Reliability of Machine and Human Examiners for Detection of Laryngeal Penetration or Aspiration in Videofluoroscopic Swallowing Studies
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Dataset
2.2. Analysis of VFSS
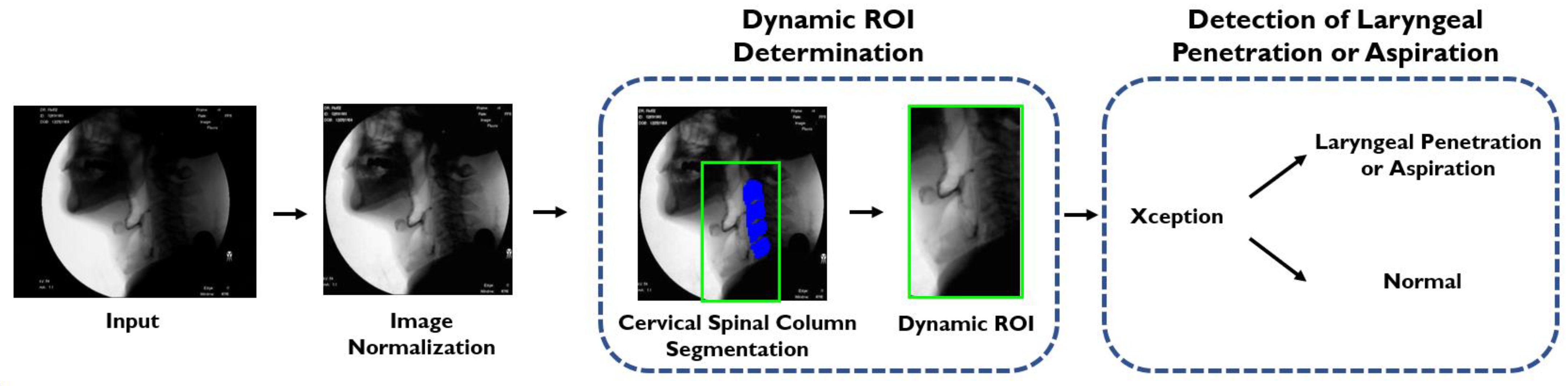
2.2.1. Machine Reading
2.2.2. Human Reading
2.3. Analysis of Intra- and Inter-Rater Reliability
2.3.1. Intrarater Reliability
2.3.2. Interrater Reliability
3. Results
3.1. Intrarater Reliability
3.2. Interrater Reliability
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Martin-Harris, B.; Logemann, J.A.; McMahon, S.; Schleicher, M.; Sandidge, J. Clinical utility of the modified barium swallow. Dysphagia 2000, 15, 136–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin-Harris, B.; Jones, B. The videofluorographic swallowing study. Phys. Med. Rehabil. Clin. N. Am. 2008, 19, 769–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Logemann, J.A. Behavioral management for oropharyngeal dysphagia. Folia Phoniatr. Et Logop. 1999, 51, 199–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robbins, J.; Coyle, J.; Rosenbek, J.; Roecker, E.; Wood, J. Differentiation of normal and abnormal airway protection during swallowing using the penetration–aspiration scale. Dysphagia 1999, 14, 228–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baijens, L.; Barikroo, A.; Pilz, W. Intrarater and interrater reliability for measurements in videofluoroscopy of swallowing. Eur. J. Radiol. 2013, 82, 1683–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.H.; Choi, K.H.; Kim, H.M.; Koo, J.H.; Kim, B.R.; Kim, T.W.; Ryu, J.S.; Im, S.; Choi, I.S.; Pyun, S.B. Inter-rater reliability of videofluoroscopic dysphagia scale. Ann. Rehabil. Med. 2012, 36, 791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCullough, G.H.; Wertz, R.T.; Rosenbek, J.C.; Mills, R.H.; Webb, W.G.; Ross, K.B. Inter-and intrajudge reliability for videofluoroscopic swallowing evaluation measures. Dysphagia 2001, 16, 110–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhlemeier, K.; Yates, P.; Palmer, J. Intra-and interrater variation in the evaluation of videofluorographic swallowing studies. Dysphagia 1998, 13, 142–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoeckli, S.J.; Huisman, T.A.; Seifert, B.A.; Martin–Harris, B.J. Interrater reliability of videofluoroscopic swallow evaluation. Dysphagia 2003, 18, 53–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aung, M.S.; Goulermas, J.Y.; Hamdy, S.; Power, M. Spatiotemporal visualizations for the measurement of oropharyngeal transit time from videofluoroscopy. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2009, 57, 432–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aung, M.; Goulermas, J.; Stanschus, S.; Hamdy, S.; Power, M. Automated anatomical demarcation using an active shape model for videofluoroscopic analysis in swallowing. Med. Eng. Phys. 2010, 32, 1170–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, M.W.; Lin, E.; Hwang, J.-N. Contour tracking using a knowledge-based snake algorithm to construct three-dimensional pharyngeal bolus movement. Dysphagia 1999, 14, 219–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hossain, I.; Roberts-South, A.; Jog, M.; El-Sakka, M.R. Semi-automatic assessment of hyoid bone motion in digital videofluoroscopic images. Comput. Methods Biomech. Biomed. Eng. Imaging Vis. 2014, 2, 25–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.H.; Chun, C.; Seo, H.G.; Lee, S.H.; Oh, B.-M. STAMPS: Development and verification of swallowing kinematic analysis software. BioMed. Eng. OnLine 2017, 16, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natarajan, R.; Stavness, I.; Pearson, W., Jr. Semi-automatic tracking of hyolaryngeal coordinates in videofluoroscopic swallowing studies. Comput. Methods Biomech. Biomed. Eng. Imaging Vis. 2017, 5, 379–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Pan, Y.; Zhang, J.; Xu, W. Learning to read chest X-ray images from 16000+ examples using CNN. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE/ACM International Conference on Connected Health: Applications, Systems and Engineering Technologies (CHASE), Philadelphia, PA, USA, 17–19 July 2017; pp. 51–57. [Google Scholar]
- Le, M.H.; Chen, J.; Wang, L.; Wang, Z.; Liu, W.; Cheng, K.-T.T.; Yang, X. Automated diagnosis of prostate cancer in multi-parametric MRI based on multimodal convolutional neural networks. Phys. Med. Biol. 2017, 62, 6497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lundervold, A.S.; Lundervold, A. An overview of deep learning in medical imaging focusing on MRI. Z. Für Med. Phys. 2019, 29, 102–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Q.; Zhao, L.; Luo, X.; Dou, X. Using deep learning for classification of lung nodules on computed tomography images. J. Healthc. Eng. 2017, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.J.; Ko, J.Y.; Kim, H.I.; Choi, S.-I. Automatic Detection of Airway Invasion from Videofluoroscopy via Deep Learning Technology. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 6179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenbek, J.C.; Robbins, J.A.; Roecker, E.B.; Coyle, J.L.; Wood, J.L. A penetration-aspiration scale. Dysphagia 1996, 11, 93–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Logemann, J.A. Evaluation and treatment of swallowing disorders. Am. J. Speech-Lang. Pathol. 1994, 3, 41–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuiderveld, K. Contrast limited adaptive histogram equalization. In Graphics Gems IV; Academic Press Professional Inc.: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1994; pp. 474–485. [Google Scholar]
- Chollet, F. Xception: Deep Learning with Depthwise Separable Convolutions. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 1800–1807. [Google Scholar]
- Scott, A.; Perry, A.; Bench, J. A study of interrater reliability when using videofluoroscopy as an assessment of swallowing. Dysphagia 1998, 13, 223–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hind, J.A.; Gensler, G.; Brandt, D.K.; Gardner, P.J.M.; Blumenthal, L.; Gramigna, G.D.; Kosek, S.; Lundy, D.; McGarvey-Toler, S.; Rockafellow, S. Comparison of trained clinician ratings with expert ratings of aspiration on videofluoroscopic images from a randomized clinical trial. Dysphagia 2009, 24, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryant, K.N.; Finnegan, E.; Berbaum, K. VFS interjudge reliability using a free and directed search. Dysphagia 2012, 27, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, J.E.; White, C.J.; Leonard, R.J.; Belafsky, P.C. Prevalence of penetration and aspiration on videofluoroscopy in normal individuals without dysphagia. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2010, 142, 208–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Factors | Number of Video Files (Number of Patients) | % | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gender | Male | 87 (21) | 50 |
| Female | 86 (21) | 50 | |
| Age (years) | 40–49 | 35 (8) | 20 |
| 50–59 | 31 (7) | 18 | |
| 60–69 | 30 (8) | 17 | |
| 70–79 | 35 (7) | 20 | |
| 80+ | 42 (12) | 24 | |
| Viscosity of diet | Thick liquid | 40 | 23 |
| Rice porridge | 41 | 24 | |
| Curd-type yogurt | 35 | 20 | |
| Thin liquid | 33 | 19 | |
| Cup drinking | 24 | 14 | |
| Laryngeal penetration or aspiration | Absent | 79 | 46 |
| PA2 2–3 | 44 | 25 | |
| PAS 4–5 | 29 | 17 | |
| PAS 6–8 | 21 | 12 |
| Kappa | PRR (%) | NRR (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Human 1 | 0.830 | 93 | 91 |
| Human 2 | 0.930 | 96 | 97 |
| Human 3 | 0.693 | 98 | 68 |
| Model | 1.000 | 100 | 100 |
| Session | Human 2 | Human 3 | Machine | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Human 1 | 1 | 0.672 | 0.781 | 0.660 |
| 2 | 0.672 | 0.668 | 0.705 | |
| Human 2 | 1 | 0.672 | 0.732 | |
| 2 | 0.457 | 0.732 | ||
| Human 3 | 1 | 0.705 | ||
| 2 | 0.488 |
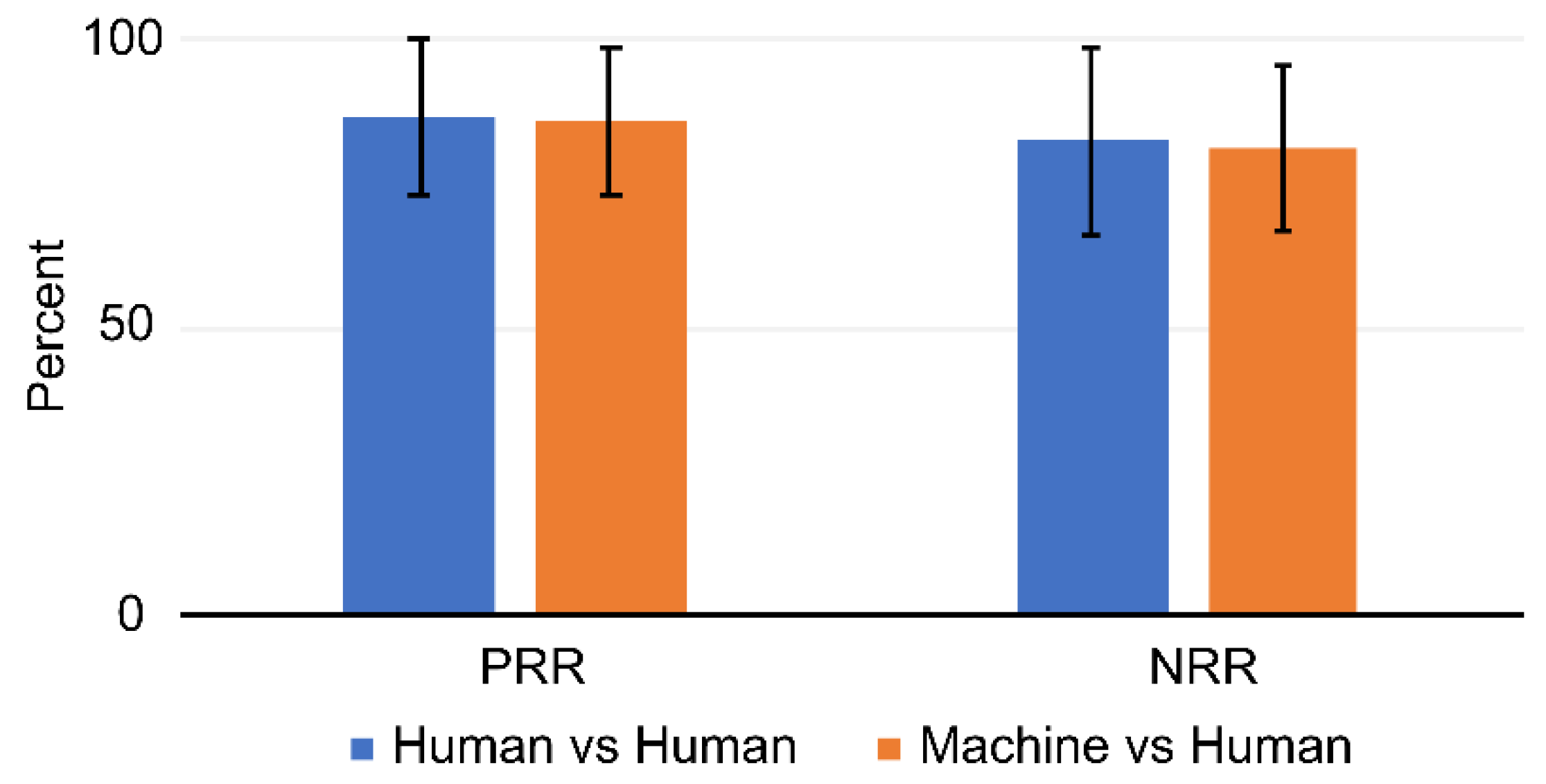
| PRR 1 (%) | NRR 2 (%) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Session | Human 1 | Human 2 | Human 3 | Machine | Human 1 | Human 2 | Human 3 | Machine | |
| Human 1 | 1 | 73 | 91 | 73 | 100 | 88 | 99 | ||
| 2 | 73 | 97 | 75 | 99 | 66 | 100 | |||
| Human 2 | 1 | 100 | 99 | 86 | 70 | 70 | 87 | ||
| 2 | 99 | 99 | 86 | 70 | 50 | 50 | |||
| Human 3 | 1 | 92 | 73 | 75 | 85 | 99 | 100 | ||
| 2 | 82 | 62 | 63 | 94 | 98 | 100 | |||
| Machine | 1 | 99 | 85 | 100 | 69 | 88 | 72 | ||
| 2 | 100 | 85 | 100 | 72 | 88 | 51 | |||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, Y.; Kim, H.-I.; Park, G.S.; Kim, S.Y.; Choi, S.-I.; Lee, S.J. Reliability of Machine and Human Examiners for Detection of Laryngeal Penetration or Aspiration in Videofluoroscopic Swallowing Studies. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 2681. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10122681
Kim Y, Kim H-I, Park GS, Kim SY, Choi S-I, Lee SJ. Reliability of Machine and Human Examiners for Detection of Laryngeal Penetration or Aspiration in Videofluoroscopic Swallowing Studies. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2021; 10(12):2681. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10122681
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Yuna, Hyun-Il Kim, Geun Seok Park, Seo Young Kim, Sang-Il Choi, and Seong Jae Lee. 2021. "Reliability of Machine and Human Examiners for Detection of Laryngeal Penetration or Aspiration in Videofluoroscopic Swallowing Studies" Journal of Clinical Medicine 10, no. 12: 2681. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10122681
APA StyleKim, Y., Kim, H.-I., Park, G. S., Kim, S. Y., Choi, S.-I., & Lee, S. J. (2021). Reliability of Machine and Human Examiners for Detection of Laryngeal Penetration or Aspiration in Videofluoroscopic Swallowing Studies. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 10(12), 2681. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10122681






