Systemic Antibiotics and Obesity: Analyses from a Population-Based Cohort
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. National Health Insurance Service–National Sample Cohort (NHIS-NSC)
2.2. Study Subjects
2.3. Data and Measurements
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Clinical Characteristics of the Subjects According to Obesity Status
3.2. Clinical Characteristics of the Subjects Classified According to Total Duration of Systemic Antibiotic Treatment for the Previous 10 Years
3.3. Risk of Obesity and Components of MS According to Total Duration of Systemic Antibiotic Treatment for the Previous 10 Years
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Di Cesare, M.; Sorić, M.; Bovet, P.; Miranda, J.J.; Bhutta, Z.; Stevens, G.A.; Laxmaiah, A.; Kengne, A.-P.; Bentham, J. The epidemiological burden of obesity in childhood: A worldwide epidemic requiring urgent action. BMC Med. 2019, 17, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Blüher, M. Obesity: Global epidemiology and pathogenesis. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2019, 15, 288–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolucci, A.C.; Hume, M.P.; Martínez, I.; Mayengbam, S.; Walter, J.; Reimer, R.A. Prebiotics Reduce Body Fat and Alter Intestinal Microbiota in Children Who Are Overweight or With Obesity. Gastroenterology 2017, 153, 711–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, R.; Hong, J.; Xu, X.; Feng, Q.; Zhang, D.; Gu, Y.; Shi, J.; Zhao, S.; Liu, W.; Wang, X.; et al. Gut microbiome and serum metabolome alterations in obesity and after weight-loss intervention. Nat. Med. 2017, 23, 859–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alang, N.; Kelly, C.R. Weight Gain after Fecal Microbiota Transplantation. Open Forum Infect. Dis. 2015, 2, ofv004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arslan, N. Obesity, fatty liver disease and intestinal microbiota. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 16452–16463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Festi, D.; Schiumerini, R.; Eusebi, L.H.; Marasco, G.; Taddia, M.; Colecchia, A. Gut microbiota and metabolic syndrome. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 16079–16094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris, K.; Kassis, A.; Major, G.; Chou, C.J. Is the Gut Microbiota a New Factor Contributing to Obesity and Its Metabolic Disorders? J. Obes. 2012, 2012, 879151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cox, L.M.; Yamanishi, S.; Sohn, J.; Alekseyenko, A.; Leung, J.; Cho, I.; Kim, S.G.; Li, H.; Gao, Z.; Mahana, D.; et al. Altering the Intestinal Microbiota during a Critical Developmental Window Has Lasting Metabolic Consequences. Cell 2014, 158, 705–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Edmonson, M.B.; Eickhoff, J.C. Weight Gain and Obesity in Infants and Young Children Exposed to Prolonged Antibiotic Prophylaxis. JAMA Pediatr. 2017, 171, 150–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heerman, W.J.; Daley, M.F.; Boone-Heinonen, J.; Rifas-Shiman, S.L.; Bailey, L.C.; Forrest, C.B.; Young, J.G.; Gillman, M.W.; Horgan, C.E.; Janicke, D.M.; et al. Maternal antibiotic use during pregnancy and childhood obesity at age 5 years. Int. J. Obes. 2019, 43, 1202–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, S.A.; Wu, R.K.S.; Oremus, M. The association between antibiotic use in infancy and childhood overweight or obesity: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Obes. Rev. 2018, 19, 1463–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasmussen, S.H.; Shrestha, S.; Bjerregaard, L.G.; Ängquist, L.; Baker, J.L.; Jess, T.; Allin, K.H. Antibiotic exposure in early life and childhood overweight and obesity: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2018, 20, 1508–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Yan, C.; Wang, H.; Jiang, F.; Li, F.; Zhang, J. Prenatal Exposure to Antibiotics and Risk of Childhood Obesity in a Multicenter Cohort Study. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2018, 187, 2159–2167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thuny, F.; Richet, H.; Casalta, J.-P.; Angelakis, E.; Habib, G.; Raoult, D. Vancomycin Treatment of Infective Endocarditis Is Linked with Recently Acquired Obesity. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e9074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, J.; Lee, J.S.; Park, S.-H.; Shin, S.A.; Kim, K. Cohort Profile: The National Health Insurance Service–National Sample Cohort (NHIS-NSC), South Korea. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2016, 46, dyv319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alberti, K.; Eckel, R.H.; Grundy, S.M.; Zimmet, P.Z.; Cleeman, J.I.; Donato, K.A.; Fruchart, J.-C.; James, W.P.T.; Loria, C.M.; Smith, S.C. Harmonizing the Metabolic Syndrome. Circulation 2009, 120, 1640–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Agarwal, D.P. Cardioprotective effects of light-moderate consumption of alcohol: A review of putative mechanisms. Alcohol Alcohol. 2002, 37, 409–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rhee, S.Y.; Han, K.-D.; Kwon, H.; Park, S.-E.; Park, Y.-G.; Kim, Y.-H.; Yoo, S.-J.; Rhee, E.-J.; Lee, W.-Y. Association between Glycemic Status and the Risk of Parkinson Disease: A Nationwide Population-Based Study. Diabetes Care 2020, 43, 2169–2175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.S.; Park, C.Y.; Oh, S.W.; Yoo, H.J. Prevalence of obesity and metabolic syndrome in Korean adults. Obes. Rev. 2007, 9, 104–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiskopf, D.; Weinberger, B.; Grubeck-Loebenstein, B. The aging of the immune system. Transpl. Int. 2009, 22, 1041–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castle, S.C.; Uyemura, K.; Fulop, T.; Makinodan, T. Host Resistance and Immune Responses in Advanced Age. Clin. Geriatr. Med. 2007, 23, 463–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, D.S.H. Changes seen in gut bacteria content and distribution with obesity: Causation or association? Postgrad. Med. 2015, 127, 863–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurdi, P.; Kawanishi, K.; Mizutani, K.; Yokota, A. Mechanism of Growth Inhibition by Free Bile Acids in Lactobacilli and Bifidobacteria. J. Bacteriol. 2006, 188, 1979–1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Leong, K.S.W.; Derraik, J.G.B.; Hofman, P.L.; Cutfield, W.S. Antibiotics, gut microbiome and obesity. Clin. Endocrinol. 2018, 88, 185–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Graul, A.; Stringer, M.; Sorbera, L. Cachexia. Drugs Today 2016, 52, 519–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breijyeh, Z.; Jubeh, B.; Karaman, R. Resistance of Gram-Negative Bacteria to Current Antibacterial Agents and Approaches to Resolve It. Molecules 2020, 25, 1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Brown, B.I. Nutritional Management of Metabolic Endotoxemia: A Clinical Review. Altern. Ther. 2017, 23, 42–54. [Google Scholar]
- Evans, M.E.; Pollack, M. Effect of Antibiotic Class and Concentration on the Release of Lipopolysaccharide from Escherichia coli. J. Infect. Dis. 1993, 167, 1336–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Variables | Non-Obesity (n = 162,838) | Obesity * (n = 103,609) | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 48.4 ± 14.1 | 50.9 ± 13.8 | <0.0001 |
| Sex, n (%) | <0.0001 | ||
| Male | 77,109 (47.4) | 64,351 (62.1) | |
| Female | 85,729 (52.6) | 39,258 (37.9) | |
| Diabetes mellitus, n (%) | 12,290 (7.55) | 16,057 (15.5) | <0.0001 |
| Hypertension, n (%) | 32,732 (20.1) | 42,012 (40.6) | <0.0001 |
| Dyslipidemia, n (%) | 32,457 (19.9) | 35,577 (34.3) | <0.0001 |
| Heavy drinker, n (%) | 79,523 (48.8) | 54,140 (52.3) | <0.0001 |
| Current smoker, n (%) | 32,592 (20.0) | 24,686 (23.8) | <0.0001 |
| Regular exercise, n (%) | 80,420 (49.4) | 52,028 (50.2) | <0.0001 |
| Subject who satisfy MS criteria | |||
| BP ≥ 130/85 mmHg | 57,024 (35.0) | 63,417 (61.2) | <0.0001 |
| FG ≥ 100 mg/dL | 48,220 (29.6) | 48,990 (47.3) | <0.0001 |
| TG ≥ 150 mg/dL | 46,138 (28.3) | 56,437 (54.5) | <0.0001 |
| HDL-C < 40/50 mg/dL | 41,052 (25.2) | 43,752 (42.2) | <0.0001 |
| Systemic antibiotic treatment duration (days) in the previous 10 years | 69.4 ± 82.5 | 72.3 ± 86.0 | <0.0001 |
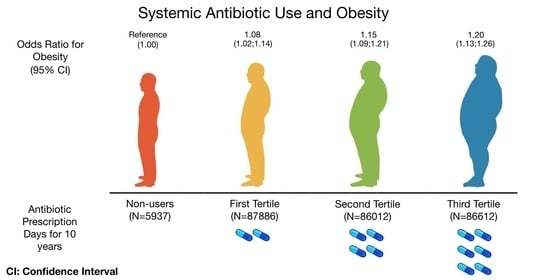
| Variables | Non-Users (n = 5937) | 1st Tertile (n = 87,886) | 2nd Tertile (n = 86,012) | 3rd Tertile (n = 86,612) | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 47.8 ± 12.8 | 47.1 ± 13.5 | 48.9 ± 14.0 | 52.2 ± 14.2 | <0.0001 |
| Sex, n (%) | <0.0001 | ||||
| Male | 4632 (78.0%) | 56,745 (64.6%) | 43,982 (51.1%) | 36,101 (41.7%) | |
| Female | 1305 (22.0 %) | 31,141 (35.4%) | 42,030 (48.9%) | 50,511 (58.3%) | |
| Diabetes mellitus, n (%) | 597 (10.1%) | 8214 (9.4%) | 8693 (10.1%) | 10,843 (12.5%) | <0.0001 |
| Hypertension, n (%) | 1599 (26.9%) | 21,619 (24.6%) | 23,067 (26.8%) | 28,459 (32.9%) | <0.0001 |
| Dyslipidemia, n (%) | 1230 (20.72%) | 19,282 (21.9%) | 21,415 (24.9%) | 26,107 (30.1%) | <0.0001 |
| Heavy drinker, n (%) | 3510 (59.1%) | 50,151 (57.1%) | 43,913 (51.1%) | 36,089 (41.7%) | <0.0001 |
| Current smoker, n (%) | 2008 (33.8%) | 24,557 (27.9%) | 17,718 (20.6%) | 12,995 (15.0%) | <0.0001 |
| Regular exercise, n (%) | 3211 (54.1%) | 45,332 (51.6%) | 42,731 (49.7%) | 41,174 (47.5%) | <0.0001 |
| Subject who satisfy criteria of MS | |||||
| BMI ≥ 25 kg/m2 | 2146 (36.2%) | 31,234 (35.5%) | 30,437 (35.4%) | 31,073 (35.9%) | 0.1401 |
| WC ≥ 90/85 cm | 1276 (21.5%) | 18,825 (21.4%) | 19,209 (22.3%) | 21,289 (24.6%) | <0.0001 |
| BP ≥ 130/85 mmHg | 2919 (49.2%) | 38,864 (44.2%) | 37,516 (43.6%) | 41,142 (47.5%) | <0.0001 |
| FG ≥ 100 mg/dL | 2441 (41.1%) | 31,920 (36.3%) | 30,568 (35.5%) | 32,281 (37.3%) | <0.0001 |
| TG ≥ 150 mg/dL | 2238 (37.7%) | 32,532 (37.0%) | 32,106 (37.3%) | 35,699 (41.2%) | <0.0001 |
| HDL-C < 40/50 mg/dL | 1353 (22.8%) | 23,305 (26.5%) | 26,896 (31.3%) | 33,250 (38.4%) | <0.0001 |
| Antibiotics Prescription Days for 10 Years | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Non-Users (n = 5937) | 1st Tertile (n = 87,886) | 2nd Tertile (n = 86,012) | 3rd Tertile (n = 86,612) | |
| Obesity 1 *, OR (95%CI) | ||||
| Event | 1129 | 16,422 | 16,515 | 17,814 |
| Model 1 ** | 1.00 (ref) | 0.98 (0.92; 1.05) | 1.01 (0.95; 1.08) | 1.10 (1.03; 1.18) |
| Model 2 ** | 1.00 (ref) | 1.06 (0.99; 1.13) | 1.15 (1.07; 1.23) | 1.26 (1.18; 1.35) |
| Model 3 ** | 1.00 (ref) | 1.05 (0.98; 1.13) | 1.13 (1.05; 1.21) | 1.19 (1.11; 1.28) |
| Model 4 ** | 1.00 (ref) | 1.05 (0.98; 1.13) | 1.13 (1.05,1.21) | 1.20 (1.12,1.38) |
| Obesity 2 *, OR (95%CI) | ||||
| Event | 2293 | 33,637 | 33,131 | 34,548 |
| Model 1 ** | 1.00 (ref) | 0.99 (0.93; 1.04) | 0.99 (0.94; 1.05) | 1.06 (0.99; 1.11) |
| Model 2 ** | 1.00 (ref) | 1.08(1.03; 1.14) | 1.17(1.10; 1.23) | 1.26 (1.19; 1.33) |
| Model 3 ** | 1.00 (ref) | 1.08 (1.02; 1.14) | 1.15 (1.09; 1.22) | 1.19 (1.13; 1.27) |
| Model 4 ** | 1.00 (ref) | 1.08 (1.02; 1.14) | 1.15 (1.09; 1.21) | 1.20 (1.13; 1.26) |
| Obesity 3 *, OR (95%CI) | ||||
| Event | 2146 | 31,234 | 30,437 | 31,073 |
| Model 1 ** | 1.00 (ref) | 0.97 (0.92; 1.03) | 0.97 (0.92; 1.02) | 0.99 (0.94; 1.04) |
| Model 2 ** | 1.00 (ref) | 1.07 (1.01; 1.13) | 1.15 (1.09; 1.21) | 1.22 (1.15; 1.29) |
| Model 3 ** | 1.00 (ref) | 1.07 (1.01; 1.13) | 1.13 (1.07; 1.19) | 1.16 (1.10; 1.23) |
| Model 4 ** | 1.00 (ref) | 1.07 (1.01; 1.13) | 1.13 (1.07; 1.19) | 1.16 (1.09; 1.23) |
| Obesity 4 *, OR (95%CI) | ||||
| Event | 1276 | 18,825 | 19,209 | 21,289 |
| Model 1 ** | 1.00 (ref) | 0.99 (0.93; 1.06) | 1.05 (0.99; 1.12) | 1.19 (1.12; 1.27) |
| Model 2 ** | 1.00 (ref) | 1.07 (1.01; 1.14) | 1.16 (1.086,1.236) | 1.28 (1.20; 1.37) |
| Model 3 ** | 1.00 (ref) | 1.07 (0.99; 1.14) | 1.14 (1.07; 1.22) | 1.22 (1.14; 1.30) |
| Model 4 ** | 1.00 (ref) | 1.07 (1.00; 1.14) | 1.14 (1.07; 1.22) | 1.23 (1.15; 1.31) |
| TG ≥ 150 mg/dL, OR (95%CI) | ||||
| Event | 2238 | 32,532 | 32,106 | 35,699 |
| Model 1 ** | 1.00 (ref.) | 0.97 (0.92; 1.03) | 0.98 (0.93; 1.04) | 1.16 (1.09; 1.22) |
| Model 2 ** | 1.00 (ref.) | 1.09 (1.04; 1.16) | 1.15 (1.08; 1.21) | 1.29 (1.23; 1.37) |
| Model 3 ** | 1.00 (ref.) | 1.08 (1.01; 1.15) | 1.09 (1.02; 1.16) | 1.17 (1.09; 1.25) |
| Model 4 ** | 1.00 (ref.) | 1.09 (1.02; 1.16) | 1.11 (1.04; 1.19) | 1.21 (1.13; 1.29) |
| HDL < 40/<50 mg/dL, OR (95%CI) | ||||
| Event | 1353 | 23,305 | 26,896 | 33,250 |
| Model 1 ** | 1.00 (ref.) | 1.22 (1.15; 1.30) | 1.54 (1.44; 1.64) | 2.11 (1.98; 2.25) |
| Model 2 ** | 1.00 (ref.) | 1.22 (1.14; 1.31) | 1.38 (1.29; 1.47) | 1.60 (1.49; 1.71) |
| Model 3 ** | 1.00 (ref.) | 1.21 (1.12; 1.30) | 1.34 (1.24; 1.44) | 1.48 (1.39; 1.60) |
| Model 4 ** | 1.00 (ref.) | 1.23 (1.14; 1.32) | 1.36 (1.27; 1.46) | 1.50 (1.39; 1.61) |
| Satisfy BMI, WC, TG, HDL-C criteria of MS, OR (95%CI) | ||||
| Event | 542 | 9552 | 11,000 | 14,304 |
| Model 1 ** | 1.00 (ref.) | 1.21 (1.11; 1.32) | 1.46 (1.33; 1.59) | 1.97 (1.79; 2.16) |
| Model 2 ** | 1.00 (ref.) | 1.28 (1.17; 1.40) | 1.47 (1.34; 1.61) | 1.79 (1.63; 1.96) |
| Model 3 ** | 1.00 (ref.) | 1.25 (1.13; 1.38) | 1.39 (1.26; 1.54) | 1.59 (1.44; 1.76) |
| Model 4 ** | 1.00 (ref.) | 1.26 (1.14; 1.39) | 1.41 (1.27; 1.55) | 1.59 (1.44; 1.76) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Park, S.Y.; Ustulin, M.; Park, S.; Han, K.-D.; Kim, J.Y.; Shin, D.W.; Rhee, S.Y. Systemic Antibiotics and Obesity: Analyses from a Population-Based Cohort. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 2601. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10122601
Park SY, Ustulin M, Park S, Han K-D, Kim JY, Shin DW, Rhee SY. Systemic Antibiotics and Obesity: Analyses from a Population-Based Cohort. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2021; 10(12):2601. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10122601
Chicago/Turabian StylePark, So Young, Morena Ustulin, SangHyun Park, Kyung-Do Han, Joo Young Kim, Dong Wook Shin, and Sang Youl Rhee. 2021. "Systemic Antibiotics and Obesity: Analyses from a Population-Based Cohort" Journal of Clinical Medicine 10, no. 12: 2601. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10122601
APA StylePark, S. Y., Ustulin, M., Park, S., Han, K. -D., Kim, J. Y., Shin, D. W., & Rhee, S. Y. (2021). Systemic Antibiotics and Obesity: Analyses from a Population-Based Cohort. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 10(12), 2601. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10122601