Small Drainage Volumes of Pleural Effusions Are Associated with Complications in Critically Ill Patients: A Retrospective Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patient Selection
2.2. Outcomes
2.3. Statistical Analyses
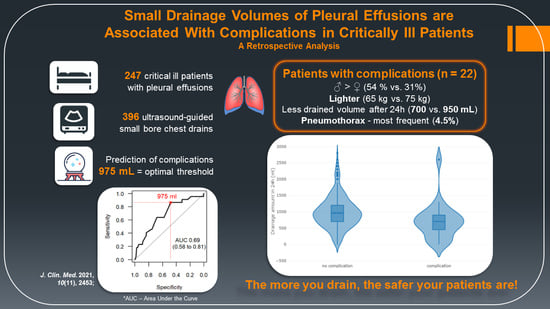
3. Results
3.1. Study Population
3.2. Drainage Volume
3.3. Complications
3.4. Oxygenation
3.5. Mortality
4. Discussion
4.1. Drainage Volume
4.2. Complications
4.3. Oxygenation
4.4. Mortality
4.5. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Light, R.W. Pleural Diseases, 6th ed.; Lippincott Williams & Wilkins (LWW): Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Zocchi, L. Physiology and pathophysiology of pleural fluid turnover. Eur. Respir. J. 2002, 20, 1545–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Light, R.W. Pleural effusions after coronary artery bypass graft surgery. Curr. Opin. Pulm. Med. 2002, 8, 308–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Light, R.W.; George, R.B. Incidence and Significance of Pleural Effusion after Abdominal Surgery. Chest 1976, 69, 621–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nielsen, P.H.; Jepsen, S.B.; Olsen, A.D. Postoperative Pleural Effusion Following Upper Abdominal Surgery. Chest 1989, 96, 1133–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Heidecker, J.; Sahn, S.A. The Spectrum of Pleural Effusions After Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting Surgery. Clin. Chest Med. 2006, 27, 267–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, C.S.; Templeton, P.A.; Attar, S. Esophageal perforation: CT findings. Am. J. Roentgenol. 1993, 160, 767–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pneumatikos, I.; Bouros, D. Pleural Effusions in Critically Ill Patients. Respiration 2008, 76, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maslove, D.M.; Chen, B.T.-M.; Wang, H.; Kuschner, W.G. The Diagnosis and Management of Pleural Effusions in the ICU. J. Intensive Care Med. 2013, 28, 24–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattison, L.E.; Sahn, S.A.; Coppage, L.; Alderman, D.F.; Herlong, J.O. Pleural Effusions in the Medical ICU. Chest 1997, 111, 1018–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bateman, M.; Alkhatib, A.; John, T.; Parikh, M.; Kheir, F. Pleural Effusion Outcomes in Intensive Care: Analysis of a Large Clinical Database. J. Intensive Care Med. 2019, 35, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estenne, M.; Yernault, J.-C.; De Troyer, A. Mechanism of relief of dyspnea after thoracocentesis in patients with large pleural effusions. Am. J. Med. 1983, 74, 813–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krell, W.S.; Rodarte, J.R. Effects of acute pleural effusion on respiratory system mechanics in dogs. J. Appl. Physiol. 1985, 59, 1458–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agustí, A.G.N.; Cardús, J.; Roca, J.; Grau, J.M.; Xaubet, A.; Rodríguez-Roisin, R. Ventilation-Perfusion Mismatch in Patients with Pleural Effusion. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1997, 156, 1205–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goligher, E.C.; Leis, J.A.; A Fowler, R.; Pinto, R.; Adhikari, N.K.; Ferguson, N.D. Utility and safety of draining pleural effusions in mechanically ventilated patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Crit. Care 2011, 15, R46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corcoran, J.P.; Psallidas, I.; Wrightson, J.M.; Hallifax, R.J.; Rahman, N.M. Pleural procedural complications: Prevention and management. J. Thorac. Dis. 2015, 7, 1058–1067. [Google Scholar]
- Fysh, E.T.H.; Smallbone, P.; Mattock, N.; McCloskey, C.; Litton, E.; Wibrow, B.; Ho, K.M.; Lee, Y.C.G. Clinically Significant Pleural Effusion in Intensive Care: A Prospective Multicenter Cohort Study. Crit. Care Explor. 2020, 2, e0070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.H.; Ouzounian, S.P.; DiRusso, S.; Sullivan, T.; Savino, J.; Del Guercio, L. Hemodynamic and Pulmonary Changes after Drainage of Significant Pleural Effusions in Critically Ill, Mechanically Ventilated Surgical Patients. J. Trauma Inj. Infect. Crit. Care 2004, 57, 1184–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.-L.; Chung, C.-L.; Hsiao, S.-H.; Chang, S.-C. Pleural space elastance and changes in oxygenation after therapeutic thoracentesis in ventilated patients with heart failure and transudative pleural effusions. Respirology 2010, 15, 1001–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talmor, M.; Hydo, L.; Gershenwald, J.G.; Barie, P.S. Beneficial effects of chest tube drainage of pleural effusion in acute respiratory failure refractory to positive end-expiratory pressure ventilation. Surgery 1998, 123, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razazi, K.; Thille, A.W.; Carteaux, G.; Beji, O.; Brun-Buisson, C.; Brochard, L.; Dessap, A.M. Effects of Pleural Effusion Drainage on Oxygenation, Respiratory Mechanics, and Hemodynamics in Mechanically Ventilated Patients. Ann. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2014, 11, 1018–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brims, F.J.H.; Davies, M.G.; Elia, A.; Griffiths, M.J.D. The effects of pleural fluid drainage on respiratory function in mechanically ventilated patients after cardiac surgery. BMJ Open Respir. Res. 2015, 2, e000080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Razazi, K.; Boissier, F.; Neuville, M.; Jochmans, S.; Tchir, M.; May, F.; De Prost, N.; Brun-Buisson, C.; Carteaux, G.; Dessap, A.M. Pleural effusion during weaning from mechanical ventilation: A prospective observational multicenter study. Ann. Intensive Care 2018, 8, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fartoukh, M.; Azoulay, E.; Galliot, R.; Le Gall, J.-R.; Baud, F.; Chevret, S.; Schlemmer, B. Clinically Documented Pleural Effusions in Medical ICU Patients. Chest 2002, 121, 178–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Havelock, T.; Teoh, R.; Laws, D.; Gleeson, F. Pleural Disease Guideline Group Pleural procedures and thoracic ultrasound: British Thoracic Society pleural disease guideline 2010. Thorax 2010, 65, i61–i76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreno, R.P.; Metnitz, P.G.H.; Almeida, E.; Jordan, B.; Bauer, P.; Campos, R.A.; Iapichino, G.; Edbrooke, D.; Capuzzo, M.; Le Gall, J.-R. SAPS 3—From evaluation of the patient to evaluation of the intensive care unit. Part 2: Development of a prognostic model for hospital mortality at ICU admission. Intensive Care Med. 2005, 31, 1345–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Statistics Austria: Health Interview Survey 2019, 2014 and 2006/07. 2020. Available online: http://www.statistik.at/web_en/statistics/PeopleSociety/health/health_determinants/bmi_body_mass_index/index.html (accessed on 23 December 2020).
- Ault, M.J.; Rosen, B.T.; Scher, J.; Feinglass, J.; Barsuk, J.H. Thoracentesis outcomes: A 12-year experience. Thorax 2014, 70, 127–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, H.Y.; Ko, B.S.; Choi, H.J.; Koh, C.Y.; Sohn, C.H.; Seo, D.W.; Lee, Y.-S.; Lee, J.H.; Oh, B.J.; Lim, K.S.; et al. Incidence and risk factors of iatrogenic pneumothorax after thoracentesis in emergency department settings. J. Thorac. Dis. 2017, 9, 3728–3734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S.-J.; Tu, C.-Y.; Chen, H.-J.; Chen, C.-H.; Chen, W.; Shih, C.-M.; Hsu, W.-H. Application of ultrasound-guided pigtail catheter for drainage of pleural effusions in the ICU. Intensive Care Med. 2008, 35, 350–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Waele, J.J.; Hoste, E.; Benoit, D.; Vandewoude, K.; Delaere, S.; Berrevoet, F.; Colardyn, F. The Effect of Tube Thoracostomy on Oxygenation in ICU Patients. J. Intensive Care Med. 2003, 18, 100–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goecke, W.; Schwerk, W.B. Die Real-Time Sonographie in der Diagnostik von Pleuraergüssen. In Ultraschall-Diagnostik ’89; Springer Science and Business Media LLC: New York, NY, USA, 1990; pp. 385–387. [Google Scholar]
- Hassan, M.; Rizk, R.; Essam, H.; Abouelnour, A. Validation of equations for pleural effusion volume estimation by ultrasonography. J. Ultrasound 2017, 20, 267–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartter, T.; Mayo, P.D.; Pratter, M.R.; Santarelli, R.J.; Leeds, W.M.; Akers, S.M. Lower Risk and Higher Yield for Thoracentesis When Performed by Experienced Operators. Chest 1993, 103, 1873–1876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colt, H.G.; Brewer, N.; Barbur, E. Evaluation of patient-related and procedure-related factors contributing to pneumothorax following thoracentesis. Chest 1999, 116, 134–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vetrugno, L.; Guadagnin, G.M.; Barbariol, F.; D’Incà, S.; DelRio, S.; Orso, D.; Girometti, R.; Volpicelli, G.; Bove, T. Assessment of Pleural Effusion and Small Pleural Drain Insertion by Resident Doctors in an Intensive Care Unit: An Observational Study. Clin. Med. Insights Circ. Respir. Pulm. Med. 2019, 13, 1179548419871527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gordon, C.E.; Feller-Kopman, D.; Balk, E.M.; Smetana, G.W. Pneumothorax Following Thoracentesis. Arch. Intern. Med. 2010, 170, 332–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duncan, D.R.; Morgenthaler, T.I.; Ryu, J.; Daniels, C.E. Reducing Iatrogenic Risk in Thoracentesis. Chest 2009, 135, 1315–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grodzin, C.J.; Balk, R.A. Indwelling Small Pleural Catheter Needle Thoracentesis in the Management of Large Pleural Effusions. Chest 1997, 111, 981–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Yu, C.J.; Yang, P.C.; Chang, D.B.; Luh, K.T. Diagnostic and therapeutic use of chest sonography: Value in critically ill patients. Am. J. Roentgenol. 1992, 159, 695–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grogan, D.R. Complications associated with thoracentesis. A prospective, randomized study comparing three different methods. Arch. Intern. Med. 1990, 150, 873–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayo, P.H.; Goltz, H.R.; Tafreshi, M.; Doelken, P. Safety of Ultrasound-Guided Thoracentesis in Patients Receiving Mechanical Ventilation. Chest 2004, 125, 1059–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seneff, M.G.; Corwin, R.W.; Gold, L.H.; Irwin, R.S. Complications Associated with Thoracocentesis. Chest 1986, 90, 97–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, T.R.; Sahn, S.A. Thoracocentesis. Chest 1987, 91, 817–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doelken, P.; Abreu, R.; Sahn, S.A.; Mayo, P.H. Effect of Thoracentesis on Respiratory Mechanics and Gas Exchange in the Patient Receiving Mechanical Ventilation. Chest 2006, 130, 1354–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roch, A.; Bojan, M.; Michelet, P.; Romain, F.; Bregeon, F.; Papazian, L.; Auffray, J.-P. Usefulness of Ultrasonography in Predicting Pleural Effusions > 500 mL in Patients Receiving Mechanical Ventilation. Chest 2005, 127, 224–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walden, A.P.; Garrard, C.S.; Salmon, J. Sustained effects of thoracocentesis on oxygenation in mechanically ventilated patients. Respirology 2010, 15, 986–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capuzzo, M.; Volta, C.A.; Tassinati, T.; Moreno, R.P.; Valentin, A.; Guidet, B.; Iapichino, G.; Martin, C.; Perneger, T.; Combescure, C.; et al. Hospital mortality of adults admitted to Intensive Care Units in hospitals with and without Intermediate Care Units: A multicentre European cohort study. Crit. Care 2014, 18, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Baseline Characteristics | Total (n = 247) | No Complications (n = 225) | Complications (n = 22) | Estimate with 95% CI b | p-Value c |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 71 | 71 | 69 | 71 (65.54; 69.22) | 0.519 |
| Female sex | 82 (33.2%) | 70 (31.1%) | 12 (54.5%) | 2.65 (0.99; 7.19) | 0.040 |
| Height (cm) | 173 (165–178) | 174 (165–178) | 171 (160–175) | 3 (0; 7) | 0.080 |
| Weight (kg) | 75 (65–85) | 75 (67–85) | 65 (55–79.5) | 8.5 (1; 15.2) | 0.028 |
| SAPS III at admission (pts) | 64 (55–74) | 64 (55–74) | 62.5 (52–70.7) | 1.7 (−5; 9) | 0.638 |
| Baseline Characteristics | Total (n = 396) | No Complications (n = 374) | Complications (n = 22) | Estimate with 95% CI b | p-Value c |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Oxygenation | |||||
| FiO2 (%) | 45 (30–55) | 45 (30–55) | 45 (31.3–50) | 0 (−5; 5) | 0.874 |
| paCO2 (mmHg) | 41.2 (36.6–45.5) | 41.4 (36.7–45.6) | 39.3 (35.8–40.9) | 1.6 (−1.4; 4.3) | 0.245 |
| paO2 (mmHg) | 83.6 (73.1–96.1) | 83.4 (72.8–95.9) | 86.8 (77.1–104.3) | −3.9 (−11.7; 4) | 0.323 |
| Respiratory quotient | 195.2 (145.9–269.8) | 195.2 (145.6–269.4) | 197.1 (154.0–296.9) | −11.9 (−50.0; 26.8) | 0.539 |
| Coagulation | |||||
| Haemoglobin (g/dL) | 8.9 (8.3–9.5) | 8.9 (8.3–9.5) | 9 (8.43–9.3) | −0.1 (−0.5; 0.3) | 0.688 |
| Sodium (mmol/L) | 142 (139–144) | 142 (139–144) | 140.5 (138.3–143.0) | 1 (−1; 3) | 0.246 |
| Platelets (G/L) | 153.5 (100.0–232.8) | 153 (97.8–232.3) | 171.5 (112.8–265.5) | −19 (−63; 23) | 0.345 |
| Prothrombin index (%) | 73 (61–81) | 73 (61–81) | 69 (59.3–92.5) | 0 (−10; 8) | 0.970 |
| aPTT (s) | 42 (37–48) | 42 (37–48.25) | 41 (36.3–47.3) | 2 (−2; 5) | 0.423 |
| Fibrinogen (mg/dL) | 437 (333.5–532.8) | 437 (333.0–532.3) | 439.5 (355–545) | −7 (−75; 59) | 0.828 |
| Outcome Parameters | Total (n = 396 SBCD) | No Complications (n = 374 SBCD) | Complications (n = 22) | Estimate with 95% CI b | p-Value c |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Drainage volume in 24 h | 900 (650–1200) | 950 (700–1200) | 700 (462.5–900) | 300 (100; 500) | 0.003 |
| Change in oxygenation after SBCD insertion | |||||
| FiO2 (%) | 0 (0–0) | 0 (0–0) | 0 (0–0) | 0 (0–0) | 0.398 |
| paCO2 (mmHg) | 0.45 (−1.9–3.0) | 0.45 (−1.9–2.9) | 0.25 (−1.3–4.4) | −0.1 (−2.2; 1.8) | 0.874 |
| paO2 (mmHg) | 8.7 (−8–23) | 9 (−7.2–22.6) | 2.8 (−11.5–25.9) | 4.1 (−7.9; 14.6) | 0.495 |
| Respiratory quotient | 20 (−15.3–56.0) | 20.7 (−15–56) | 8.5 (−25.8–44.3) | 11.8 (−14.8; 37.4) | 0.372 |
| Change in coagulation parameters after SBCD insertion | |||||
| Hemoglobin (g/dL) | 0 (−0.3–0.2) | −0.1 (−0.3–0.2) | 0.1 (−0.5–0.2) | 0 (−0.2; 0.3) | 0.602 |
| Sodium (mmol/L) | 0 (−1–1) | 0 (−1–1) | 0 (−1–2) | 0 (−1; 1) | 0.778 |
| Platelets (g/L) | 4 (−9–17) | 3 (−8.5–16) | 10.5 (−20.8–29.5) | −5 (−20; 11) | 0.514 |
| Prothrombin index (%) | 0 (−5–4) | 0 (−5–4) | 0.5 (−8.5–8.5) | 0 (−5; 4) | 0.884 |
| aPTT (s) | 0 (−2–2) | 0 (−2–3) | 1 (−2–2) | 0 (−2; 1) | 0.794 |
| Fibrinogen (mg/dL) | 1 (−29.8–30.8) | 0 (−30–30) | 16 (−20–36) | −11 (−34; 11) | 0.306 |
| Outcome Parameters | Total (n = 247) | No Complications (n = 225) | Complications (n = 22) | Estimate with 95% CI b | p-Value c |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ICU mortality | 41 (16.6%) | 39 (17.3%) | 2 (9.1%) | 0.48 (0.05; 2.1) | 0.547 |
| In-hospital mortality | 55(22.3%) | 52 (23.1%) | 3 (13.6%) | 0.53 (0.1; 1.89) | 0.424 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Treml, B.; Rajsic, S.; Diwo, F.; Hell, T.; Hochhold, C. Small Drainage Volumes of Pleural Effusions Are Associated with Complications in Critically Ill Patients: A Retrospective Analysis. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 2453. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10112453
Treml B, Rajsic S, Diwo F, Hell T, Hochhold C. Small Drainage Volumes of Pleural Effusions Are Associated with Complications in Critically Ill Patients: A Retrospective Analysis. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2021; 10(11):2453. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10112453
Chicago/Turabian StyleTreml, Benedikt, Sasa Rajsic, Felix Diwo, Tobias Hell, and Christoph Hochhold. 2021. "Small Drainage Volumes of Pleural Effusions Are Associated with Complications in Critically Ill Patients: A Retrospective Analysis" Journal of Clinical Medicine 10, no. 11: 2453. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10112453
APA StyleTreml, B., Rajsic, S., Diwo, F., Hell, T., & Hochhold, C. (2021). Small Drainage Volumes of Pleural Effusions Are Associated with Complications in Critically Ill Patients: A Retrospective Analysis. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 10(11), 2453. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10112453