IgA Vasculitis and IgA Nephropathy: Same Disease?
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Epidemiology
3. Clinical Presentation and Outcome
4. Treatment
5. Physiopathology
6. Biomarkers
| IgAN | IgAV | IgAN + IgAV | |
|---|---|---|---|
| GdIgA1 | [74,75] | [76,77,78] | [40,79] |
| GdIgA1/sCD89 | [80] | [77,78] | |
| GdIgA1/IgG | [81] | [77,78] | |
| sCD89 | [82] | ||
| Transglutaminase2 | [83] | ||
| CD71 | [83] | ||
| TLR9 | [84,85] | [68] | |
| TLR4 | [67,68] | ||
| TGF-β1 MCP1 | [40] | ||
| Complement system | [70,73] | [86] |
7. Genetics
8. Discussion and Future Research
- -
- To include both diseases;
- -
- To agree on a common histological classification. Thus far, in fact, there is no consensual renal histologic classification for IgAV. Although the International Study of Kidney Disease in Children (ISKDC) classification is widely use in child IgAV, it is more and more questioned because it does not completely correlate with the clinical presentation and long term renal outcome. Few teams have applied to IgAV the Oxford classification widely used now for IgAN and have shown discordant results [95,96,97,98]. Its prognostic interest is actually disputed. A large international study, based on the model, which has resulted in the Oxford classification, is currently being developed for the IgAV;
- -
- To stratify the cohorts on age and genetic background, which are, to date, the only prognostic factors so far clearly identified.
9. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Meadow, S.R.; Scott, D.G. Berger Disease: Henoch-Schönlein Syndrome without the Rash. J. Pediatr. 1985, 106, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicoara, O.; Twombley, K. Immunoglobulin A Nephropathy and Immunoglobulin A Vasculitis. Pediatr. Clin. N. Am. 2019, 66, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montoliu, J.; Lens, X.M.; Torras, A.; Revert, L. Henoch-Schönlein Purpura and IgA Nephropathy in Father and Son. Nephron 1990, 54, 77–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, F.J.; Wolfish, N.M.; McLaine, P.N. Henoch-Schonlein Syndrome and IgA Nephropathy: A case report suggesting a common pathogenesis. Pediatr. Nephrol. 1988, 2, 389–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araque, A.; Sánchez, R.; Alamo, C.; Torres, N.; Praga, M. Evolution of Immunoglobulin a Nephropathy into Henoch-Schönlein Purpura in an Adult Patient. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 1995, 25, 340–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravelli, A.; Carnevale-Maffè, G.; Ruperto, N.; Ascari, E.; Martini, A. IgA Nephropathy and Henoch-Schönlein Syndrome Occurring in the Same Patient. Nephron 1996, 72, 111–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamei, K.; Ogura, M.; Sato, M.; Ito, S.; Ishikura, K. Evolution of IgA Nephropathy into Anaphylactoid Purpura in Six Cases—Further Evidence That IgA Nephropathy and Henoch–Schonlein Purpura Nephritis Share Common Pathogenesis. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2016, 31, 779–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachman, U.; Biava, C.; Amend, W.; Feduska, N.; Melzer, J.; Salvatierra, O.; Vincenti, F. The clincial course of IgA-nephropathy and henoch-schönlein purpura following renal transplantation. Transplantation 1986, 42, 511–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sotoodian, B.; Robert, J.; Mahmood, M.N.; Yacyshyn, E. IgA Cutaneous Purpura Post–Renal Transplantation in a Patient With Long-Standing IgA Nephropathy: Case Report and Literature Review. J. Cutan. Med. Surg. 2015, 19, 498–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNally, A.; McGregor, D.; Searle, M.; Irvine, J.; Cross, N. Henoch-Schonlein Purpura in a Renal Transplant Recipient with Prior IgA Nephropathy Following Influenza Vaccination. Clin. Kidney J. 2013, 6, 313–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waldo, F.B. Is Henoch-Schonlein Purpura the Systemic Form of IgA Nephropathy? Am. J. Kidney Dis. 1988, 12, 373–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davin, J.C. Henoch-Schonlein Purpura Nephritis: Pathophysiology, Treatment, and Future Strategy. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2011, 6, 679–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanders, J.T.; Wyatt, R.J. IgA Nephropathy and Henoch–Schönlein Purpura Nephritis. Curr. Opin. Pediatr. 2008, 20, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Shaughnessy, M.M.; Hogan, S.L.; Thompson, B.D.; Coppo, R.; Fogo, A.B.; Jennette, J.C. Glomerular Disease Frequencies by Race, Sex and Region: Results from the International Kidney Biopsy Survey. Nephrol. Dial. Transplantat. 2018, 33, 661–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gardner-Medwin, J.M.; Dolezalova, P.; Cummins, C.; Southwood, T.R. Incidence of Henoch-Schonlein Purpura, Kawasaki Disease, and Rare Vasculitides in Children of Different Ethnic Origins. Lancet 2002, 360, 1197–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piram, M.; Maldini, C.; Biscardi, S.; De Suremain, N.; Orzechowski, C.; Georget, E.; Regnard, D.; Koné-Paut, I.; Mahr, A. Incidence of IgA vasculitis in children estimated by four-source capture–recapture analysis: A population-based study. Rheumatology 2017, 56, 1358–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mossberg, M.; Segelmark, M.; Kahn, R.; Englund, M.; Mohammad, A. Epidemiology of Primary Systemic Vasculitis in Children: A Population-Based Study from Southern Sweden. Scand. J. Rheumatol. 2018, 47, 295–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.H.; Hung, C.F.; Hsu, C.R.; Wang, L.C.; Chuang, Y.H.; Lin, Y.T.; Chiang, B.L. A Nationwide Survey on Epidemiological Characteristics of Childhood Henoch-Schonlein Purpura in Taiwan. Rheumatology 2005, 44, 618–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okubo, Y.; Nochioka, K.; Sakakibara, H.; Hataya, H.; Terakawa, T.; Testa, M.; Sundel, R.P. Nationwide epidemiological survey of childhood IgA vasculitis associated hospitalization in the USA. Clin. Rheumatol. 2016, 35, 2749–2756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watts, R.A.; Lane, S.; Scott, D.G. What is known about the epidemiology of the vasculitides? Best Pract. Res. Clin. Rheumatol. 2005, 19, 191–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penny, K.; Fleming, M.; Kazmierczak, D.; Thomas, A. An epidemiological study of henoch-schonlein purpura. Paediatr. Nurs. 2010, 22, 30–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero-Gómez, C.; Aguilar-García, J.A.; García-de-Lucas, M.D.; Cotos-Canca, R.; Olalla-Sierra, J.; García-Alegría, J.J.; Hernández-Rodríguez, J. Epidemiological study of primary systemic vasculitides among adults in southern spain and review of the main epidemiological studies. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2015, 33, S-11–S-18. [Google Scholar]
- Hočevar, A.; Rotar, Z.; Ostrovršnik, J.; Jurčić, V.; Vizjak, A.; Dolenc Voljč, M.; Lindič, J.; Tomšič, M. Incidence of IgA Vasculitis in the Adult Slovenian Population. Br. J. Dermatol. 2014, 171, 524–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillebout, E.; Thervet, E.; Hill, G.; Alberti, C.; Vanhille, P.; Nochy, D. Henoch-schonlein purpura in adults: Outcome and prognostic factors. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2002, 13, 1271–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Wu, X.; Le, W.; Hao, Y.; Wu, J.; Zeng, C.; Liu, Z.; Tang, Z. Renal prognosis and related risk factors for henoch-schönlein purpura nephritis: A Chinese adult patient cohort. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 5585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGrogan, A.; Franssen, C.F.M.; de Vries, C.S. The incidence of primary glomerulonephritis worldwide: A systematic review of the literature. Nephrol. Dial. Transplantat. 2011, 26, 414–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibano, T.; Takagi, N.; Maekawa, K.; Mae, H.; Hattori, M.; Takeshima, Y.; Tanizawa, T. Epidemiological Survey and Clinical Investigation of Pediatric IgA Nephropathy. Clin. Exp. Nephrol. 2016, 20, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coppo, R. Pediatric IgA Nephropathy in Europe. Kidney Dis. 2019, 5, 182–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshikawa, N.; Tanaka, R.; Iijima, K. Pathophysiology and Treatment of IgA Nephropathy in Children. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2001, 16, 446–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.; Fang, X.; Xia, Z.; Gao, C.; Peng, Y.; Li, X.; Zhang, P.; Kuang, Q.; Wang, R.; Wang, M. Long-term renal survival and undetected risk factors of IgA nephropathy in Chinese Children—a Retrospective 1243 cases analysis from single centre experience. J. Nephrol. 2020, 33, 1263–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magistroni, R.; D’Agati, V.; Appel, G.; Kiryluk, K. New developments in the genetics, pathogenesis, and therapy of IgA Nephropathy. Kidney Int. 2015, 88, 974–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lassalle, M.; Couchoud, C.; Prada-Bordenave, E.; Jacquelinet, C. Éditorial. Néphrol. Thér. 2013, 9, S1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komatsu, H.; Fujimoto, S.; Yoshikawa, N.; Kitamura, H.; Sugiyama, H.; Yokoyama, H. Clinical manifestations of henoch-schonlein purpura nephritis and iga nephropathy: Comparative analysis of data from the Japan Renal Biopsy Registry (J-RBR). Clin. Exp. Nephrol. 2016, 20, 552–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozen, S.; Pistorio, A.; Iusan, S.M.; Bakkaloglu, A.; Herlin, T.; Brik, R.; Buoncompagni, A.; Lazar, C.; Bilge, I.; Uziel, Y.; et al. EULAR/PRINTO/PRES criteria for henoch-schonlein purpura, childhood polyarteritis nodosa, childhood wegener granulomatosis and childhood takayasu arteritis: Ankara 2008. Part II: Final classification criteria. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2010, 69, 798–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comprehensive Clinical Nephrology, 6th ed.; Feehally, J., Ed.; Elsevier: Edinburgh, UK ; New York, NY, USA, 2019; ISBN 978-0-323-47909-7. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, J.; Huang, A.; Liu, T.; Kuang, Y. A clinico-pathological study comparing Henoch-Schonlein purpura nephritis with IgA nephropathy in children. Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi 2003, 41, 808–812. [Google Scholar]
- Calvo-Rio, V.; Loricera, J.; Martin, L.; Ortiz-Sanjuan, F.; Alvarez, L.; Gonzalez-Vela, M.C.; Gonzalez-Lamuno, D.; Mata, C.; Gortazar, P.; Rueda-Gotor, J.; et al. Henoch-schonlein purpura nephritis and IgA nephropathy: A comparative clinical study. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2013, 31, S45–S51. [Google Scholar]
- Oh, H.J.; Ahn, S.V.; Yoo, D.E.; Kim, S.J.; Shin, D.H.; Lee, M.J.; Kim, H.R.; Park, J.T.; Yoo, T.H.; Kang, S.W.; et al. Clinical outcomes, when matched at presentation, do not vary between adult-onset henoch-schonlein purpura nephritis and IgA nephropathy. Kidney Int. 2012, 82, 1304–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, S.; Xuan, X.; Sha, Y.; Zhao, S.; Zhu, C.; Zhang, A.; Huang, S. Clinico-pathological association of henoch-schoenlein purpura nephritis and IgA nephropathy in children. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2015, 8, 2334–2342. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sugiyama, M.; Wada, Y.; Kanazawa, N.; Tachibana, S.; Suzuki, T.; Matsumoto, K.; Iyoda, M.; Honda, H.; Shibata, T. A cross-sectional analysis of clinicopathologic similarities and differences between henoch-schönlein purpura nephritis and IgA nephropathy. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0232194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohey, H.; Laurent, B.; Mariat, C.; Berthoux, F. Validation of the absolute renal risk of dialysis/death in adults with IgA nephropathy secondary to henoch-schönlein purpura: A monocentric cohort study. BMC Nephrol. 2013, 14, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selewski, D.T.; Ambruzs, J.M.; Appel, G.B.; Bomback, A.S.; Matar, R.B.; Cai, Y.; Cattran, D.C.; Chishti, A.S.; D’Agati, V.D.; D’Alessandri-Silva, C.J.; et al. Clinical characteristics and treatment patterns of children and adults with IgA nephropathy or IgA vasculitis: Findings from the cureGN study. Kidney Int. Rep. 2018, 3, 1373–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radhakrishnan, J.; Cattran, D.C. The KDIGO practice guideline on glomerulonephritis: Reading between the (guide)lines-Application to the individual Patient. Kidney Int. 2012, 82, 840–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Praga, M.; Gutierrez, E.; Gonzalez, E.; Morales, E.; Hernandez, E. Treatment of IgA Nephropathy with ACE Inhibitors: A randomized and controlled trial. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2003, 14, 1578–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coppo, R.; Peruzzi, L.; Amore, A.; Piccoli, A.; Cochat, P.; Stone, R.; Kirschstein, M.; Linne, T. IgACE: A placebo-controlled, randomized trial of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors in children and young people with IgA nephropathy and moderate proteinuria. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2007, 18, 1880–1888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.K.; Leung, C.B.; Chow, K.M.; Cheng, Y.L.; Fung, S.K.; Mak, S.K.; Tang, A.W.; Wong, T.Y.; Yung, C.Y.; Yung, J.C.; et al. Hong Kong study using valsartan in IgA nephropathy (HKVIN): A double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled study. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2006, 47, 751–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Floege, J.; Barbour, S.J.; Cattran, D.C.; Hogan, J.J.; Nachman, P.H.; Tang, S.C.W.; Wetzels, J.F.M.; Cheung, M.; Wheeler, D.C.; Winkelmayer, W.C.; et al. Management and treatment of glomerular diseases (Part 1): Conclusions from a kidney disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) controversies conference. Kidney Int. 2019, 95, 268–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tesar, V.; Troyanov, S.; Bellur, S.; Verhave, J.C.; Cook, H.T.; Feehally, J.; Roberts, I.S.; Cattran, D.; Coppo, R. Corticosteroids in IgA nephropathy: A retrospective analysis from the VALIGA study. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2015, 26, 2248–2258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauen, T.; Eitner, F.; Fitzner, C.; Sommerer, C.; Zeier, M.; Otte, B.; Panzer, U.; Peters, H.; Benck, U.; Mertens, P.R.; et al. Intensive supportive care plus immunosuppression in IgA nephropathy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 2225–2236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, J.; Zhang, H.; Wong, M.G.; Jardine, M.J.; Hladunewich, M.; Jha, V.; Monaghan, H.; Zhao, M.; Barbour, S.; Reich, H.; et al. Effect of oral methylprednisolone on clinical outcomes in patients with IgA nephropathy: The TESTING randomized clinical trial. JAMA 2017, 318, 432–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natale, P.; Palmer, S.C.; Ruospo, M.; Saglimbene, V.M.; Craig, J.C.; Vecchio, M.; Samuels, J.A.; Molony, D.A.; Schena, F.P.; Strippoli, G.F. Immunosuppressive agents for treating IgA nephropathy. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauen, T.; Wied, S.; Fitzner, C.; Eitner, F.; Sommerer, C.; Zeier, M.; Otte, B.; Panzer, U.; Budde, K.; Benck, U.; et al. After Ten Years of Follow-up, No Difference between Supportive Care plus Immunosuppression and Supportive Care Alone in IgA Nephropathy. Kidney Int. 2020, 98, 1044–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maes, B.D.; Oyen, R.; Claes, K.; Evenepoel, P.; Kuypers, D.; Vanwalleghem, J.; Van Damme, B.; Vanrenterghem, Y.F. Mycophenolate mofetil in IgA nephropathy: Results of a 3-year prospective placebo-controlled randomized study. Kidney Int. 2004, 65, 1842–1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frisch, G.; Lin, J.; Rosenstock, J.; Markowitz, G.; D’Agati, V.; Radhakrishnan, J.; Preddie, D.; Crew, J.; Valeri, A.; Appel, G. Mycophenolate Mofetil (MMF) vs placebo in patients with moderately advanced IgA nephropathy: A double-blind randomized controlled trial. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2005, 20, 2139–2145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hogg, R.J.; Bay, R.C.; Jennette, J.C.; Sibley, R.; Kumar, S.; Fervenza, F.C.; Appel, G.; Cattran, D.; Fischer, D.; Hurley, R.M.; et al. Randomized controlled trial of mycophenolate mofetil in children, adolescents, and adults with IgA nephropathy. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2015, 66, 783–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, J.H.; Le, W.B.; Chen, N.; Wang, W.M.; Liu, Z.S.; Liu, D.; Chen, J.H.; Tian, J.; Fu, P.; Hu, Z.X.; et al. Mycophenolate mofetil combined with prednisone versus full-dose prednisone in IgA nephropathy with active proliferative lesions: A randomized controlled trial. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2017, 69, 788–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillebout, E.; Alberti, C.; Guillevin, L.; Ouslimani, A.; Thervet, E. Addition of cyclophosphamide to steroids provides no benefit compared with steroids alone in treating adult patients with severe henoch schonlein purpura. Kidney Int. 2010, 78, 495–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Audemard-Verger, A.; Terrier, B.; Dechartres, A.; Chanal, J.; Amoura, Z.; Le Gouellec, N.; Cacoub, P.; Jourde-Chiche, N.; Urbanski, G.; Augusto, J.F.; et al. Characteristics and management of IgA vasculitis (henoch-schonlein) in adults: Data from 260 patients included in a french multicenter retrospective survey. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017, 69, 1862–1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lafayette, R.A.; Canetta, P.A.; Rovin, B.H.; Appel, G.B.; Novak, J.; Nath, K.A.; Sethi, S.; Tumlin, J.A.; Mehta, K.; Hogan, M.; et al. A Randomized, controlled trial of Rituximab in IgA nephropathy with proteinuria and renal dysfunction. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2017, 28, 1306–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maritati, F.; Fenoglio, R.; Pillebout, E.; Emmi, G.; Urban, M.L.; Rocco, R.; Nicastro, M.; Incerti, M.; Goldoni, M.; Trivioli, G.; et al. Brief report: Rituximab for the treatment of adult-onset iga vasculitis (henoch-schonlein). Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017, 70, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahn, D.; Hodson, E.; Willis, N.; Craig, J.C. Interventions for preventing and treating kidney disease in henoch-schonlein purpura (HSP) (Review). Cochrane Libr. 2015, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudley, J.; Smith, G.; Llewelyn-Edwards, A.; Bayliss, K.; Pike, K.; Tizard, J.; Tuthill, D.; Millar-Jones, L.; Bowler, I.; Williams, T.; et al. Randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial to determine whether steroids reduce the incidence and severity of nephropathy in Henoch-Schonlein Purpura (HSP). Arch. Dis. Child. 2013, 98, 756–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronkainen, J.; Koskimies, O.; Ala-Houhala, M.; Antikainen, M.; Merenmies, J.; Rajantie, J.; Ormala, T.; Turtinen, J.; Nuutinen, M. Early prednisone therapy in henoch-schonlein purpura: A Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. J. Pediatr. 2006, 149, 241–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozen, S.; Marks, S.D.; Brogan, P.; Groot, N.; de Graeff, N.; Avcin, T.; Bader-Meunier, B.; Dolezalova, P.; Feldman, B.M.; Kone-Paut, I.; et al. European consensus-based recommendations for diagnosis and treatment of immunoglobulin a vasculitis—the SHARE Initiative. Rheumatology 2019, 58, 1607–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jauhola, O.; Ronkainen, J.; Koskimies, O.; Ala-Houhala, M.; Arikoski, P.; Holtta, T.; Jahnukainen, T.; Rajantie, J.; Ormala, T.; Nuutinen, M. Outcome of Henoch-Schonlein Purpura 8 years after treatment with a placebo or prednisone at disease onset. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2012, 27, 933–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novak, J.; Rizk, D.; Takahashi, K.; Zhang, X.; Bian, Q.; Ueda, H.; Ueda, Y.; Reily, C.; Lai, L.Y.; Hao, C.; et al. New insights into the pathogenesis of IgA nephropathy. Kidney Dis. 2015, 1, 8–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donadio, M.E.; Loiacono, E.; Peruzzi, L.; Amore, A.; Camilla, R.; Chiale, F.; Vergano, L.; Boido, A.; Conrieri, M.; Bianciotto, M.; et al. Toll-like receptors, immunoproteasome and regulatory t cells in children with henoch-schonlein purpura and primary IgA nephropathy. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2014, 29, 1545–1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, A.; Komatsuda, A.; Kaga, H.; Sato, R.; Togashi, M.; Okuyama, S.; Wakui, H.; Takahashi, N. Different expression patterns of toll-like receptor MRNAs in blood mononuclear cells of IgA nephropathy and IgA vasculitis with nephritis. Tohoku J. Exp. Med. 2016, 240, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.-H.; Tsai, I.-J.; Chang, C.-J.; Chuang, Y.-H.; Hsu, H.-Y.; Chiang, B.-L. The interaction between circulating complement proteins and cutaneous microvascular endothelial cells in the development of childhood henoch-schönlein purpura. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0120411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maillard, N.; Wyatt, R.J.; Julian, B.A.; Kiryluk, K.; Gharavi, A.; Fremeaux-Bacchi, V.; Novak, J. Current understanding of the role of complement in IgA nephropathy. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2015, 26, 1503–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medjeral-Thomas, N.R.; Lomax-Browne, H.J.; Beckwith, H.; Willicombe, M.; McLean, A.G.; Brookes, P.; Pusey, C.D.; Falchi, M.; Cook, H.T.; Pickering, M.C. Circulating complement factor h-related proteins 1 and 5 correlate with disease activity in IgA nephropathy. Kidney Int. 2017, 92, 942–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawasaki, Y.; Maeda, R.; Ohara, S.; Suyama, K.; Hosoya, M. Serum IgA/C3 and Glomerular C3 Staining Predict Severity of IgA Nephropathy. Pediatr. Int. 2018, 60, 162–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizk, D.V.; Maillard, N.; Julian, B.A.; Knoppova, B.; Green, T.J.; Novak, J.; Wyatt, R.J. The emerging role of complement proteins as a target for therapy of IgA nephropathy. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, H. Biomarkers for IgA nephropathy on the basis of multi-hit pathogenesis. Clin. Exp. Nephrol. 2018, 23, 26–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wada, Y.; Matsumoto, K.; Suzuki, T.; Saito, T.; Kanazawa, N.; Tachibana, S.; Iseri, K.; Sugiyama, M.; Iyoda, M.; Shibata, T. Clinical significance of serum and mesangial galactose-deficient IgA1 in patients with IgA nephropathy. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0206865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, A.C.; Willis, F.R.; Beattie, T.J.; Feehally, J. Abnormal IgA Glycosylation in henoch-schonlein purpura restricted to patients with clinical nephritis. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 1998, 13, 930–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berthelot, L.; Jamin, A.; Viglietti, D.; Chemouny, J.M.; Ayari, H.; Pierre, M.; Housset, P.; Sauvaget, V.; Hurtado-Nedelec, M.; Vrtovsnik, F.; et al. Value of biomarkers for predicting immunoglobulin a vasculitis nephritis outcome in an adult prospective cohort. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2017, 33, 1579–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillebout, E.; Jamin, A.; Ayari, H.; Housset, P.; Pierre, M.; Sauvaget, V.; Viglietti, D.; Deschenes, G.; Monteiro, R.C.; Berthelot, L. Biomarkers of IgA vasculitis nephritis in children. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0188718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, K.K.; Wyatt, R.J.; Moldoveanu, Z.; Tomana, M.; Julian, B.A.; Hogg, R.J.; Lee, J.Y.; Huang, W.Q.; Mestecky, J.; Novak, J. Serum levels of galactose-deficient IgA in children with IgA nephropathy and henoch-schonlein purpura. Pediatr Nephrol 2007, 22, 2067–2072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esteve Cols, C.; Graterol Torres, F.-A.; Quirant Sánchez, B.; Marco Rusiñol, H.; Navarro Díaz, M.I.; Ara del Rey, J.; Martínez Cáceres, E.M. Immunological pattern in IgA nephropathy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, H.; Moldoveanu, Z.; Julian, B.A.; Wyatt, R.J.; Novak, J. Autoantibodies specific for galactose-deficient IgA1 in IgA vasculitis with nephritis. Kidney Int. Rep. 2019, 4, 1717–1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moresco, R.N.; Speeckaert, M.M.; Zmonarski, S.C.; Krajewska, M.; Komuda-Leszek, E.; Perkowska-Ptasinska, A.; Gesualdo, L.; Rocchetti, M.T.; Delanghe, S.E.; Vanholder, R.; et al. Urinary myeloid IgA Fc alpha receptor (CD89) and Transglutaminase-2 as new biomarkers for active IgA Nephropathy and henoch-schonlein purpura nephritis. BBA Clin. 2016, 5, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delanghe, S.E.; Speeckaert, M.M.; Segers, H.; Desmet, K.; Vande Walle, J.; Laecke, S.V.; Vanholder, R.; Delanghe, J.R. Soluble transferrin receptor in urine, a new biomarker for IgA nephropathy and henoch-schonlein purpura nephritis. Clin. Biochem. 2013, 46, 591–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, H.; Suzuki, Y.; Narita, I.; Aizawa, M.; Kihara, M.; Yamanaka, T.; Kanou, T.; Tsukaguchi, H.; Novak, J.; Horikoshi, S.; et al. Toll-like receptor 9 affects severity of IgA nephropathy. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2008, 19, 2384–2395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, D.; Suzuki, Y.; Kano, T.; Suzuki, H.; Matsuoka, J.; Yokoi, H.; Horikoshi, S.; Ikeda, K.; Tomino, Y. Tonsillar TLR9 expression and efficacy of tonsillectomy with steroid pulse therapy in IgA nephropathy patients. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2012, 27, 1090–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Jia, M.; Zhu, L.; Zhai, Y.; Chen, P.; Xu, B.; Guo, W.; Shi, S.; Liu, L.; Lv, J.; Zhang, H. Variation in complement factor H affects complement activation in immunoglobulin A vasculitis with nephritis. Nephrology 2020, 25, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moldoveanu, Z.; Wyatt, R.J.; Lee, J.Y.; Tomana, M.; Julian, B.A.; Mestecky, J.; Huang, W.-Q.; Anreddy, S.R.; Hall, S.; Hastings, M.C.; et al. Patients with IgA nephropathy have increased serum galactose-deficient IgA1 levels. Kidney Int. 2007, 71, 1148–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasutake, J.; Suzuki, Y.; Suzuki, H.; Hiura, N.; Yanagawa, H.; Makita, Y.; Kaneko, E.; Tomino, Y. Novel lectin-independent approach to detect galactose-deficient IgA1 in IgA nephropathy. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2015, 30, 1315–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiryluk, K.; Moldoveanu, Z.; Sanders, J.T.; Eison, T.M.; Suzuki, H.; Julian, B.A.; Novak, J.; Gharavi, A.G.; Wyatt, R.J. Aberrant glycosylation of IgA1 is inherited in both pediatric IgA nephropathy and henoch-schonlein purpura nephritis. Kidney Int. 2011, 80, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gharavi, A.G.; Moldoveanu, Z.; Wyatt, R.J.; Barker, C.V.; Woodford, S.Y.; Lifton, R.P.; Mestecky, J.; Novak, J.; Julian, B.A. Aberrant IgA1 glycosylation is inherited in familial and sporadic IgA nephropathy. JASN 2008, 19, 1008–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Ding, J.; Zhu, L.; Shi, S.; Jiang, L.; Zhao, M.; Zhang, H. Aberrant galactosylation of IgA1 is involved in the genetic susceptibility of chinese patients with IgA nephropathy. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2009, 24, 3372–3375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hastings, M.C.; Moldoveanu, Z.; Julian, B.A.; Novak, J.; Sanders, J.T.; McGlothan, K.R.; Gharavi, A.G.; Wyatt, R.J. Galactose-deficient IgA1 in African Americans with IgA nephropathy: Serum levels and heritability. CJASN 2010, 5, 2069–2074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiryluk, K.; Li, Y.; Sanna-Cherchi, S.; Rohanizadegan, M.; Suzuki, H.; Eitner, F.; Snyder, H.J.; Choi, M.; Hou, P.; Scolari, F.; et al. Geographic differences in genetic susceptibility to IgA nephropathy: GWAS replication study and geospatial risk analysis. PLoS Genet. 2012, 8, e1002765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-Mejías, R.; Castañeda, S.; Genre, F.; Remuzgo-Martínez, S.; Carmona, F.D.; Llorca, J.; Blanco, R.; Martín, J.; González-Gay, M.A. Genetics of immunoglobulin-A vasculitis (Henoch-Schönlein Purpura): An updated review. Autoimmun. Rev. 2018, 17, 301–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, C.H.; Lim, B.J.; Bae, Y.S.; Kwon, Y.E.; Kim, Y.L.; Nam, K.H.; Park, K.S.; An, S.Y.; Koo, H.M.; Doh, F.M.; et al. Using the Oxford classification of IgA Nephropathy to predict long-term outcomes of henoch-schonlein purpura nephritis in adults. Mod. Pathol. 2014, 27, 972–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inagaki, K.; Kaihan, A.B.; Hachiya, A.; Ozeki, T.; Ando, M.; Kato, S.; Yasuda, Y.; Maruyama, S. Clinical impact of endocapillary proliferation according to the Oxford classification among adults with henoch-schönlein purpura nephritis: A multicenter retrospective cohort study. BMC Nephrol. 2018, 19, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, K.; Zhang, L.; Ding, J.; Wang, S.; Su, B.; Xiao, H.; Wang, F.; Zhong, X.; Li, Y. Value of the Oxford classification of IgA nephropathy in children with henoch–schönlein purpura nephritis. J. Nephrol. 2018, 31, 279–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Tang, M.; Yao, X.; Zhang, N.; Fan, J.; Zhou, N.; Sun, Q.; Chen, Z.; Meng, Q.; Lei, L.; et al. A clinicopathological comparison between IgA nephropathy and henoch–schönlein purpura nephritis in children: Use of the Oxford classification. Clin. Exp. Nephrol. 2019, 23, 1382–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| IgA Nephropathy | IgA Vasculitis | |
|---|---|---|
| Age at onset | 30 to 39 years | 1 to 19 years and 60 to 69 years |
| Clinical presentation | Only renal | Extra-renal symptoms (skin, gastro-intestinal, joint, neurologic, pulmonary, urologic) ± renal involvement |
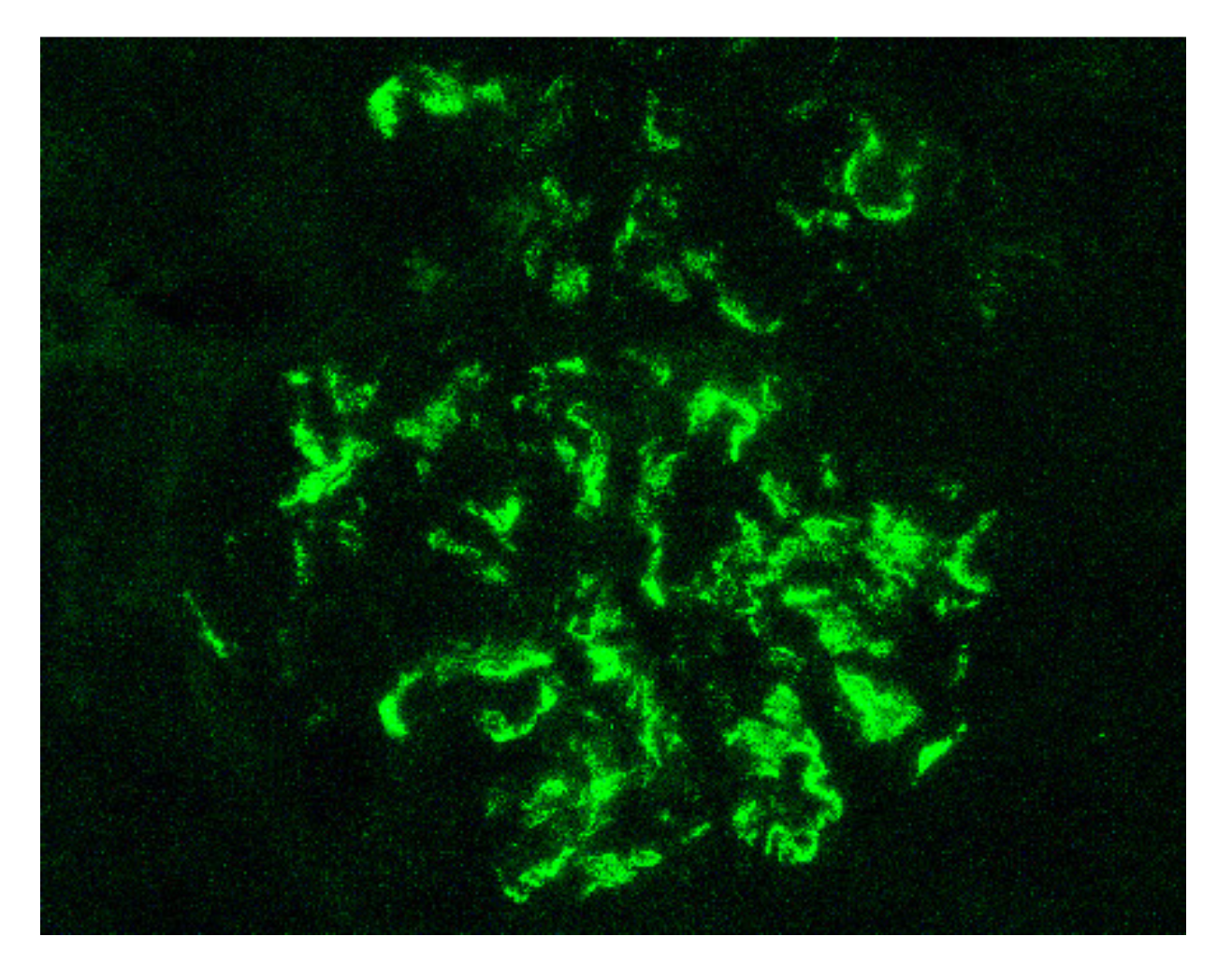
| Renal biopsy | Mesangial IgA1, IgG, IgM, C3 and fibrin on immunofluorescence Mesangial hyper-cellularity with increased mesangial matrix, endo-capillary hyper-cellularity, segmental glomerular sclerosis, cellular crescents on light microscopy | |
| Outcome | More severe in adults | |
| Physiopathology | Multi-hit model involving IgA1 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pillebout, E. IgA Vasculitis and IgA Nephropathy: Same Disease? J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 2310. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10112310
Pillebout E. IgA Vasculitis and IgA Nephropathy: Same Disease? Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2021; 10(11):2310. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10112310
Chicago/Turabian StylePillebout, Evangeline. 2021. "IgA Vasculitis and IgA Nephropathy: Same Disease?" Journal of Clinical Medicine 10, no. 11: 2310. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10112310
APA StylePillebout, E. (2021). IgA Vasculitis and IgA Nephropathy: Same Disease? Journal of Clinical Medicine, 10(11), 2310. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10112310






