 2 | 78 (43.4%) |
| 3 | 51 (28.3%) |
| 4 | 9 (5.0%) |
| Lobar | 143 (79.4%) |
| Deep | 37 (20.6%) |
| Presence of Aneurysm (intranidal/flow-related) | 27 (15.0%) |
| Initial ruptured AVMs | 79 (43.9%) |
| Radiation induced changes (RICs) | 79 (43.9%) |
| Grade 1 | 38 (48.1%) |
| Grade 2 | 37 (46.8%) |
| Grade 3 | 4 (5.1%) |
| Symptomatic RICs | 20 (25.3%) |
| Permanent RICs | 8 (8.9%) |
| Median duration from treatment to RICs, months | 11 (6, 17) |
| Obliteration | 122 (67.8%) |
| Angiography | 108 (88.5%) |
| Magnetic resonance imaging and angiography | 14 (11.5%) |
| Median duration from treatment to obliteration, months | 36 (31, 45) |
| Latent period hemorrhage | 5 (2.8%) |
| Delayed cyst formation | 7 (3.9%) |
| Non-RIC (n = 101) | RIC (n = 79) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Median age | 32 (16,45) | 37 (25,47) | 0.0576 |
| Sex | 0.7604 | ||
| Male | 56 (55.5%) | 42 (53.2%) | |
| Female | 45 (44.5%) | 37 (46.8%) | |
| Median marginal dose, Gy | 16 (15, 17) | 16 (15, 17) | 0.1079 |
| Median target volume, cc | 2.0 (0.9, 4.8) | 6.5 (2.9, 13.5) | <0.0001 |
| Median measured volume within 50% isodense line, cc | 2.3 (1.0, 5.6) | 6.7 (3.6, 15.8) | <0.0001 |
| Median nidus volume within 50% isodense line, cc | 0.9 (0.5, 2.6) | 2.6 (1.1, 5.9) | <0.0001 |
| Median parenchyma volume within 50% isodense line, cc | 1.3 (0.6, 2.8) | 4.7 (2.2, 9.8) | <0.0001 |
| Median N/M (nidus/measured volume within 50% isodense line) | 0.5 (0.3, 0.6) | 0.3 (0.3, 0.4) | <0.0001 |
| Median P/M (parenchyma/measured volume within 50% isodense line) | 0.5 (0.4, 0.7) | 0.7 (0.6, 0.8) | <0.0001 |
| VRAS | 0.0075 | ||
| 0 | 11 (10.9%) | 1 (1.3%) | |
| 1 | 24 (23.8%) | 14 (17.7%) | |
| 2 | 37 (36.6%) | 23 (29.1%) | |
| 3 | 23 (22.8%) | 34 (43.0%) | |
| 4 | 6 (5.9%) | 7 (8.9%) | |
| Pollock–Flickinger score | <0.0001 | ||
| < 1 | 48 (47.5%) | 11 (13.9%) | |
| 1.01–1.50 | 29 (28.7%) | 26 (32.9%) | |
| 1.51–2.00 | 15 (14.9%) | 20 (25.3%) | |
| > 2 | 9 (8.9%) | 22 (27.9%) | |
| SM grade | 0.0005 | ||
| 1 | 32 (31.7%) | 10 (12.7%) | |
| 2 | 47 (46.5%) | 31 (39.2%) | |
| 3 | 20 (19.8%) | 31 (39.2%) | |
| 4 | 2 (2.0%) | 7 (8.9%) | |
| Location | 0.1151 | ||
| Lobar | 76 (75.3%) | 67 (84.8%) | |
| Deep | 25 (24.7%) | 12 (15.2%) | |
| Presence of Aneurysm (intranidal/flow-related) | |||
| Initial ruptured AVMs | 56 (55.5%) | 23 (29.1%) | 0.0004 |
| Obliteration | 74 (73.3%) | 48 (60.8%) | 0.0748 |
| Angiography | 65 (87.8%) | 43 (89.6%) | |
| Magnetic resonance imaging and angiography | 9 (12.2%) | 5 (10.4%) | |
| Latent period hemorrhage | 2 (2.0%) | 3 (3.8%) | 0.6551 |
| Delayed cyst formation | 1 (1.0%) | 6 (7.6%) | 0.0446 |
| Univariate Analysis | Multivariate Analysis | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Factors | HR | CI | p-Value | HR | CI | p-Value |
| Sex (female) | 1.092 | (0.702, 1.699) | 0.6965 | |||
| Age | 1.010 | (0.998, 1.023) | 0.1099 | |||
| Target volume | 1.017 | (1.007, 1.027) | 0.0008 | |||
| Marginal dose | 0.912 | (0.779, 1.068) | 0.2525 | |||
| Deep location | 0.625 | (0.338, 1.155) | 0.1335 | |||
| Initial rupture | 0.446 | (0.274, 0.725) | 0.0011 | 0.312 | (0.179, 0.541) | <0.0001 |
| SM grade | 1.703 | (1.317, 2.203) | <0.0001 | |||
| VRAS | 1.441 | (1.155, 1.798) | 0.0012 | |||
| Pollock–Flickinger score | 1.180 | (1.074, 1.295) | 0.0005 | |||
| Measured volume within 50% isodense | 1.008 | (1.002, 1.014) | 0.0138 | |||
| Nidus volume within 50% isodense line | 1.027 | (1.000, 1.055) | 0.0475 | 0.878 | (0.792, 0.974) | 0.0139 |
| Parenchyma volume within 50% isodense line | 1.011 | (1.003, 1.019) | 0.0104 | 1.042 | (1.008, 1.077) | 0.0140 |
| Nidus/Measured volume within 50% isodense line | 0.028 | (0.006, 0.137) | <0.0001 | |||
| Parenchyma/Measured volume within 50% isodense line | 35.323 | (7.300, 170.921) | <0.0001 | |||
| Univariate Analysis | Multivariate Analysis | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Factors | OR | CI | p-Value | OR | CI | p-Value |
| Sex (female) | 1.046 | (0.594, 1.842) | 0.8766 | |||
| Age | 1.012 | (0.996, 1.029) | 0.1450 | |||
| Target volume | 1.061 | (1.032, 1.091) | <0.0001 | |||
| Marginal dose | 0.773 | (0.622, 0.960) | 0.0198 | |||
| Deep location | 0.522 | (0.247, 1.104) | 0.0891 | |||
| Initial rupture | 0.336 | (0.184, 0.615) | 0.0004 | 0.217 | (0.104, 0.455) | <0.0001 |
| SM grade | 2.433 | (1.678, 3.528) | <0.0001 | |||
| VRAS | 1.753 | (1.302, 2.360) | 0.0002 | |||
| Pollock–Flickinger score | 1.816 | (1.389, 2.375) | <0.0001 | |||
| Measured volume within 50% isodense | 1.035 | (1.013, 1.057) | 0.0016 | |||
| Nidus volume within 50% isodense line | 1.092 | (1.036, 1.152) | 0.0011 | 0.842 | (0.738, 0.962) | 0.0114 |
| Parenchyma volume within 50% isodense line | 1.056 | (1.018, 1.095) | 0.0036 | 1.095 | (1.028, 1.165) | 0.0045 |
| Nidus/Measured volume within 50% isodense line | 0.006 | (<0.001, 0.052) | <0.0001 | |||
| Parenchyma/Measured volume within 50% isodense line | 169.033 | (19.408, >999.999) | <0.0001 | |||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, M.J.; Chang, K.W.; Park, S.H.; Chang, W.S.; Chang, J.H.; Chang, J.W.; Jung, H.H. Predictive Factors of Radiation-Induced Changes Following Single-Session Gamma Knife Radiosurgery for Arteriovenous Malformations. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 2186. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10102186
Kim MJ, Chang KW, Park SH, Chang WS, Chang JH, Chang JW, Jung HH. Predictive Factors of Radiation-Induced Changes Following Single-Session Gamma Knife Radiosurgery for Arteriovenous Malformations. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2021; 10(10):2186. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10102186
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Myung Ji, Kyung Won Chang, So Hee Park, Won Seok Chang, Jong Hee Chang, Jin Woo Chang, and Hyun Ho Jung. 2021. "Predictive Factors of Radiation-Induced Changes Following Single-Session Gamma Knife Radiosurgery for Arteriovenous Malformations" Journal of Clinical Medicine 10, no. 10: 2186. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10102186
APA StyleKim, M. J., Chang, K. W., Park, S. H., Chang, W. S., Chang, J. H., Chang, J. W., & Jung, H. H. (2021). Predictive Factors of Radiation-Induced Changes Following Single-Session Gamma Knife Radiosurgery for Arteriovenous Malformations. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 10(10), 2186. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10102186






